Intracellular Accumulation
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Intracellular, extracellular, pigmentation
What are the three general categories of cellular accumulations
true
True/false: cellular accumulations can be relatively harmless or promote cell degeneration and death.
lipidosis
__________ Accumulation of lipids within parenchyma cells
liver and kidney
lipidosis can occur in many organs and tissue but which two are 'classic'.
steatosis, fatty change
what are two other names for lipidosis
its role in lipid metabolism
why does lipidosis commonly occur in the liver?
liver,
adipose tissue or GI
lipids are transported to the ______ from ______ or _______
esterified to triglycerides, converted to cholesterol or phospholipids, oxidized to ketone bodies
within hepatocytes, free fatty acids can be __________ , ______________, or _______________
apoproteins,
lipoproteins,
an energy source
Triglycerides can be complexed with _______ to form low-density ________ for release into the plasma as _______ for tissue
increased mobilization of free fatty acids, abnormal hepatocellular metabolism, impaired release of lipoproteins
what are three causes of lipidosis?
high dietary fat, increased fat mobilization (starvation cat, diabetes, lactation)
what two main things can cause increased mobilization of free fatty acids?
free fatty acids, triglycerides, apoproteins
if there is abnormal hepatocellular metabolism, what do you expect to see>
hypoxia, cellular injury
what two things may cause abnormal hepatocellular metabolism
possible mechanisms that lead to lipid accumulation
What do these things all potentially have in common?
1.Excessive delivery of free fatty acids (FFAs) from fat stores or diet
2. Decreased oxidation or use of FFAs
3. Impaired synthesis of apoprotein
4. Impaired combination of protein and triglycerides to form lipoproteins
5. Impaired release of lipoproteins
from hepatocytes
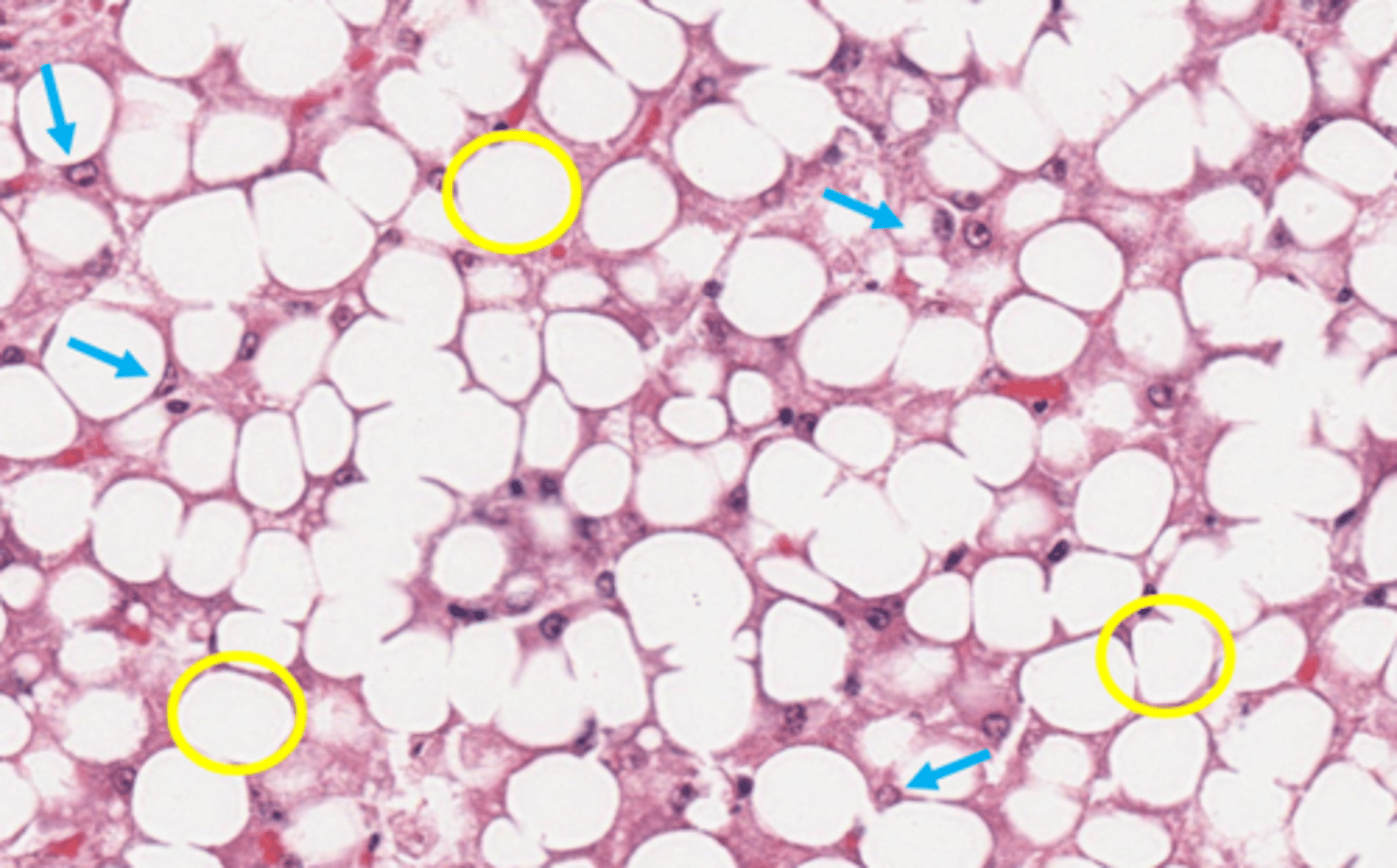
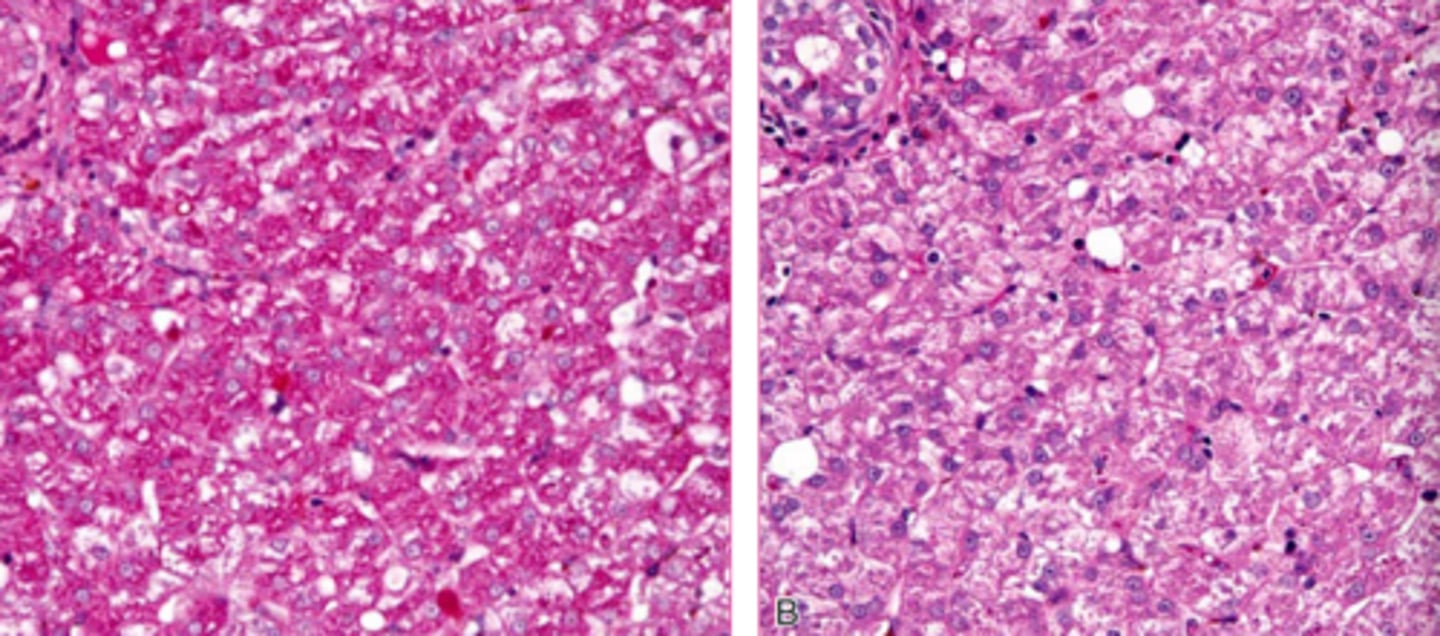
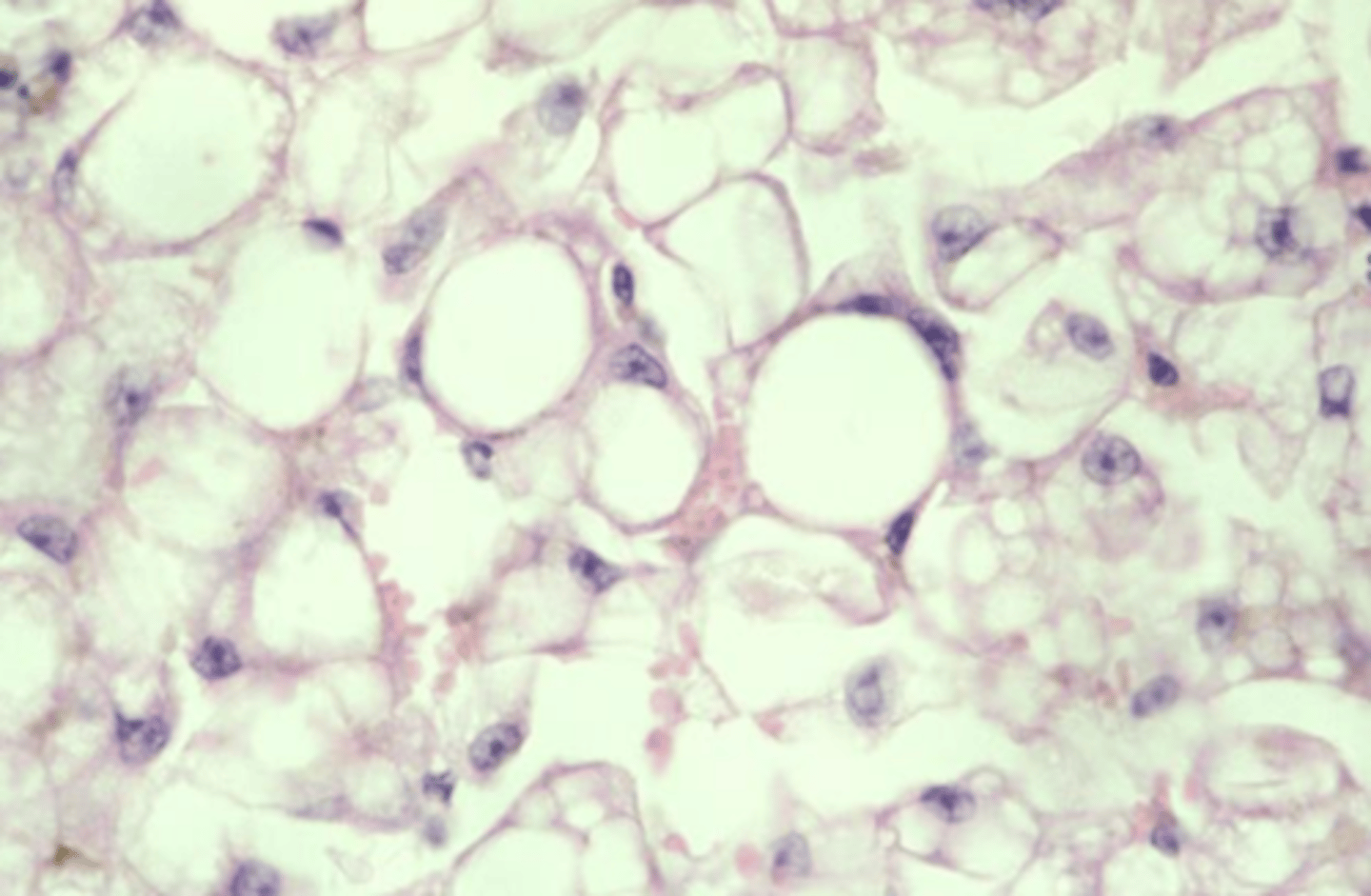
macrovesicular (most common) , microvesicular
what are the two classifications of microscopic lipidosis? And which is more common?
macrovesicular lipidosis
Which type of lipidosis is this describing?
