GB1-Chapter 18
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Gene Expression Regulation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
feedback inhibition
regulates the production of enzymes
the end product of metabolic pathway shuts down further synthesis of product by inhibiting enzyme activity
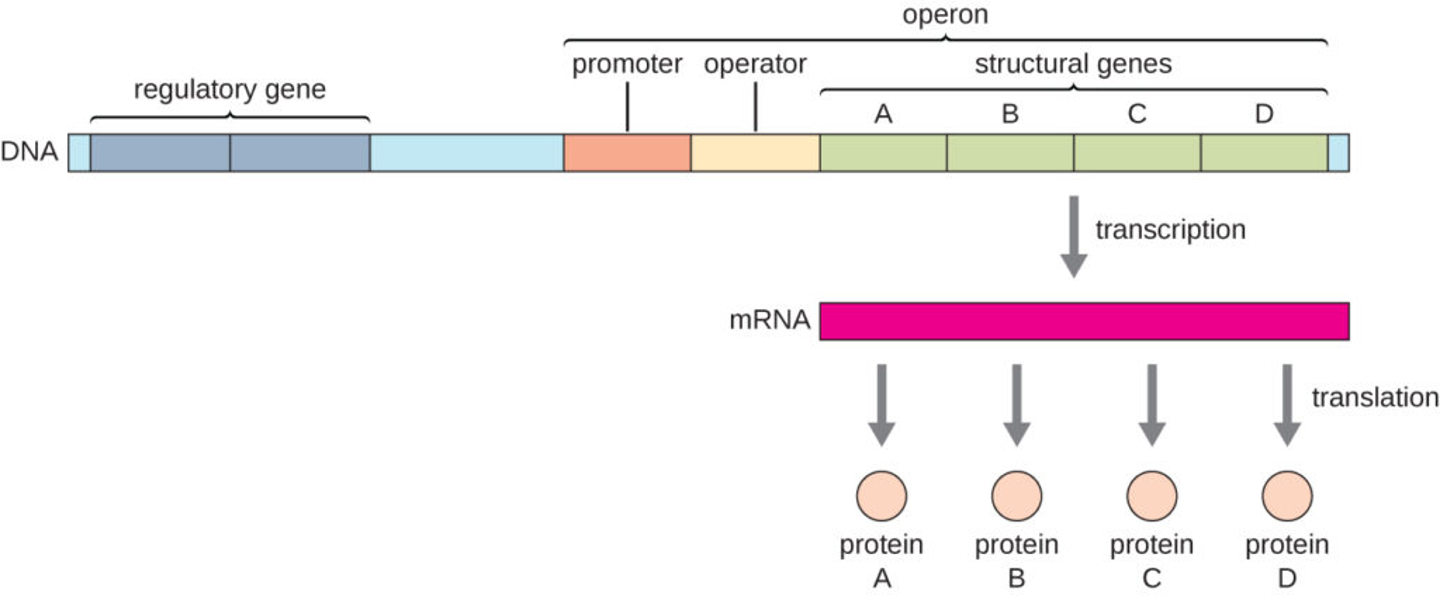
operon
operon is the entire stretch of DNA inclduing operator, promoter, and genes they control
a cluster of functionally related genes that can be coordinately controlled by a single on and off switch called operator that is within the promoter or between promoter and the enzyme coding genes.
