Breathing Circuits & CO2 Absorption (exam #1)
1/209
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam #1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
210 Terms
what constitutes fresh gas flow/inspired mixture?
gases from flowmeters, anesthetic agent from vaporizer, and should be a dry & clean mixture
normal inhaled air is ____ & ____ by our upper airway, but breathing circuit bypasses the upper airway. This is why we do what to our fresh gas flow?
warmed & humidified
warm & humidify
anatomic dead space is due to?
conducting airways
physiologic dead space is due to?
mismatch V/Q (normal 0.8)
mechanical dead space is due to?
breathing circuit
what constitutes alveolar gas/exhaled mixture?
O2 (left over after metabolism)
N2O (not taken up by body)
air mixture (left over)
any contaminants (not taken up by body)
anesthetic agent (not taken up by body)
what is added (from the alveoli) to the exhaled mixture?
CO2, water vapor, gases from body (methane, acetone, nitrogen/N2)
what should the breathing circuit not allow rebreathing of?
CO2
what should the breathing circuit allow rebreathing of?
O2, N2O or air, anesthetic agent
upper airway is ____ vocal cords & is also called what?
above, conducting airway
lower airway is ____ vocal cords?
below
larynx relationship to vocal cords?
protective structure
muscle relaxants (paralytics) affect what muscle?
smooth
the drugs that anesthesia providers give to the patient affect 4 things?
central respiratory center, peripheral chemoreceptors, lung receptors, and effects of anesthesia
How does Boyle’s Law apply to mechanics of breathing?
chemoreceptors stimulate breath→diaphragm & intercostals expand volume of lungs→increased lung volume→intrapleural pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure→atmospheric air flows into lungs based on pressure differences.
volume inside lungs inversely related to relationship between intrapleural pressure & atmospheric pressure
inc vol in lungs=intrapleural pressure lower than atm pressure (makes you inhale)
dec vol in lungs=intrapleural pressure higher than atm pressure (makes you exhale)
where is the chemical regulation of respiration located & what is it’s function?
brainstem (medulla & pons) and maintains proper O2 (PaO2) & CO2 (PaCO2) levels
what is the biggest stimulator to breathe?
CO2
what/where controls voluntary breathing?
cerebral cortex
when is voluntary control of breathing abolished?
once patient deeply sedated or anesthetized past stage II
how do you check for abolishment of voluntary control of breathing?
compare eye reflexes to laryngeal reflexes (lid reflex directly correlates to/mirrors laryngeal reflex)
what happens if you try to instrument a patient’s airway before they lose their voluntary control of breathing (aka still has an intact eyelid reflex=intact laryngeal reflex)?
they will laryngospasm
what is something you can do to a patient (besides intubate) once their voluntary control of breathing is abolished?
bag/mask ventilate
inhalation agents inc or dec TV & inc or dec RR?
dec, inc (opposite of narcotics)
narcotics inc or dec TV & inc or dec RR?
inc, dec (opposite of inhalation agents)
what happens with limbic system stimulation?
anticipation of activity, emotional anxiety, increases rate and depth of ventilation (hyperventilation)
how does temperature affect RR?
increased temp=increased RR
decreased temp=decreased RR
what type of ventilation is recommended for febrile and/or cold patients?
controlled
sudden severe pain causes what type of breathing?
apnea
prolonged somatic pain inc or dec RR?
increases
visceral pain inc or dec RR?
decreases
listen and react to respiratory clues about anesthetic depth.
For example, if patient is not paralyzed, upon surgical incision what would you expect to see if patient is light/under anesthetized?
patient takes big, deep breath and/or RR increases
why is sevoflurane the only agent used for inhalation inductions?
it is the only agent that does not cause airway irritation
difference between inhalation induction versus IV induction and stage II?
inhalation takes patient through stage II gently and noticeably (to anesthesia provider) whereas IV take patient through stage II in under 30 seconds
sudden inc in BP = ___ RR?
sudden dec in BP = ___RR?
dec
inc
when we affect a patient’s chemical drive to breathe (like CO2) or we affect their central mechanisms of breathing (in their brainstem) what do we have to do to ensure their O2, CO2, and pH remain balanced?
physiologically mimic their voluntary breathing
what pressure changes can affect respiration?
alveolar pressure, pleural cavity pressure, diaphragm
pleural cavity pressure is always more or less than atmospheric pressure & what could be the cause for this not being true?
less
pneumothorax caused by trauma (outside) or ventilation (alveolar/inside)
definition of diffusing capacity for hemoglobin and normal value?
volume of gas that is diffused through membrane each minute for a pressure difference of 1 mmHg and is normally 21 mL/min/mmHg
normal TV & what % reaches alveoli (participates in gas exchange) vs what % does not reach alveoli (anatomic dead space)
500 mL or 5-7 cc/kg IBW
70%
30%
expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
volume of air that can be forcefully exhaled after normal exhalation
residual volume (RV)
the volume left in your lungs after exhaling to fullest capacity
functional residual capacity (FRC) & normal value?
