Gross Anatomy Module 3: Pericardium and the Heart (internal and external features)
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Mediastinum is the
Central compartment of thoracic cavity, extending from superior thoracic aperture to diaphragm inferiorly and from sternum and costal cartilages anteriorly to thoracic vertebrae posteriorly. It is occupied by mass of tissue between the two pulmonary cavities.
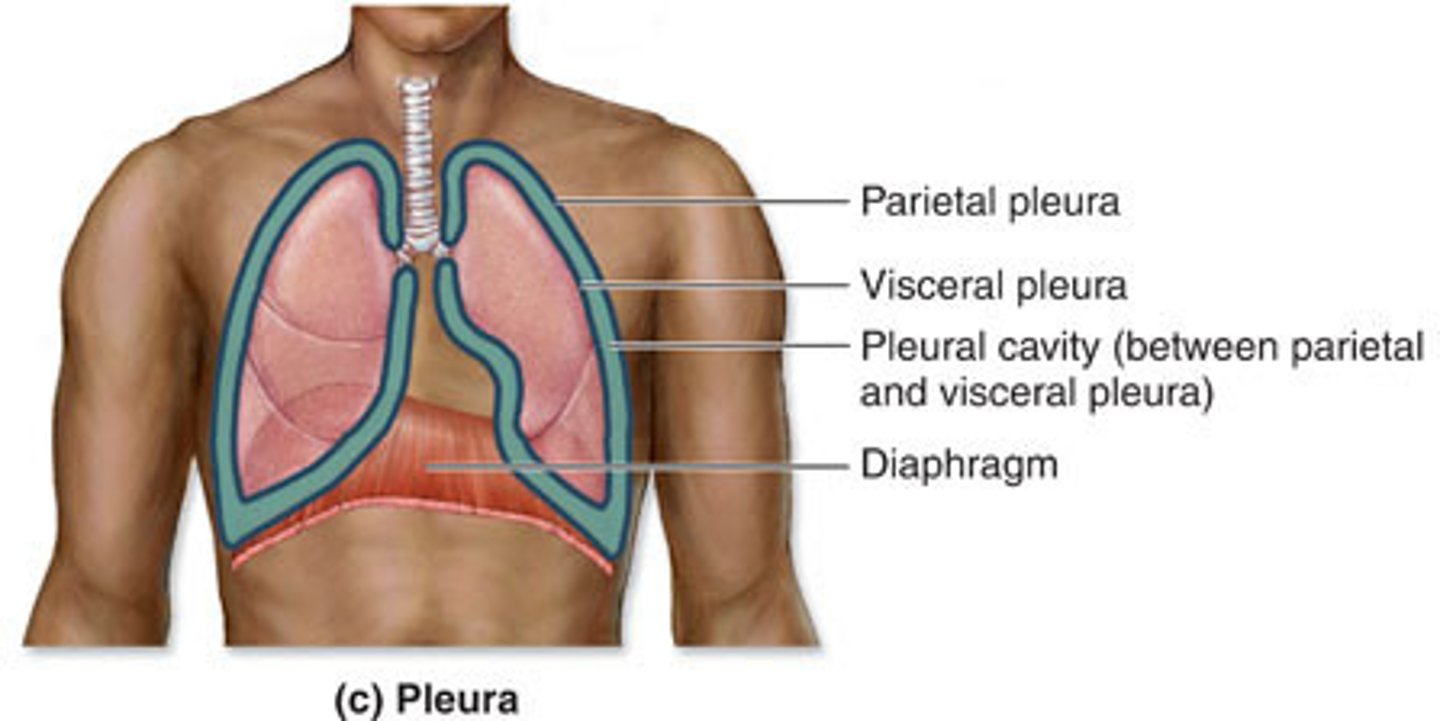
Mediastinum is covered
on each side by the mediastinal surface of the parietal pleura
Mediastinum contains
all thoracic viscera except the lungs, and it's highly mobile owing to containing hollow (air- or liquid-filled) visceral structures united by loose connective tissue
