Coverings of the CNS, the Ventricular System and Blood Supply
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANHB2217
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Neurocranium
Viscerocranium
Neurocranium = cranial bones enclosing the brain
Viscerocranium = facial bones enclosing/supporting viscera
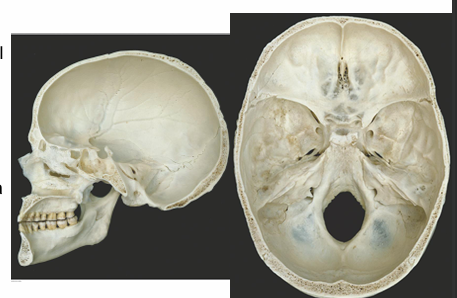
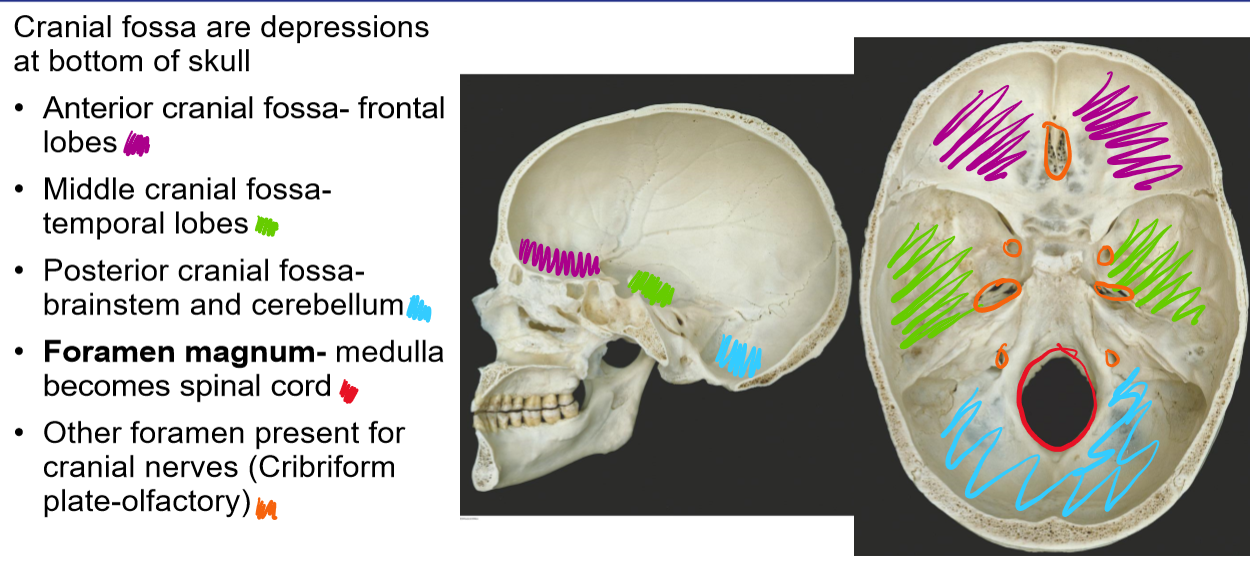
What are cranial fossa
Name the cranial fossa and their location
AMPF
Depression at the bottom of the skull
Anterior cranial fossa- frontal lobes
Middle cranial fossa- temporal lobes
Posterior cranial fossa- brainstem and cerebellum
Foramen magnum- medulla becomes spinal cord
Other foramen present for cranial nerves (Cribriform plate-olfactory)
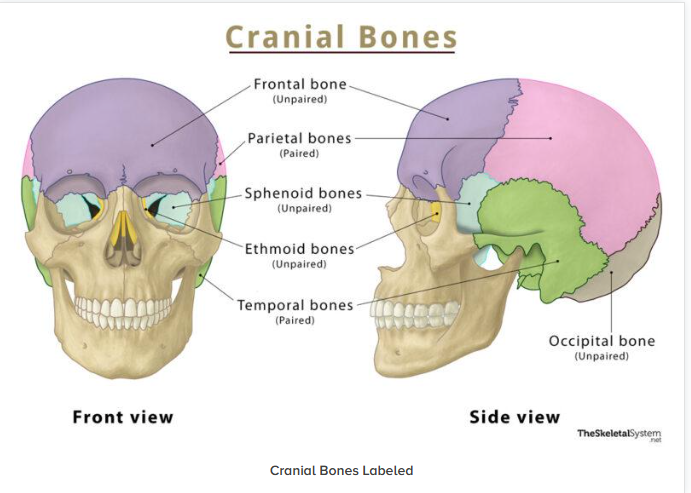
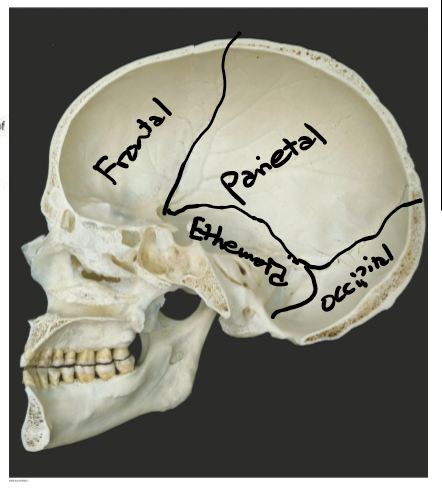
Label the bones
