BIO153 Practicum 3 Heymann
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
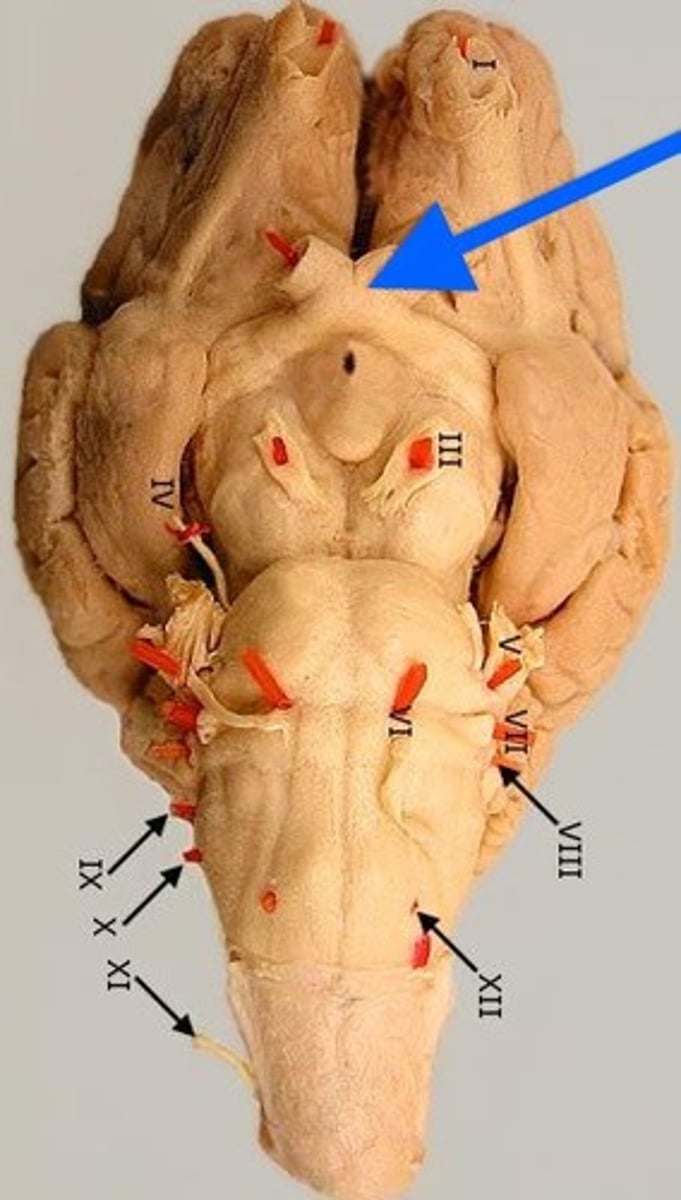
Olfactory; smell
What is the name and primary function of the number 1 cranial nerve?
Optic; vision
What is the name and primary function of the number 2 cranial nerve?
Oculomotor; Controls superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, and inferior oblique muscles moving the eye
What is the name and primary function of the number 3 cranial nerve?
Trochlear; Controls superior oblique eye muscle
What is the name and primary function of the number 4 cranial nerve?
Trigeminal; Major sensory nerve of face; Controls muscles in mastication (chewing)
What is the name and primary function of the number 5 cranial nerve?
Abducens; Controls lateral rectus muscle of eye
What is the name and primary function of the number 6 cranial nerve?
