Biodiversity and Organization of Marine Ecosystems (BIO 260) - Exam #1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is a watershed?
An area of land where surface water drains down to a single point.
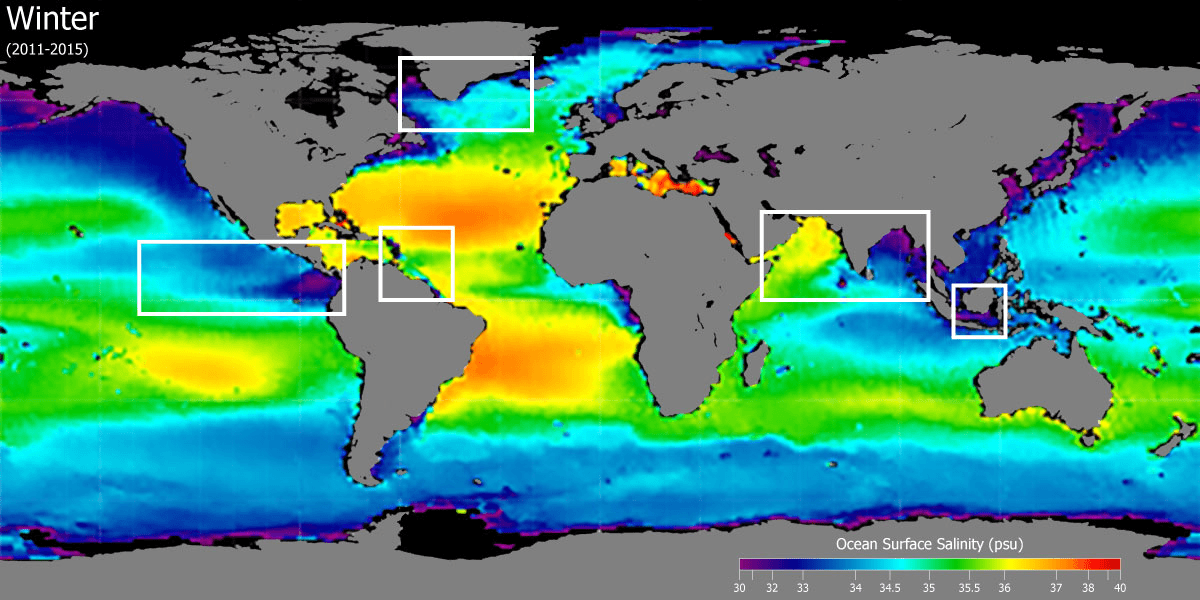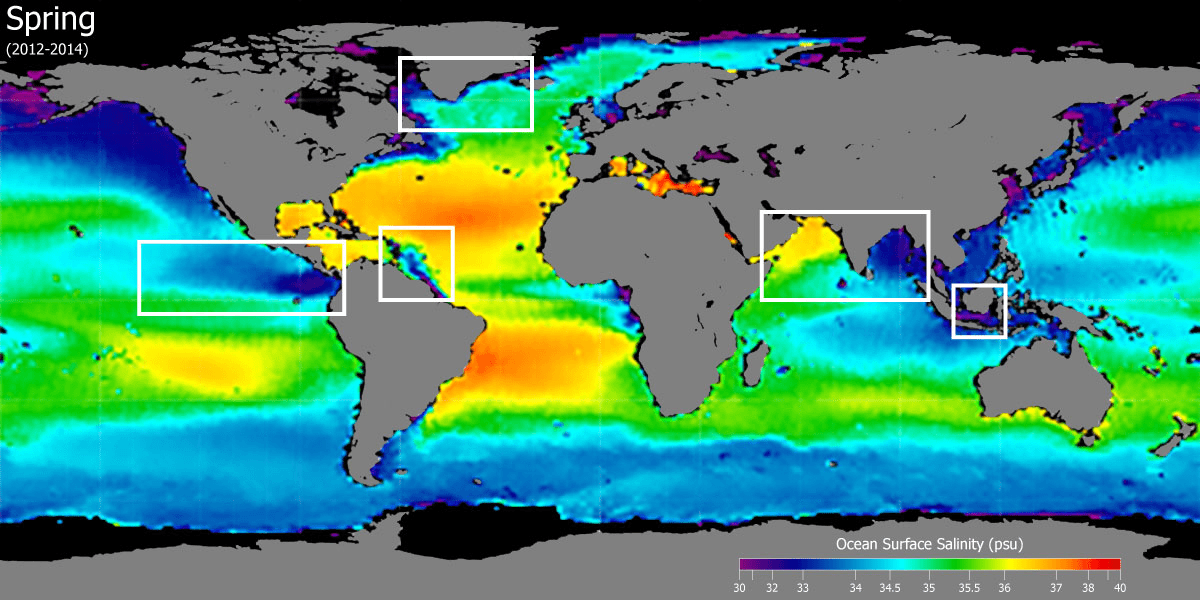