What do cranial meninges do
Hold and protect CNS
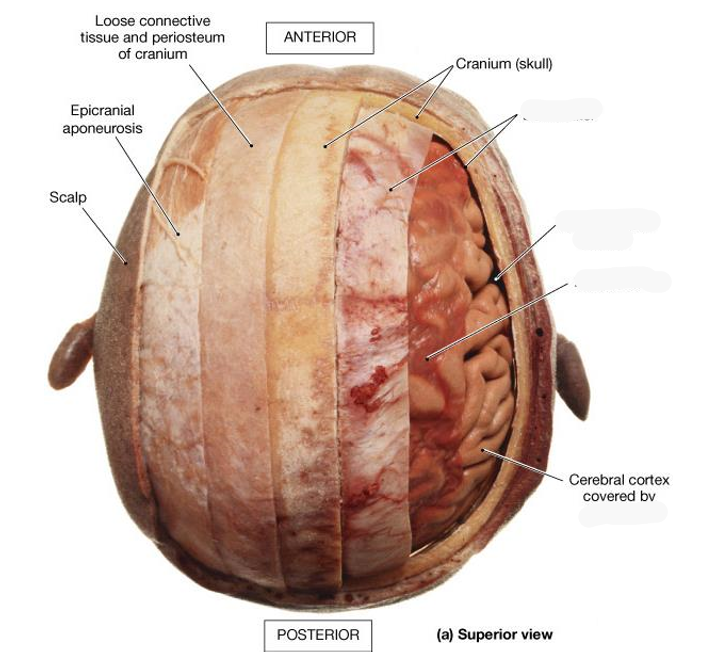
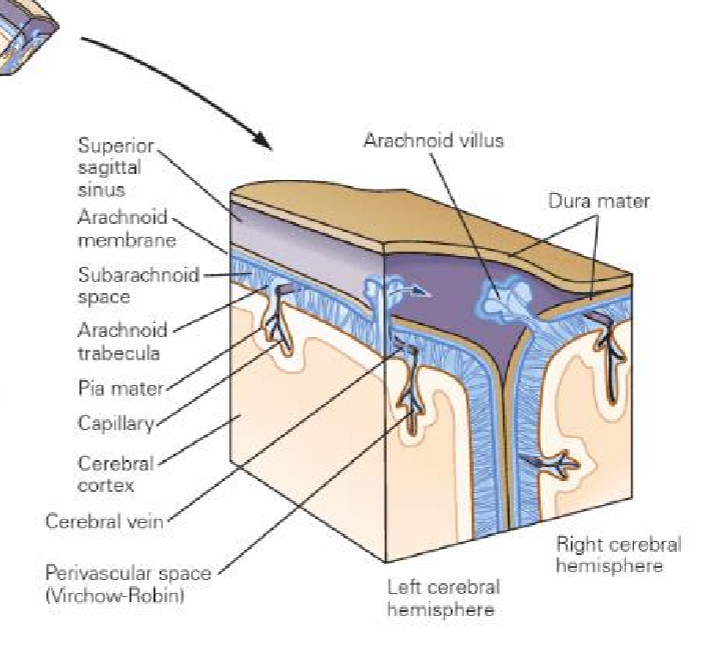
What are the 3 meningeal layers
DASP and their roles
Dura mater- tough fibrous membranes
Falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli- adhere to the skull, contains folds that separate the lobes of the brain, surrounds CNS and SC, ensures tight fit to prevent movement of brain
Arachnoid mater- soft translucent, avascular
Subarachnoid space- contains CSF produced from choroid plexus
Pia mater- microscopically small and highly vascular
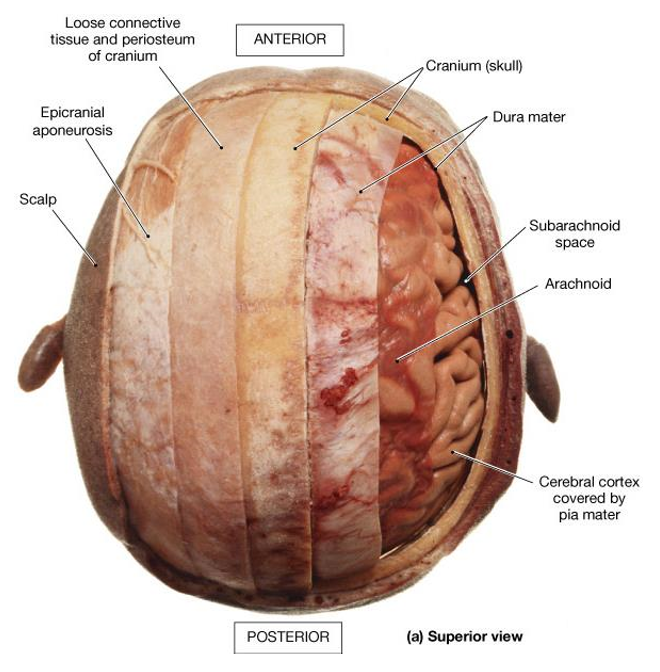
Dura mater
FFT
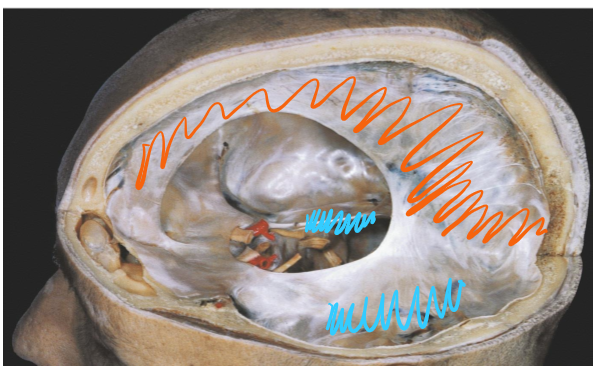
Identify the two folds of the three in the diagram
Falx cerebri-separates the two cerebral hemispheres
Falx cerebelli- separates the two cerebellum hemispheres