Large, clear, sharply defined vacuoles that are larger than the nucleus, distend the
cytoplasm, and displace the nucleus to the periphery of the cell
macrovesicular hepatic lipidosis
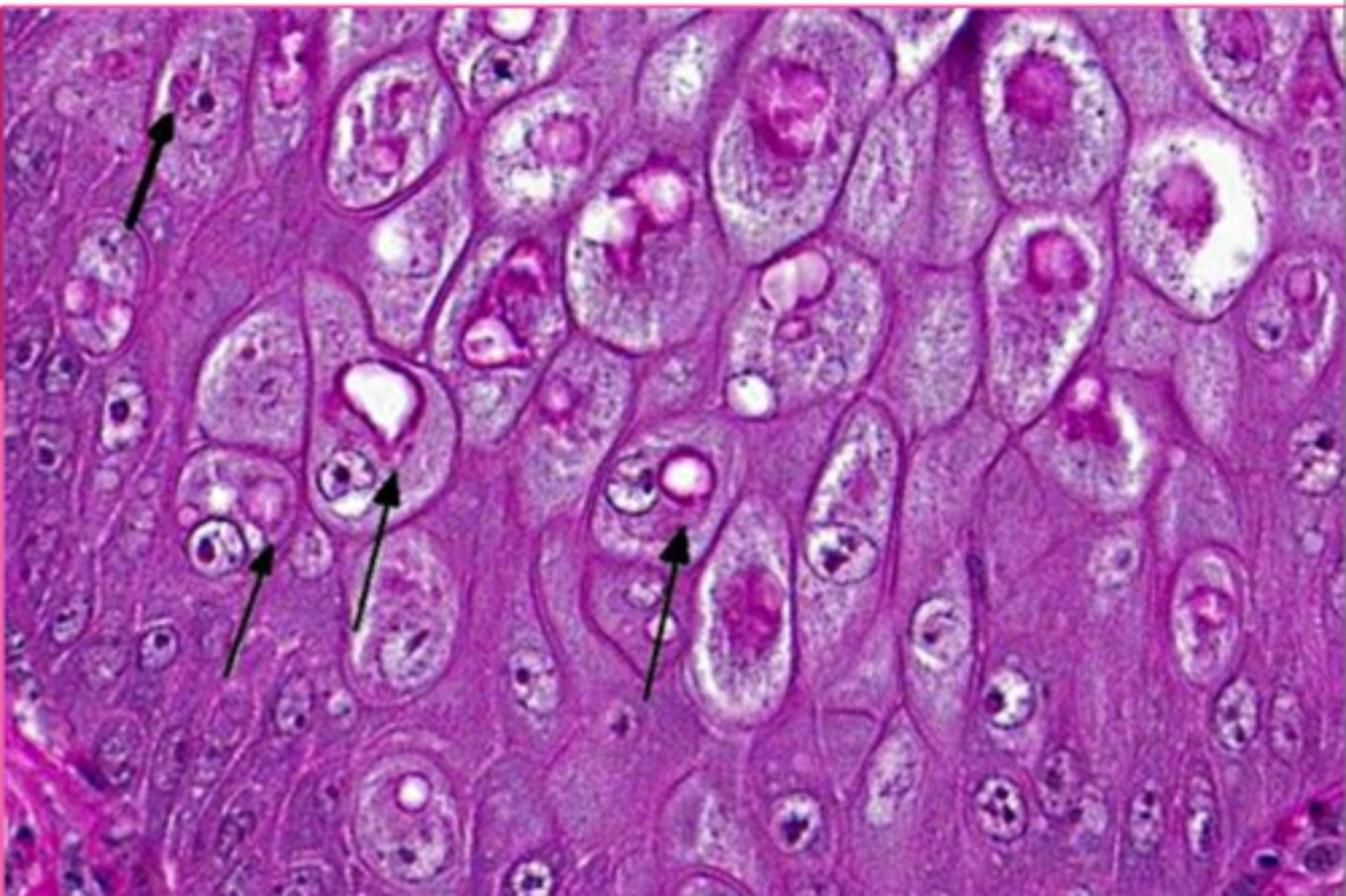
yellow arrow?
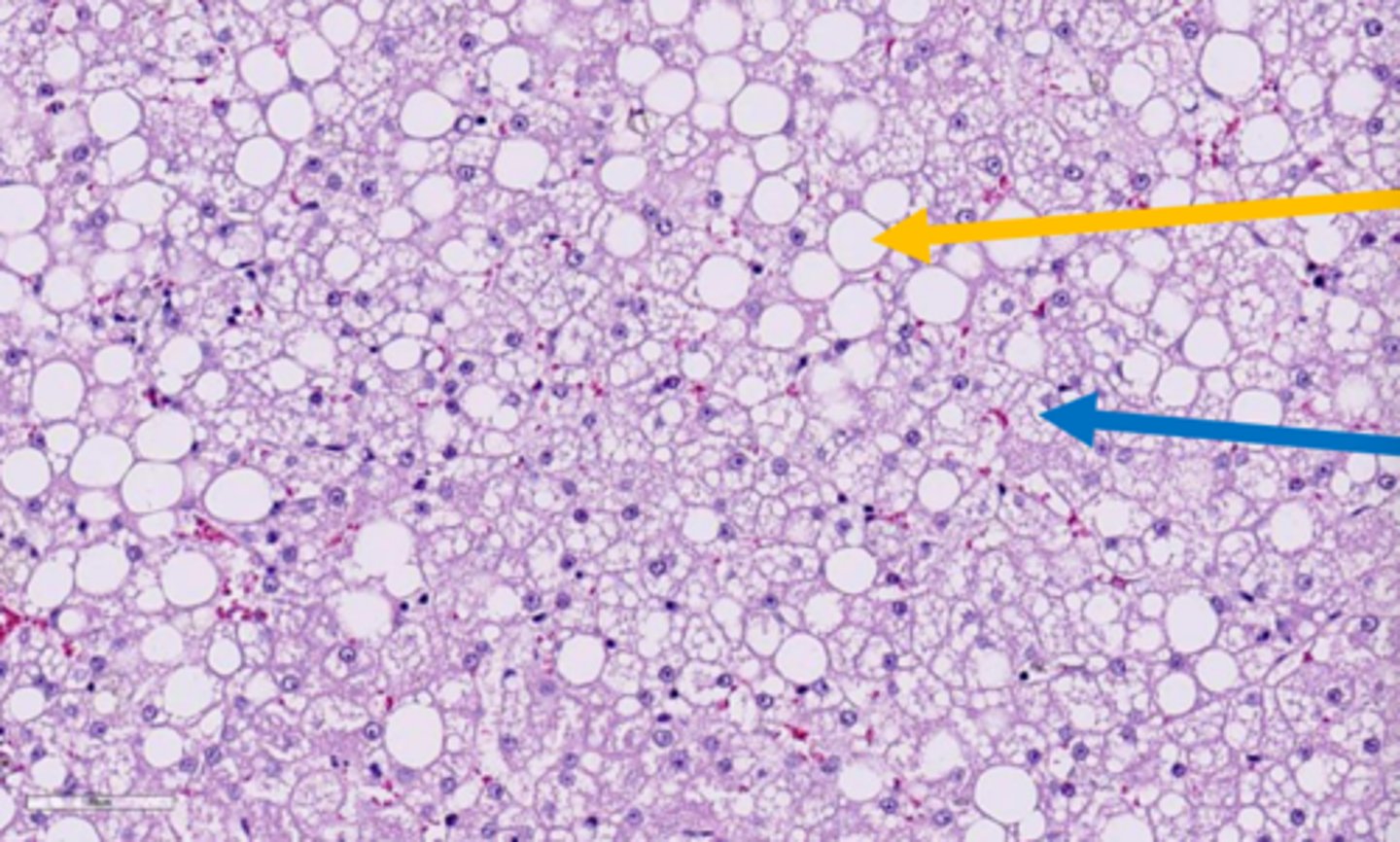
microvesicular hepatic lipidosis
blue arrow?
displaced nucleus
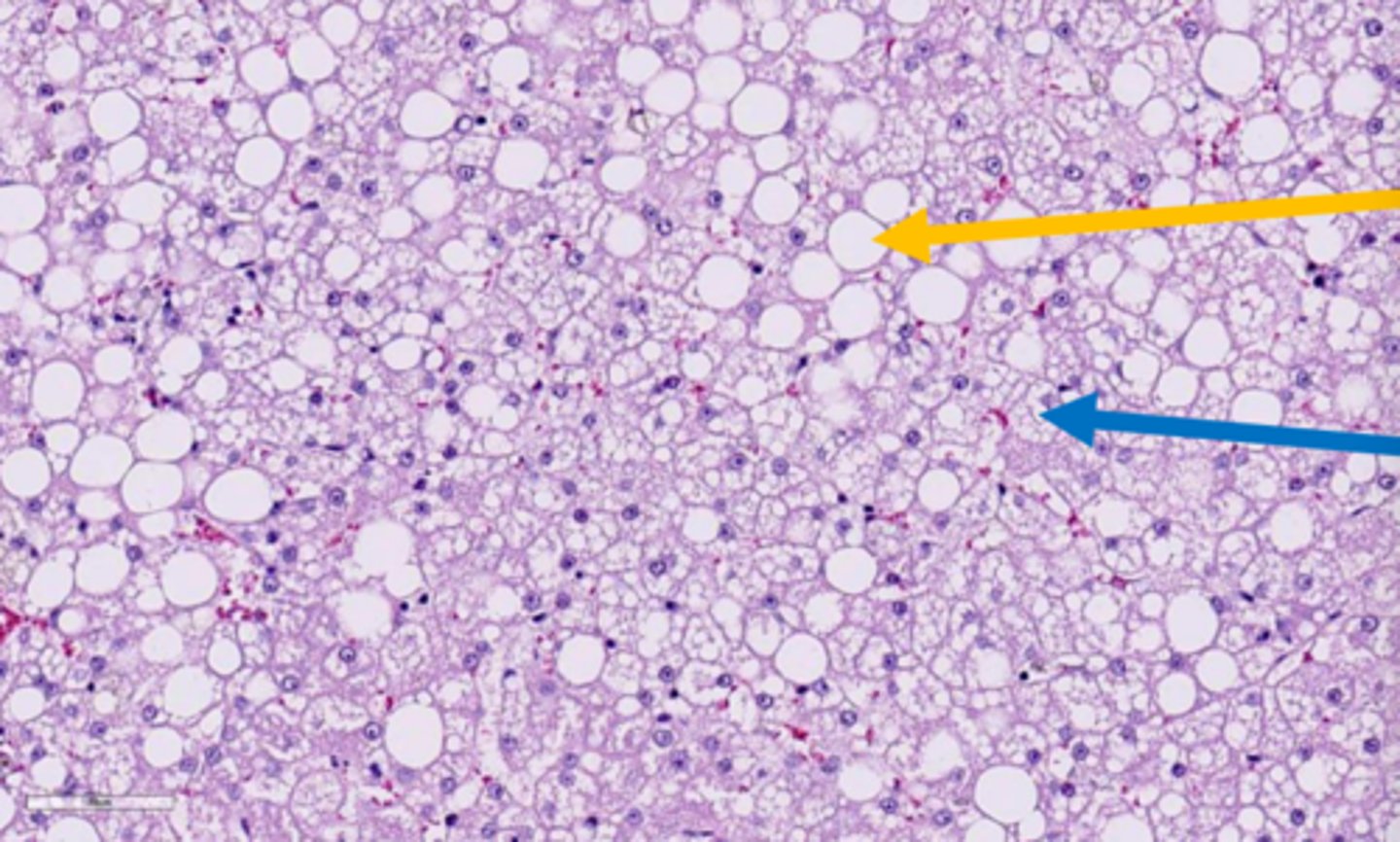
blue arrow
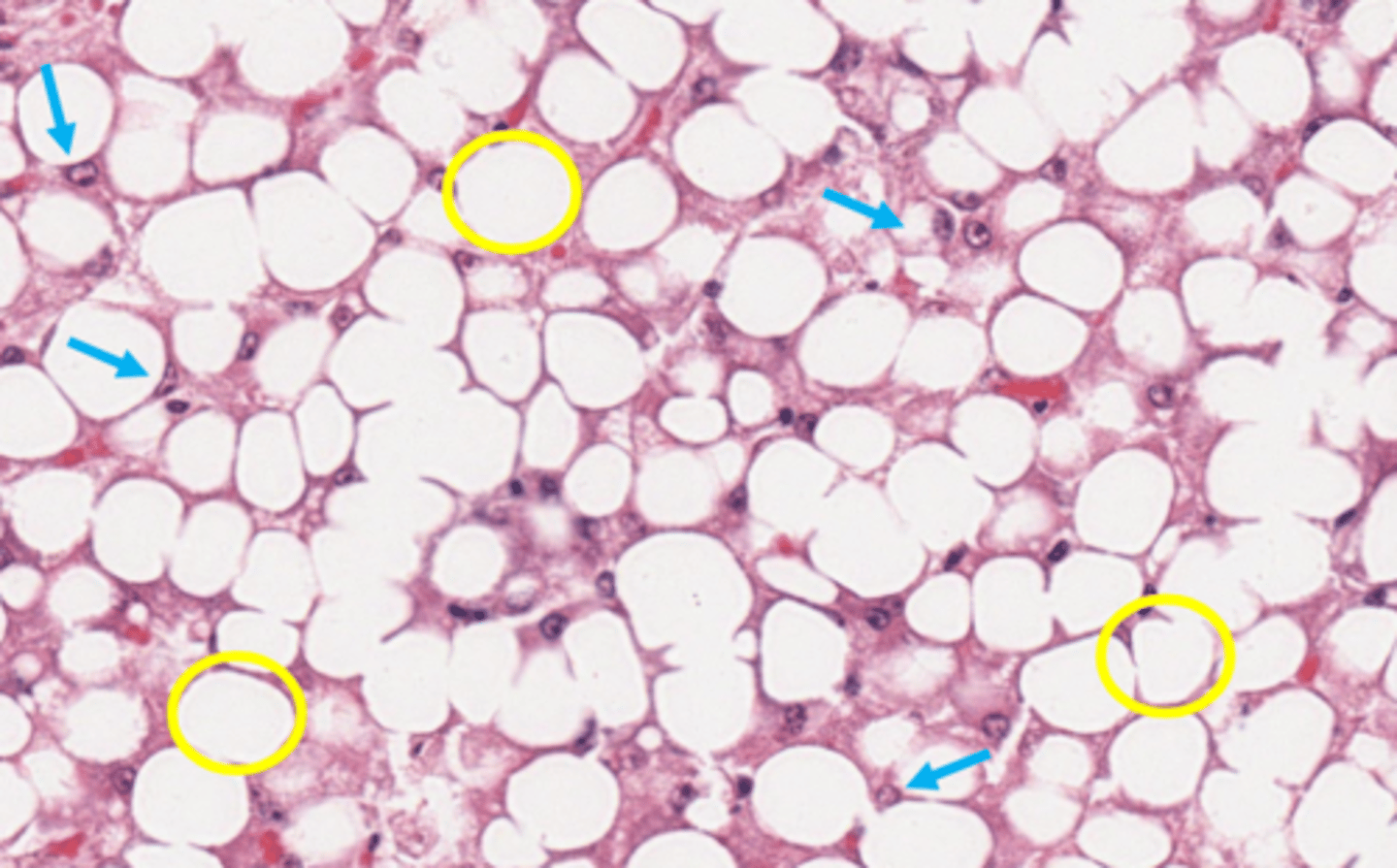
macrocytic lipidosis - large cytoplasmic vacuole
yellow circle?
