CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 10: Disease and immunity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
pathogen
A disease causing organism
transmissible disease
a disease in which the pathogen can be passed from one host to another
Method of pathogen transmission
- blood or other body fluids
- contaminated surfaces or food, from animals, or from the air
Mechanical barriers
dead skin and hairs in the nose
Chemical barriers
mucus and stomach acid
Blood defences
phagocytosis and antibody production by white blood cells
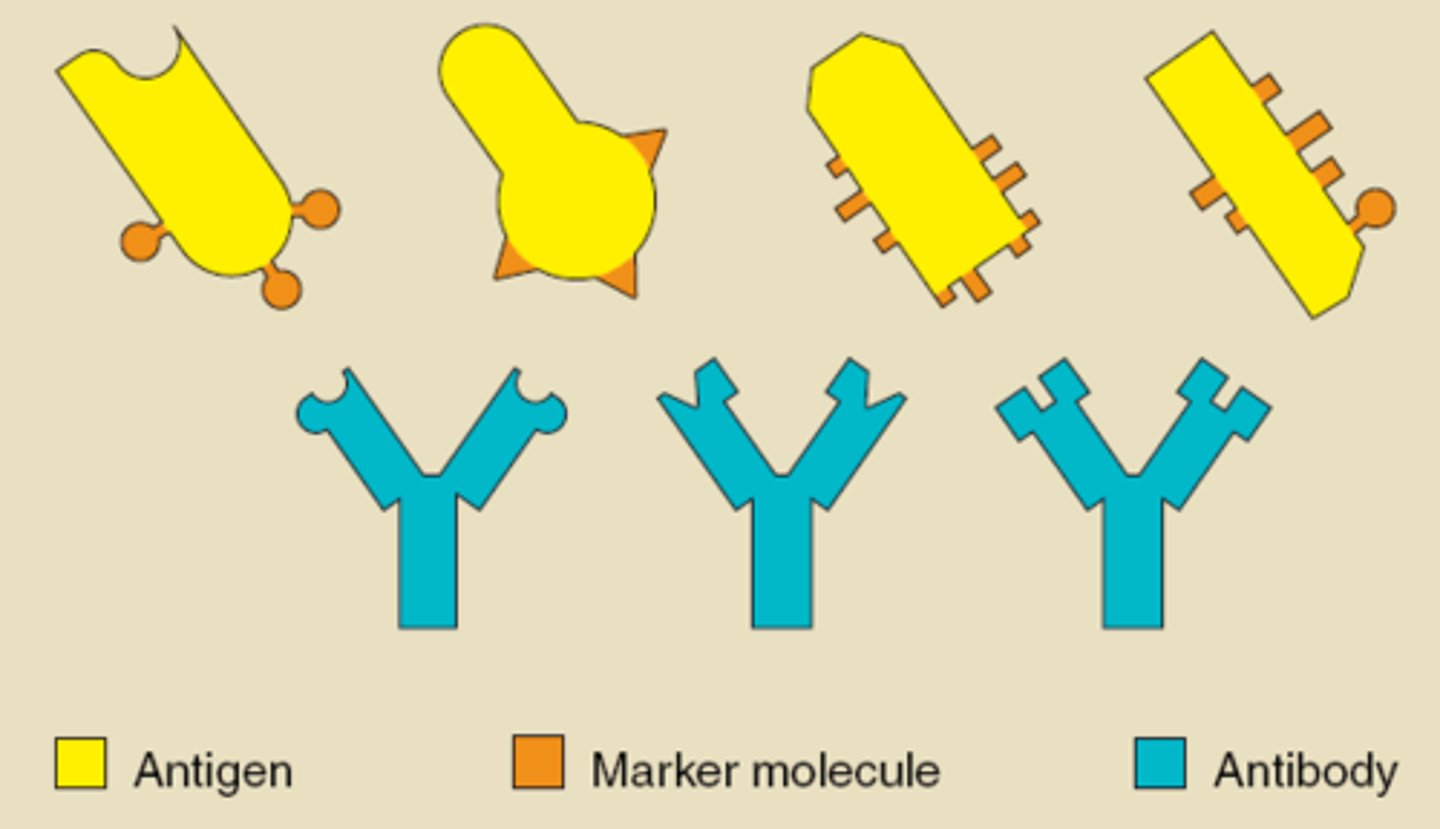
Antigens
Chemical that stimulates lymphocytes to produce antibodies, have specific shapes, so specific antibodies which fit the specific shapes of the antigens are needed
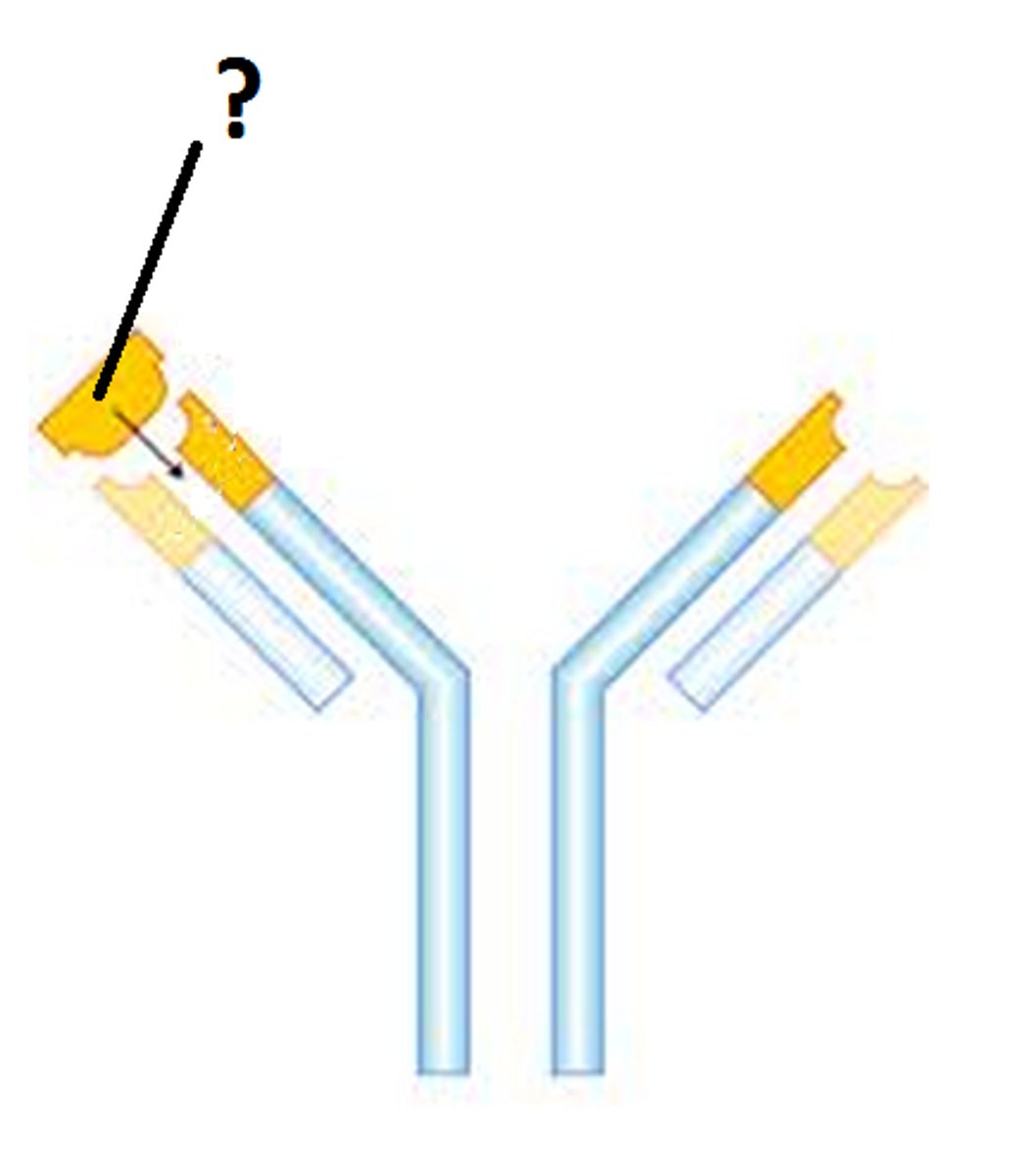
Antibodies
lock on to antigens leading to direct destruction of pathogens, or marking of pathogens for destruction by phagocytes
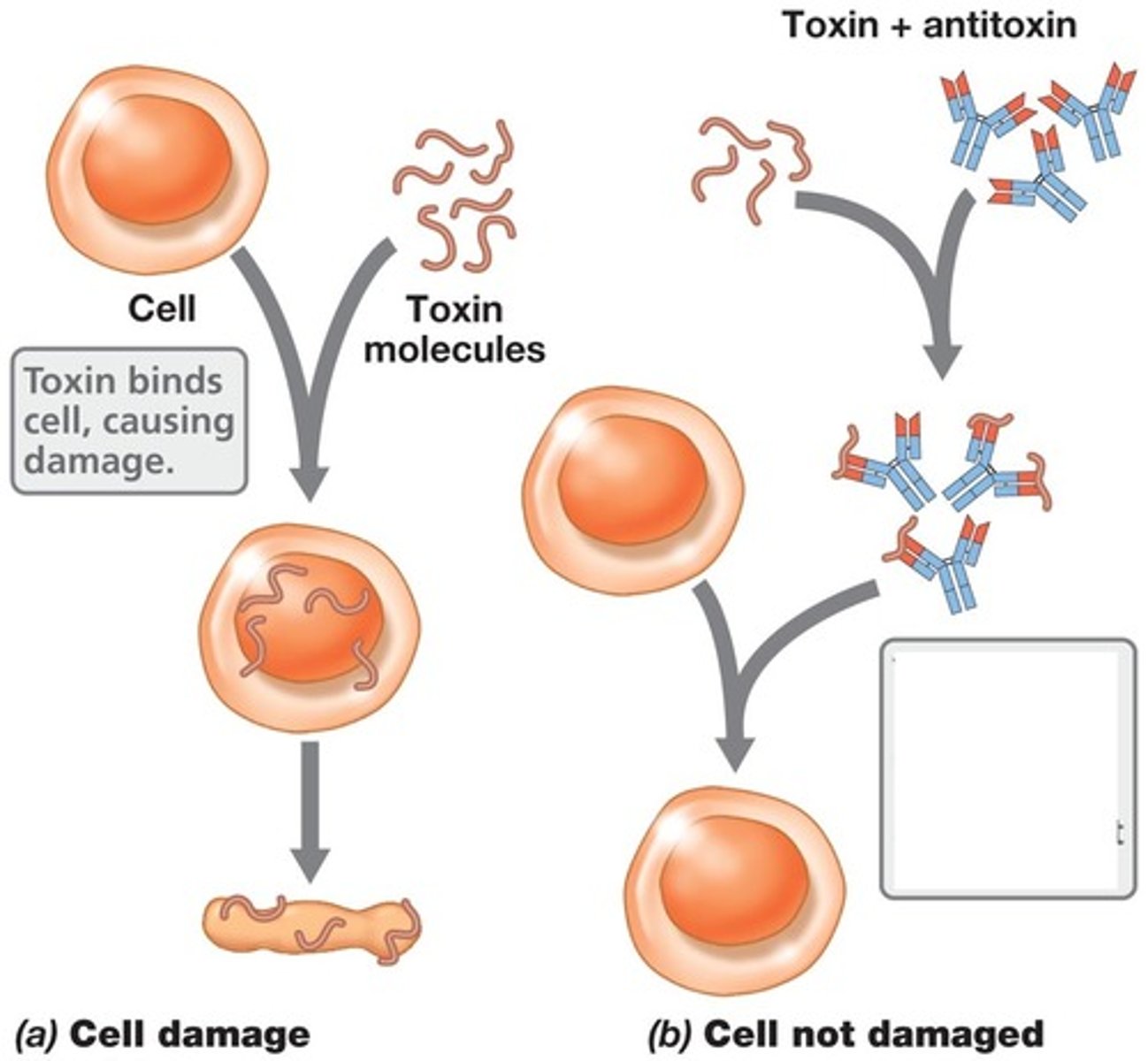
Antitoxins
Antibodies that make toxins harmless
active immunity
