Visual Pathways: From Eye to Brain in Perception
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the two types of photoreceptors in the retina?
Rods and cones.
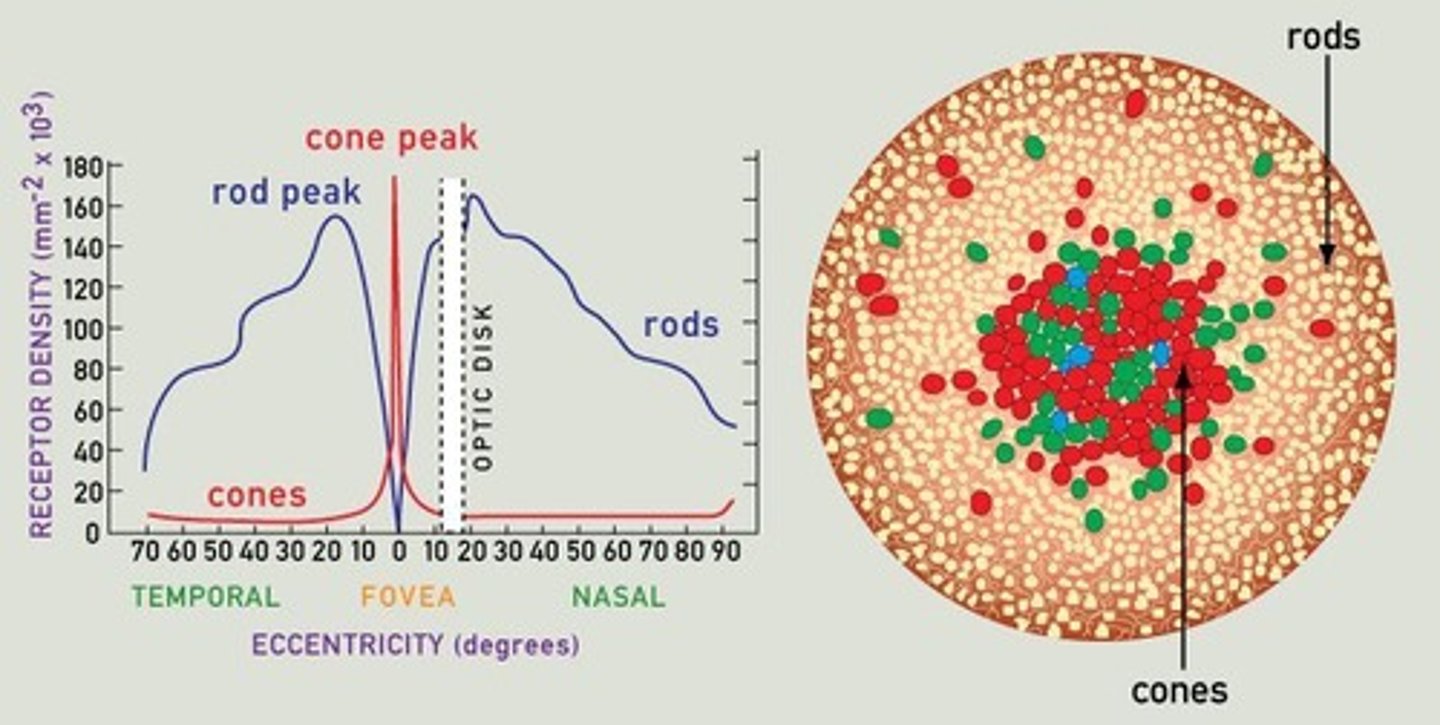
What is the convergence ratio of rods to ganglion cells?
About 100 rods project to a single ganglion cell.
What is the convergence ratio of cones to ganglion cells?
About 1-3 cones project to a single ganglion cell.
How do cones contribute to ganglion cells despite being a small fraction of the retina's receptors?
Cones project to about half of the ganglion cells in the optic nerve.
What is cortical magnification in the context of V1?
Cortical magnification refers to the disproportionate representation of the fovea in the visual field map of V1.
What types of cells create excitatory and inhibitory connections to ganglion cells?
Amacrine, bipolar, and horizontal cells.
What is lateral inhibition?
A process where adjacent receptors are connected by inhibitory synapses, enhancing contrast detection.
What types of receptive fields do ganglion cells have due to lateral inhibition?
Center-surround receptive fields.
What are the two types of center-surround receptive fields?
