Economic Growth
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Ways of measuring national income
Output, income, expenditure
Nominal GDP
The total value of goods/sercvices or the level of output, incomes or expenditure at raw prices WITHIN an economy. This will rise if EITHER more goods and services are produced OR the prices of goods and services rises.
Real GDP
GDP adjusted for inflation. While rising prices cause nominal GDP to rise, even if the number of goods and services produced remains the same, real GDP will only rise if more is produced. This is also GDP at constant prices.
Total GDP
This is the value of all output produced across the whole economy, over a period of time.
GDP per capita
GDP divided by the total population
Volume
This is a measure of the number of goods and services produced i.e. real GDP.
Gross National Income (GNI)
GDP + income residents have received from abroad (in the interest, rent, profits or dividends) - income leaving the country. GNI = GDP + Net income from abroad.
Repatriate/Repatriation
Sending money or profits back to your own country from the country you make the money in.
Double counting
A potential mistake to avoid in measuring GDP, in which output is counted more than once as it travels through the stages of production
Informal activity
Untaxed, unregulated jobs in an economy such as the black market or off the record business ventures but can also be more innocent things such as DIY or subsistence farming.
Remittance
A domestic worker in one country leaves the country and works abroad to earn a higher income, then this income is sent back , opposite flow of repatriation. Negative of GDP per Capita
FDI
Investment made by a foreign company in the economy of another country, income generated by the foreign firm will often be repatriated. Increases GDP but doesn't necessarily mean you become richer.
Green GDP
Gross domestic product which has been adjusted to take account environmental destruction and/or health consequences of environmental problems.
Positives of Economic Growth
Higher disposable income, employment and profits for firms, fiscal dividends.
Negatives of Economic Growth
Inflation, Income inequality, environmental costs, current account deficits.
Fiscal Dividend
A growing economy boosts income, corporation and VAT tax revenues and generates the money to finance spending on public goods and services without having to raise tax rates.
Current Account Deficit
The current account of the balance of payments is in deficit when a country imports more goods and services than it exports.
Welfare State
A government that undertakes responsibility for the welfare of its citizens through programs in public health and public housing and pensions and unemployment compensation, funded by income redistribution.
Inclusive Growth
Growth where the benefits are spread across all sections of society - broad based growth, shared growth and pro-poor growth.
Standard of Living
The amount of goods and services that households have access to; Financial health of a population measured by consumption per head and the welfare of people living in the economy.
Big Mac Index
Tool for calculating purchasing power parity that compares prices of a Big Mac throughout the world. This index states how much a currency exchange rate needs to be adjusted upwards or downwards to restore parity between purchasing powers.
Purchasing Power Parity
Required to improve accuracy when comparing data between countries. The rate at which the currency of one country would have to be converted into that of another country to buy the same amount of goods and services in each country. expresses the ratio between the quantity of monetary units required in different countries to purchase the same "basket" of goods and service in order to analyse cost of living.
Purchasing Power
Measure of goods and services that can be purchased with a currency.
Market Exchange Rate
Currency exchange rate given by the relative supply and demand for currencies in the global market
PPP exchange rate
This exchange rate attempts to equate the purchasing power of currencies in different countries, and is calculated by comparing the prices of identical goods and services in different countries.
Non-marketed output
Good or services which are being provided free of charge or at economically insignificant prices, such as subsistence farming and voluntary work, which is valued by the ONS to be worth £24bn every year.
External Costs of Production
When a business's activities result in harmful effects on other people not directly involved in production but is not accounted for in GDP such as costs to healthcare, pollution and waste.
Shadow Economy
illicit economic activity (such as black market transactions and undeclared work such as organised crime) existing alongside a country's official economy, which output's is not included in GDP statistics. Example of this is Italy's shadow economy which dominates 24% of its total GDP.
Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC Curve)
An inverted U-shaped curve illustrating that as gross domestic product rises in emerging economies, pollution goes through stages of rapid increase, levelling off, and decline.