Tentorium cerebelli- separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum
Superficial veins vs deep veins
In subarachnoid space eg cerebral veins
Drain the internal structures of the forebrain eg great cerebral vein
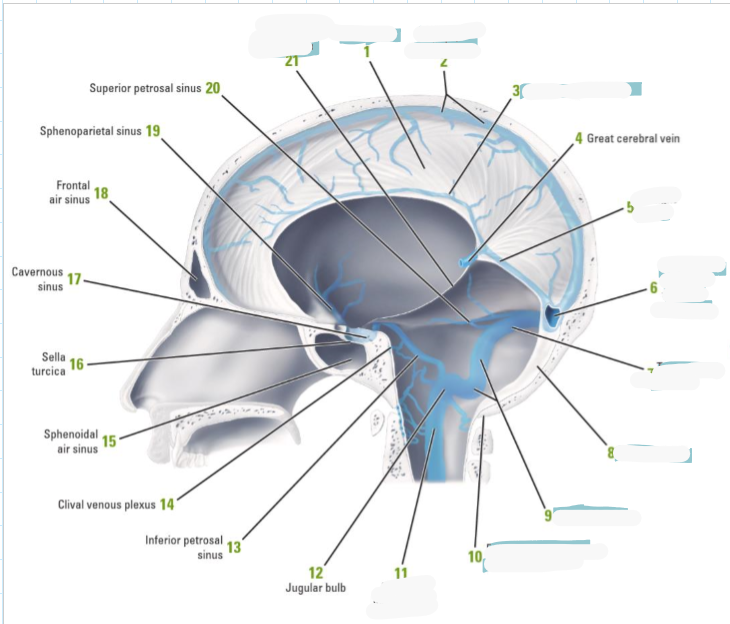
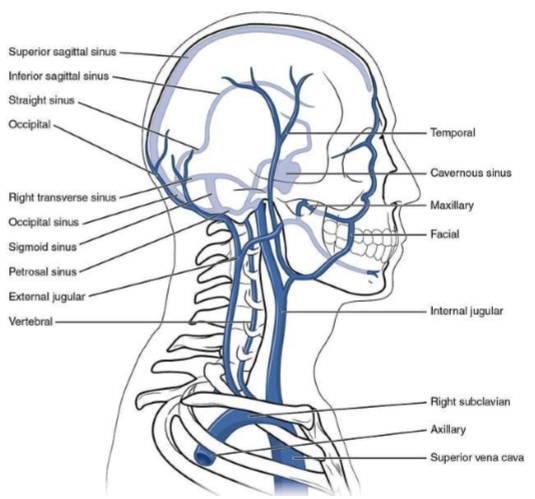
Name the 6 dural venous sinuses
Superior sagittal
Inferior sagittal
Straight
Confluence of sinuses
Transverse
Sigmoid
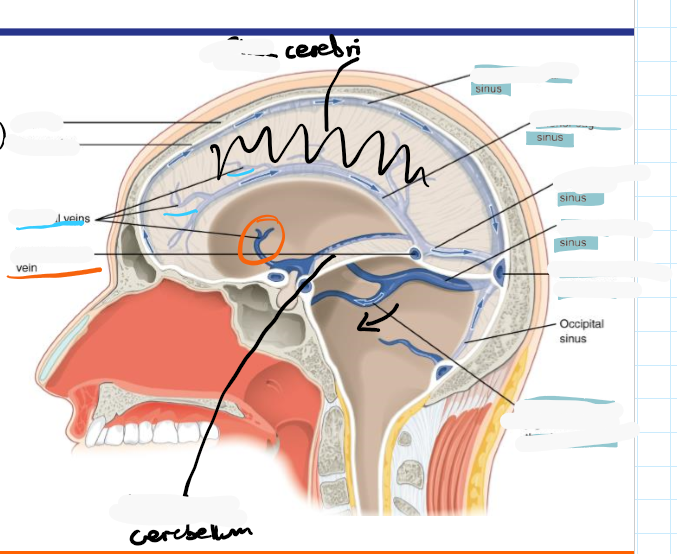
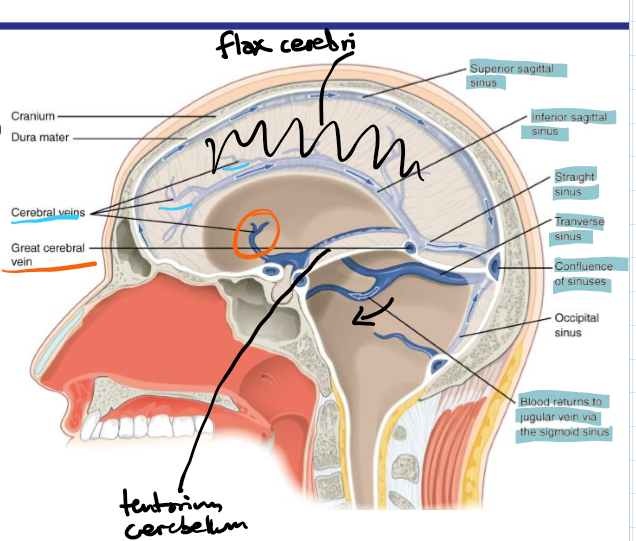
Identify roughly where the superior sagittal sinus, inferior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, transverse sinus, and confluence of sinuses are located
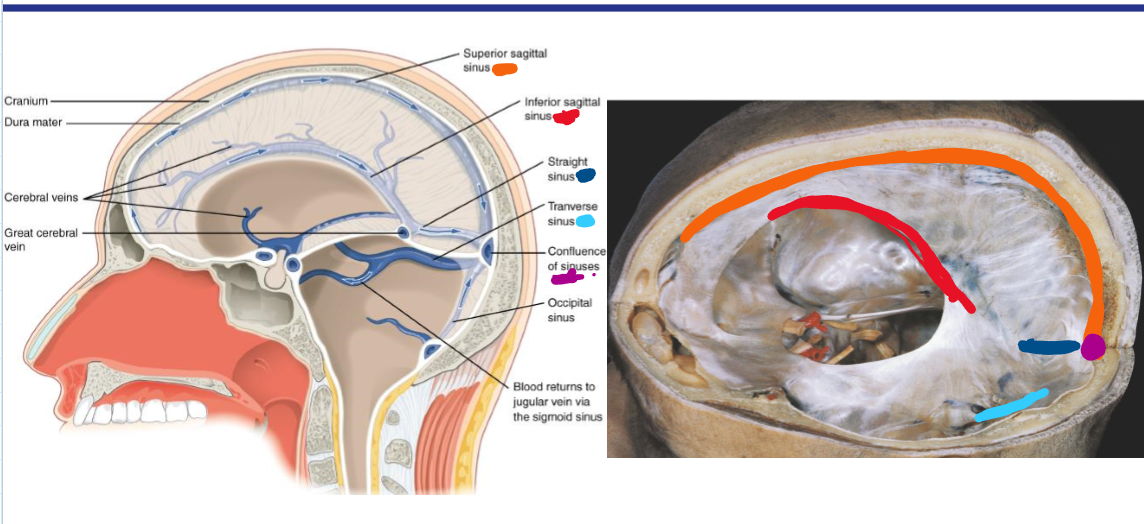
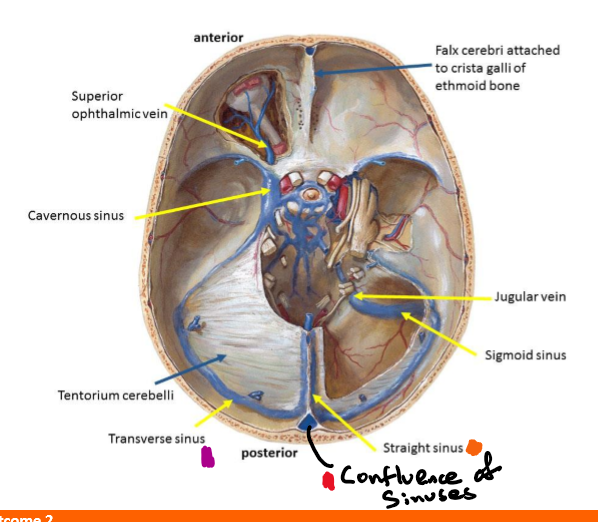
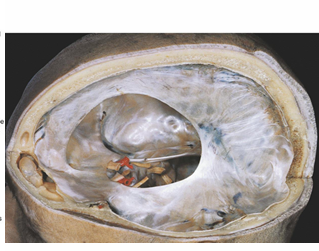
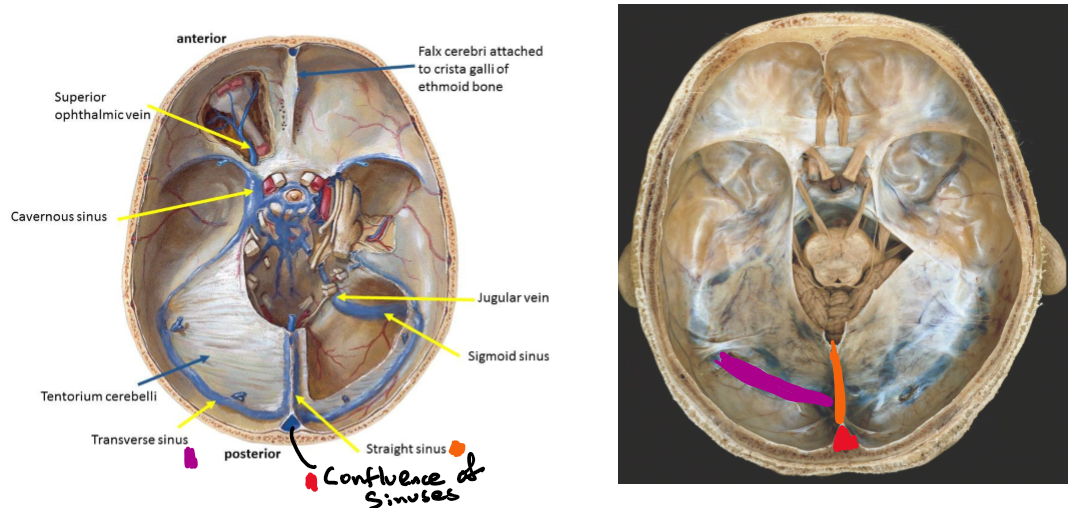
