IB Biology Year 1 - Inheritance
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
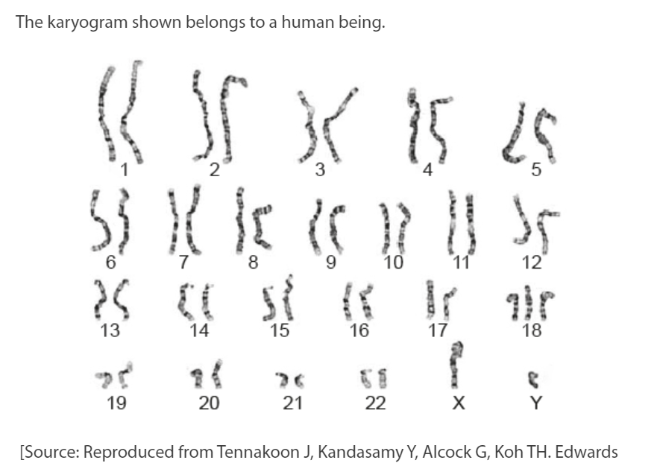
Male with genetic disorder
At which stage of meiosis are bivalents formed?
Prophase I
In humans, male pattern baldness is caused by a recessive sex-linked gene found only on the X chromosome. If a father who does not have male pattern baldness and a mother who is a carrier for it have a child, what is the probability that the child will develop male pattern baldness in adulthood?
25%
Huntington’s disease can develop in middle age and leads to death of brain cells. It is carried by an autosomal dominant gene. What can be deduced about a man who has the disease?
Female grasshoppers have XX sex chromosomes and males have XO, signifying a single X chromosome. An X chromosome will be present in only half of the male gametes. A recessive mutation is induced by radiation in the X chromosome of a male. In which generation will the effect of this radiation appear?
F2 Males
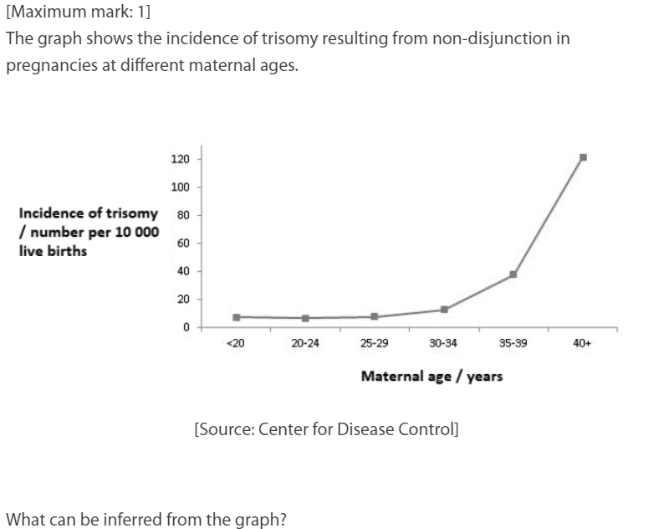
The incidence of three copies of a chromosome increases the most from age 35
A woman with blood type A has three children with a man who has blood type AB. The first child has blood type B. What is the probability that the second child born to the couple will have blood type AB?
25%
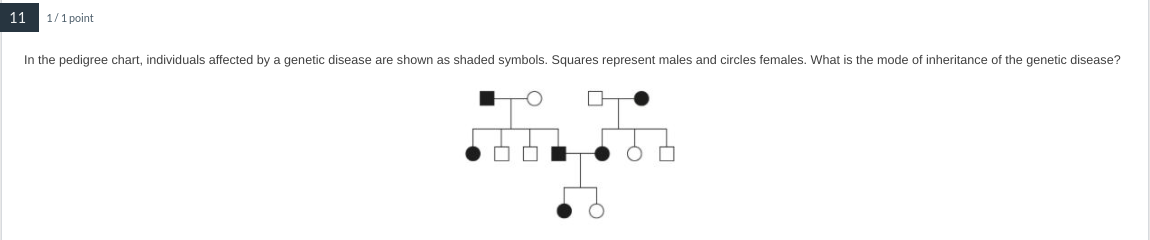
Inherited as a dominant autosomal allele
Tall heterozygous pea plants were crossed and the resulting seeds grown. Out of 360 plants, 270 were tall and 90 dwarf. What describes the expected genotypes resulting from the cross?
All dwarf plants were homozygous.
