LAB 8 SPECIAL SENSES
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Lateral rectus muscle
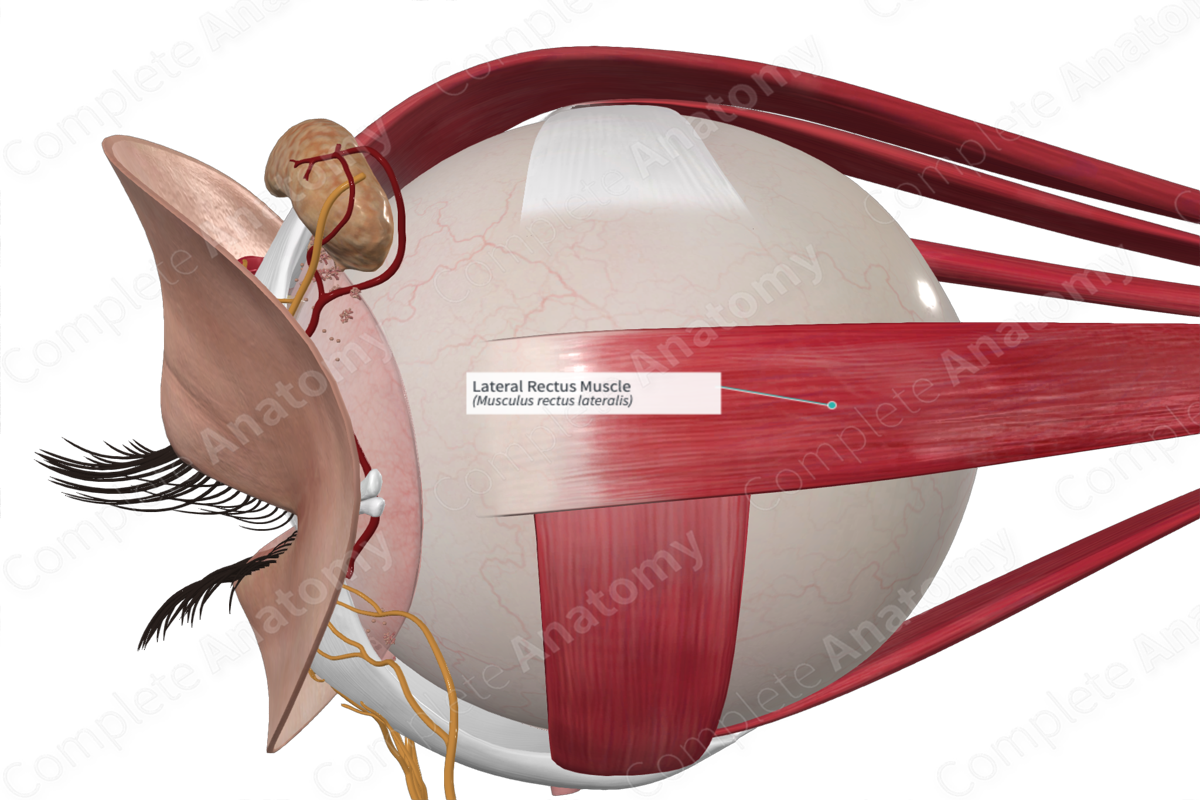
Moves eye laterally
Medial rectus muscle
Moves eye medially

Moves eye medially
superior rectus muscle

elevates eye and turns it medially
inferior rectus muscle
depresses eye and turns it medially