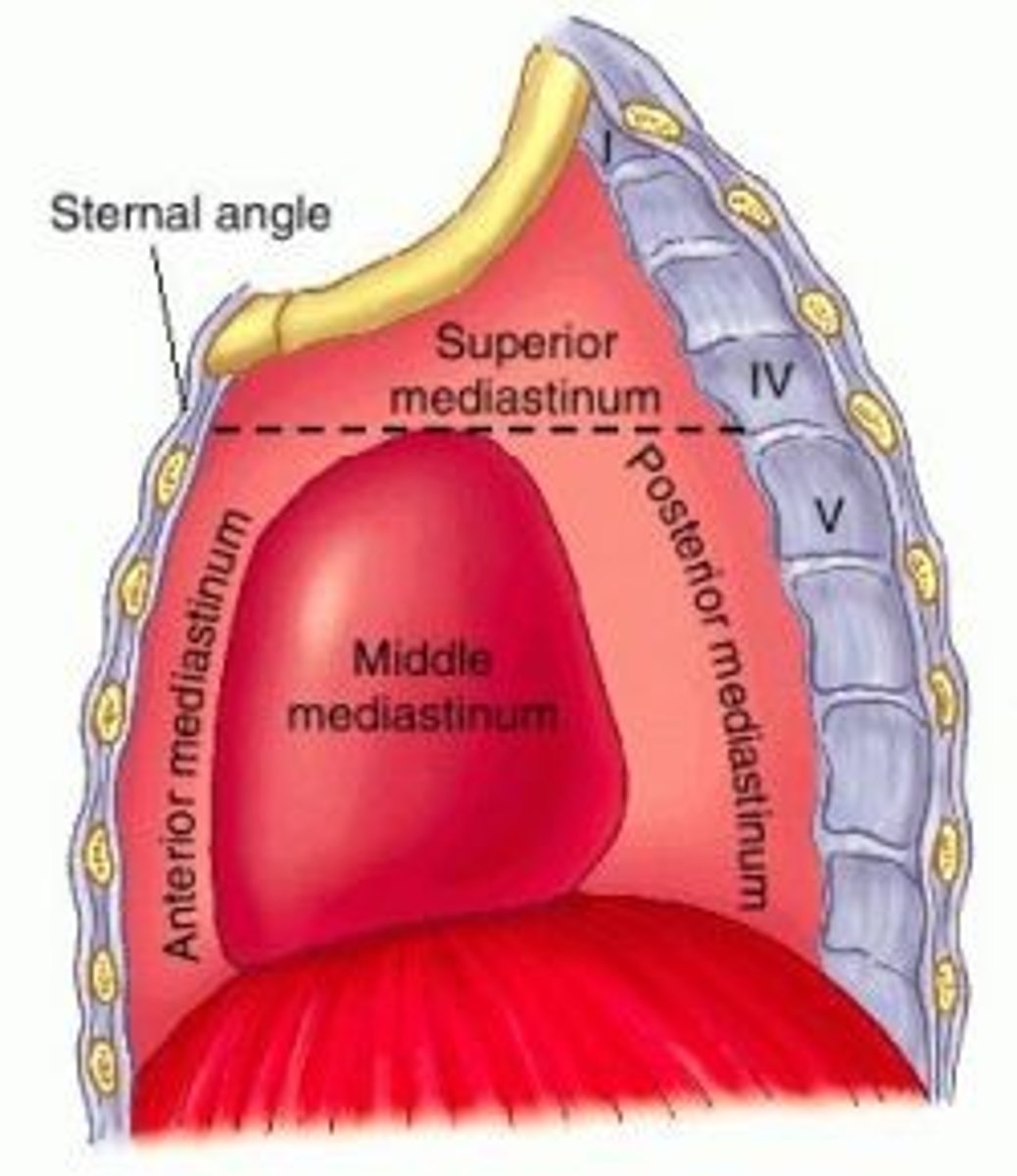
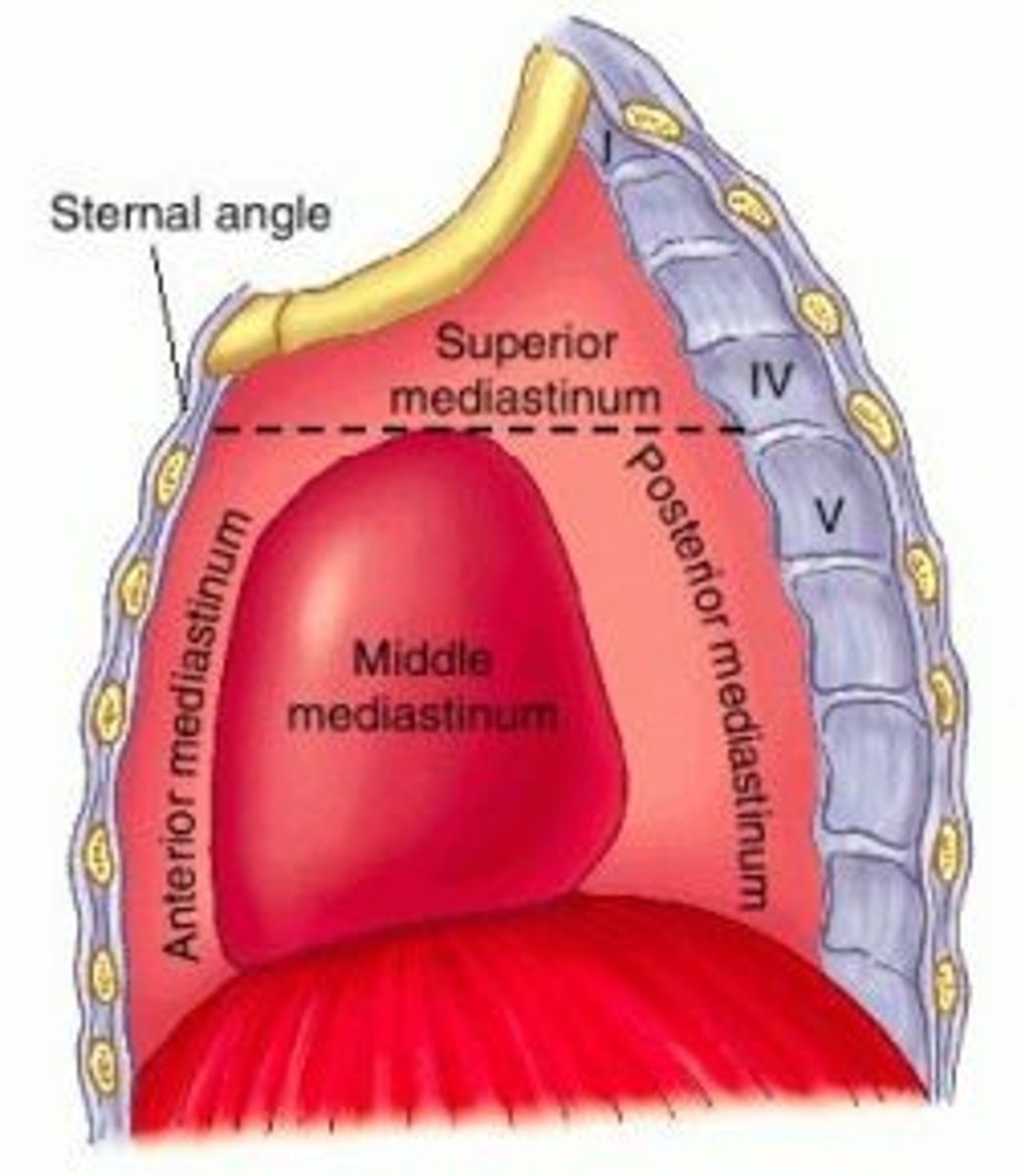
Mediastinum parts
-Superior mediastinum
-Inferior mediastinum
-Anterior mediastinum
-Middle mediastinum
-Posterior mediastinum
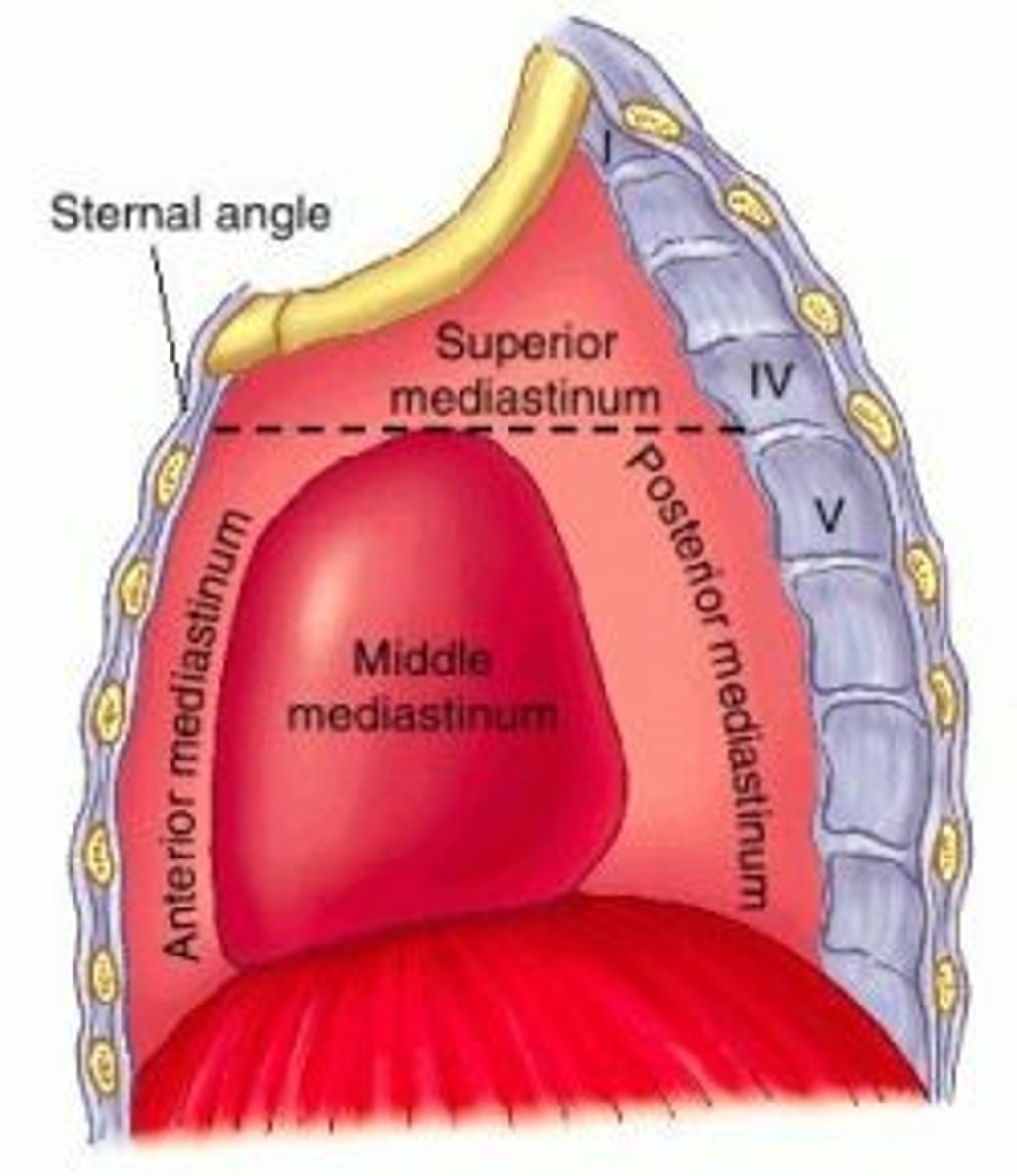
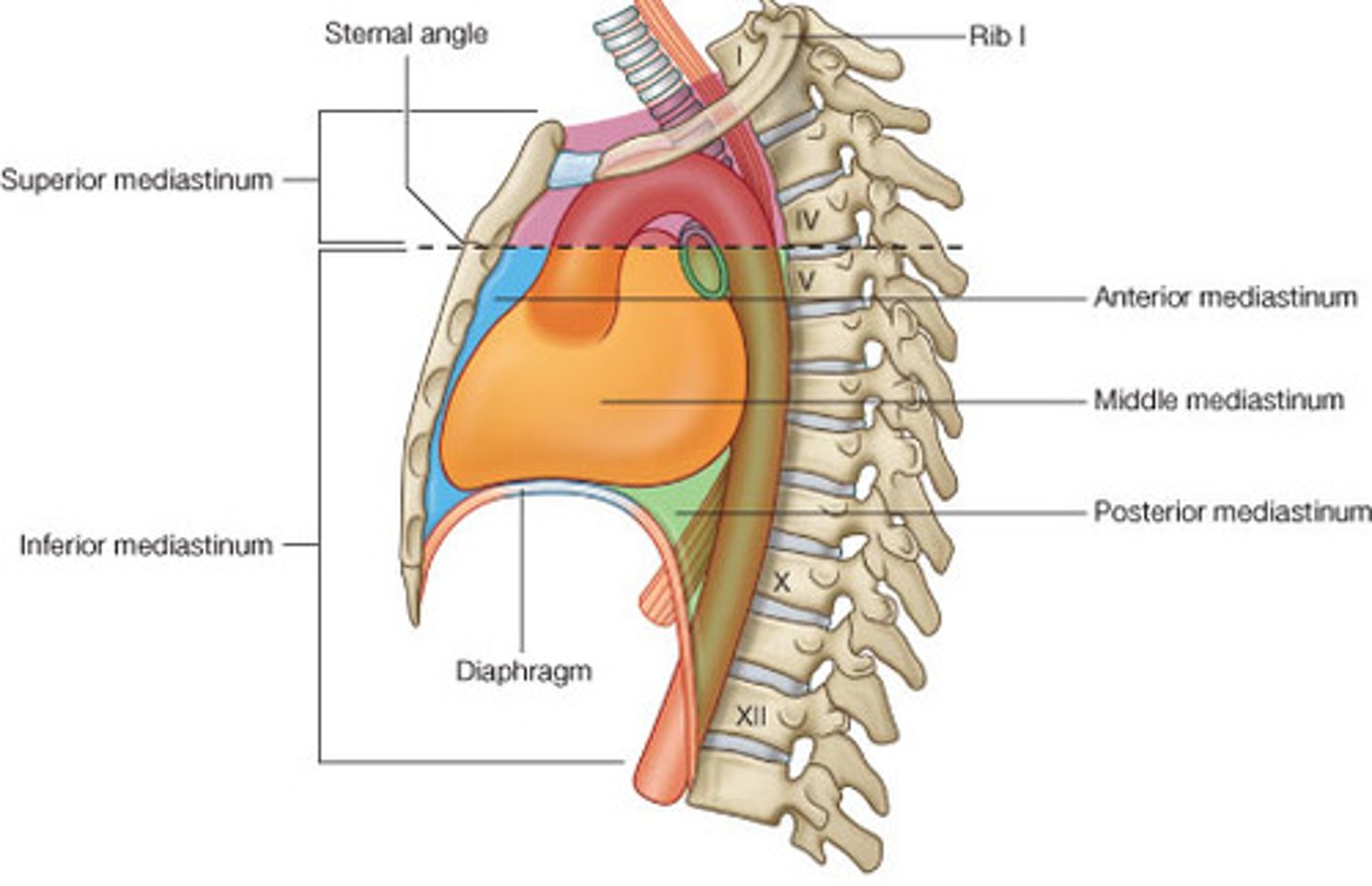
Superior mediastinum:
extends inferiorly from the superior thoracic aperture to the horizontal plane (transverse thoracic plane: sternal angle → IV disk of T4 - T5)
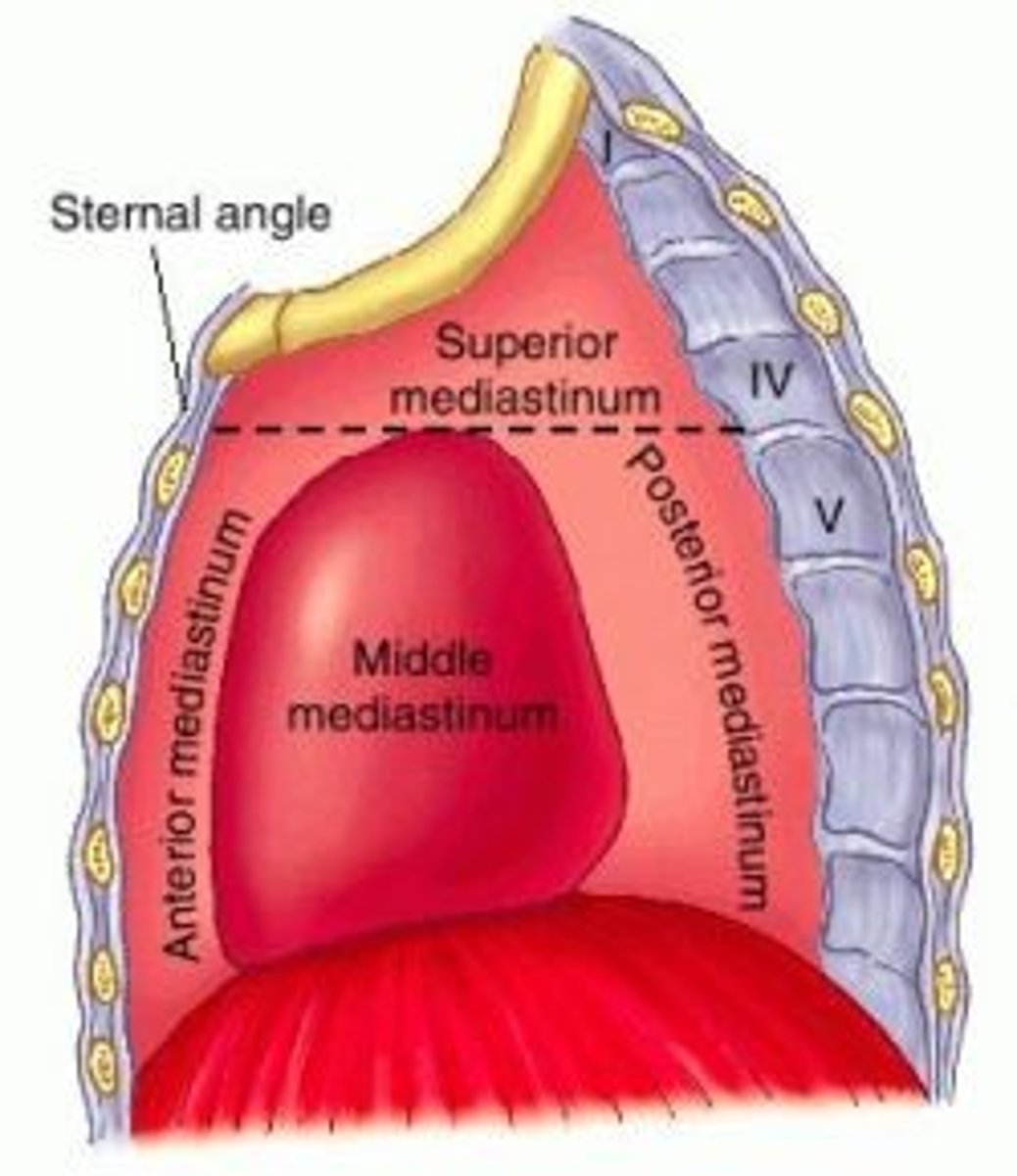
Inferior mediastinum:
between transverse thoracic plane and diaphragm, further divided by pericardium
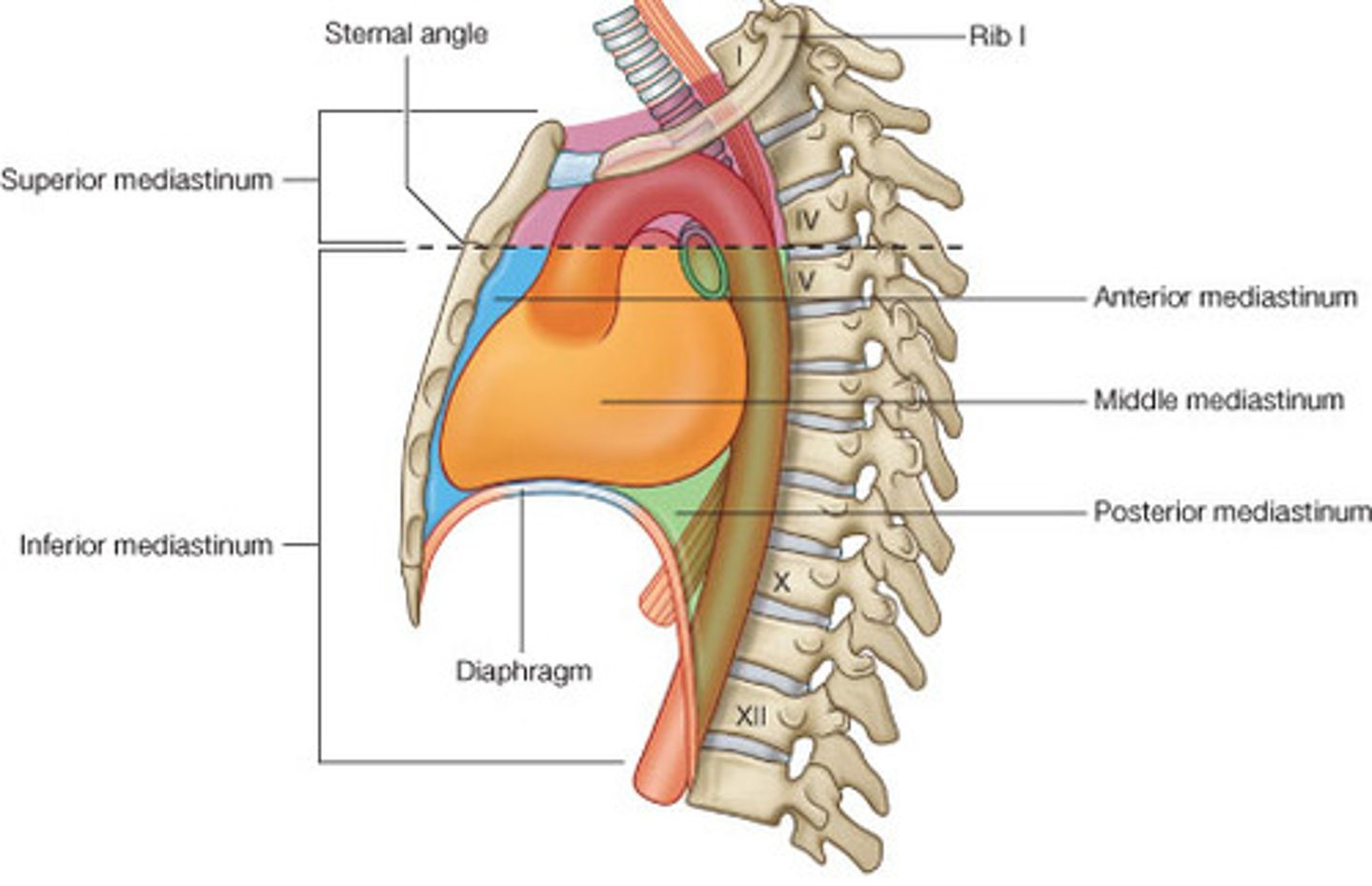
Middle mediastinum:
contains the heart, roots of great vessels, and pericardium
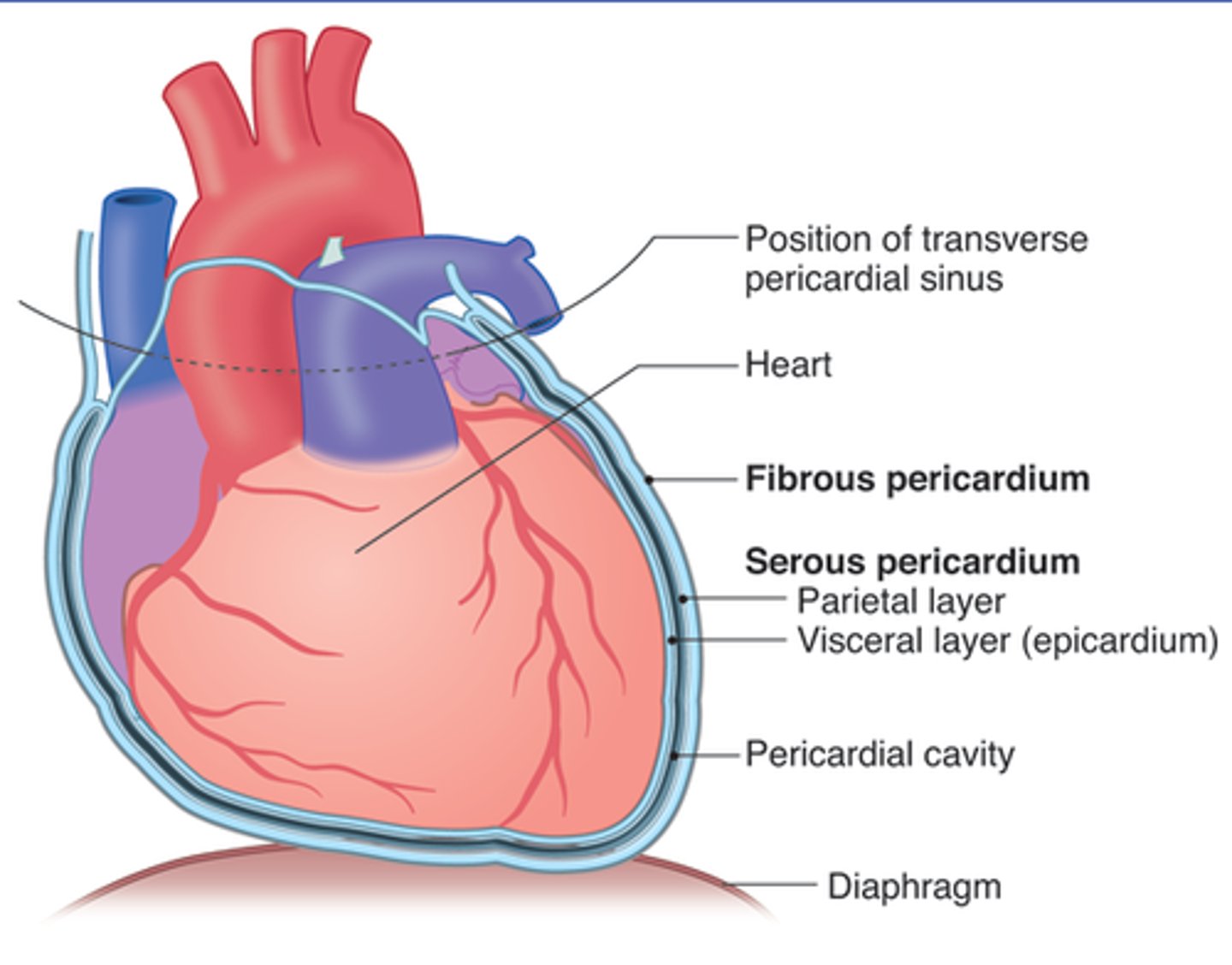
