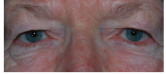
eyelids 2 (ptosis)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
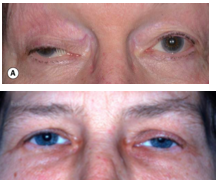
neurogenic ptosis
innervational defect such as third nerve palsy and Horner syndrome
>Horner’s mild ptosis (about 3mm down)
>3rd nerve palsy: down and out & ptosis
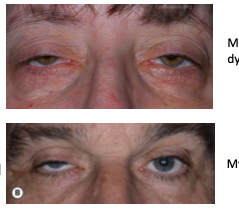
myogenic
caused my myopathy of levator muscle
usually myasthenia gravis
a common sign of MG is tiredness throughout the eye
young females
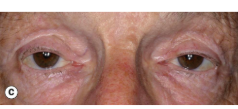
aponeurotic or involutional
levator aponeurosis
dropping down/sagging
elderly
mechanical
tumors, gravitational effect of mass or scarring
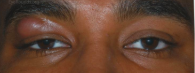
pseudoptosis
dermatochalasis simulates ptosis
symmetrical
measure MRD if pt really has ptosis
palpebral fissure heights
males vs females
males 7-10mm
females 8-12mm
avg 10mm
ptsosis crease measurement
look for superior crease
aponeurotic: elevation in distance
congenital: NO crease
associated signs (pupils)
· Horner’s syndrome (miosis)
· 3rd nerve palsy
causes of pseudoptosis
-lack of support
-contralateral lid retraction
-ipsilateral hypotropia
-brow ptosis (excessive skin on brow) or CN7 palsy
>recognize by doing Hirchburg test
-dermatochalasis
simple congenital ptosis
failure of neuronal migration
signs: absent lid crease
due to poor levator function
congenital vs acquired ptosis
CONGENITAL
downgaze ptotic lid is higher than normal due to poor relaxation of levator muscle
>pts may elevate chin to see better
ACQUIRED
downgaze ptotic lid is level with or lower due to superior rectus weakness
tx: surgical tx
(levator resection)
marcus gunn
5% of all cases
unilateral
CN 7 misdirected to levator muscle
easy and fast to diagnose
horner’s syndrome cocaine 2-4% test
eye should dilate
if positive, pupil will not dilate
3rd nerve misdirection syndrome
3rd nerve misdirection syndromes
may be congenital
more frequently follow acquired 3rd nerve palsy
>bizarre movements of upper lid
eye in down and out position
involutional ptosis
age related
caused by dehiscence, disinsertion or stretching or levator aponeurosis
>fatigue of Muller’s muscle
worsens towards end of day
eyelid crutches
used if pt doesn’t want sx
uncommon but can be used
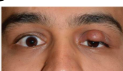
mechanical ptosis
result of impaired mobility of the upper lid
ectropion
Outward turning of the eyelid margin
Symptoms:
• Tearing
• FBS
• Epiphora
• Redness
• Asymptomatic
signs:
-positive snap-back test
-SPK
-dry eye
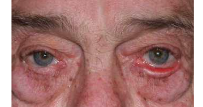
involutional ectropion
Eyelid horizontal laxity and gravity act to evert lid or disinsertion of lower lid retractors
age related
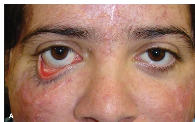
cicatricial ectropion
caused by scarring or contracture of the skin and underlying tissues, which pulls the eyelid away from the globe
Causes:
Trauma
Burns
Dermatitis
Ichthyosis
Excessive skin excision (or laser) in blepharoplasty
Glaucoma drops (dorzolamide (Trusopt), brimonidine (alphagan)) due to allergic reaction – d/c

paralytic ectropion
mainly caused by ipsilateral facial nerve palsy
signs: Flattening of the entire face with loss of forehead wrinkles, infraorbital fold and nasolabial fold
tx: -protect cornea (lubrication and close eye during sleep)
>botulinum toxin injection into levator
>temporary tarsorrhaphy
>permanent paralytic ectropoin
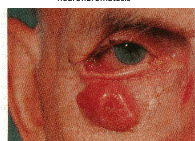
mechanical ectropion
Caused by tumors on or near the lid margin that mechanically evert the lid
tx: removal of cause
correction of lid laxity
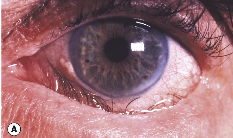
entropion
Symptoms: • Irritation
• FB sensation
• Pain
• Spastic closure of lids
Signs
• Lid margin toward the globe
• Trichiasis (“secondary trichiasis)
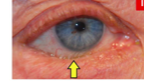
involutional entropion
age related
affects mainly lower lid

floppy eyelid syndrome
uncommon unilateral or bilateral
soft, rubbery easily everted lid
obese middle-age who sleep face down
blepharochalasis
uncommon
>recurrent episodes of painless, non-pitting edema of both upper eyelids
eyelid becomes stretched (wrinkled cigarette paper)
how does blepharochalasis differ from dermatochalasis
blepharochalasis has recurrent episodes of edema but derm does not
eyelid myokimia
signs:
-eyelid twitching, fasciculations or orbicularis muscle
symptoms:
my eye appears to jump
unknown pathogenesis
blepharospasm
Involuntary hyper-contractions of Orbicularis muscle–uncontrollable lid closure
essential blepharospasm
Patient complains that eyes
keep closing from “spasm”
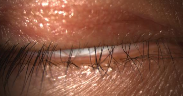
lagophtalmos
Incomplete lid closure
3 types
mild
mod
severe