AP Biology Unit 8
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
A ______________ is a group of individuals of the same species.
population
A ______________ is a group of all living things in a certain area.
community
An __________________ is all the living and nonliving factors in an area.
ecosystem
A ___________ is a large area of a certain climate.
biome
Earth is our ______________, the collection of all the biomes and ecosystems.
biosphere
The order of living things on earth from smallest to largest:
organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere
Factors that determine where the different biomes on Earth are located are ___________, ____________, and ___________.
climate (rainfall and temperature), latitude, and elevation
The Conservation of Matter:
Matter cannot be created or destroyed
The Conservation of Energy:
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
Good illustrations of the conservation of matter are the different __________________ _____________ on Earth, where matter like Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Sulfur, and Phosphorus are recycled.
Biogeochemical cycles
A good example of the conservation of energy is how energy flows through ecosystems, illustrated by ______ _________
food webs
Organisms need energy for _________, __________, and _________. It is also needed for maintaining stable conditions within the body, which is known as ___________________.
growth, repair, and maintenance; homeostasis
__________ ___________ _______ is one's metabolic rate at resting position. This is used when comparing the metabolic rate of two different _____________.
basal metabolic rate; organisms
Smaller animals tend to have a _________ basal metabolic rate than larger animals, which means that they need ______ food.
higher; more
_________________ (aka regulators) are organisms that generate heat by metabolism. Ex. birds and mammals.
Endotherms
________________ (aka conformers) are organisms that gain heat from external sources. Ex. invertebrates, fishes, amphibians, and reptiles)
Ectotherms
The different levels on an energy pyramid are known as ________ _________
trophic levels
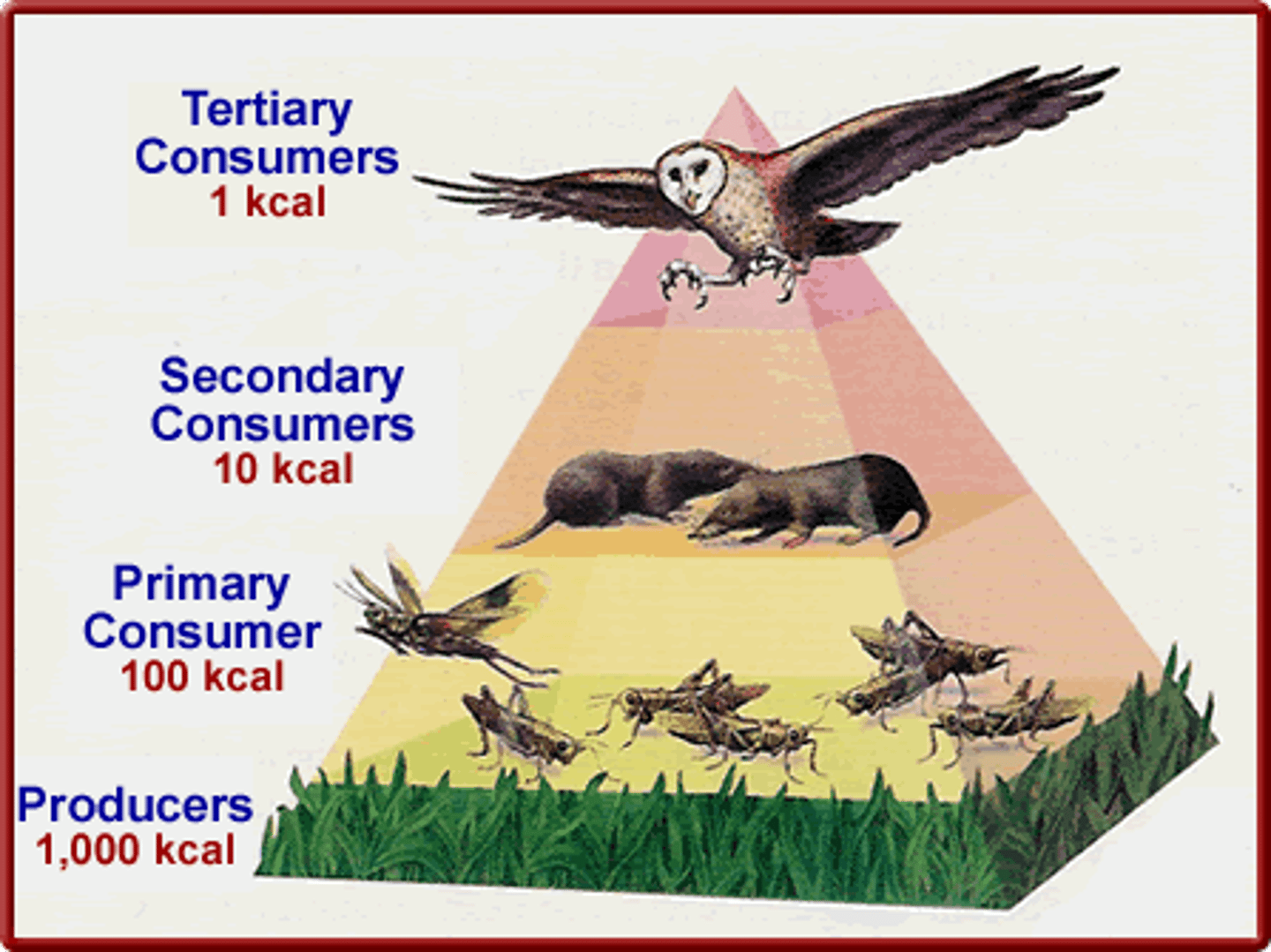
Plants are considered _______________ when placed on a trophic level, and are then consumed by ____________ consumers.