Identify where the transverse sinus, confluence of sinuses and straight sinus would be
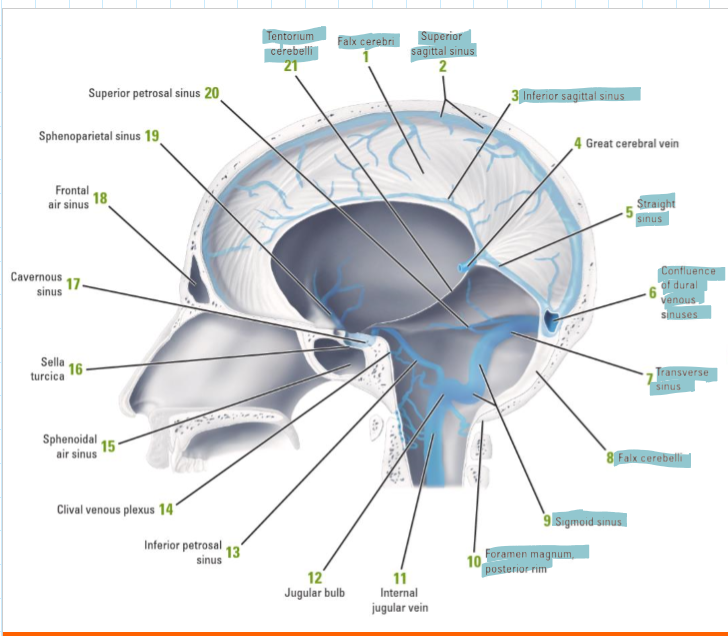
How does deoxygenated blood drain from the brain
Inferior sagittal sinus drains to straight sinus which with superior sagittal sinus and occipital sinus drains to the confluence of sinuses
These drain into the 2 transverse sinuses which drain to the two sigmoid sinuses which drain to the 2 internal jugular vein (2 for left and right)
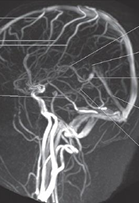
Identify the superior sagittal, inferior sagittal and straight sinuses
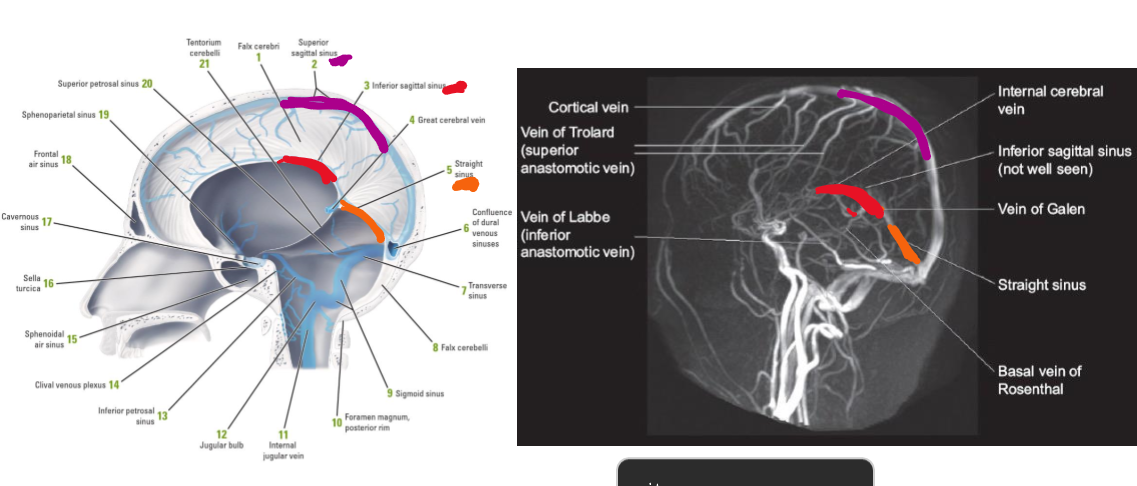
Which veins do the neck and face drain from?
Neck- internal, external and anterior jugular veins
Face- mainly internal jugular veins
Where is CSF created and by what cells?
What cells regulated entry of blood to the brain?