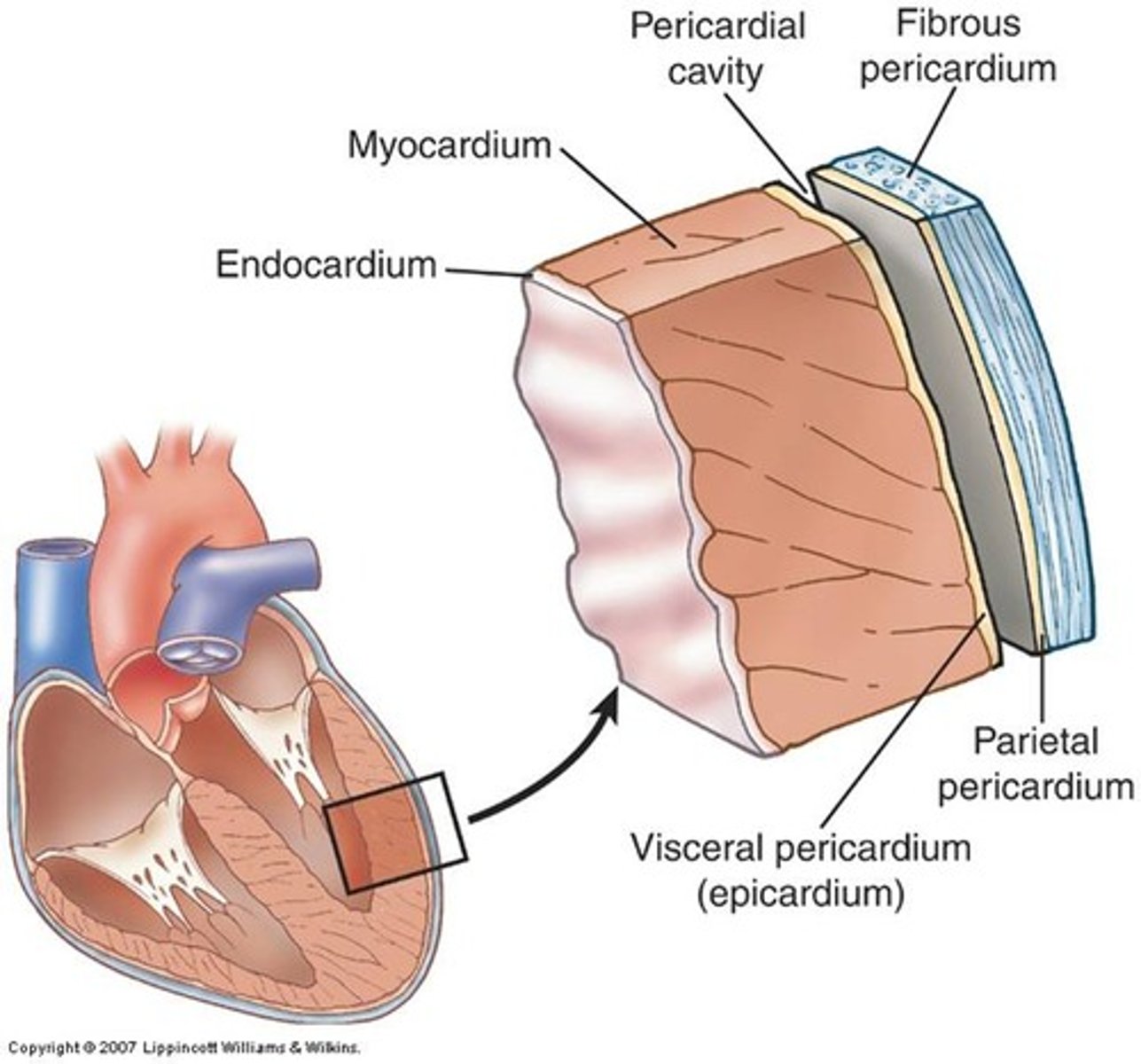
Pericardium
A fibroserous membrane that comprises the middle mediastinum and covers the heart and the roots of its great vessels (ascending aorta, pulmonary trunk, and SVC)
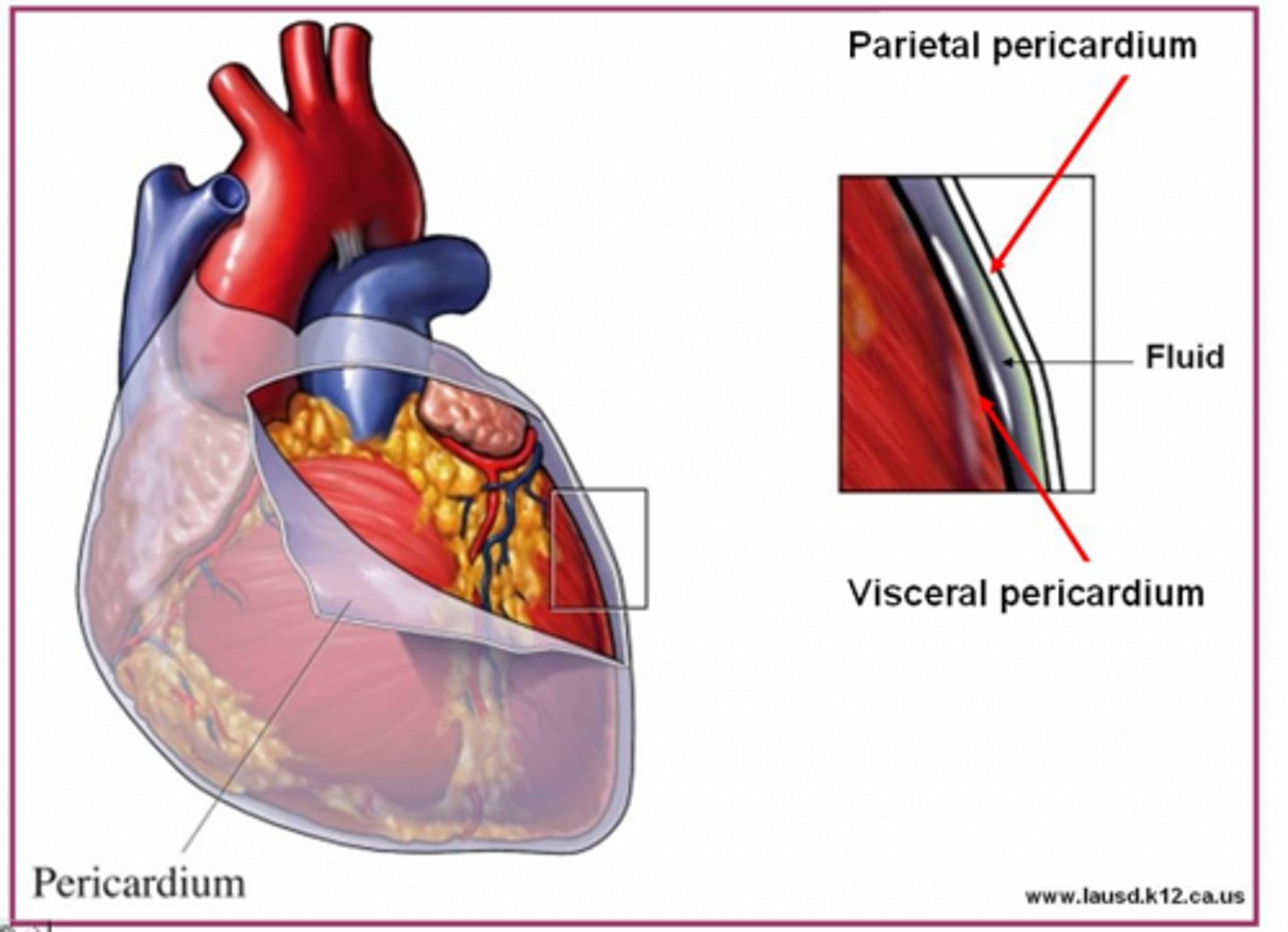
Pericardium layers
fibrous and serous (parietal and visceral)

fibrous pericardium
tough, white fibrous connective tissue that is the outer layer of the pericardium. contains Sternopericardial ligament
Fibrous pericardium stabilizes
the heart and protects it against sudden overfilling
Fibrous pericardium is continuous superiorly with...
the great vessels entering and leaving the heart, and with the pretracheal layer of deep cervical fascia
Fibrous pericardium is continuous inferiorly with...