Facial; Controls muscles of facial expression; sense of taste
What is the name and primary function of the number 7 cranial nerve?
Vestibulocochlear; Sense of equilibrium and hearing
What is the name and primary function of the number 8 cranial nerve?
Glossopharyngeal; Controls pharyngeal muscles and salivary glands; sense of taste
What is the name and primary function of the number 9 cranial nerve?
Vagus; Largest parasympathetic nerve
What is the name and primary function of the number 10 cranial nerve?
Accessory; Controls neck muscles
What is the name and primary function of the number 11 cranial nerve?
Hypoglossal; Controls muscles of tongue
What is the name and primary function of the number 12 cranial nerve?
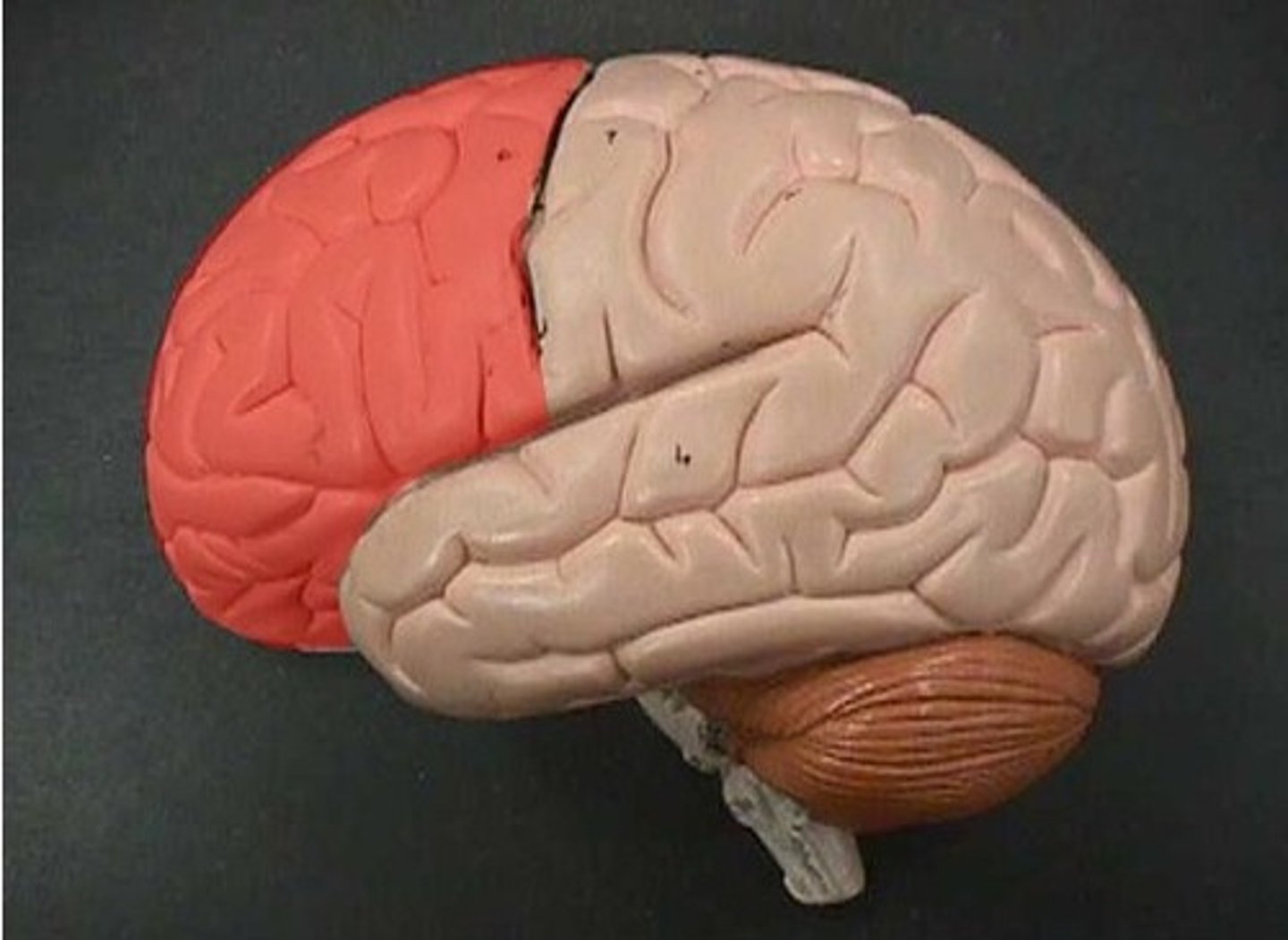
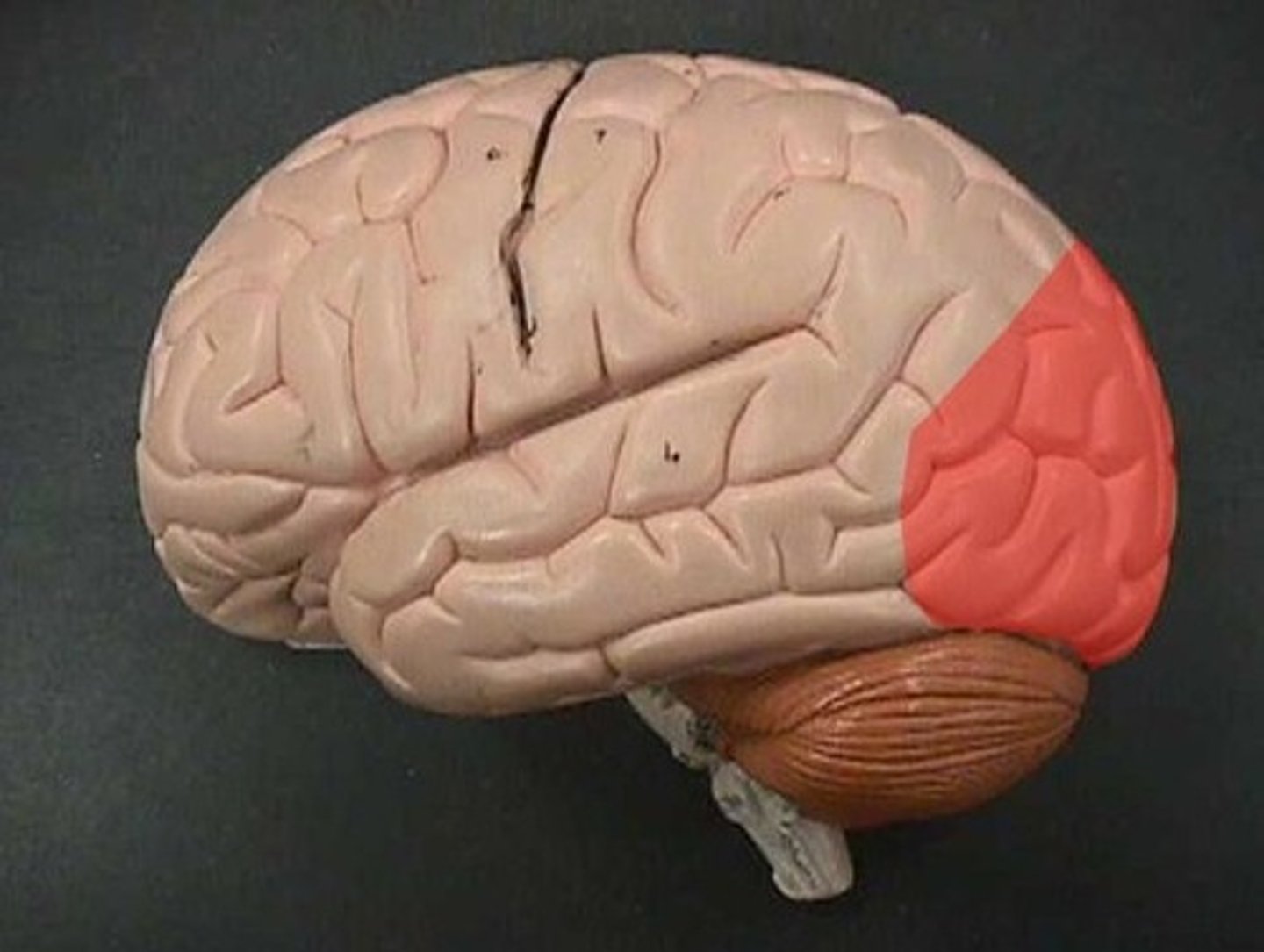