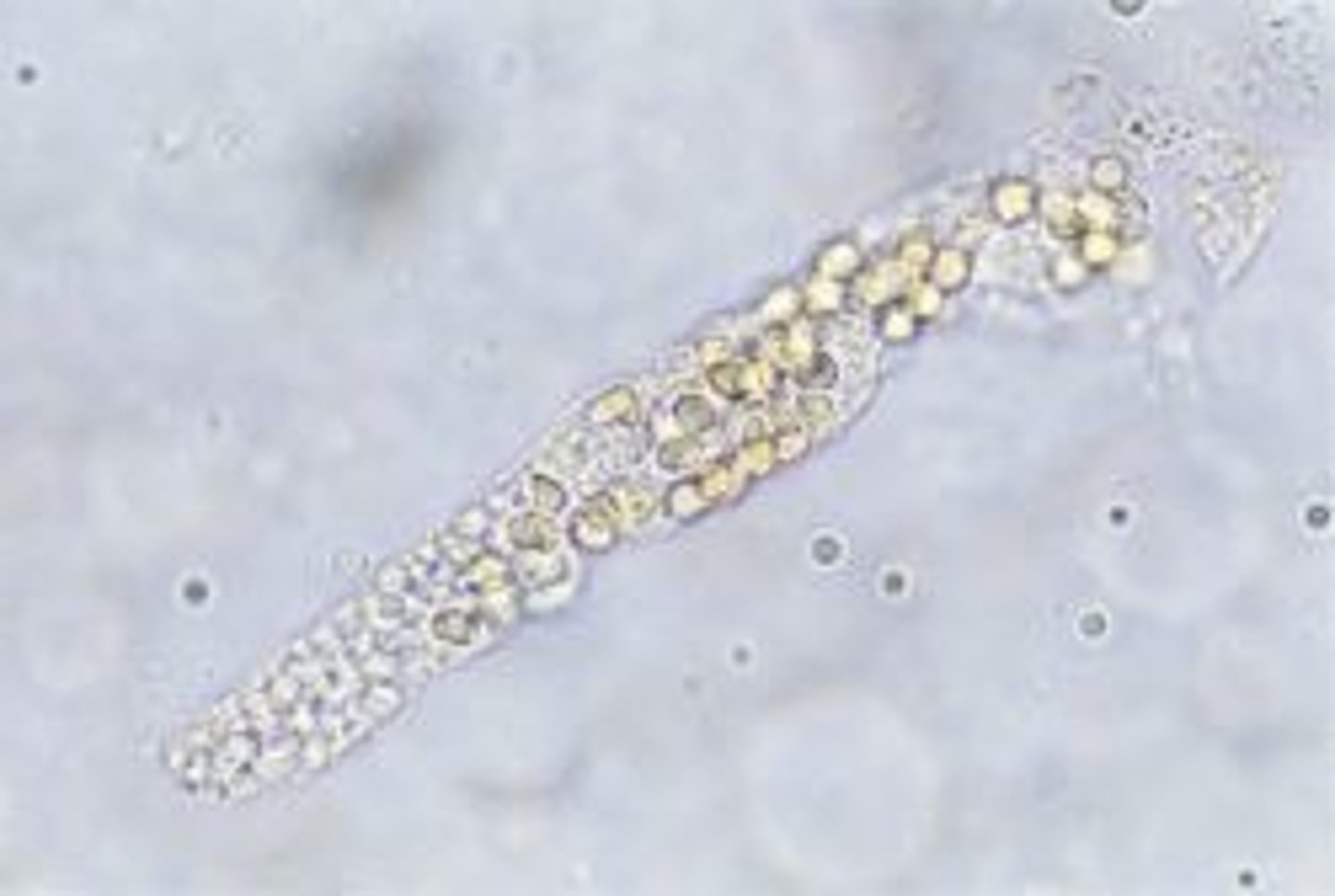
oil red O stain (or Sudan Black B)
What stain is used to prove that an intracellular accumulation is lipid?
no! must use frozen samples
Can you do oil red O staining on tissue processed for the regular paraffin embedding?
oil red O stain, staining lipid inclusions
What the hell is happening to these cells???
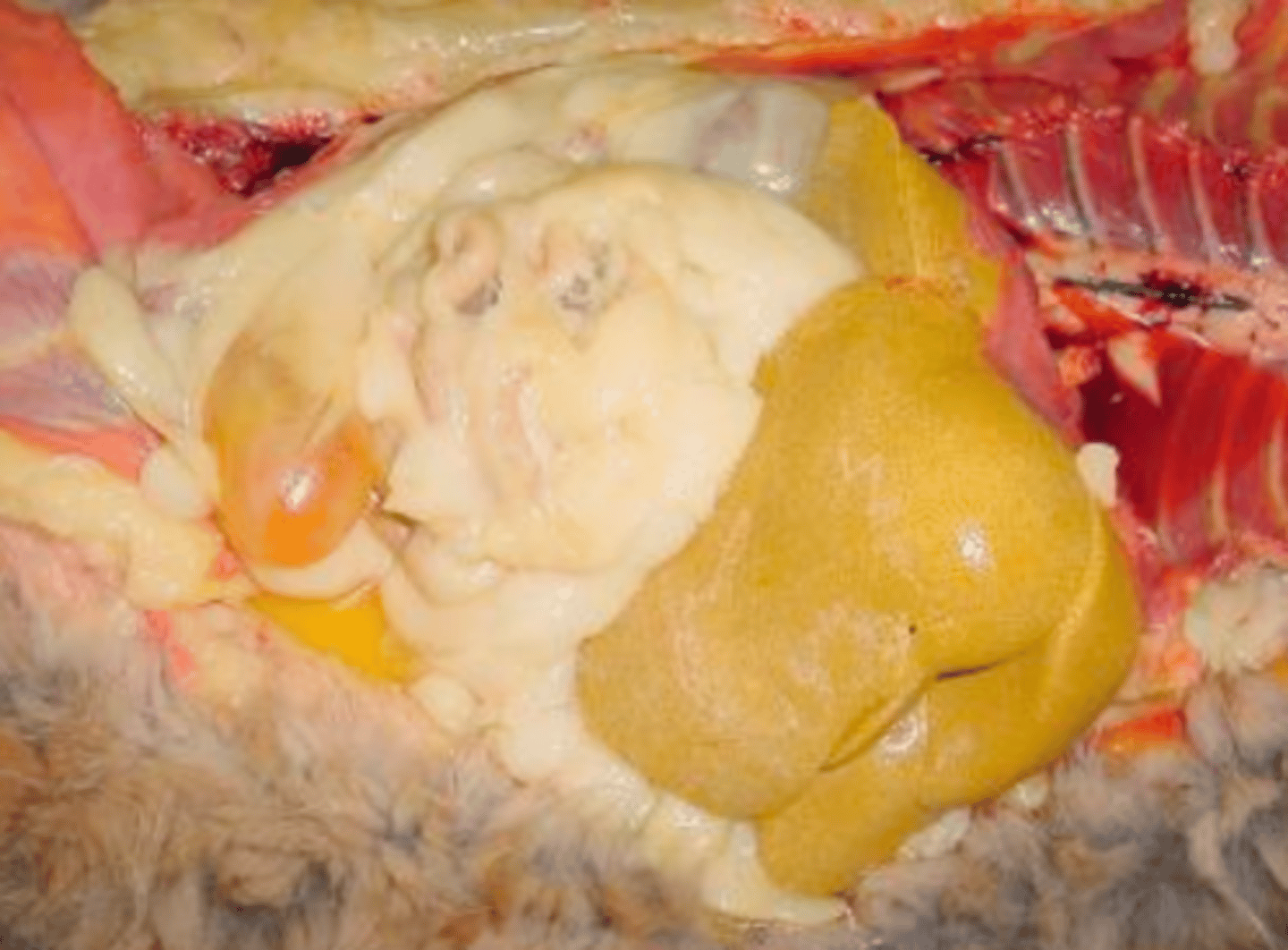
swollen, yellow, greasy texture, maybe friable and floats in formalin, rounded margins
What are the characteristics grossly of an organ with lipidosis?
true
true/false: lipidosis can be physiologic and normal (its just like that sometimes)
late pregnancy, heavy lactation in ruminants, equine hyperlipidemia, feline hepatic lipidosis
what are some classic examples of hepatic lipidosis?
serum triglycerides
In equine hyperlipidemia, the negative energy balance leads to marked elevation of _________
feline fatty liver syndrome
what is the common term for feline hepratic lipidosis in an obese nutritionally stressed cat?
