[2.1.1b.] Economics - Inflation
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is inflation?
A sustained rise in the average price level over time across the economy.
What is disinflation?
A fall in the rate of inflation (where inflation is still positive)
What is deflation?
When inflation is negative and prices are falling.
How is inflation measured and with what metric?
Metric: CPI (consumer price index)
A basket of goods and services is formed based on typical purchases of consumers in the economy.
Different items are given different weightings based on their relative importance in terms of how much a price change impacts consumers.
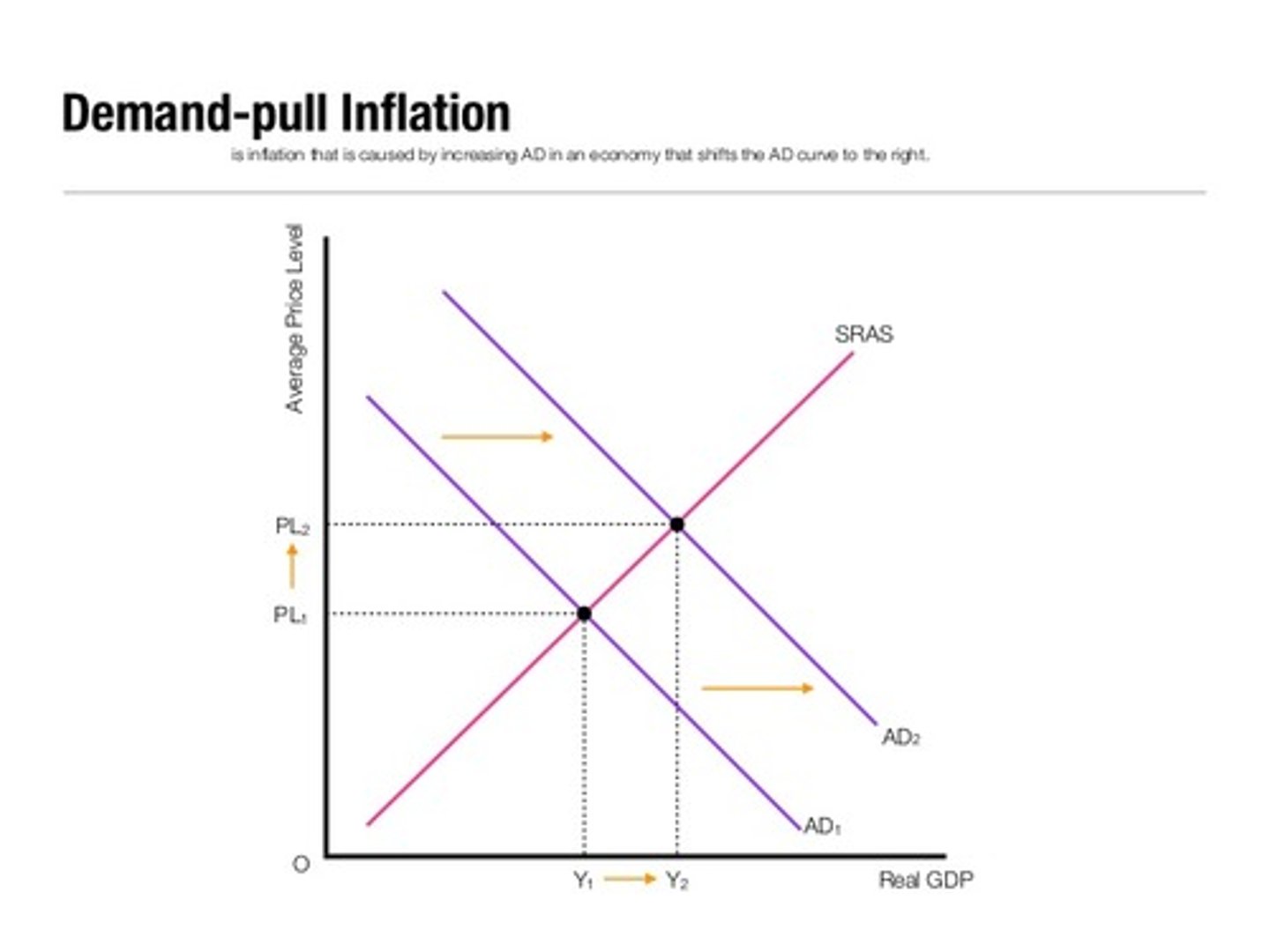
What is demand-pull inflation?
When excess demand chases too few goods it puts inflationary pressure on the price. The price must go up to make a new equilibrium.