Inferior oblique muscle

elevates eye and turns it laterally
superior oblique muscle

depresses eye and turns it laterally
cornea
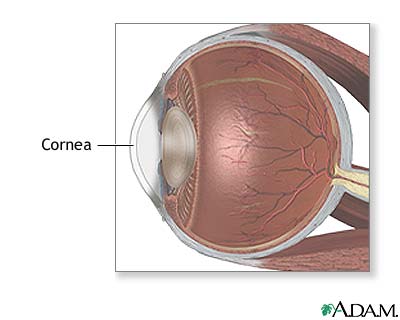
Transparent, allows light to enter. (Most outerlayer of the eye)
iris
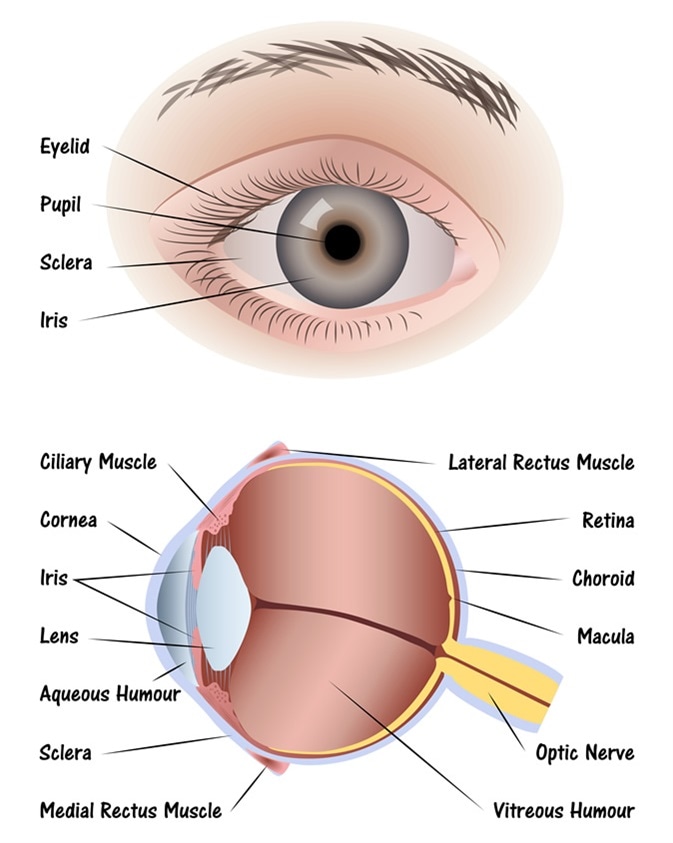
Colored part of the eye; controls size of the pupil and shows eye color
pupil
The black, center part of the eye; controls the amount of light entering the eye.
lens

RIght behind the iris and pupil; focuses light onto the retina.
ciliary body
Adjust shape of lens
suspensory ligament

Holds lens in place.
aqueous humor
Watery liquid that nourishes lens; its between the cornea and lens
vitreous humor
Gel-like substance that fills the space between the lens and retina, maintaining the eye's shape. It also helps to keep the retina in place.
Retina
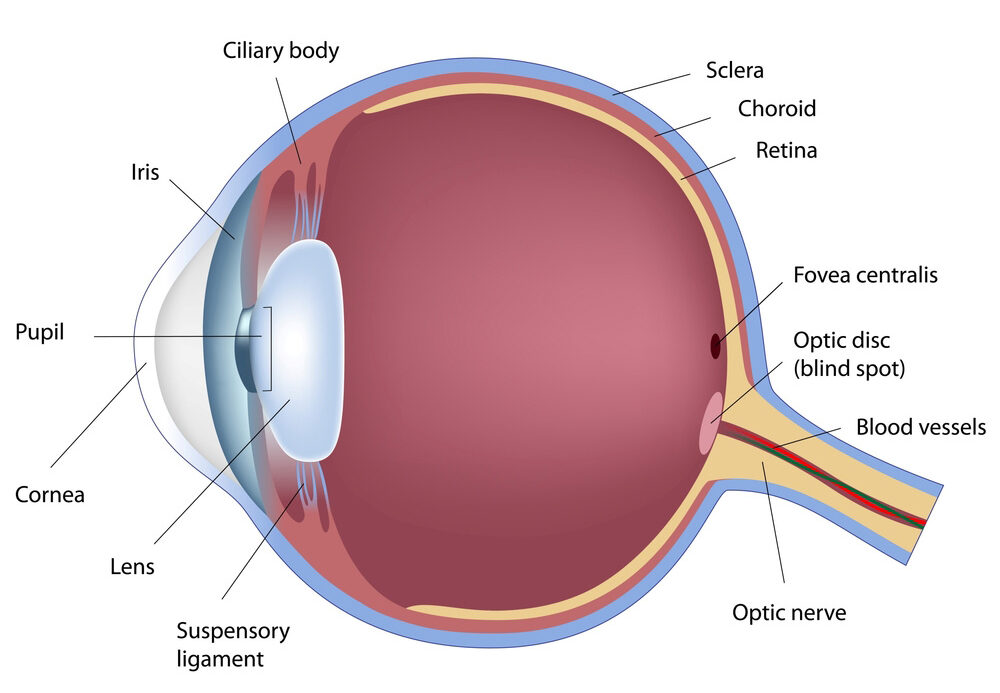
contains neurons that respond to light. (Sensory layer)
choroid

contains blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the retina. (Vascular layer)
sclera
the white outer layer of the eyeball that maintains its shape and protects the inner components. (Fibrous layer)

optic nerve

bundle of neurons that carry visual signals
optic disc

The blind spot where retina lacks photoreceptors
if the shape of the eye is abnormal, producing blurred vision, what condition is present?
astigmatism.
Auricle (Pinna)
The outer part of the ear that collects sound waves and directs them into the ear canal.
External acoustic meatus (External auditory canal)
The passage leading from the outer ear to the eardrum, allowing sound waves to travel to the inner ear.
Tympanic membrane (Eardrum)
A thin membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear and vibrates in response to sound waves. (Middle ear)