Center-on/surround-off and center-off/surround-on.
What phenomenon do ganglion cells help explain regarding visual perception?
They act as contrast detectors, responding most to high contrast visual stimuli.
What is the significance of Mach bands in visual perception?
Mach bands illustrate how edges are over-perceived due to lateral inhibition.
What is the function of the optic chiasm in visual processing?
It is where signals from each half of the retina meet, with half going to the ipsilateral LGN and half to the contralateral LGN.
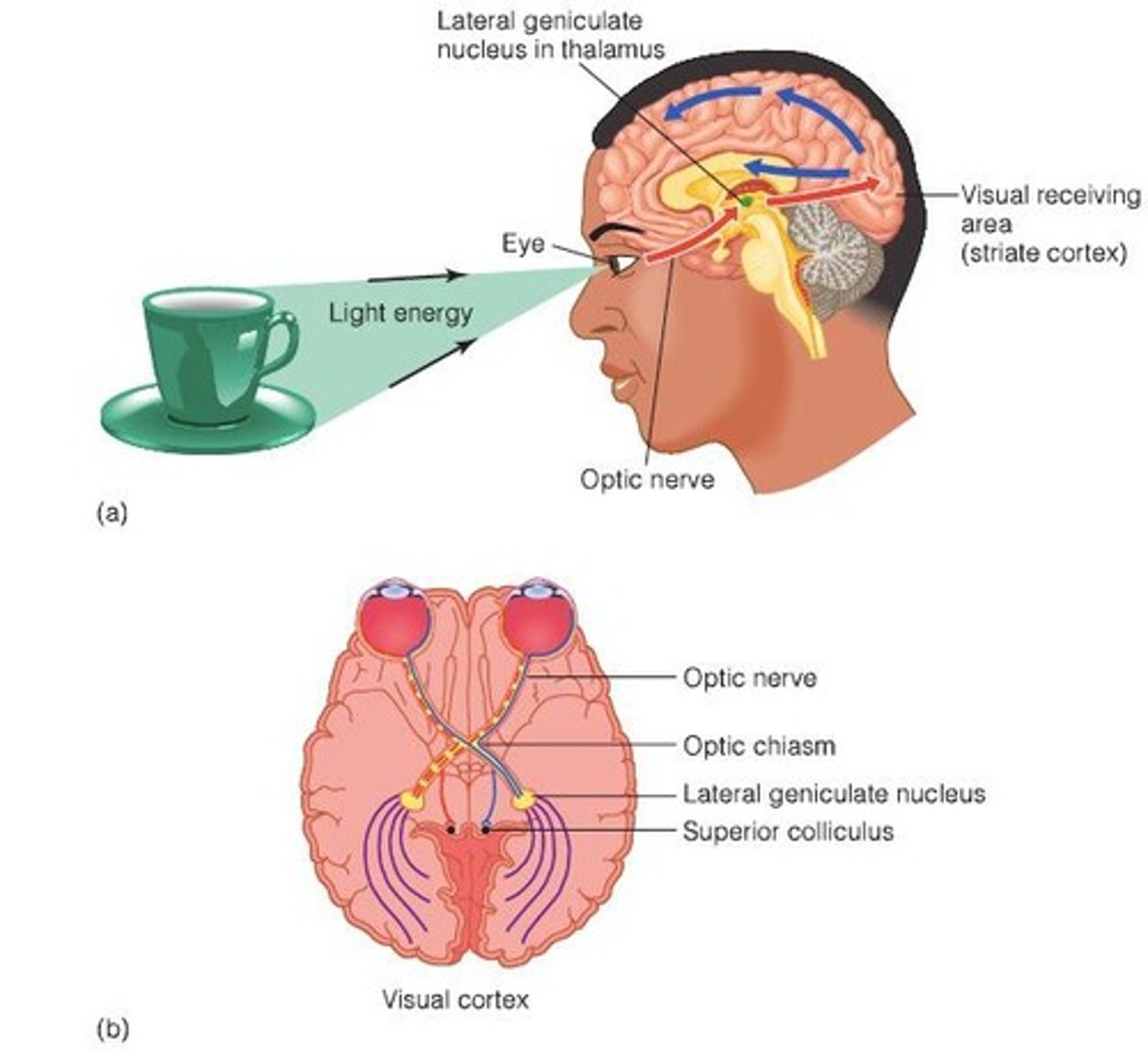
What percentage of ganglion cell fibers end up at the LGN?