*on the graph, SRAS is supply, AD is demand, GDP is output
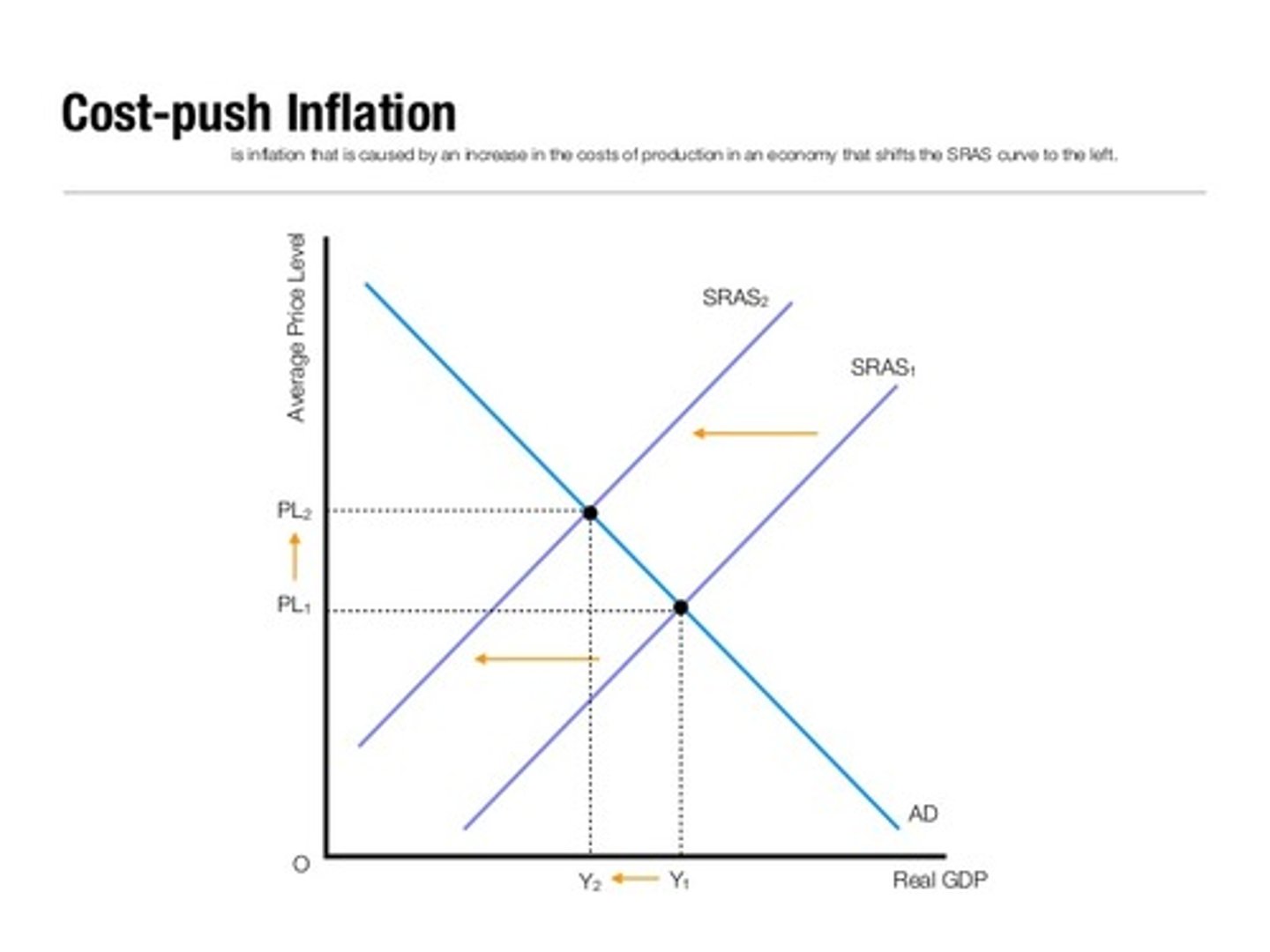
What is cost-push inflation?
When a rise in costs of production for businesses leads to a higher price that consumers have to pay.
*on the graph, SRAS is supply, AD is demand, GDP is output
How does a change in interest rates affect inflation?
An increase in interest rates encourages people to save more of their money and spend less, slowing economic growth and inflation.
A decrease in interest rates encourages people to spend more of their money, speeding up economic growth and putting inflationary pressure on the economy.
How does inflation impact purchasing power/prices?
As a result of price rising inflation reduces the purchasing power of money.
How does inflation affect wages?
When prices rise workers need an increase in wages to compensate for their loss in purchasing power.
How does inflation affect exports?
It's harder for others to buy your products since your prices are higher.
How does inflation affect unemployment?
When inflation rises, demand is usually rising - and so unemployment reduces as firms are more keen to increase outputs and thus hire more labour.
What are menu costs of inflation?
The costs for producers associated with having to constantly adjust price lists or labels if there's a high rate of inflation.
What are shoe leather costs of inflation?
The cost of the consumer to try to find the cheapest product.
How does inflation affect uncertainty and investment?
If inflation is high and varying firms do not know what prices will be in 3 or 6 months time and thus anticipation is impossible.
Decisions still have to be made now but they could impact businesses very badly which makes investment harder.
How does inflation affect business/consumer confidence?
Uncertainty caused by inflation could have an effect on the confidence of consumers and businesses, meaning consumers could start to save more and businesses could reduce spending.
How does deflation affect consumer spending?
When consumers know that prices will go down, they will wait for prices to go down further before making a purchase, causing spending to fall.
How does deflation affect wages?
Given lower consumer spending, consumers will make less wages given that business make less (costs rise relative to revenue, business spend less on wages)
How does deflation thus create a spiral of negative effects for the economy?
Since wages go down, they are less incentivized to spend their money, creating a spiral where businesses make less and consumers spend less, slowing the circular flow of income.