Auditory ossicles
The three small bones (Maleus, incus, and stapes) located in the middle ear that amplify sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear.
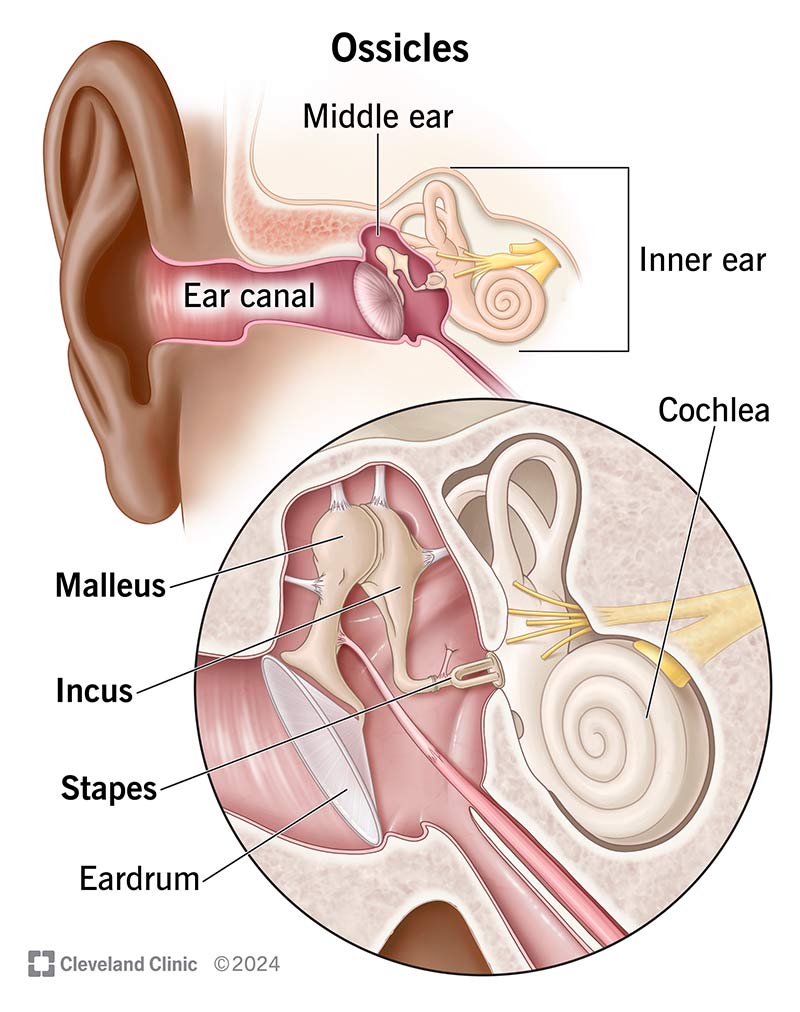
Pharyngotympanic tube (Eustachian tube)
helping to equalize pressure in the ear. (Inner ear)
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/eustachian-tube/CTiHbb7pCJuzlJn7EITS4g_X2GDF4lSYOXRdujSrjKMQ_Tuba_auditiva_01.png)
Vestibular nerve
Relays info. about motion and position. (Inner ear)
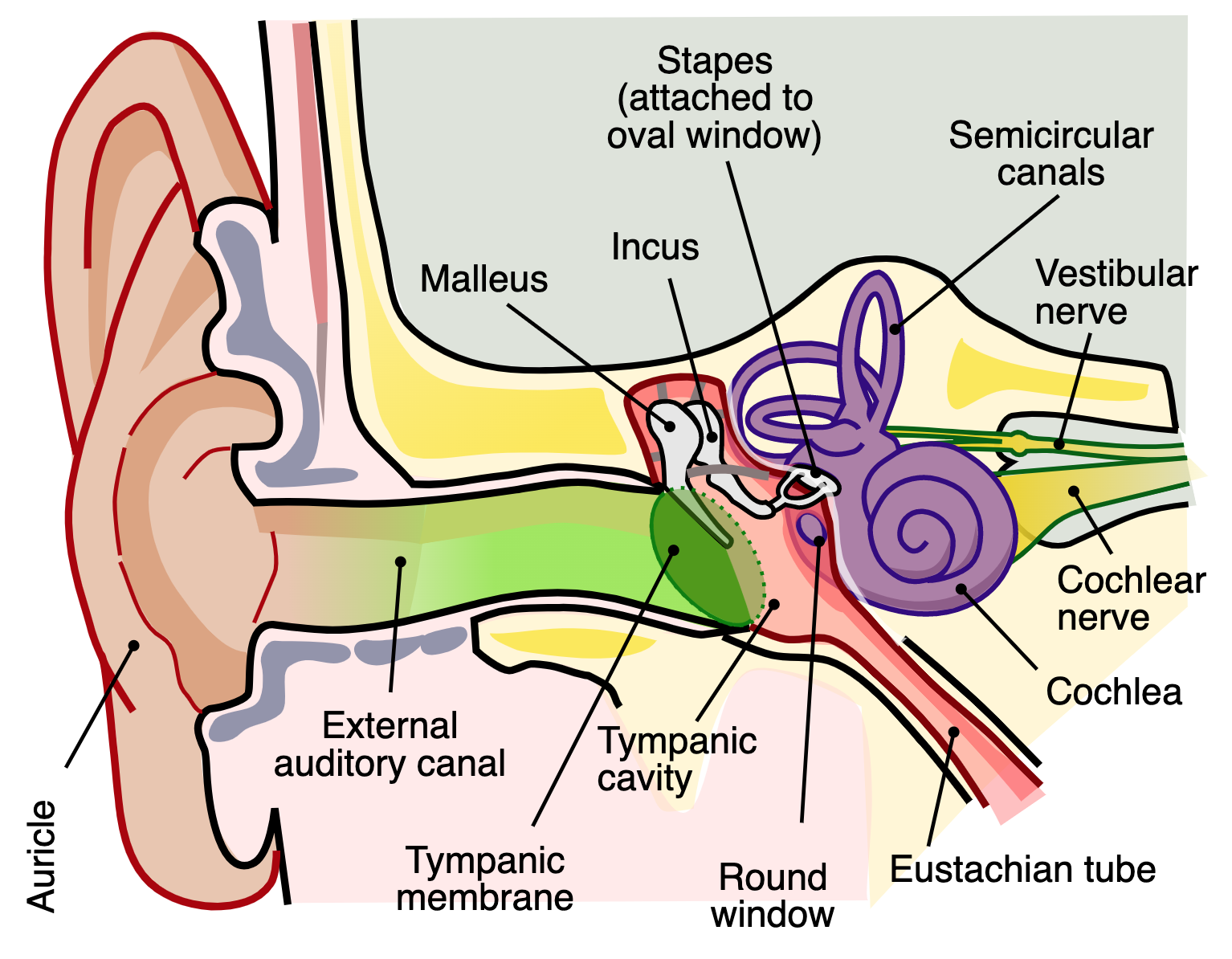
Cochlear nerve
relays info. on auditory signals (Inner ear)