Epithelial cells of the choroid plexuses create CSF
Endothelial cells of blood-brain barrier regulate the entry of blood to the brain
Where are choroid plexuses found?
lateral, 3rd and 4th ventricle space
Description of ventricular system
A set of interconnected “spaces/cavities” that circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
CSF flow pathway
Most CSF exits through what
Choroid plexus, lateral ventricle, interventricular foramen (foramen of Monro), 3rd ventrile, cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius), 4th ventricle, CSF leaves via the 2 lateral (foramina of Luschka) and 1 median aperture (foramen of Magendie) of 4th ventricle and enter subarachnoid space
Most CSF exits through median aperture → cistern magna (between the cerebellum and medulla)
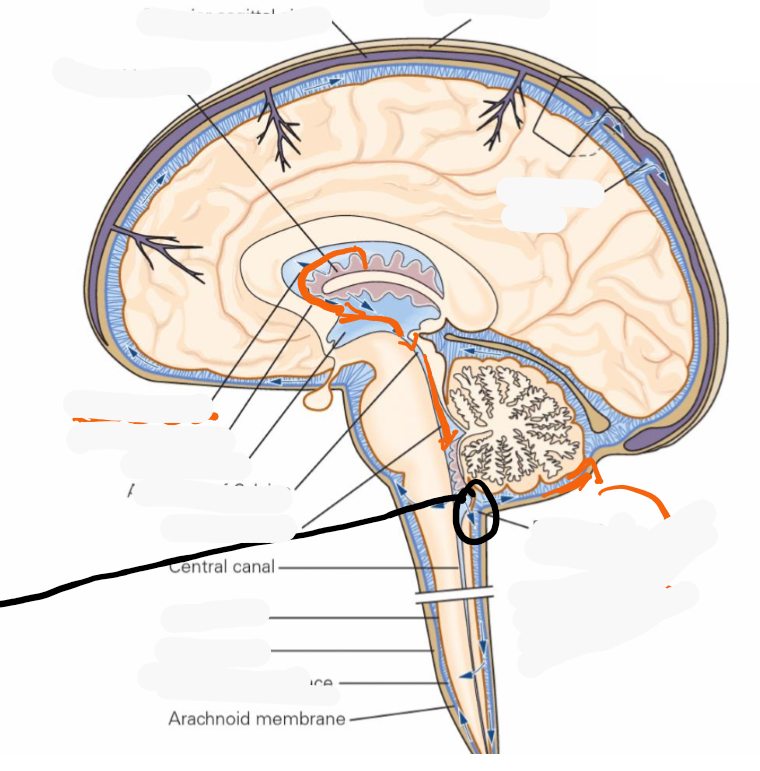
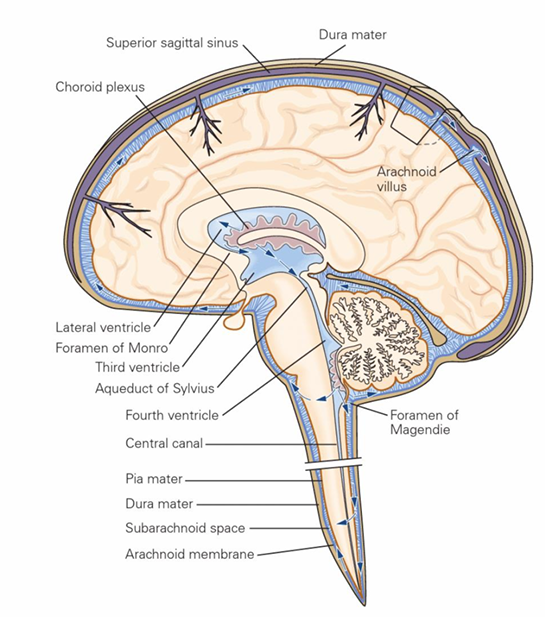
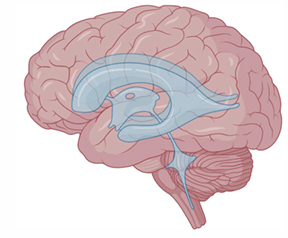