hepatic lipidosis
grossly.. what is this
hepatocytes , skeletal muscle
Glycogen is normally stored in _____ and __________
starvation or illness;
metabolic abnormalities, storage diseases, endocrine disorders
glycogen can be depleted in: _________ or ________
Excessive glycogen accumulation can occur with: __________-, _______ or _______
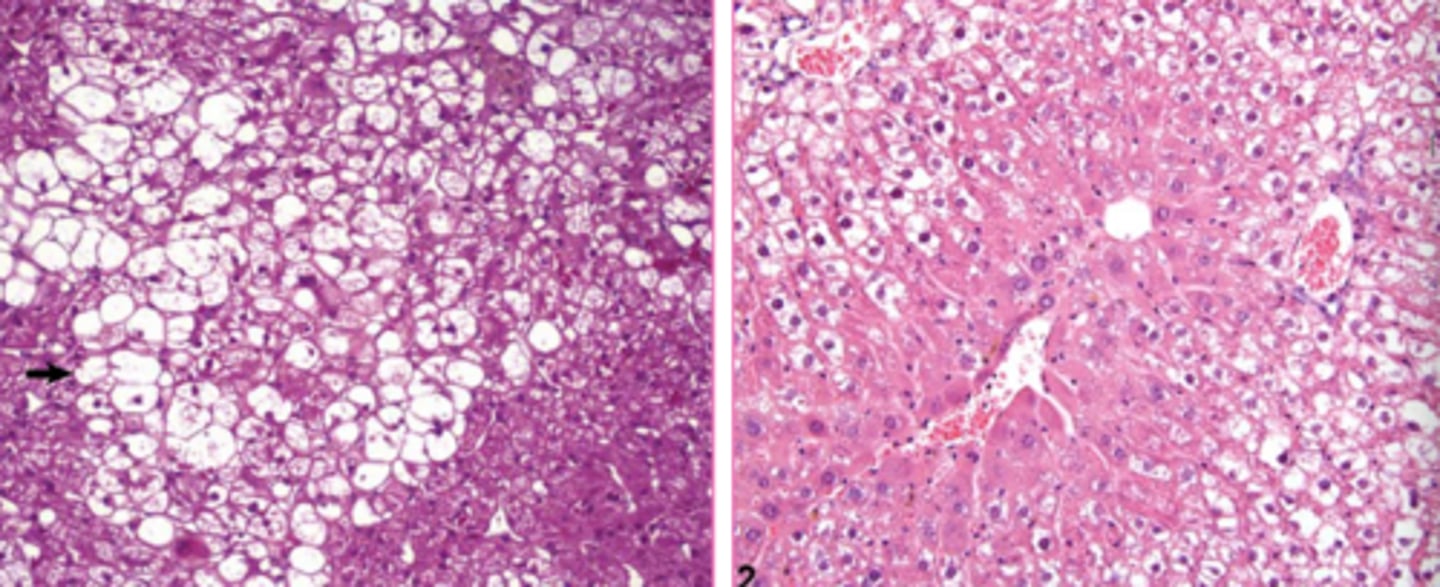
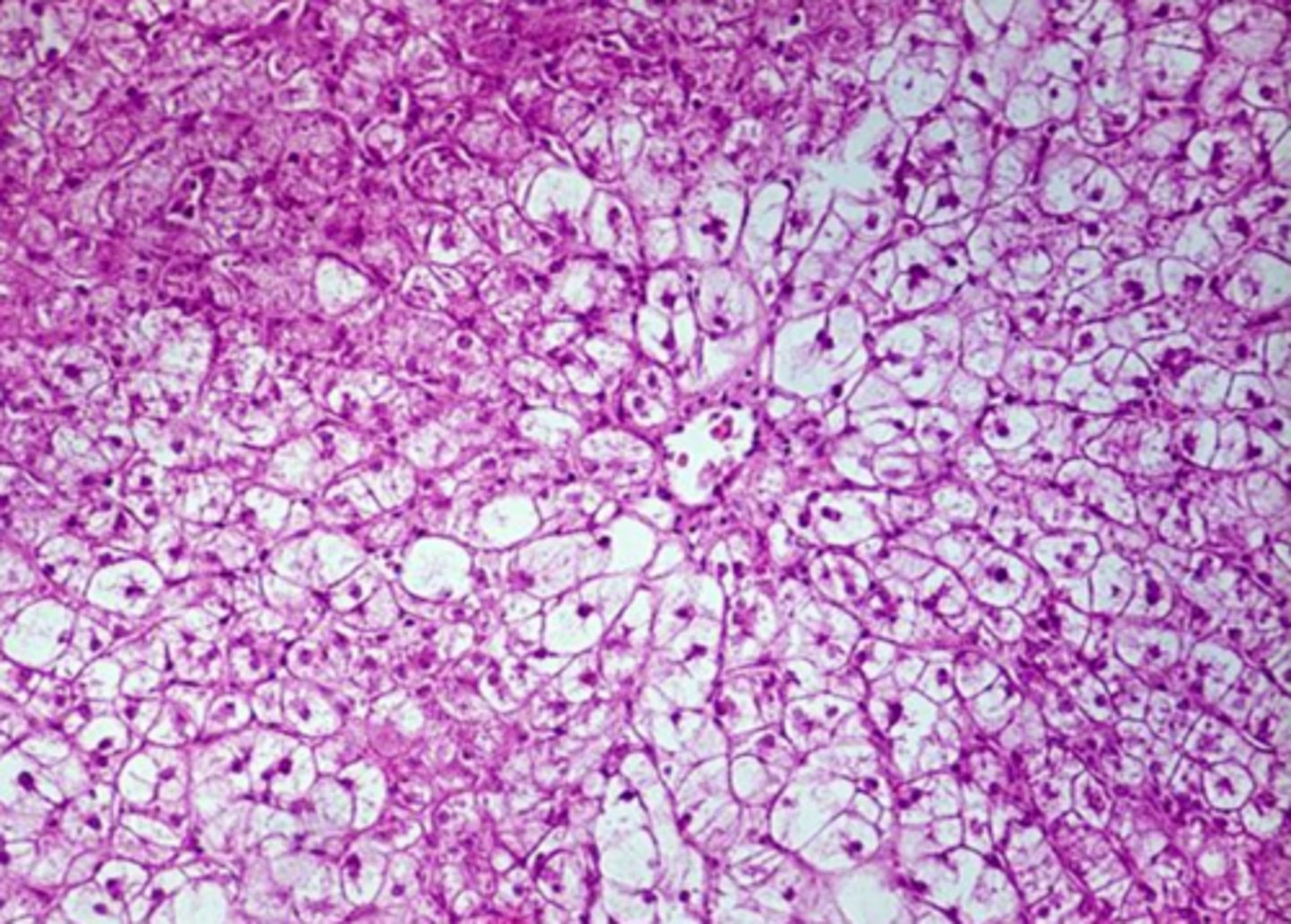
clear granules/vacuoles, "feathered cytoplasm", not displaced nuclei
what are the microscopic features of glycogen in the cytoplasm?
hepatocellular vacuolar change - glycogen type (glycogen in cytoplasm)
Both of these images are showing what?
amount of glycogen observed microscopically
What do all three of these things affects?:
Glycogen concentration, delay between death and fixation, type of fixation
periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
which histochemical stain is sued to detect lgycogen?
false; its not
True/false: the PAS stain is specific to glycogen
diastase
what is PAS stain used in conjunction with in order to visualize glycogen?
right side sample has been treated with diastase
Both of these images are PAS stains to see glycogen... what's different about them?
swollen, pale brown, mottled
What are some gross characteristics of an organ (liver) with glycogen inclusions?
glycogen
glycogen or lipid inclusions?
lipid
glycogen or lipid inclusions?
glycogen
gycogen or lipid inclusions?
eosinophilic (pink/orange/red)
proteins are what color?
hyaline
What is the term for a proteinatious cellular inclusion? Often homogenous/eosinophilic/translucent substance that is internal or external to the cell.
Yes! Russel bodies are normal in plasma cells
can Hyaline inclusions be normal in any cells?
well, protein accumulation in proximal renal tubular epithelial cells is abnormal... so duh.
Oh, so russel bodies are normal protein accumulation in plasma cells... is hyaline inclusions ever abnormal?
Russel bodies in Mott cells
These are plasma cells. what is circled?
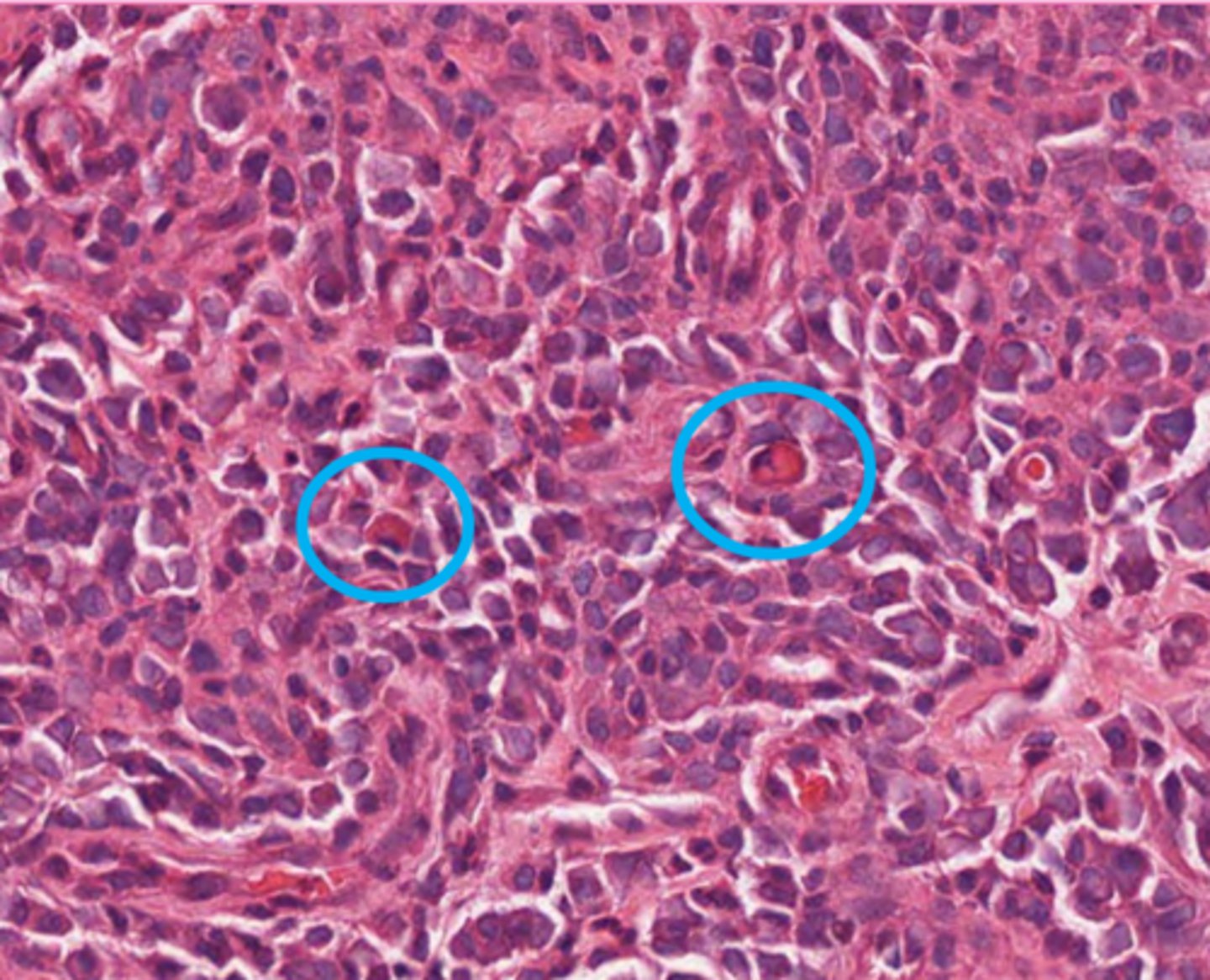
hyaline droplet
these are renal tubular epithelial cells... what is circled?
hyaline droplet
what are these bright esosinophilic 'dip dops'
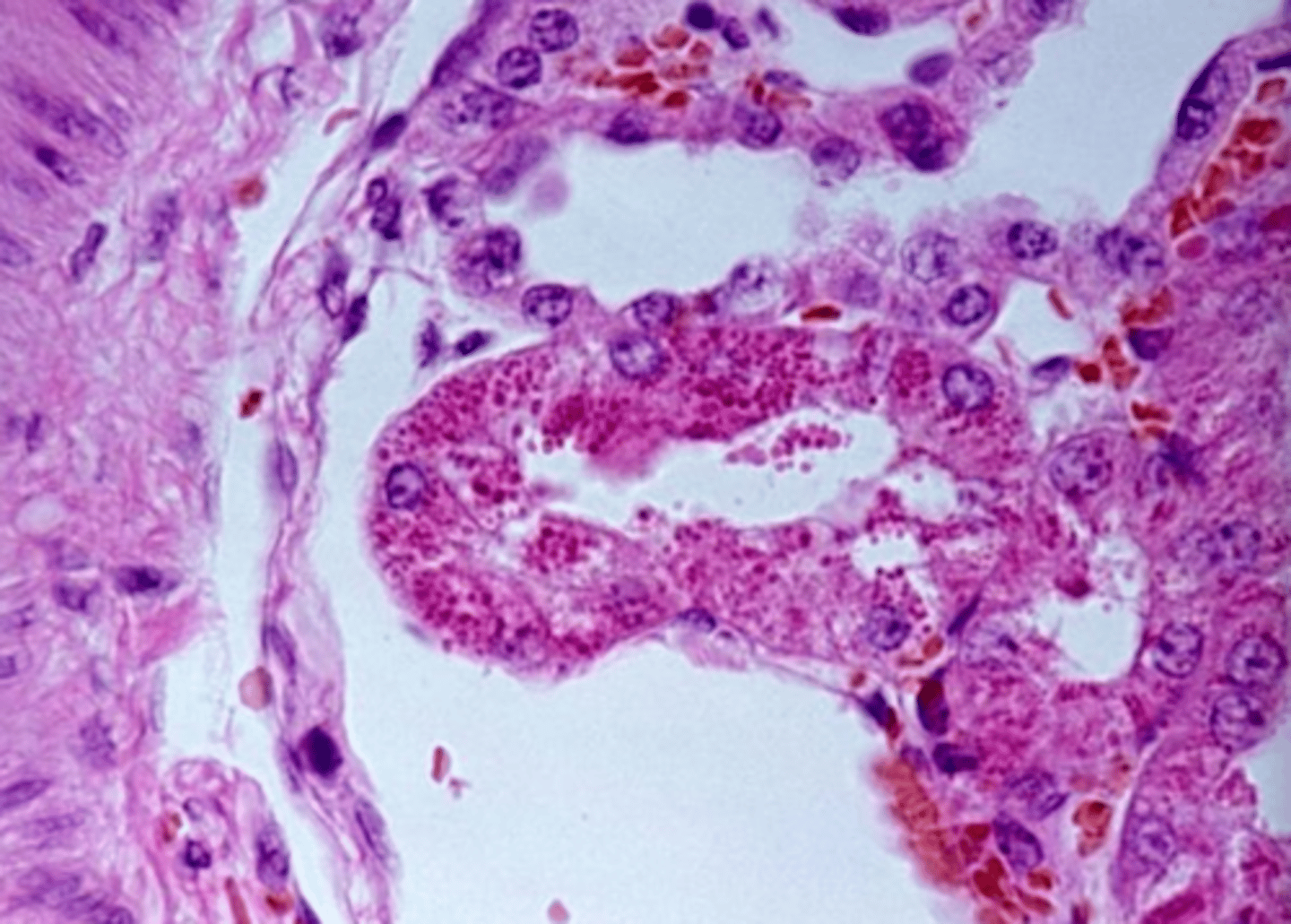
can be extruded or remain as lipofuscin pigment
what is an important to know about autophagic vacuoles?
increase with age, common in hepatocytes/renal tubular epithelial cells
what are important to know about crystalline protein inclusions? (2)
intranuclear
Where are lead inclusions found in a renal tubular epithelial cell?
lead and protein mixture, acid-fast stains
What are lead inclusions made of? how best are they seen?
crystalline protein inclusions
What is the inclusion?