About 90%.
What are the two types of layers in the LGN?
Magnocellular layers (1 and 2) and Parvocellular layers (3, 4, 5, and 6).
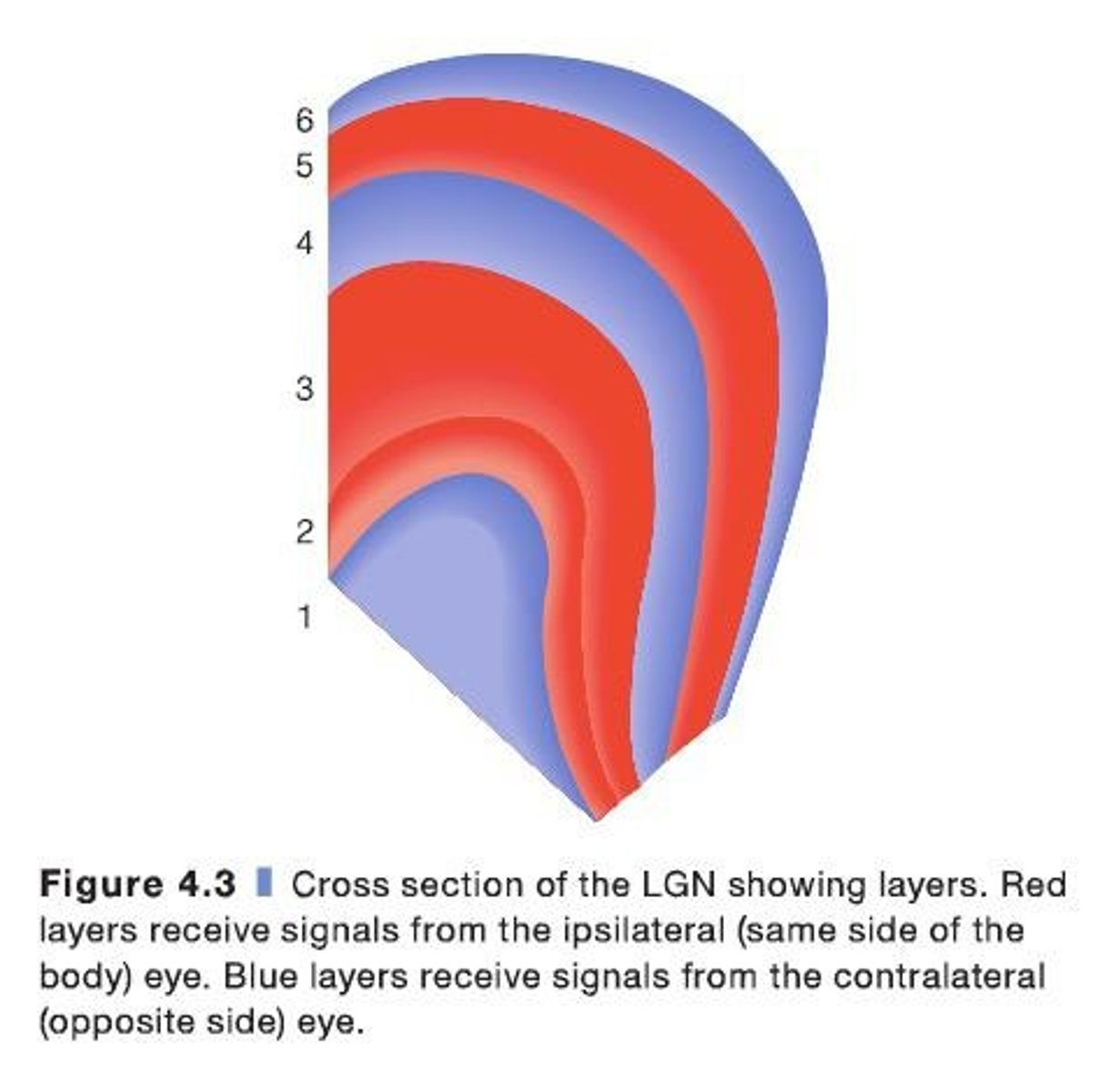
What is the primary function of the magnocellular layers in the LGN?
They primarily process inputs from rod receptors, important for motion and depth perception.
What is the primary function of the parvocellular layers in the LGN?
They primarily process inputs from cone receptors, important for color and fine detail.
What is the retinotopic organization of the LGN?
