B2- Scaling up
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
what is diffusion?
the net movement of particles from an area oh high concentration to a low concentration
when is diffusion faster?
when there’s a larger surface area of the plant and a greater concentration gradient
what is diffusion used for?
to move substances in and out of cells across cell membranes
what is active transport?
active transport is the net movement of particles against a concentration gradient- area of low concentration to high
requires energy
what is osmosis?
osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a partially permeable membrane from a dilute solution (high concentration of water) to a more concentrated solution (low concentration of water)
what is mitosis?
type of cell division that produces 2 daughter cells needed to replaced damaged cells, growth and repair.
what type of daughter cells does mitosis produce?
2 identical daughter cells
what are the stages of mitosis?
parent cell contains 2 chromosomes
each chromosome replicates itself
chromatids (2 sets of chromosomes) are pulled apart
2 new daughter cells are created identical to parent, process starts again
what are the stages of the cell cycle?
Growth stage- extra ribosomes, mitochondria+ other sub-cellular structures are produced
Mitosis- 2 sets of chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite ends, nucleus divides
Cell divides- cytoplasm + cell membrane divide to create 2 identical cells
what is differentiation?
it is the process by which a cell changes to become specialised for it’s job.
what are stem cells?
undifferentiated cells that can divide to produce more and can differentiate into any type of cell depending on what instructions they’re given.
what are specialised cells?
cells designed to do a specific job or function
how is a root hair cell specialised for its job?
its function is to absorb water and minerals, so it has hair-like extensions that increase the surface area for absorption
how is a muscle cell specialised for its job?
its function is to contract quickly so it has long cells with space and contain lots of mitochondria for energy
how is a nerve cell specialised?
it is long and slender, axons can carry nerve impulses as long
how is a sperm cell specialised?
it has a tail which allows it to move
how is a xylem cell specialised?
it is long, thin and hollow cells are used to transport water through stem and root
what are embryonic stem cells?
stem cells that come from human embryos, can differentiate into most cells
what are adult stem cells?
stem cells that come from bone marrow, can only differentiate into some cells from type of tissue where they come from eg blood cells
what are stem cells used for?
cure diseases, replace dying cells and damaged tissues
where are plant stem cells found in?
found in meristematic tissue usually in roots and tips of shoots
what are the disadvantages of stem cells?
ethical beliefs- life begins at conception, so would be against killing an embryo
viral infection- could transfer diseases and infections
what type of circulatory system do humans have?
double circulatory system- one from heart to lungs and one from heart to body
advantages of double circulatory system?
it can achieve a higher blood pressure so create a greater blood flow to and oxygen to tissues and muscles.
what substances are transported by the circulatory system?
oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, antibodies, dissolved food molecules
what are the stages of blood flow?
from vena cava, to right atrium and ventricle, then through pulmonary artery to lungs, from lungs through pulmonary vein, in left atrium and ventricle then through aorta to the body.
purpose of vena cava?
carry deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart
purpose of atrium and ventricle?
atrium contracts pushing blood into ventricle which pushes blood through pulmonary artery (right) or the aorta (left)
what is a valve?
makes sure blood flows in the right directions so it doesn’t go backwards
purpose of pulmonary artery?
carry deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
purpose of pulmonary vein?
carry oxygenated blood from lungs to the heart
purpose of aorta?
the main artery that carries oxygenated blood to the rest of the body
what does the heart do?
pumping organ that pumps blood to the lungs and rest of the body
what do red blood cells do?
they carry oxygen around body through blood
how are blood cells adapted to their function?
have a biconcave disc shape that maximises surface area for absorbing oxygen
don’t have a nucleus- more space to carry oxygen
contain a red pigment called haemoglobin which binds to the oxygen in the lungs to oxyhemoglobin and releases it to tissues as oxyhemoglobin splits into haemoglobin and oxygen
what does plasma carry?
it is a pale straw-coloured liquid that carries white and red blood cells, platelets, hormones, waste substances and nutrients
what do arteries do?
carry blood away from heart at high pressure
arteries adaptations?
contain thick walls and layers of muscle to make them strong and elastic fibres that help them stretch compared to small lumen
what do capillaries do?
are really small and deliver nutrients to cells and remove waste products
capillaries adaptations?
carry blood really close to to lungs and have permeable walls one cell thick to increase rate of diffusion
get rid of waste like co2 and carry oxygen and food
what are veins?
they take blood back to the heart, capillaries join up to make veins
vein adaptations?
have thinner walls and thicker lumen as blood is at lower pressure, have valves to make sure blood flows one way
what do plants need water for?
photosynthesis and minerals for general health
what minerals do plant need?
nitrates, phosphates, potassium
how are root cells adapted?
they have a large surface area to maximise absorption of water and minerals and have thin cell membrane
how does water travel through the root?
water enters root cells through osmosis and minerals through active transport
water travels up stem
some water used in photosynthesis and some evaporates
what do xylem vessels do?
transports water and minerals from the soil to other parts of the plant
how are xylem vessels adapted?
made from dead cells
thick cell wall and hollow lumen
no end walls
water only moves one way- up
what do phloem vessels do?
transports glucose made in photosynthesis to other parts of the leaf
how are phloem vessels adapted?
made from living cells
have lots of mitochondria to to release energy
have end walls
have a 2 way flow to move water up and down
what is translocation?
happens in phloem
food produced by photosynthesis is transported from leaves to growing regions of plant and storage organs
what is transpiration?
upward flow of water from roots to leaves from where it evaporates into the atmosphere.
what affects the rate of transpiration?
brighter light- greater transpiration
warmer conditions- greater transpiration
good air flow- greater transpiration
more humid- slower transpiration
transpiration equation?
transpiration= volume of water lost/time
how do you measure water uptake?
using a potometer- as water is lost from the leaves, the air bubble moves to the left
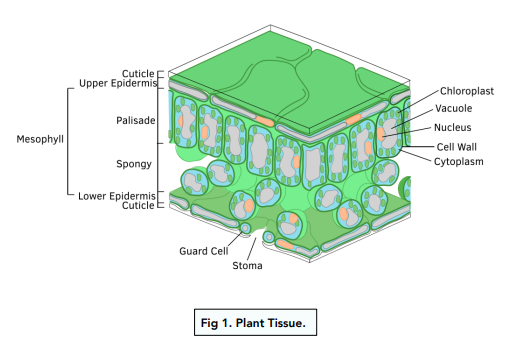
what happens in the stomata?
found in lower epidermis of plant, guard cells open and close stomata and this is where water is lost during transpiration and ensures diffusion of gasses in and out
structure of plant cell?