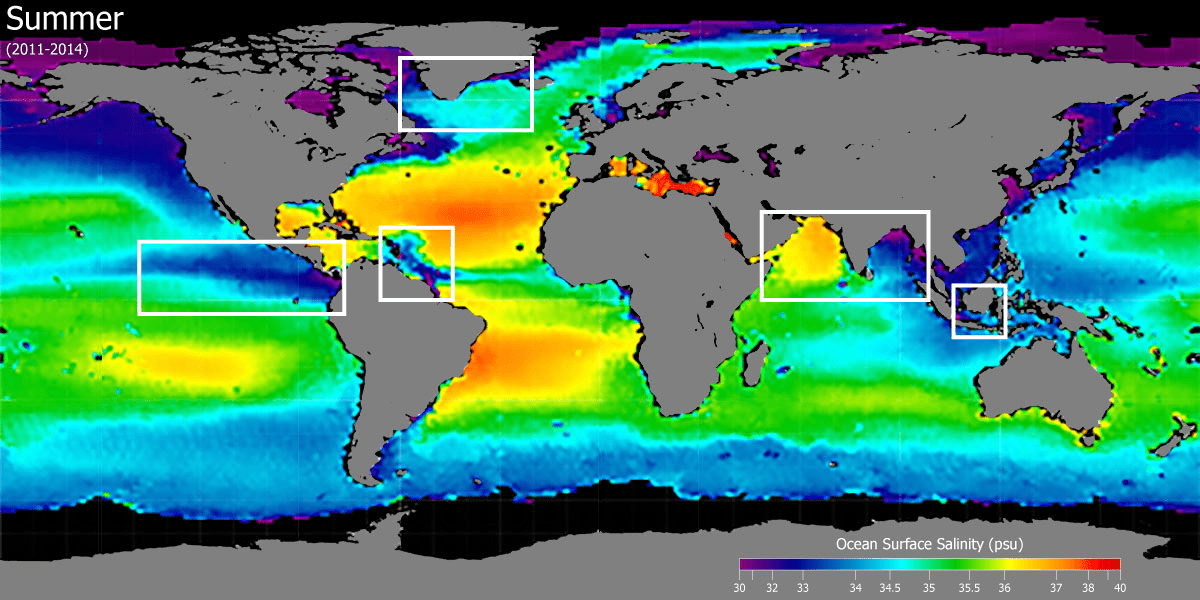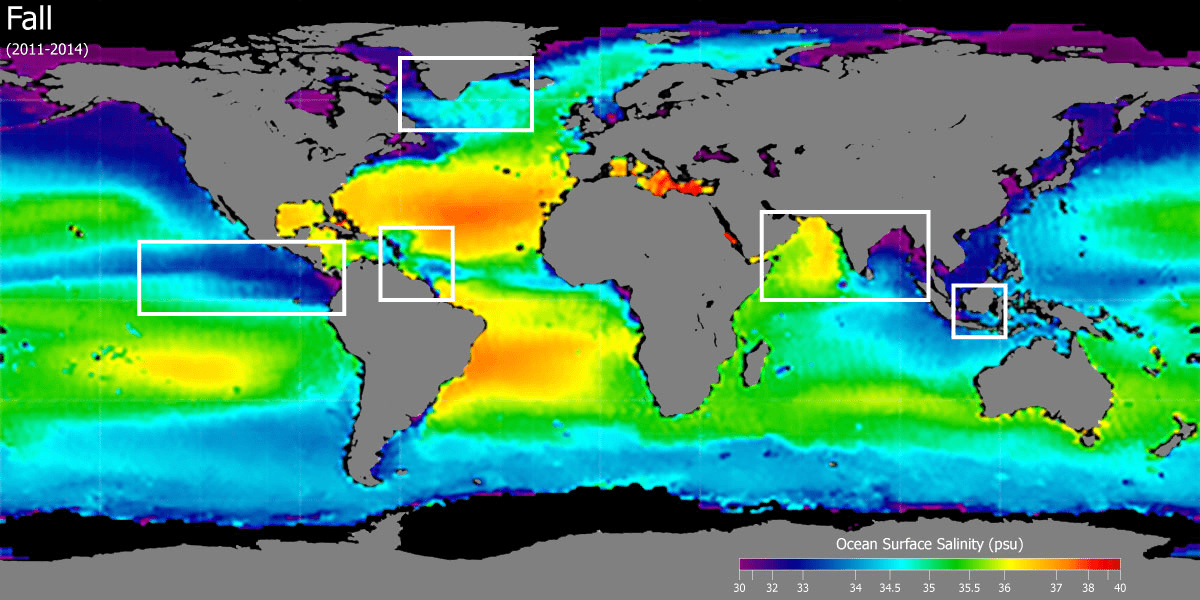
What is salinity?
The amount of salt found in 1000 grams of water (ppt).
What is the global mean salinity?
35 ppt
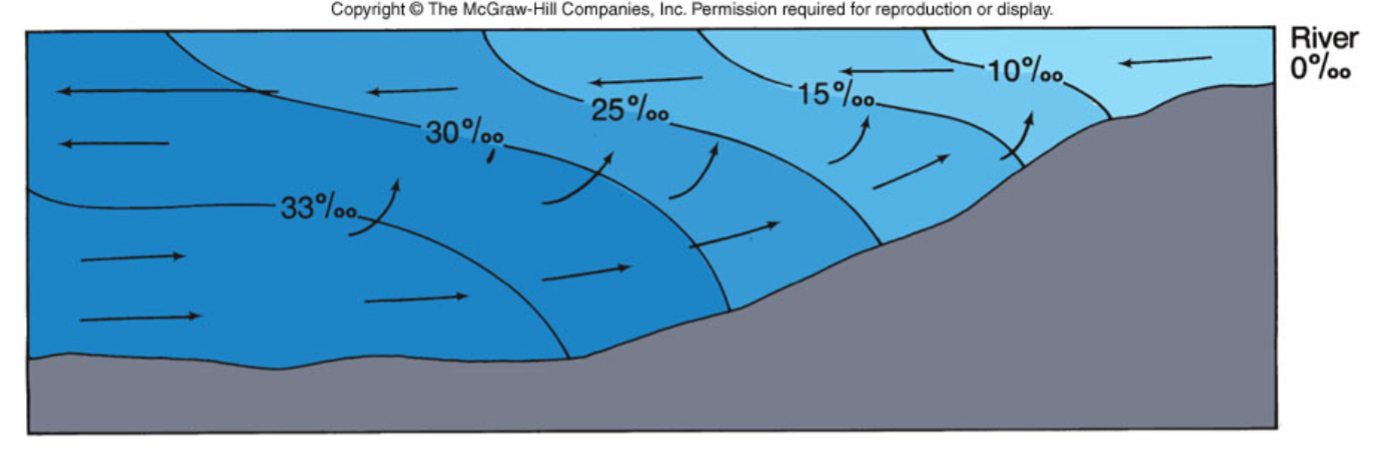
What does a partially mixed estuary look like?