ERV + RV
stays in lungs at end expiration
2,400 mL @ end expiration
minute ventilation (VE) equation & definition?
RR x TV
displaces the appropriate volume of CO2 in the blood
lower than normal minute ventilation called? Could be caused by?
hypoventilation
patient lung disease
how would you know if you are hypo/hyperventilating the patient with the VE you have set for them?
end tidal CO2
alveolar ventilation (VA) equation and definition and what does it consist of?
VA = RR x (TV - mechanical dead space)
total volume of new gas entering each minute
fresh gas - metabolized gas
CO2
water vapor
normal amount of mechanical dead space in a standard breathing circuit?
150 mL
FRC + size of TV (washing out room air and taking in O2) will tell you what?
how much time it will take to fully pre-oxygenate (de-nitrogenate) a patient
FRC + minimum O2 requirement will tell you what?
amount of apnea time you have to instrument an airway before your patient’s SaO2 starts to drop
why is slow replacement of alveolar air important?
prevents sudden changes in gas concentration and makes respiratory control more stable
if giving O2, FRC represents 10 minutes of metabolic consumption
2500 FRC / 230 = 10 minutes
is O2 solubility low or high in the blood and what does this mean for O2?
low, needs transport protein in adequate concentration in order to be maximally effective
keep BP within ___ % of patient’s normal?
20
is ventilation necessary for oxygenation?
no
what is ventilation necessary for?
removal of CO2
does CO2 have high or low solubility in blood?
high! (that’s why it has to be removed)
Quantity of CO2 dictates what?
minute ventilation
spontaneous breathing keeps PCO2 around what value, but what are 3 exceptions to this?
40 mmHg
disease, high altitude, pharmacologic intervention
what is the function of the breathing circuit?
provide final conduit for the delivery of anesthetic gases (links patient to anesthesia machine and is where respiratory exchange takes place)
what are the 4 classifications of breathing circuits?
open, semi-open, semi-closed, closed
open (insufflation) breathing circuit?
blowing anesthetic gas across patient’s face
avoids direct contact between pt airway & circuit
**pediatric anesthesia
no rebreathing of exhaled gases if high flows used (>10L/min)
ventilation CANNOT be controlled
do you have to be giving patient inhalation anesthetic agent in order to use insufflation circuit?
no, can be used for inhalation agent OR just O2
is there rebreathing of exhaled gases in an open (insufflation) breathing circuit?
no, as long as high flows used (>10L/min)
can ventilation be controlled in an open (insufflation) breathing circuit?
no
open-drop anesthesia
not used in modern medicine
air is carrier gas and supplemental O2 can be used
rebreathing can be significant
4 disadvantages of open breathing circuits?
poor control of inspired gas concentration & anesthesia depth
cannot assist/control ventilation
does not conserve exhaled heat or humidity
OR pollution with large vol of waste gases
draw-over anesthesia
used mostly in the military
nonrebreathing open circuits that use ambient air as carrier gas
can use supplemental O2
never use N2O
advantage of draw-over anesthesia?
simple and portable
disadvantages of draw-over anesthesia?
depth of TV not well known due to no rebreathing bag
awkward to use for ENT/head surgery d/t components near pt head
Semi-Open breathing circuit example?
Mapleson systems
what components are added to the Mapleson system (semi-open) that solves the problems that insufflation/draw-over circuits have?
breathing tubes
fresh gas inlet (allows us to use O2)
adjustable pressure limiting valves (APLs)
reservoir bags (can control ventilation)
can use with scavenger system (reduces OR pollution)
what helps prevent rebreathing in a Mapleson system?
high fresh gas flows (FGF)
how do Mapleson systems allow quick change in anesthetic concentration?
the high FGFs because it dilutes the CO2 (helps wake the patient up)
In a Mapleson system:
the ____ the FGFs = pt breathes more warm, humid gas
is this good or bad? Cost more or less $?
lower, good, less $
In a Mapleson system:
the ____ the FGFs = pt breathes more dry, cold gas
is this good or bad? Cost more or less $?
higher, bad, more $
how many types of Mapleson’s are there?
6
what Mapleson is best for spontaneous ventilation?
Mapleson A
what Mapleson is best for controlled ventilation?
Mapleson D
what is a Bain?
a modified Mapleson D
what Mapleson is best for lowest resistance?
Mapleson E (Ayre’s T Piece) (think Easy to breathe)
what Mapleson is the best compromise?
Mapleson F (Jackson-Rees)
Mapleson A, B, C have ____ closest to patient?
APL valve
Mapleson D, E, F have ____ closest to patient?
FGF inlet
which is the only Mapleson that does not have corrugated tubing?
Mapleson C
what is the only Mapleson that does not have a reservoir bag?
