Prokaryotes and Microbial Diversity: Bacteria, Archaea, and Pathogens
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
Prokaryotes
The oldest and most abundant form of life on Earth, existing for over 3.8 billion years.
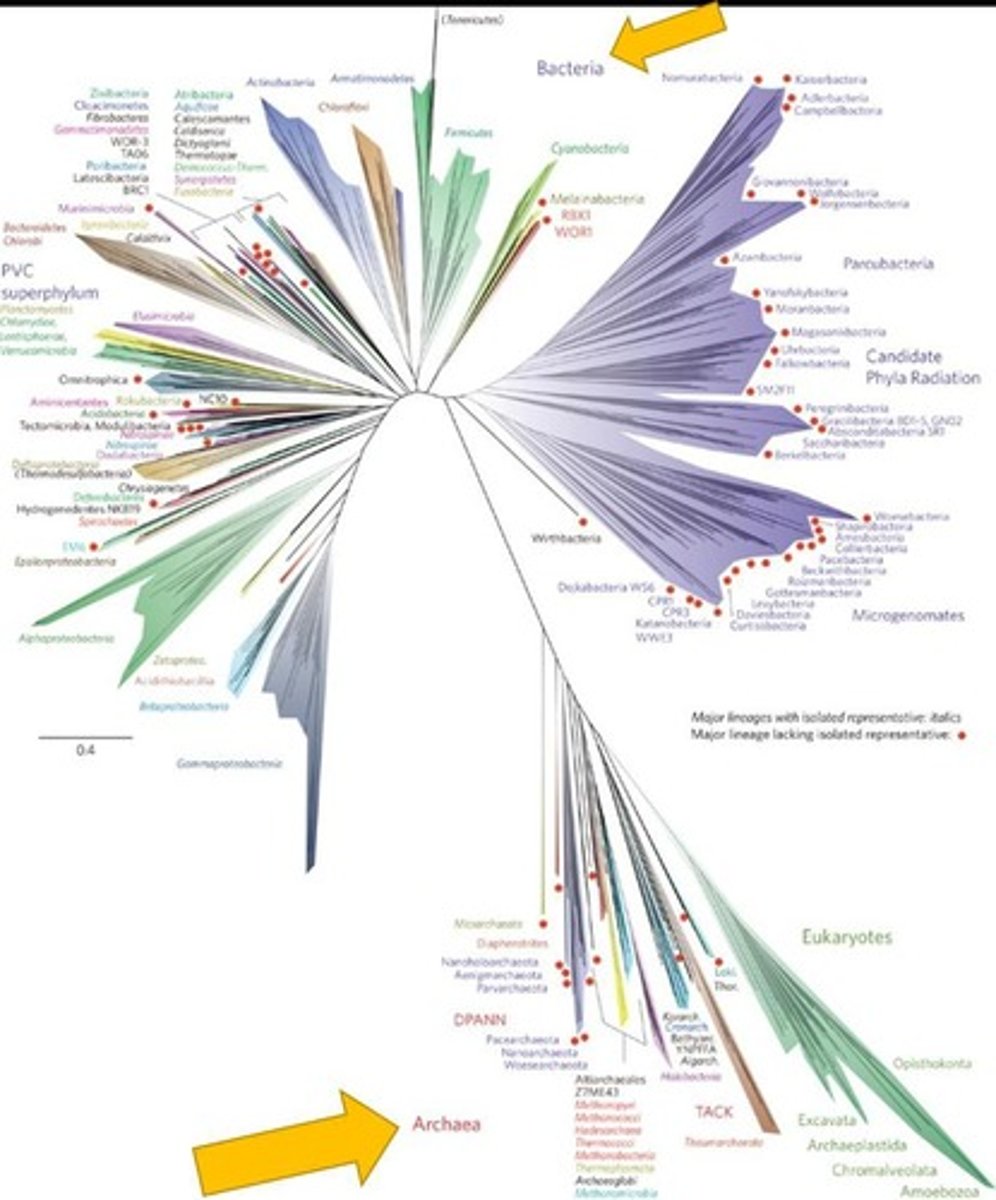
Bacteria
One of the two domains of prokaryotes.
Archaea
The second domain of prokaryotes.
Nucleus
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus; their genetic material is located in a single, circular chromosome within a nucleoid region.
Membrane-bound organelles
Prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles; processes like energy production occur in the cytoplasmic membrane.
Binary fission
The method of cell division in prokaryotes that produces genetically identical offspring.