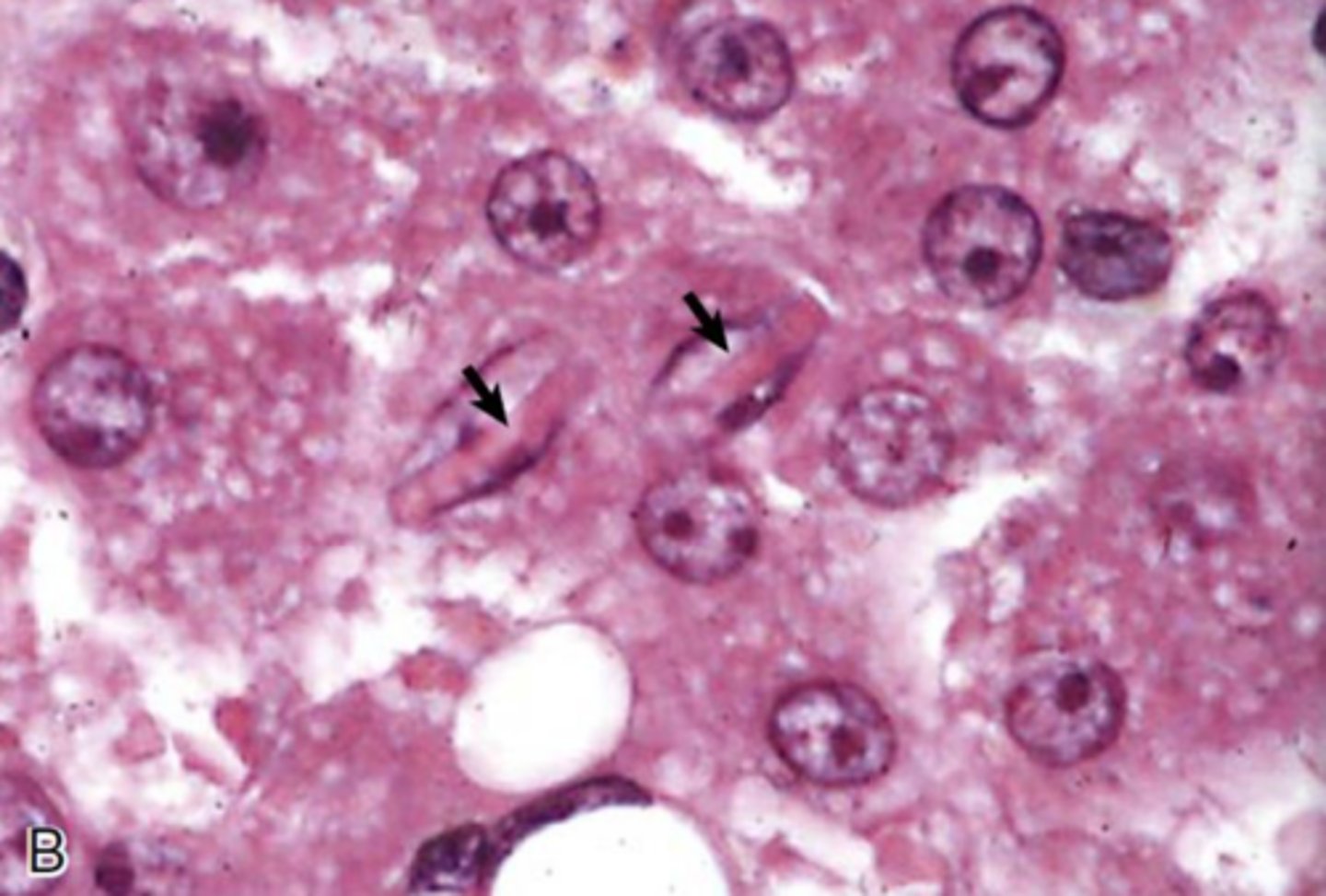
lead inclusions
what is the inclusion?
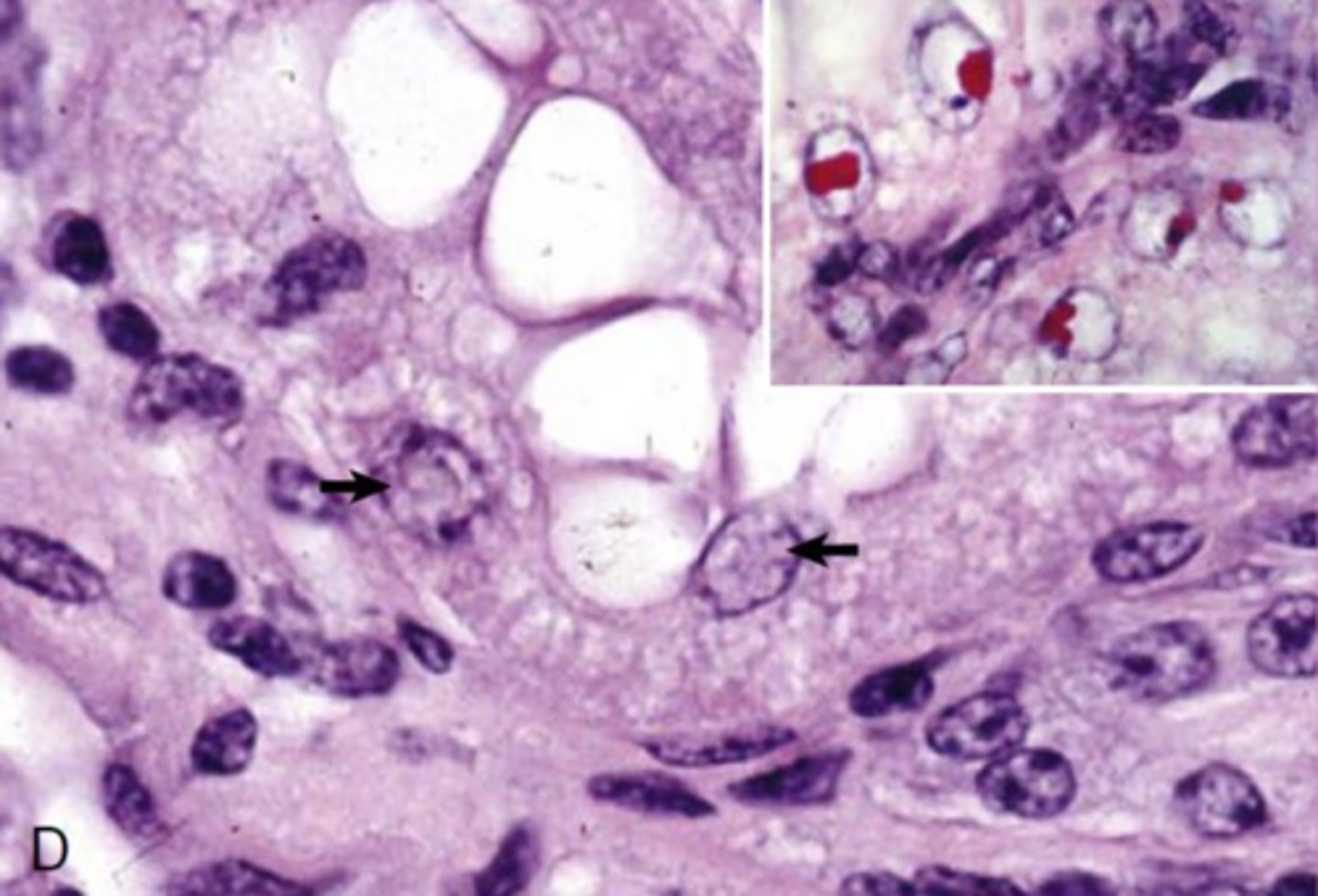
intracytoplasmic, intranuclear
what are the two types of viral inclusion bodies?
(location, not specific virus)
eosinophilic, basophilic, amphophilic, round to oval
the intranuclear DNA virus inclusions look... how? (variable)
herpesvirus, adenovirus, parvovirus
what three DNA virus inclusions are intranuclear? (that we were given at least)
poxviruses, large eosinophilic
What is the one viral cytoplasmic inclusion and what does it look like?
Rabies, canine distemper
what two RNA virus inclusions were we given as examples?
negri bodies
rabies inclusions are called?
both!
Is canine distemper a nuclear or cytoplasmic inclusion?
herpesvirus
which viral inclusion?
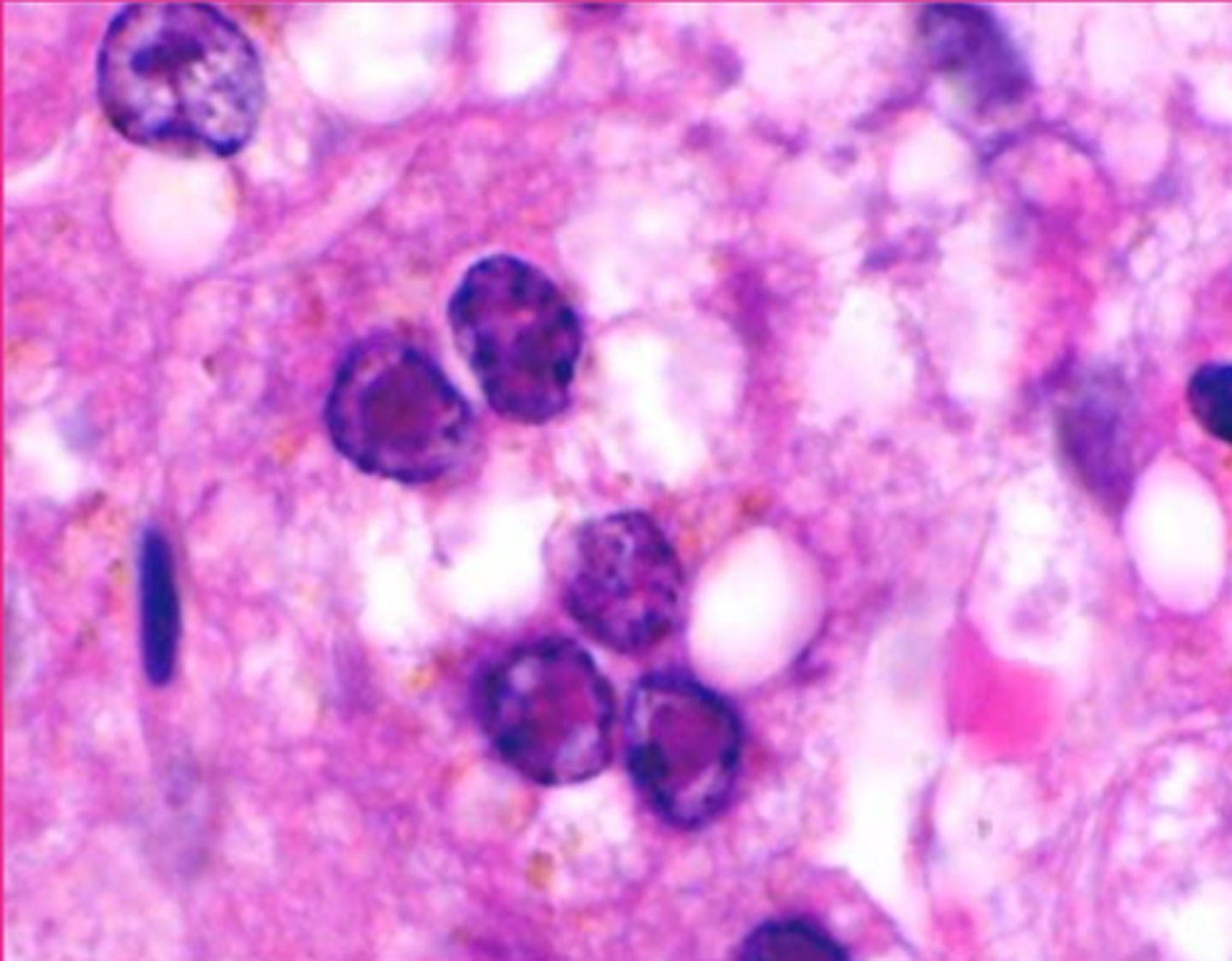
adenovirus
which viral inclusion
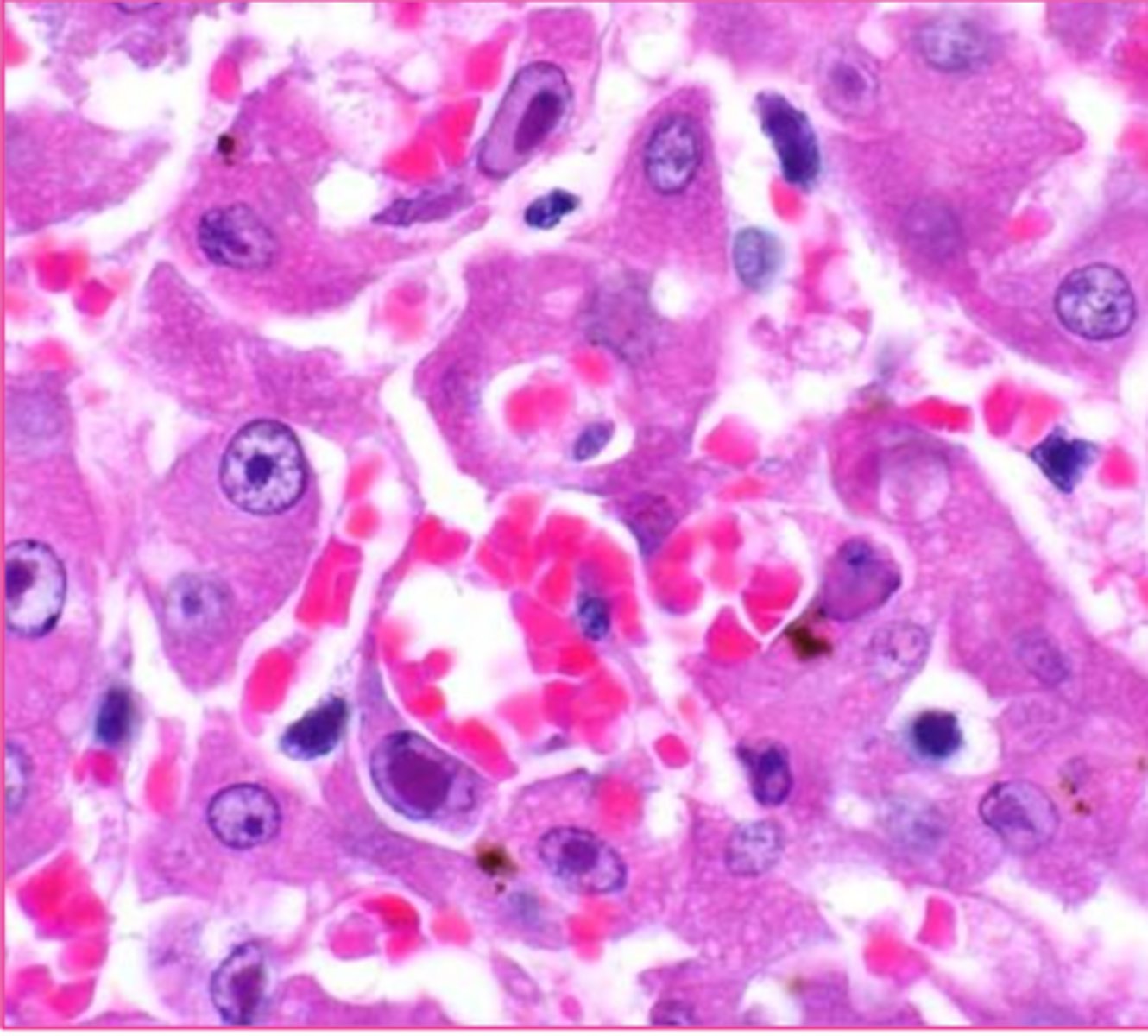
poxvirus
which viral inclusion?
