Oral histology LO3 part 1
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
1. Initiation stage, 2. Bud stage, 3. Cap stage, 4. Bell stage, 5. Stages of apposition and maturation
What are the 5 stages of tooth development in order?
Odontogenesis
The continuous process of physiological changes. 5 stages: initiation, proliferation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and maturation.
Embryonic and fetal stages
Primary teeth begin to develop during these 2 stages of pregnancy:
Fetal period
Most of the permanent teeth begin forming during this period of pregnancy:
Anterioposteriorly
Teeth develop in this direction, coinciding with the growth of the mandible.
Mandibular anteriors
What are the 1st teeth to develop?
Initiation stage
This stage of tooth development takes place in the 6th-7th week. The main process of odontogenesis involved is induction. The ectoderm lining the stomodeum gives rise to oral epithelium and then to dental lamina; adjacent to deeper ectomesenchyme, which is influenced by the neural crest cells. Both tissue types are separated by the basement membrane.
Bud stage
This stage of tooth development takes place in the 8th week. The main process of odontogenesis involved is proliferation. Growth of dental lamina into bud shape that penetrates growing ectomesenchyme.
Cap stage
This stage of tooth development takes place in the 9th-10th week. The main processes of odontogenesis involved are proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis. The formation of tooth germ as enamel organ forms into a cap shape that surrounds the inside mass of dental papilla, with an outside mass of dental sac, both from the ectomesenchyme.
Bell stage
This stage of tooth development takes place in the 11th-12th week. The main processes of dentinogenesis involved are proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis. Differentiation of enamel organ into bell shape with 4 cell types and dental papilla into 2 cell types.
Anodontia (missing teeth)
The lack of initiation within the dental lamina results in the absence of a single tooth (partial) or multiple teeth (complete) produces ———————.
Hypodontia
Partial anodontia is known as ———————.
Permanent max laterals
These teeth are most commonly affected by hypodontia.
3rd molars
These are the teeth 2nd most likely to be affected by hypodontia.