the central tendon of the diaphragm as the pericardiacophrenic ligament
Sternopericardial ligament:
attaches fibrous pericardium anteriorly to the posterior surface of sternum
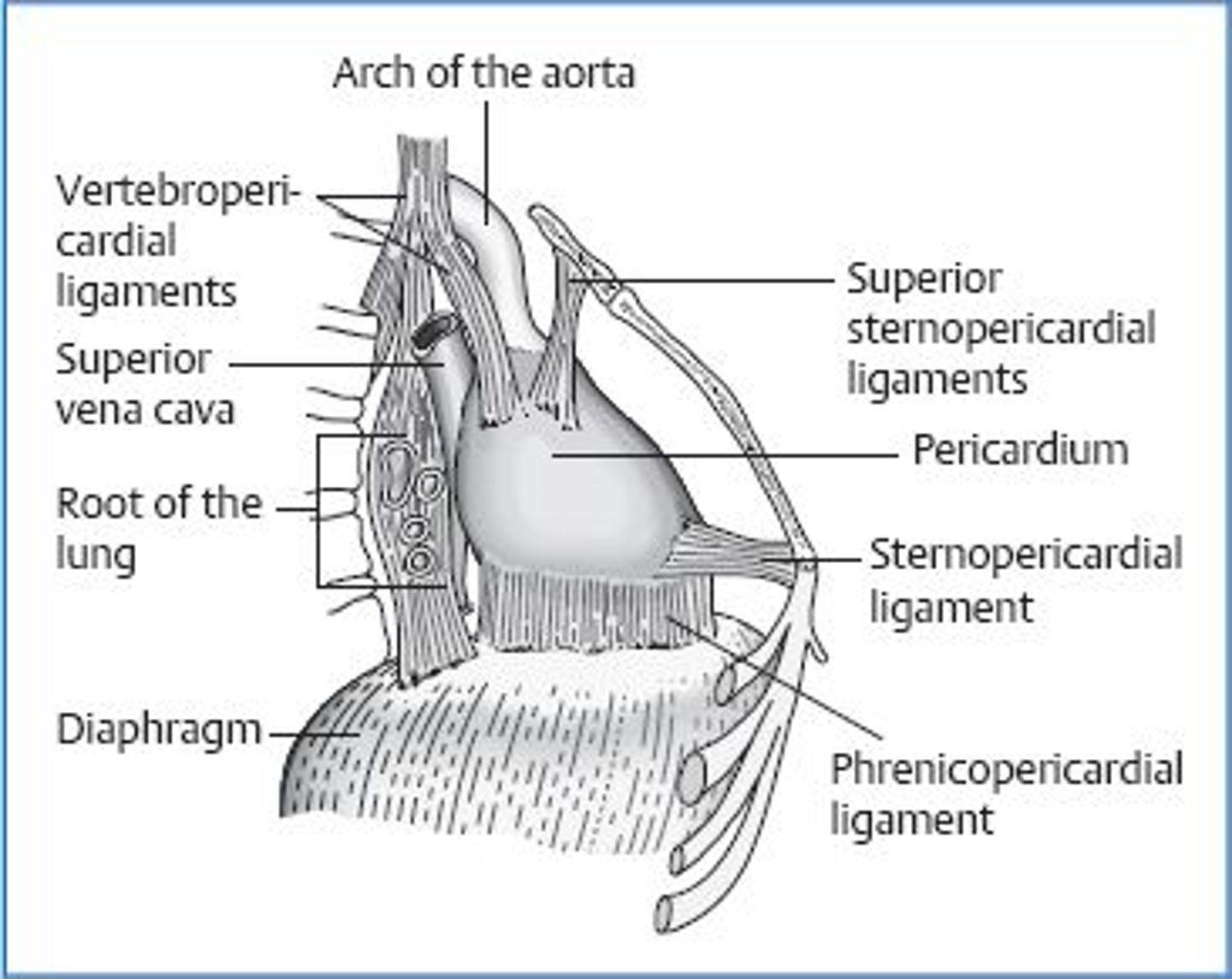
fibrous pericardium bound posteriorly to
structures of the posterior mediastinum by loose connective tissue
serous pericardium
the inner layer of pericardium, which IS a serous tissue and made of two layers (parietal layer and the visceral layer)
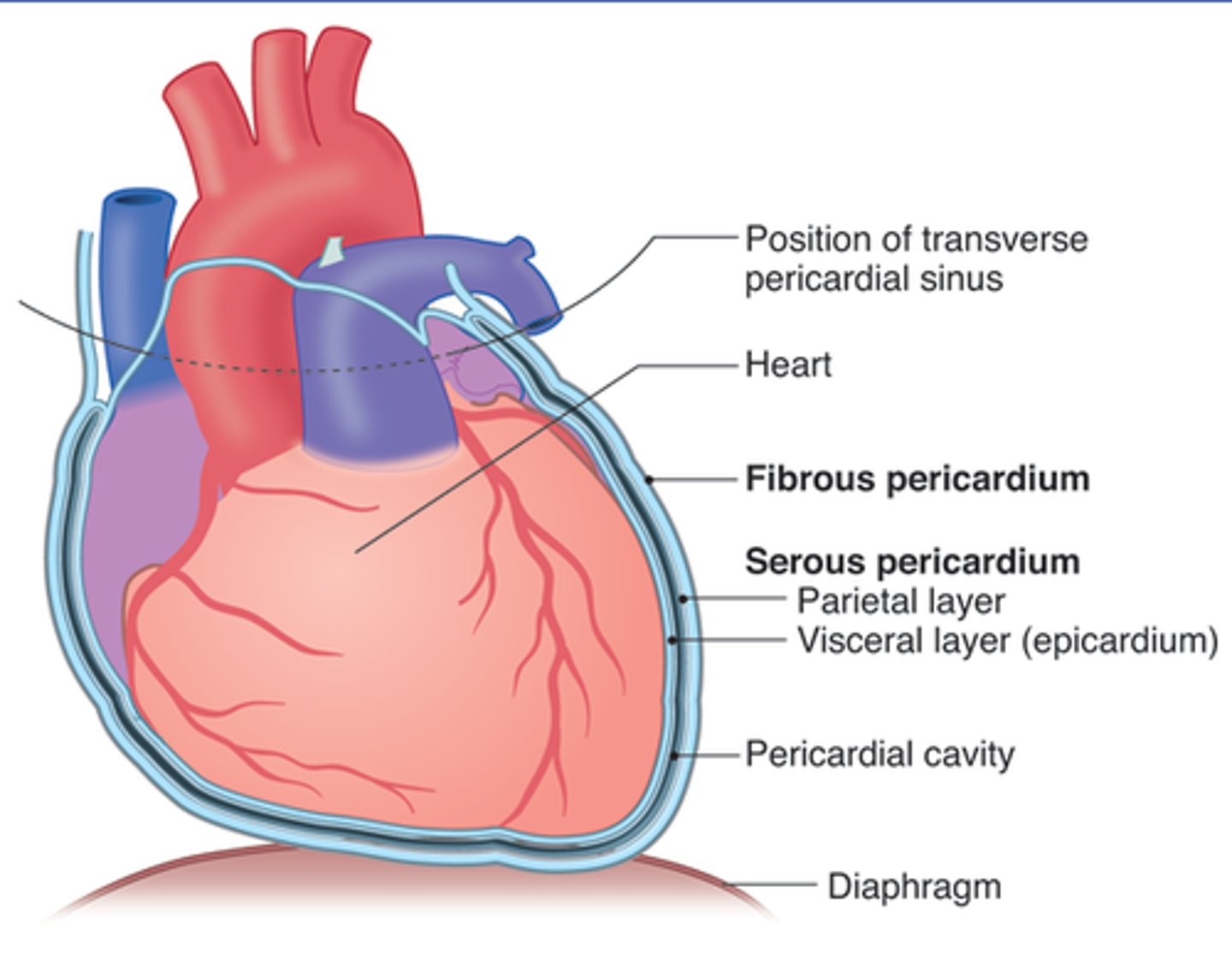
Serous pericardium parietal layer
lines internal surface of the fibrous pericardium and it reflects onto heart at the great vessels
Serous pericardium visceral layer