Size of Prokaryotes
Most prokaryotes measure 0.5-5 micrometers.
Diverse metabolism
Prokaryotes are capable of photosynthesis, respiration, or fermentation under varied conditions.
Classification
Based on phenotypic and genotypic traits, with modern classification relying heavily on rRNA sequences and molecular data.
Species
A group of organisms that share high genetic similarity and common characteristics, e.g., Escherichia coli.
Subspecies
Minor genetic or physiological variation, e.g., Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii.

Strain
Specific isolate or variant of a species, e.g., E. coli K-12 vs E. coli O157:H7.
Serotype
Differ by surface antigens, e.g., Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.
Coccus
Spherical prokaryotes that may appear alone or in clusters.
Bacillus
Rod-shaped prokaryotes that are cylindrical and often longer than wide.
Vibrio
Curved rod-shaped prokaryotes that are slightly curved or comma-shaped.

Spirillum
Rigid spiral-shaped prokaryotes with external flagella.
Spirochete
Flexible spiral-shaped prokaryotes with internal axial filaments.
Pleomorphic
Prokaryotes with variable shape depending on the environment.
Diplococci
Cocci that appear in pairs.
Streptococci
Cocci that appear in chain-like formations.
Tetrads
Cocci that appear in groups of four.
Sarcinae
Cocci that appear in cubelike groups of eight.
Staphylococci
Cocci that appear in grapelike clusters.
Bacilli
Rod-shaped bacteria that divide across their short axis.
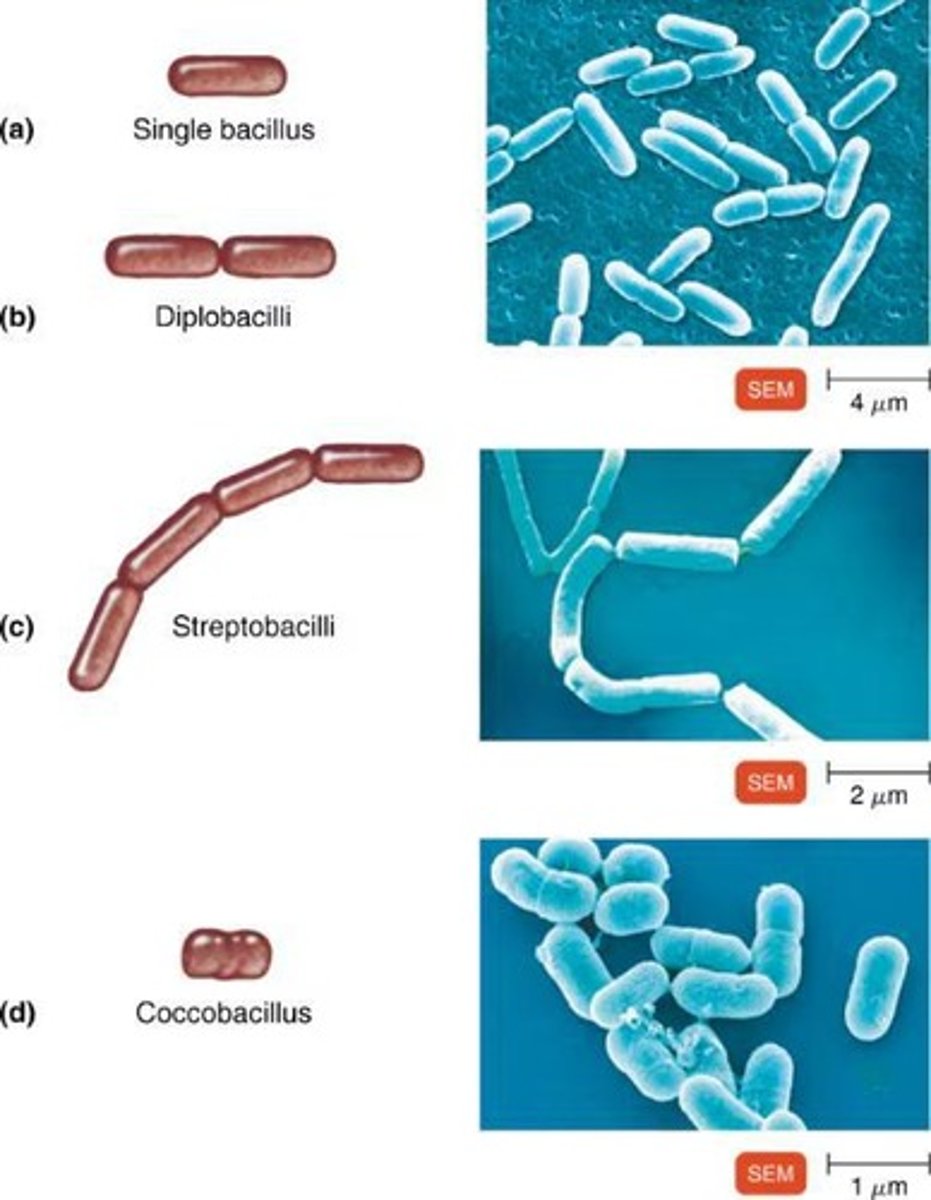
Single bacillus
A single rod-shaped bacterium.