What is a perihelion?
The point in orbit at which the earth is closest to the sun.
What is an epihelion?
The point in orbit at which the earth is farthest away from the sun.
Explain how GPS works.
Currently 31 satellites
Orbiting 20,000 km above the Earth
12-hour circular orbits
Satellites transmit signals that a receiver uses to calculate its distance from each satellite
1 Nautical Mile = ___
One minute of arc length of longitude or latitude at the equator; 1852 m; 1.15 mi
Decimal Degrees = ___
Whole number of degrees, plus minutes divided by 60, plus seconds divided by 3600
A value in decimal degrees to five decimal places is precise to ___ meters at the equator.
1.1
What is the Prime Meridian?
The 0-degree line of longitude that divides Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres
Longitude in the West is recorded as a ___ value.
Negative
What is a primary coastline?
Coastline shaped by non-marine processes
Erosion
Terrestrial processes
Glacial processes
Riverine processes
Sediment Deposition
Volcanos
Uplift
What is a secondary coastline?
Coastline shaped by marine processes
Erosion from marine processes
Marine sediment deposition
Alteration by organisms
What is a glacial coast?
A coastline that is currently, or has been in the past, directly influenced by glacial ice or ice sheets.
Formed by glacial scouring
U-shaped in cross section
Common in Norway, Greenland, New Zealand, Chile, and Alaska
What is a drowned river valley?
A river valley that has been submerged by rising sea levels, becoming a coastal estuary or bay
Since the last glaciation the sea level has risen 100 m
Silt deposits from the entire watershed create new land at the river outlet
What are the three types of sediment movement?
Seasonal
Alongshore
Offshore
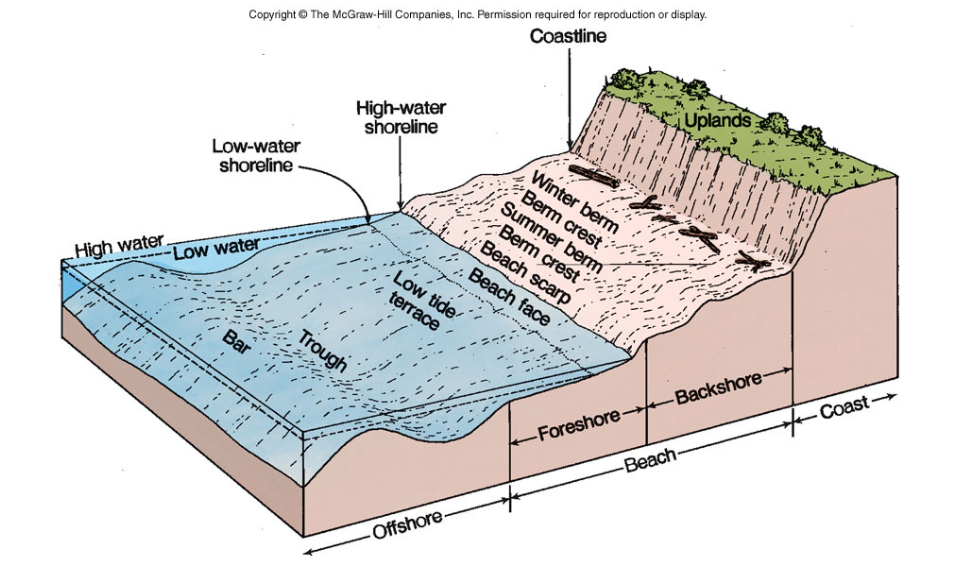
What is seasonal movement of sediment?
The predictable shift of sediment, such as sand, in coastal and riverine environments that occurs due to changing weather and energy patterns over the course of a year
Winter and summer berms
Winter berm exists all year long
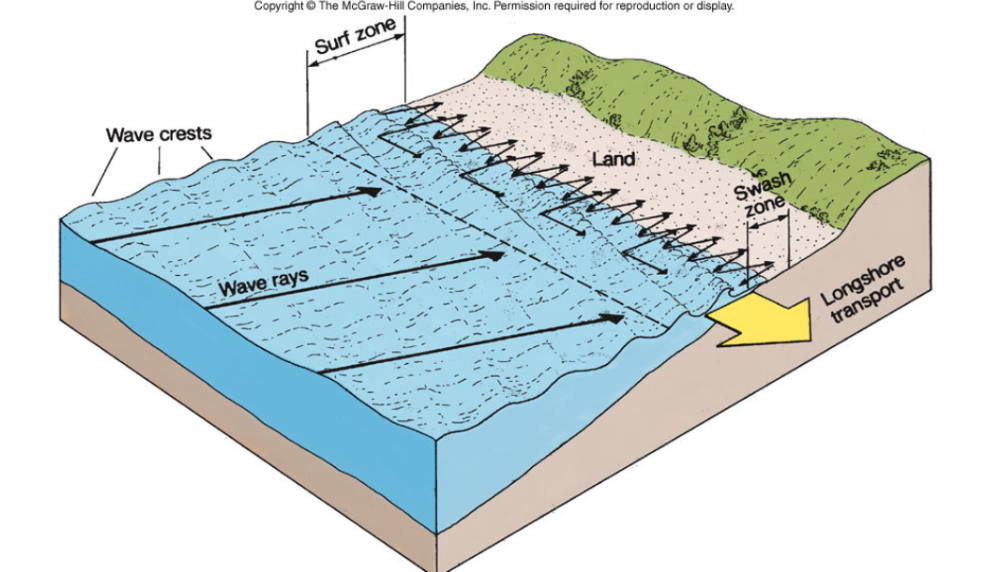
What is alongshore movement of sediment?