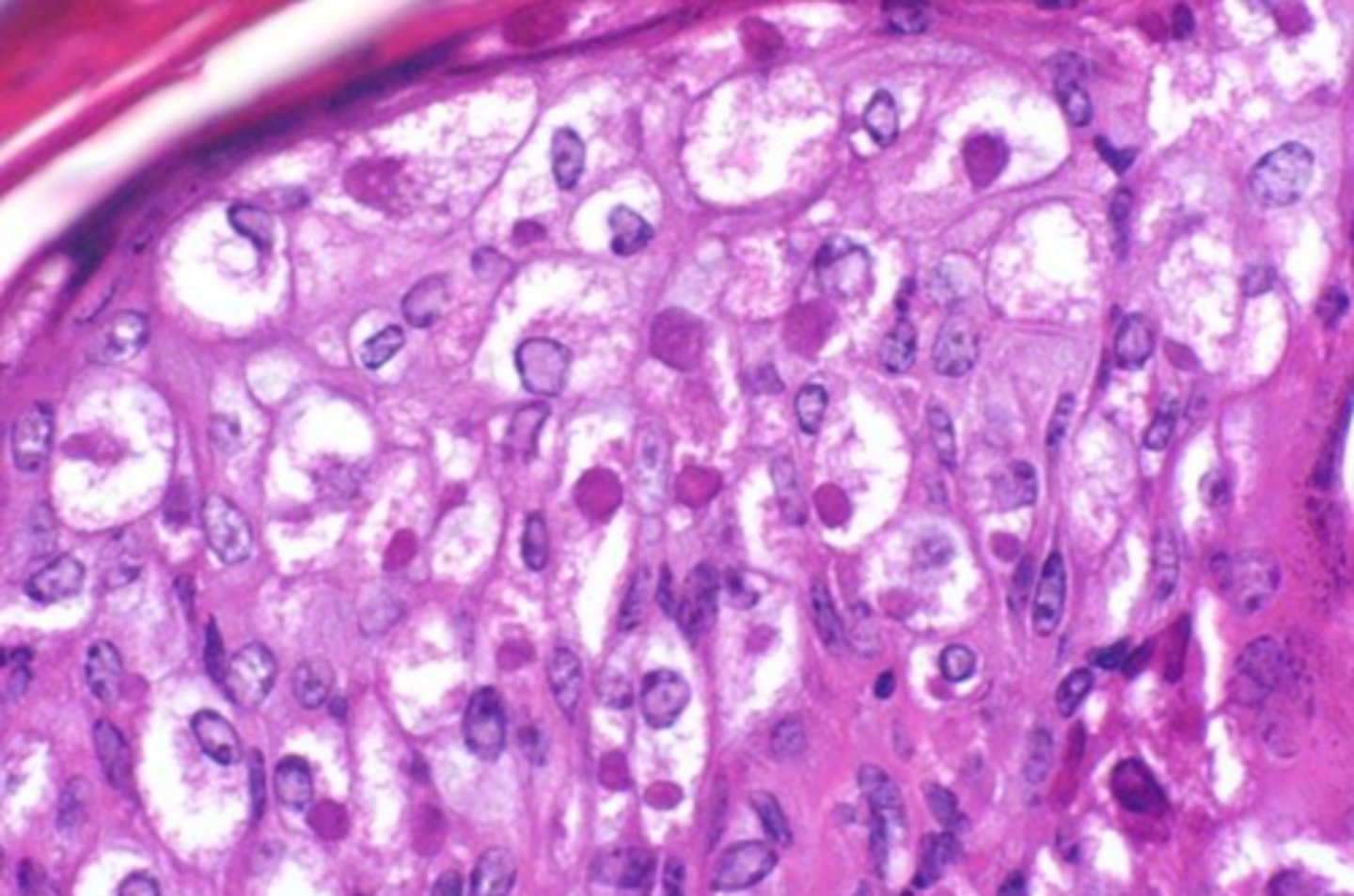
rabies
which viral inclusion?
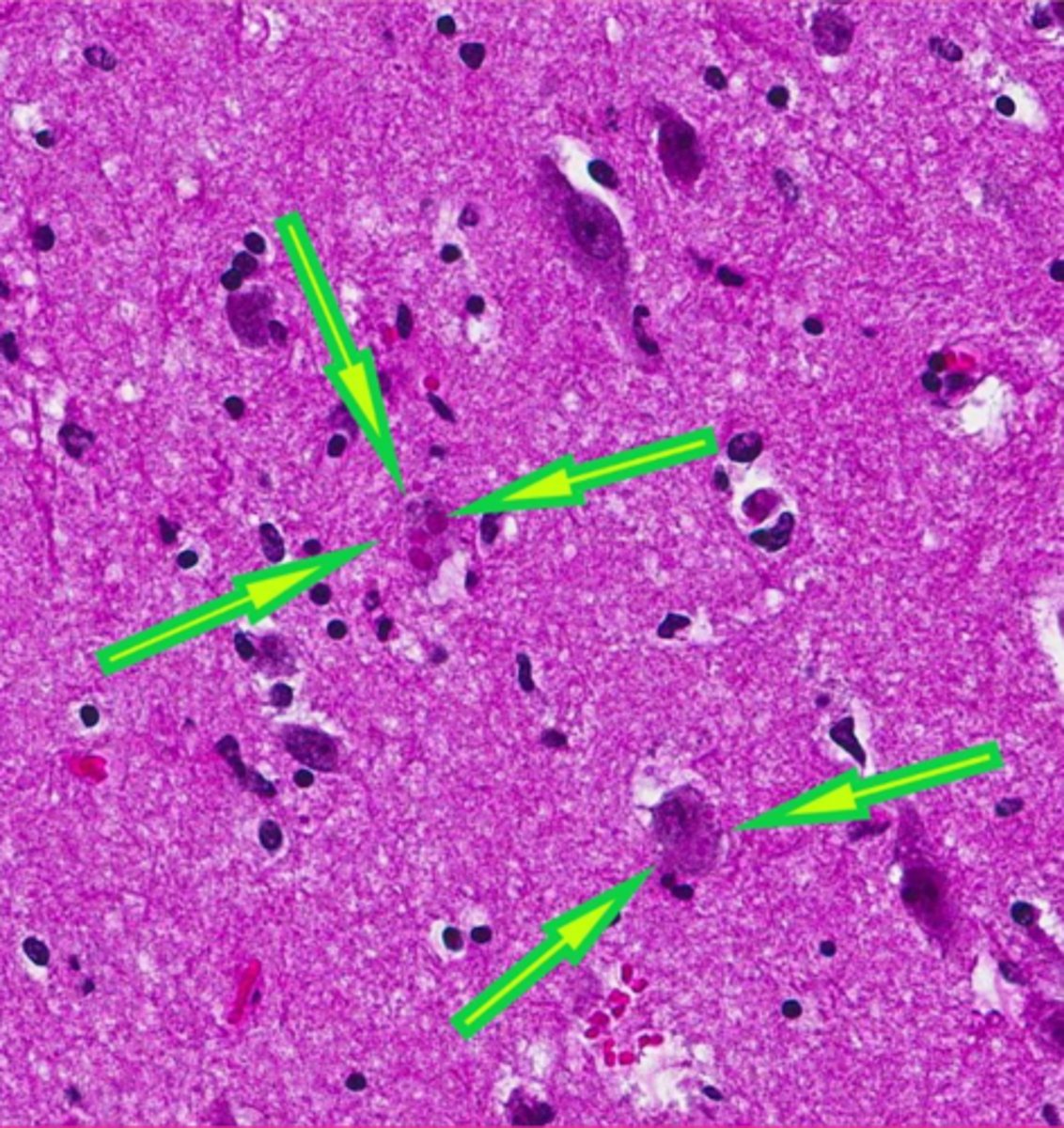
canine distemper virus
which viral inclusions?
storage diseases
Group of diseases characterized by mutations that result in the
accumulation of complex substrates or blockage of metabolic
pathways
lysosomal storage disease
which storage disease is characterized by a deficiency of lysosomal acid hydrolases
incomplete breakdown of substrates, accumulating partially degraded, insoluble metabolites
What shows up as a result of lysosomal storage diseases?
lysosomal
lysosomal galactocerebroside beta-galactosidase (sorry)
Globoid cell leukodystrophy is an example of what type of storage disease?
Specifically, it is a functional deficiency of ___________________________
galactocerebroside, macrophages of the CNS
Globoid cell leukodystrophy is an accumulation of __________ within the ________ cells of the _________ system
GM1 gangliosidosis, lysosomal, GM1 ganglioside
what storage disease is marked by a deficiency of GM1 ganglioside beta-galactosidase.
What type of storage disease is this and what accumulates?
hexosaminidase, tay-sachs disease, sandhoff disease
GM2 gangliosidosis is a deficiency or ______
If its a deficiency of the alpha subunit its called ________.
