Physics -Periodic Motion/Waves and Sound (ch 10)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
damping
the gradual loss of amplitude of an oscillator due to friction
resonance
A phenomenon that occurs when two objects naturally vibrate at the same frequency - they are in phase
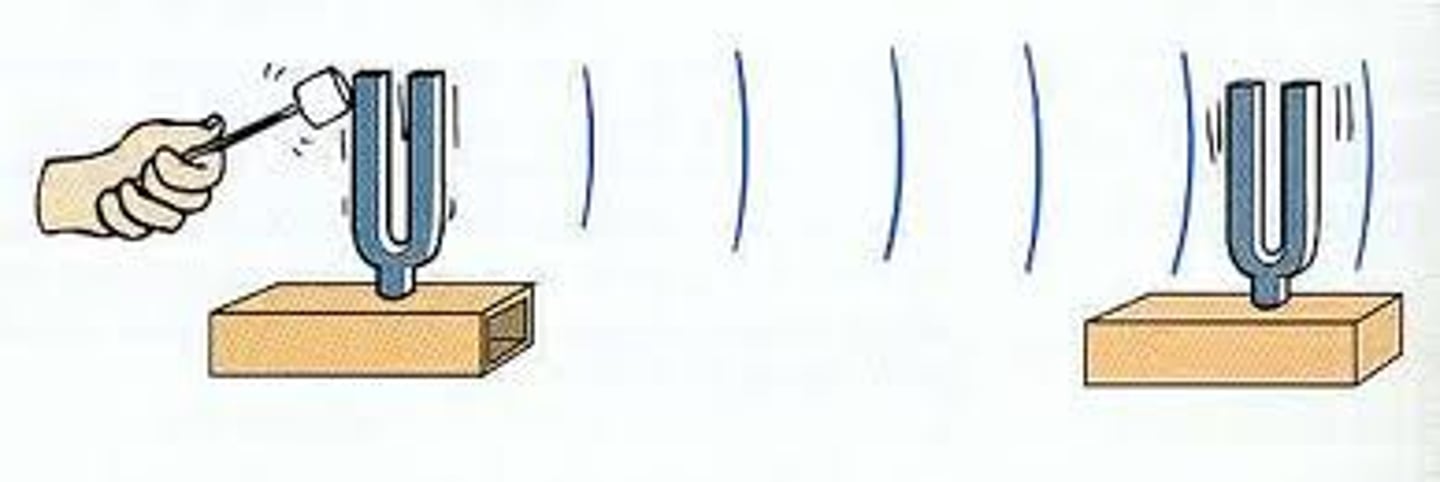
sound
A disturbance that travels through a medium as a longitudinal wave
solid
the state of matter sound travels best through
Frequency
if an oboe and piano are both playing middle-C they will have the same___
periodic motion
any motion that repeats at regular time intervals
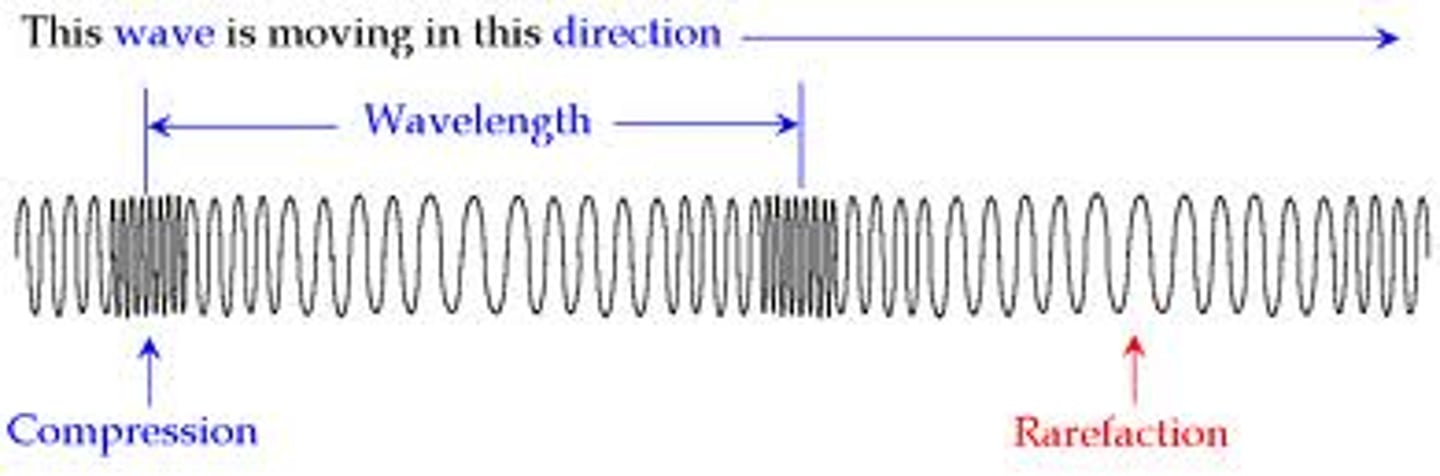
rarefaction zone
The region where the medium particles are farther apart than average
longitudinal and transverse
What are the two types of waves?