The process of sediment transport parallel to the shoreline
Sand is dredged in harbors in order to keep them open
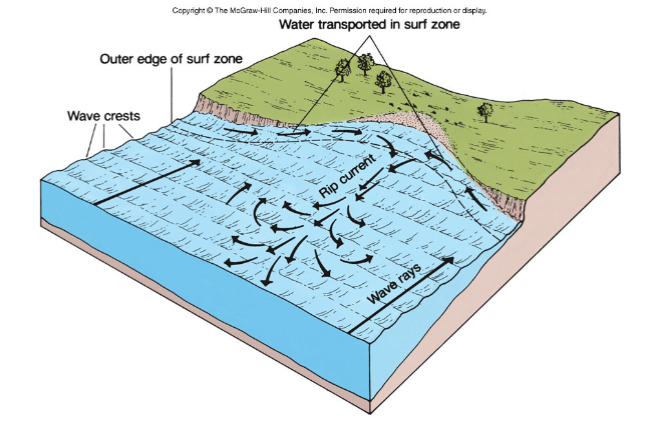
What is offshore movement of sediment?
The transport of sand, silt, and other particles away from the shoreline and into deeper water, often by powerful storm waves, which can erode the beach and form underwater sandbars
Erosion and sediment transport by rip currents and submarine landslides cause underwater canyons
What is an estuary?
A river mouth, fjord, salt bay, or other semi enclosed body of salt water that has a free connection with the ocean and is diluted with fresh water so that the average salinity is less than the adjacent sea
Salt wedge estuary
Well mixed estuary
Partially mixed estuary
Fjords
What is a salt wedge estuary?
Strong river flow
Weak tidal currents
Shallow estuary
Sea water wedge moves back and forth tidally
Ex: Columbia River (WA/OR)
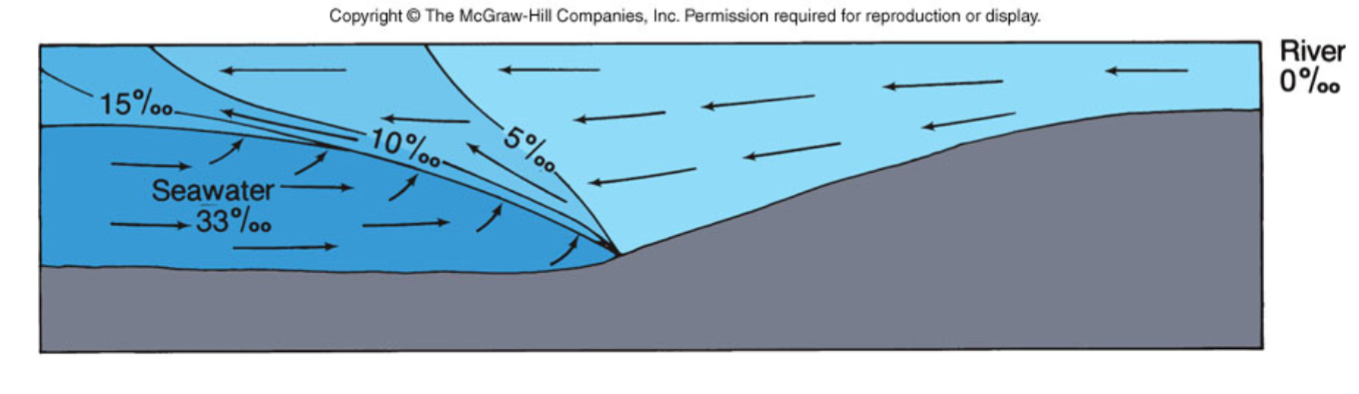
What is a well mixed estuary?
Strong tidal mixing
Low river flow
Characteristic of shallow estuaries
Can become a ‘reverse estuary’ without runoff and small opening to ocean
Ex: Chesapeake and Delaware Bays
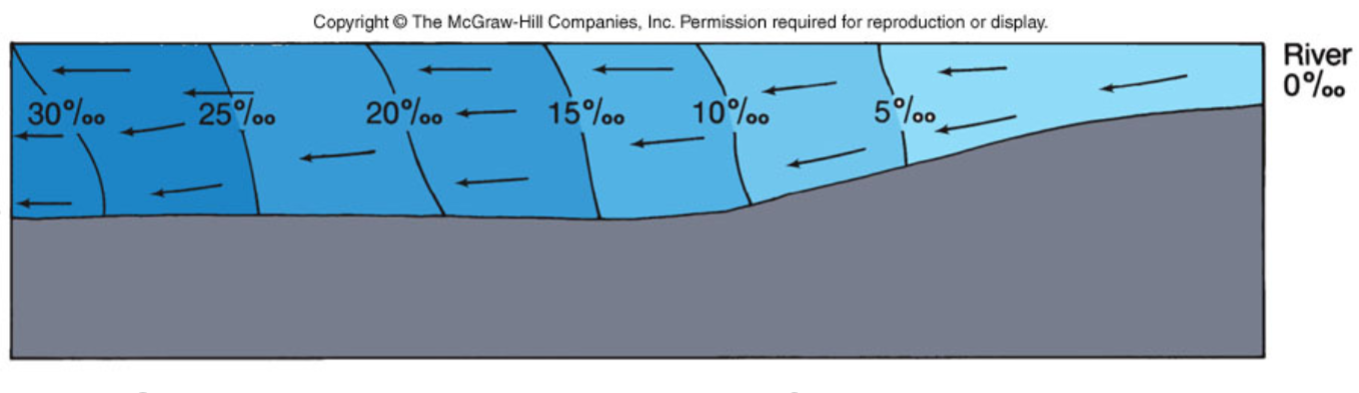
What is a partially mixed estuary?