Identify the lateral, 3rd and 4th ventricles
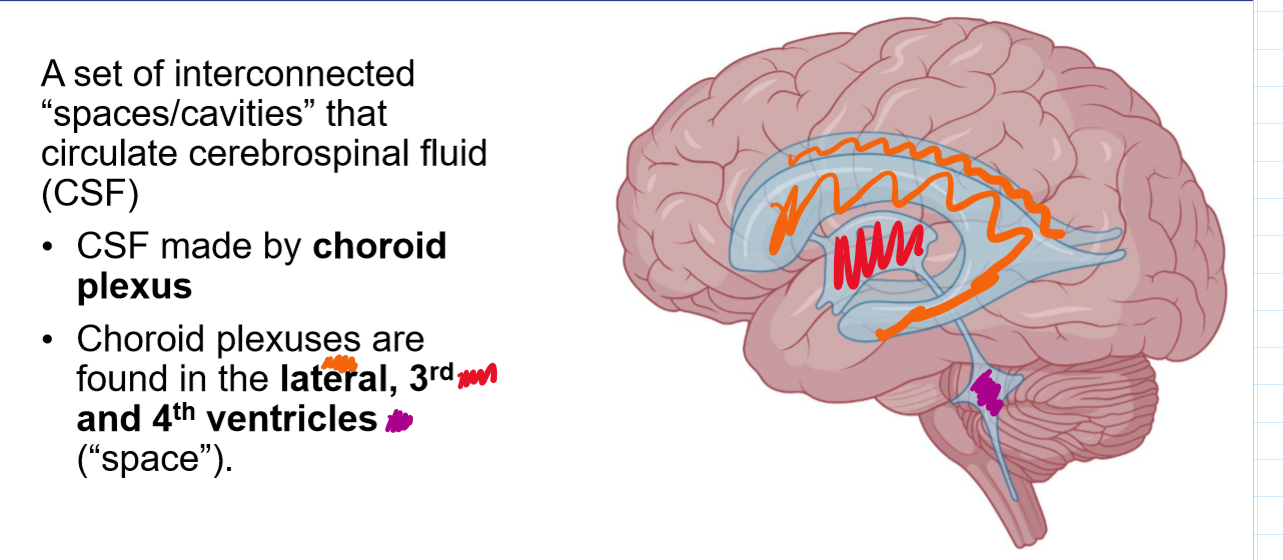
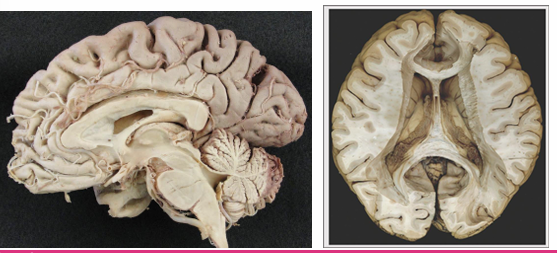
Draw roughly where the lateral, 3rd and choroid plexus would sit
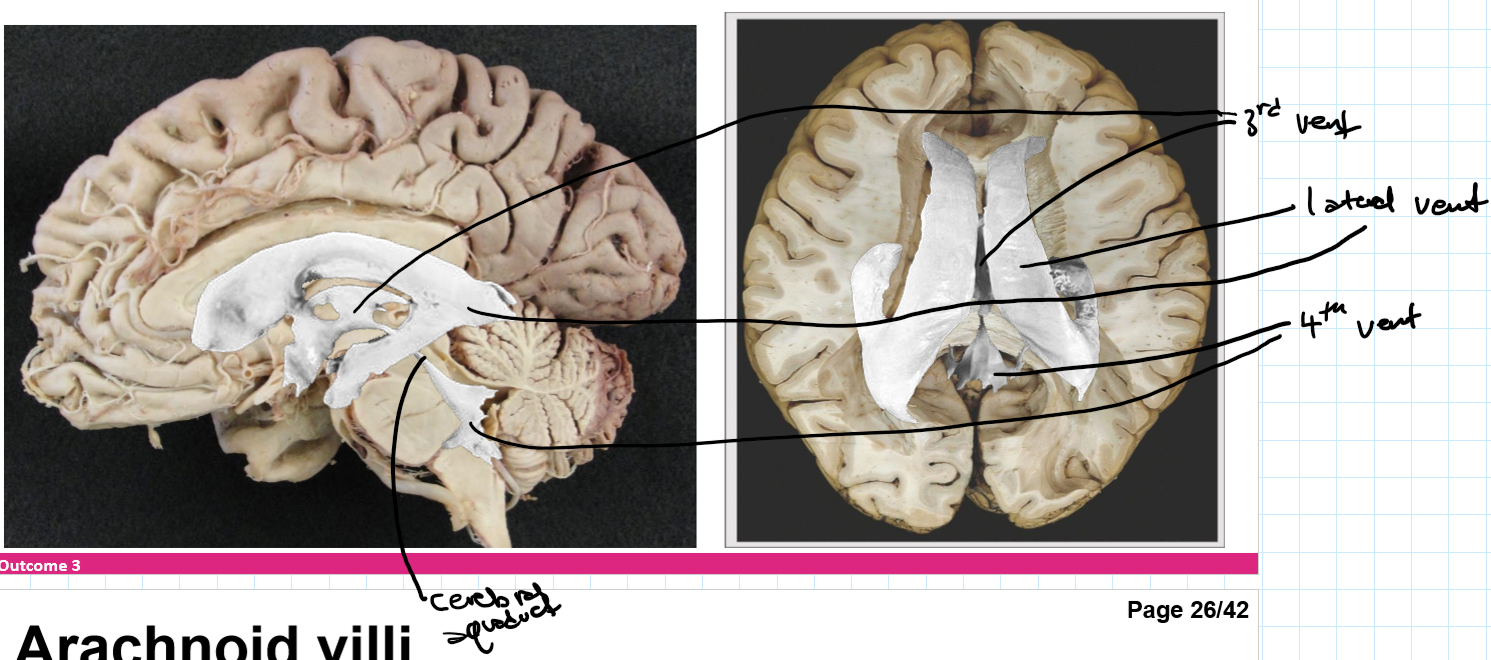
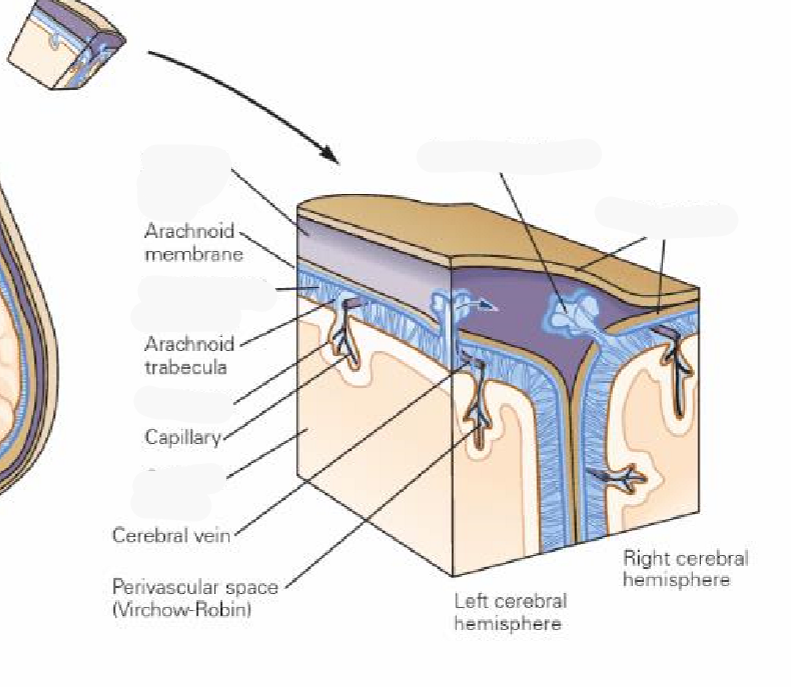
CSF circulates around what and how is it reabsorbed
What happens with age
CSF circulates around the CNS and is reabsorbed mostly at the superior sagittal sinus via arachnoid villi
With age the arachnoid villi become hypertrophic and are called granulations
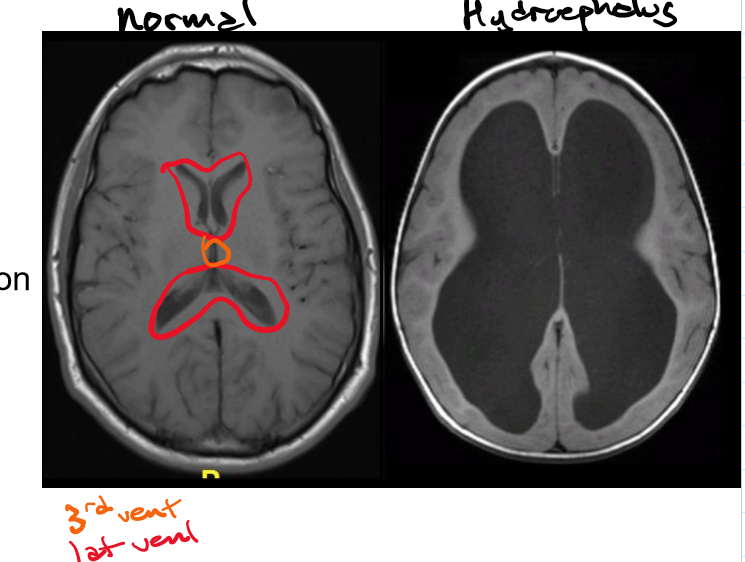
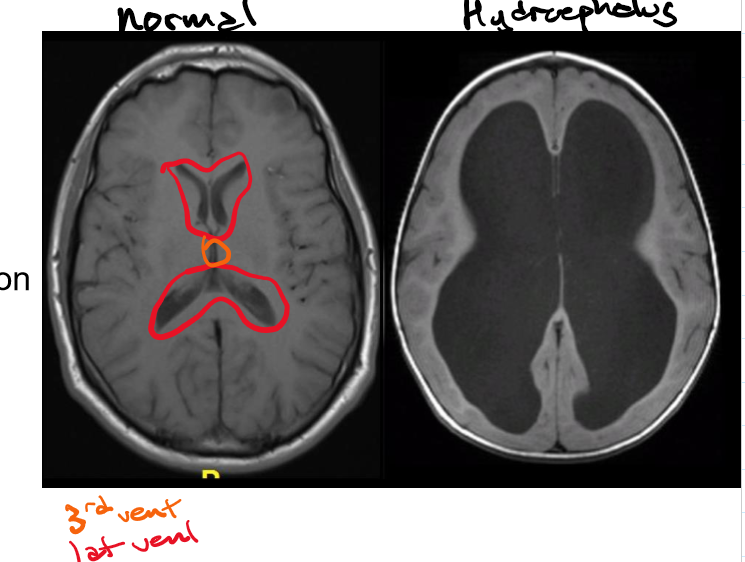
Hydrocephalus and how it’s caused
Communicating and non-communicating: how they’re caused, examples and side effect of non-communicating
Caused by abnormal buildup of CSF within the ventricular system
Communicating (nonobstructive) -impaired CSF reabsorption w/o obstruction