Mand 2nd premolars
These are the teeth 3rd most likely to be affected by hypodontia.
Ectodermal dysplasia
Hypodontia can be associated with the syndrome of ——————— ——————— because many parts of the tooth are indirectly or directly of ectodermal origin.
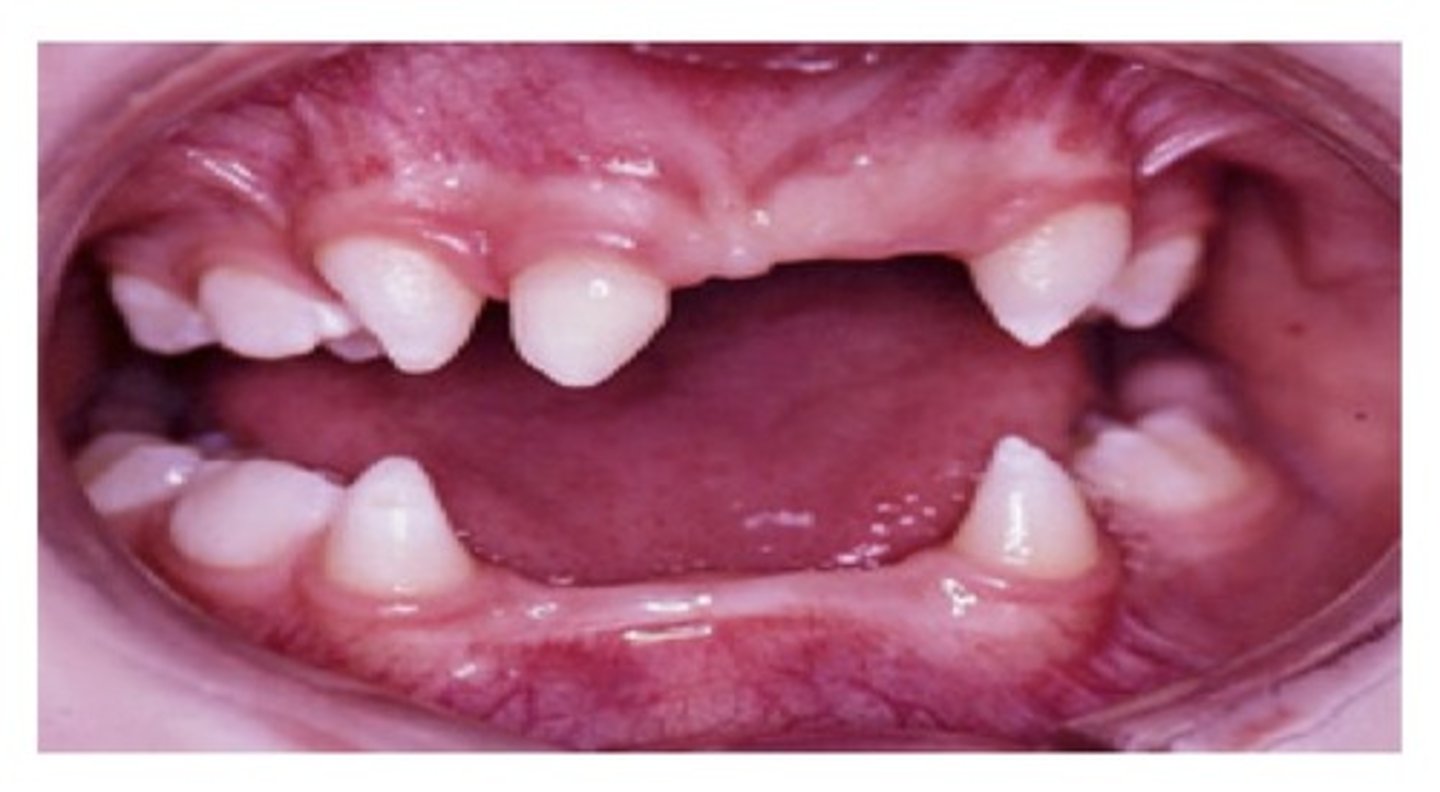
Supernumerary teeth
Abnormal initiation may result in the development of one or more extra teeth or —————————— teeth (hyperdontia). These extra teeth are initiated from the dental lamina and have hereditary etiology.
Tooth germ
In the bud stage: each bud from the dental lamina, along with the surrounding ectomesenchyme, will develop into a:
Microdontia or macrodontia
Abnormal proliferation in the bud stage can lead to partial or total:
Hypodontia or hyperdontia
Developmental disturbances in the initiation stage can cause partial or total:
Shape
Morphodifferentiation = the change of:
Dental papilla
The pulp and dentin are inside of this part of a developing tooth:
Dental sac (follicle), dental papilla, and enamel organ
The tooth germ is comprised of these 3 parts:
Enamel organ
In the cap stage, what was once called the "dental lamina", is now called the:
Enamel
During the cap stage, a depression results in the deepest part of each tooth bud of dental lamina and forms a cap, or enamel organ. The innermost margin of the cap shape of the enamel organ signals the tooth's future crown form. In the future, the enamel organ will produce ————— for the outer surface of the tooth.
Dental papilla
A part of the ectomesenchyme deep to the buds has now condensed into a mass within the concavity of the cap of the enamel organ. This inner mass of ectomesenchyme is now called the:
Dentinoenamel junction (DEJ)
During the cap stage, a basement membrane still exists between the enamel organ and the dental papilla and is the site of the future:
Dental sac
Condensed mass of ectomesenchyme surrounding the outside of the enamel organ— future cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone.
Dens in dente (tooth in a tooth) or dens invaginatus
During the cap stage, the enamel organ may abnormally invaginate into the dental papilla, resulting in this developmental anomaly:
Gemination
This occurs as the single tooth germ tries unsuccessfully to divide into 2 tooth germs, which results in a large single-rooted tooth with a common pulp cavity.