Strong flow of fresh water
Weak tidal flow
Characteristic of deep estuaries
Ex: San Francisco Bay
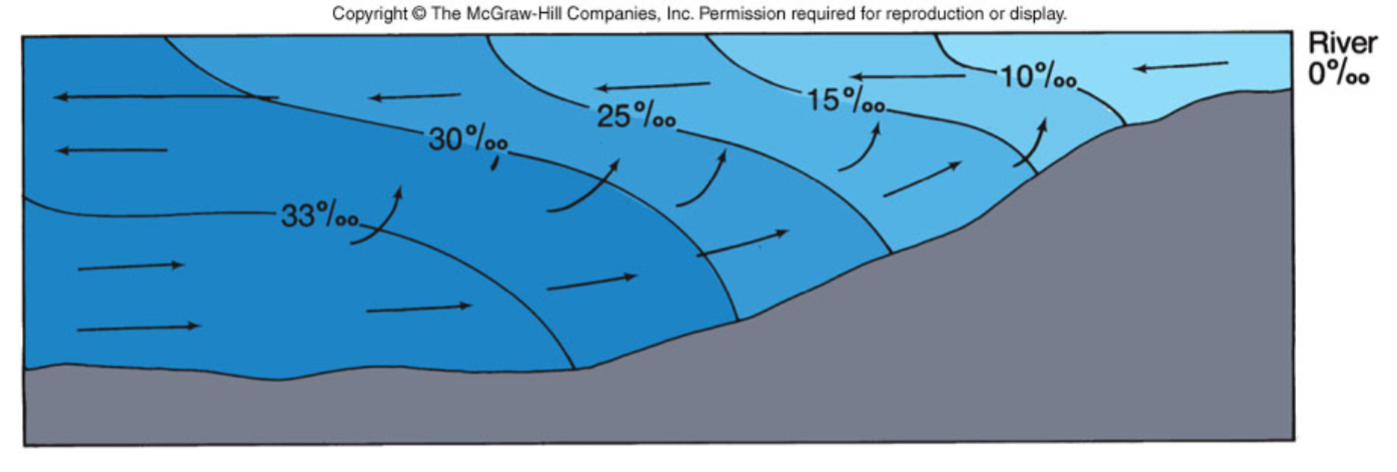
What is a fjord?
Deep, small surface area
High freshwater input
Little tidal mixing
Ex: Milford Sound, New Zealand
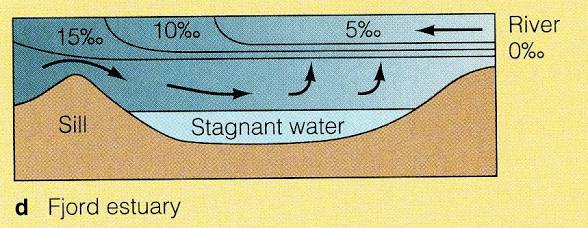
What are the requirements for residency?
Physiological adaptations to fluctuations in…
Temperature
Salinity
Dissolved oxygen
Sedimentation
If biomass is high and biodiversity is low, dominance is (high/low) and evenness is (high/low)
High, low
Non-resident species only occupy areas during ___ conditions
Optimum
What are the five benefits of nurseries?
High primary productivity
Warm temperatures
Protected area
Relatively few predators
Decreased visibility
What are the five orders of fish that are considered the most important in North America?
Salmoniformes (salmon and trout)
Atheriniformes (smelt and silversides)
Gasterosteiformes (sticklebacks)
Clupeiformes (herring)
Perciformes (most other fish)
What are the main five aquatic organism classifications based on life history?
Freshwater
Diadromous
Estuarine residents
Marine migrants
Marine (seasonals and occasionals)
Describe freshwater species.
Low tolerance to increased salinities
Occur in the upstream (sometimes brackish) areas where salinities are generally less than 1 ppt
Describe diadromous species.
Migrate between marine and freshwater (sometimes brackish) environments for spawning purposes
Anadromous: live in marine, spawn in fresh
Catadromous: live in fresh, spawn in marine
Describe estuarine resident species.
Include euryhaline and eurythermal species
Spawn and complete entire life cycle in bays and estuaries
Includes species residing in salt marshes
Describe marine migrant species.
Migrate into estuaries to spawn or to give birth
Ex: sharks, rays, and surfperches
Spawned offshore, recruit into estuaries, and use as nursery during juvenile stage
Ex: some flatfish and guitarfish
Describe marine species.
Eggs, larvae, juveniles, and adults found throughout the nearshore environment
Occasionally found in bays and estuaries
The number of species (increases/decreases) with latitude.
Increases
Variance in the number of species is largely due to ___.
The size of the bay
Define teleconnection.
A phenomenon where distant atmospheric events cause long-term local events
How is the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) an example of teleconnection?
It demonstrates how atmospheric anomalies in one region — specifically, the sea-level pressure difference between Tahiti and Darwin — are correlated with climate conditions in distant areas of the globe
How is the North Pacific Gyre Oscillation (NPGO) an example of teleconnection?
It links large-scale atmospheric pressure fluctuations in the North Pacific to changes in ocean circulation and marine ecosystems across the entire Pacific basin
How is the Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) an example of teleconnection?