Diplobacillus
Bacilli that occur in pairs after division.
Streptobacilli
Bacilli that form chain-like arrangements.
Coccobacillus
Bacilli that are oval and resemble cocci.
Palisades
Cells of a chain that remain partially attached by a small hinge region at the ends.
Spiral bacteria
Bacteria that have one or more twists.
Spirillum/Spirilla
Bacteria with a slightly curled or spiral-shaped body.
Monomorphic
Most bacteria that maintain a single shape.
Pleomorphism
Variations in cell wall structure caused by slight genetic or nutritional differences.
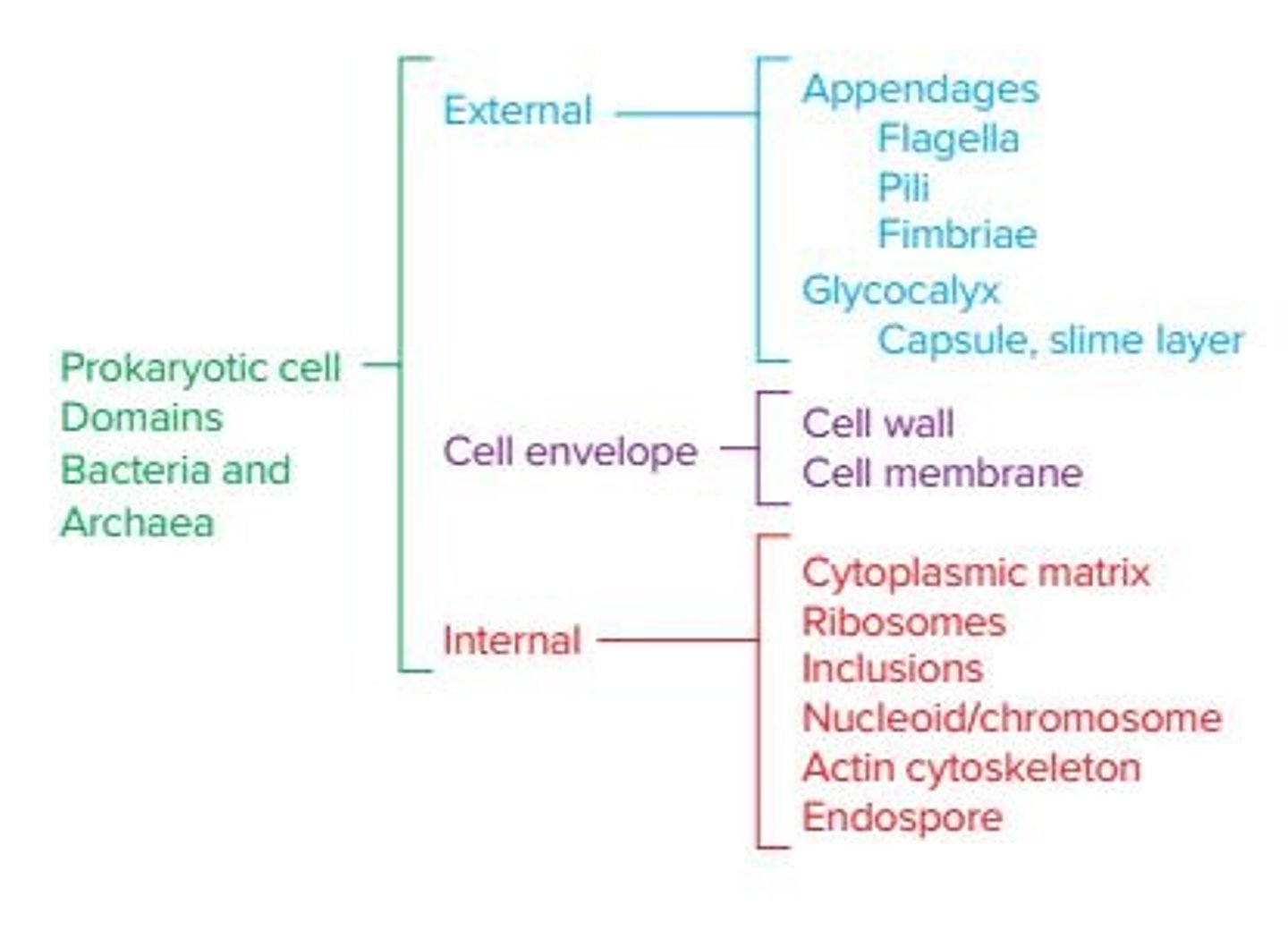
Prokaryotic Cell
Cells that lack a nucleus and histones, have a unique cell wall makeup, and lack membrane-bound organelles.