defence against a pathogen by antibody production in the body, gained after an
infection by a pathogen, or by vaccination
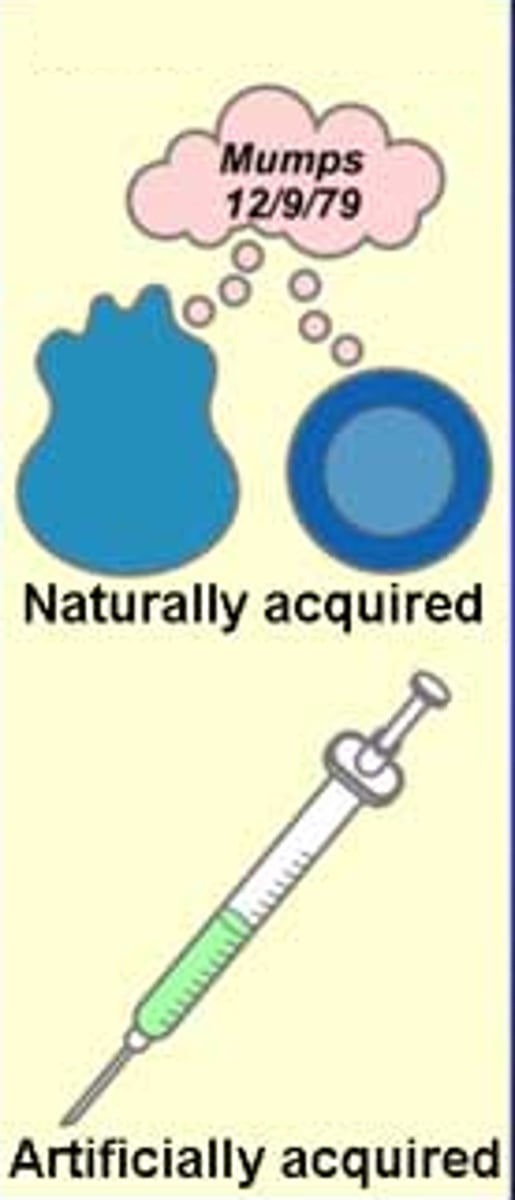
memory cells
a long-lived lymphocyte capable of responding to a particular antigen on its reintroduction, long after the exposure that prompted its production.
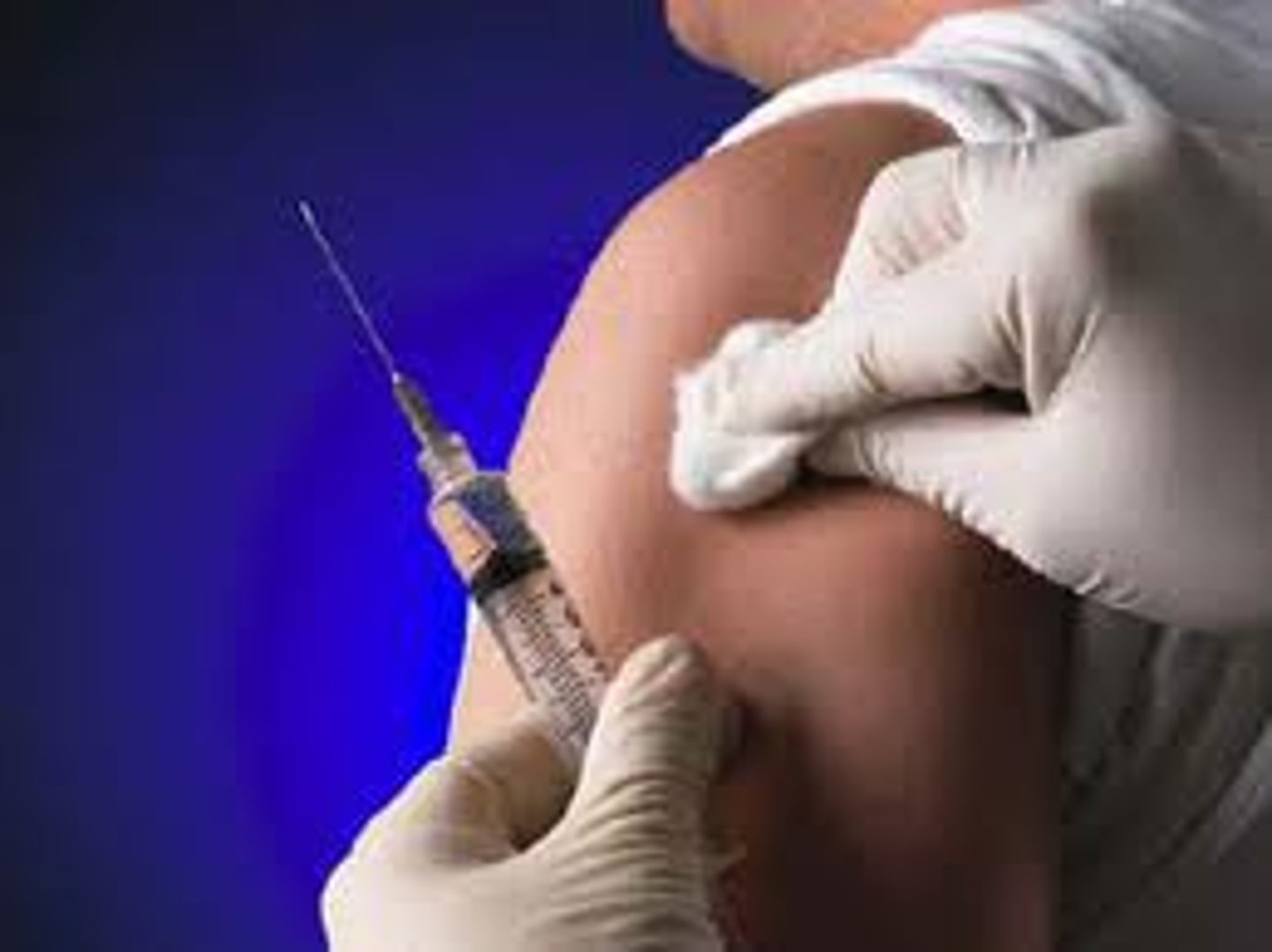
process of vaccination
- harmless pathogen given which has
antigens
- antigens trigger an immune response by
lymphocytes which produce antibodies
- memory cells are produced that give