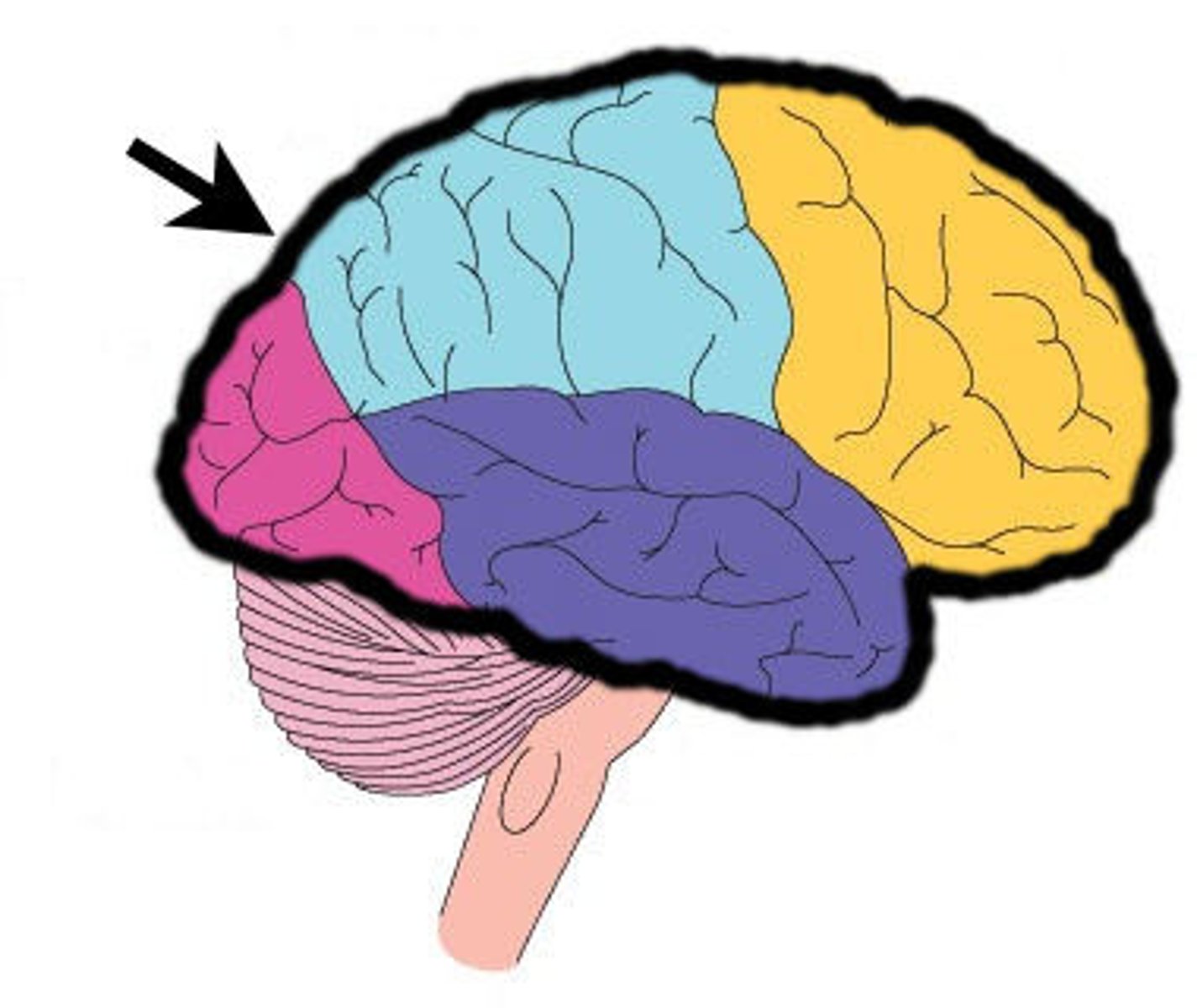
Frontal lobe
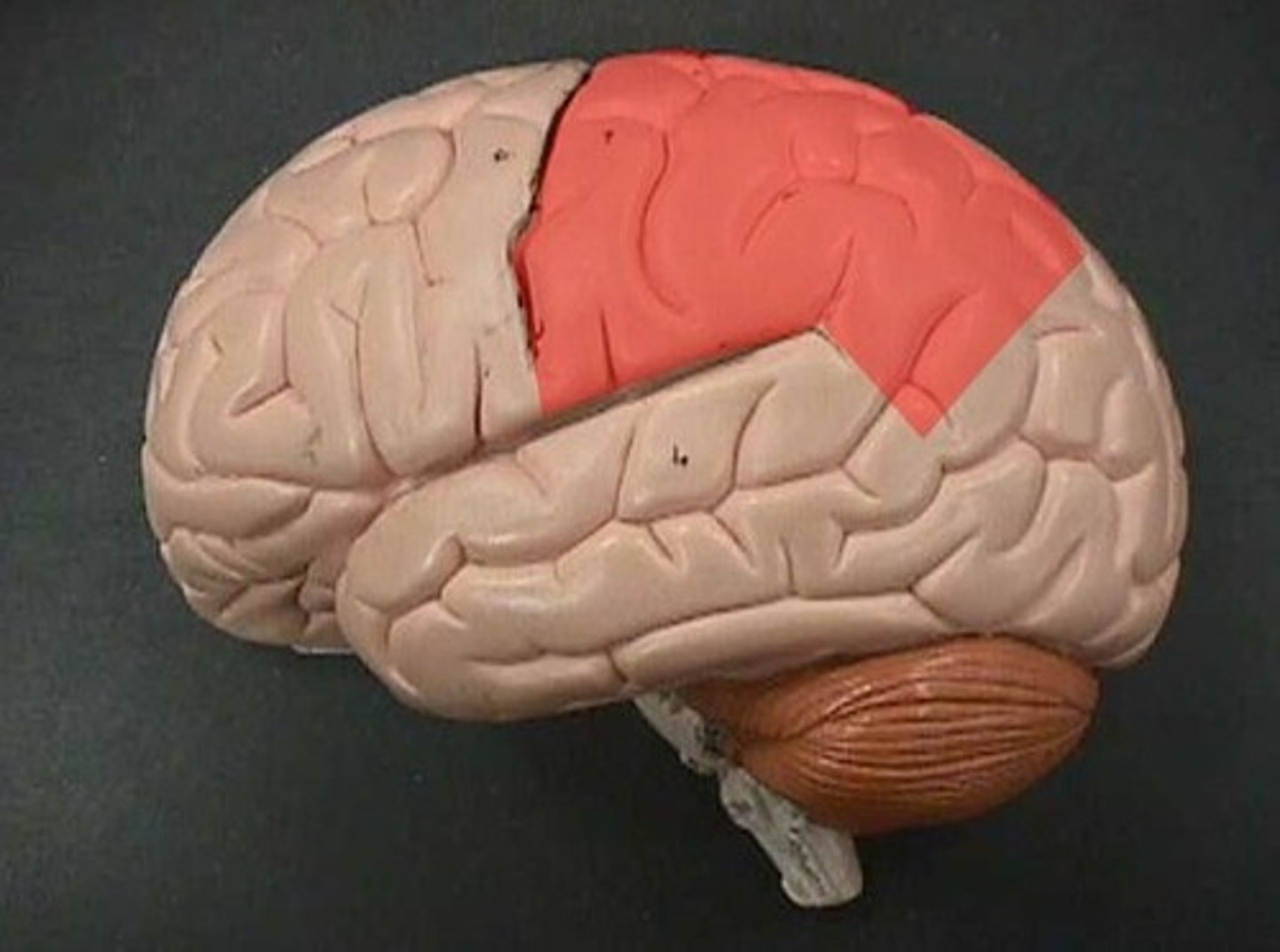
Parietal lobe
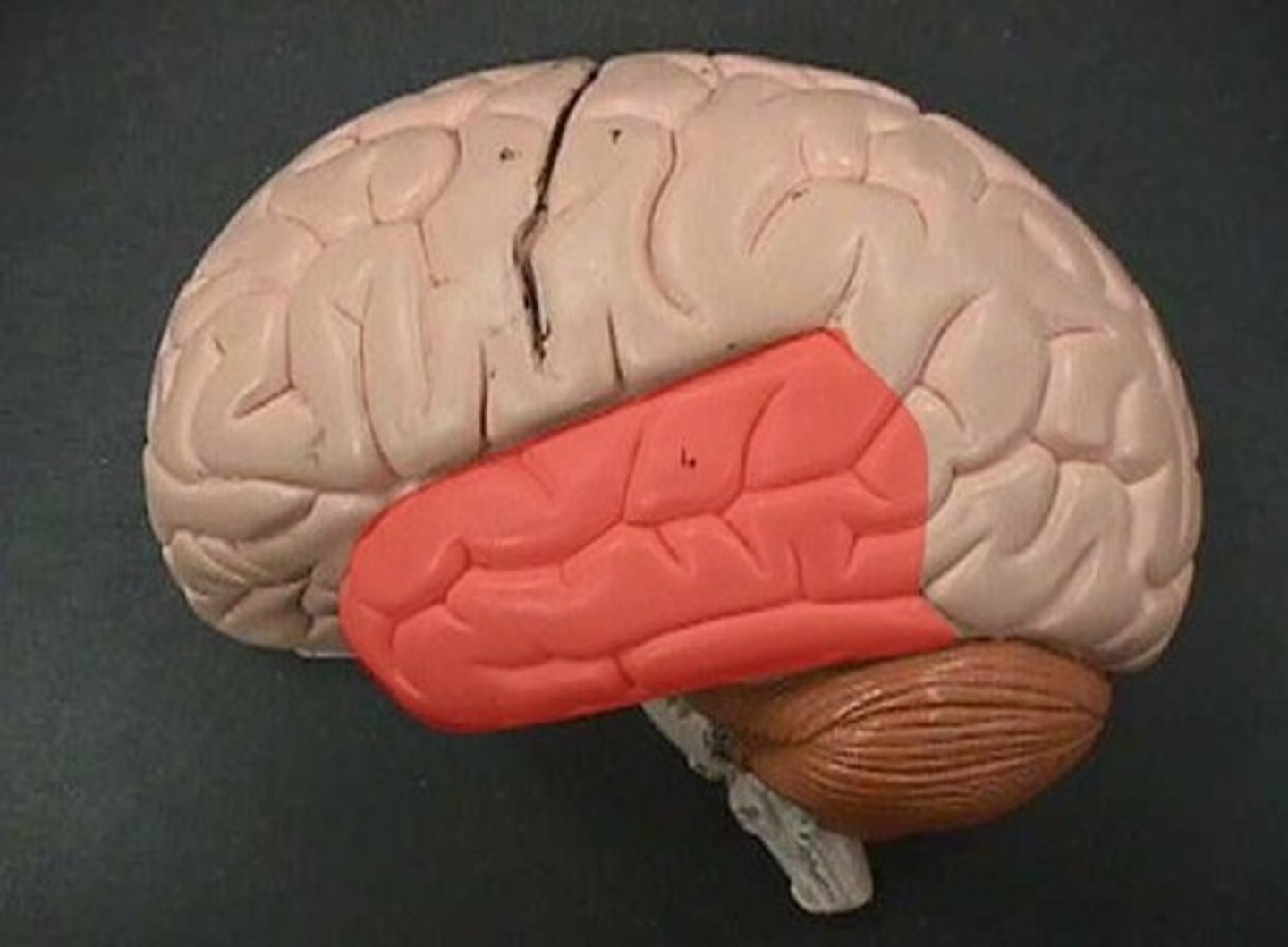
Temporal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
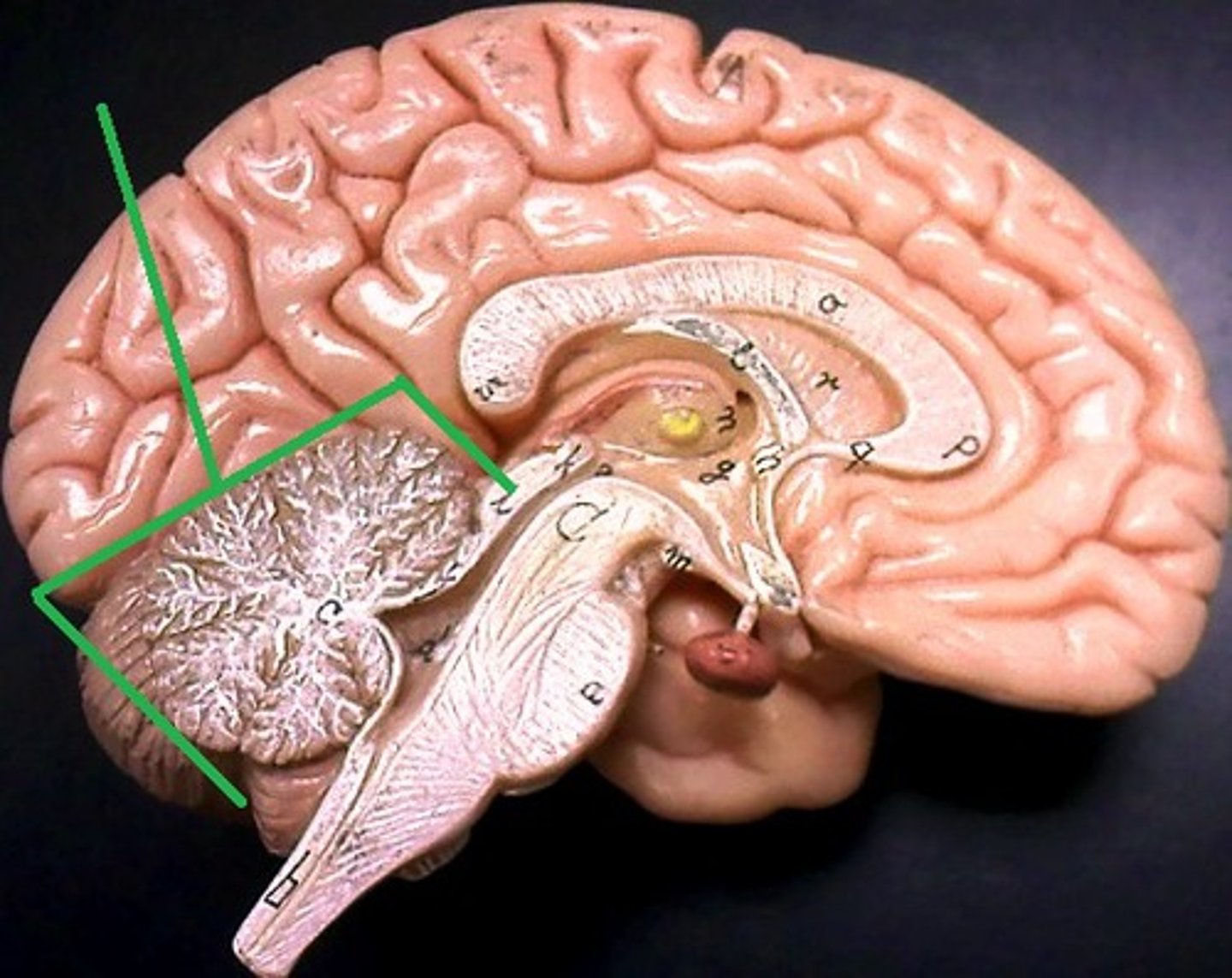
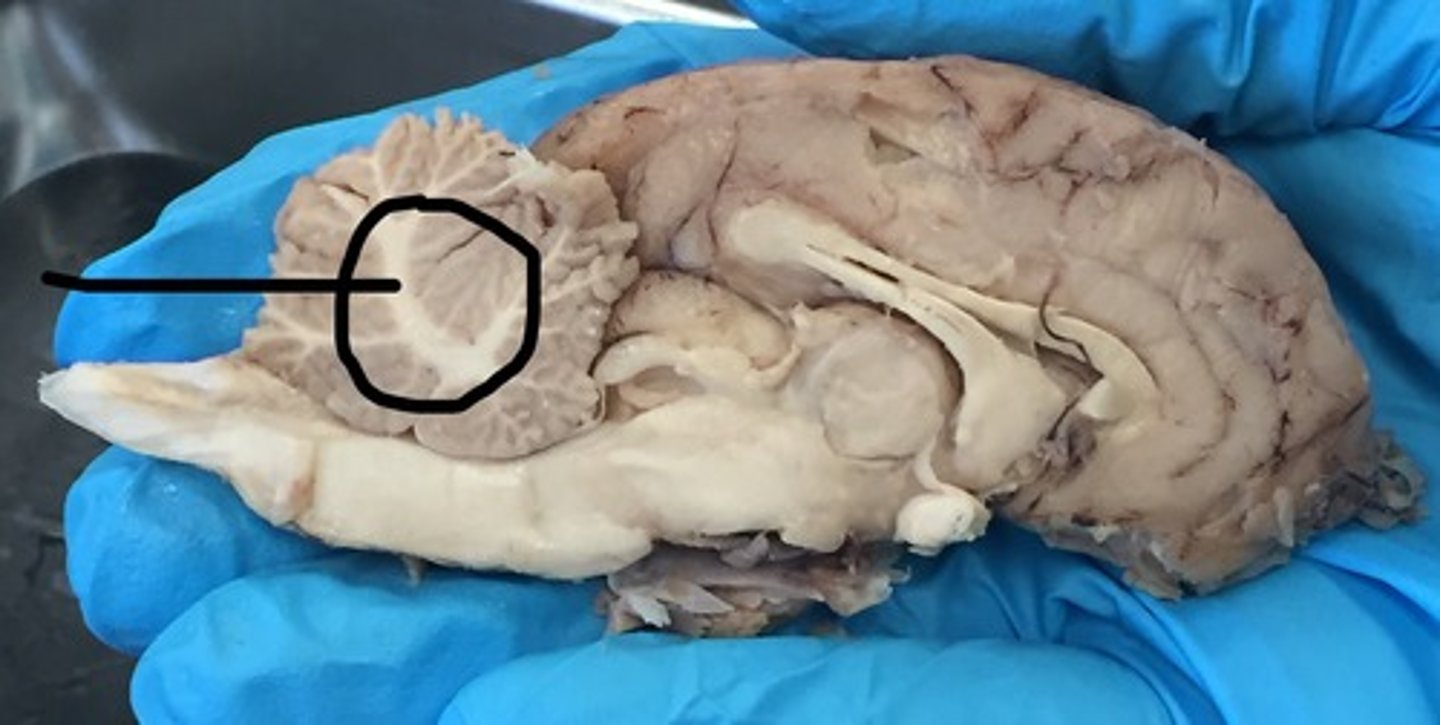
Arbor Vitae
Medulla Oblongata
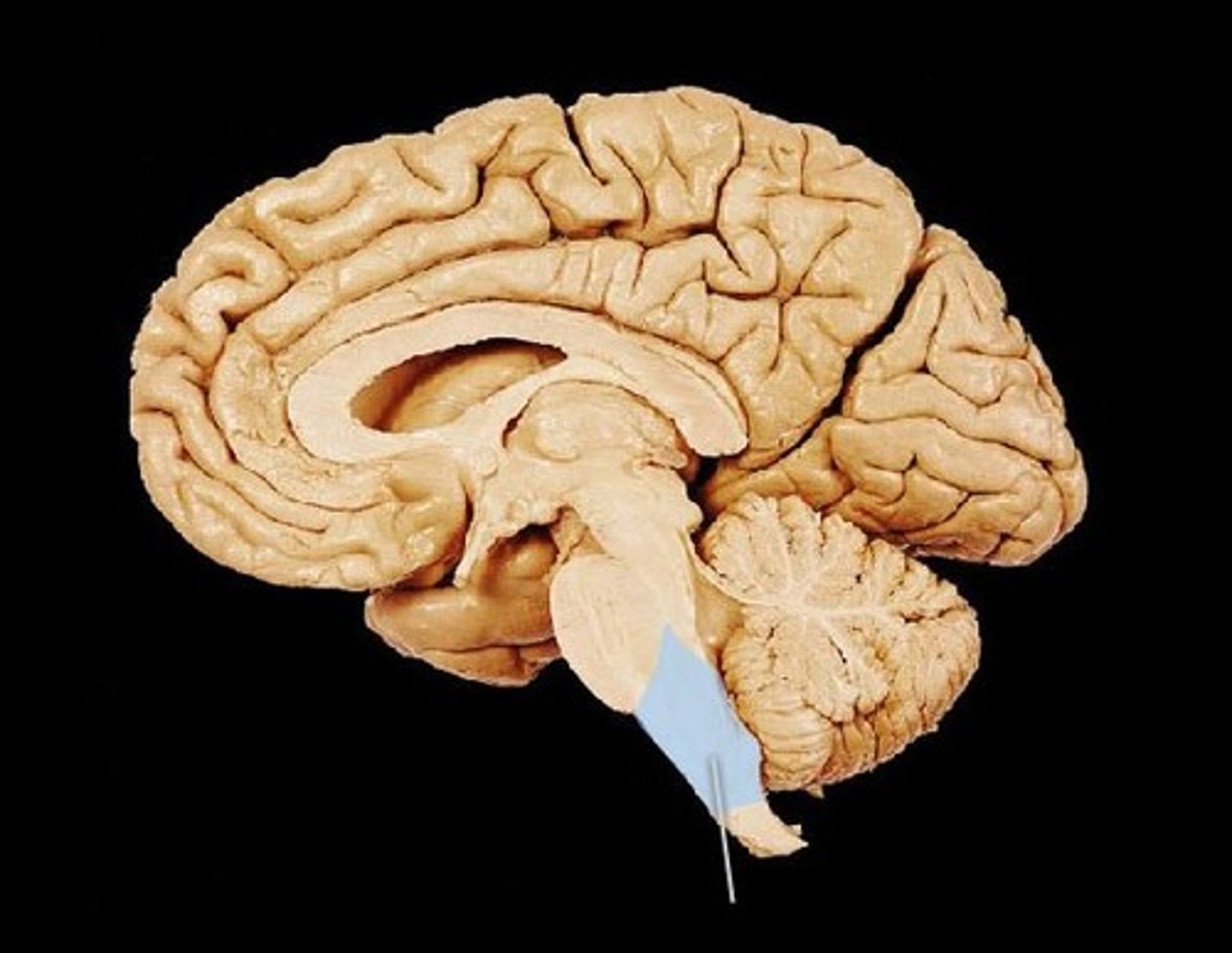
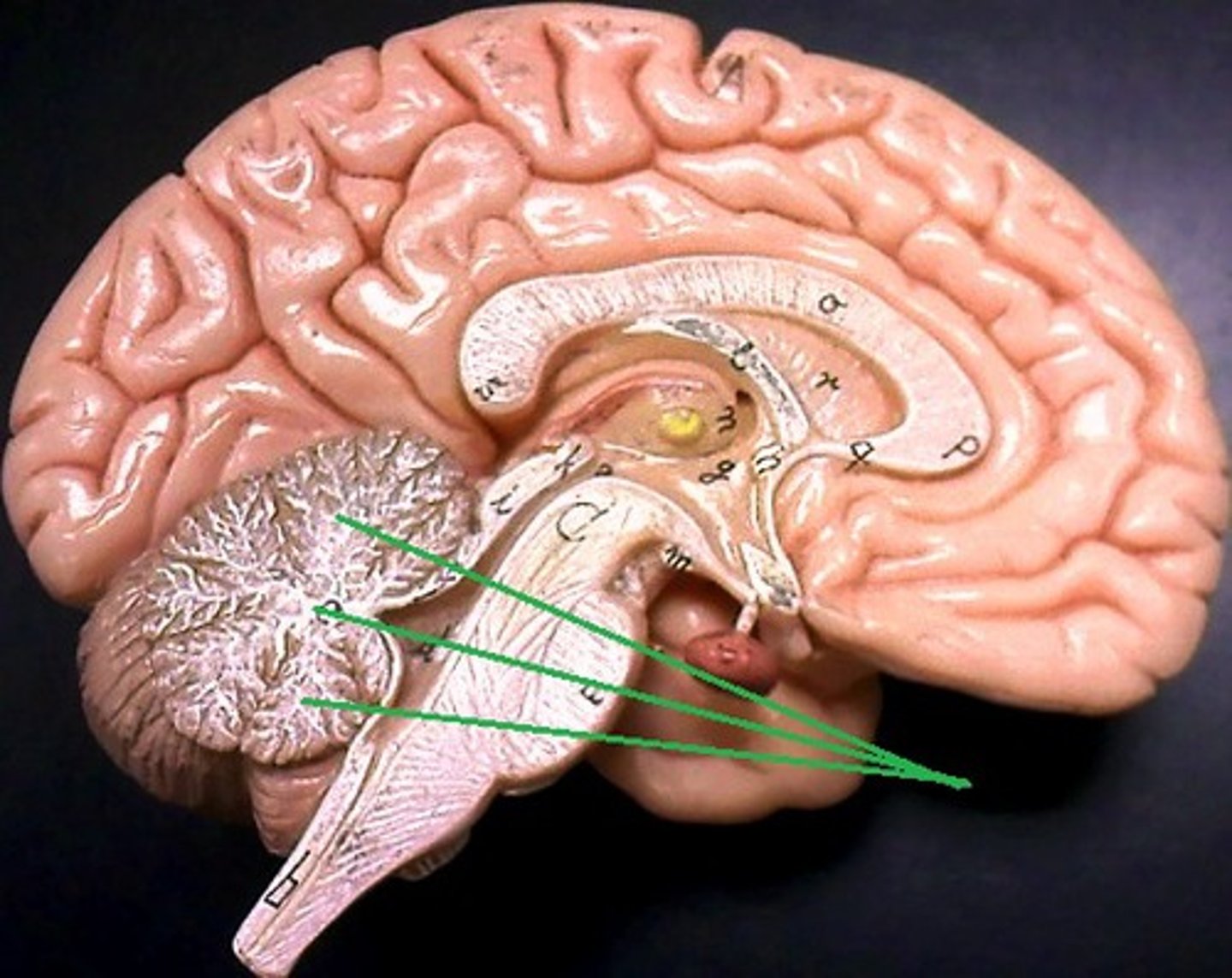
Pineal body/gland
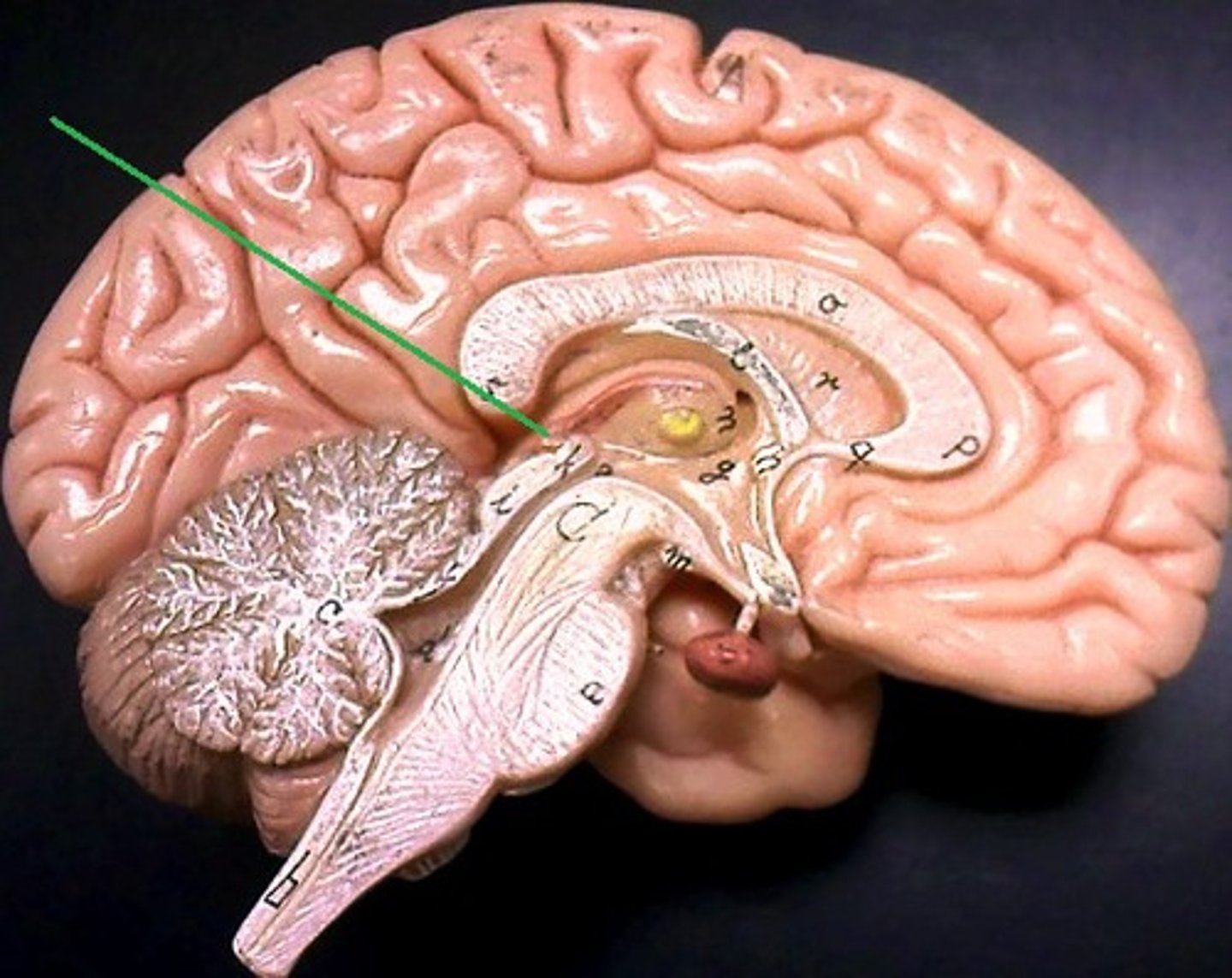
Corpus Callosum
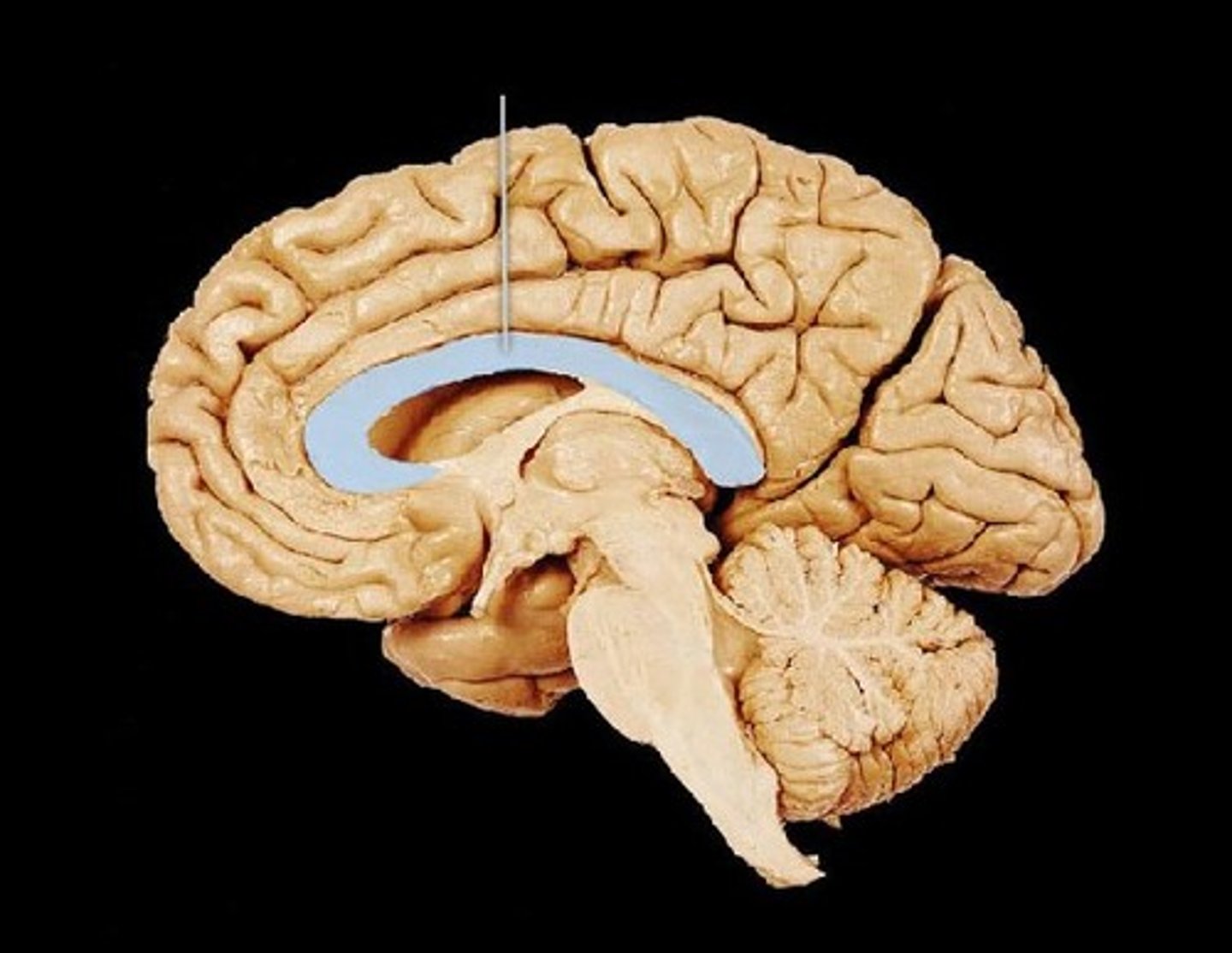
Choroid Plexus
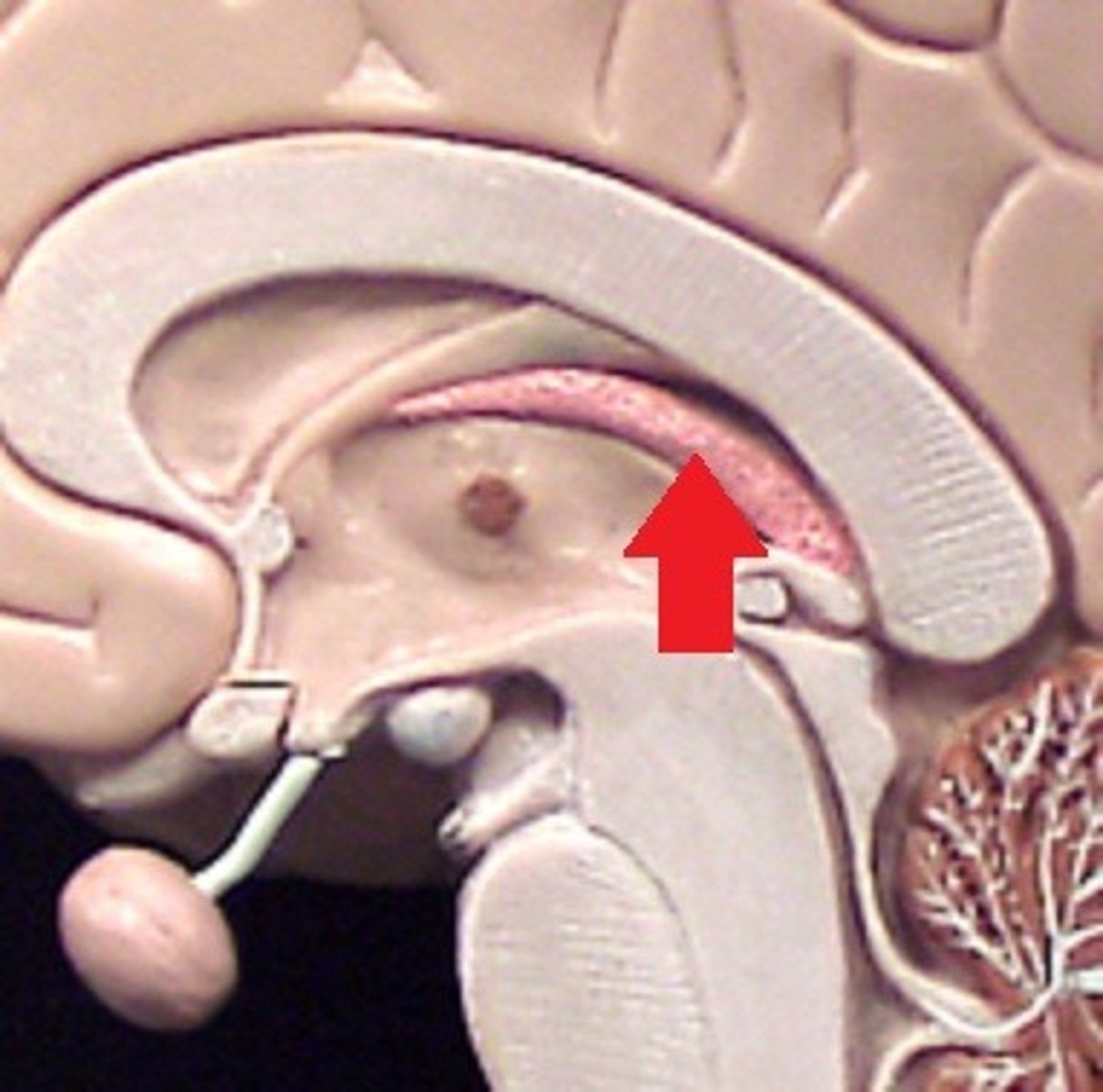
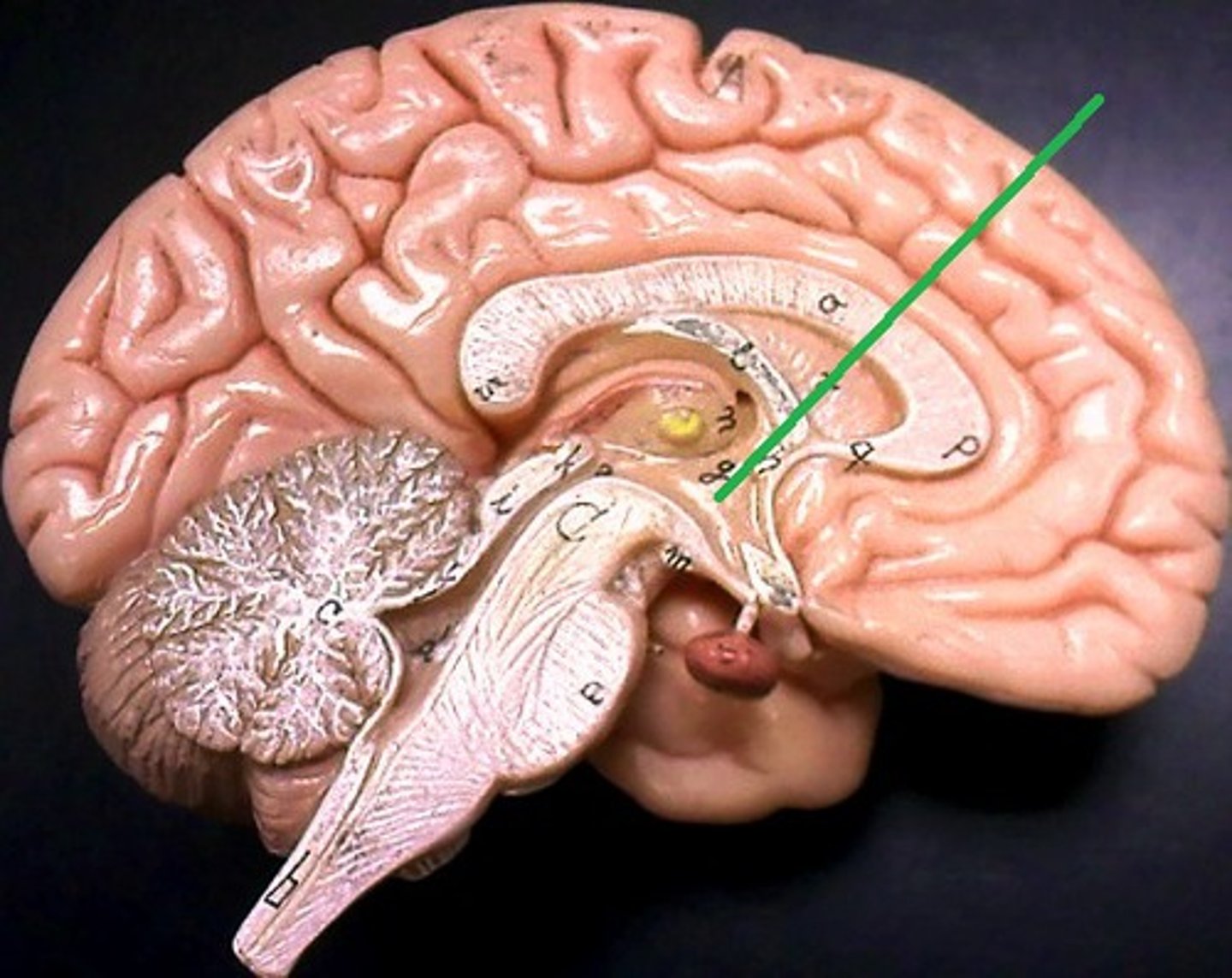
Fornix
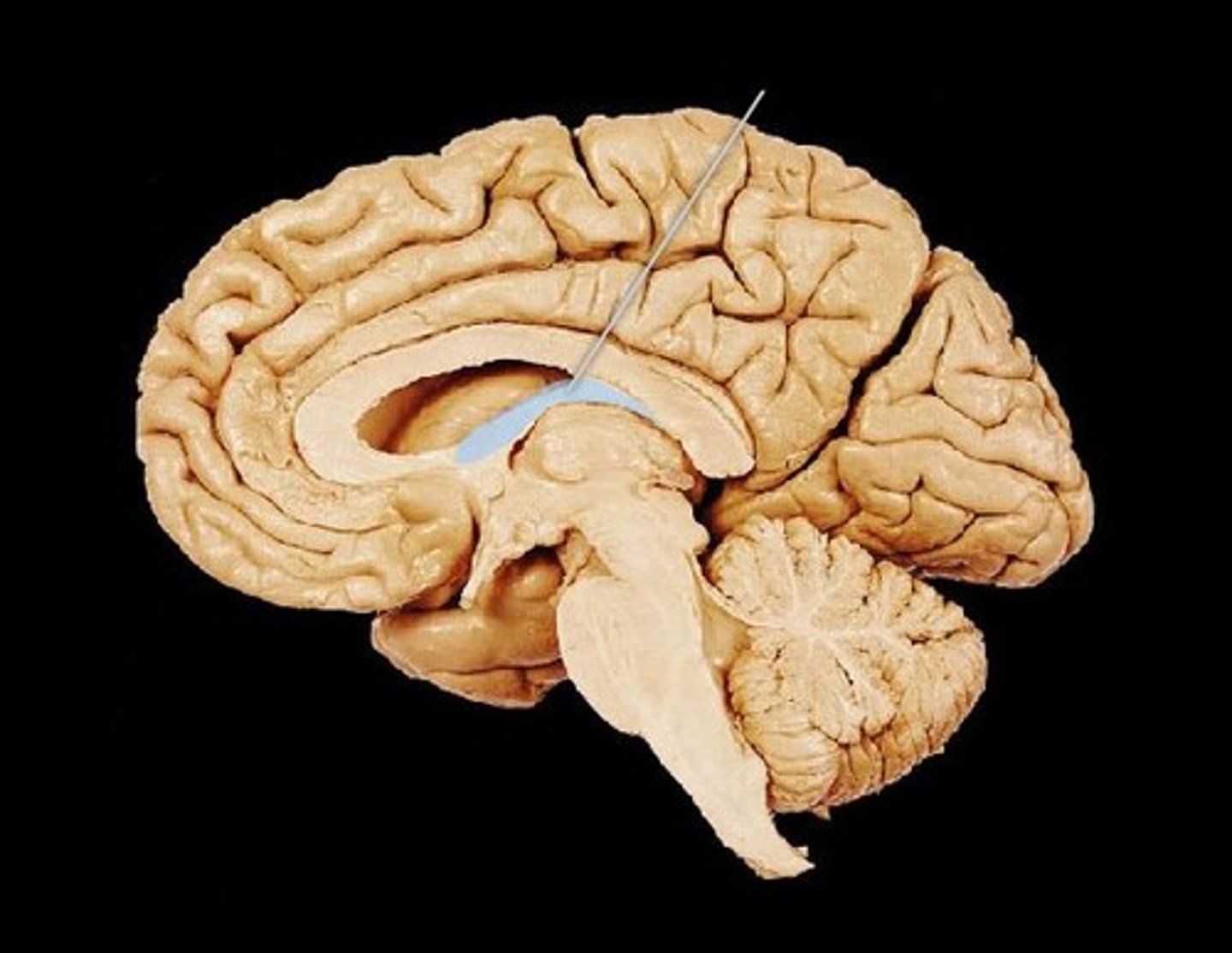
Optic Chiasm
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Infundibulum
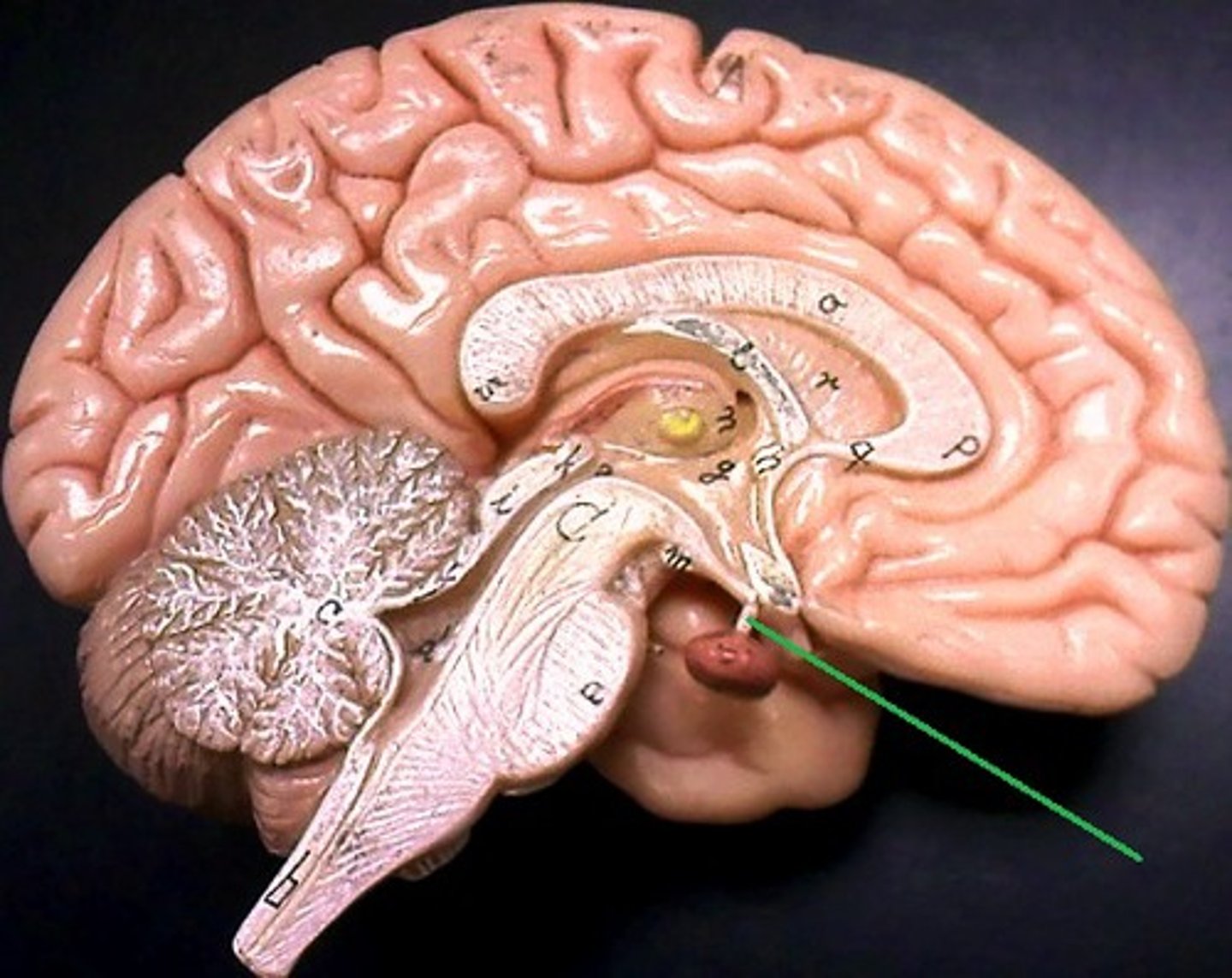
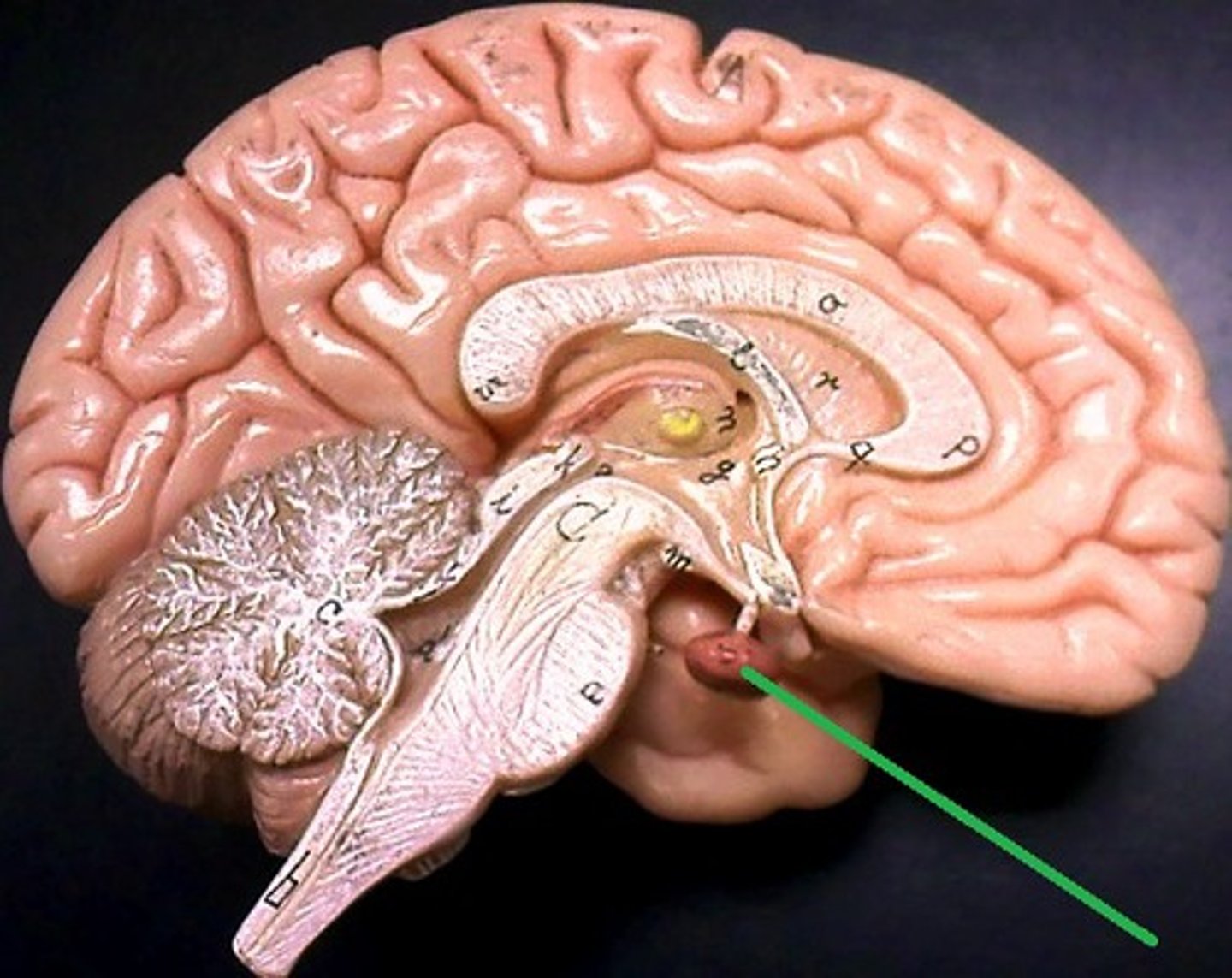
Pituitary Gland