Ex. Impairment of arachnoid villi
Non-communicating (obstructive) -obstruction of CSF
Notable side effect: Chiari malformation- downward displacement of cerebellum through foramen magnum
Ex. Tumour in the cerebral aqueduct
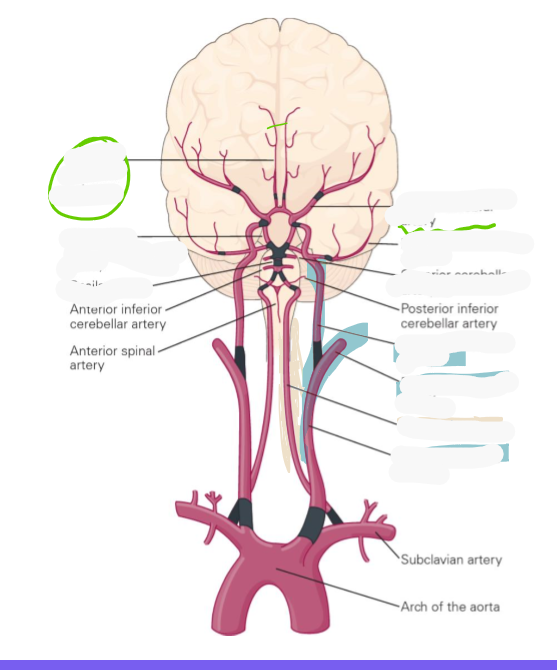
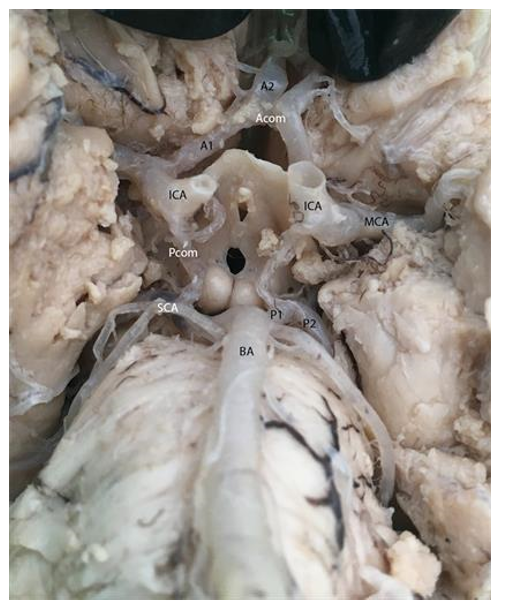
Brian is supplied by which two vessels?
Carotids terminate into what 2 arteries?
Internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries
Carotids terminate into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries
Vertebral arteries converge where to create what artery and what 2 arteries does this artery terminate into
Medulla/pons to create basilar artery
Basilar artery gives rise to many arteries before terminating into the superior cerebellar arteries and posterior cerebral arteries
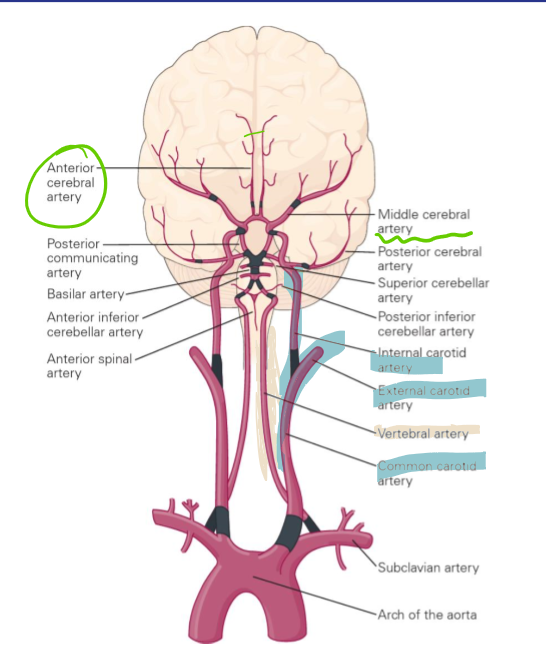
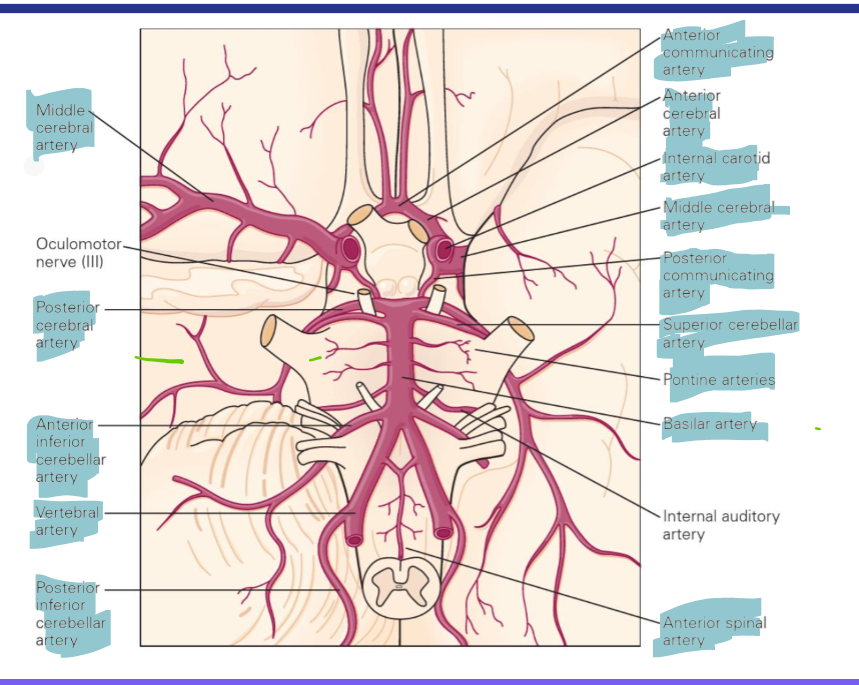
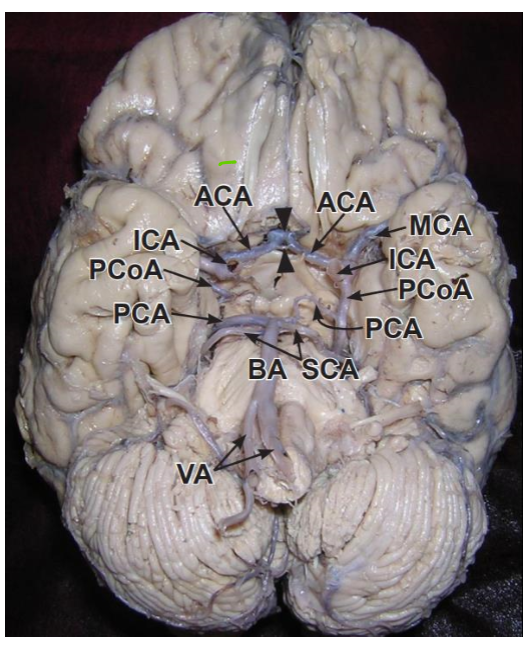