lines external surface of the heart, forms epicardium (outermost layer of the heart wall)
pericardial sac
potential space between parietal and visceral layers of serous pericardium
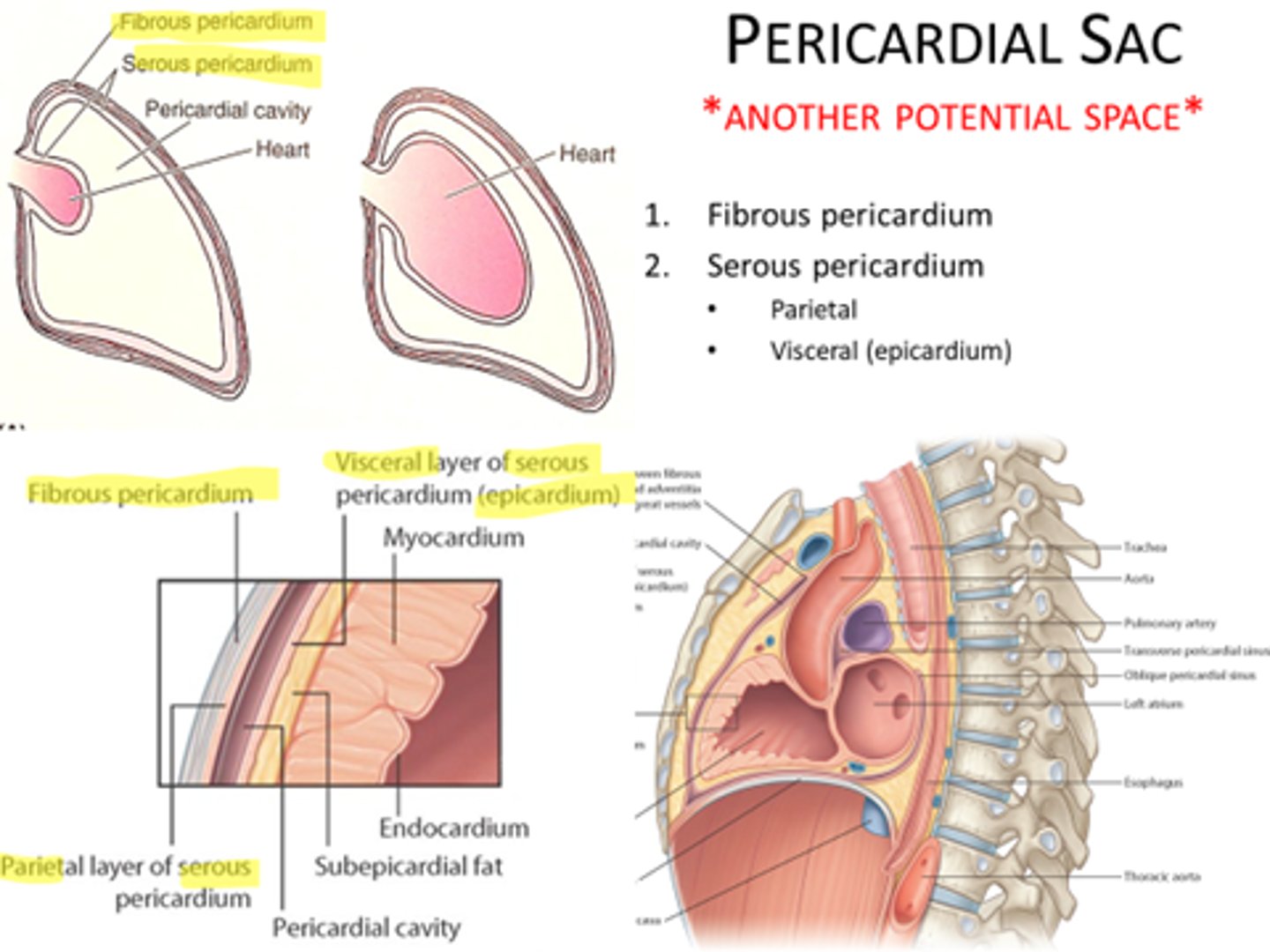
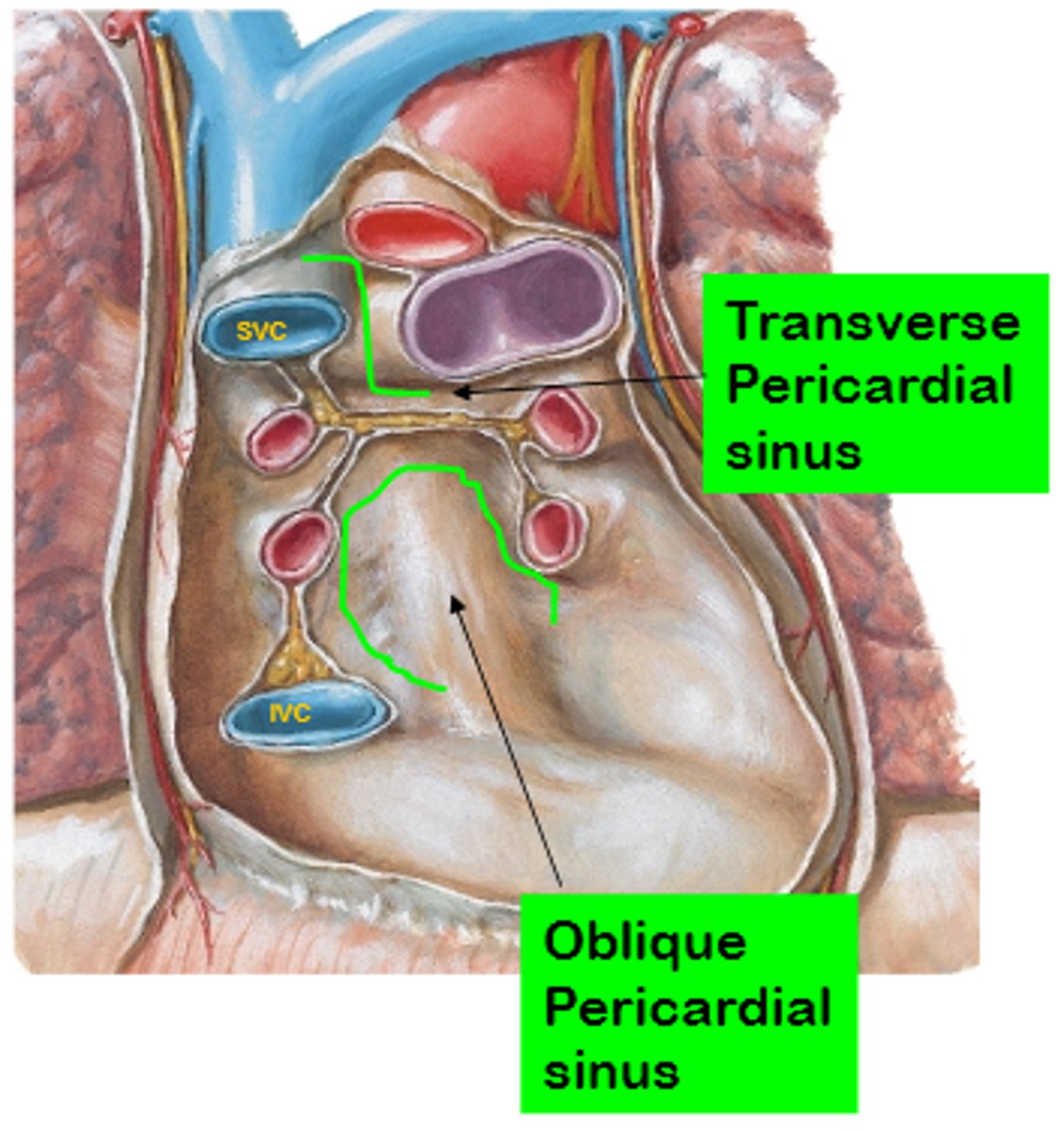
transverse pericardial sinus
runs transversely within the pericardial cavity between the aorta and pulmonary trunk & the superior vena cava
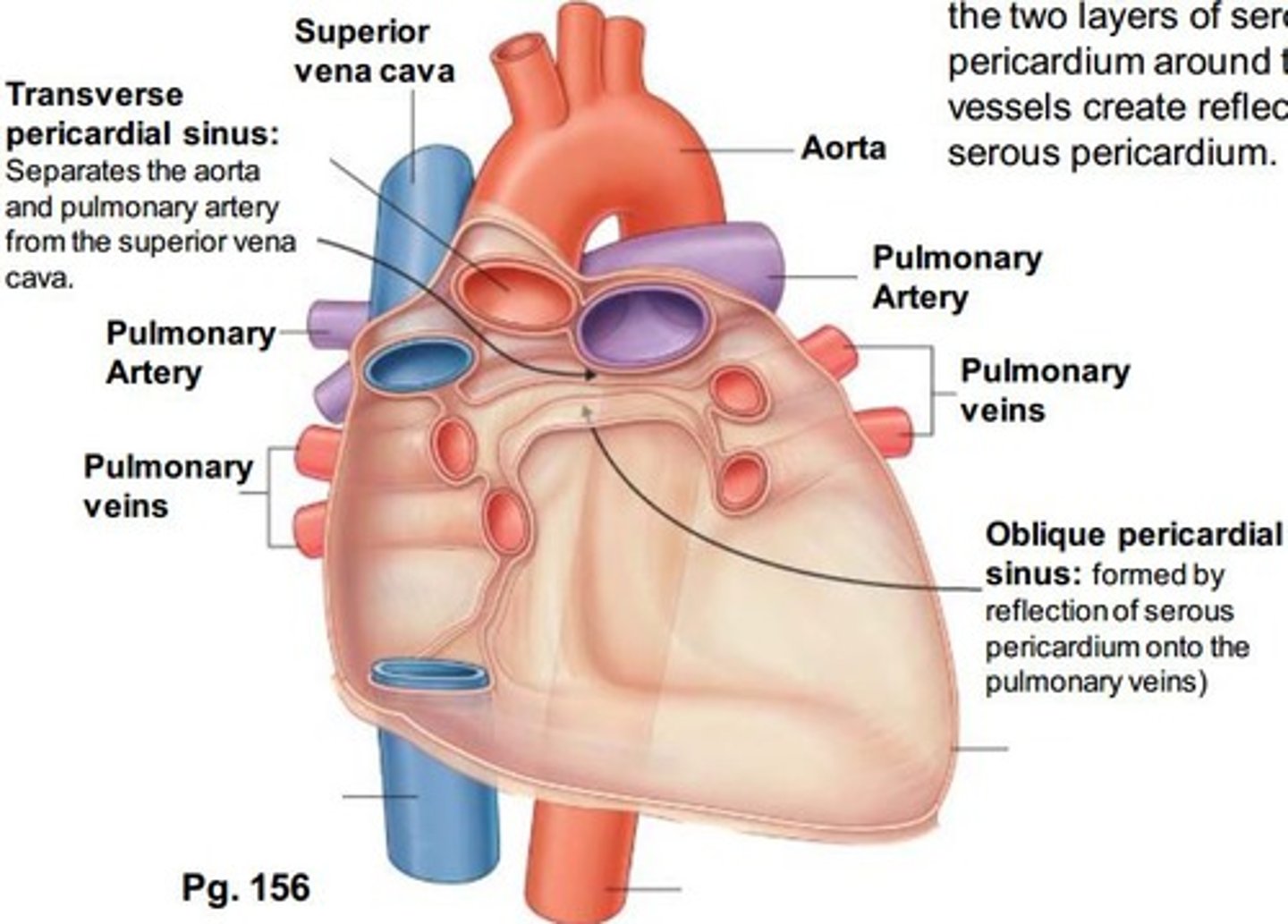
Oblique pericardial sinus
pocket-like recess in the pericardial cavity formed by the L atrium. It is a blind sac
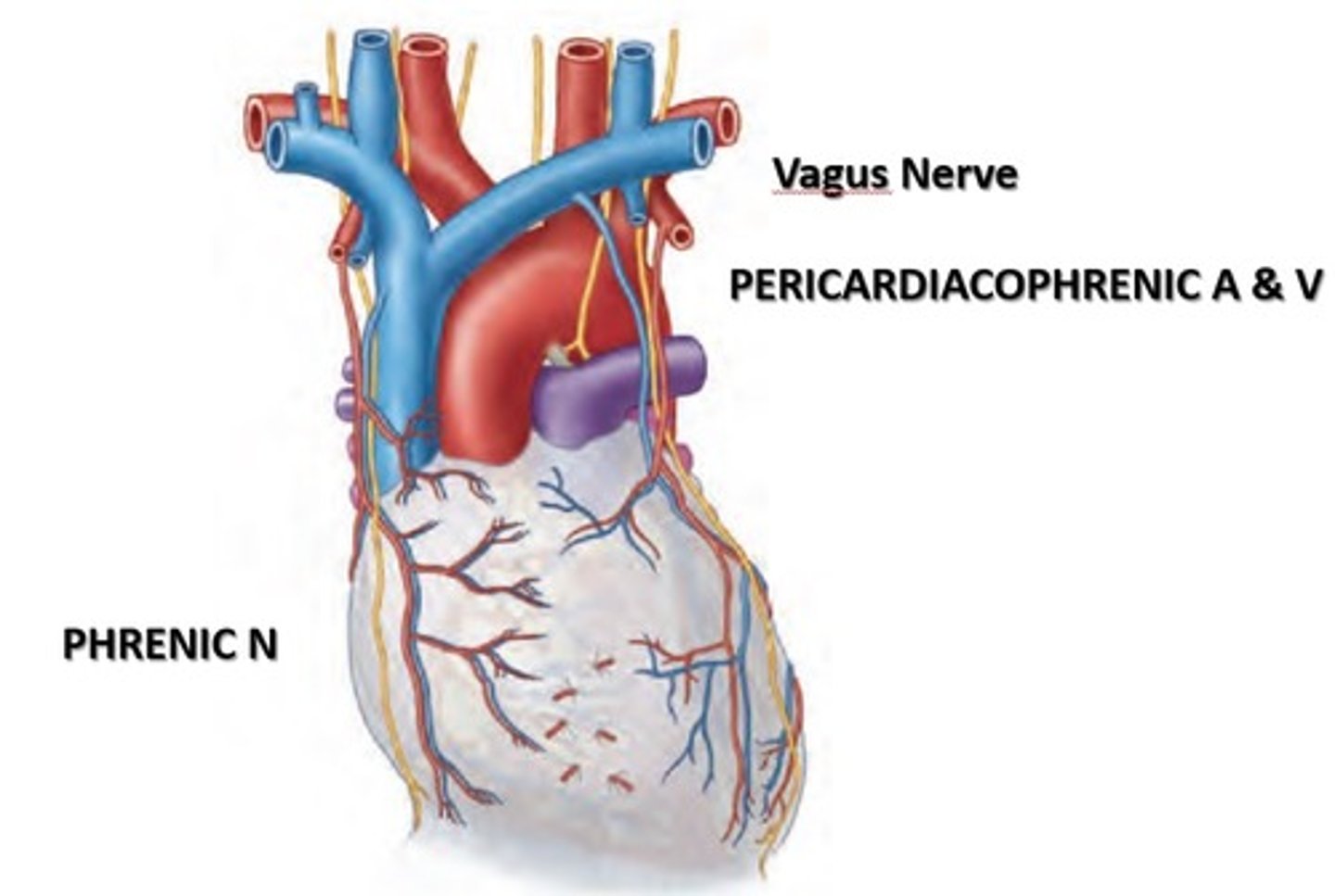
Pericardium Arteries-Pericardiacophrenic artery:
branch of the internal thoracic artery that accompanies the phrenic nerve to the diaphragm