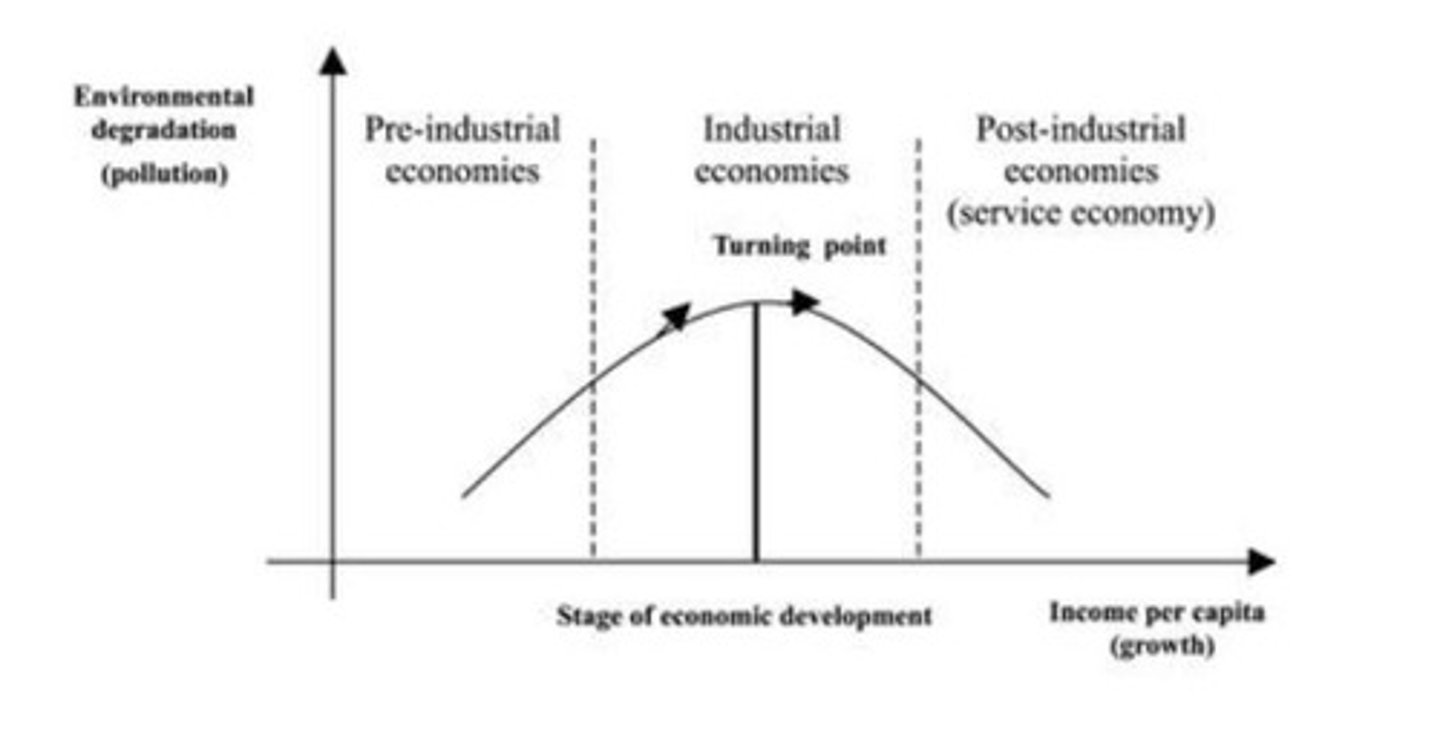
Problems with environmental Kuznets Curve
The environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) doesn't cover all aspects of environmental degradation, only covers air pollution, when there are other forms of environmental degredation such as biodiversity loss, climate change and water loss.
Consumerism
Ideology that encourages the acquisition of goods and services in a greater amount.
Kuznets Curve
A formula showing that inequality increases during the early stages of capitalist development, then declines, and eventually stabilizes at a relatively low level once the country becomes developed; advanced by the economist Simon Kuznets.
Lawson Boom
Period of rapid economic growth in the 1980s formed by a strong economy, low taxation rates and low unemployment. However, heavy inflation began to happen as the economy was operating very close to its full productive capacity.