producers; primary
__________________ get energy from dead organic matter and play an important role in nutrient cycling. These typically work at the _____________ level, rather than physically consuming the decaying matter.
decomposers; microscopic
______________ break down dead organisms and organic matter by consuming it (ex. worms).
Detrivores
________ _________ ___________ is typically only 10% efficient between trophic levels.
Energy Transfer Efficiency
__________ ______________ is the rate of photosynthesis in a food web/chain.
primary production
_________ ___________ __________ is the total amount of energy made by plants in photosynthesis.
Gross Primary Production (GPP)
__________ _________ ___________ is the GPP minus the energy used by the primary producers for respiration (K).
Net Primary Production
The Water Cycle includes processes like _____________ (rain or snowfall), _____________________ (water goes back to clouds), ___________________ (evaporation off of plants/trees), __________ (water runs along the ground into lakes/ponds), and ___________________ (water runs through the soil into groundwater).
precipitation; evaporation; transpiration; runoff; percolation
In the Carbon Cycle, CO2 removed from the atmosphere by _________________ is returned to the atmosphere by burning _________ ________ and cellular ______________.
photosynthesis; fossil fuels; respiration
The Phosphorus Cycle occurs when ________ weather down and release phosphorus into the ________ for plants.
rocks; soil
The Nitrogen Cycle has 3 steps. 1, Nitrogen _____________ (N2 is unsuitable for use by organisms while in the atmosphere, so it is changed into NH4, ______________, by bacteria).
fixation; ammonium
Step 2 of the Nitrogen Cycle: ________________ (ammonium becomes NO2, ____________, and NO3, ______________, and is absorbed by plants)
nitrification; nitrite; nitrate
Step 3 of the Nitrogen Cycle: _____________________ (The Nitrogen returns to the atmosphere in the form of N2 because of _____________).
Denitrification; bacteria
Population density is the number of __________________ per area.
individuals
Population ______ is the number of individuals in the population.
size
__________________ is the pattern of spacing between individuals. Can be ____________ (most commons type, near a common resource, working together), ____________ (usually compete for resources), or _____________ (unpredictable spacing, solitary)
dispersion; clumped; uniform; random
________________ is the study of vital statistics of populations and how they change over time.
Demography
dY = amount of _________
change
dt = change in _______
time
B = ________ rate
birth
D = _________ rate
death
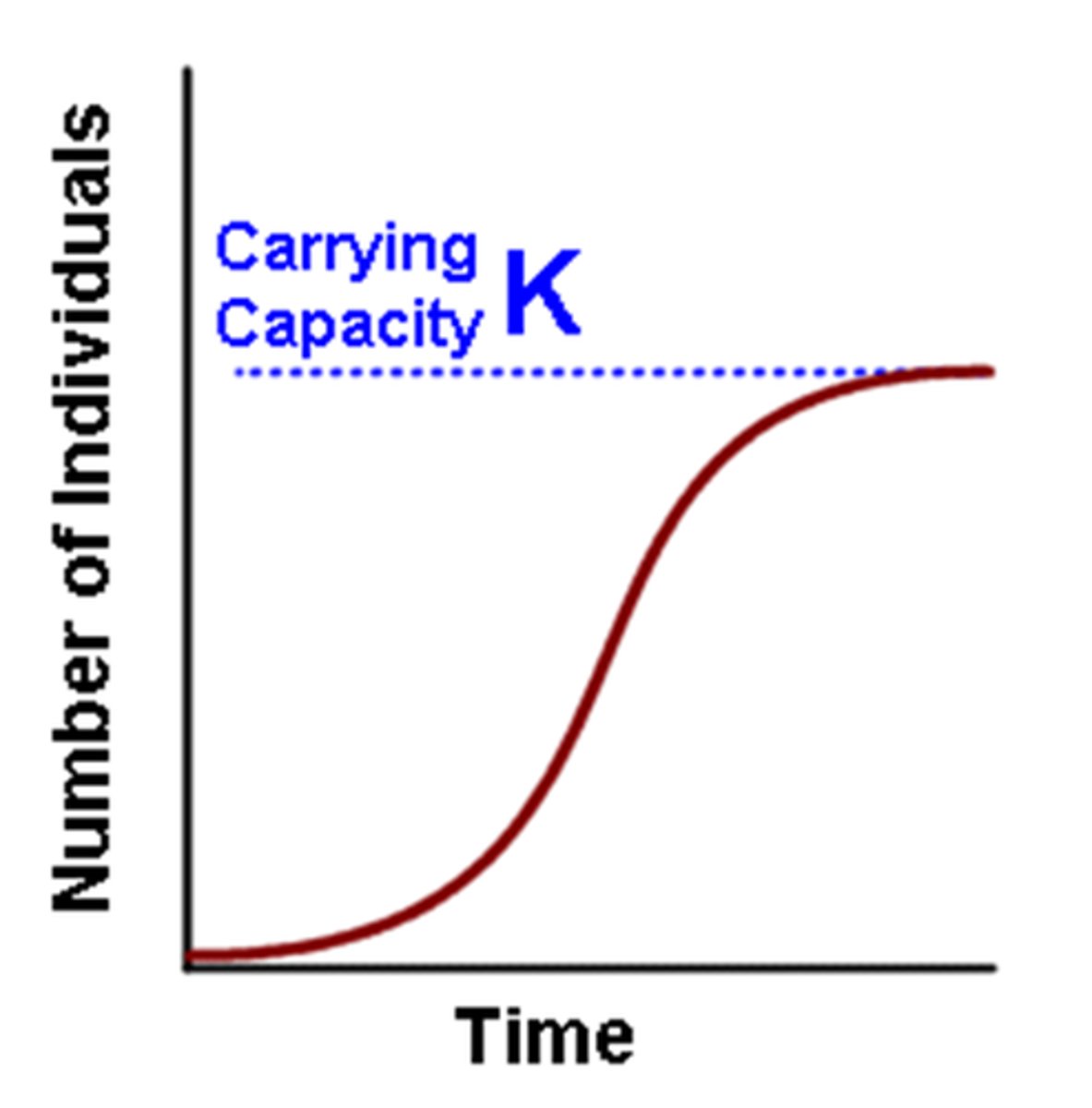