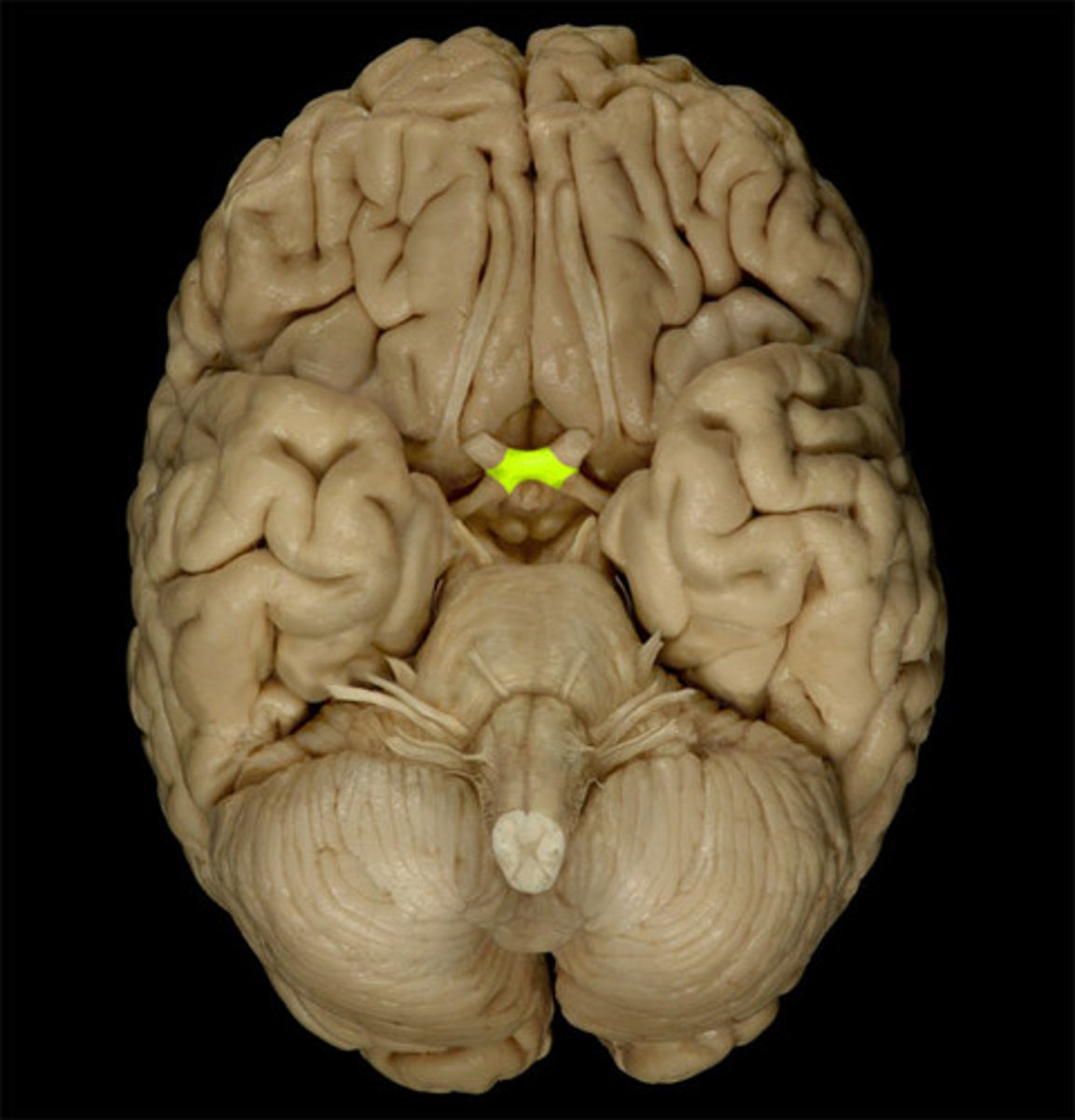
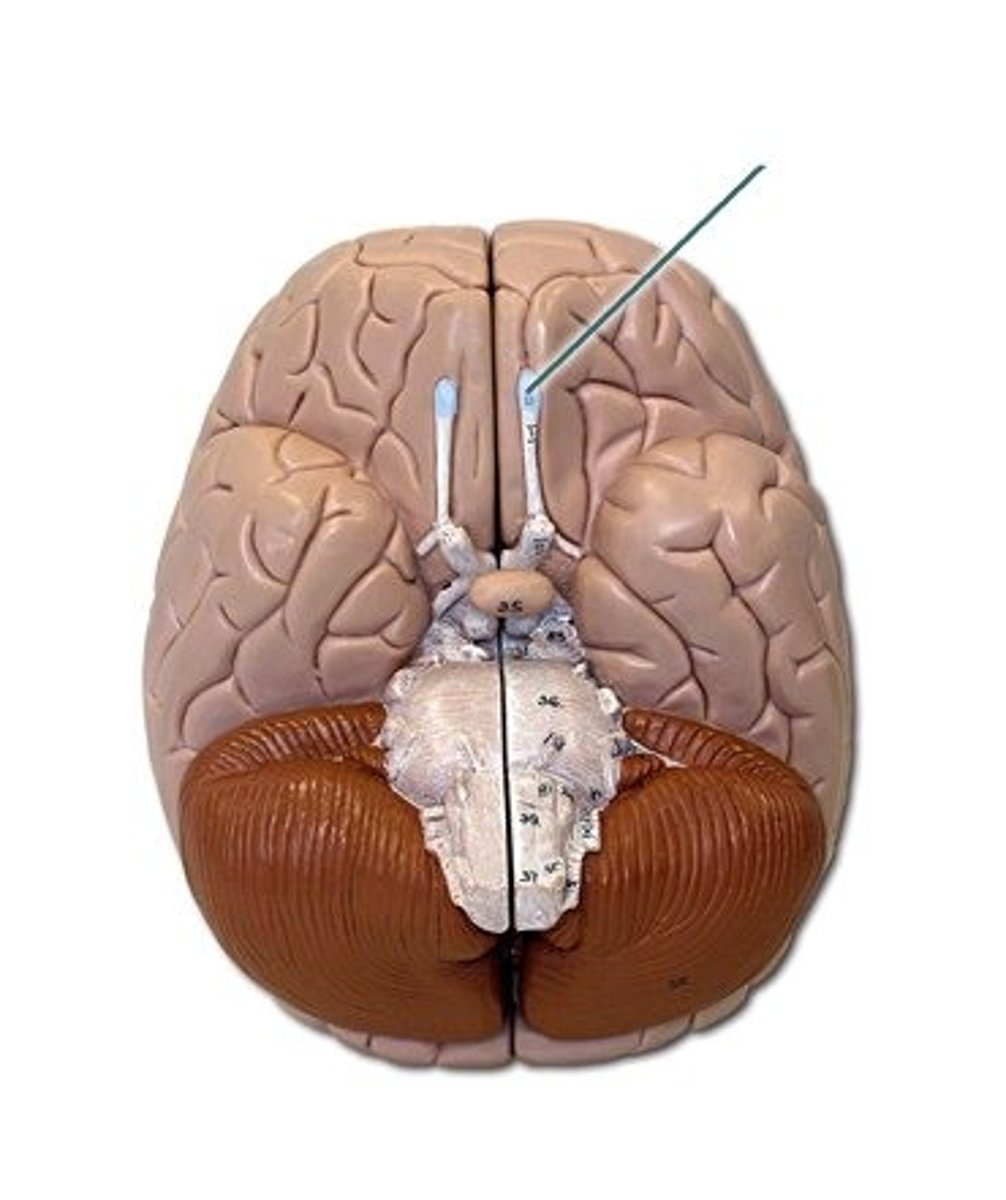
Olfactory bulb
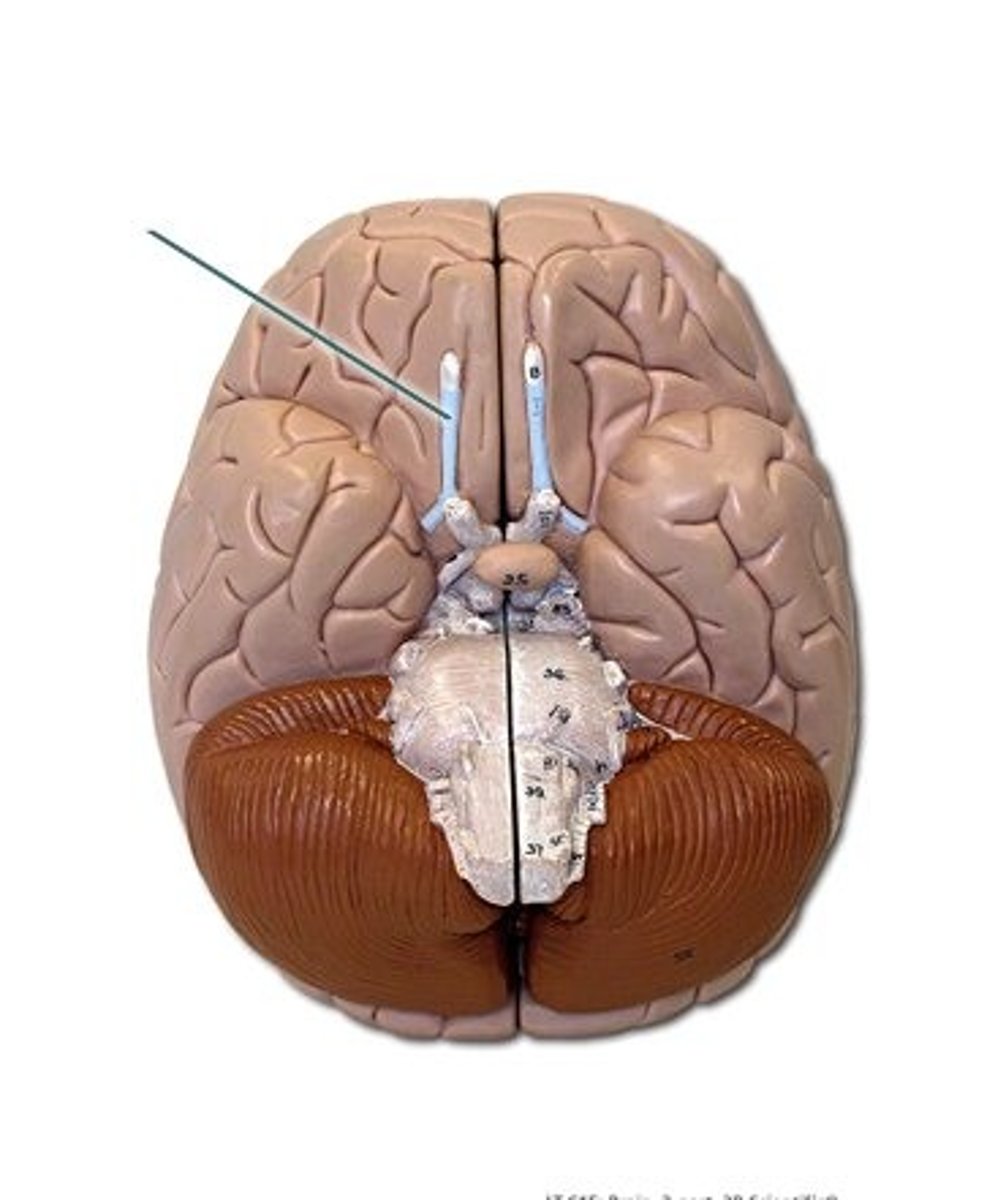
Olfactory tract
Optic
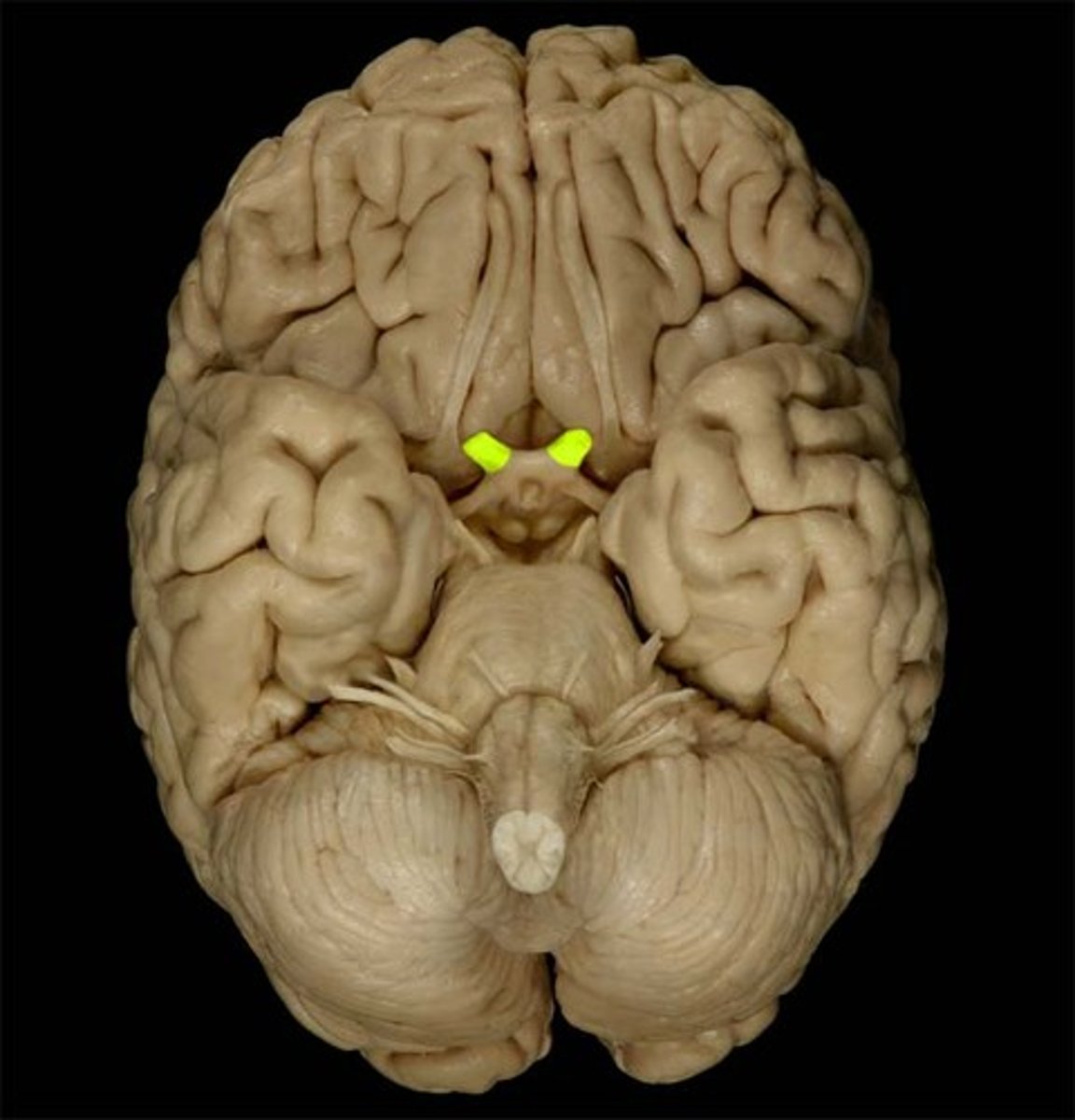
Oculomotor
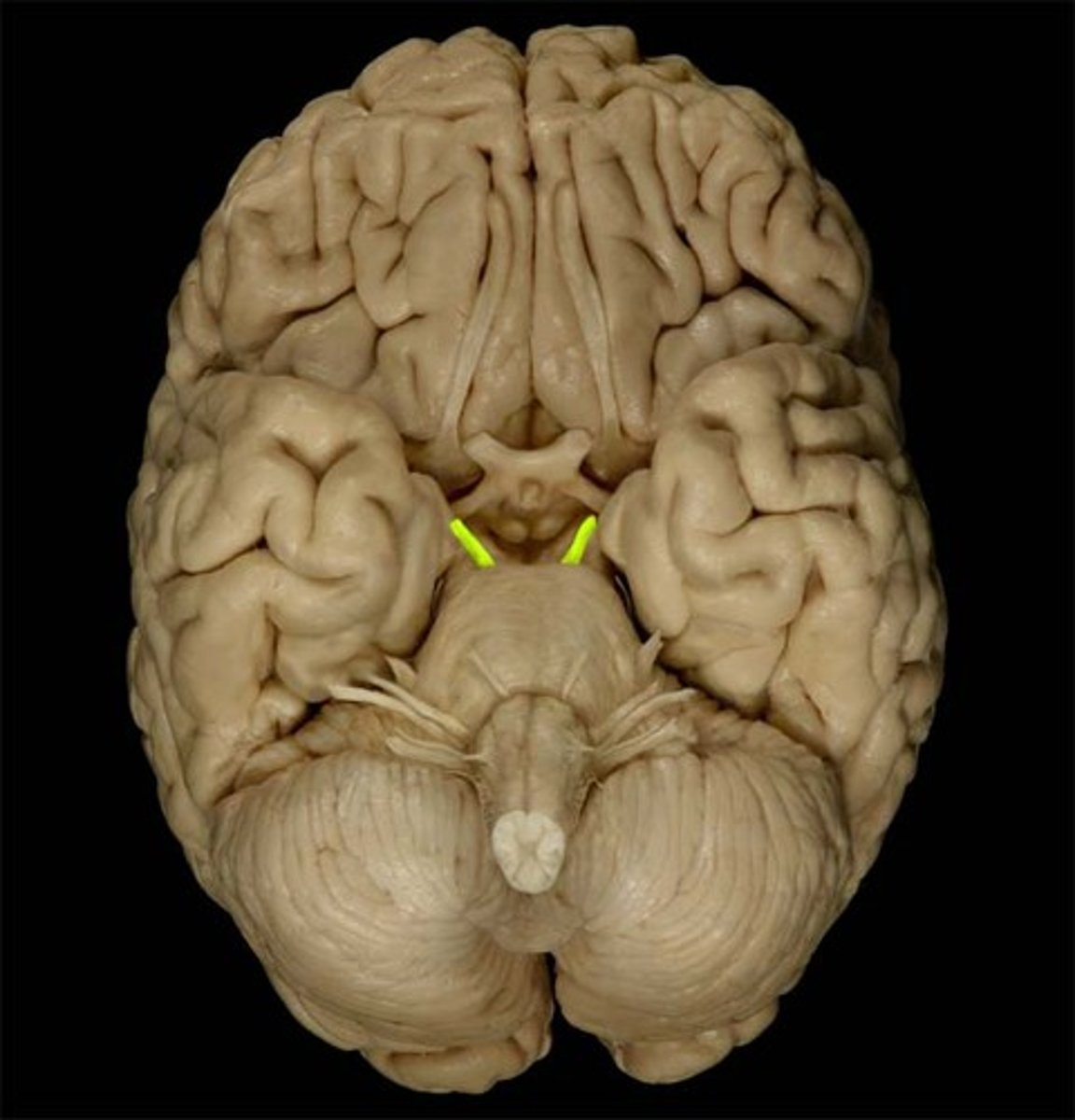
Trigeminal

Superior Colliculus
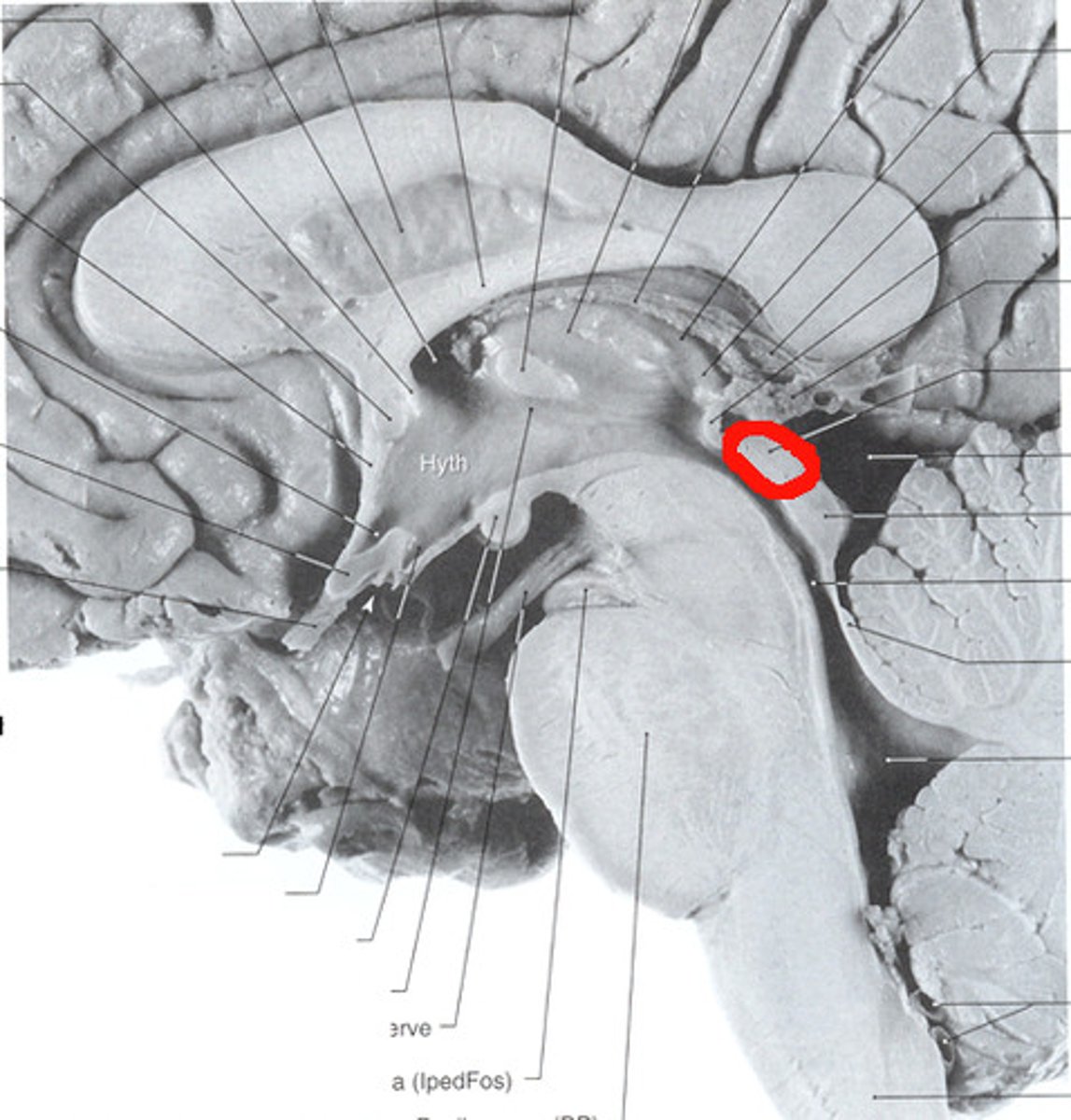
Inferior colliculus
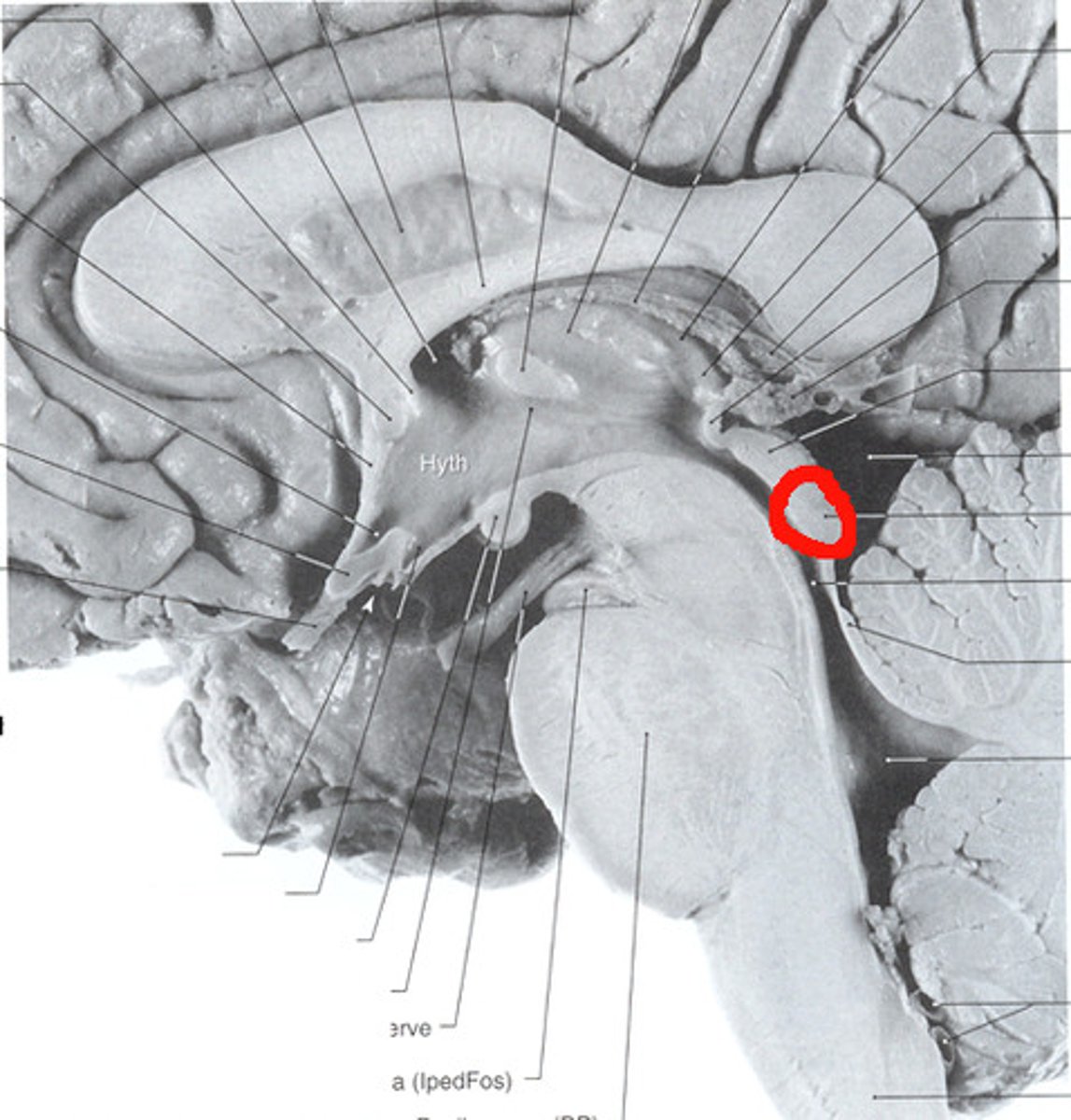
Lateral ventricle
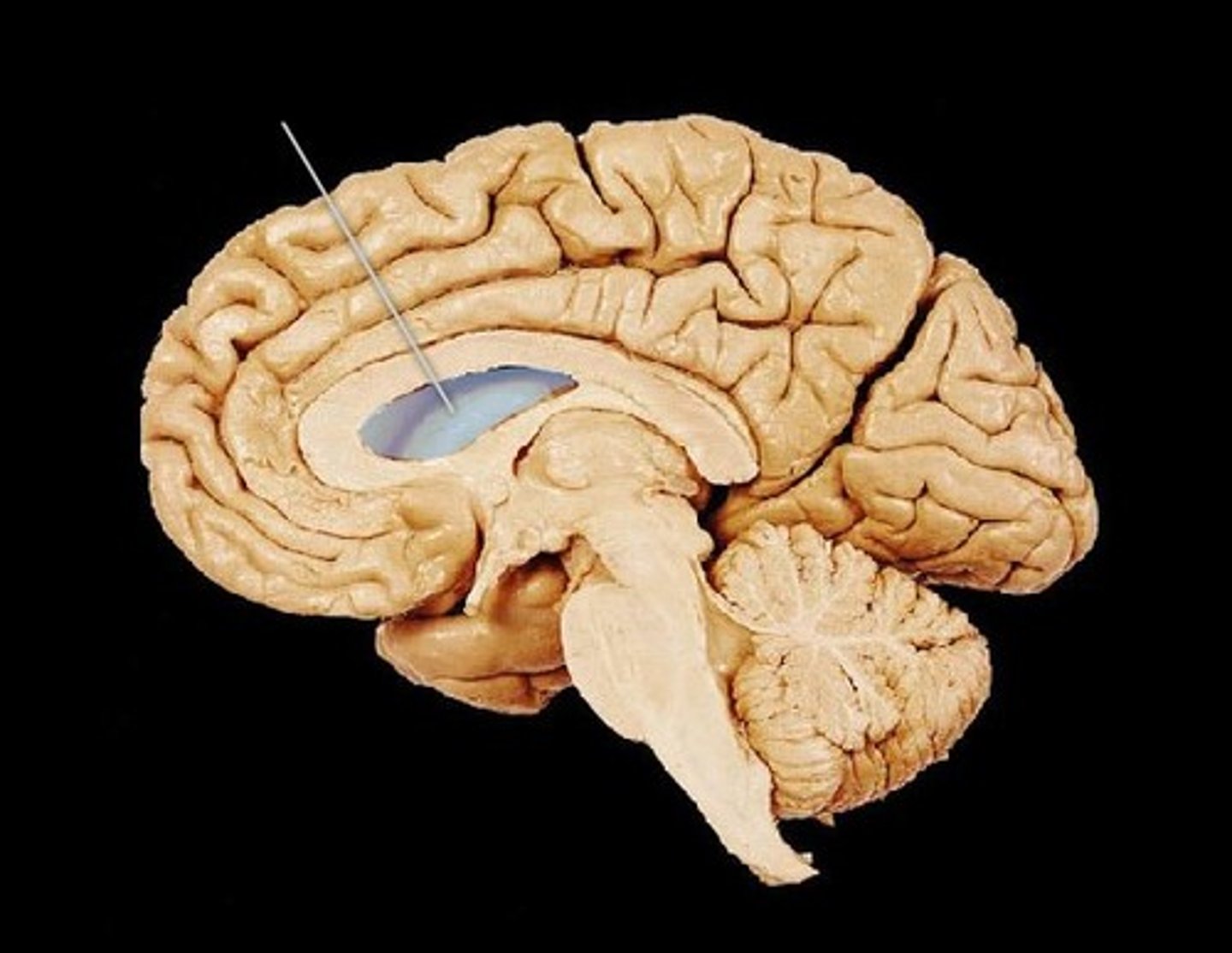
third ventricle
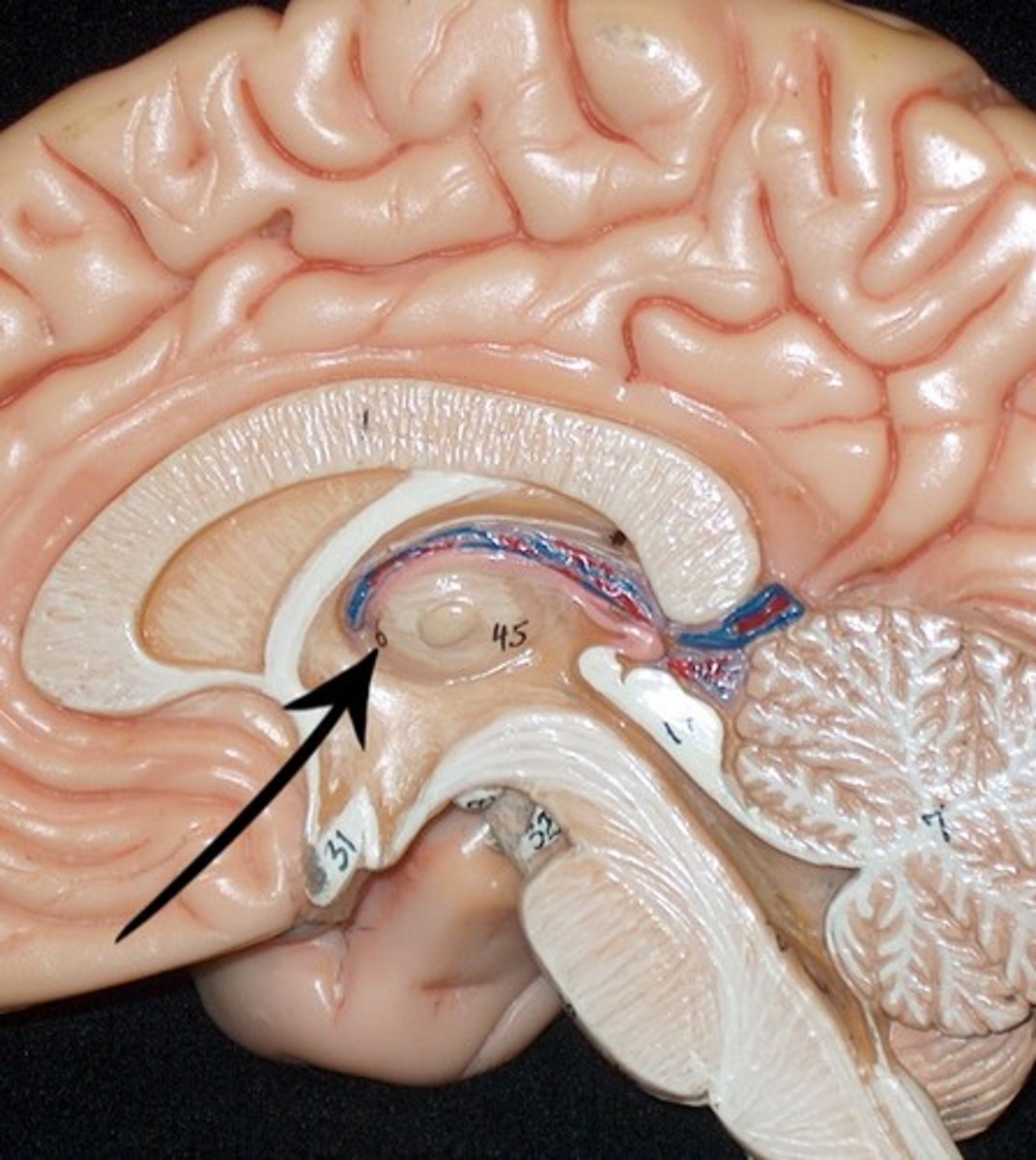
cerebral aqueduct
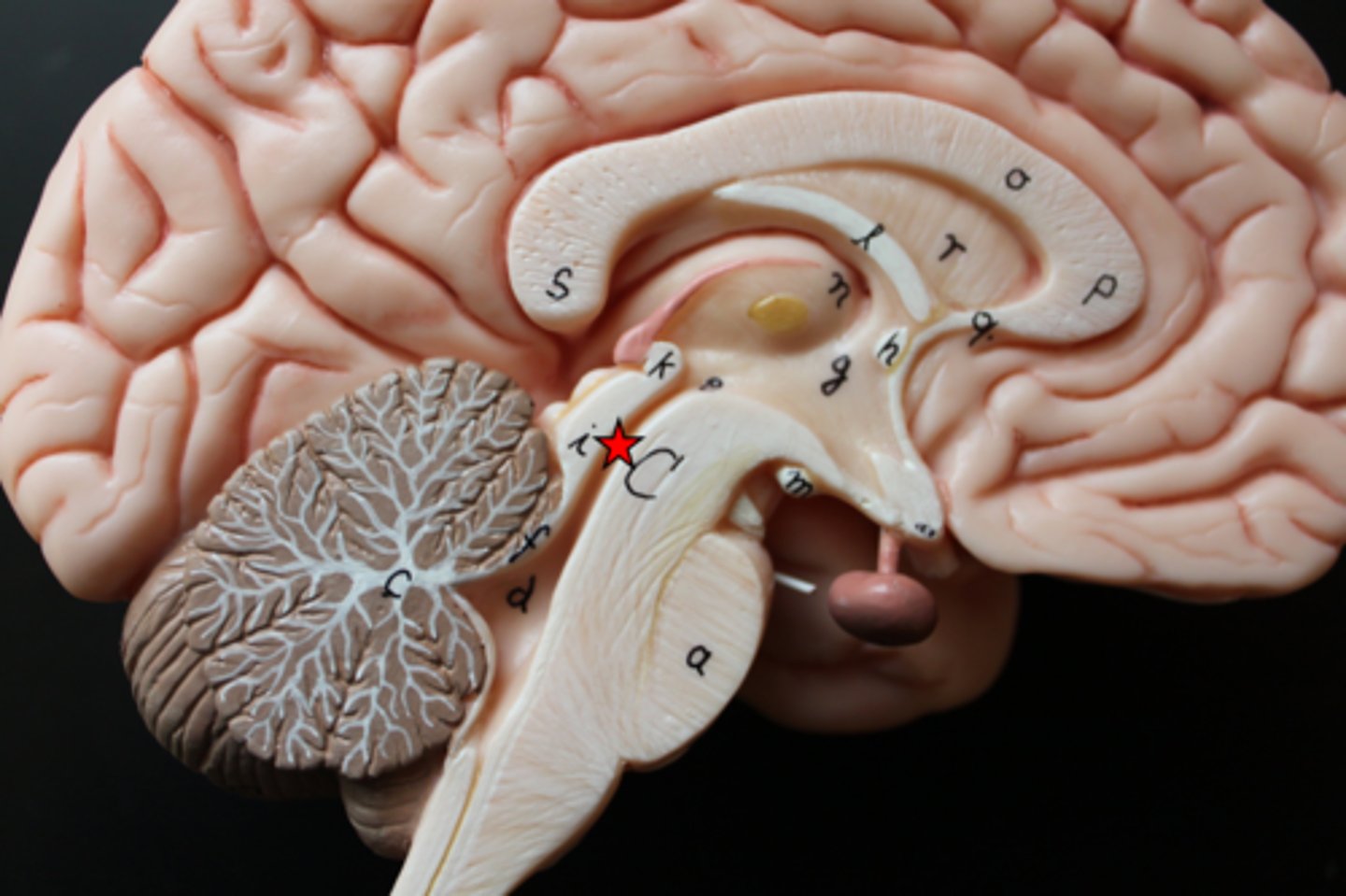
fourth ventricle
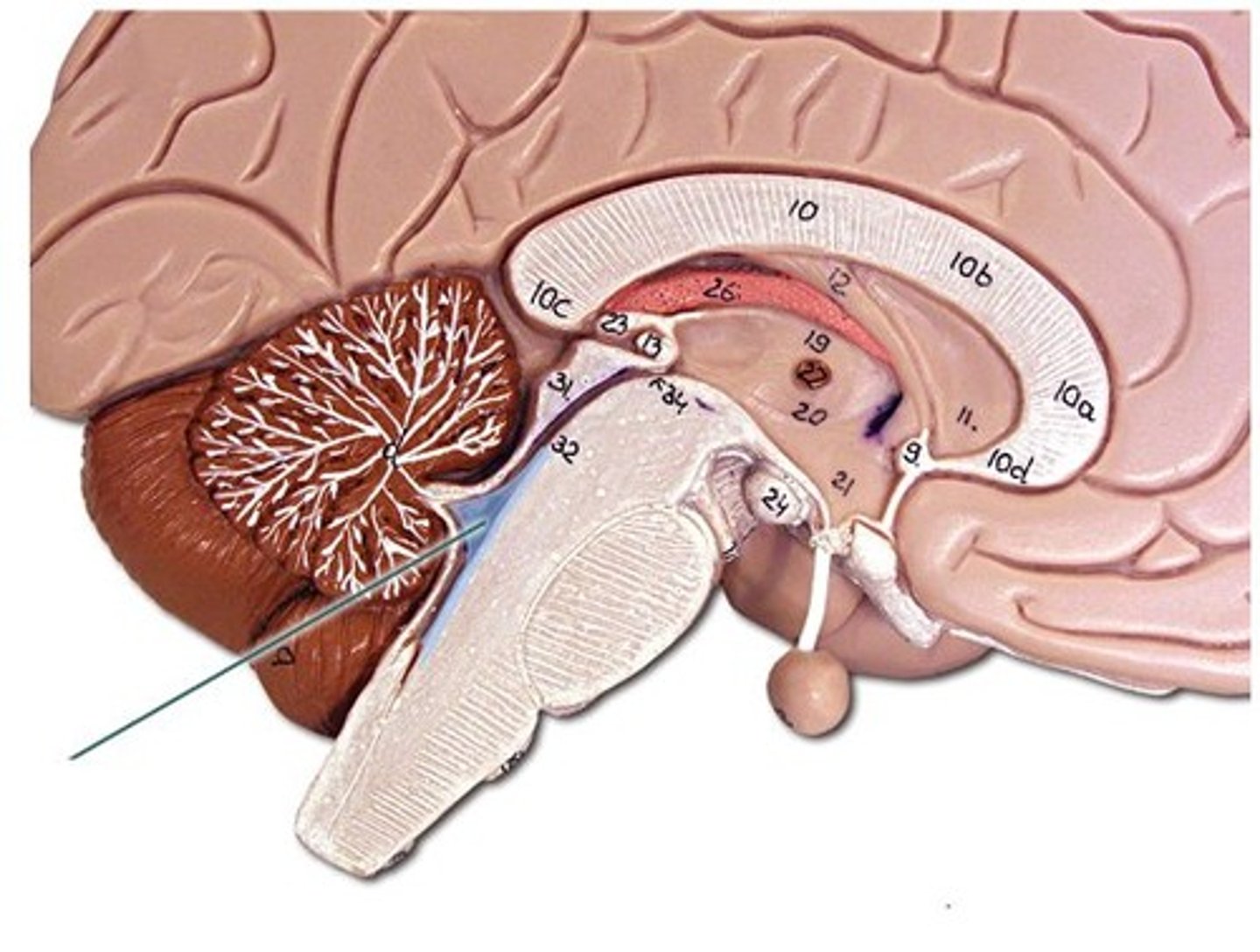
Meninges (dura mater)
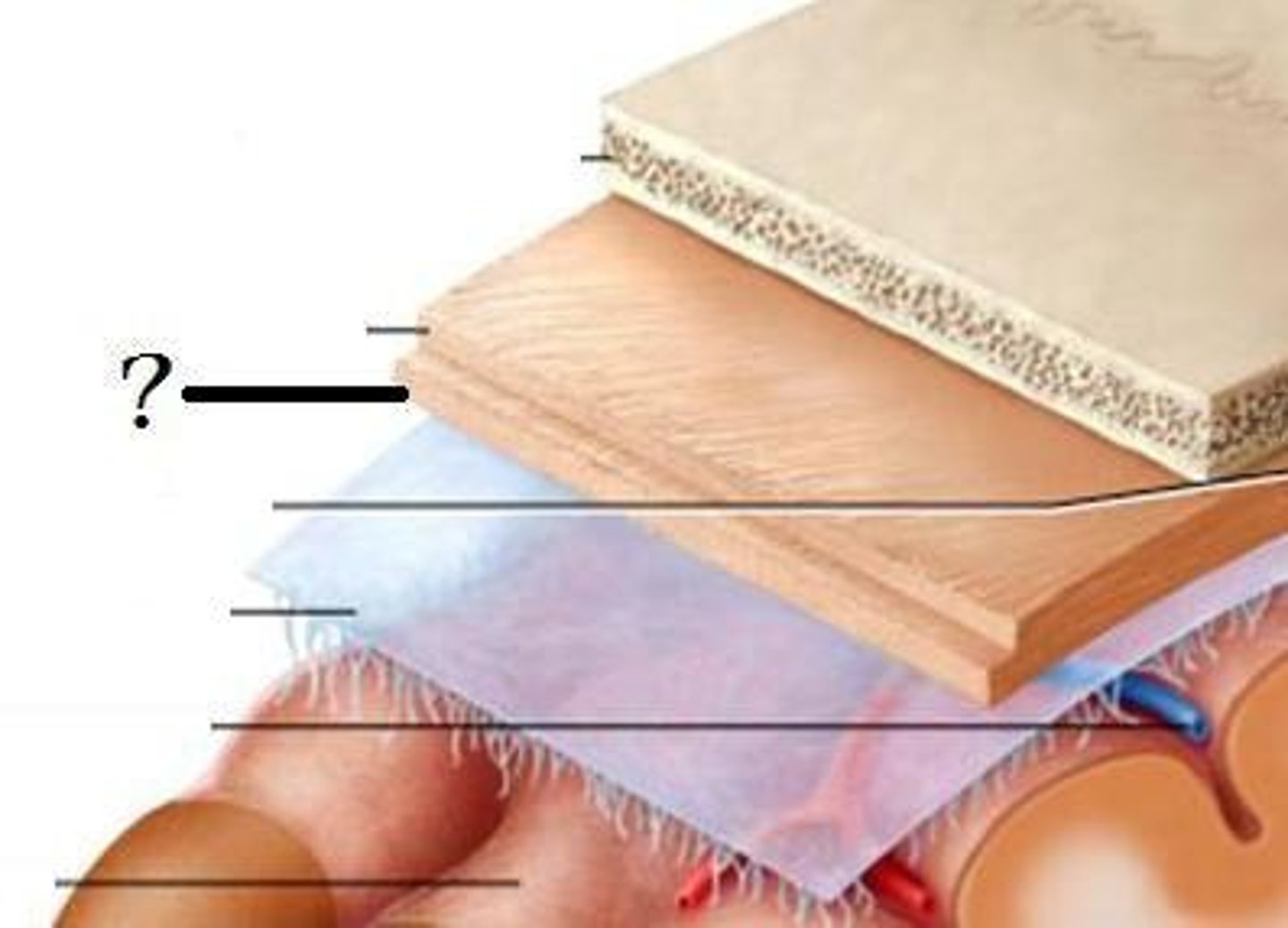
Meninges (arachnoid mater)
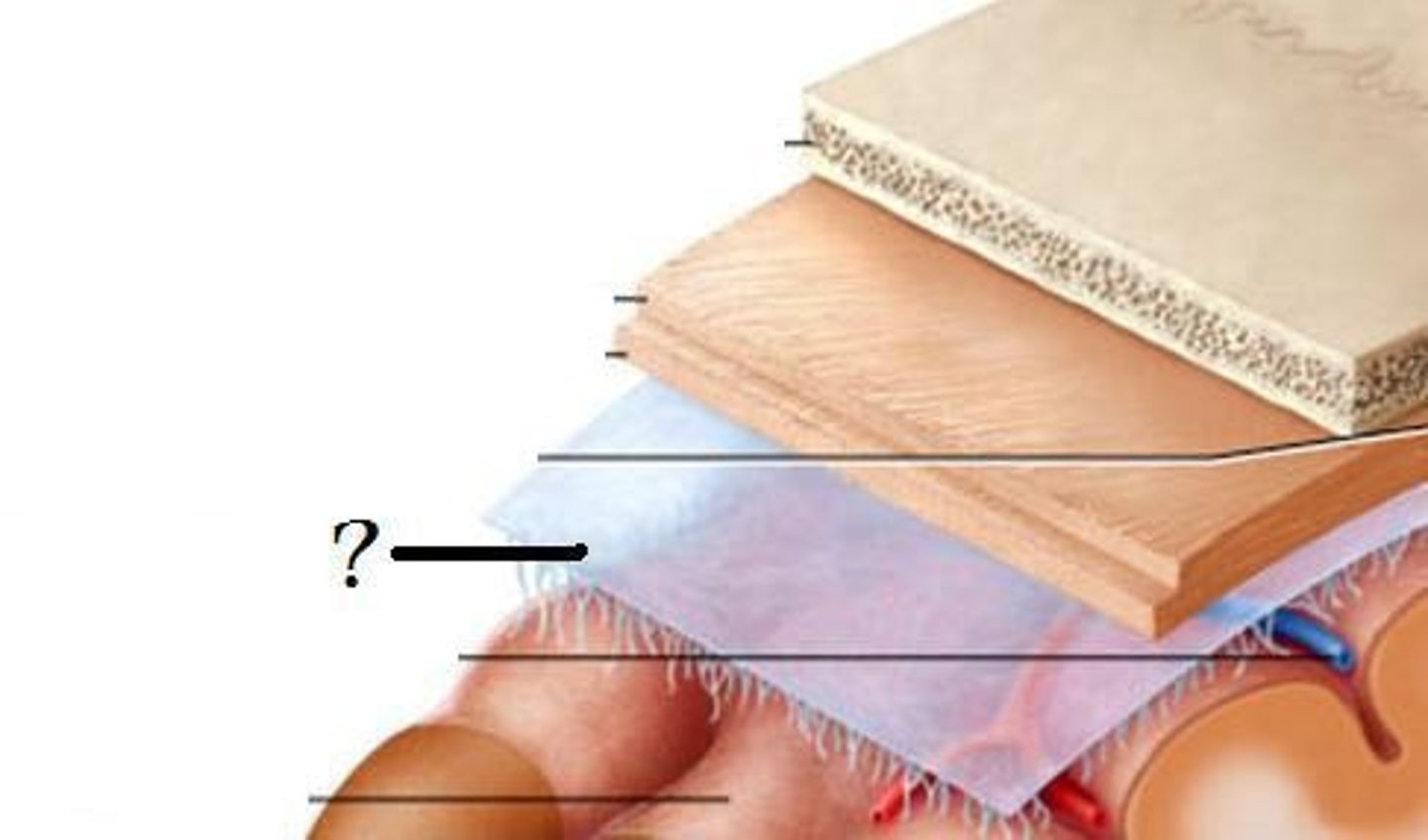
Meninges (pia mater)
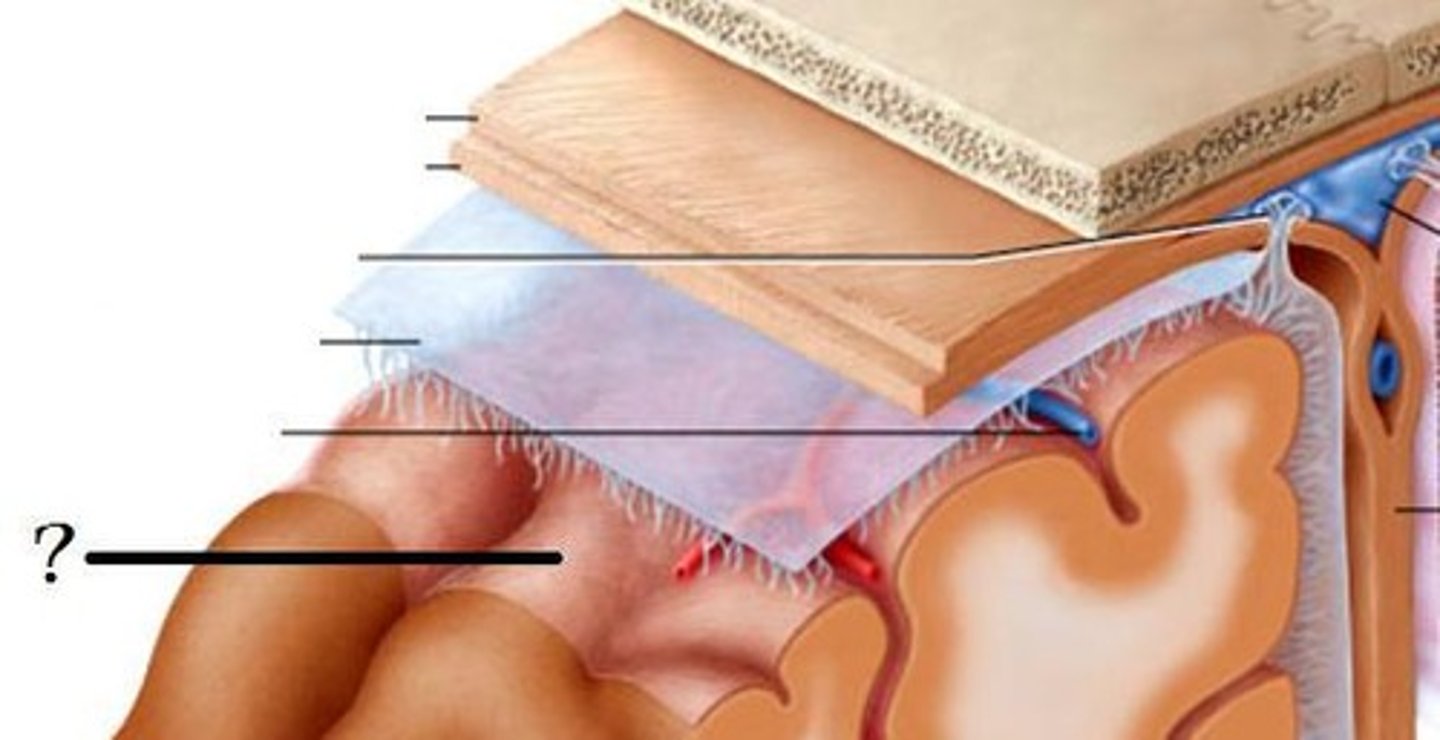
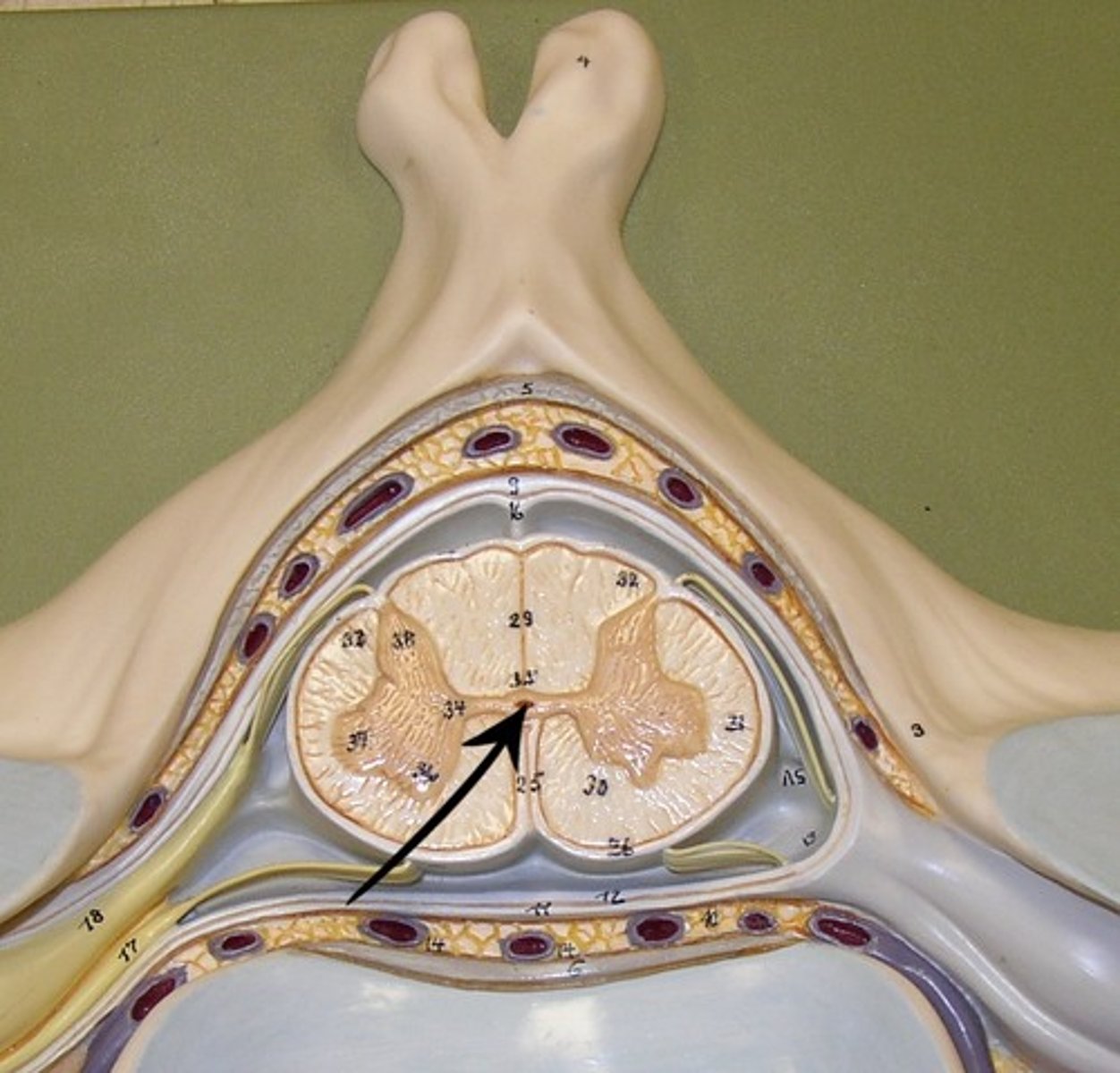