If its the beta subunit, it's called ___________
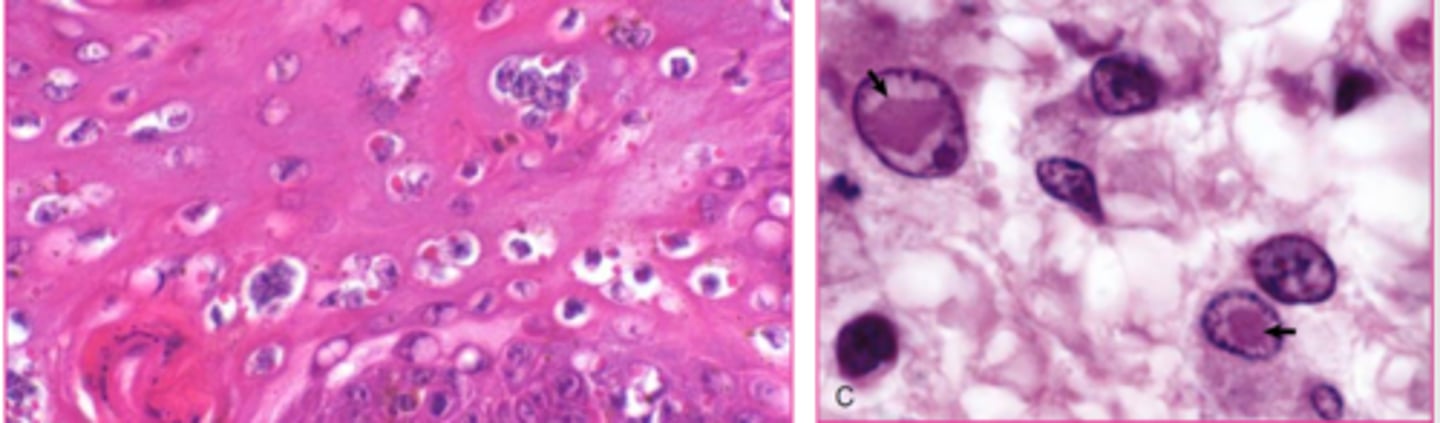
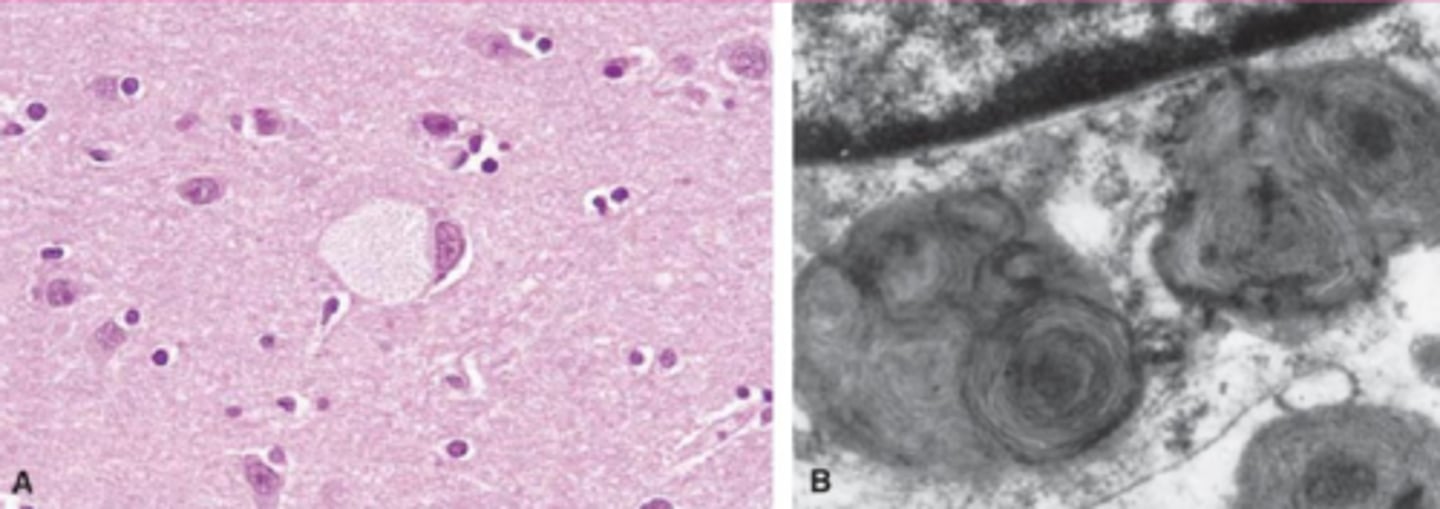
globoid cell leukodystrophy
What?
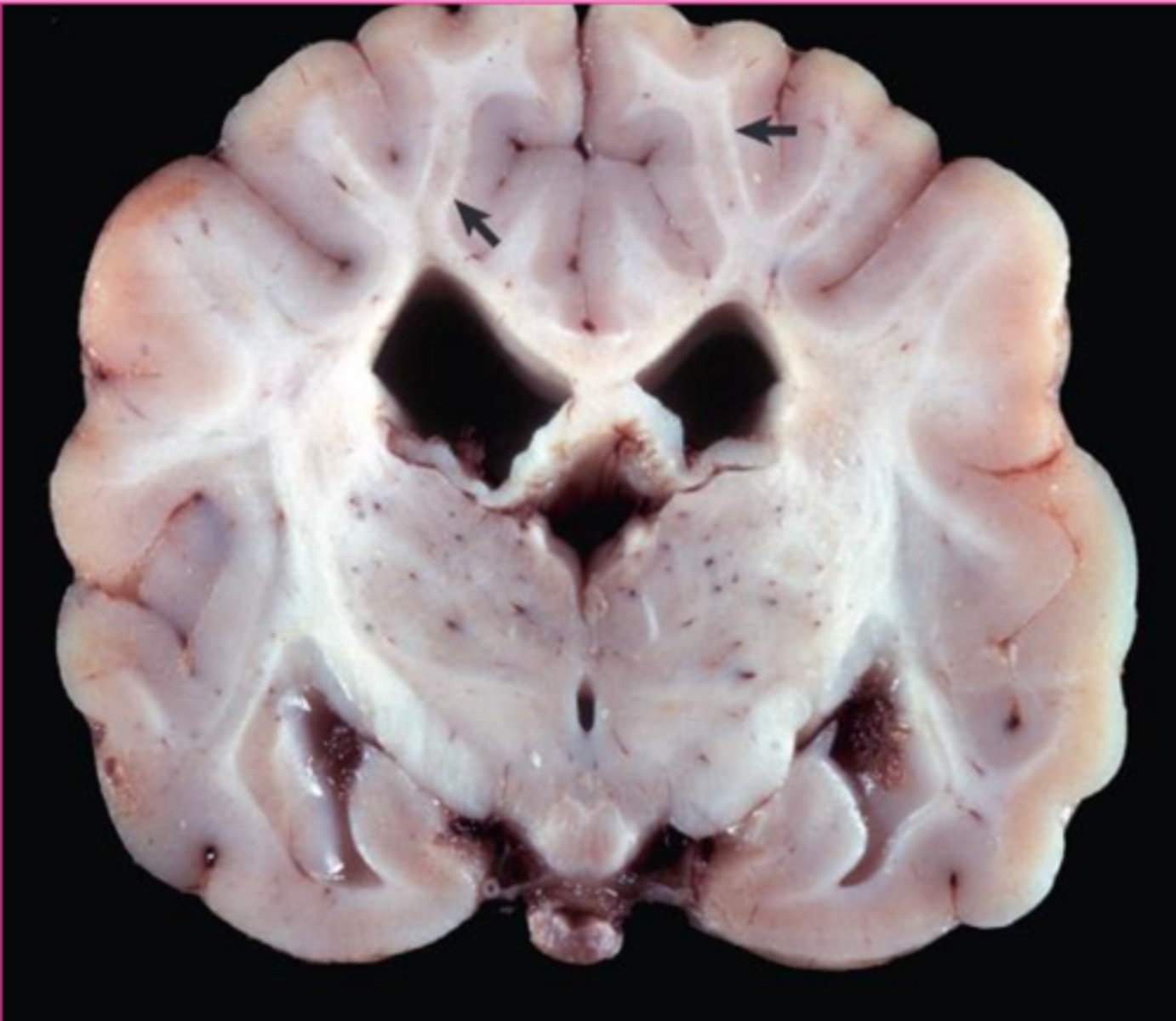
globoid cell leukodystrophy
what?
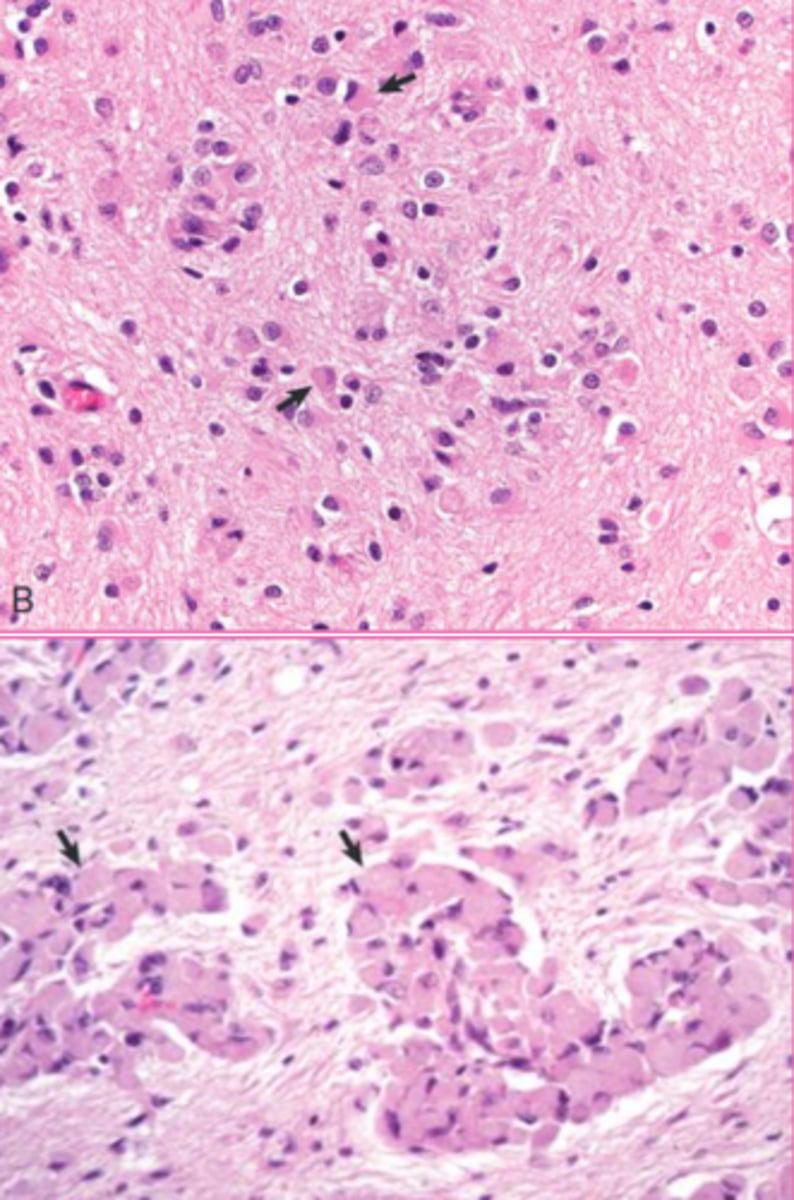
globoid cell leukodystrophy
what?
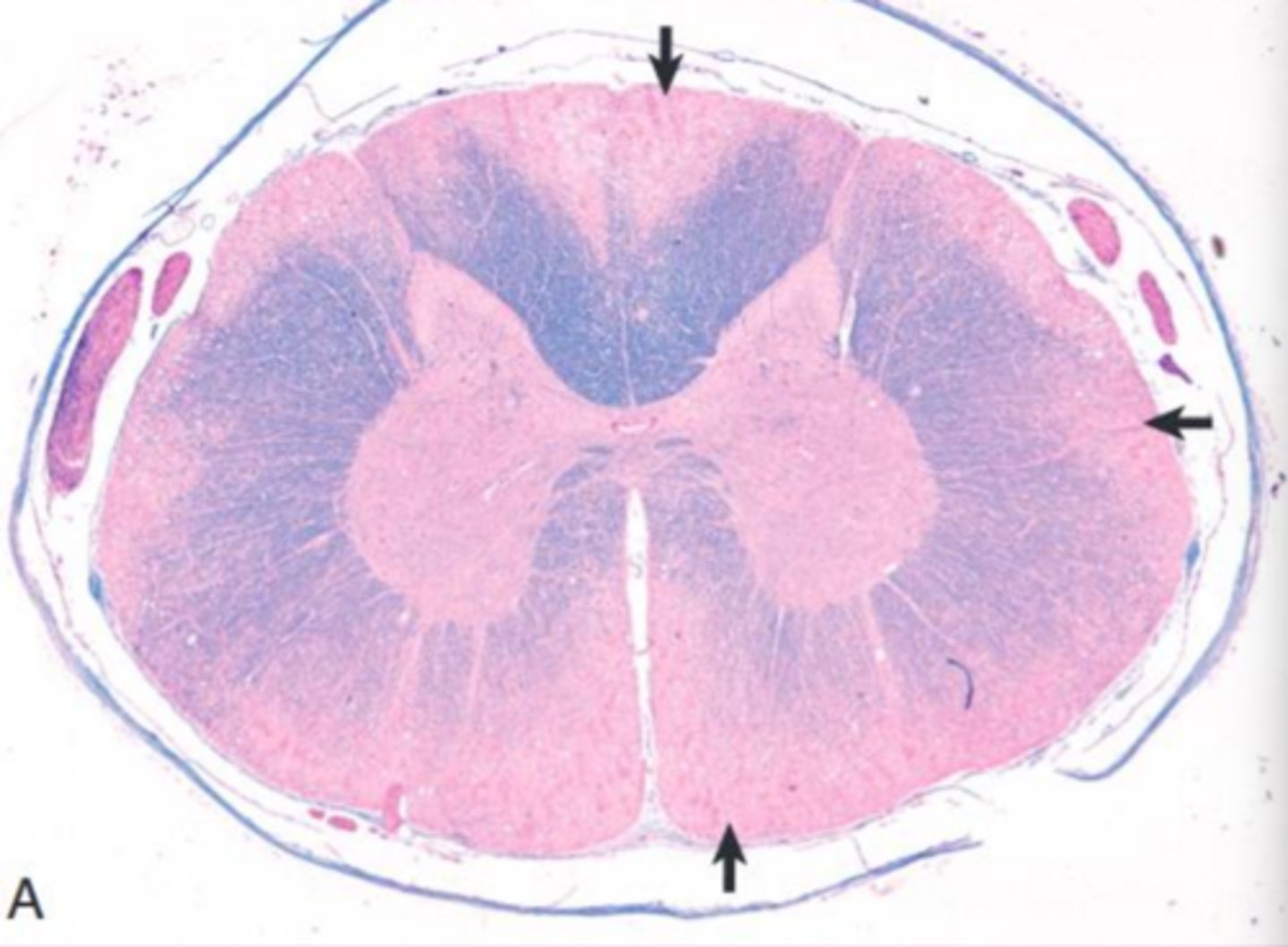
Tay-sachs disease
what?