It measures the ENSO in the equatorial Pacific Ocean—which then triggers large-scale, remote weather patterns across the globe
How is the Pacific Decadal Oscillation an example of teleconnection?
It describes a long-term linkage between weather patterns in the North Pacific and distant regions, such as North America, over several decades
How is the North Pacific Gyre Oscillation an example of teleconnection?
It is the oceanic expression of the North Pacific Oscillation (NPO), a large-scale atmospheric circulation pattern that links atmospheric and oceanic conditions across distant regions
What is El Niño / Southern Oscillation (ENSO)?
A natural, recurring climate pattern involving changes in Pacific Ocean temperatures and atmospheric pressure, which swings between three phases
El Niño (warm phase)
La Niña (cool phase)
ENSO-Neutral (normal conditions)
Water piles up in the western pacific
Warm water builds near Indonesia and Australia
Cold water upwells in the eastern Pacific
What is an El Niño characterized by (ONI)?
A positive ONI greater than or equal to +0.5°C
What is a La Niña characterized by (ONI)?
A negative ONI less than or equal to -0.5°C
How has the ONI data changed since 1950?
El Niño periods have become longer / more intense
What are the results of a higher metabolic rate?
Faster growth
More food required
Describe Length-frequency Distribution.
Uses peaks and valleys to determine age classes
Not exact — produces wide, overlapping ranges
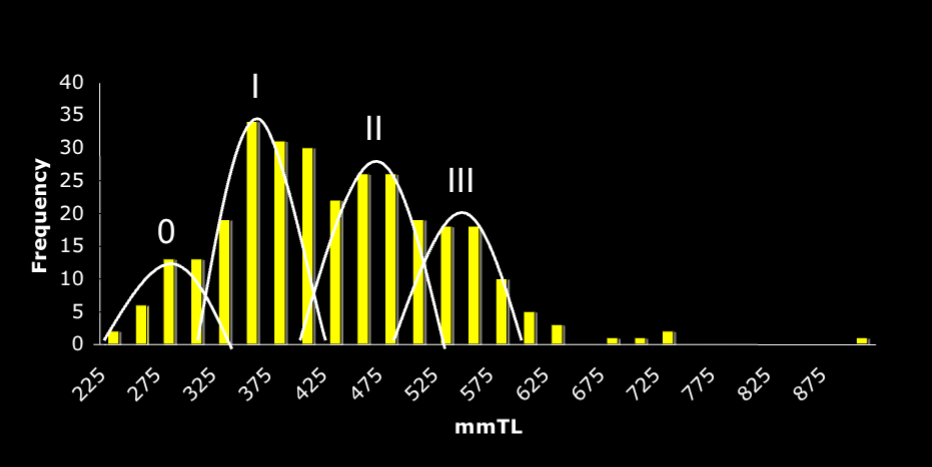
Describe Otolith Reading.
Uses banding patterns created by different nutrient levels
Accurate
Provides more specific information about age
Far more time consuming
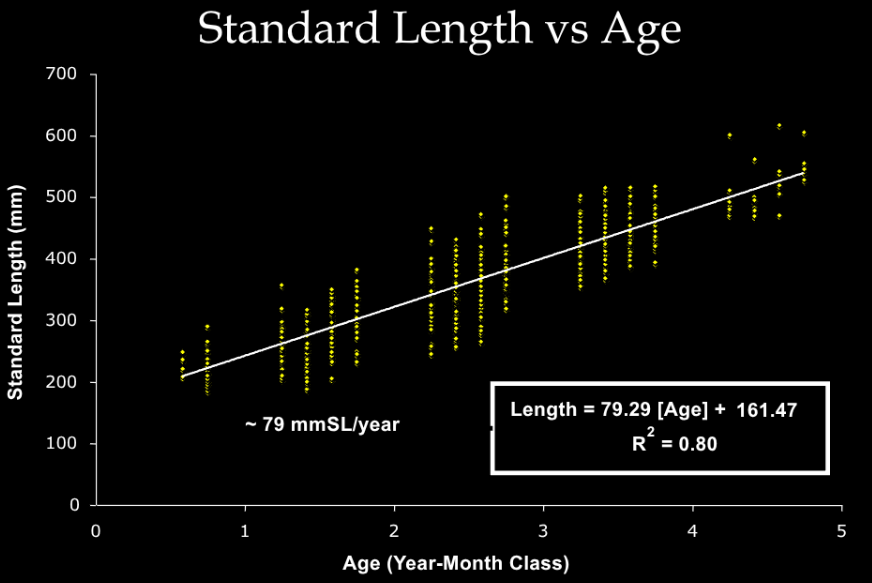
What is the Intertropical Convergence Zone?
The ring of clouds around the equator
Bay and estuary fish thrive in ___ water.
Warm and salty
How does temperature affect salinity?
When temperature increases, there is more evaporation—this leaves behind salt (higher salinity).
How does rainfall affect salinity?
When rainfall increases, there is more freshwater—this makes the water less salty (lower salinity).
Why is there typically low salinity at the equator?
There is constant rainfall inputting large quantities of freshwater.