white columns/matter
gray matter
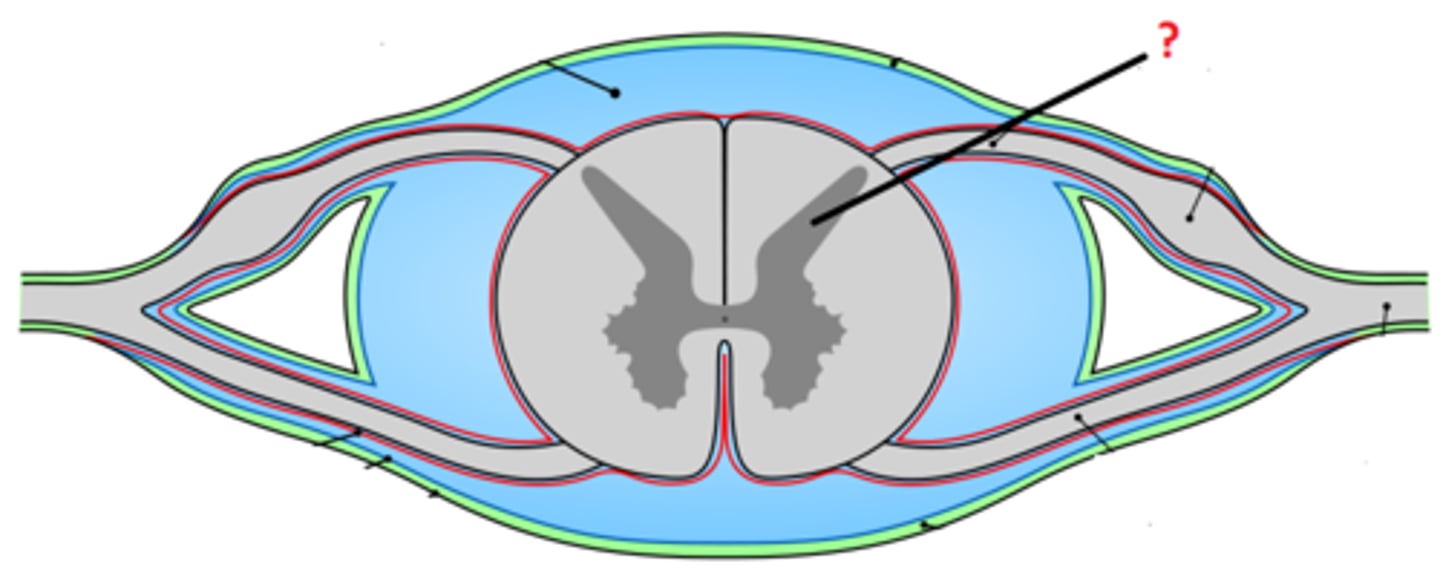
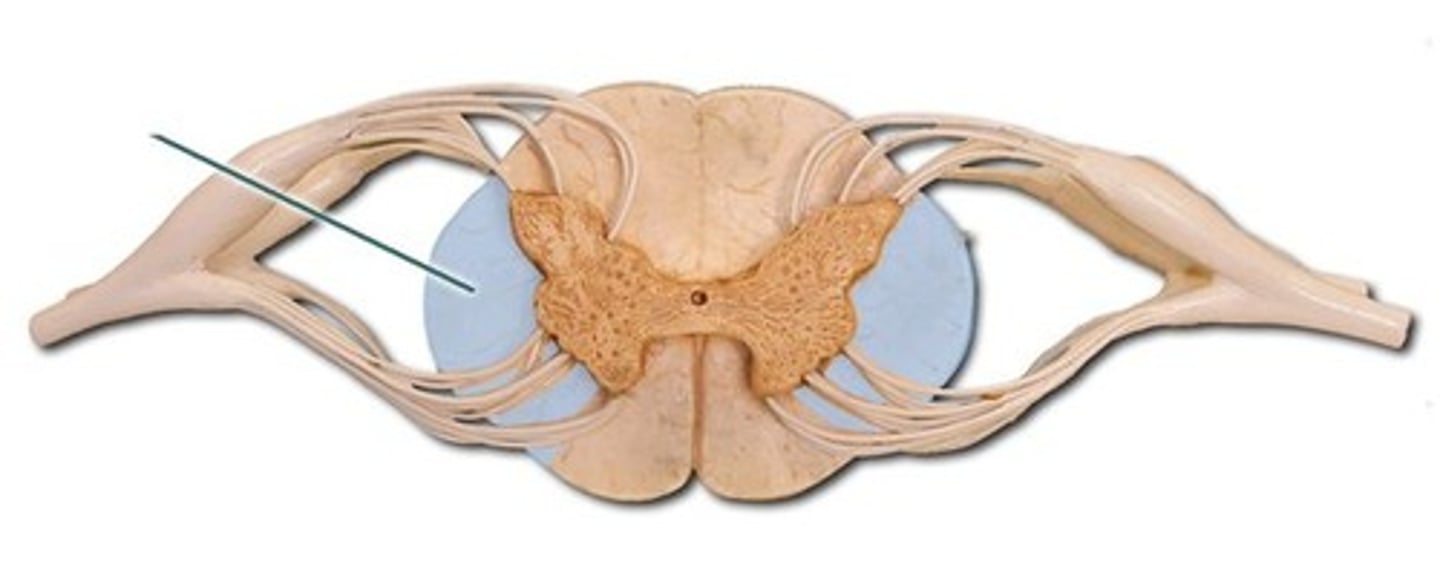
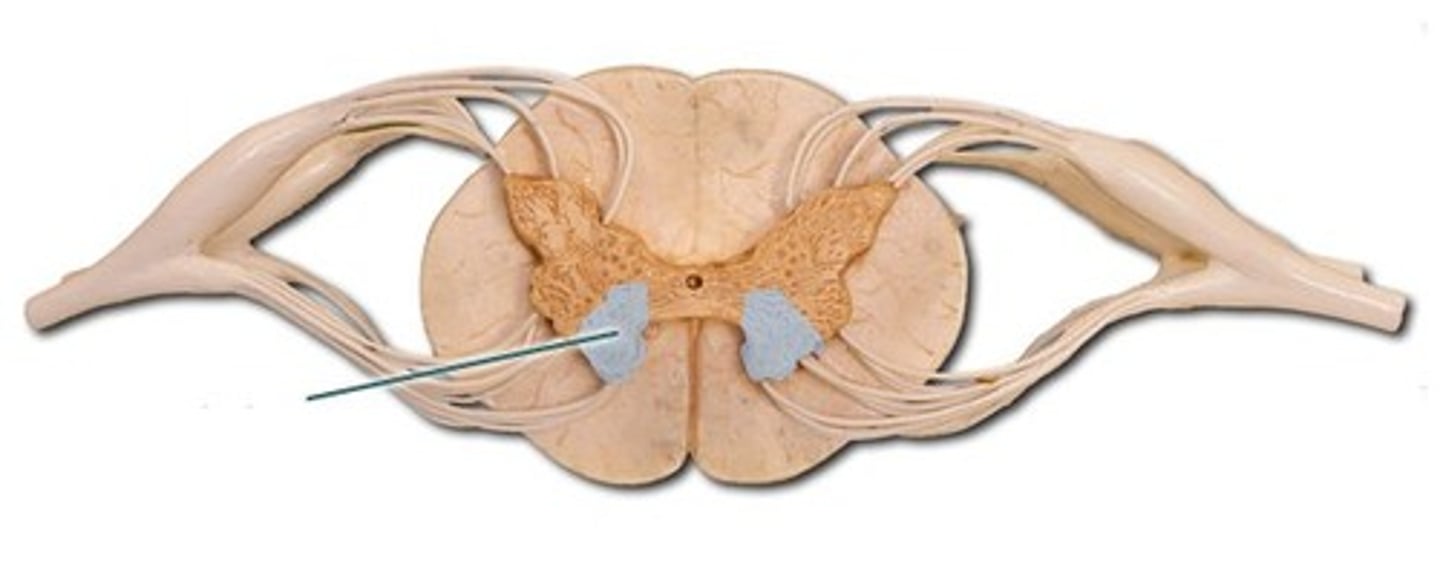
dorsal horn
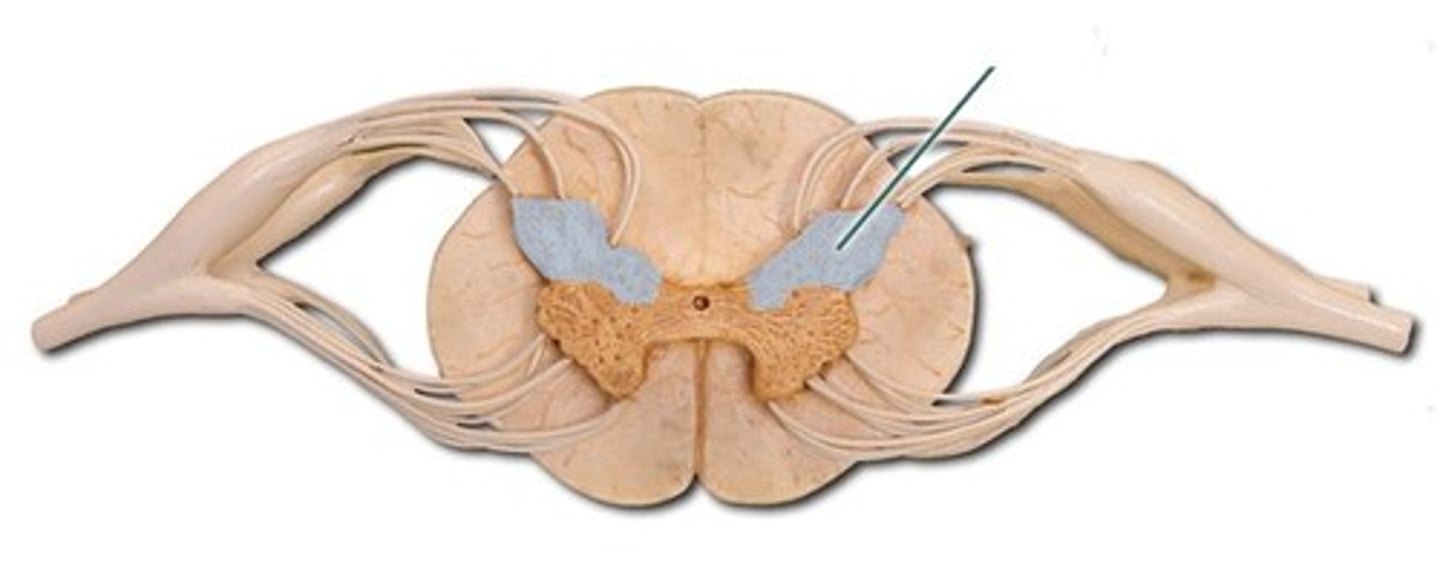
lateral horn
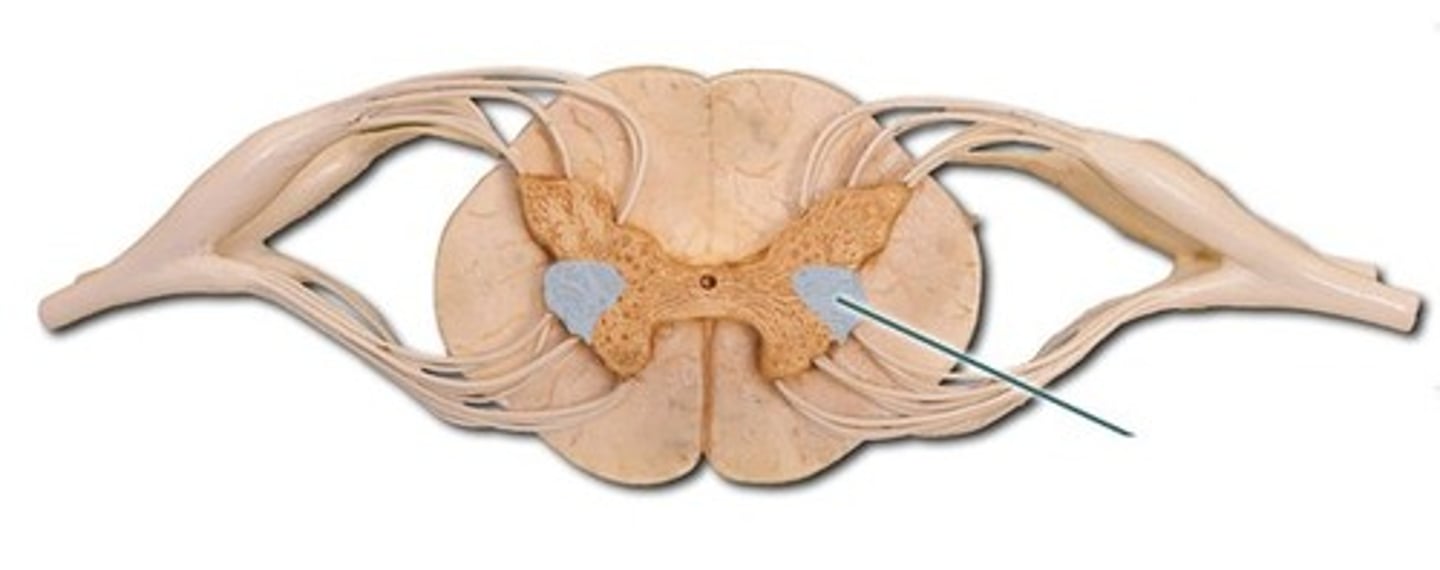
ventral horn
dorsal median sulcus
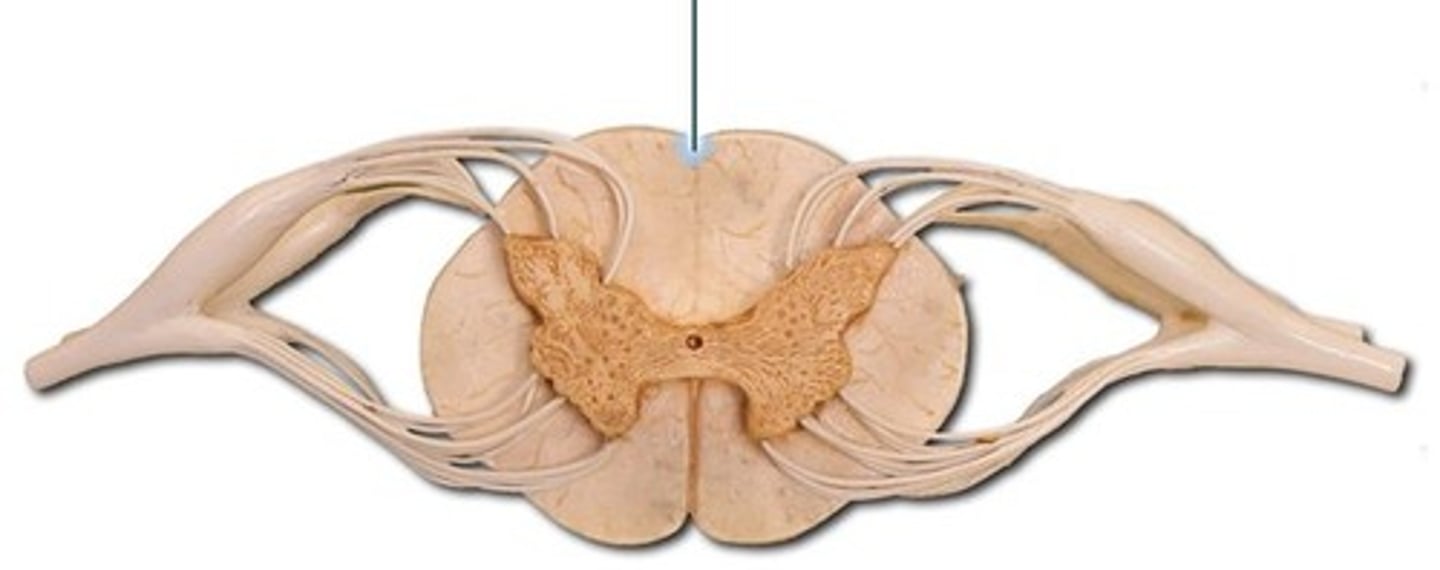
ventral median fissure
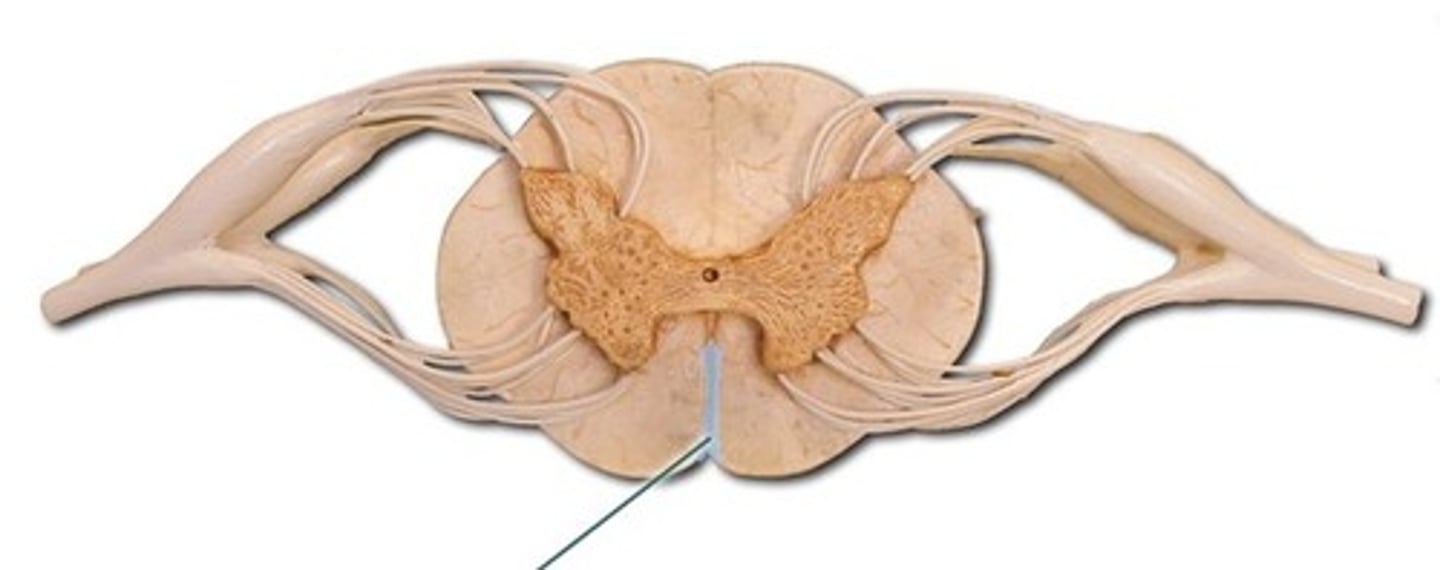
central canal
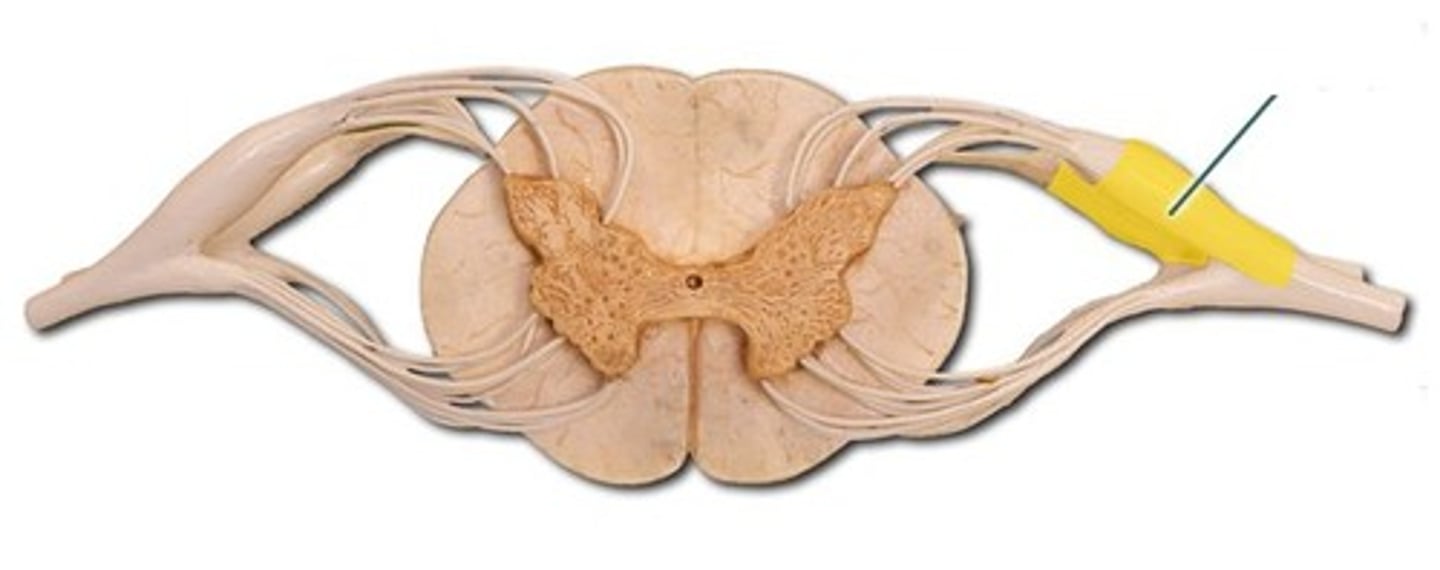
ventral root
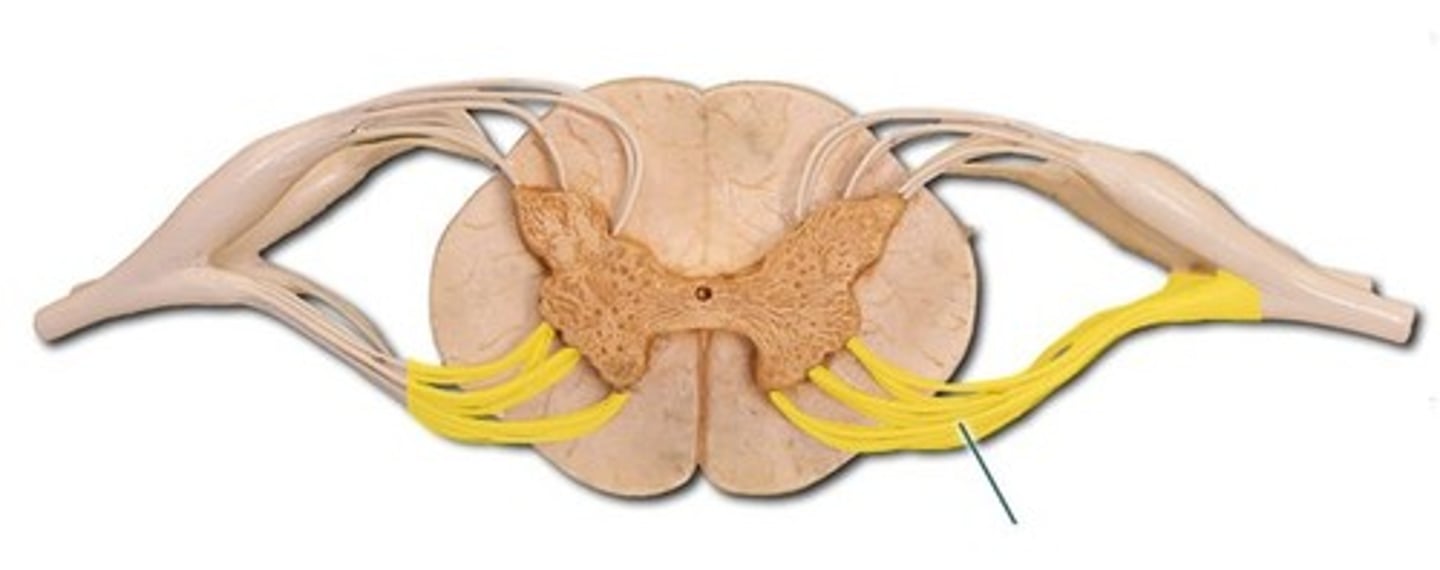
dorsal root
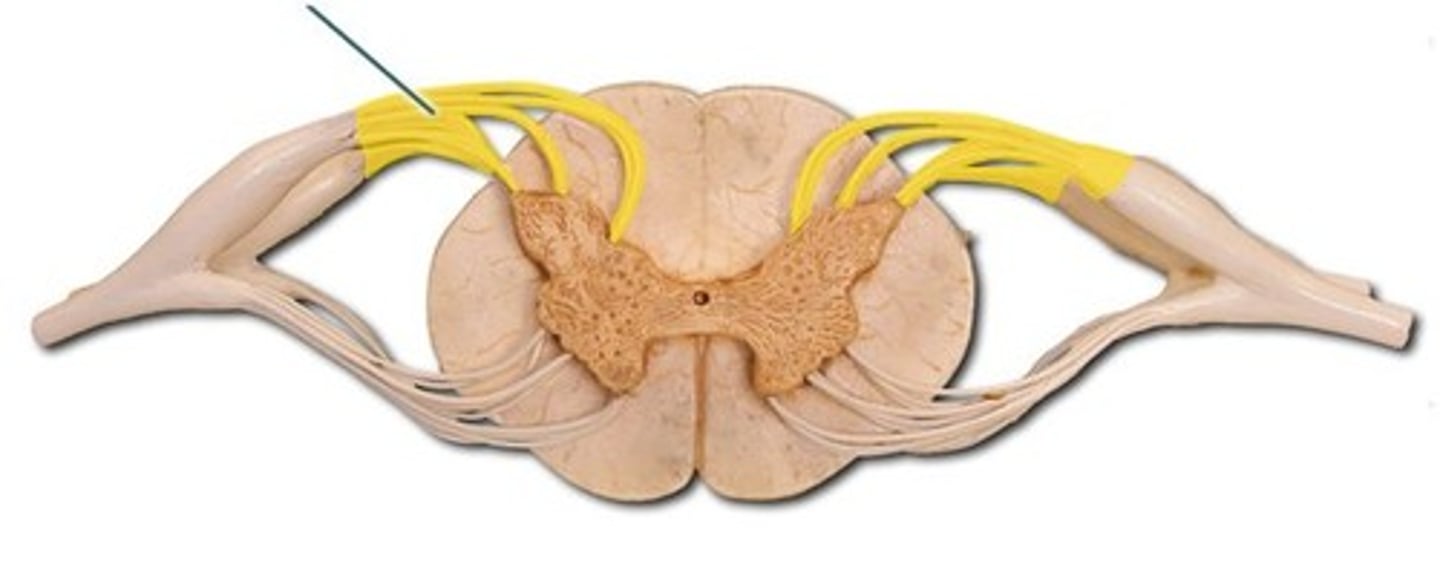
dorsal root ganglion
Dura mater
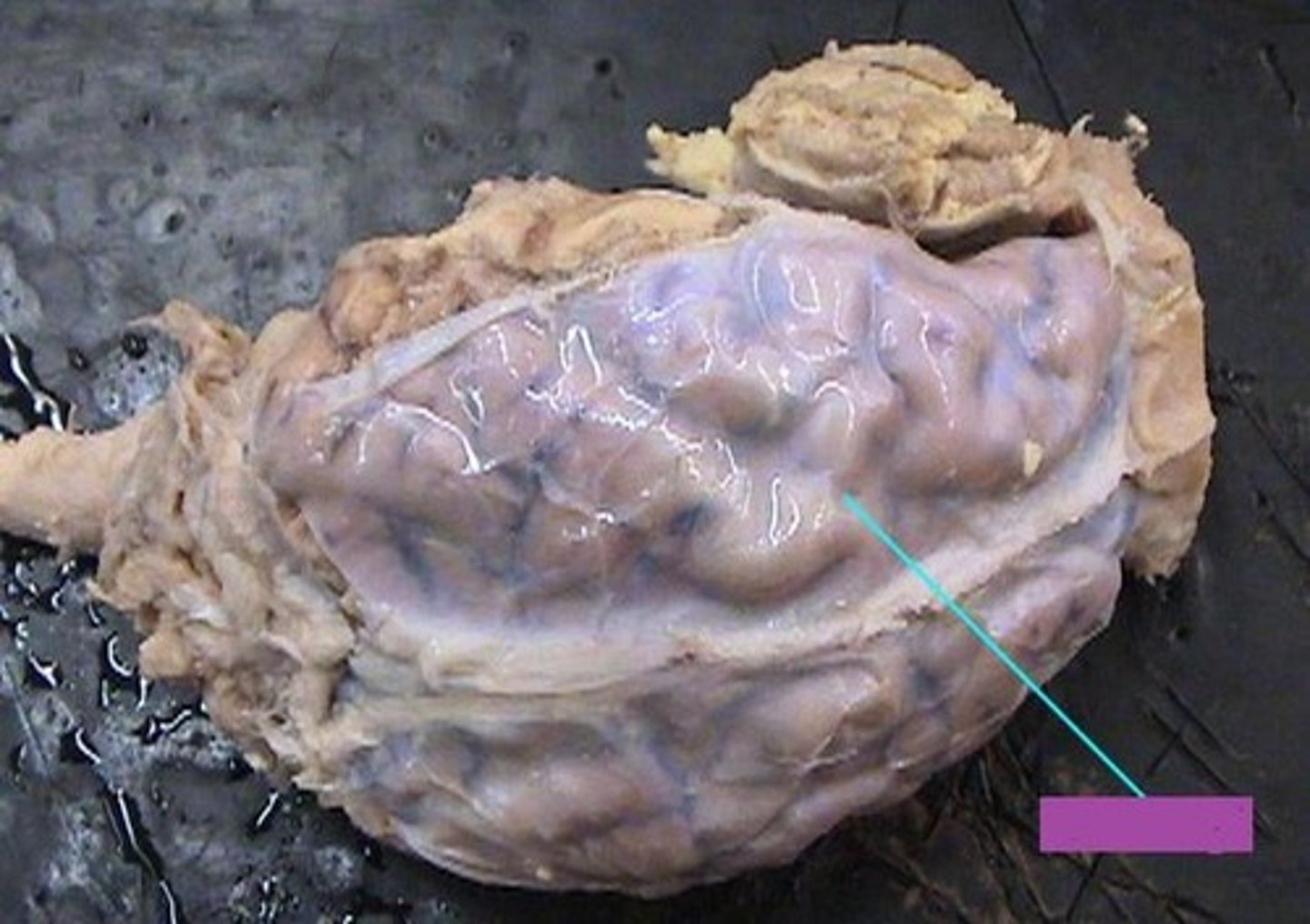
Pia mater
Left hemisphere
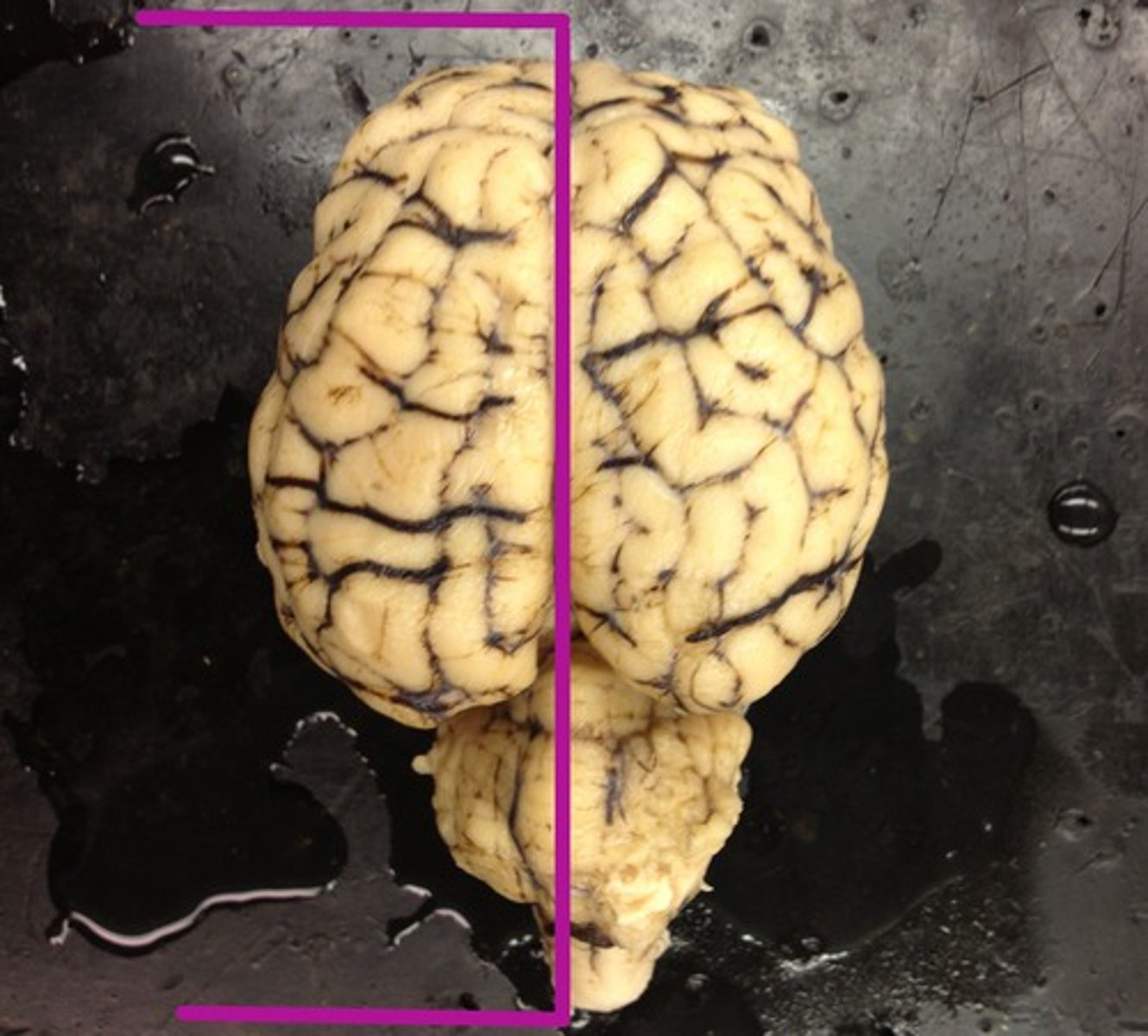
right hemisphere
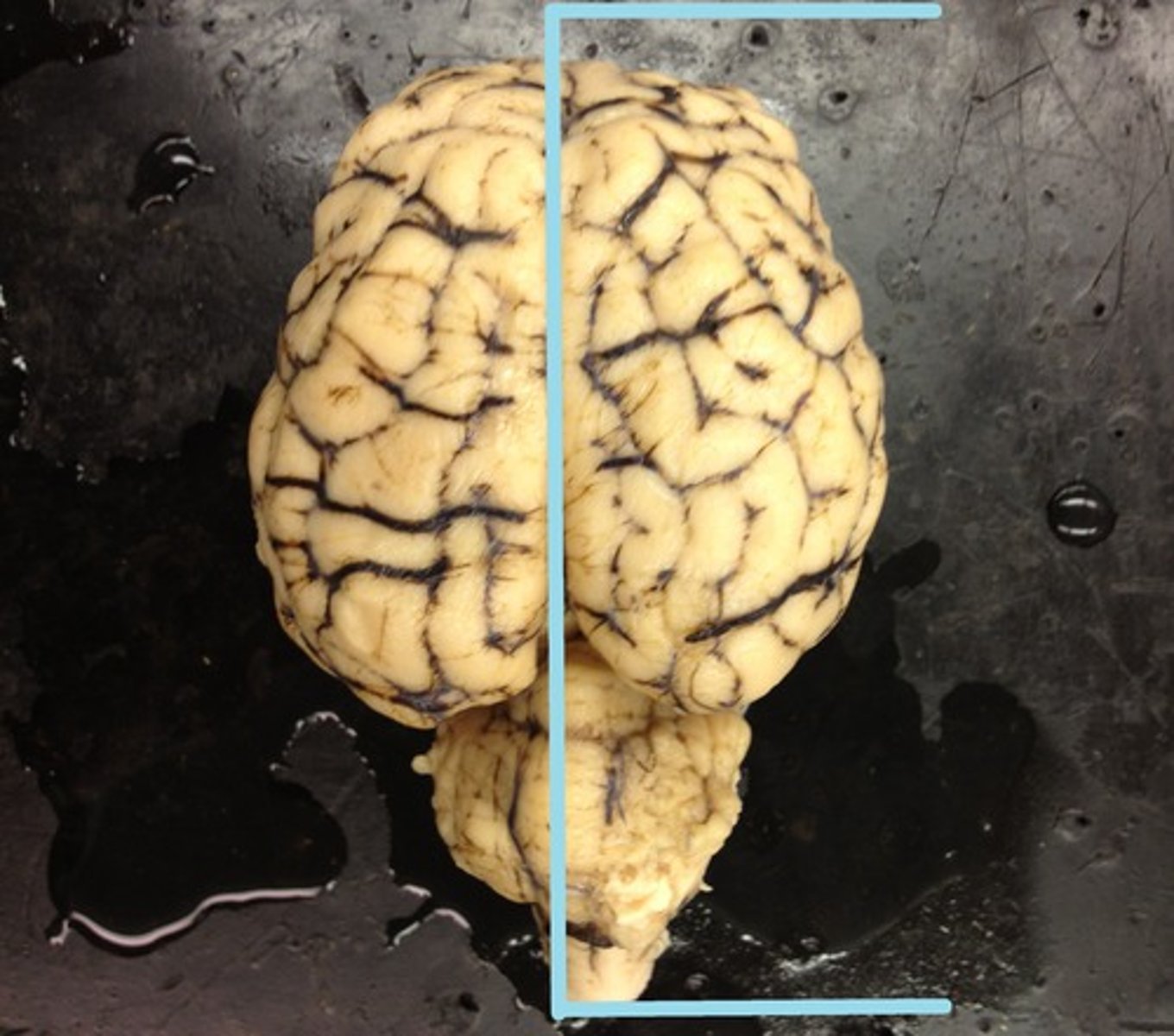
Gyri
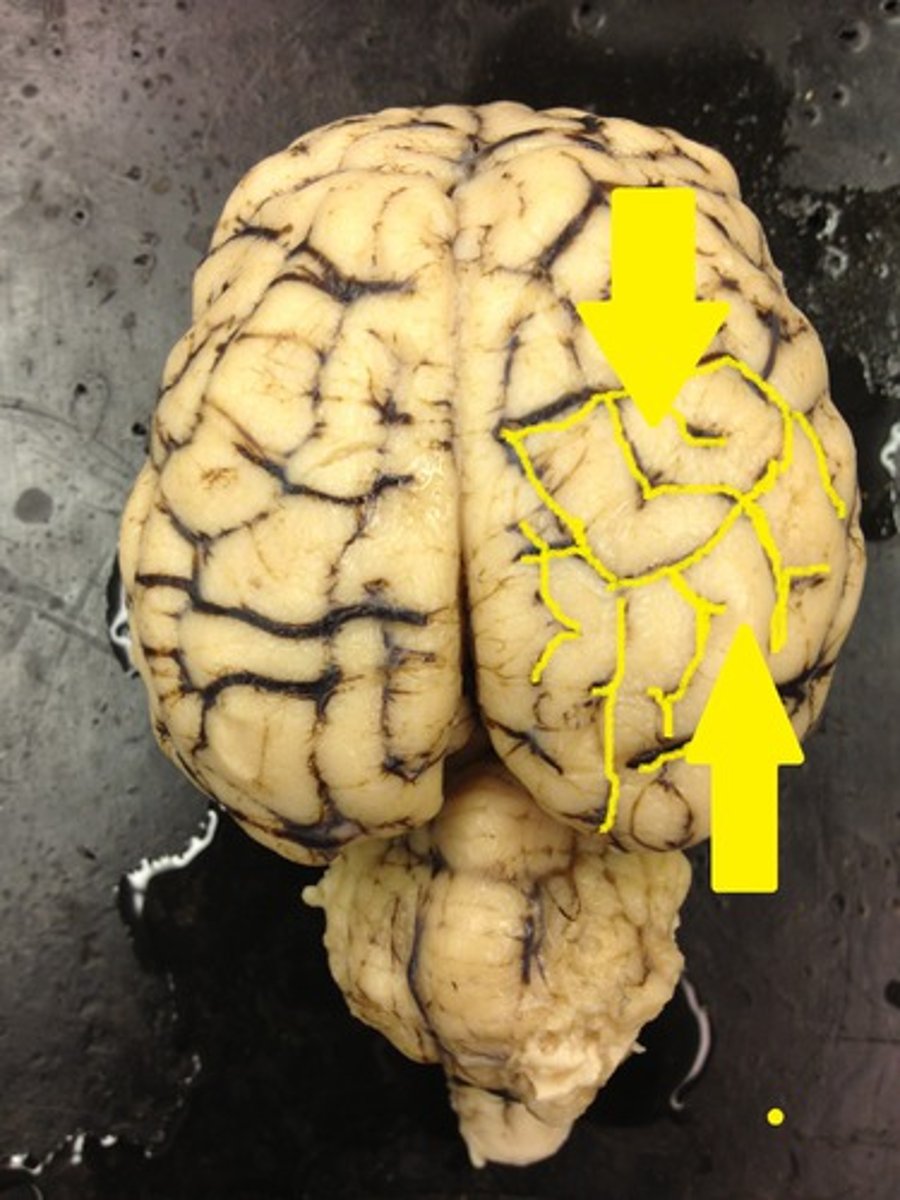
The ridges
What are the gyri?