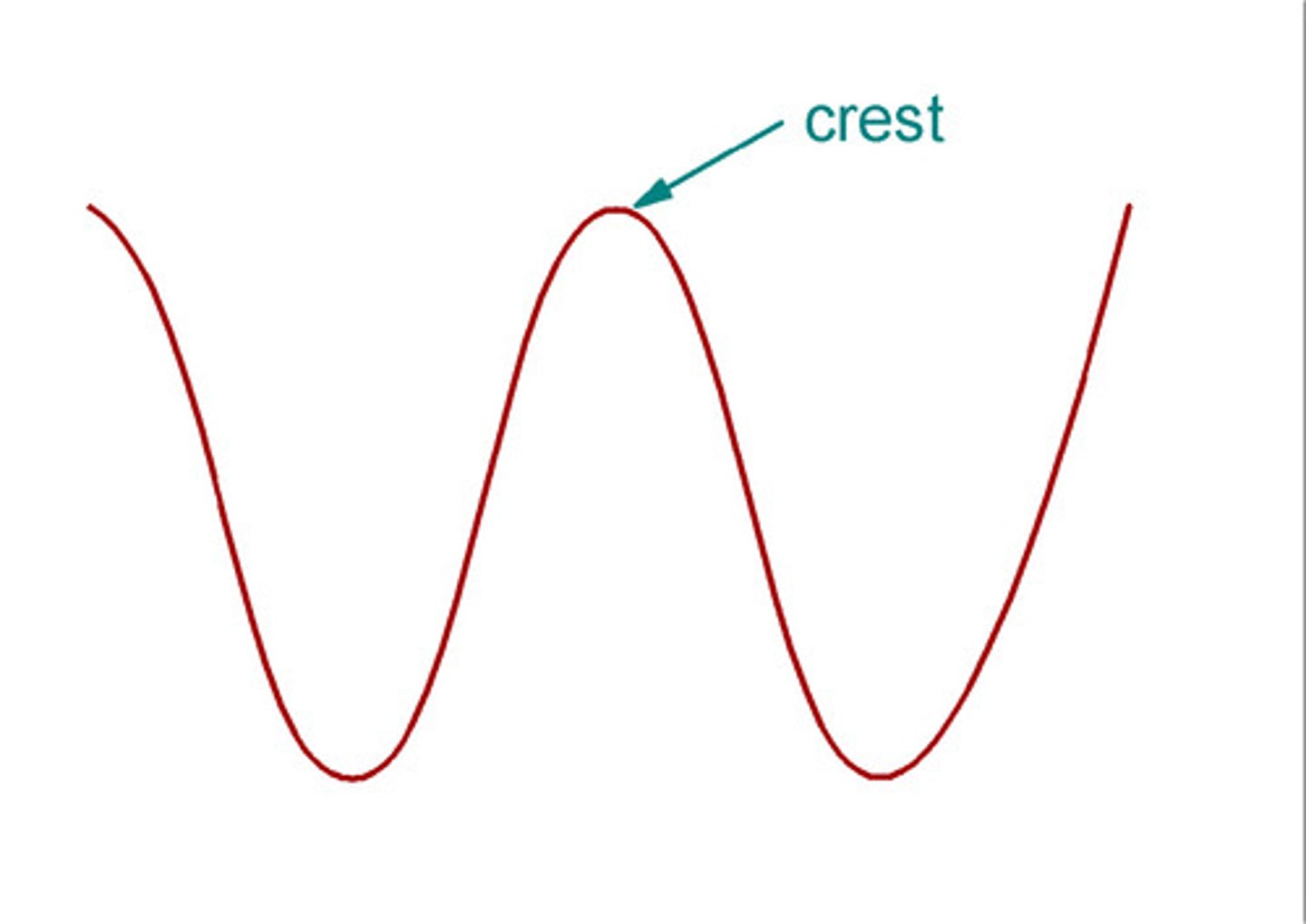
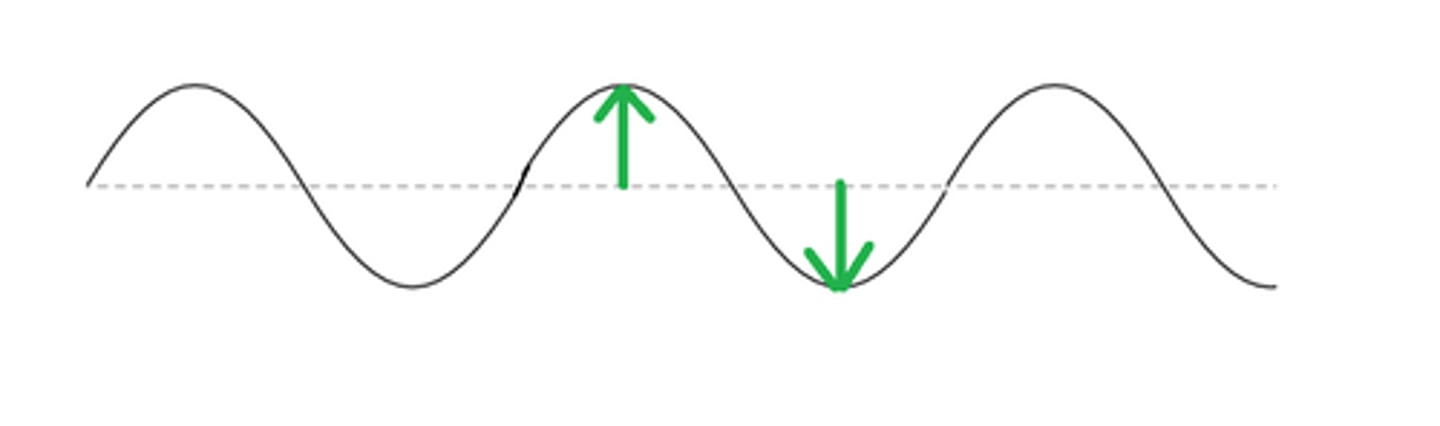
crest
Highest point of a wave