K = ___________ __________
carrying capacity
r(max) = maximum per capita __________ rate of a population
growth
This graph is an example of ____________ growth.
logistic
__________ __________________: two species use different parts of a resource
resource partitioning
__________________ = interactions between two different species. _________________ = interactions between two members of the same species.
interspecific; intraspecific
A _____________ is an organism's home in the physical environment, while a _________ is an organism's role/job in the community.
habitat; niche
Competition (-/-): two or more species compete for a __________ that is in short supply.
resource
Predation (+/-): A predator ____ and eats a prey.
kills
Herbivory (+/-): An herbivore eats part of a ________ or algae
plant
Parasitism (+/-): The parasite derives its nourishment from a second organism, its _____, which is harmed.
host
Mutualism (+/+): both species ____________ from an interaction.
benefit
Commensalism (+/0): one benefits, one is _________________.
unaffected
Amensalism (-/0): one is harmed, one is ________________.
unaffected
A _____________ species is necessary for the community to maintain homeostasis.
keystone
_____________ species are organisms that become established outside native range. These species usually tolerate a wide range of conditions, have a ______ growing season, _______ generation time, few ___________, and __________ easily.
Invasive; long; short; predators; disperses
The _____________________ of an ecosystem is the number of different species.
richness
The ________________ of an ecosystem is the relative abundance of each species (the number of each species)
evenness
More _______________ ecosystems are more resistant to invasive species.
diverse
____________'s Diversity Index calculates diversity based on species richness and relative abundance. You will always get a __________ as a result, and the closer it is to 1, the more ___________ your data is.
Simpson's; decimal; diverse
_____ = total number of organisms of a particular species
n
___ = total number of organisms of all the species.
N
A ______________ changes a community by removing organisms or changing ___________ availability (ex. fire, drought, flood, storm, human activity)
disturbance; resource
___________ _______________ is the transition in species composition in a certain area over ecological time.
ecological succession
__________ ecological succession is restarting an ecosystem from scratch with no _________ yet formed (ex. after a volcano or glacier).
Primary; soil
______________ ecological succession is restarting an ecosystem from scratch, but the soil is left _________ (ex. an abandoned farm, forest fire).