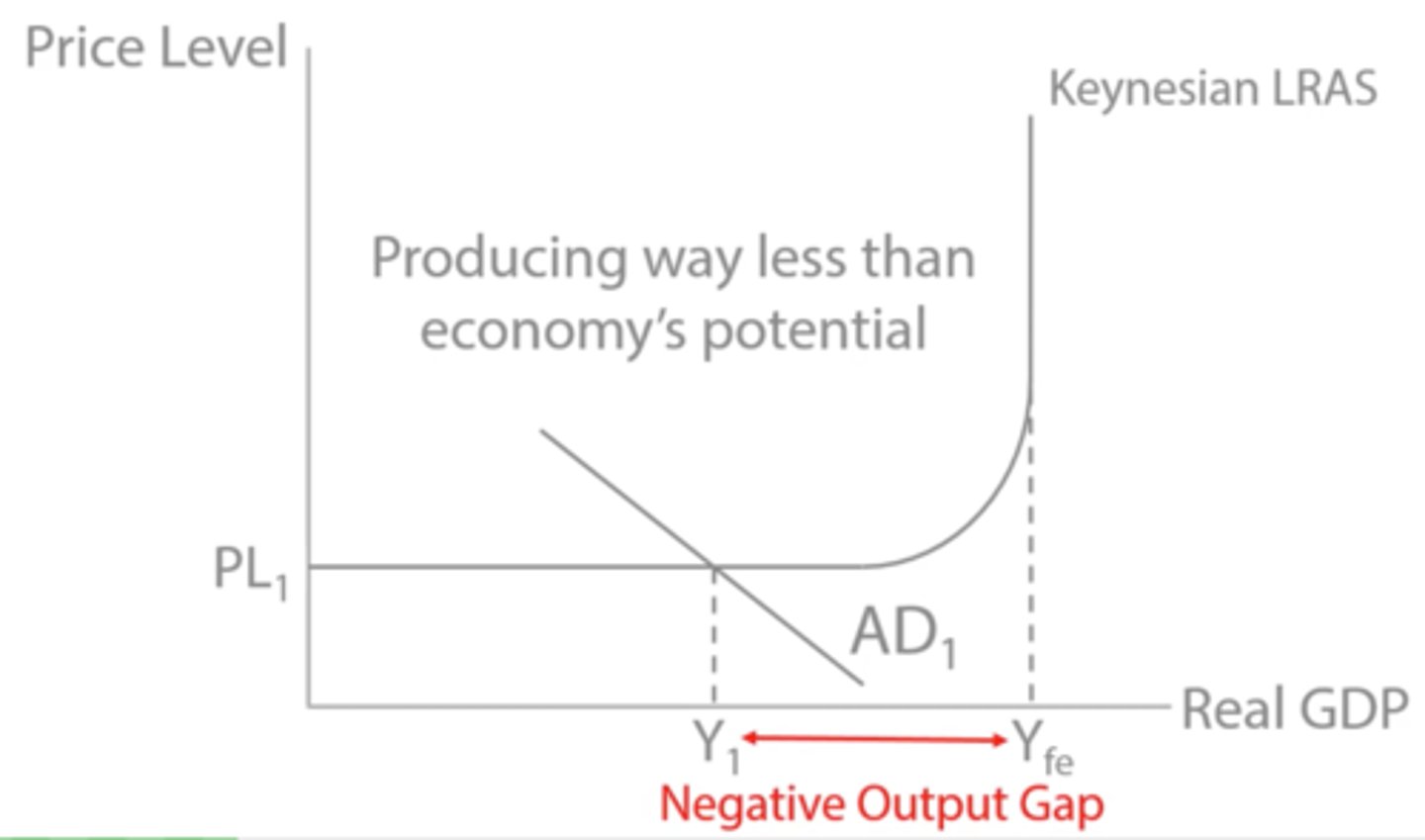
Negative output gap
The level of actual real output (GDP) in the economy is lower than the trend/potential output level
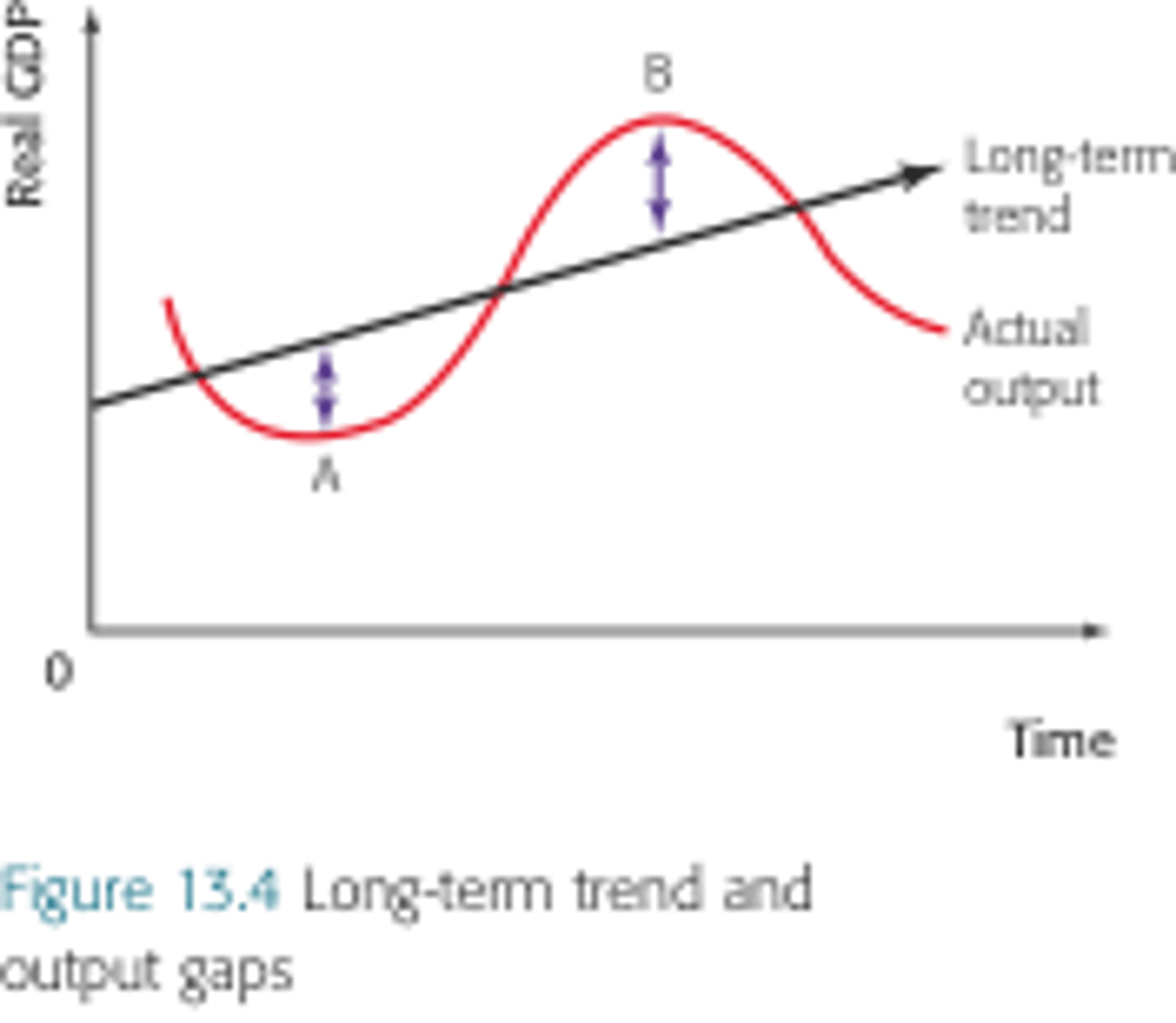
Positive output gap
The level of actual real output in the economy is greater than the trend output level
Easterlin Paradox
High incomes do correlate with happiness, but long term, increased income doesn't correlate with increased happiness. Rich societies are not generally much happier than poorer societies and the marginal gain in happiness declines past a certain threshold. Wealth is relative
Problems with using GDP as a measure of living standards
GDP rise doesn't account for potential rises in income inequality (median household income), doesn't account for externalities, increased production doesn't mean improved living standards (improved consumption) and it doesn't count the shadow economy or non-marketed output.
Recession
Decline in real GDP lasting at least two quarters or more
Index Number
A unit-free number derived from the price level over a number of years, which makes computing patterns and rates easier, since this number has values around 100