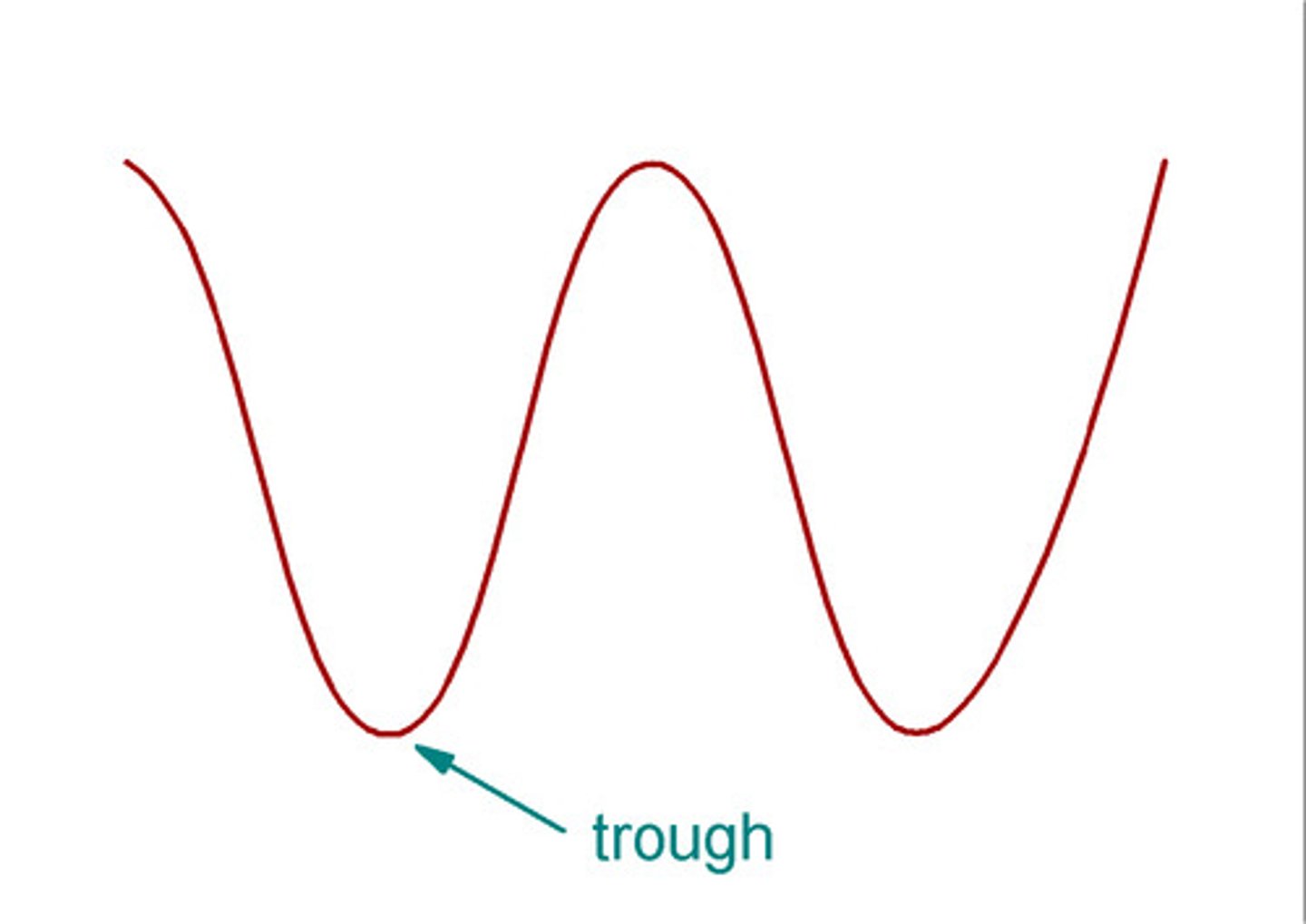
trough
Lowest point of a wave
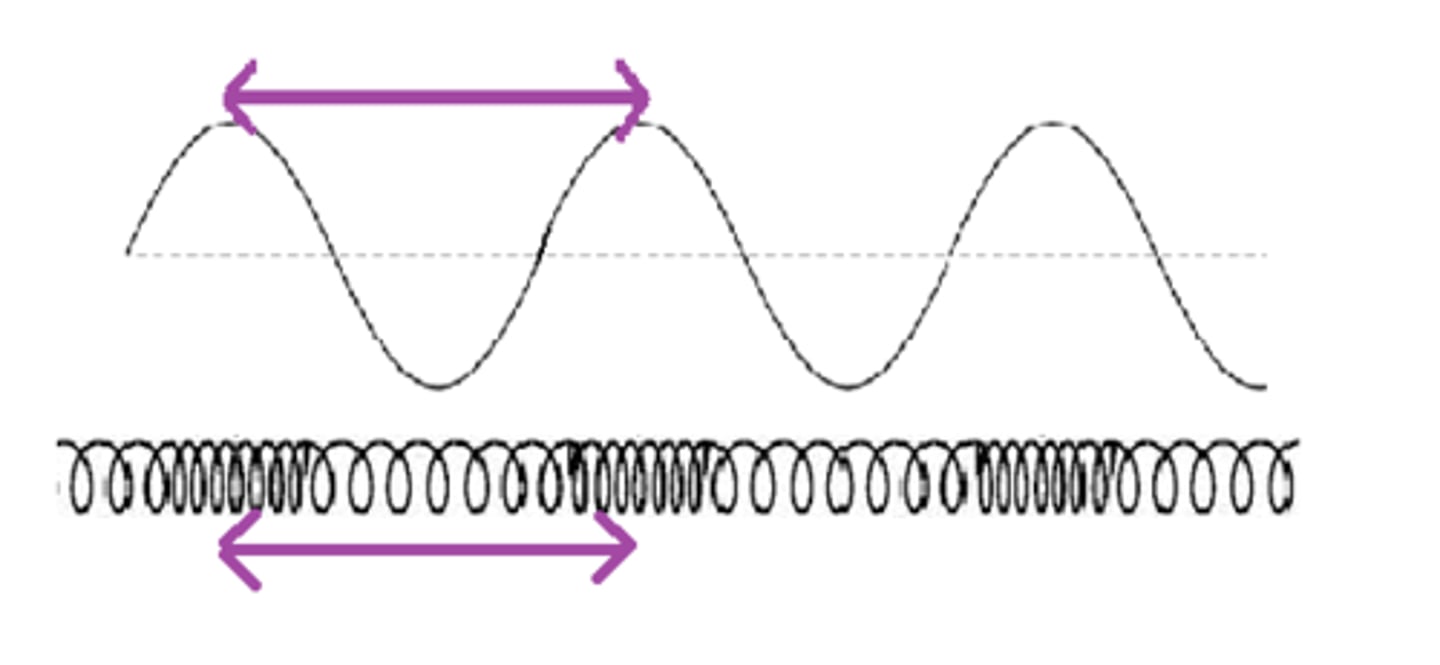
wavelength
Horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves
wave height
vertical distance between crest and trough
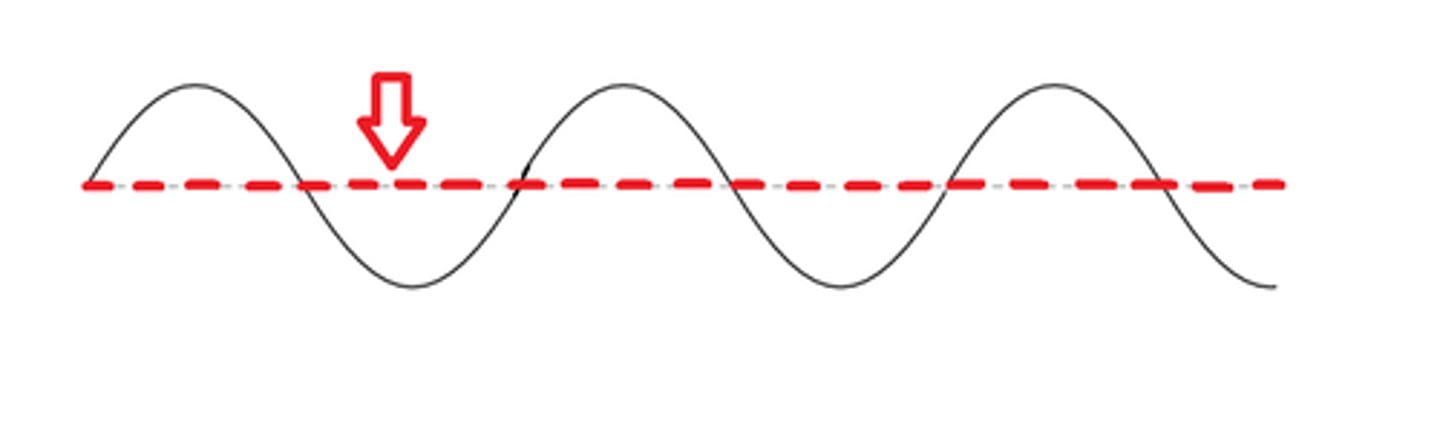
rest position
The position where the wave is at rest, half way between the crest and trough.