Cell Envelope
Includes all layers surrounding the cytoplasm: cytoplasmic membrane, cell wall, and outer membrane (in Gram-negative bacteria).
Cytoplasmic Membrane
A selectively permeable barrier that controls what enters and leaves the cell, made of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.

Gram-Positive Bacteria
Bacteria with a thick peptidoglycan layer (20-80 nm) and no outer membrane.
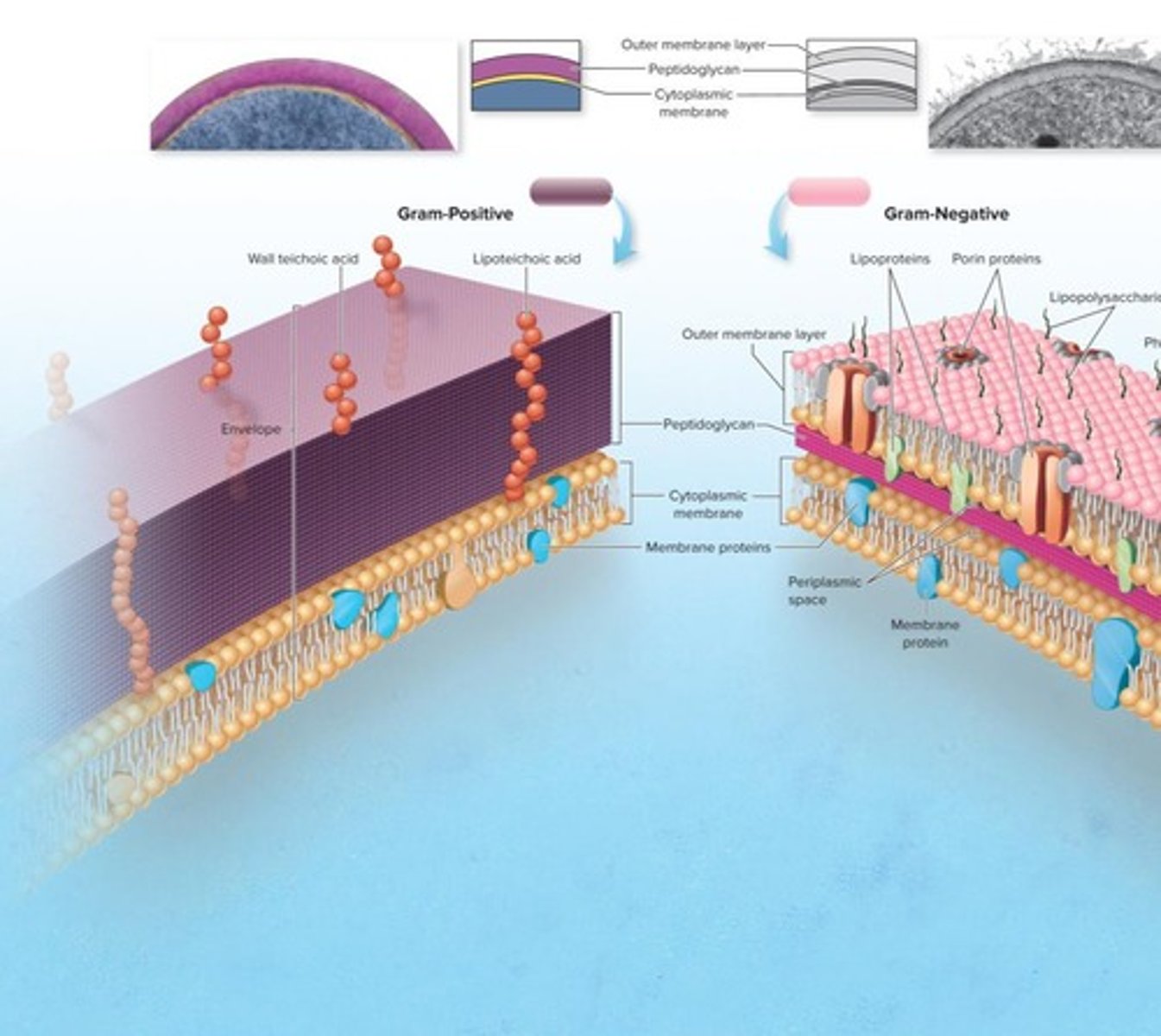
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Bacteria with a thin peptidoglycan layer (2-7 nm) and an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharide (LPS).

Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
An endotoxin found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria that acts as a powerful antigen and can trigger strong immune responses.
Acid-Fast Bacteria
Bacteria with atypical cell walls that have a peptidoglycan layer surrounded by a thick coat of waxy mycolic acids, making them extremely resistant to drying, disinfectants, and many antibiotics.

Acid-fast stain
A staining technique used for bacteria with waxy layers that prevent standard Gram staining.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
A bacterium that causes tuberculosis.
Mycoplasma
A type of prokaryote that lacks a cell wall, making it resistant to antibiotics like penicillin.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
A bacterium that causes atypical or 'walking' pneumonia.
L-forms
Prokaryotes that have a temporary or permanent loss of the cell wall.
Pseudomurein
A wall material found in Archaea that is similar but chemically distinct from peptidoglycan.
S-layers
Crystalline sheets of protein or glycoprotein that form the outermost cell covering in many prokaryotes.
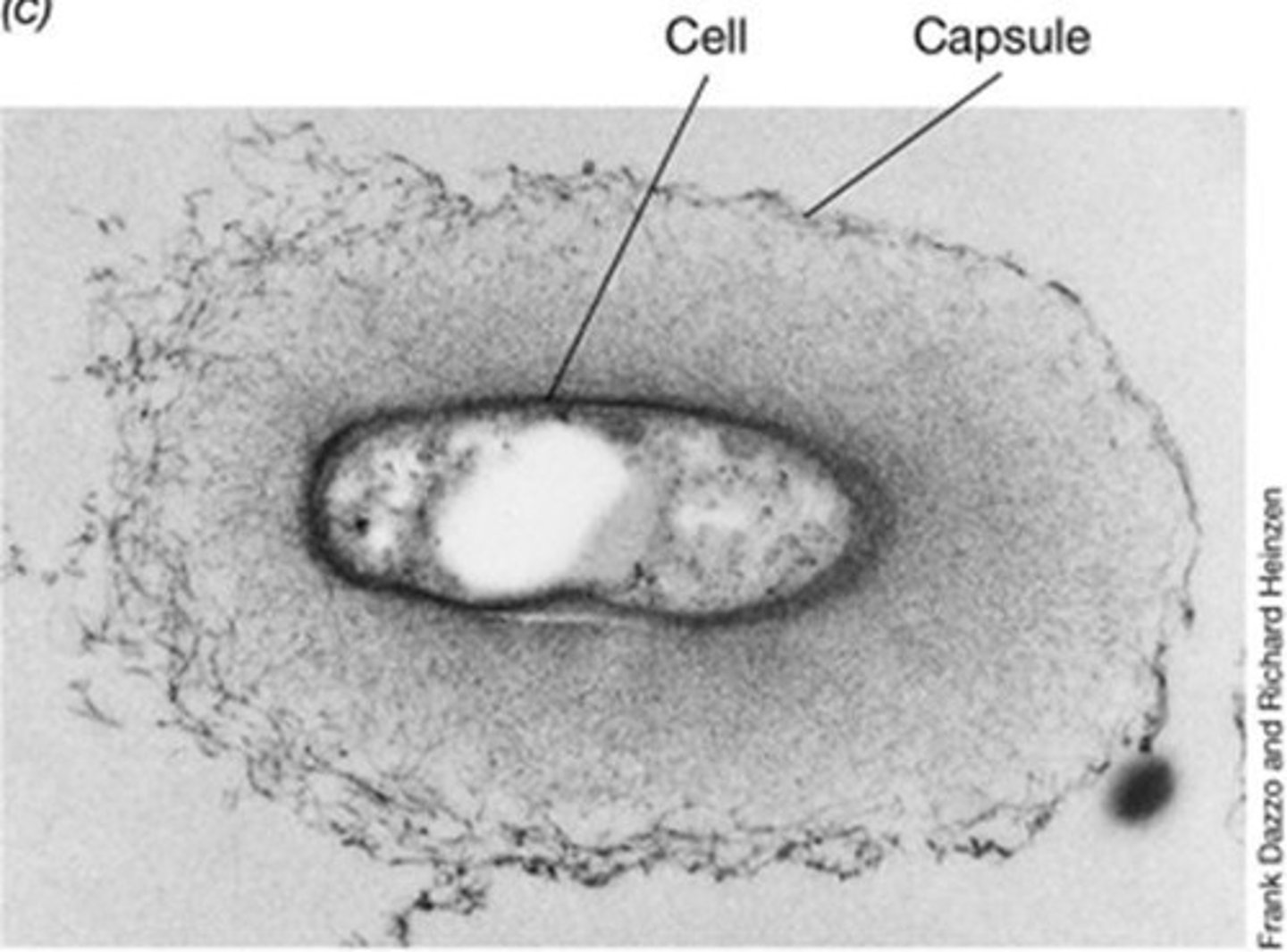
Glycocalyx
A sticky layer of polysaccharide and protein outside the cell wall, existing in capsule and slime layer forms.
Capsule
A well-organized and firmly attached form of glycocalyx.
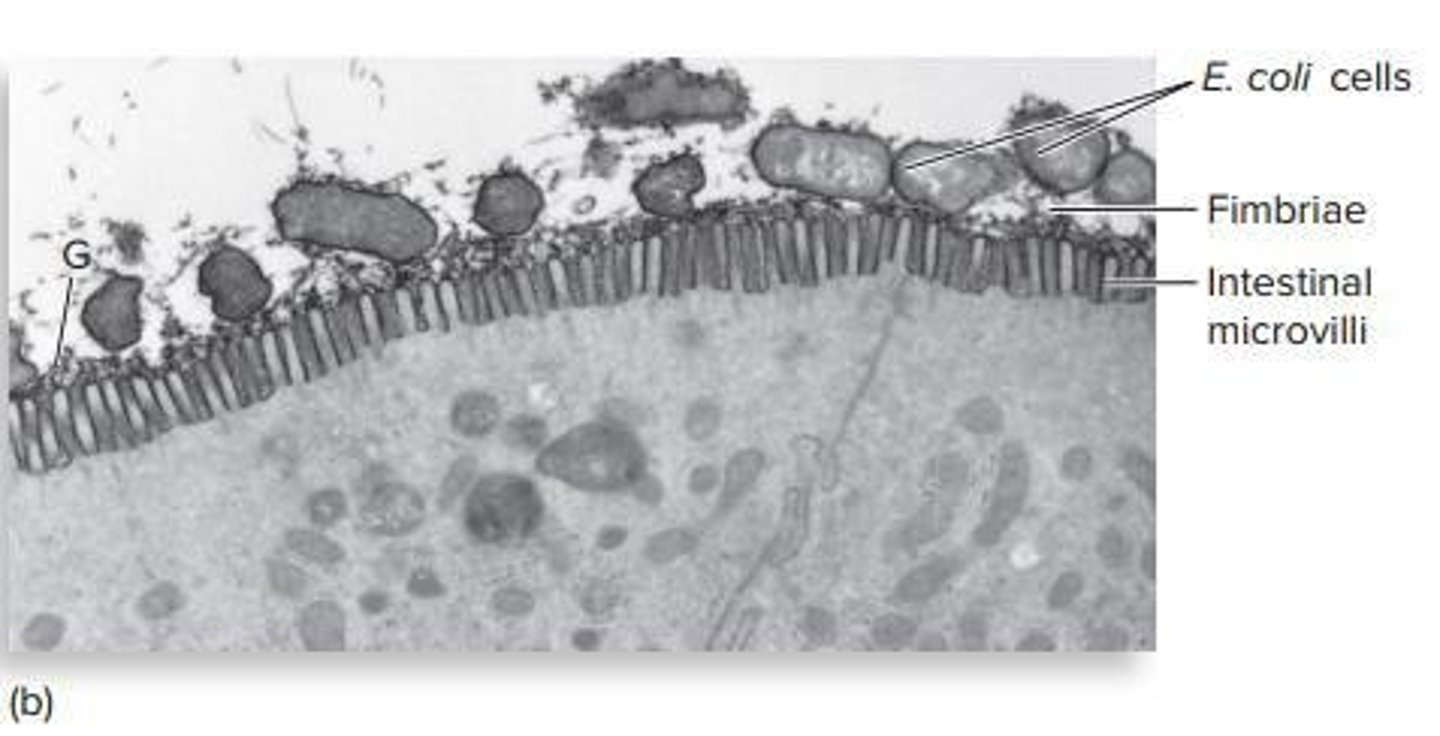
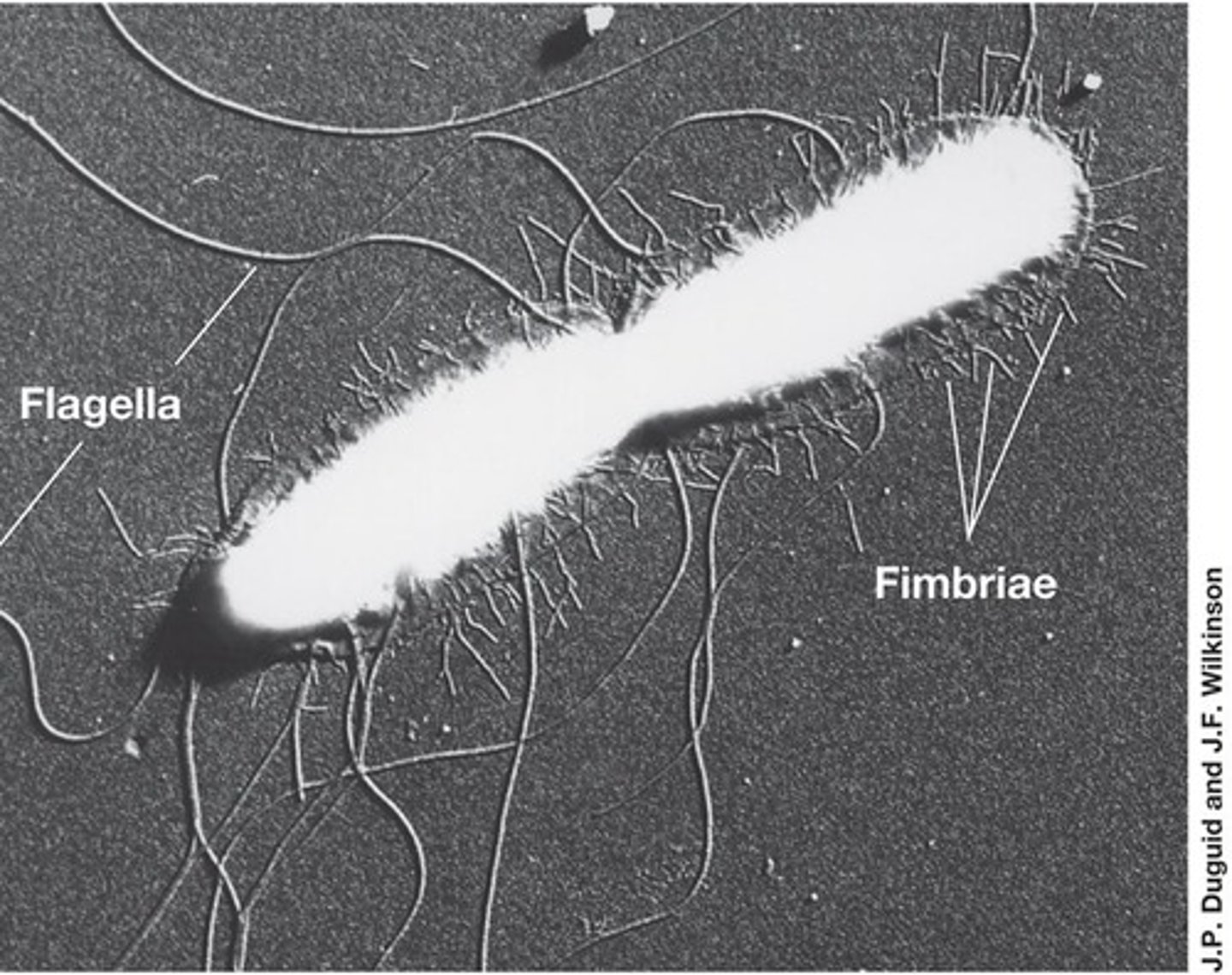
Fimbriae
Hair-like structures that help bacteria adhere to surfaces.