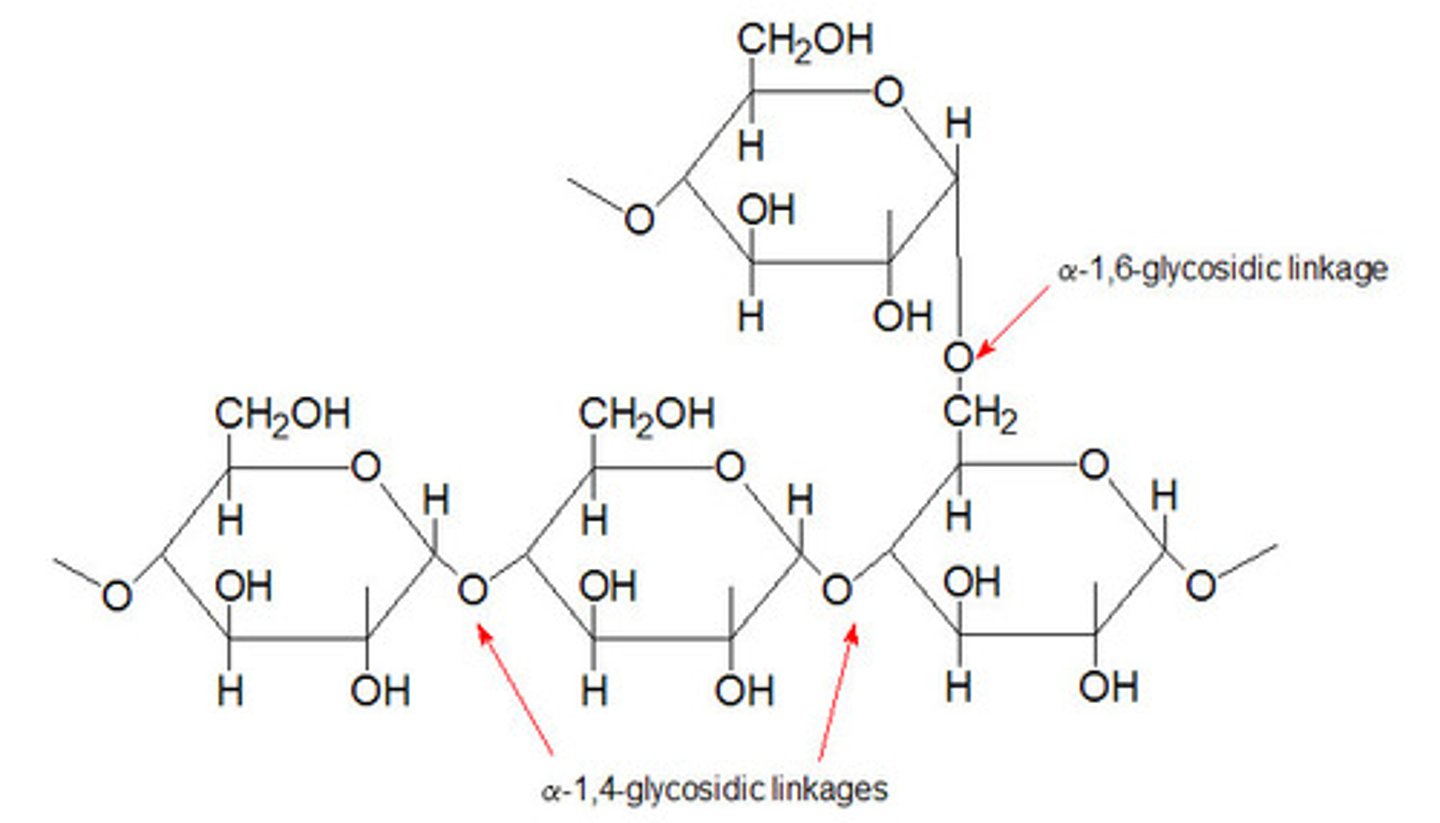
an enzyme involved in synthesis or degradation of gylcogen (accumulates glycogen)
generally, glycogen storage diseases are characterized as a deficiency in _______________________________
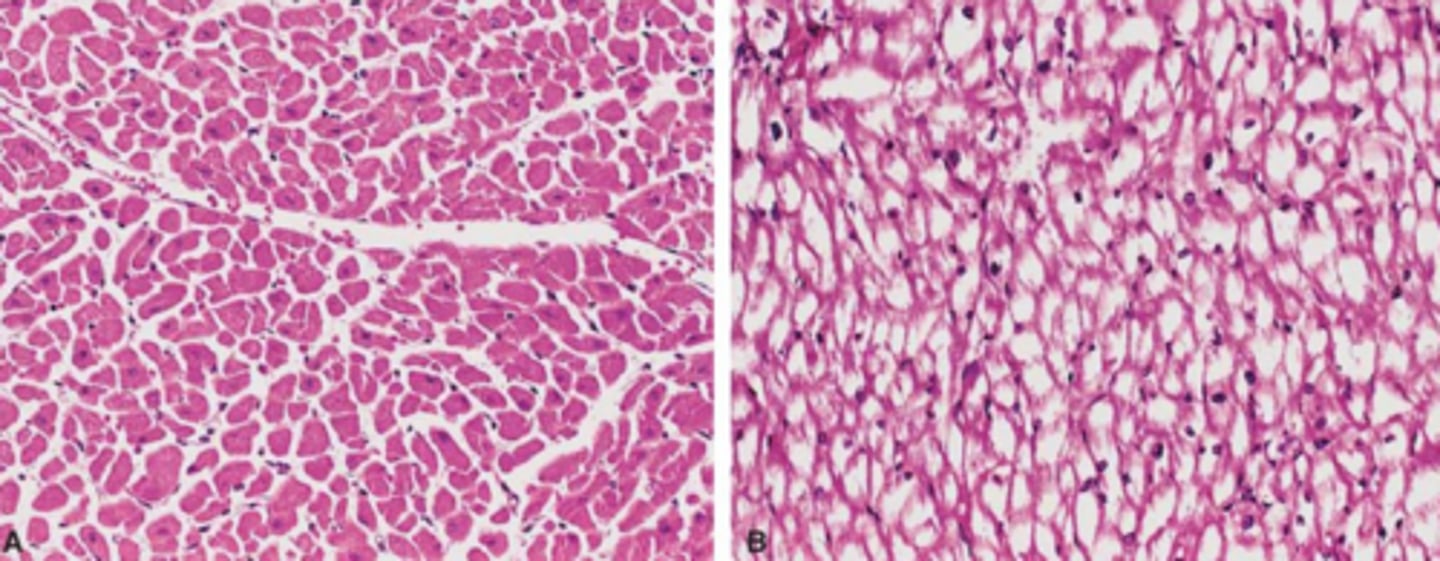
Pompe disease, alpha-glucosidase enzyme
what is another name for glycogenesis type II?
Where is the deficiency?
Cori's disease,
function of amylo-1,6 glucosidase debranching enzyme (IM SORRY OKAY?)
Whta is another name for glycogenosis type III?
where is the deficiency?
Pompe disease
What?
induced storage diseases
What do you call an inhibition of enzymes due to outside sources like the ingestion of locoweed
lysosomal alpha mannosidase
what is inhibited in locoweed toxicosis?
proprioceptive defects and abnormal behavior
chronic consumption of locoweed causes _________ and __________
locoweed toxicosis
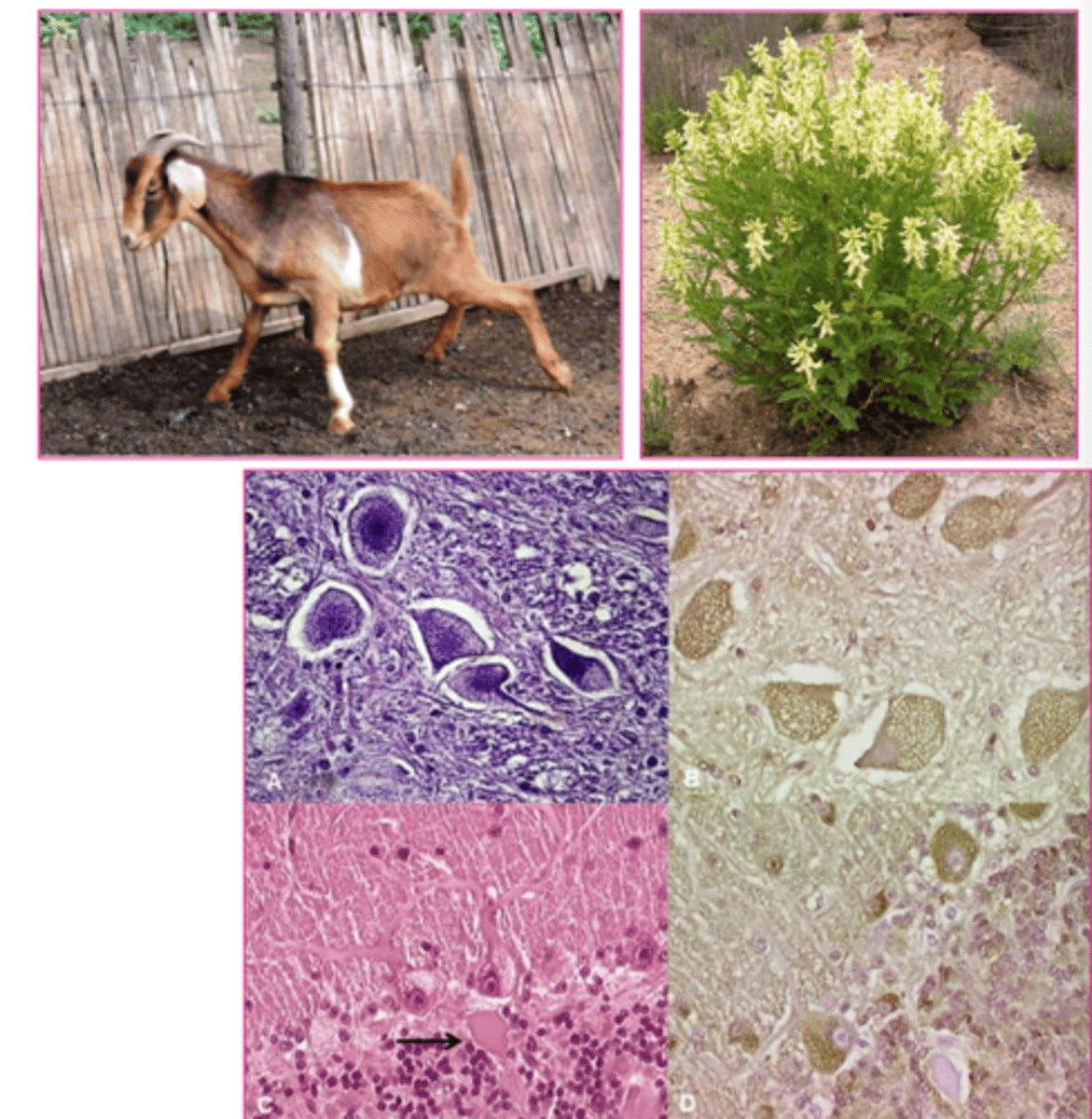
if you have a goat standing around like this, and this plant is in his habitat, and his cells look like this... what do we think this is?

viral inclusions
What is this?
(Options are like, glycogen, lipid, viral, iron inclusions.... options are all the inclusions a cell can have)