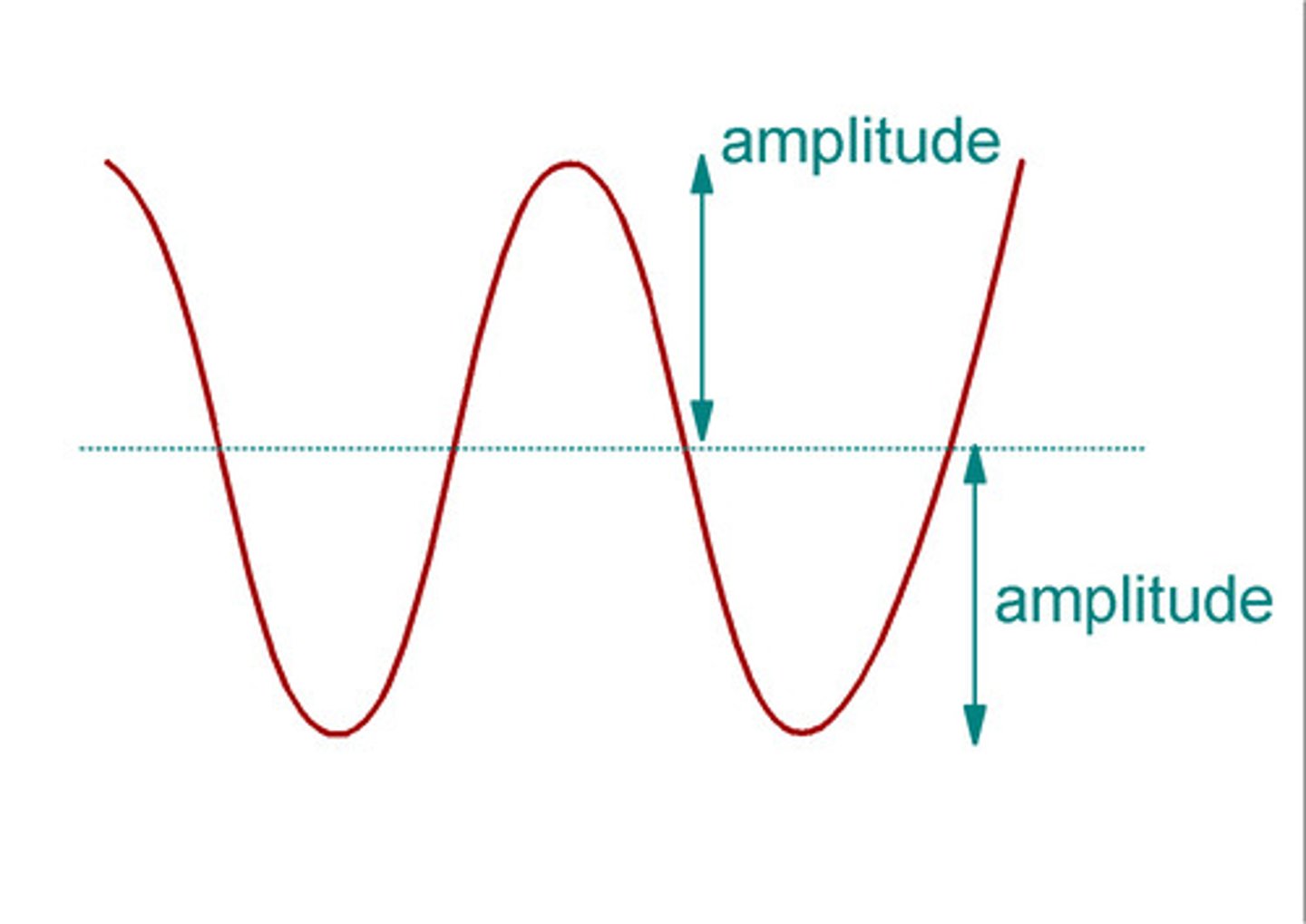
amplitude
the height of a wave from the origin to a crest, or from the origin to a trough
damped oscillation
an oscillation that runs down and stops
driven oscillation
motion of an oscillator that is subjected to a periodic external force to overcome forces working to slow the oscillations
simple harmonic motion
repeated motion in which the force causing oscillations is directly proportional to the system's displacement
fundamental frequency
the lowest frequency of vibration of a standing wave
harmonic
frequencies that are multiples of fundamental frequency
timbre
quality of sound; voice of an instrument that is a result of all the simultaneous frequencies
doppler effect
An observed change in the frequency of a wave when the source or observer is moving
Electromganetic wave
A wave the can transfer electric and magnetic energy through the vacuum of space.
mechanical wave
A wave that requires a medium through which to travel
standing wave
a pattern of vibration that simulates a wave that is standing still
longitudinal wave
A wave in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels
transverse wave
A wave that moves the medium in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels
longitudinal wave examples
sound waves and p waves
transverse wave examples
water waves and electromagnetic waves
destructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a smaller amplitude
constructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a larger amplitude
vibrations
produces all sound waves
interference
the combination of two or more waves that results in a single wave