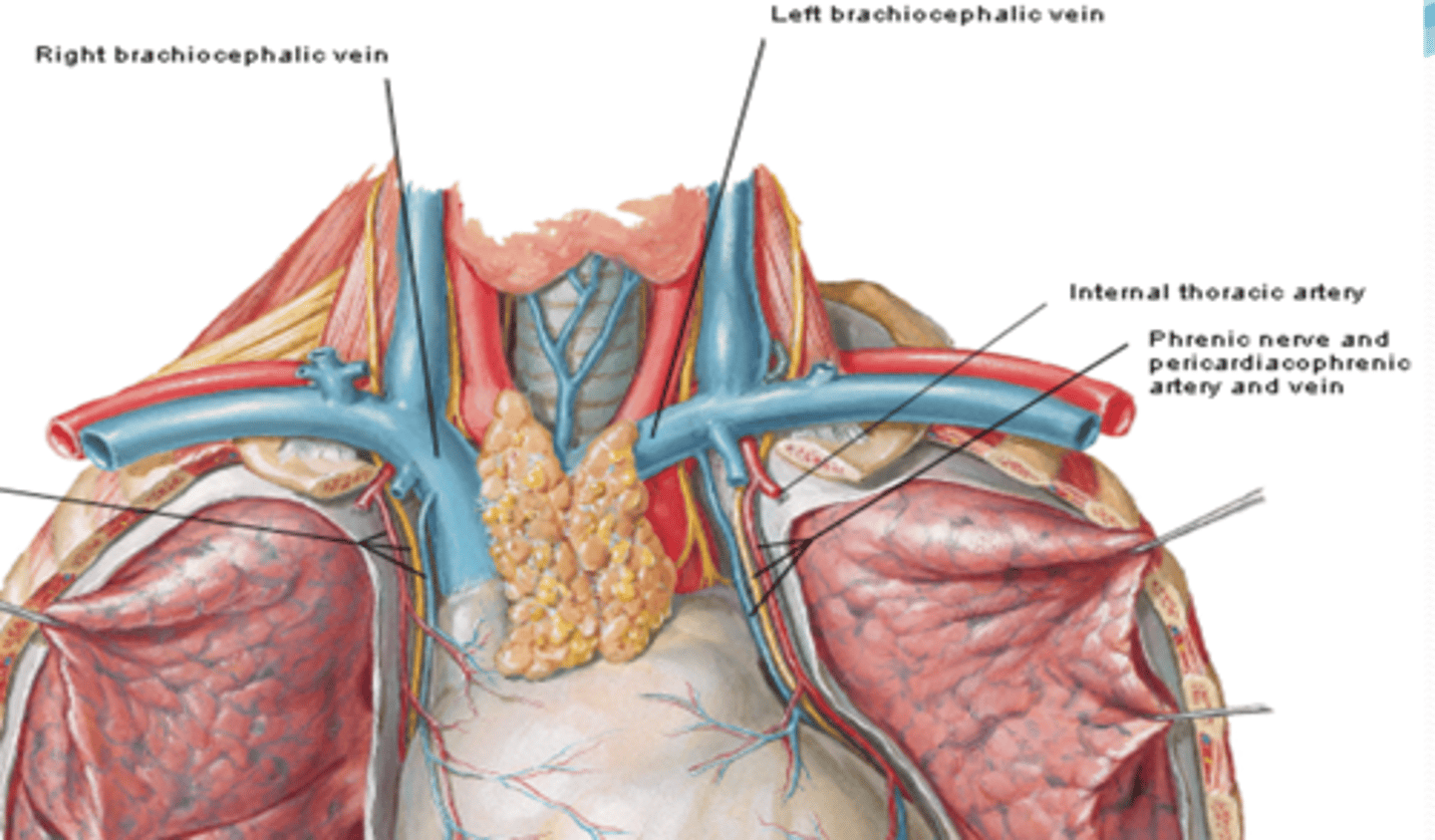
Pericardium veins-Pericardiacophrenic vein:
tributary of the brachiocephalic (or internal thoracic) veins
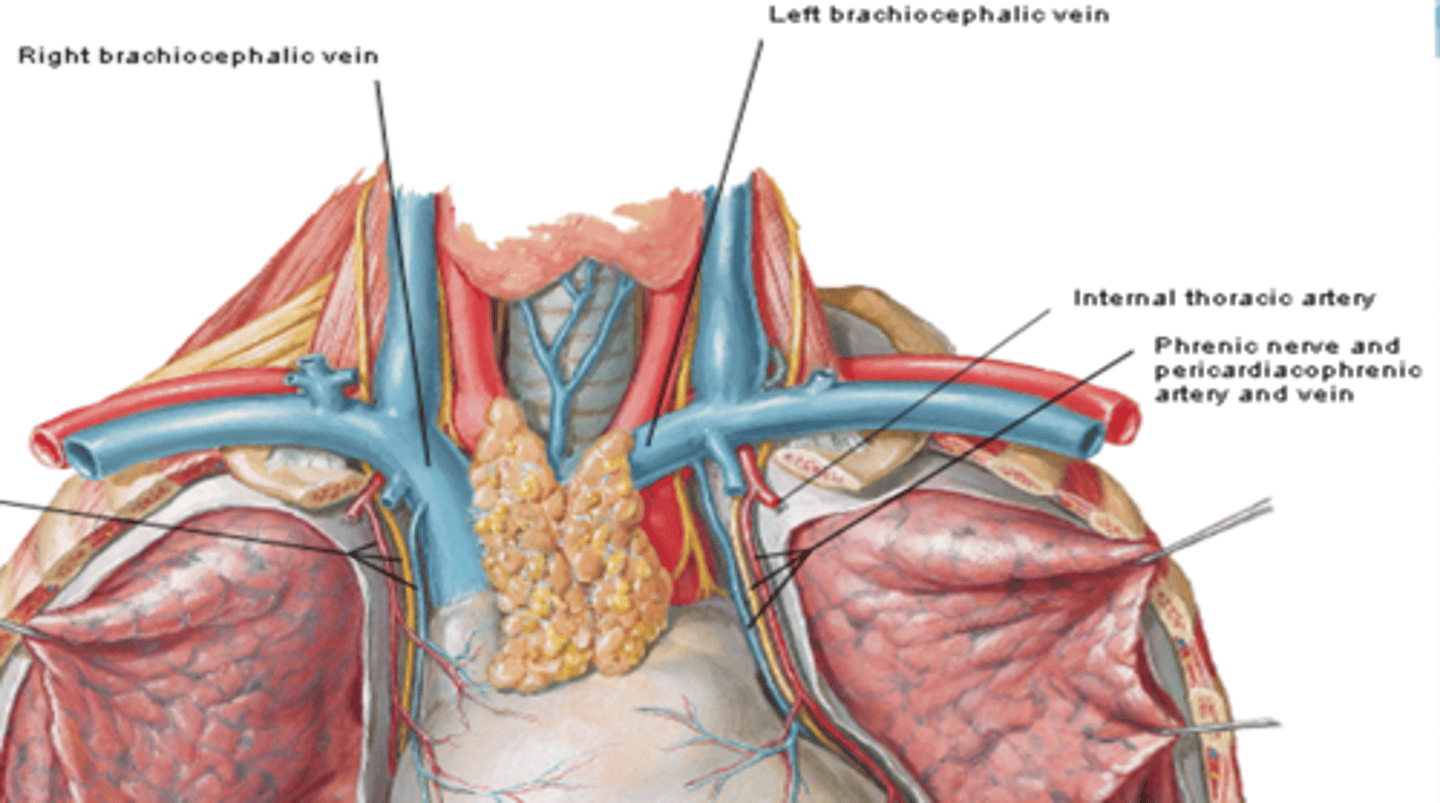
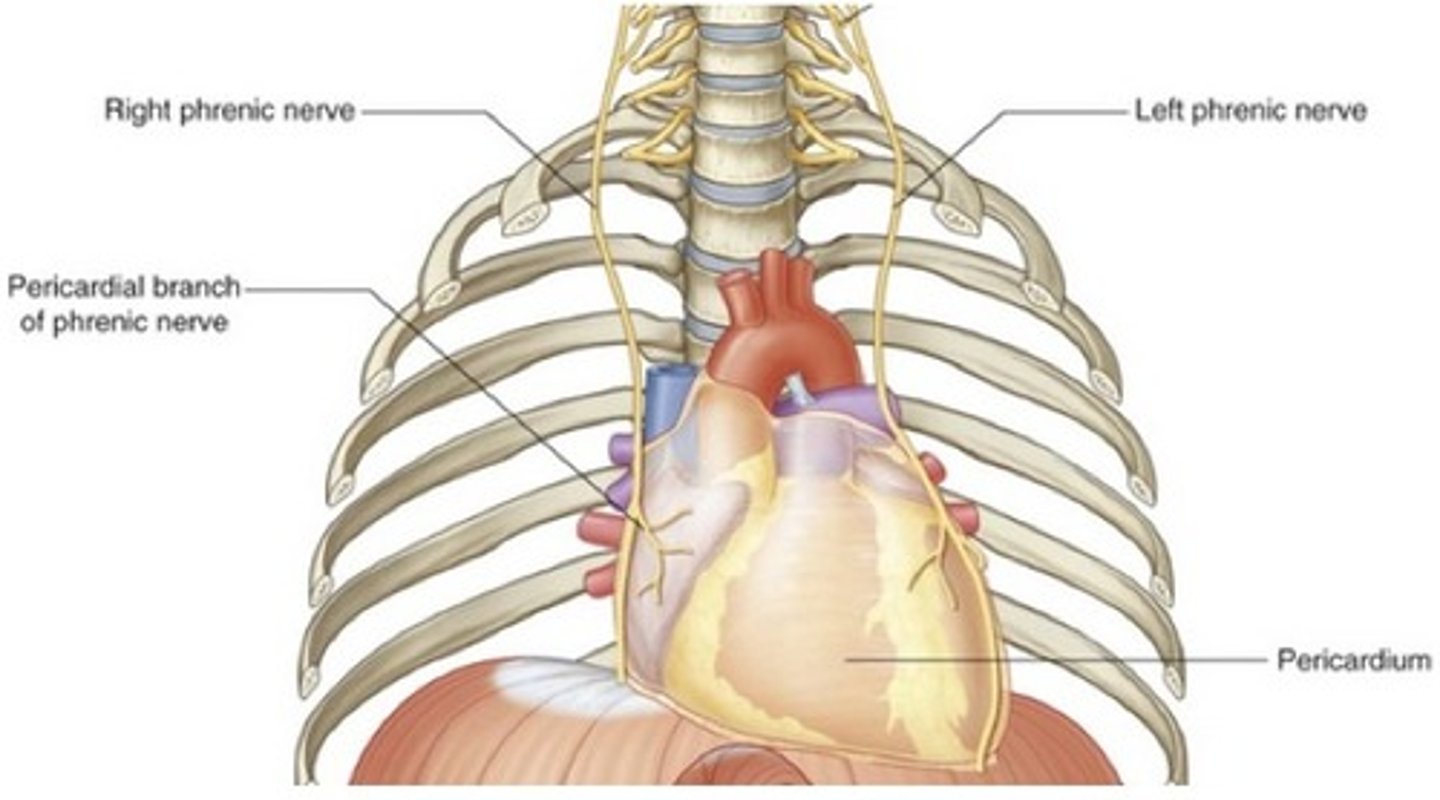
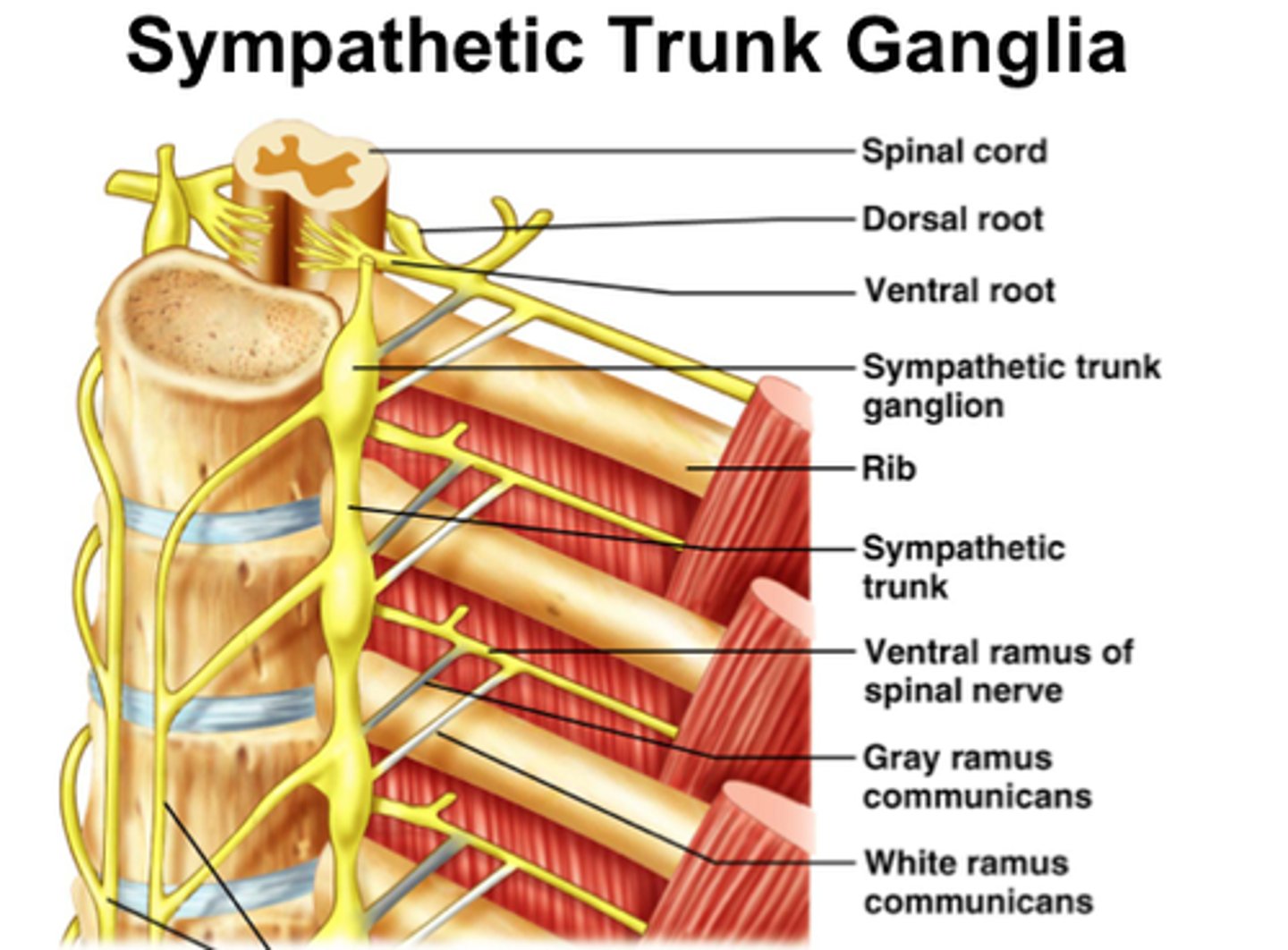
Pericardium nerves
Phrenic nerve (C3 - C5)
Sympathetic trunk
Vagus nerve
Pericardium phrenic nerve
sensory (pain is referred to the skin of dermatomes C3 - C5, area where we more commonly receive sensation)
Pericardium sympathetic trunk
vasomotor
Pericardium Vagus nerve
function uncertain
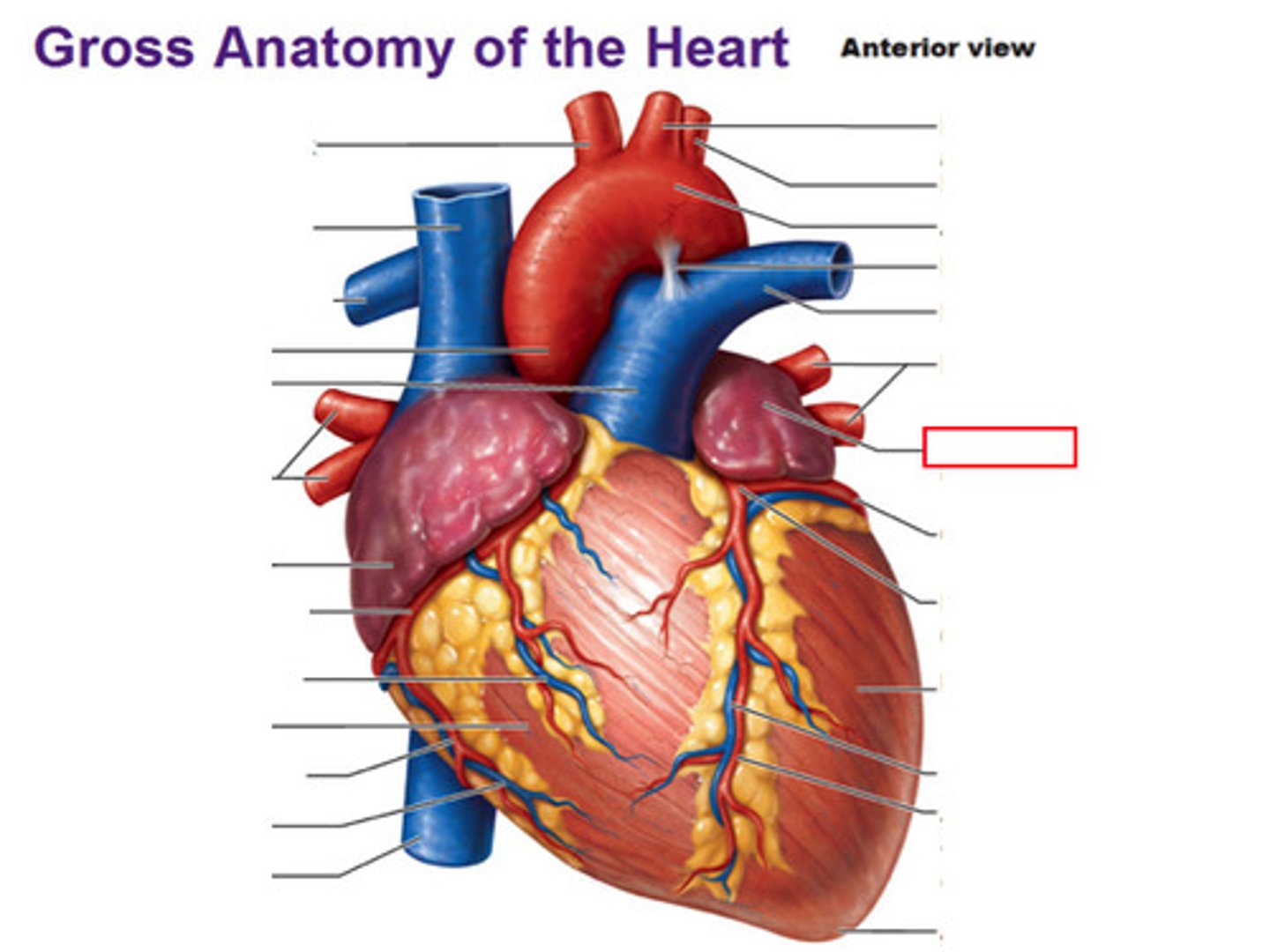
Heart's external feature
-4 chambers: 2 atria & 2 ventricles