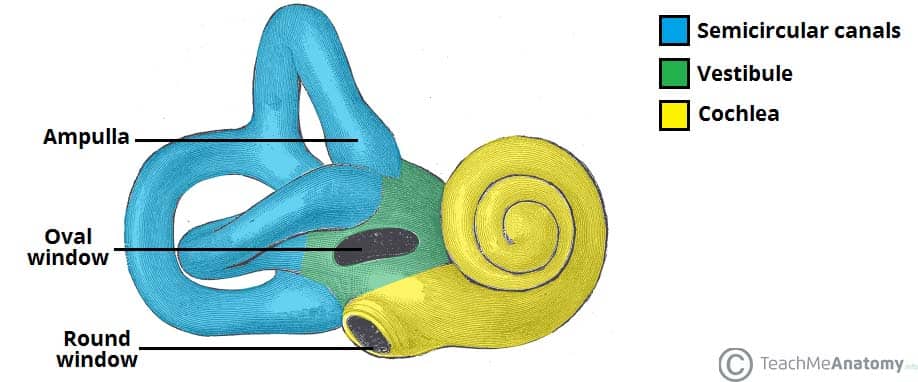
Cochlea
A spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear responsible for converting sound vibrations into neural signals for hearing.

semicircular canals
Sense equilibrium (Inner ear) by detecting rotational movements of the head and maintaining balance.

Vestibule
sense equilibrium (Inner ear) and linear movement.
understand and interpret the weber test. distuinguish between conduction and sensorineural deafness
Weber Test:
A vibrating tuning fork is placed on the middle of the forehead.
Normal: Sound is heard equally in both ears.
Conduction deafness: Sound is louder in the affected ear.
Sensorineural deafness: Sound is louder in the unaffected (good) ear.
understand and interpret the rinne hearing tests. distuinguish between conduction and sensorineural deafness
Rinne Test:
A vibrating tuning fork is placed on the mastoid bone (behind the ear) until the sound fades, then moved next to the ear canal.
Normal: Air conduction (hearing next to the ear) is better than bone conduction (hearing on the bone).
Conduction deafness: Bone conduction is better than air conduction.
Sensorineural deafness: Both air and bone conduction are reduced, but air conduction is still better than bone.
distuinguish between conduction and sensorineural deafness
Conduction Deafness:
Caused by a problem conducting sound waves (e.g., earwax blockage, ear infection, damage to ossicles).
Sensorineural Deafness:
Caused by damage to inner ear structures or auditory nerve (e.g., aging, loud noise exposure, nerve damage).