The organization of LGN is retinotopic within each layer and aligned across layers.
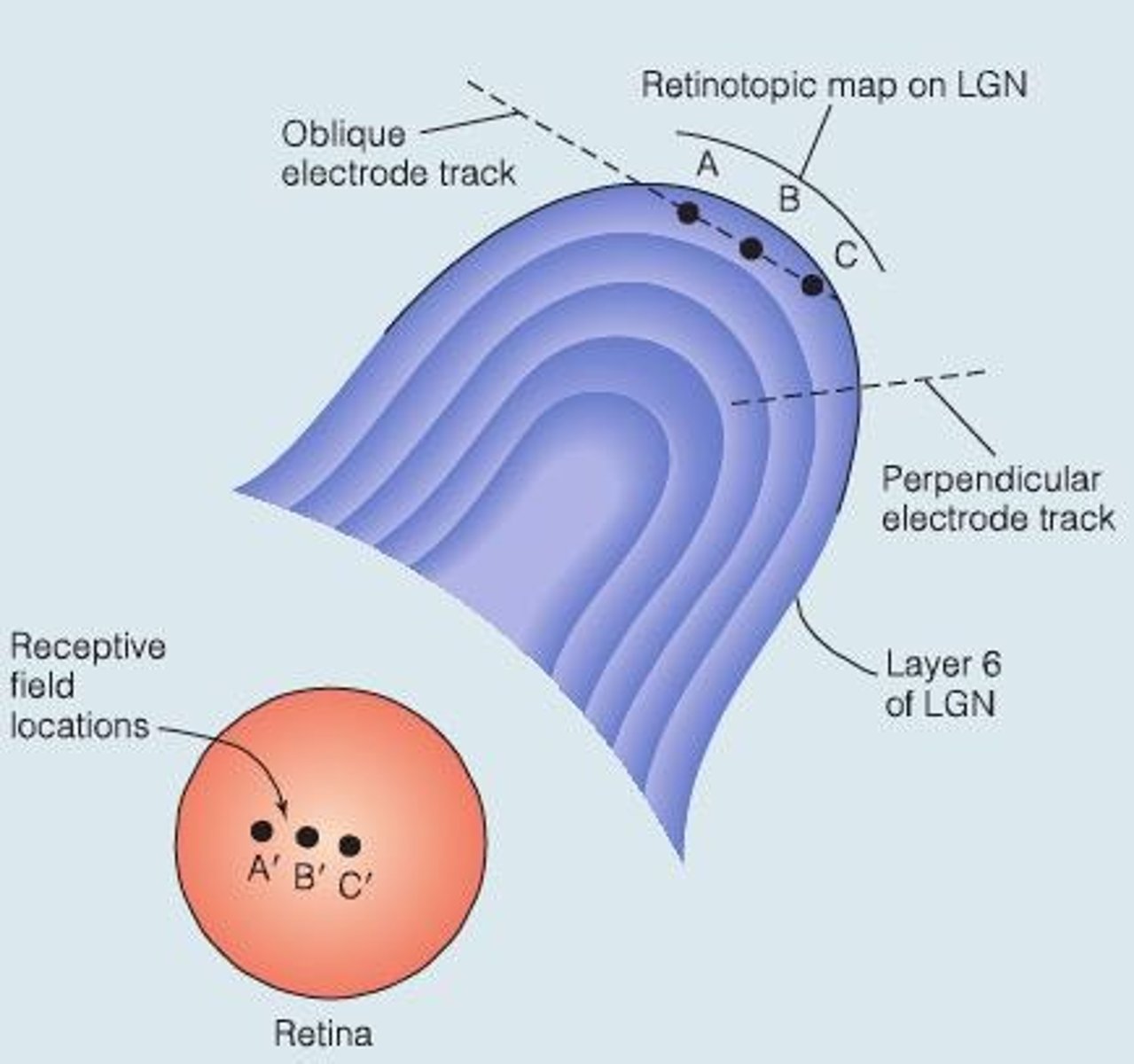
What feedback does the LGN receive from the cortex?
Top-down signals that can modulate attention.
What did Hubel and Wiesel discover about neurons in V1?
Most V1 neurons respond best to oriented edges rather than just contrast.