long-term immunity
role of vaccination in controlling the spread of diseases
Gives active immunity against a disease to large population and protect those who cannot get vaccines by decreasing the chances of coming into contact with the disease
passive immunity
short-term defence against a pathogen by antibodies acquired from another individual, e.g. mother to infant. Memory cells are not produced in passive immunity
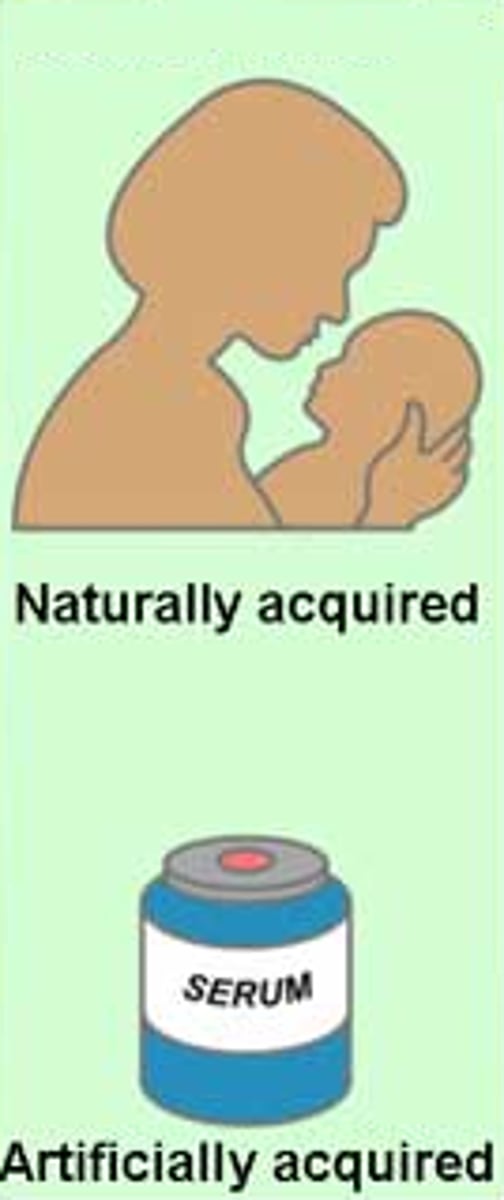
Importance of passive immunity for breast-fed infants
Antibodies in breast milk protect the baby against diseases until it develops its own lymphocytes
autoimmune disease
a disease in which the immune system attacks the organism's own cells
Type 1 Diabetes
autoimmune disease caused by the immune system attacking and destroying pancreas cells that produce insulin

Insulin
Protein hormones that stimulates the liver and muscles to store glucose as glycogen.
Methods of preventing transmissible diseases
- personal hygiene
- hygienic food preparation
- proper waste disposal
- sewage treatment