Population growth curves / predation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What 4 factors affect the size of a population
births
Deaths
Emigration
Immigration
What is emigration
Individuals leaving a population
What is immigration
Individuals joining a population
what does a logistic growth graph look like
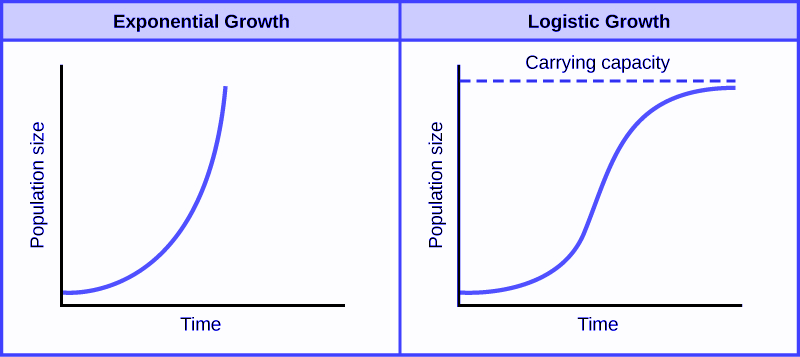
what are the 4 phases of a population growth curve
lag phase
log phase
stationary phase
death phase
what happens in the lag phase of population growth
a species colonises an area, and there is no increase in population size
what happens in the log phase of population growth
there is no limiting factors and more resources available, so there is exponential growth
max growth rate occurs here
what happens in the stationary phase of population growth
the carrying capacity is reached, so no more individuals can be held by the resources
a plateau is reached
rate of cell division=rate of cell death
what happens in the death phase of population growth
a sudden change in environment (eg drought or food storage) causes an exponential decrease in population
when are logarithmic scales useful
when investigating bacteria
when managing experimental data relating to large scales
what is interspecific competition
competition between different species
what is intraspecific competition between species
competition within same species
what is the competitive exclusion principle
if conditions remain the same, this will lead to the complete removal of one species
the species that uses the resources most effectively will ultimately eliminate the other
the 2 species can’t occupy the same niche indefinitely
what does an increased food supply lead to
increased birth rate or bigger individuals
explain the cyclical nature of a predator/prey relationship
predators eat prey so prey numbers reduced
fewer prey= greater predator competition
predator population reduces
prey population increases
more prey available so predator population increases, repeats