Fusion
This developmental anomaly results from the union of 2 adjacent tooth germs, possibly resulting from pressure in the area, which leads to a broader, falsely macrodontic tooth similar to gemination. There are 2 pulp cavities and there is 1 fewer tooth in the dentition.
Successional dental lamina
Initially formed permanent teeth appears as an extension of the dental lamina into the ectomesenchyme lingual to the developing primary tooth germs. It's site of origin is called the:
Succedaneous
Permanent teeth formed from successional dental lamina are called:
Bell stage
Crown morphology (the shape of the crown) is expressed in this stage of tooth development.
Outer enamel epithelium (OEE)
This is the protective barrier for the rest of the enamel organ during enamel production. Bell stage.
Inner enamel epithelium (IEE)
This layer, in the bell stage, differentiates into enamel-secreting cells called ameloblasts.
Stellate reticulum and stratum intermedium
Between the OEE and the IEE are 2 layers that support the production of enamel.
Odontoblasts (dentin forming cells)
In the bell stage, the outer cells of the dental papilla differentiate into these cells.
Primordium of the pulp
In the bell stage, the inner cells of the dental papilla differentiate into cells that form the:
Apposition stage and/or maturation stage
The late bell stage is also known as these 2 names:
Apposition
This is one of the final stages of odontogenesis. The enamel, dentin, and cementum are secreted in successive layers. They are initially secreted as a matrix that is partially calcified. The framework for later calcification (mineralization).
Maturation
This is the final stage of odontogenesis. ——————— is reached when the dental tissue types are fully mineralized.
Preameloblasts
IEE in the bell-shaped enamel organ differentiate into ——————————. The —————————— induce dental papilla cells to differentiate into dentin forming cells (odontoblasts) and then differentiate themselves into cells that secrete enamel (ameloblasts).
Dentinogenesis
Odontoblasts are lined up adjacent to the basement membrane but in a mirror image orientation compared with preameloblasts. The odontoblasts now begin the process of——————————, which is the apposition of dentin matrix, or predentin, on their side of the basement membrane.
1. Collagen matrix formation, and 2. Calcification with deposition of calcium phosphate (hydroxyapatite) crystals.
There are 2 phases
Cusp or incisal edge
The crown formation starts at this part of the tooth:
Amelogensis
After the formation of predentin and the basement membrane disintegrates, the ameloblasts (used to be preameloblasts) benign this process, or the apposition of enamel matrix.
25%
Initial enamel matrix (amelogen) is ——% mineralized.
95%
During maturation an influx of mineral as and loss of organic matter and water takes place. 70% of enamel mineralization result of growth in size of crystals. Mature enamel is ——% mineralized.
Odontoblastic processes
The odontoblasts, leave attached cellular extensions in the length of the predentin called:
Dentinal tubule
The odontoblastic processes is contained in a mineralized cylinder, called the:
Pulp tissue
The cell bodies of odontoblasts will remain within the ———— tissue.
Enamel dysplasia
This is a developmental disturbance during the stages of apposition and maturation. ————— ———————, factors interfere with the metabolic processes of the ameloblasts and/or maturation of enamel.
Local enamel dysplasia
This is a disturbance either the metabolic process of the ameloblasts or the maturation of enamel that results from something like a trauma or an infection occurring in a small group of ameloblasts.
Systemic enamel dysplasia
This is a disturbance either the metabolic process of the ameloblasts or the maturation of enamel involving larger numbers of ameloblasts and may result from a traumatic birth, systemic infections, nutritional deficiencies, or dental fluorosis.
Enamel hypoplasia
This is the reduced quantity of enamel matrix. Results in pitting, notches, and grooves.
Enamel hypocalcification
This is the reduced quality of enamel maturation. Results in teeth looking opaque, yellow, and stained.
Dentin dysplasia
————— ———————, or the faulty development of dentin, can result from an interference with the metabolic processes of the odontoblasts during dentinogenesis.
Hypocalcified enamel
If enamel does not go through the maturation stage of development, what will be the clinical result?