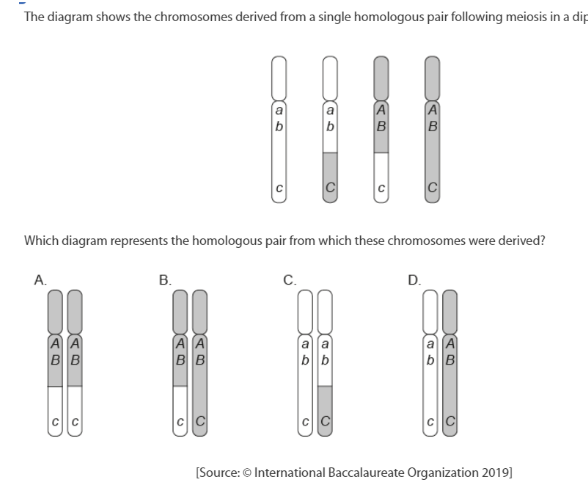
D
Which process occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
Movement of homologous chromosomes to opposite ends
There’s a variation in height of adult humans. What can explain the variation?
Polygenic inheritance and nutrition
Which statement is valid regarding chromatids?
Chiasmata form between non-sister chromatids.
Which event happens in meiosis II but not in meiosis I?
Sister chromatids move to opposite poles.
In a plant, dark leaves are dominant to pale leaves and yellow seeds are dominant to white seeds.
A heterozygous dark-leaved plant with yellow seeds was crossed with a pale-leaved plant with white seeds. A large number of offspring were produced. They were either dark-leaved with yellow seeds or pale-leaved with white seeds in equal number.
What is the most likely cause of this pattern?
The two genes are linked.
Red eyes are dominant to white eyes in flies. Long wings are dominant to short wings. In a cross between two heterozygous red-eyed, long-winged flies, there were 152 flies with red eyes and long wings, 37 red-eyed short-winged flies, 43 white eyed long winged flies, and 24 flies with white eyes and short wings. Which statistical test can be used to determine if the genes for eye color and wing length are linked or not?
chi-square test
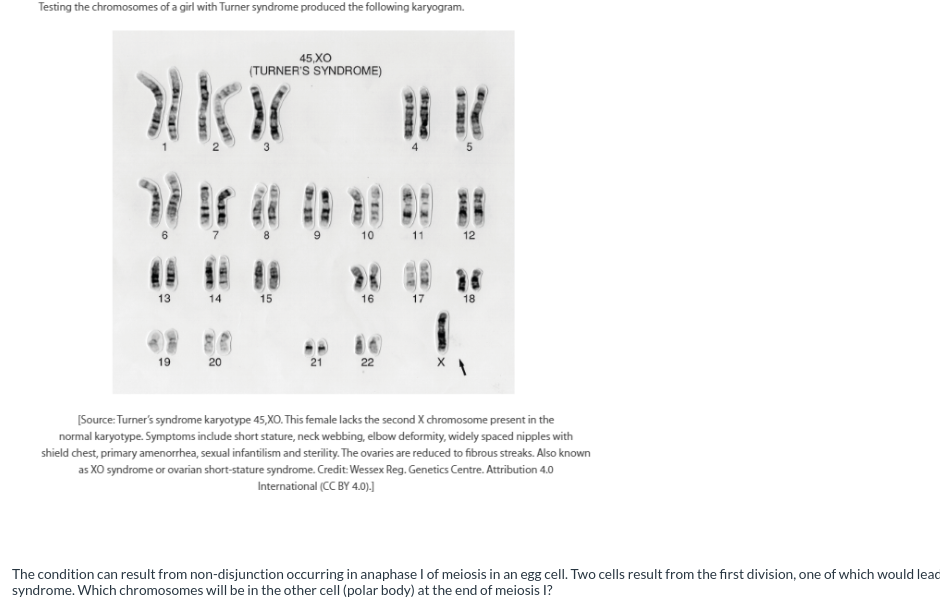
22 autosomes and XX
Two genes A and B are linked together as a genotype shown below in linkage notation. The genes are so close together on the chromosome that crossing over very rarely occurs. Which of the following statements is true of the gametes produced by an organism with this genotype?
The genes for pollen shape and flower color are located on the same chromosome as each other. Purple (P) and long pollen (L) are dominant to red (p) and round pollen (l). What are the possible gametes if the parents are PPLL × ppll?