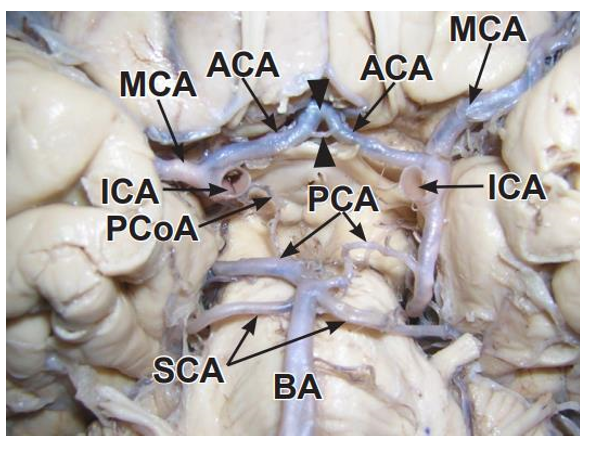
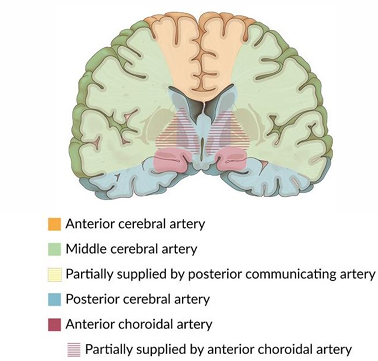
Anterior cerebral artery, middle cerebral artery and posterior cerebral artery stroke symptoms
Anterior cerebral artery stroke symptoms
Loss of smell (anosmia): olfactory bulb and tract
Weakness or paralysis of lower limb: motor cortex
Middle cerebral artery stroke symptoms
Speech impairments/aphasia: Broca’s & Wernicke’s
Weakness or paralysis of the face and upper limb: motor cortex
Posterior cerebral artery stroke symptoms
Cortical blindness: occipital lobe
Face blindness (prosopagnosia): temporal lobe
Identify what arteries supply these regions
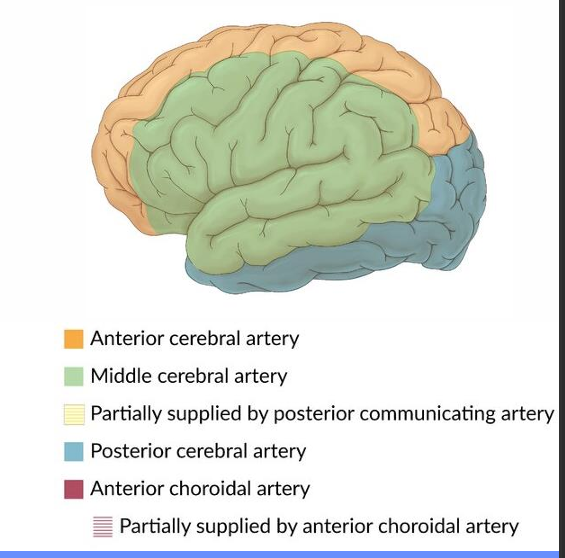
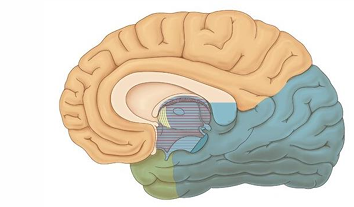
Identify what arteries supply these regions
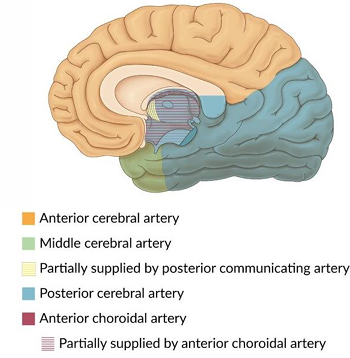
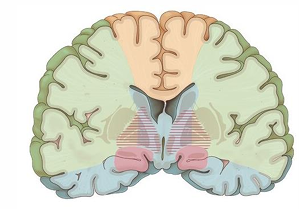
Identify what arteries supply these regions