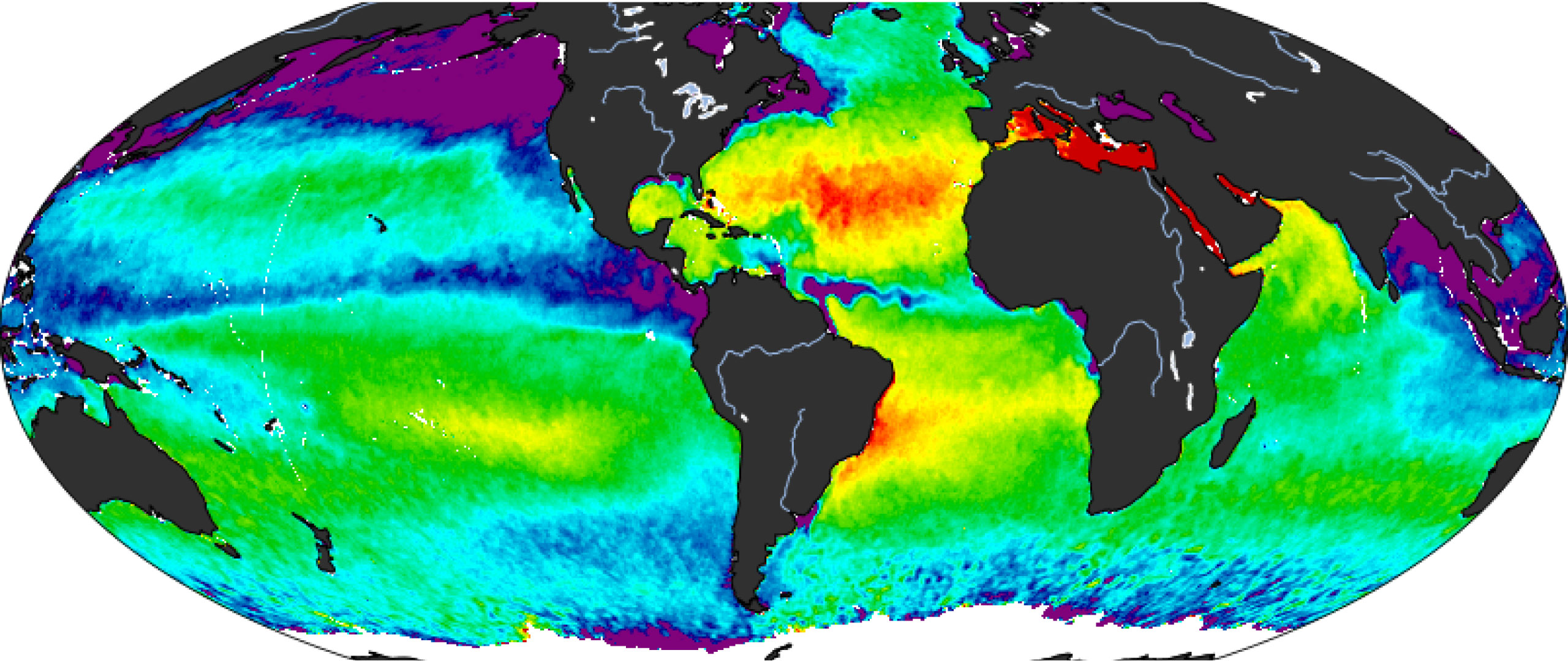
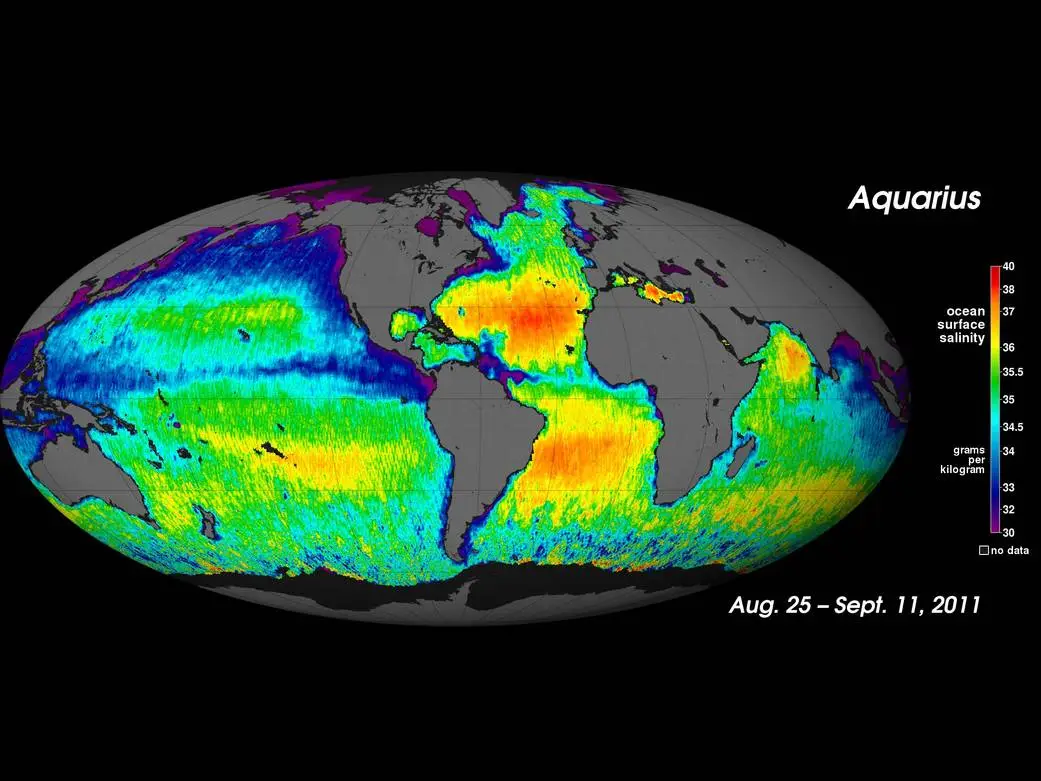
Why might there be low salinity near the North Pole at the end of the summer?
Ice melting at the end of the summer can cause freshwater input.
What is a quiet bay?