Secondary; intact
________ ___________ is the warming of the Earth due to excess carbon dioxide.
Carbon Dioxide
The ___________ ______________ is the absorption of heat the Earth experiences due to certain greenhouse gasses (CO2). Humans effect the greenhouse effect by adding more ____ and other gasses into the atmosphere.
greenhouse effect; CO2
__________ ____________ is when chlorine-containing compounds erode the ozone layer. Ozone = ___
Ozone depletion; O3
_______________ __________________ is the study of conserving biological diversity at all levels.
Conservation biology
_______ ________ is rain, snow, or fog, with a pH of less than ____. This is caused by the burning of fossil fuels which releases sulfur and nitrogen oxides, which react with the water in the atmosphere and create __________ (H2SO4) and ________ (HNO3) acids.
acid rain; 5.6; sulfuric; nitric
___________________ is when excess nitrogen from agriculture enters aquatic ecosystems. _________ blooms, reduces __________, and causes fish and invertebrates to die.
Eutrophication; Algae; oxygen
____________ ________________ is how toxins become more concentrated in successive trophic levels of a food web. Toxins can't be broken down and ____________ in concentration up the food chain.
Biological magnification; magnify
Density-dependent factors that regulate population growth depend on ________________ __________ (ex. predation, disease, competition, etc.)
population density
Density-independent factors that regulate population growth do not rely on population density (ex. _________ ______________)
natural disasters
A ___-selected species has a population ______ to carrying capacity, with low birth numbers, high _____________ care, good survival of ___________, etc.
K; close; prenatal; young
A _____-selected species maximizes _______________ success, has ___________ growth, little to no prenatal care, _____ birth numbers, poor survival of young, etc.
R; reproductive; exponential; high
Type I survivorship curves have _____ death rate early in life (humans), type II have __________ death rates throughout life (birds, squirrels), and type III have ______ death rate early in life (trees).
low; constant; high
Endotherms typically have a _________ metabolic rate, while ectotherms have a _______ metabolic rate, as endotherms regulate their own body _____________.
higher; lower; temperature
_________________ is important for maintaining homeostasis because it helps an organism control its internal body temperature no matter the surrounding environment.
Thermoregulation
_______________________ is the use of solar energy in an organism to convert CO2 and water into sugars. _________________ is the obtaining of energy from chemical compounds to build sugars.
Photosynthesis; chemosynthesis
An ______________ obtains energy by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis and are known as producers. A ____________ obtains energy by eating other organisms and consuming the organic compounds synthesized by other organisms (broken down through ______________)
autotroph; heterotroph; catabolism
Arrows on a food web or chain show the movement of _________. Producers are always found at the _________ of a food web.
energy; beginning
Population growth is measured by the ______ and ________ rates of a population.
birth and death
Other than birth rate, ______________ can increase a population size
immigration
Other than death rate, ________________ can decrease a population size
emigration
N =
population size
___ ____________ ______ ______ is calculated in order to assess how rapidly a population is expected to grow or shrink.
per capita growth rate
___________ _____________ is the largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
carrying capacity
When a population overshoot occurs, a large ________ follows
die-off
Some factors that have affected human population growth include advanced __________ equipment which provides more food for the population, and advanced ___________ equipment that reduces death rates.
farming; medical
A ___________ ________ is when indirect effects are initiated by the presence of a predator.
trophic cascade
Humans are causing disruptions to Earth's ecosystems through __________ ____ (deforestation and infrastructure), ________________ (large agricultural output), ________________ (use of harsh chemicals and fossil fuels), _________ ________ _______ (the greenhouse effect), and _________ species.
habitat loss; overharvesting; pollution; global climate change; invasive
The disruption of __________ _______ caused isolation of lands, which led to independently operating natural selection. Also major changes of ecosystems as landmasses changed _____________.
Continental drift; latitudes
The disruption of _____ ______ caused ecological succession to proceed after glaciers melted away.
ice ages
The disruption of ________ ________ events caused 99% of Earth's species over the past 3.5 billion years to go extinct. The extinction of many large herbivores caused the landscape of North America to become a mix of _______ and open areas.
mass extinction; forest
The disruption of ________________ events can destroy ecosystems in a matter of hours with effects that last for decades (ex. hurricanes, tornados, etc.) and cause droughts and flooding worldwide (_________ events).
meteorological; ENSO
_________ _________ disrupt an ecosystem's balance by exploiting unoccupied niches and creating new competition.
Invasive species
Humans can decrease the effect of climate change on ecosystems by combating invasive species by reintroducing ________ species, ________ protection, reduced __________, and reducing global ________ change.
native; habitat; harvesting; climate