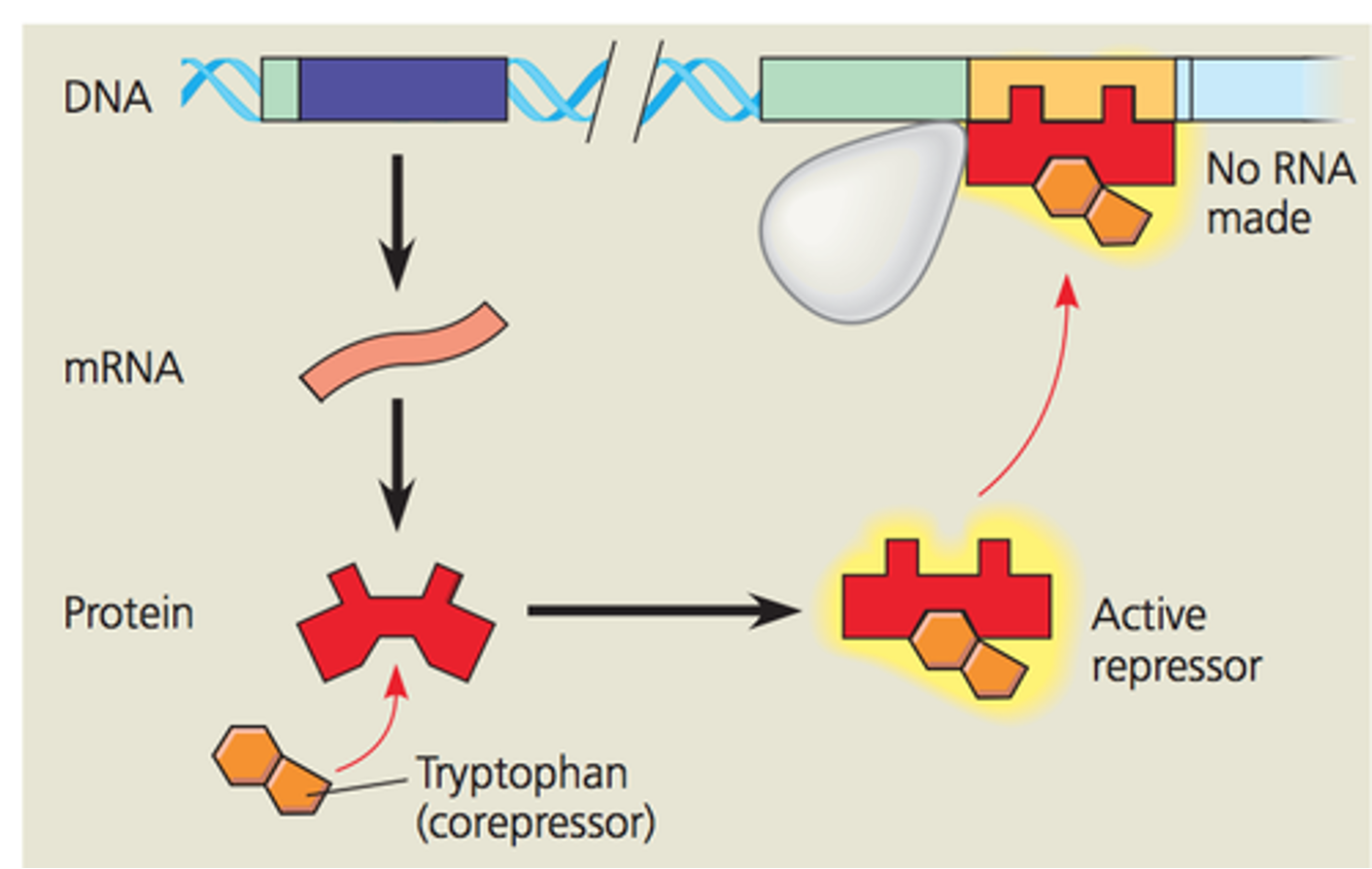
repressible operon
The regulatory gene secretes a repressor that can repress the operon by binding to the operator and preventing RNA polymerase from transcribing.
corepressor- a molecule that works with a repressor to repress the operon
negative feedback
negative control- operon is switched off by an active form of repressor
only active in the presence of tryptophan. Tryptophan (corepressor) binds to the repressor, activating it.
usually function in anabolic pathways
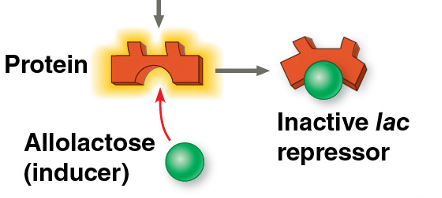
inducible operon
usually turned off by a lac repressor, but it can be activated by an inducer, allolactose, that inactivates the repressor by causing it to change shape and allows transcription
Lac operon- contains genes that code for enzymes used in hydrolysis and metabolism of lactose
regulatory gene: lacl
negative control- active form of repressor
usually function in catabolic pathways
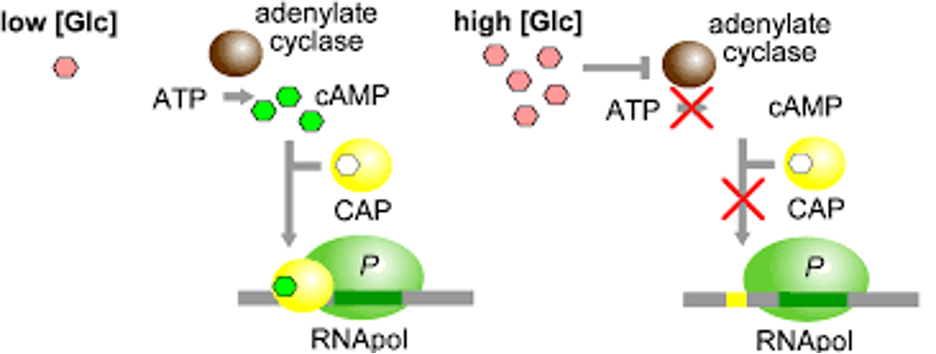
positive control
active form of activator
When glucose is scarce, Cyclic AMP receptor protein (CRP) is activated by binding of cyclic AMP (cAMP). Activated CRP attaches to lac operon promoter and increases the affinity of RNA polymerase = speeding up transcription
When glucose level increase CRP detaches from lac operon and the activator falls off with it. This makes transcription fall back into a normal, low level without the activator.