sulci
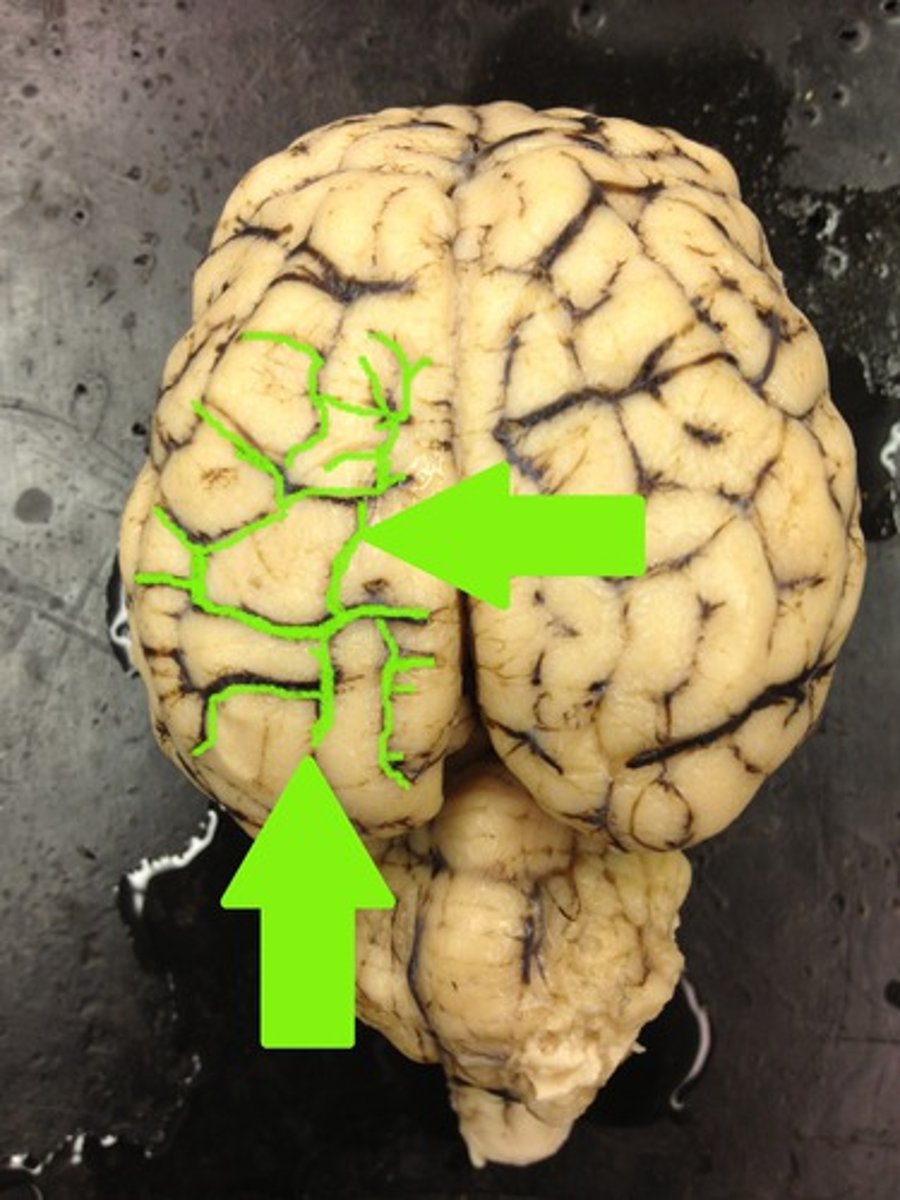
The grooves
What are the sulci?
Cerebrum
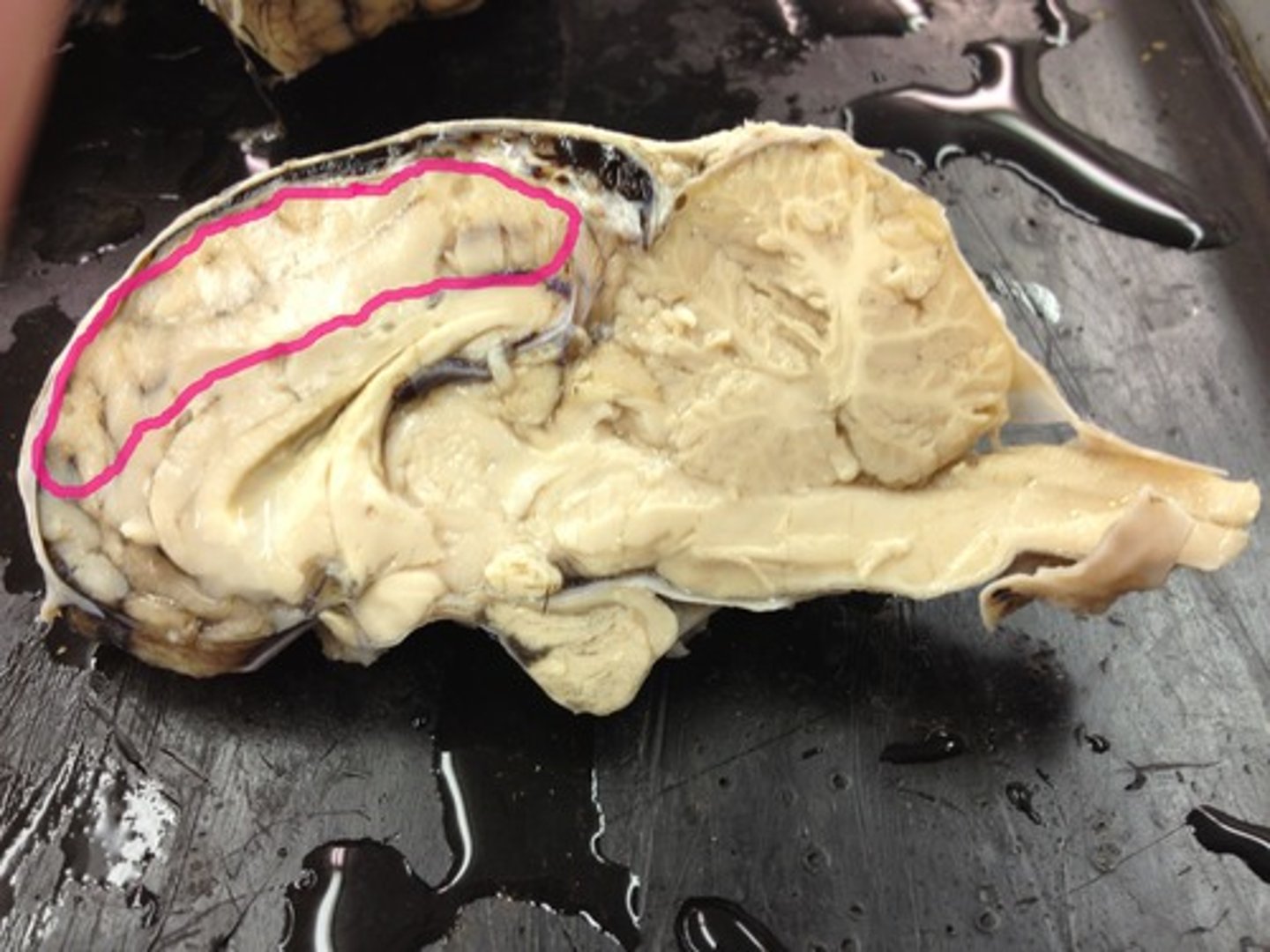
Conscious brain
What is the cerebrum?
longitudinal fissure
Coordinates muscle movements; muscle memory
What does the cerebellum do?
Cerebellum
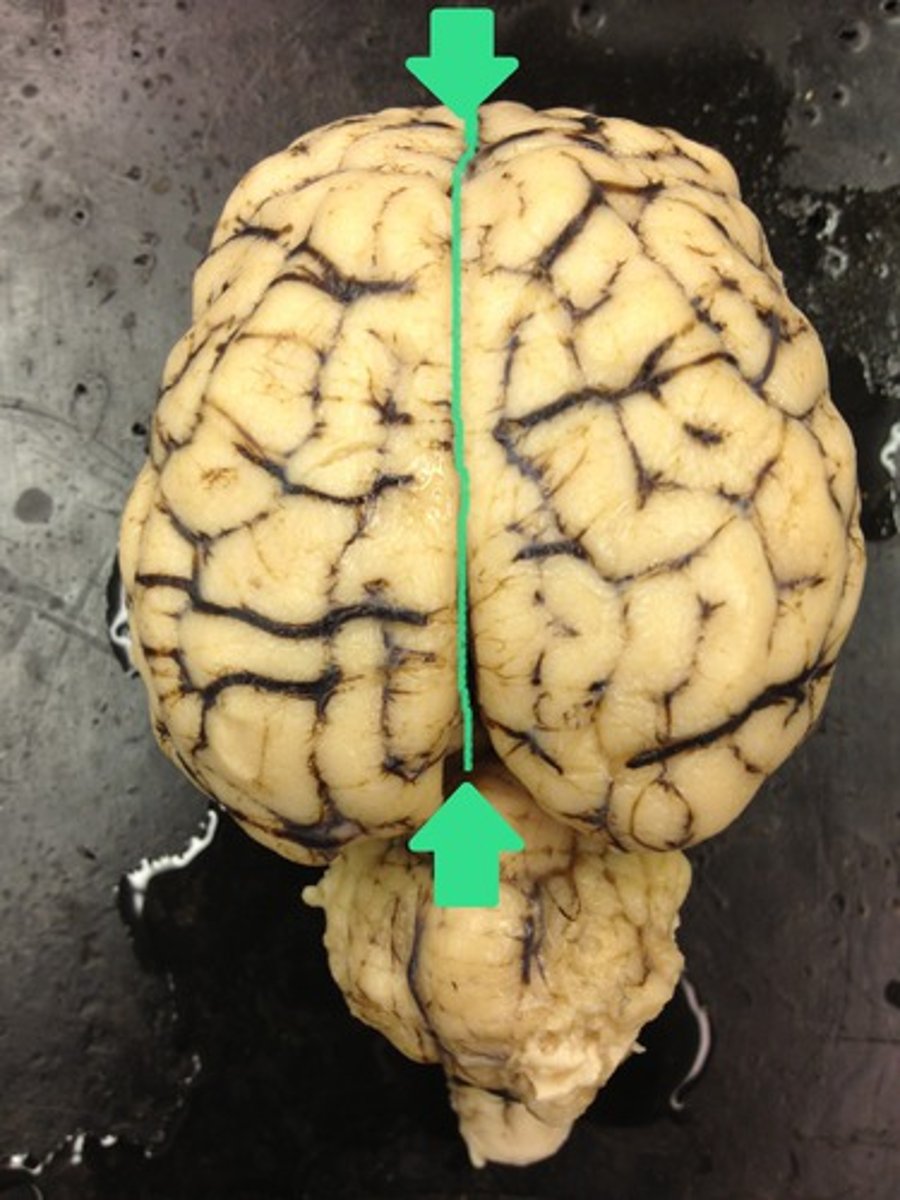
transverse fissure
Separates cerebrum and cerebellum
What does the transverse fissure do?
spinal cord
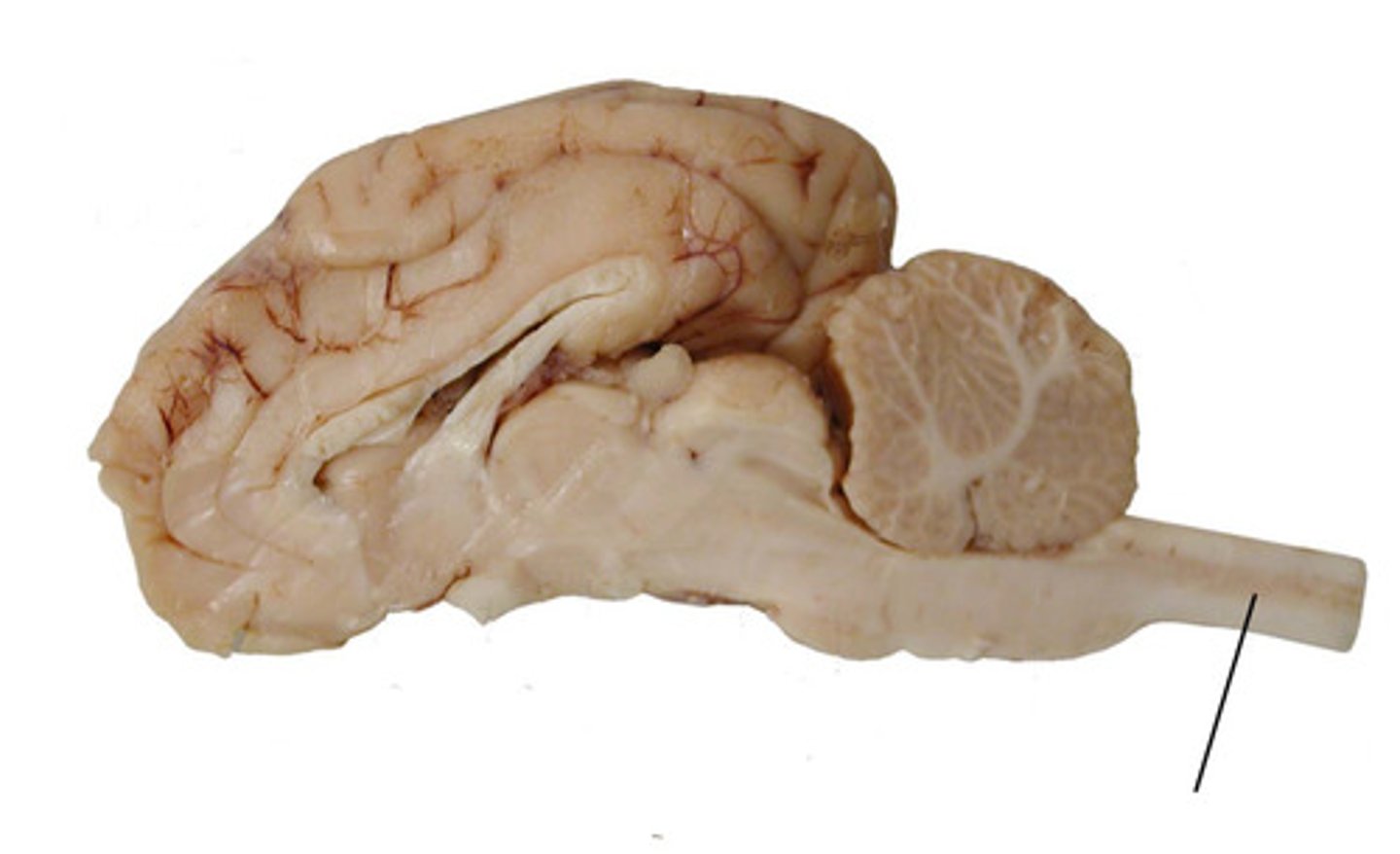
inferior colliculi
Auditory reflexes
What is the function of the inferior colliculi?
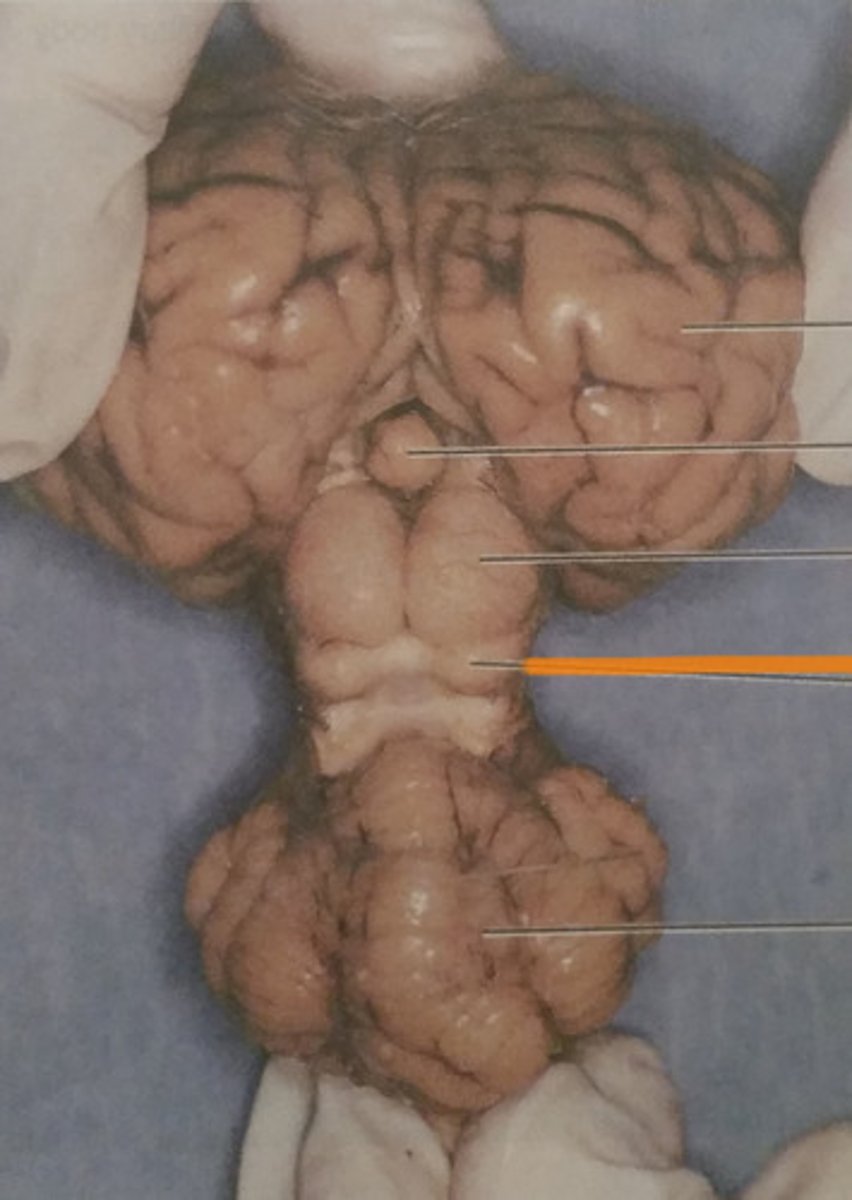
superior colliculi
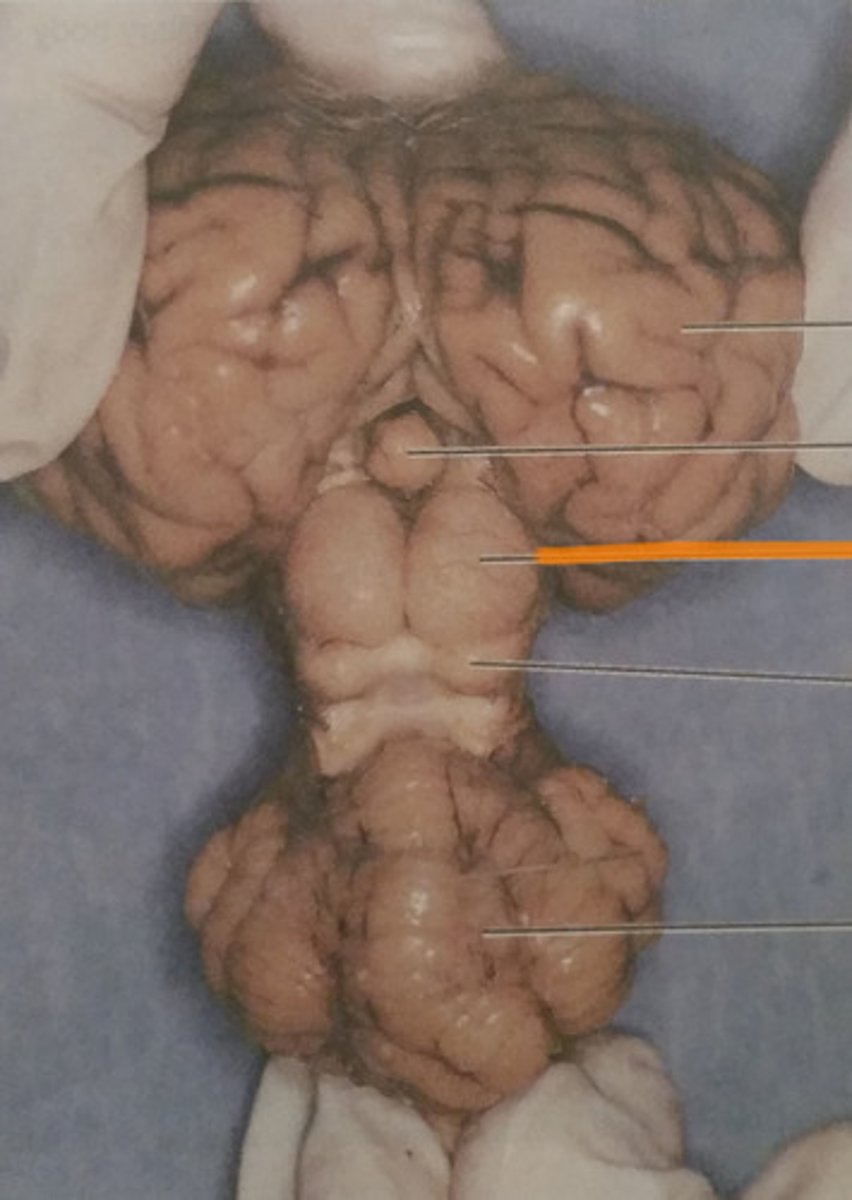
Visual reflexes
What is the function of the superior colliculi?