-Coronary sulcus (atrioventricular groove)
-Anterior and Posterior interventricular sulci
-Apex
-Base
Coronary sulcus (atrioventricular groove):
demarcate atria from ventricles
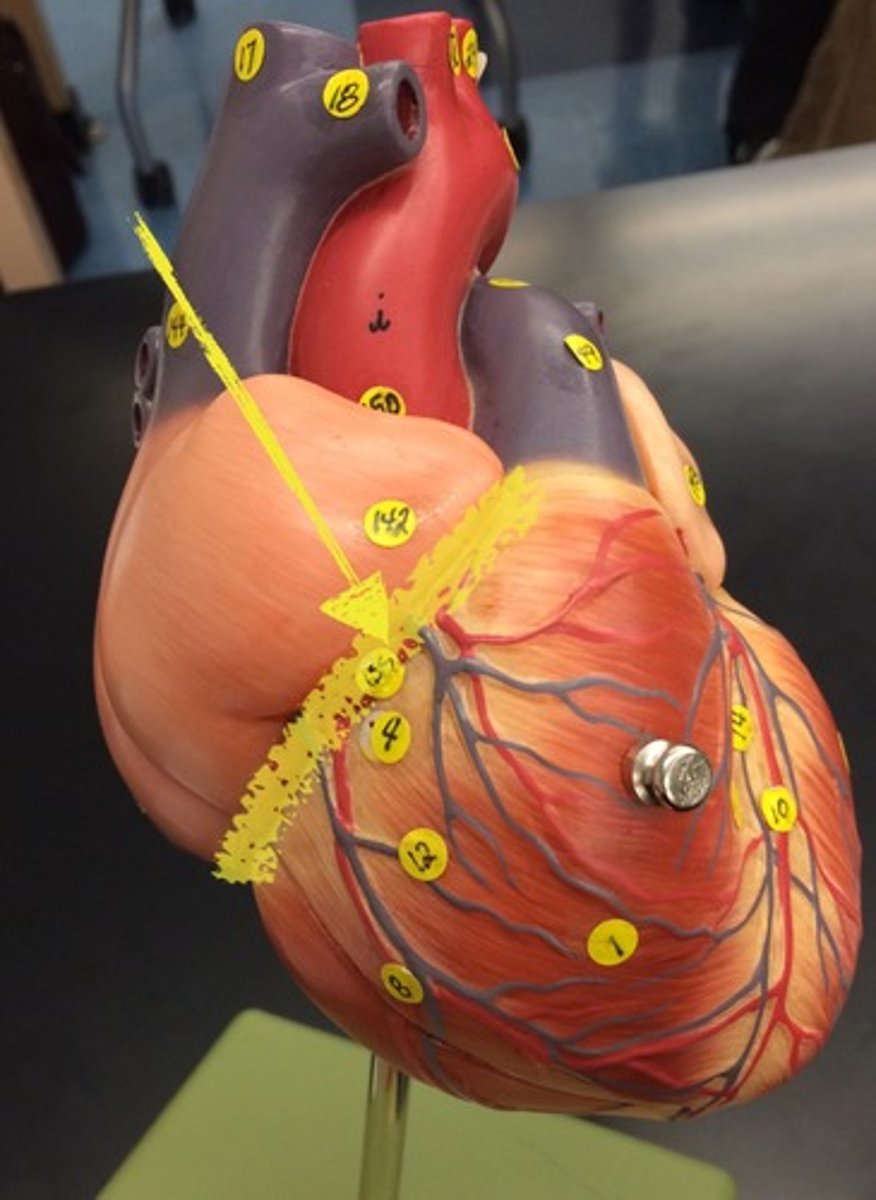
Anterior and Posterior interventricular sulci:
demarcate the R & L ventricles
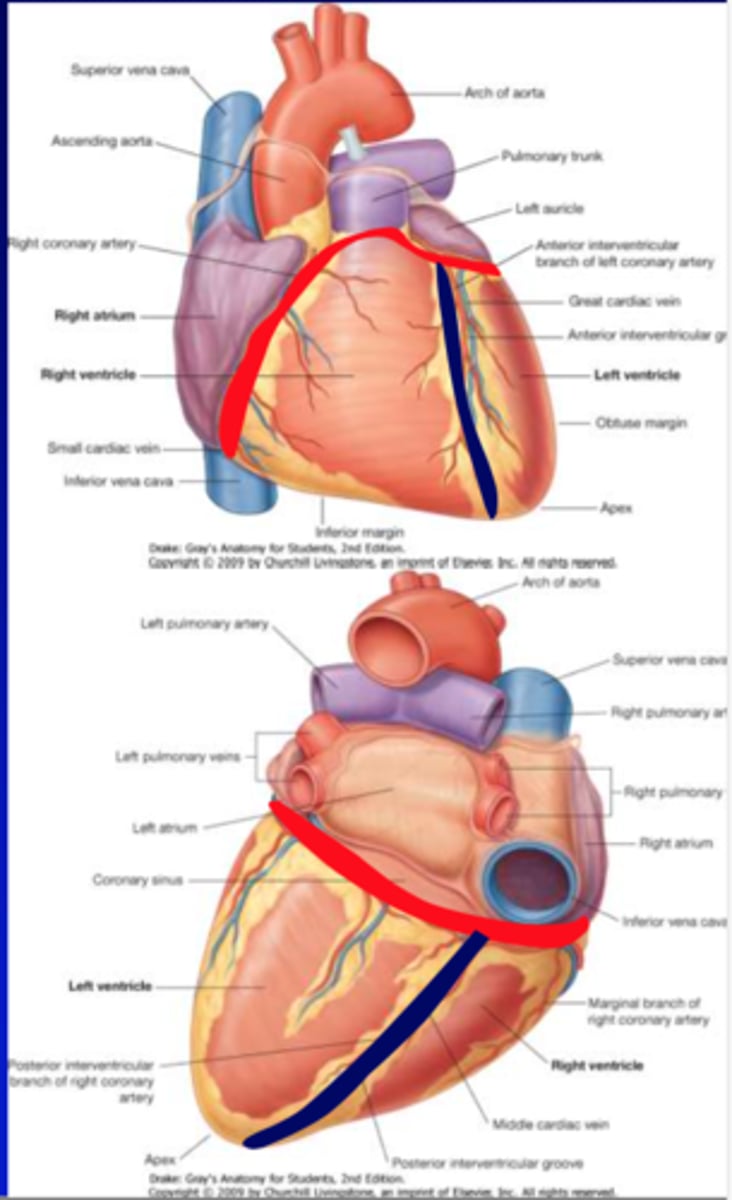
apex of the heart
-Inferolateral part of L ventricle
-Posterior to left 5th intercostal space
-Remains motionless during the cardiac cycle
-Sound of mitral valve closure is maximal
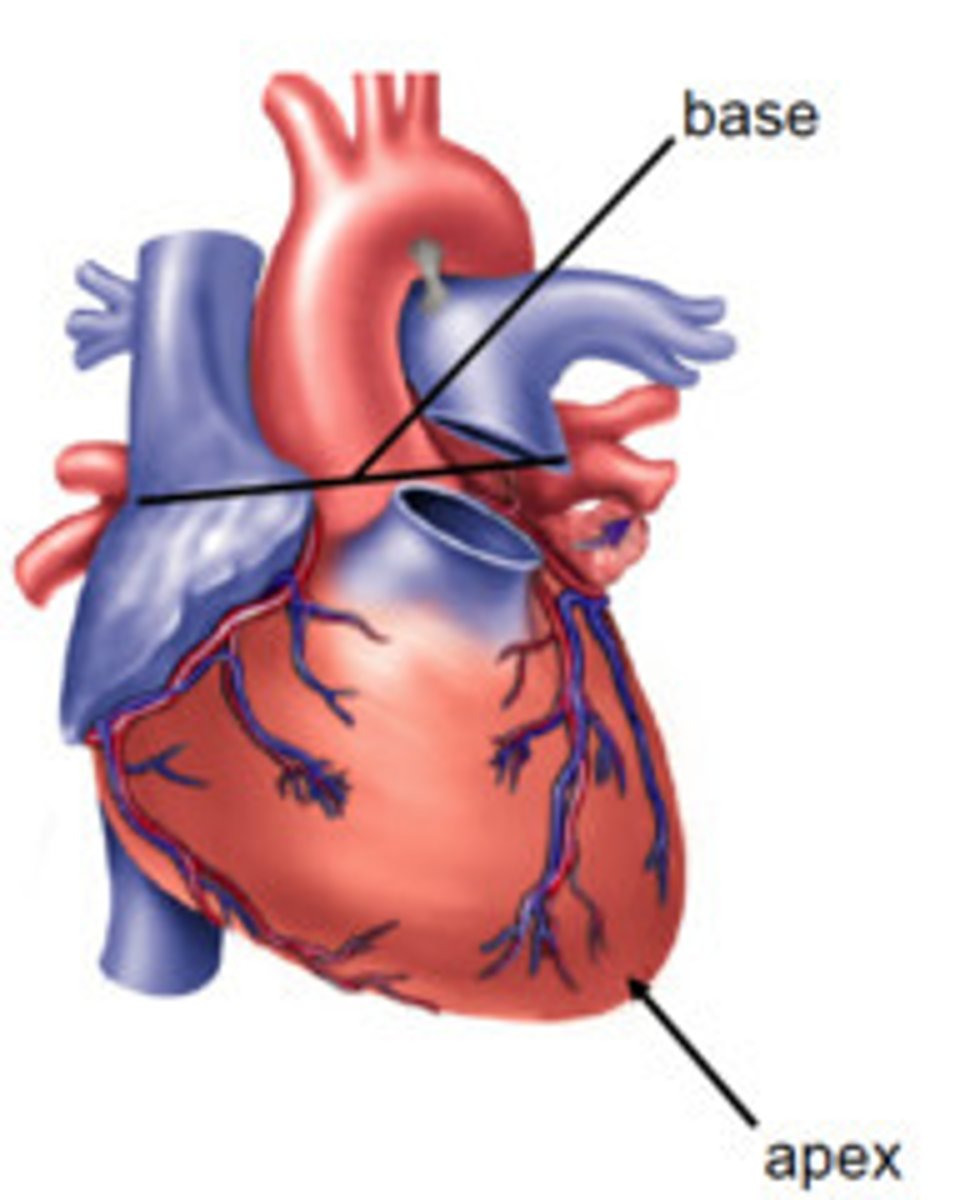
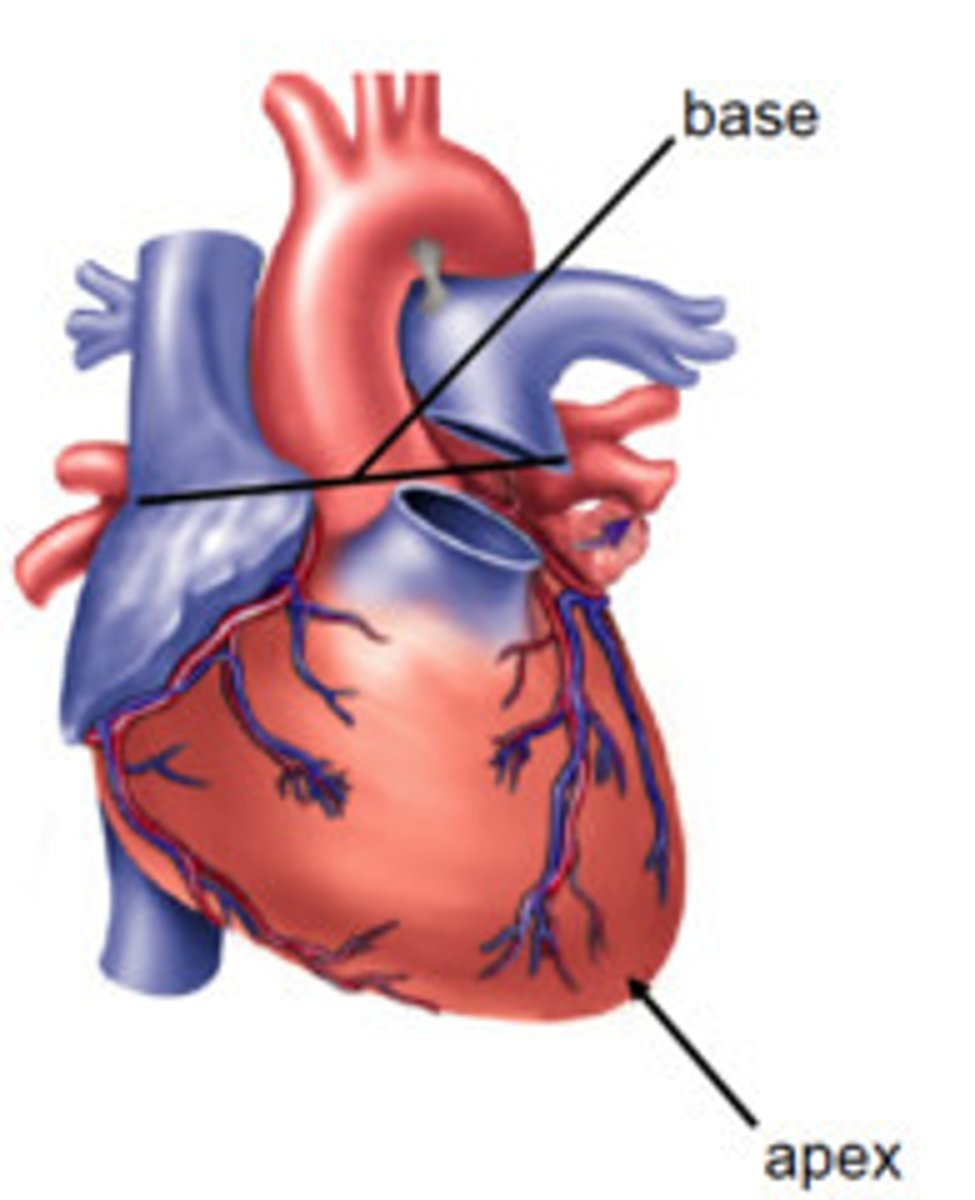
Base of the heart
-Opposite the apex, facing posteriorly toward the body of thoracic vertebrae (T6 - T9)