differential gene expression
the expression of different genes by cells with the same genome
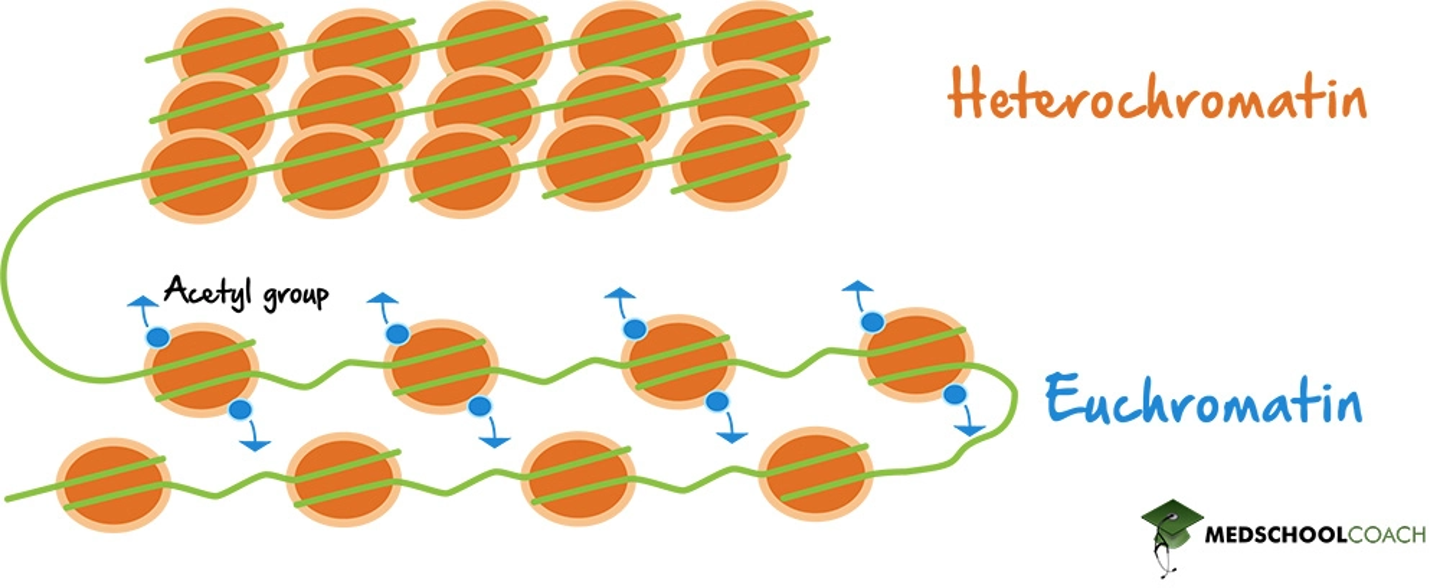
regulation of chromatin structure
heterochromatin- highly packed genes- usually not expressed
euchromatin- loosely packed genes- expressed. Gene transcription is affected by location of nucleosomes along the promoter and where the DNA attaches to chromosome.
histone acetylation- acetyl groups are attached to histone tail’s amino acid and opens up chromatin strcuture- promoting transcriptiton
DNA methylation- addition of methyl groups that reduces transcription- long term inactivation of genes. methylation regulates genomic imprinting determination of maternal of paternal alleles
epigenetics
inheritance of traits transmitted by not directly involving the nucleotide sequence
ex) identical twins- one of them develops genetically based disease, other does not.
chromatin modifications may be passed unto offsprings