Mapleson E (Ayre’s T Piece)
Mapleson A
APL valve (closest to pt)
corrugated tubing
FGF
reservoir bag (furthest from pt)
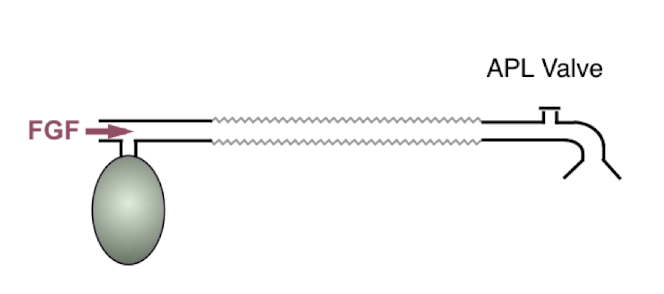
Mapleson B
APL valve (closest to pt)
corrugated tubing
FGF
reservoir bag (furthest from pt)
Mapleson C
APL valve (closest to pt)
NO corrugated tubing
FGF
reservoir bag (furthest from pt)
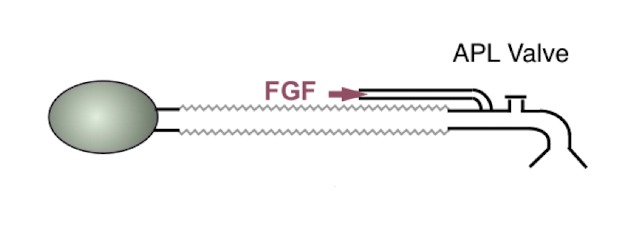
Mapleson D
APL valve (closer to reservoir bag)
corrugated tubing
FGF (closest to pt)
reservoir bag (furthest from pt)
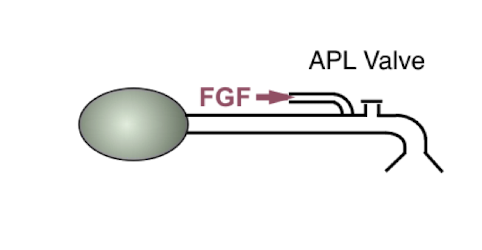
Mapleson E (Ayre’s T Piece)
NO APL valve
corrugated tubing
FGF (closest to pt)
NO reservoir bag
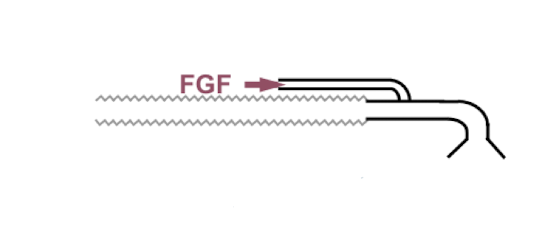
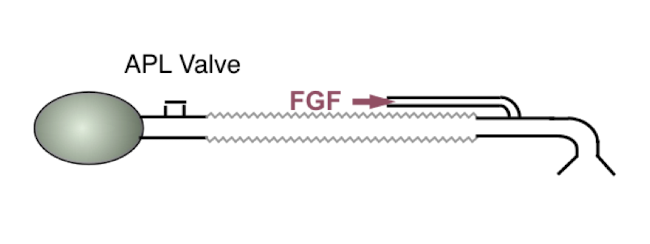
Mapleson F (Jackson-Rees)
APL valve (furthest from pt)
corrugated tubing
FGF (closest to pt)
reservoir bag
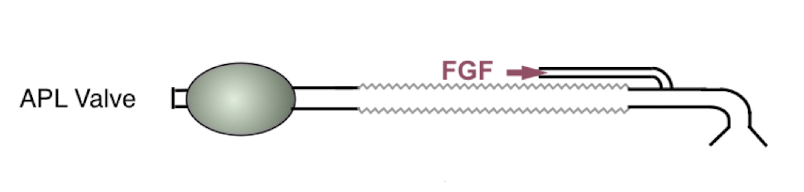
what are you basing your choice of Mapleson on ultimately? (not including if pt has or does not have airway)
lowest flow rate able to be used but still maintain PaCO2 levels
advantages of Mapleson system?
some retention of heat & humidity
low resistance to breathing
less WOB (bc low resistance)
simple, portable
easy to assemble
minimal moving parts
disadvantages of Mapleson system?
most advantages overshadowed by need for high flow rates
more $
dry, cold airway secondary to inc flow rates, low humidity levels
OR pollution (no scavenger system)
hard to change from spontaneous to controlled ventilation
what is a Bain Circuit and how does it work?
Modified Mapleson D
fresh gas enters circuit thru thin inner tubing & exhaled gas exits via corrugated tube
why should the outer tube be clear on a Bain circuit?
to be able to see and ensure integrity of inner tube
what is an advantage of the Bain circuit related to exhaled gas?
exhaled gas warms and humidifies FGF
For Bain circuit, FGF must be ____ MV to prevent rebreathing?
2.5x
disadvantages of Bain circuit?
inner tubing kinked or disconnected possible
converts all corrugated tubing to dead space
risk of hypercapnia (bc FGF has to be 2.5x MV to prevent rebreathing)