Erosion occurring in an estuary, inlet, or bay protected from the full force of open ocean waves by headlands or other landforms
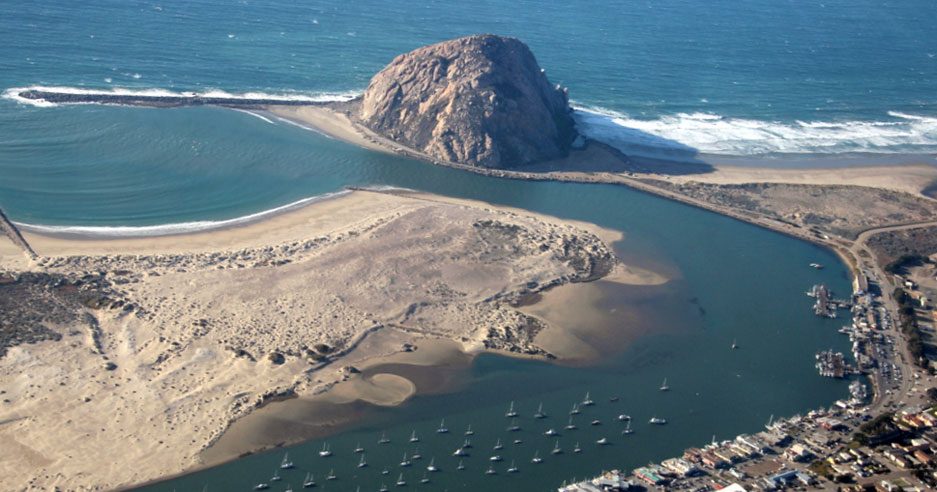

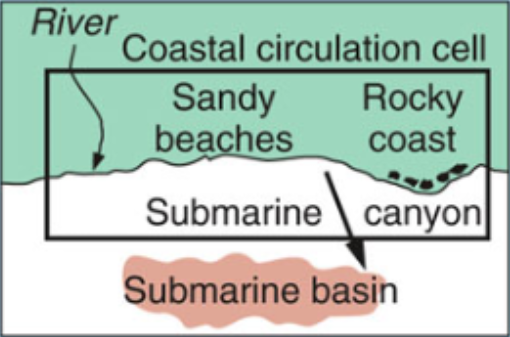
Describe the relationship between rip currents and submarine canyons.
Rip currents form focus points where sediment is pulled into a basin (submarine canyons)
Define a coastal circulation cell.
A relatively self-contained compartment within which sediments circulate
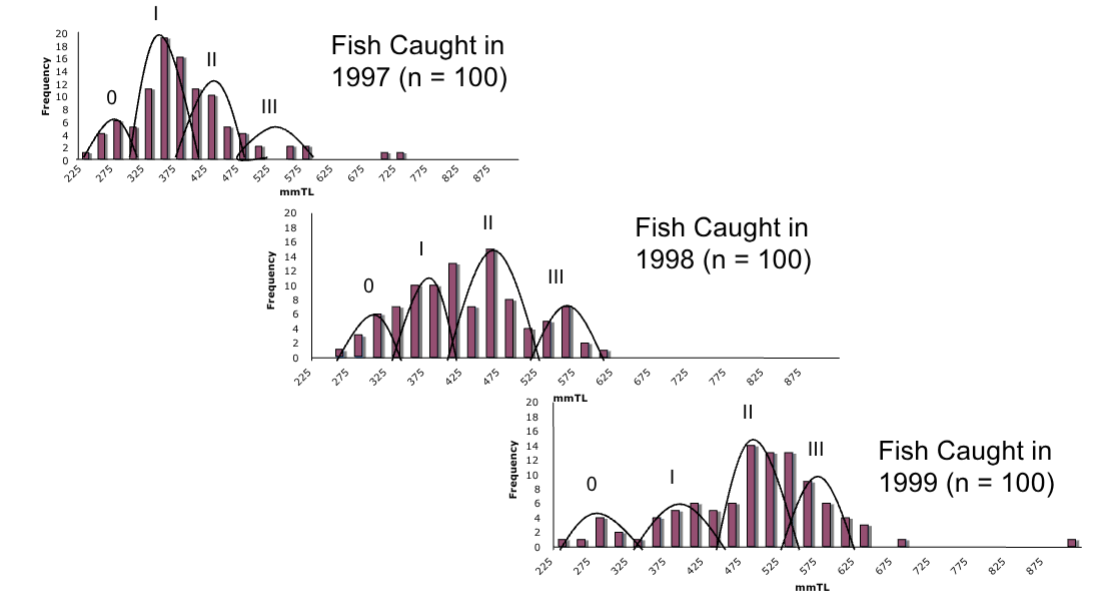
Explain how water temperature affected the growth of juvenile White Sea bass in 1996-2001.
El Niño / La Niña event in 1997-2000
Data was analyzed using Length-frequency Distributions and Otolith Readings
Data indicated accelerated growth in 1996-1997 (high SST)
Data indicated slowed growth in 1998-2001 (low SST)
Describe the movement of sediment/sand over time in the marine environment. Be very thorough, use appropriate terminology, and feel free to use diagrams in your explanation.
Alongshore Movement
The process of sediment transport parallel to the shoreline
Offshore Movement
The transport of sand, silt, and other particles away from the shoreline and into deeper water, often by powerful storm waves, which can erode the beach and form underwater sandbars
Seasonal Movement
The transport of sand, silt, and other particles away from the shoreline and into deeper water, often by powerful storm waves, which can erode the beach and form underwater sandbars
Where would you expect to find higher sea-surface salinity and where would you expect to find lower salinity? Assume it is summer in the northern hemisphere.
Higher salinity is found in the subtropical high-pressure zones due to high evaporation and low rainfall, while lower salinity is found in the Arctic regions and near the equator from high rainfall and melting ice