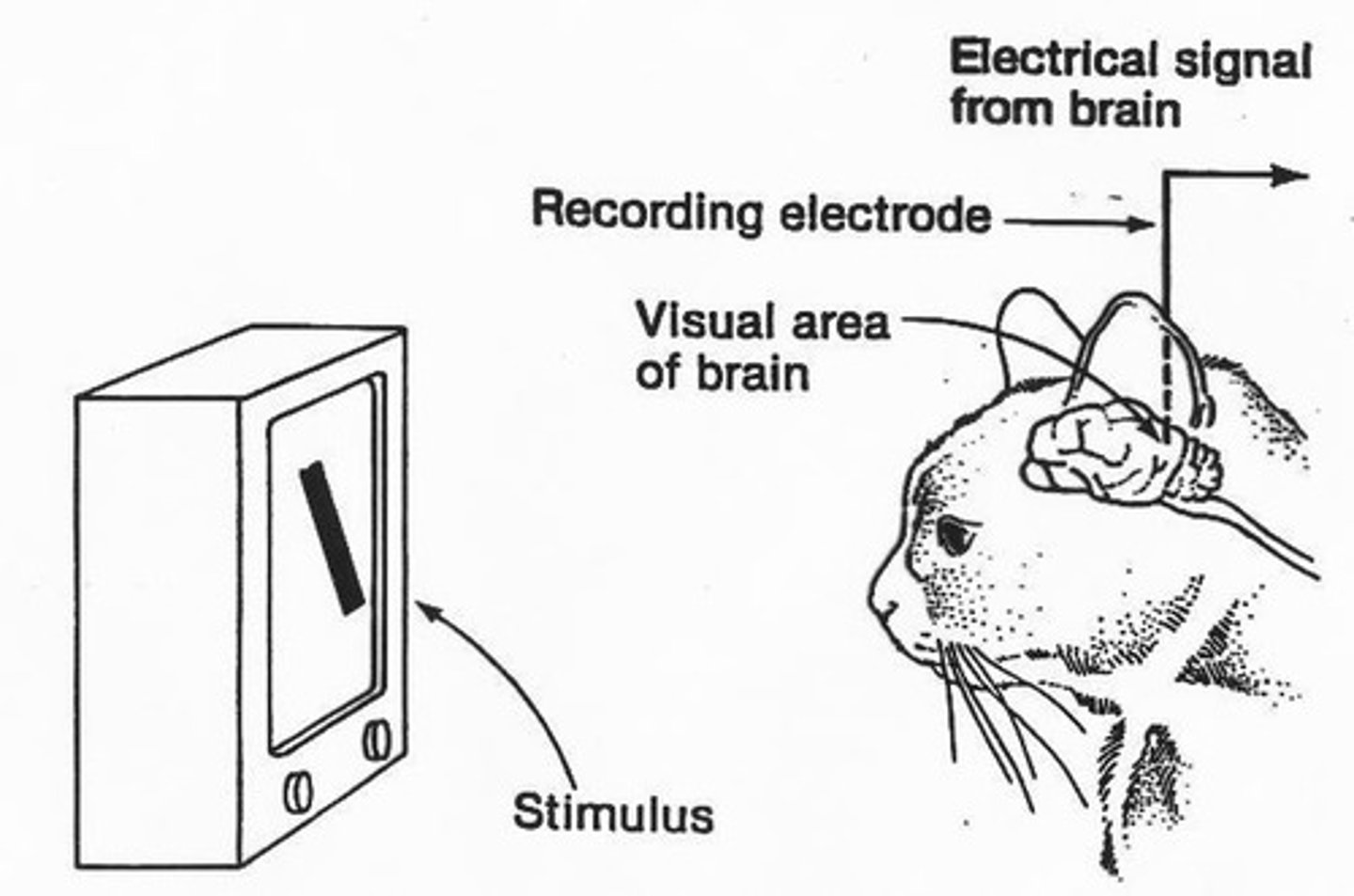
What are the three types of neurons identified by Hubel and Wiesel in V1?
Simple cells, complex cells, and hypercomplex cells.
What do simple cells in V1 respond best to?
Bars of a particular orientation.
What do complex cells in V1 respond best to?
Movement of a correctly oriented bar across their receptive field.
What do hypercomplex cells in V1 respond best to?
Corners, angles, or particular length bars moving in a specific direction.
What is the orientation tuning curve in V1?
It shows that V1 neurons have graded tuning to their preferred stimulus.
What should students prepare for the next class?
Read Chapter 9 on color perception and complete Homework 1 due Sunday by midnight.