Pineal body
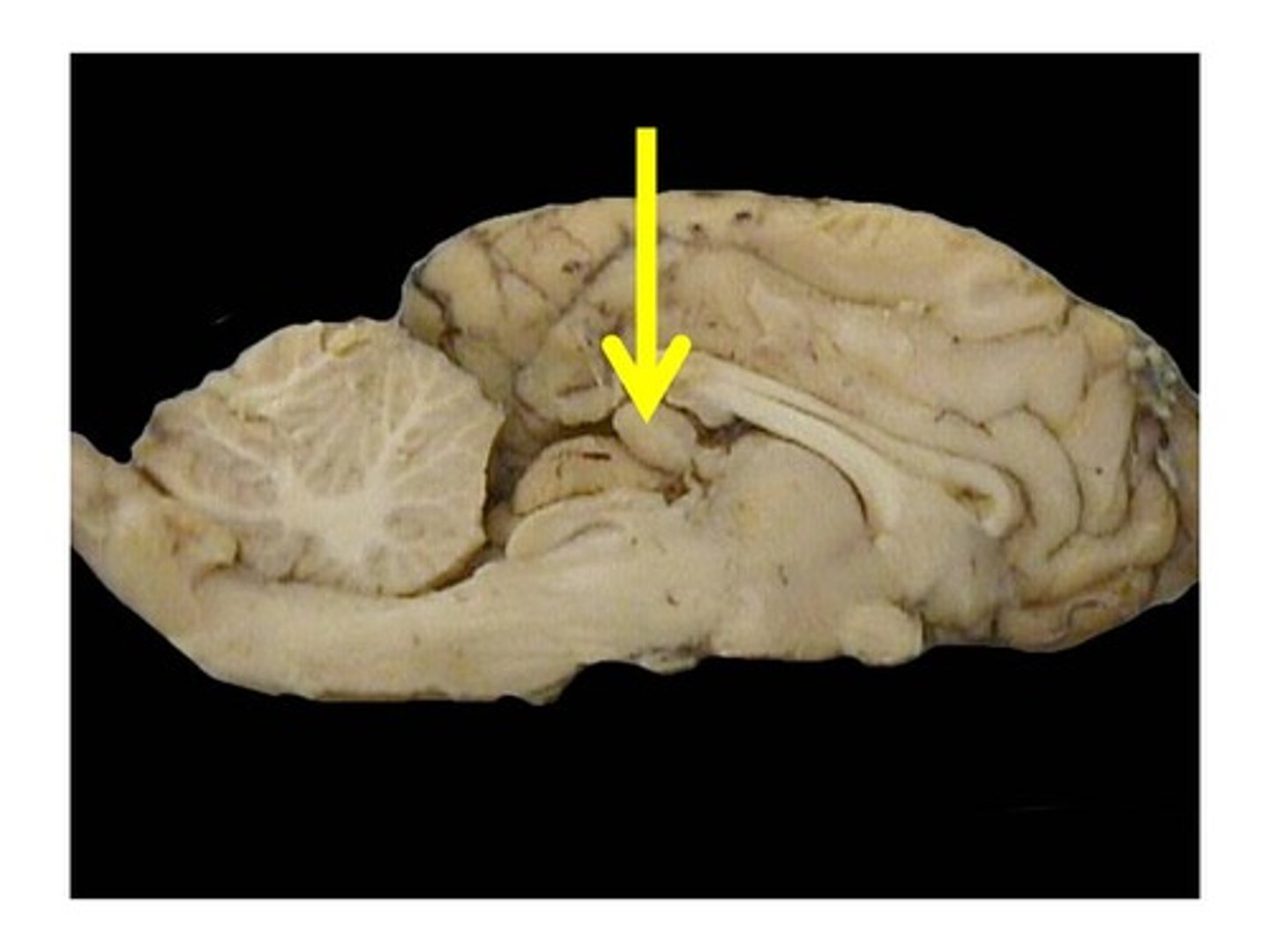
Controls sleep/wake cycles
What is the function of the pineal body?
Olfactory bulb (sense of smell; nerve 1)
What does it do and what number is it?
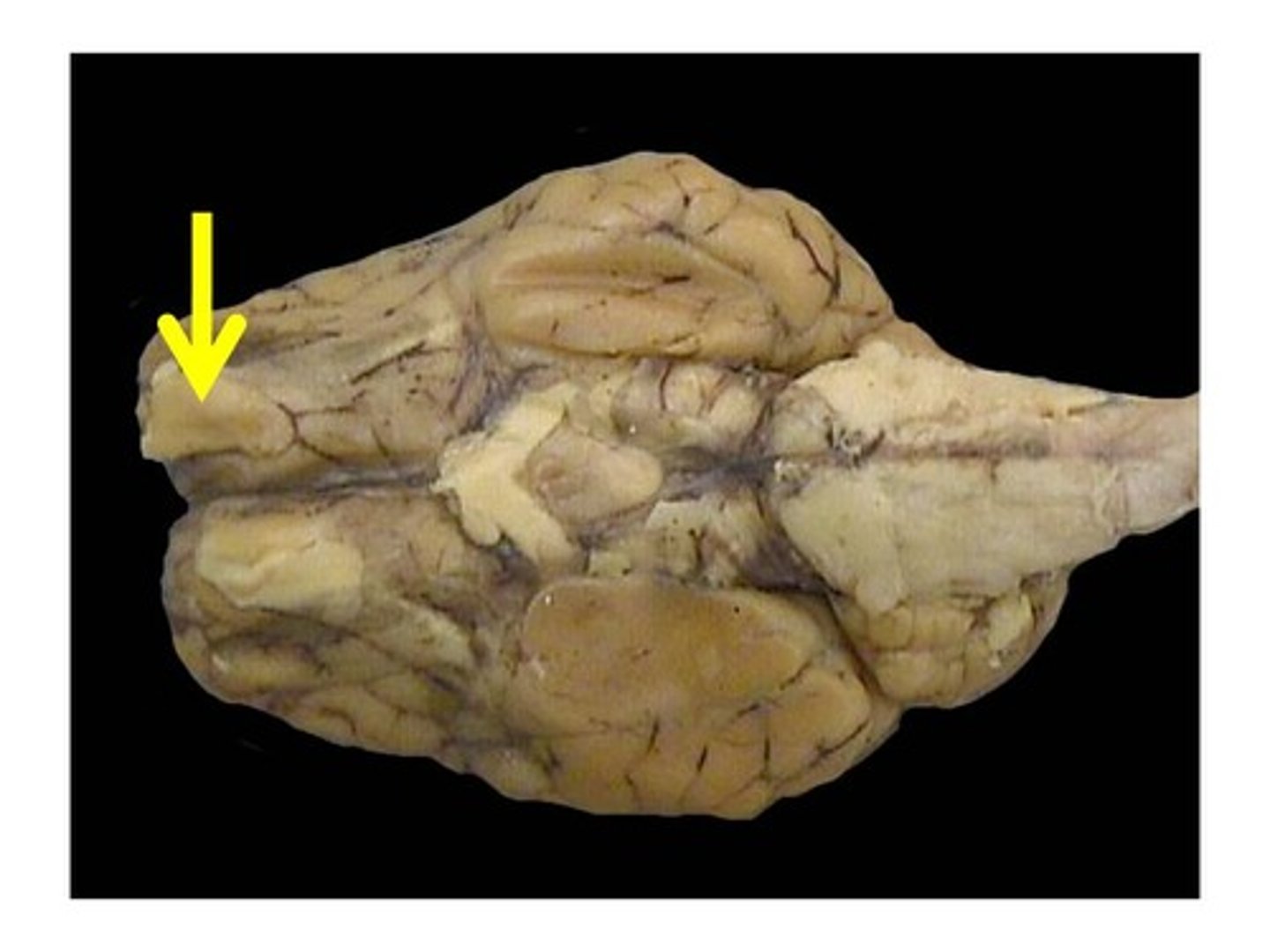
Olfactory tract
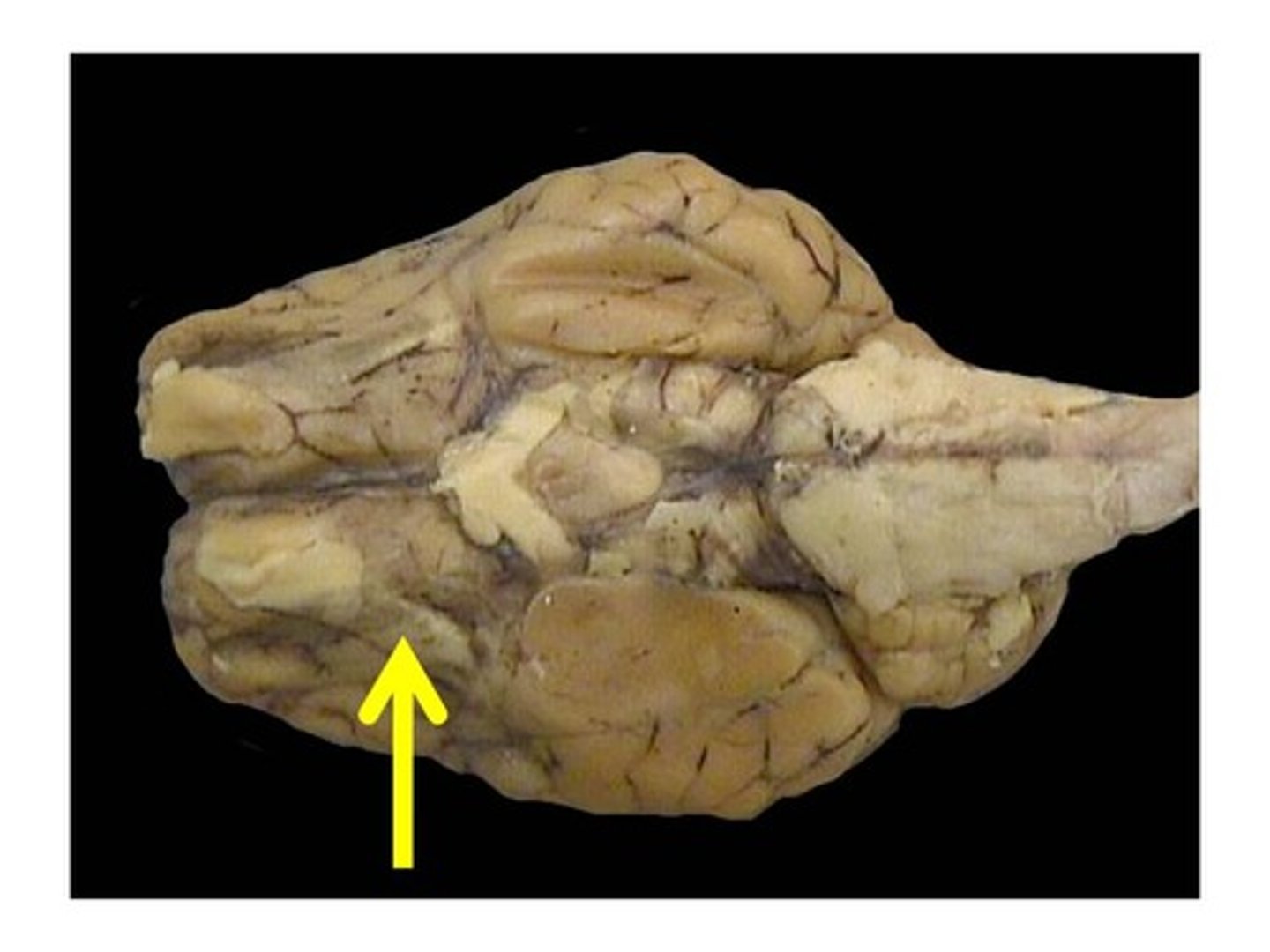
Optic nerve (vision; nerve 2)
What does it do and what number is it?
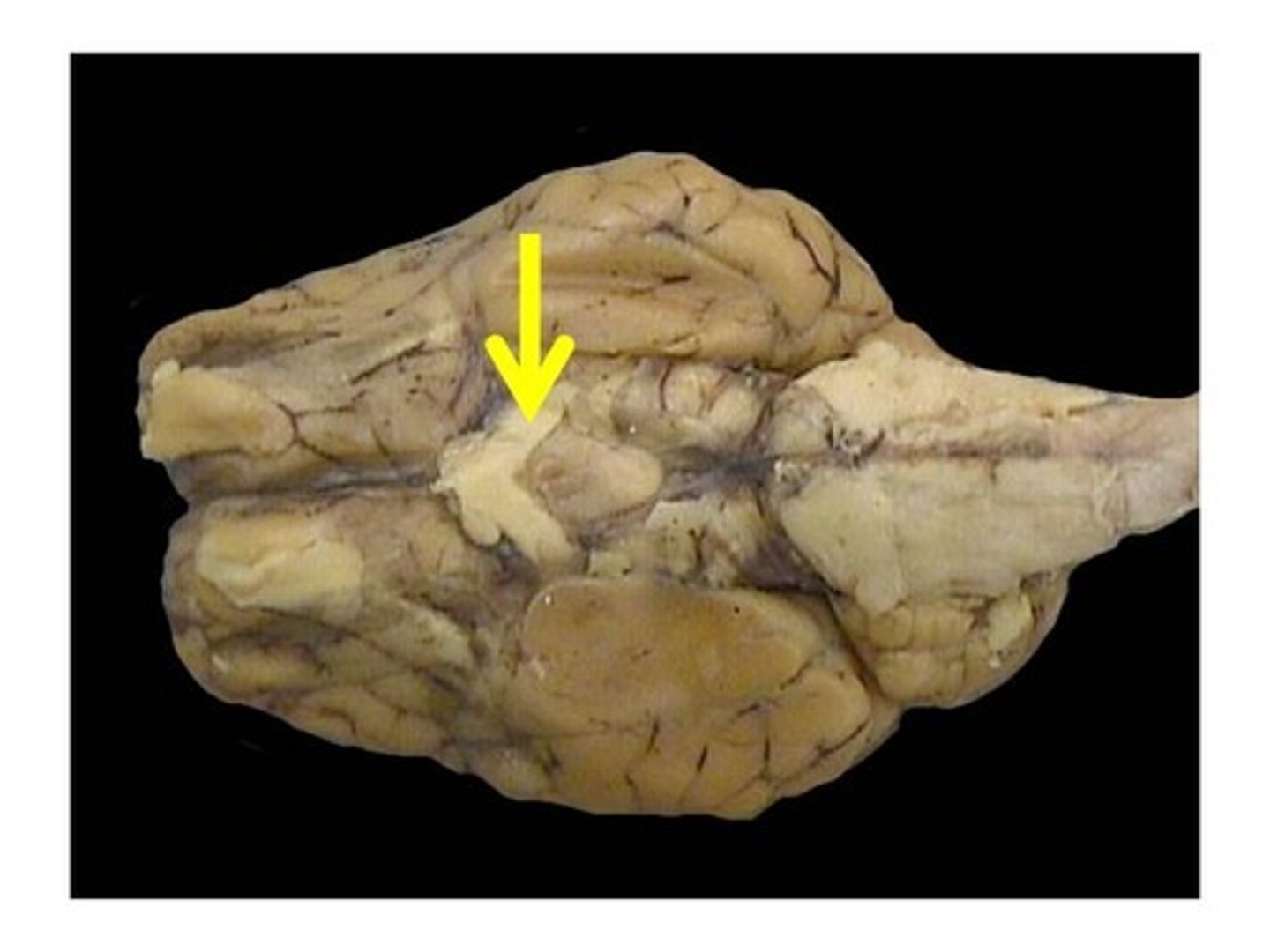
Optic chiasm
Oculomotor nerve
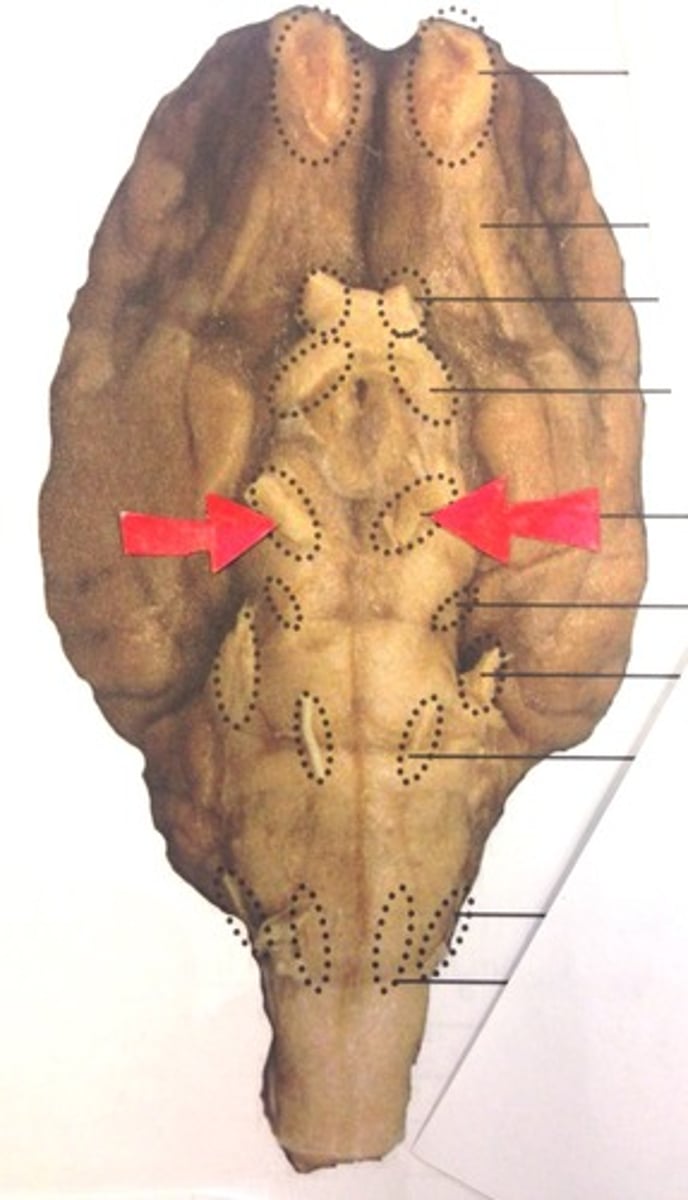
Trigeminal nerve
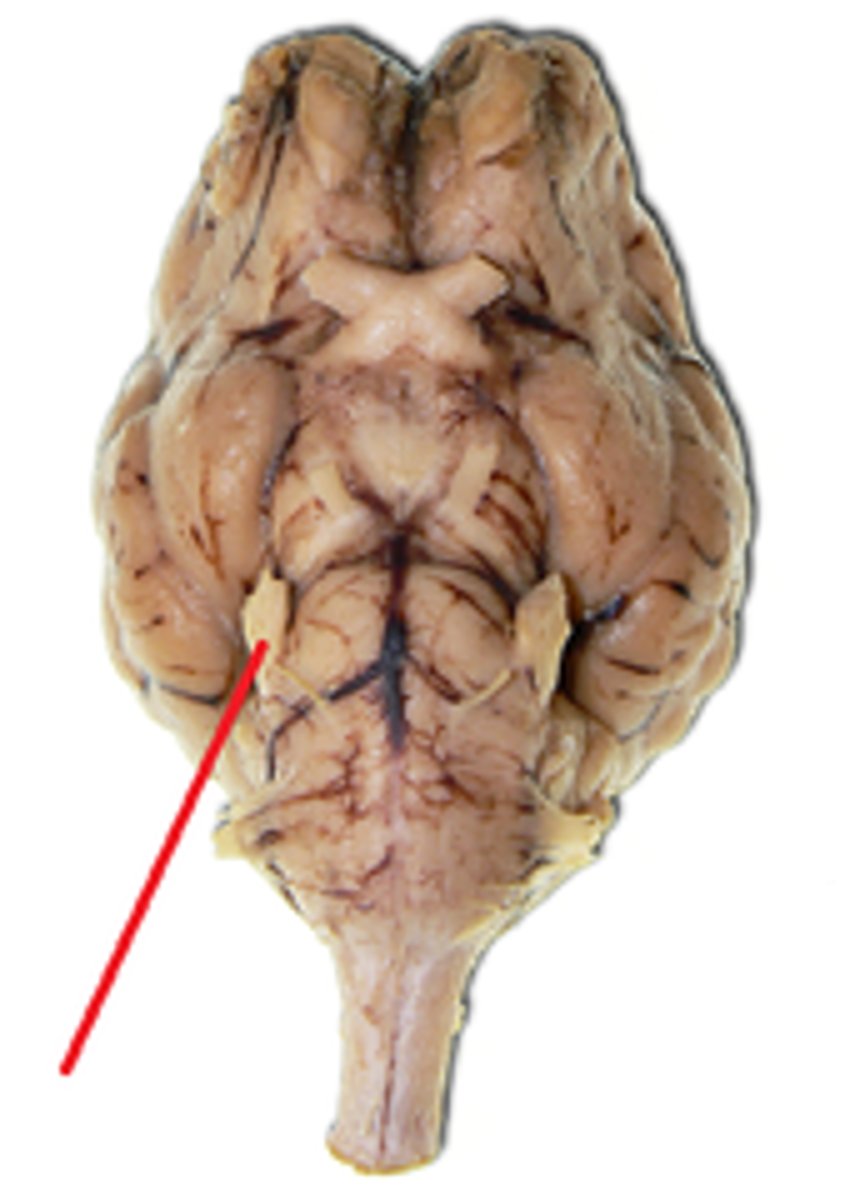
Pons
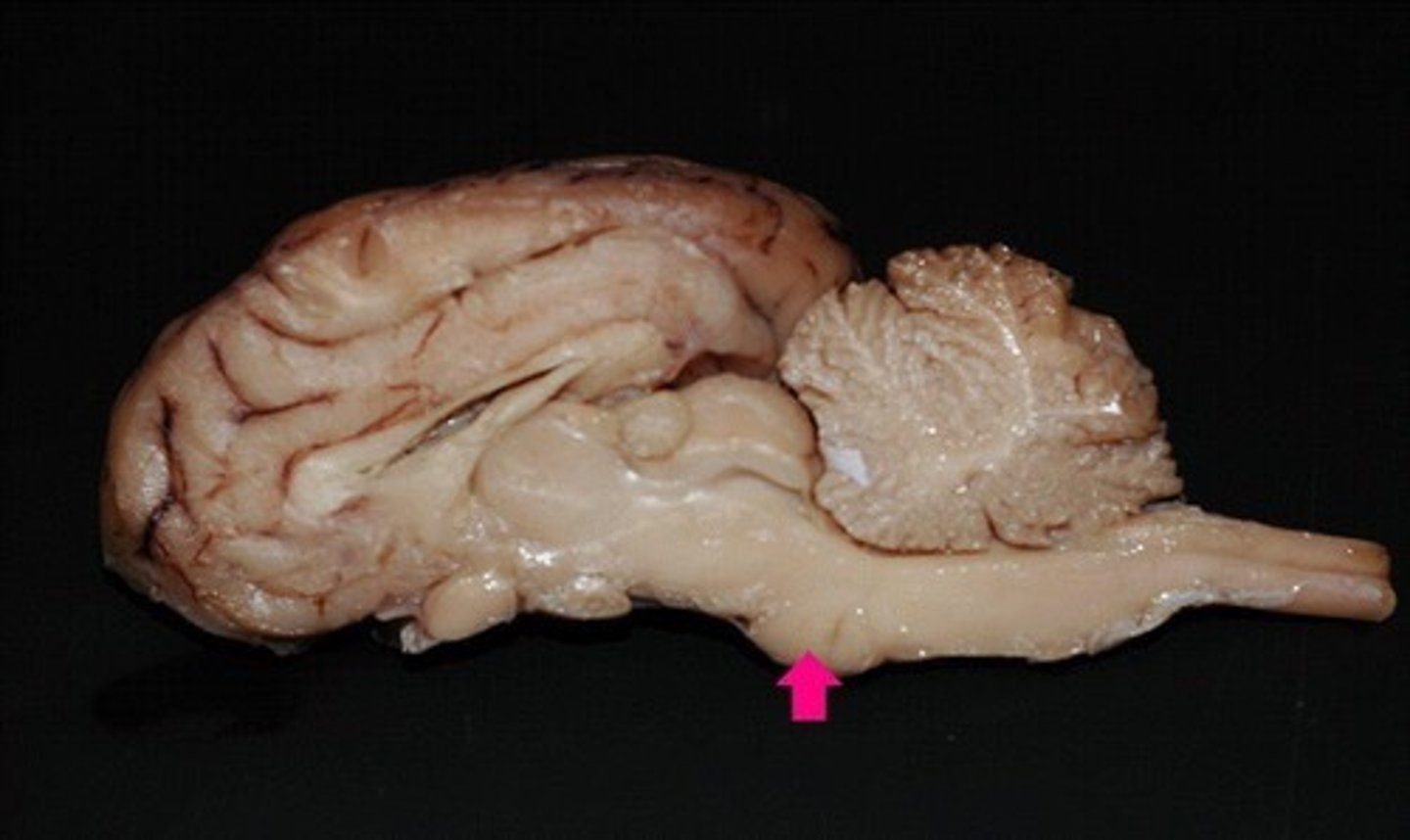
The "bridge" that links the medulla oblongata to thalamus
What is the function of the pons?
Medulla oblongata
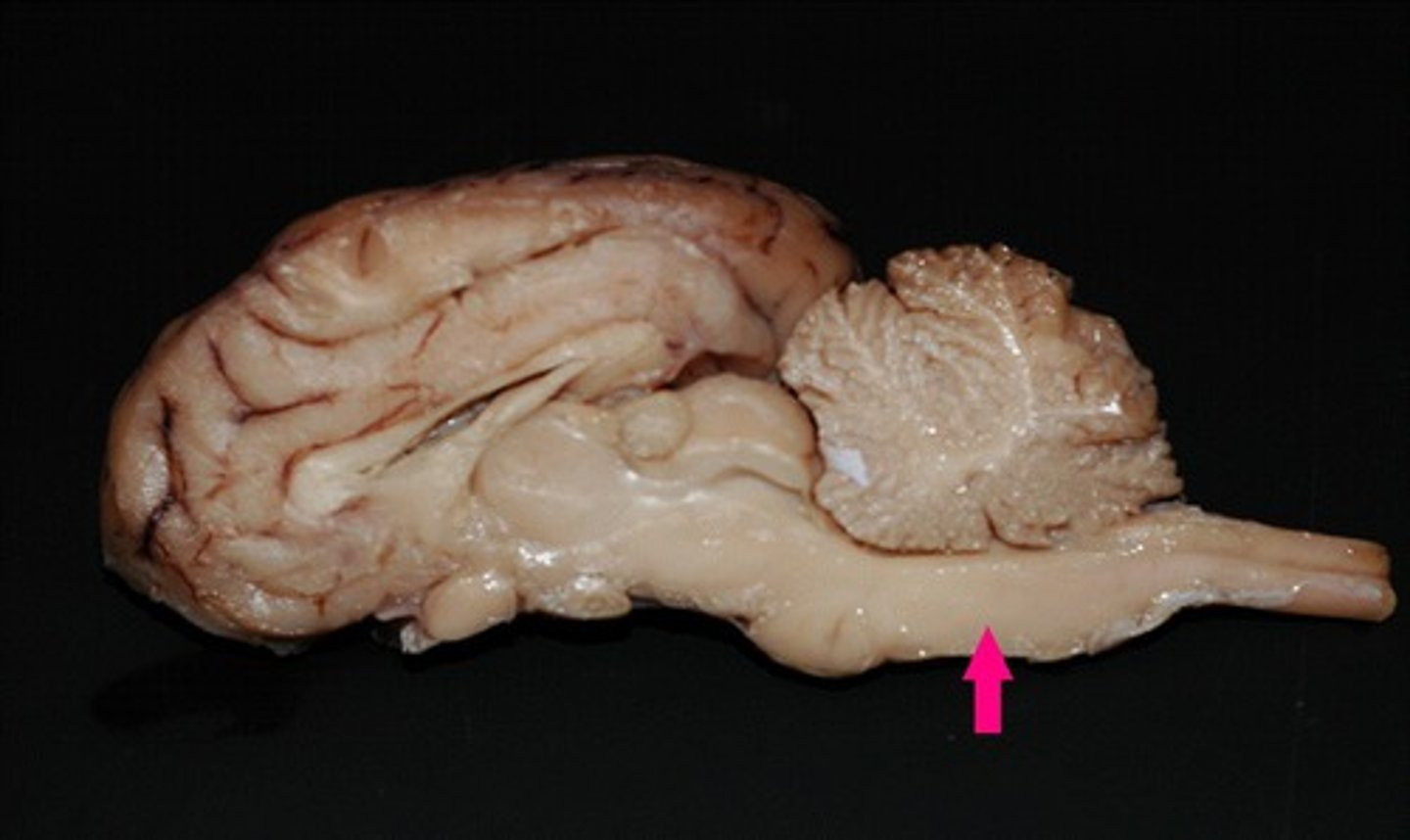
Houses autonomic centers
What does the medulla oblongata house?