Pili
Structures that facilitate genetic exchange between bacteria.
Flagella
Long, whip-like structures that provide motility to bacteria.
Axial filaments
Specialized structures that enable movement or communication in certain prokaryotes.
Alcohol-based compounds
Substances that can dissolve lipids in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, damaging the cell.
External structures
Extensions or coatings that project from or surround the cell wall in many bacteria and archaea.
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that can be part of the cell wall materials in Archaea.
Glycoproteins
Proteins that can be part of the wall materials in Archaea.
S-layers in Archaea
Often the only wall structure in Archaea, providing rigidity and osmotic protection in extreme environments.
Slime Layer
A loose and irregular form of glycocalyx.
Functions of Glycocalyx
Prevents desiccation, shields cells from phagocytosis, promotes adhesion, and starts biofilm formation.
Conjugation Pili
Pili that connect cells for DNA transfer.
Flagellum
A structure with three distinct parts: filament, hook (sheath), and basal body.
Polar Arrangement of Flagella
Flagella attached at one or both ends of the cell.
Monotrichous
A flagellar arrangement with a single flagellum.
Lophotrichous
A flagellar arrangement with small bunches or tufts of flagella emerging from the same site.
Amphitrichous
A flagellar arrangement with flagella at both poles of the cell.
Peritrichous Arrangement
Flagella are dispersed randomly over the surface of the cell.
Movement (Motility)
Powered by rotating flagella acting like tiny propellers.
Run
Flagella rotate in one direction, causing the cell to move straight.
Tumble
Rotation reverses, causing the cell to reorient.
Chemotaxis
Directed movement in response to chemical signals.
Attractants
Nutrients that cause longer runs and fewer tumbles.
Repellents
Toxins that increase tumbles and random reorientation.
Periplasmic Flagella
Internal flagellum enclosed in the space between the cell wall and the cytoplasmic membrane.
Spirochetes
Corkscrew-shaped bacteria with a wriggly mode of locomotion caused by periplasmic flagella.
Sex Pilus
Forms a bridge between bacterial cells for DNA transfer during conjugation.
Type IV Pili
Pili that extend and retract for twitching or gliding movement and aid in adhesion and biofilm formation.
Nanotubes
Structures that connect neighboring cells to exchange nutrients, waste products, or signals.
Archaella
Archaeal motility structures that rotate for movement, similar in function to bacterial flagella but made of different proteins.
Hami
Grappling-hook-like appendages in some archaea used for strong surface attachment.
Internal Organization of Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles but maintain high internal organization.
Cytoplasm
The gel-like matrix that fills the cell interior, composed mostly of water, along with enzymes, ions, ribosomes, and macromolecules.
Nucleoid
Region containing the bacterial chromosome, a single, circular molecule of DNA, not surrounded by a membrane.
Plasmids
Small, circular DNA molecules separate from the main chromosome that carry nonessential genes providing advantages such as antibiotic resistance or virulence traits.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis composed of rRNA and protein subunits (30S + 50S = 70S ribosome), smaller than eukaryotic (80S) versions.
Inclusions
Specialized internal structures for storage and adaptation that allow cells to conserve energy and resources for changing conditions.
Glycogen or Starch Granules
Types of inclusions that serve as carbon and energy storage.
Polyphosphate Granules
Inclusions that store phosphate for ATP and nucleic acids.
Sulfur Granules
Energy source for sulfur-oxidizing bacteria.
Lipid Inclusions
Long-term energy reserves in prokaryotic cells.
Gas Vesicles
Structures that confer buoyancy and allow cells to position themselves in regions of the water column that best suit their metabolisms.
Magnetosomes
Inclusions that contain magnetite particles, allowing cells to align with Earth's magnetic field.
Endospores
Dormant, highly resistant cell forms produced by some Gram-positive bacteria, serving as survival structures.
Germination
The process of an endospore converting back to a vegetative cell rapidly.
Cytoskeleton
A structure in prokaryotic cells that maintains cell shape, aids cell division, and organizes internal contents.
Methanogens
Major group of Archaea that produce methane.
Halophiles
Major group of Archaea that thrive in high salt concentrations.
Thermophiles
Major group of Archaea that thrive in extreme and moderate temperatures.
Microbial Dark Matter
The portion of archaeal diversity that remains uncultured.