Psych Exam 1 Review (MSU)
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study religiously
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Goals of psych
study the mind, brain, and behavior scientifically
study the physical neurons of the brain
how and why do people do what they do?
unconscious forces: people do things without realizing
Hindsight Bias
claiming to have a prediction about something after it happens (“I knew it all along”)
Confirmation Bias
looking for evidence that confirms predictions and beliefs
Correlational Research
measures 2 variables and sees if they’re related, and how strongly they are related
correlational coefficient
(-1 to 1)
positive correlational coefficient
high values of one variable ( r ) are associated with high values of the other
negative correlational coefficient
high values of one variable are associated with low values of the other
Does correlation always mean causation?
CORRELATION DOES NOT ALWAYS MEAN CAUSATION
Descriptive studies
seeks out ways to observe or describe a certain phenomenon
A case study
a study of one person or a small group
strengths of case studies
they have a powerful impact on our understanding of a phenomenon
weaknesses of a case study
have a small sample size 2. susceptability to research bias 3. cannot establish causality
naturalistic observation
analyzing a natural occurrence
advantage of naturalistic observation
generalizability
disadvantage of naturalistic observation
observation can alter behavior
cannot infer the cause of behavior
survey research
asking questions to a large number of people to gain insight on attitude and behavior
advantage of survey research
very large sample sizes, increase reliability and replicability
disadvantage of survey research
sampling issues
people may not respond accurately
Descriptive Research strength
may be only way to analyze phenomenon
descriptive research weakness
cannot determine the cause of the behavior
may have observer bias
Experimental Research
when there are 2 variables and one is being changed to measure the others outcome
independent variable
the variable that is manipulated or changed
dependent variable
variable that is measured after the change of the first variable
population of an experinent
the group that the researcher is interested in studying (ex. people or monkeys)
sample
individuals taken randomly from a population that are being tested on
control group
a group that is identical to the experimental group, except it has not been exposed to treatment
used because other factors can vary with the independent variable
what are the neuroimaging methods
single cell recordings
electroencephaloraphy (EEG)
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI)
single cell recording
inserting a microelectrode to record changes in the voltage or current, often in response to stimuli or during specific behaviors
single cell recording strength
direct observation of cells activity
good temporal resolution
single cell recording weakness
hole in the brain
limited number of cells at once
only animal research
electroencephalography
scalp electrodes measure the summed electrical activity of large populations of neurons
EEG strength
good temporal resolution
EEG weakness
bad spatial resolution
FMRI- functional magnetic resonance imagine
magnetic resonance imaging of relative amounts of oxygenated vs deoxygenated blood
FMRI strength
good spatial resolution
FMRI weakness
bad temporal resolution
Midbrain and hindbrain
The midbrain and hindbrain are for basic life functions: respiration, cardiac function, regulation of homeostasis, sleep/wake cycles
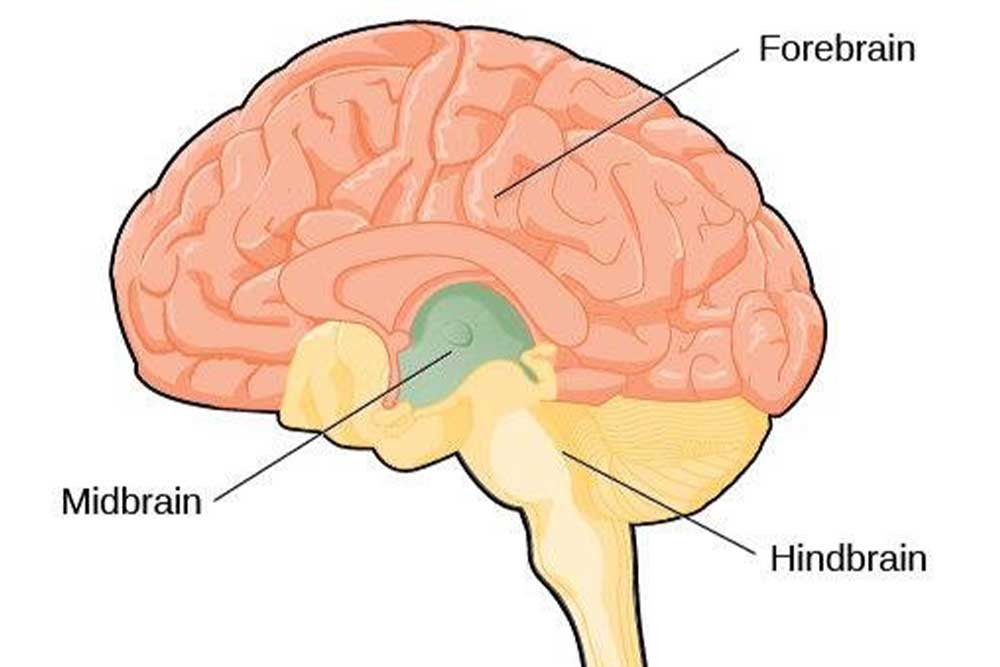
Pons
involved in respiration
Medulla
controls heart rate, respiration
Reticular formation:
involved in respiration, heart rate, wakefulness
Cerebellum
coordinates smooth movements, balance, posture
Thalamus-
one on the left and right side of the brain
Considered to be the relay station of the brain
Receives all of the incoming sensory information and relays to other parts of the cortex
One exception for senses: The smell sense (olfaction)
Hypothalamus
Sits right in front of the thalamus
Regulates vital functions: body temp, hunger, hormone release, biological rhythms
Amygdala
Processes emotional information
Fear, aggression
Hippocampus
Formation of declarative and spatial memory
Not permanent storage area
Memory will be distributed throughout brain
Hippocampus helps form new memories
The cortex:
Specialized for higher level processes
Humans can sustain life without the cortex
Grey matter: cell bodies and dendrites
White matter: axons
Gyri and Sulci:
Exaction of differ for each brain
Relative positioning consistent across brains
To cram(technical term) more brains have many more gyri and sulci than other primates
Cerebral lateralization
Relatively greater location of function
Cortex
Partially specialized functions in humans, less so in other animals
Left-more often controls language
Better at spatial processing
Cerebral Lateralization
LH is dominant for language
RH is dominant for non-linguistic functions (e.g. mental imagery, spatial relationships)
Brocas Aphasia
In 1861, paul broca evaluated leborgne
Known today as “Tan” or “Tan Tan”
Brocas Aphasia: language production: affects ability to speak and find words
Patients can understand speech of others
Aphasia
Brocas: Language production: affects ability to speak and find words: can usually understand the speech of others