Pituitary gland
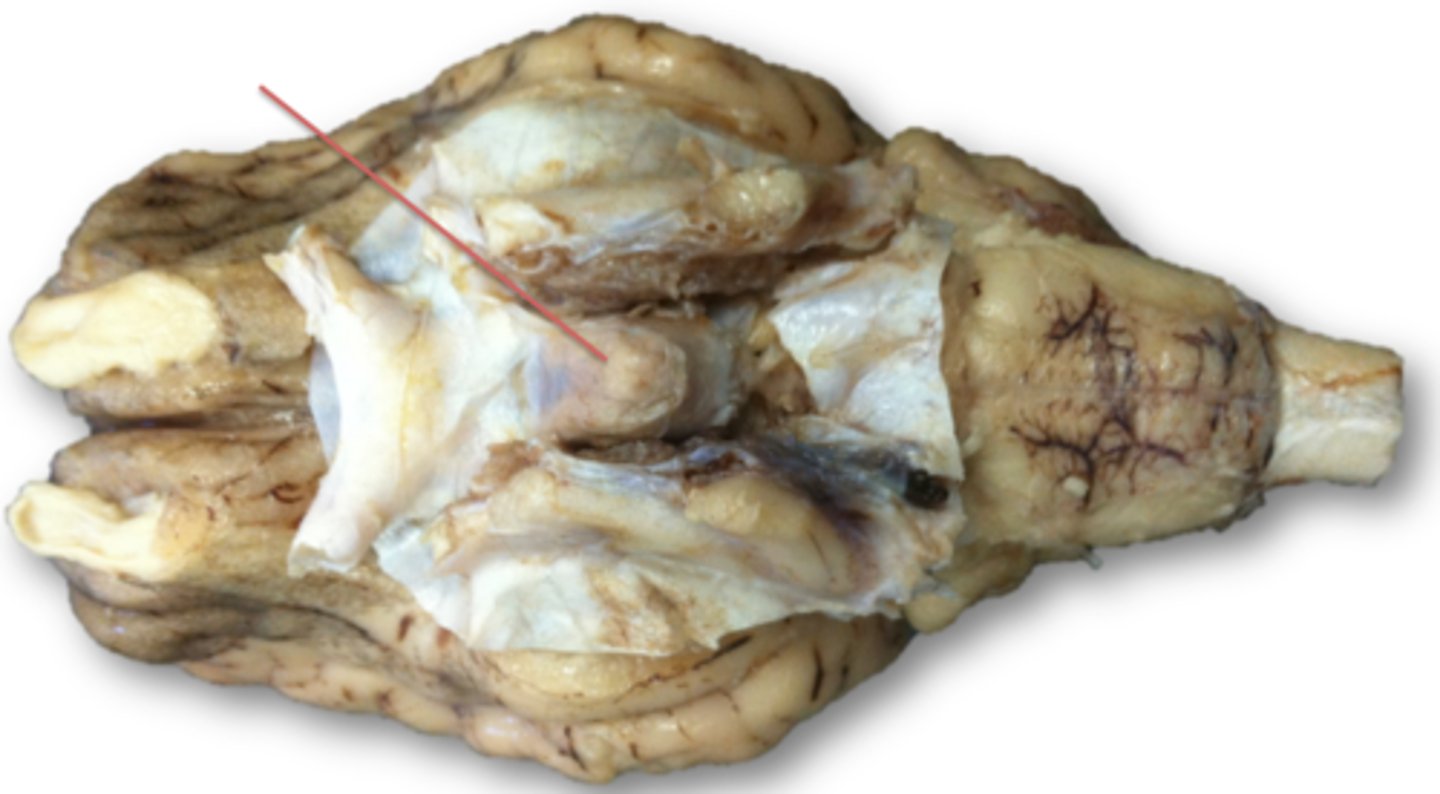
"Master" gland of endocrine system
What is the pituitary gland?
Corpus callosum
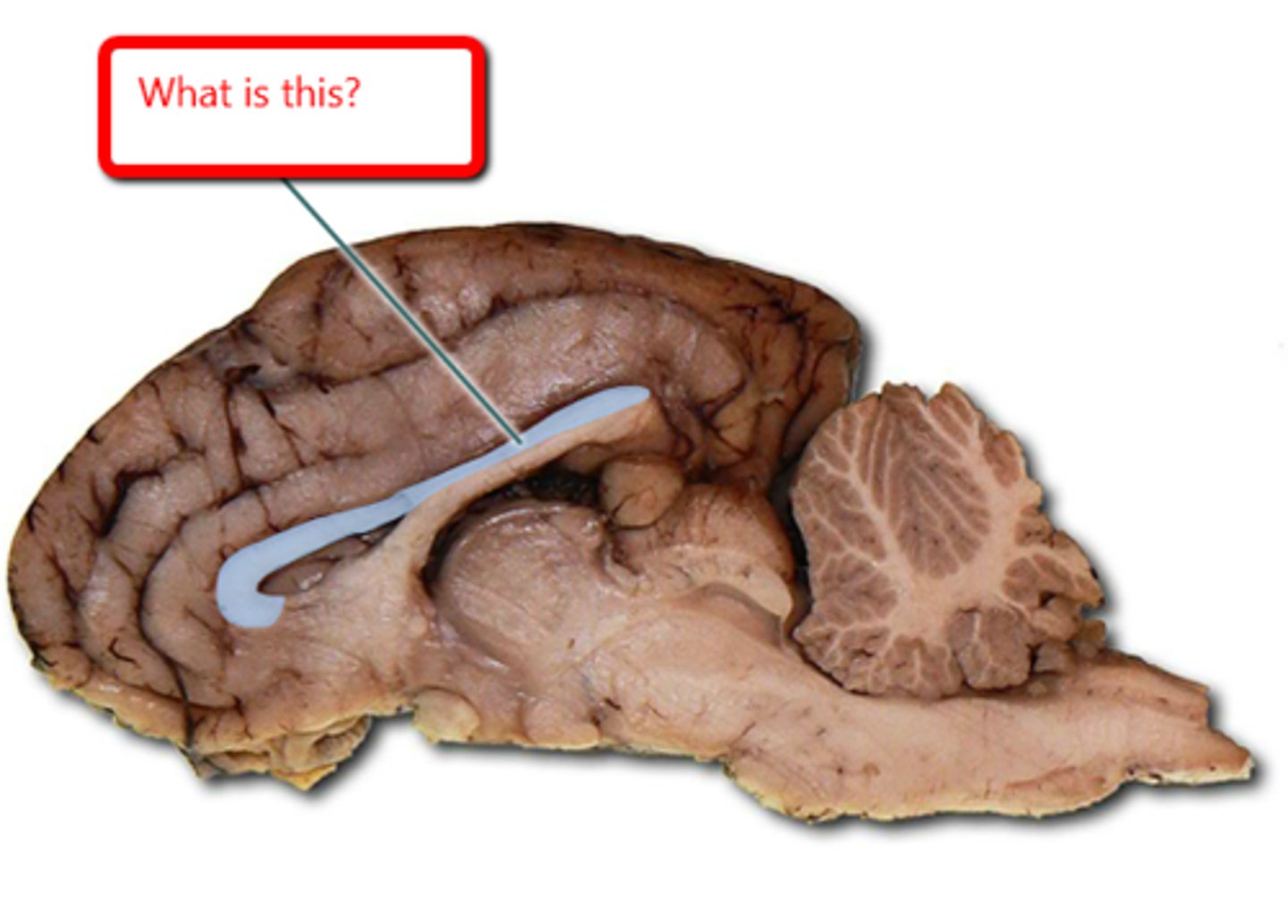
connects left and right brain hemispheres
What does the corpus callosum do?
Lateral ventricle
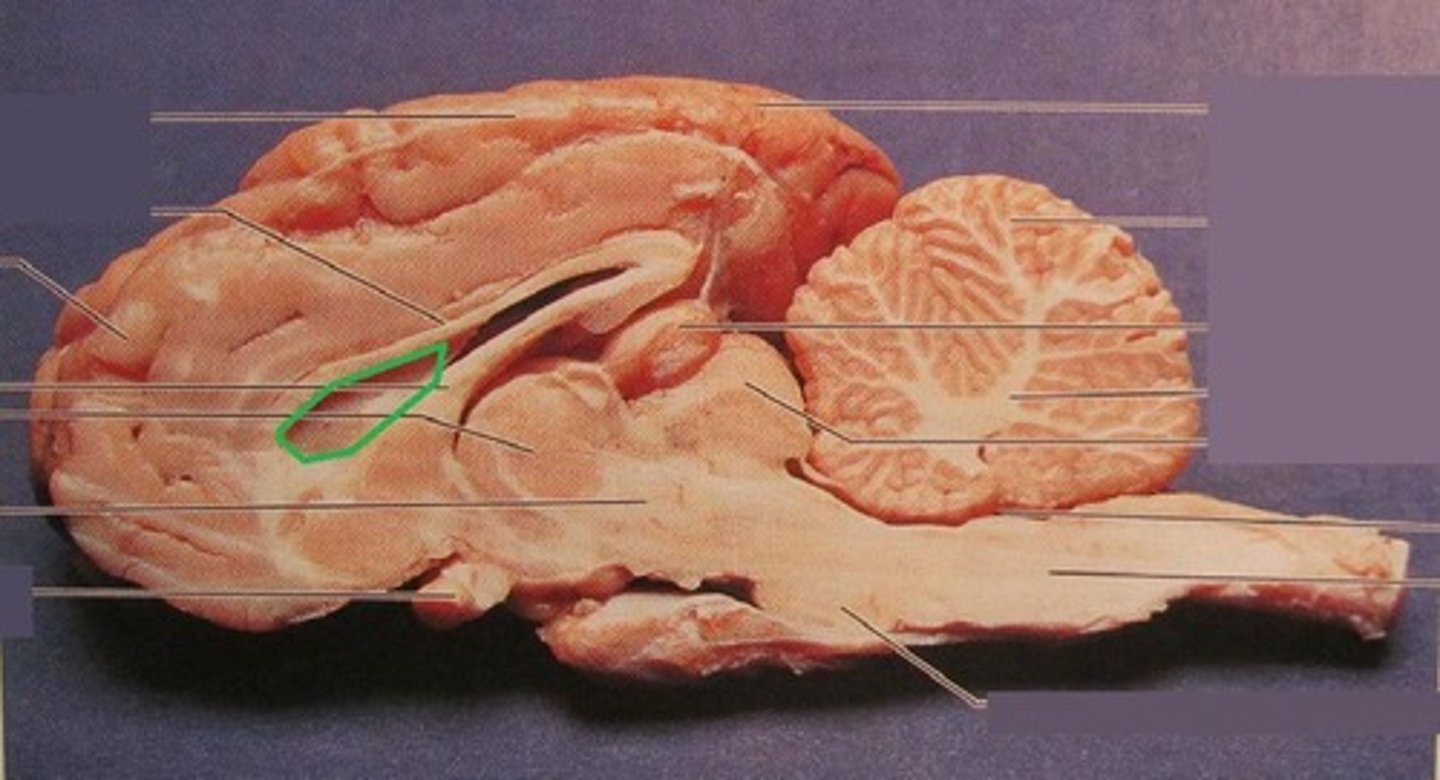
Produces and contains cerebrospinal fluid
What is the function of the lateral ventricle?
Fornix
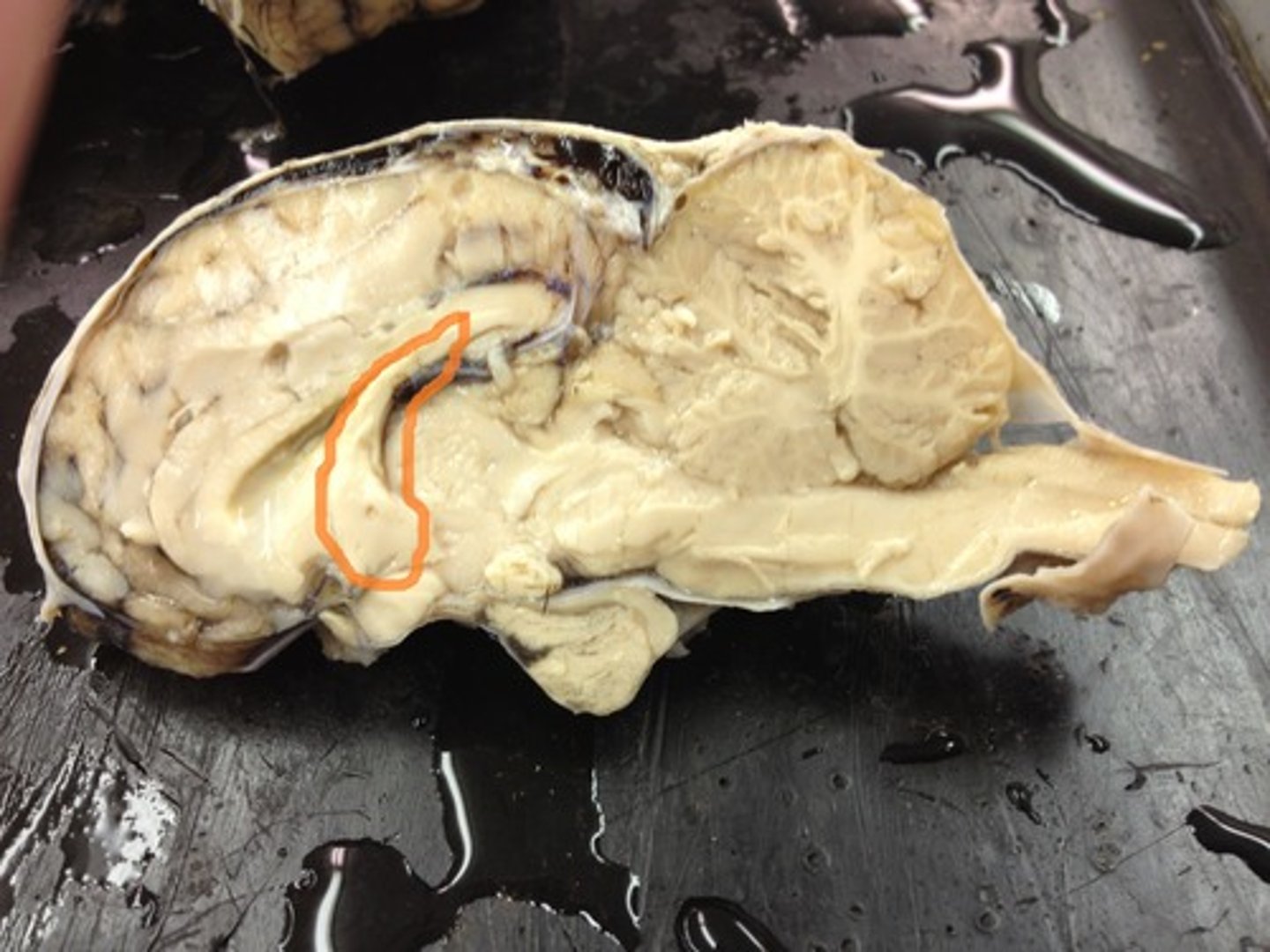
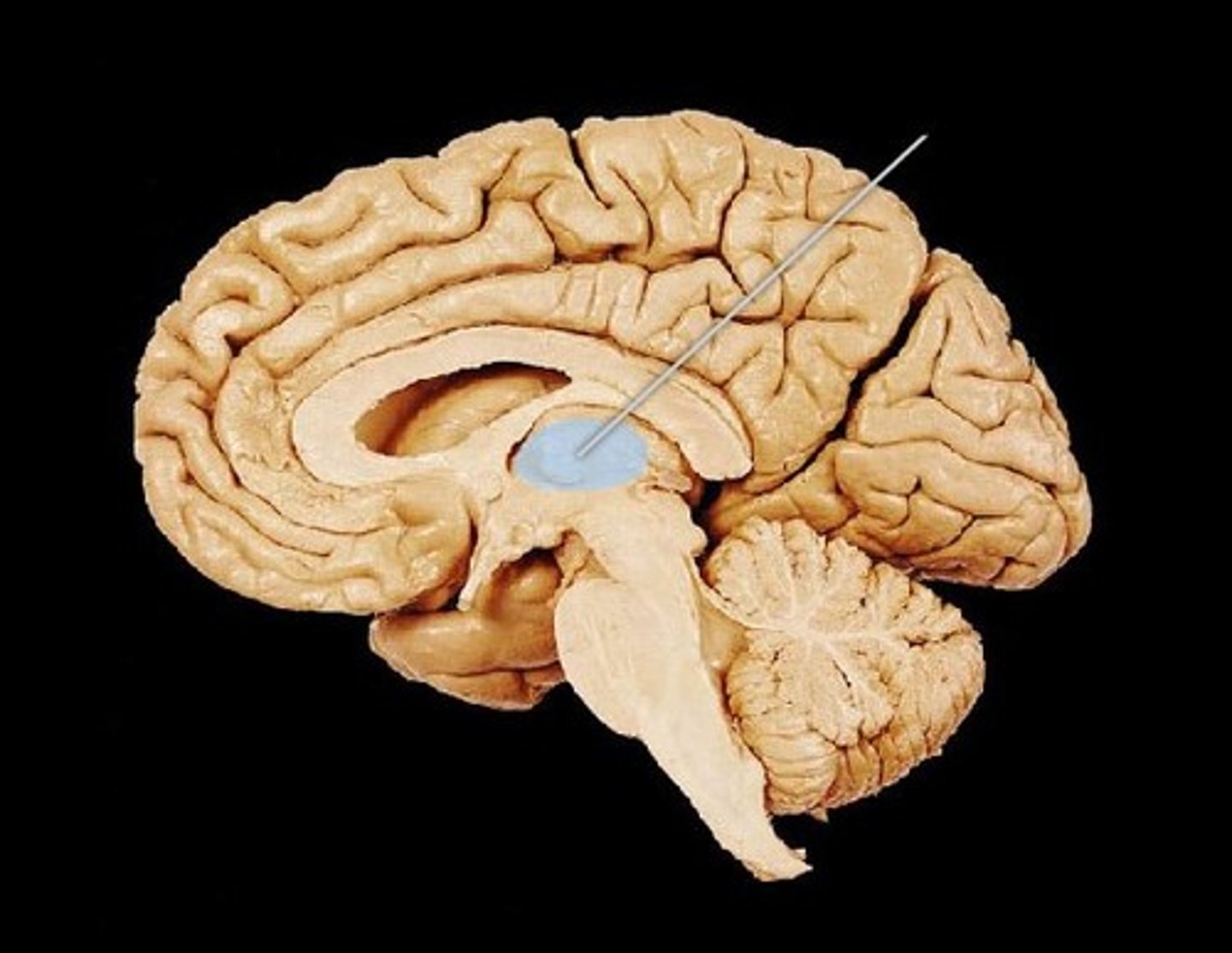
Thalamus
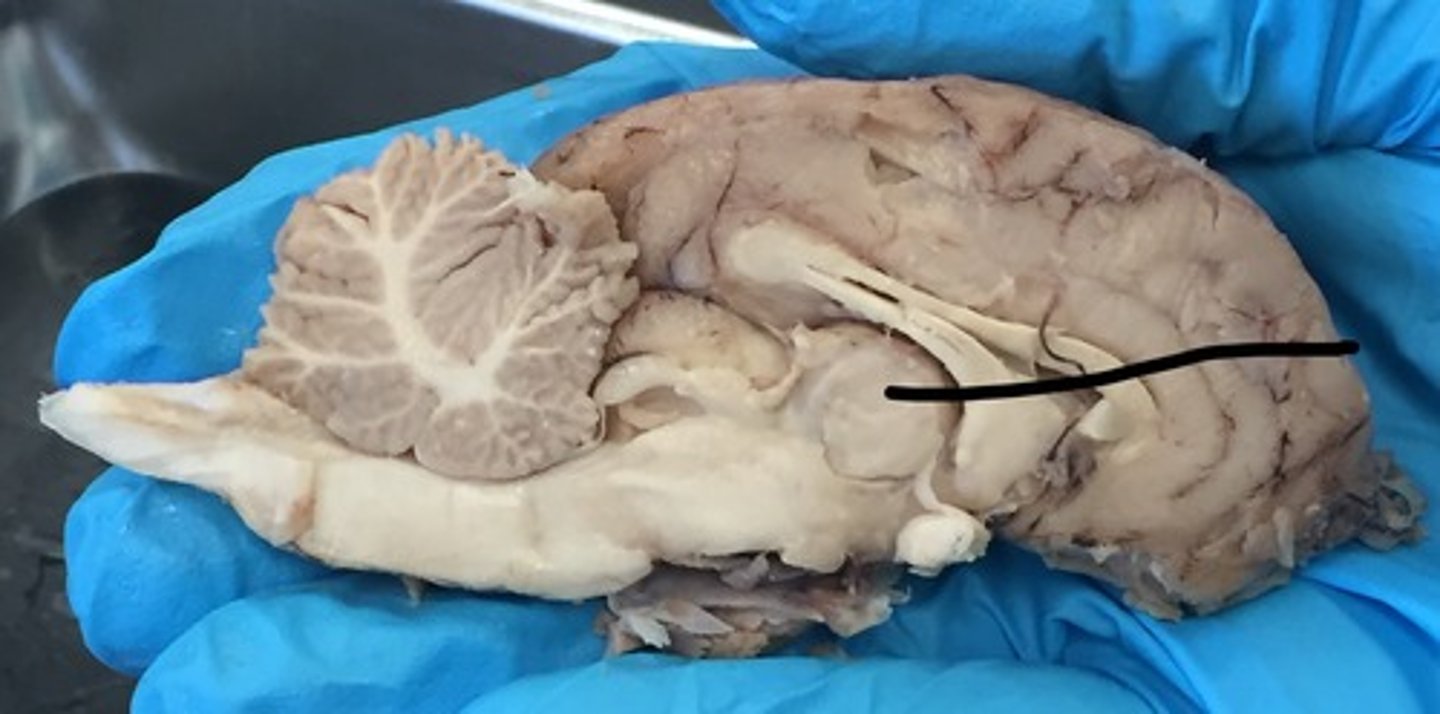
Gateway to cerebral cortex
What is the function of the thalamus?
Hypothalamus
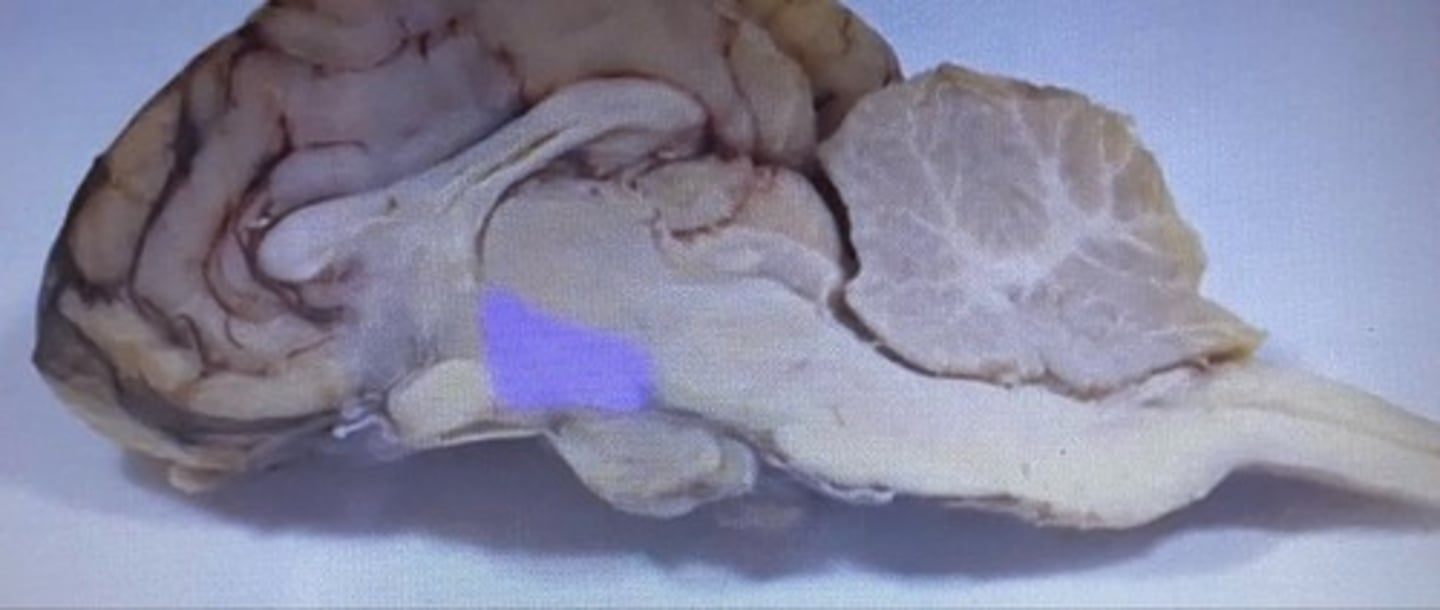
controls pituitary gland autonomic centers of medulla oblongata
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
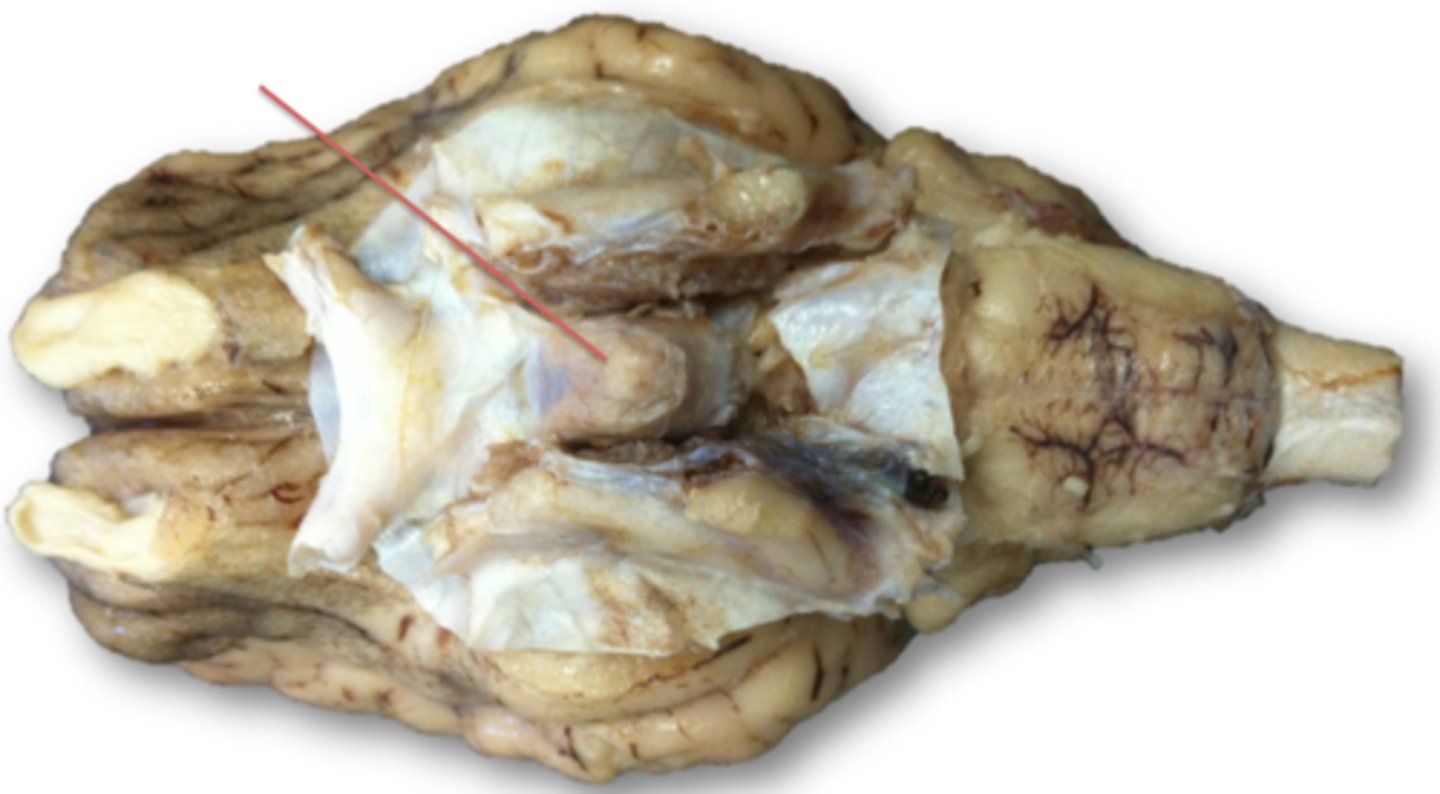
Pituitary gland
Pineal body
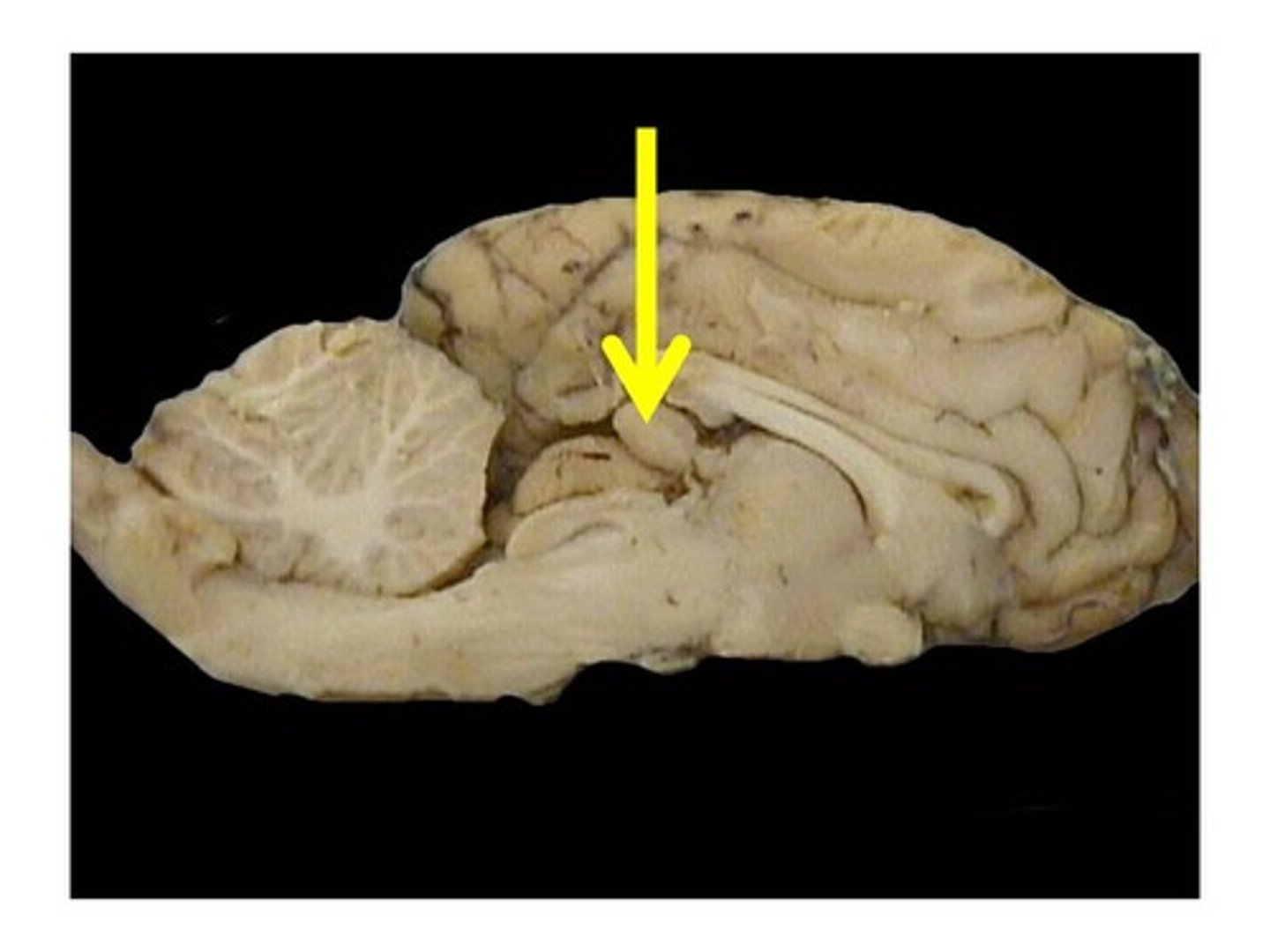
Arbor vitae