Neurons and Glia
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
two categories of cells in the nervous system
neurons and glia
neurons
nerve cells that recieve info, process it, and generate output
glia
(glial cells or neuroglia) suporting roles
2 ways that neurons communicate
electrical and chemical signals
when do neurons use electrical signals
to communicate within a neuron
when do neurons use chemical signals
to communicate between neurons
what encases neurons
cell membrane
cytoplasm
material inside the cell membrane; full of organelles
3 primary components of a neuron
cell body
dendrite
axon
other names for cell body
soma or perikaryon
cell body def
sit for synthesis of nearly all of the neuron’s enzymes, structural proteins, membrane components, organelles and some neurotransmitters
dendrites def
tapering extenstions of a cell body; specialized to receive information; increase surface area available for synaptic inputs
dendritic tree
totaly array of a neuron’s dendrites
in relation ot the cell body, how is information transmitted in the dendrites
distally → proximally
dendrite organelles
same as in cell body
dendritic spines
spiky protuberances that are preferred sites for synaptic inputs
axon
single output of a neuron; transmits actions potentials from cell body distally
what does the axon hillock give rise to
the initial segment
initial segment
just distal to axon hillock; most excitable part of neuron
what covers most axons
myelin
myelin def
glial membranes that increase the speed of APs
cytoskeleton
network of protein filaments contained within nearly all parts of neurons that give neurons their shape and assist in transport within the neuron
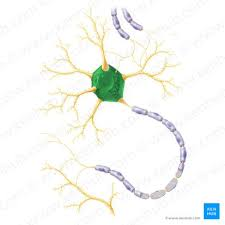
cell body
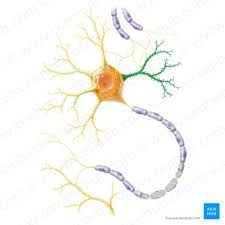
dendrite

neuron axon
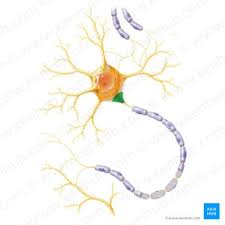
axon hillock
3 types of cytoskeleton
microtubules
neurofilaments
microfilaments
axonal tranport def
active process by which cells send macromolecules and organelles along an axon
fast anterograde transport
material travels from cell body to the presynaptic temrinal along microtubules
fast retrograde transport
material travels from synapse back to the cell body along microtubules
poliovirus
can gain access ot the CNS thru fast retrograde transport causing poliomyelitis (polio)
herpes
the virus gains access to soma through retrograde transport
chemotherapy
stops cell division and also axonal transport; can lead to neuropathies and cancer pain
alzheimer’s disease
marked by neurofibrillary tangles, problem with tau proteins on microtubules; progressive degenerative brain disease
Chronic traumatic encephalophathy CTE
progressive degenerative brian disease found in athletes with a history of repetivie brain trauma, including symptomatic concussion as well as asymptomatic subconcussive hits to the head; marked by same neurofibrillary tangles as in AD; symptoms include behavioral, mood, and cognitive impairments
3 ways in which neurons are classified by shape
multipolar
bipolar
pseudounipolar
multipolar neuron
have multiple dendrites and a single axon; most common in vertebrates; designed to receive and accomodate large amounts of input
ex of multipolar neuron
spinal motor cell
bipolar neuron
have 2 primary processes that extend from cell body
two types of bipolar neurons
olfactory epithelium and retina
pseudounipolar
subclass of bipolar neurons; appear to have a single projection from the cell body that divides into two axonal roots and no true dendrites
what type of neuron is exclusive to pseuounipolar
sensory
location of sensory and motor neurons
lie partly in CNS and partly in PNS
sensory neurons reception
receptive to sensory input either directly or thorugh cconnections with receptor cells
motor neurons
end on muscles, gland, or other neurons
interneurons
located in a small area in the CNS (connectors)
projection neurons
neurons in the CNS with long axons that project to another part of the CNS
what types of neurons make up 99%
interneurons and projection neurons
synaptic transmission def
mechanism by which neurons communicate with each other
synapse
special zone of contact in whcih one neuron communicates with another
presynaptic element
distal end of axon
postsynaptic element
part of another neuron
synaptic cleft
separation between two elements
synaptic vesicles
structures that contain neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic element into the cleft and bind to receptor sites in postsynaptic membrane, causing an electrical signal in postsynaptic neuron
axodendritic synapse
axon of one cell to dendrite of another
axosomatic synapse
axon to soma
axoaxonic synapse
axon to axon
dendrodendrtic
dendrite to dentrite
what are the main PNS glia
schwann cells
satellite cells
2nd type of PNS glial cell, but flattened schwann cells
schwann cells are made of
lipid substance
schwann cells function (3)
facilitating regrowth of axons after peripheral nerve injury- glial cells provide the sheath
regulating extracellular ionic environment
metabolic suppoort
schwann cells role in myelination
schwann cells wrap around segments of most individual axons
what interrupts myelin sheaths
nodes of ranvier
internode
area of myelin between nodes of ranvier
internode relationship to schwann cell
one schwann cell myelinates one internode
what surrounds cell bodies
satellite cells
principal function of oligodendrocytes
form myelin sheaths
principle function of astrocytes
provide mechanical and metabolic support; response to injry
microglia function
phagocytosis; response to injury
ependymal cells function
line ventricles and choroid plexus, secrete CSF
what is the CNS counterpart of a schwann cell
oligodendrocytes
primary difference for oligodendrocytes
can produce several internodes and can do so on several different axons
astrocytes
largest of the CNS glia, highly branched
two types of astrocytes
protoplasmic and fibrous
protoplasmic astrocytes location
in gray matter
fibrous astrocytes location
in white matter
3 main roles of astrocytes
structural support
end-feet of astrocyte branches provide “carpet” over capillaries and neurons (part of blood brain barrier)
can multiply in response to CNS injury
what is the smallest CNS glia
microglia
what activates microglia and what happens
injury activates microglia to migrate and clean up debris
ependymal cells location
line the walls of ventricles and choroid plexus
ependymal cells function
produce and secrete CSF
gliomas
tumors of glial cell origin
what is usually the origin of a tumor in the PNS
schwann cells
schwannoma characteristics
usually encapsulated with no nerve fiber involvement; easily removed
neurofibroma
encapsulated but infiltrating nerves; difficult to remove
what is the origin of many brain tumors
astrocytic origin
astrocytoma
tumor of astrocytic origin
glioblastoma multiforme
grade IV astrocytoma
conditions that result in damge to the myelin sheath
demyelinating diseases
result of demyelinating disease
myelin sheath is damaged, nerve impulses slow or even stop, causing neurological problems
causes of demyelinating diseases
autoimmune disorders
metabolic abnormalities
viruses
trauma
toxic chemicals
demyelinating disease of the CNS
Multiple Sclerosis
what happens in MS
body produces antibodies that attack oligodendrocytes
etiology of MS
genetic predisposition with an environmental trigger
demyelination in MS
destruction of oligodendrocytes produces patches of demyelination
what replaces areas of demyelination in MS
astrocytic plaques which cuases slowed or blocked action potentials
prognosis of MS
variable, some may completely resolve, some linger
treatment of MS
immunosuppressants
rehabilitiation
demyelinating disease of the PNS
guillian-barre syndrome