Wernicke's: difficulty with comprehension: patients will speak long sentences but often do not make sense
Dominant gene:
expressed whenever present
Recessive gene:
only when matched with similar gene from both parents
Genotype
genetic constitution
phenotype
the set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment
monozygotic
one fertilized egg divides into 2 (same looking twins)
dizygotic
two seperately fertliized eggs develop simultaneously
heritability
estimate the extent to which variation in a given trait is due to genetic factors
McGurk Principles
top down interpretation of movements
based off of knowledge (knowing what mouth movements make certain sounds)
hear “da” instead of “ba”
S cone color
blue
M cone color
green
L cone color
red
color blindness malfunction
often caused by malfunction of M cones
how can people identify colors outside of the 3 cone colors?
your brain can identify color by comparing patterns of activity across multiple different cones by using a bit of each instead of one whole
Binocular cues
each eye sees a different image
the brain compares them
the greater the difference, the closer the object
convergence: when you look at something close, your eyes turn inward, the mount of tension helps estimate the difference
monocular views
relative size: if two objects are known to have the same size, the smaller retinal image looks farther away
interposition: monocular views
if one object blocks another, the blocked one is seen as farther
linear perspective: monocular cues
parallel lines appear to meet in the distance
texture gradient: monocular views
fine detail is visible up close but the texture gets blurier and more dense farther away
relative height: monocular views
objects higher in the visual field are seen as farther
light and shadow: monocular views
give us a sense of depth
motion parallax: monocular views
when you move the closer objects zip by faster than the farther ones
SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptae inhibitors)
block reuptake of serotonin into neuron
effect: more serotonin remians in the synapse
clinical use: antidepressants
MOAIs (monomine oxidase inhibitors)
block the enzyme that breaks down monoamines
increase dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin
depression treatment
Acytlcholinesterase (AChE)
prevent breakdown of acetylcholine
effect: ACh in the synapse, imporved cholinergic signaling
alzheimers disease (helps memory learning) and alzheimers, myasthenia gravis
Receptive field
the specific area where a sensory neuron responds to stimulation
In other words: the patch of the world” a neuron cares about
Vision
a photoreceptor in your retina only responds to light in one spot of your visual field
If the ligh hits outside that spot, the cell doesnt do anything
touch receptor
a touch receptor in your fingertip responds only when that tiny patch of skin is pressed
Touch somewhere else: the receptor doesn't fire
Area VI
Also called the striate cortex
In the occipital lobe
First place in the cortex that receives visual input from the retina
Neurons respond to simple features:
Edges, lines, orientation, motion, color, and spacial frequency
Builds foundation for high level processing
Ventral stream (“what” pathway)
Object identification and recognition
Shape, color, texture (“what am i looking at)
Dorsal stream (where and how pathway)
neuron
receive, integrate, and transmit information
operate through electrical impulses
communicate through chemical signals
dendrites
component of a neuron that branches to a dendritic tree dendritic tree, tapering with each branch
receives information that atatches to a dendritic tree
sensory neurons
transmit information form the bodys organs and tissues to the central nervous system
bodys internal sensors
action potential
momentary reversal of membrane potential that is the bases for electrical signaling between neurons
when the neurotransmitters bind to the receptors on the dendrites of a neuron, they depolarize it
influx of positive ions, creates electrical signal
potasium flows out of the cell
depolarize: make the membrane less polarized and it gets closer to zero
motor neurons
carry signals to central nervous system to muscle and glands
steps of action potential
resting state
depolarization
repolarization
hyperpolarization
resting potential
glial cells
support and protect neurons in the nervous system
provide insulation
they form in myelin sheaths
acetylcholine
memory motor control
acts on serotonin
monoamines
affect arousal, and motivation
prevents breakdowns
amino acids
general inhibatory
used in alzheimers to boost cholingeic signaling
resting potential
at rest, neurons are polarized
charged difference that sits from the inside of the cell compared to the outside of the cell
is waiting to be excited so it can do its activity
what happens resting potential
more prevalent inside the cell, inside is more negatively charged than the outside of the cell
-70 millivolts
transport protein that uses sodium (na) and potasium (K) pump, 3 sodium out of the cell and 2 negative potasium ions into the cell
bottom up processing
raw sensory data is analyzed
builds complex systems from what you see and hear
top down processing
starts with big picture
knowledge based
what do you expect?
gestalt principles of perception
proximity: grouping nearby objects
similarity: grouping alike objects
closure: seeing incomplete figures as complete
continuity: perceiving continuous paths
pragnanz: simples possible form