-Formed primarily by L atrium, and lesser contribution by R atrium
-Receives pulmonary vv. and SVC and IVC
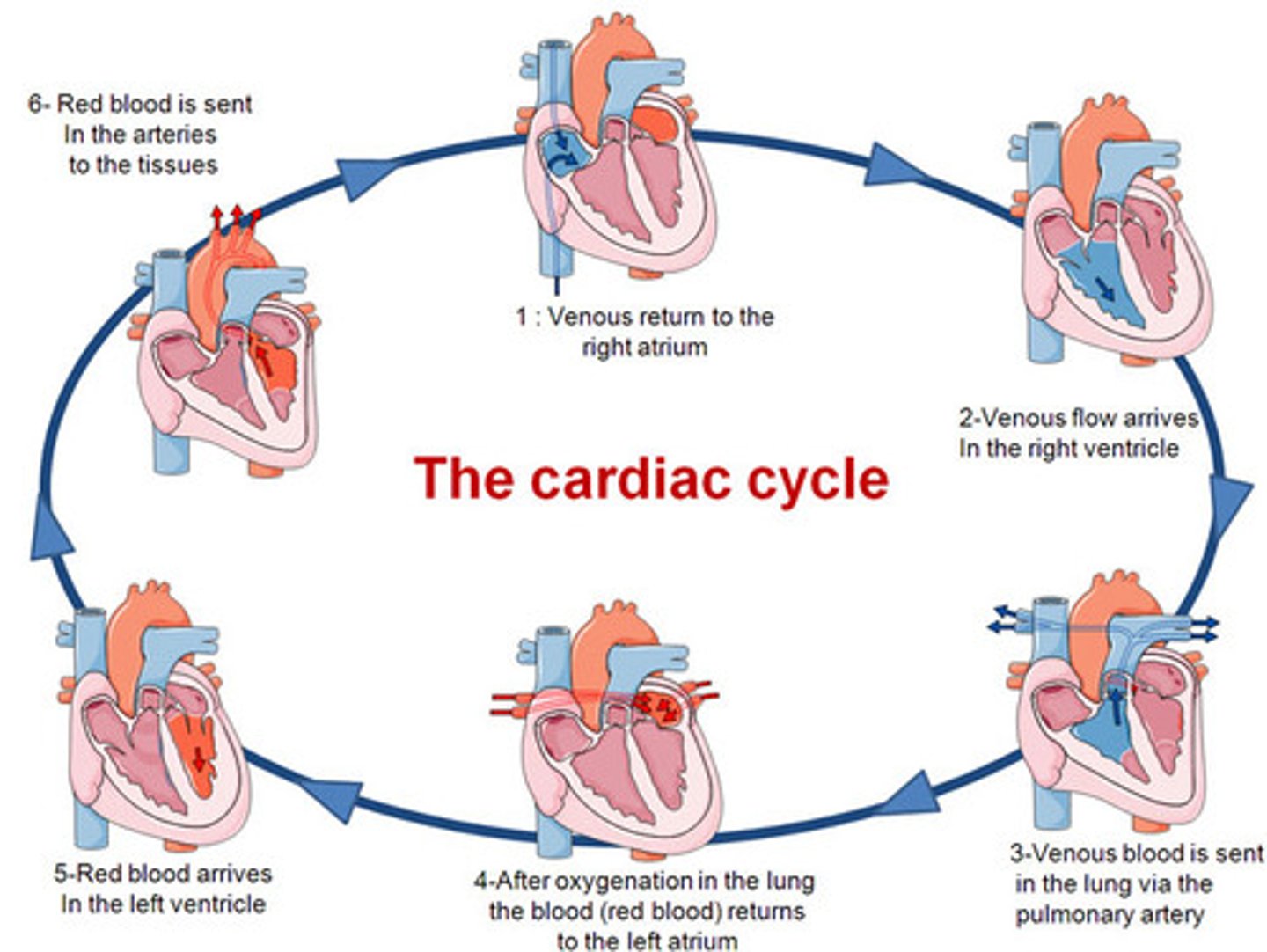
Cardiac cycle
synchronous pumping action of the atrioventricular chambers
-Diastole
-Systole
Heart Sounds
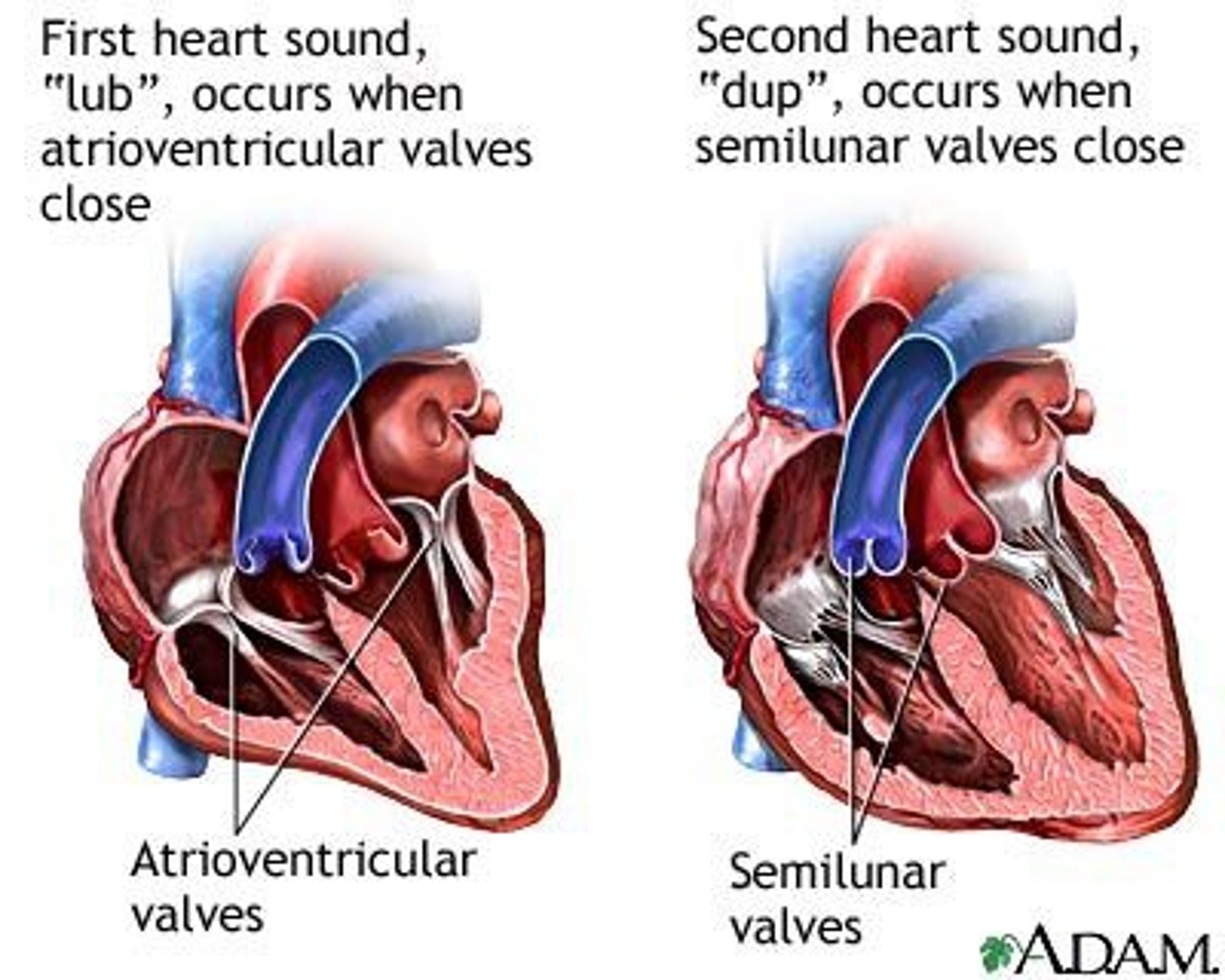
snap shut of the oneway valves of the heart
1st sound (lub)
closure of the tricuspid and mitral valves, after emptying of atria
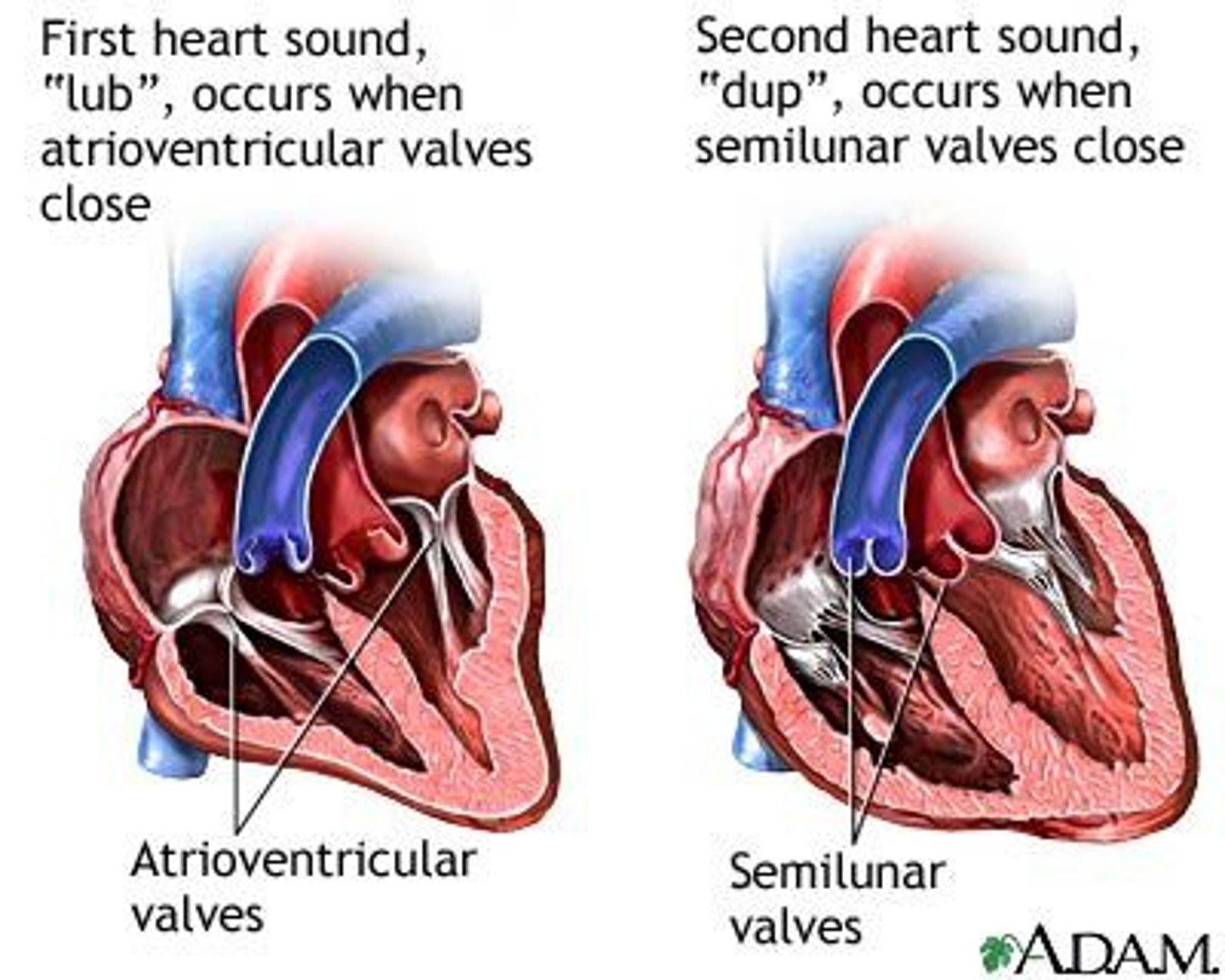
2nd sound (dub)
closure of the semilunar (aortic and pulmonary) valves, after emptying of ventricles
The wall of the heart consists of three layers
the epicardium (external layer), the myocardium (middle layer) and the endocardium (inner layer).
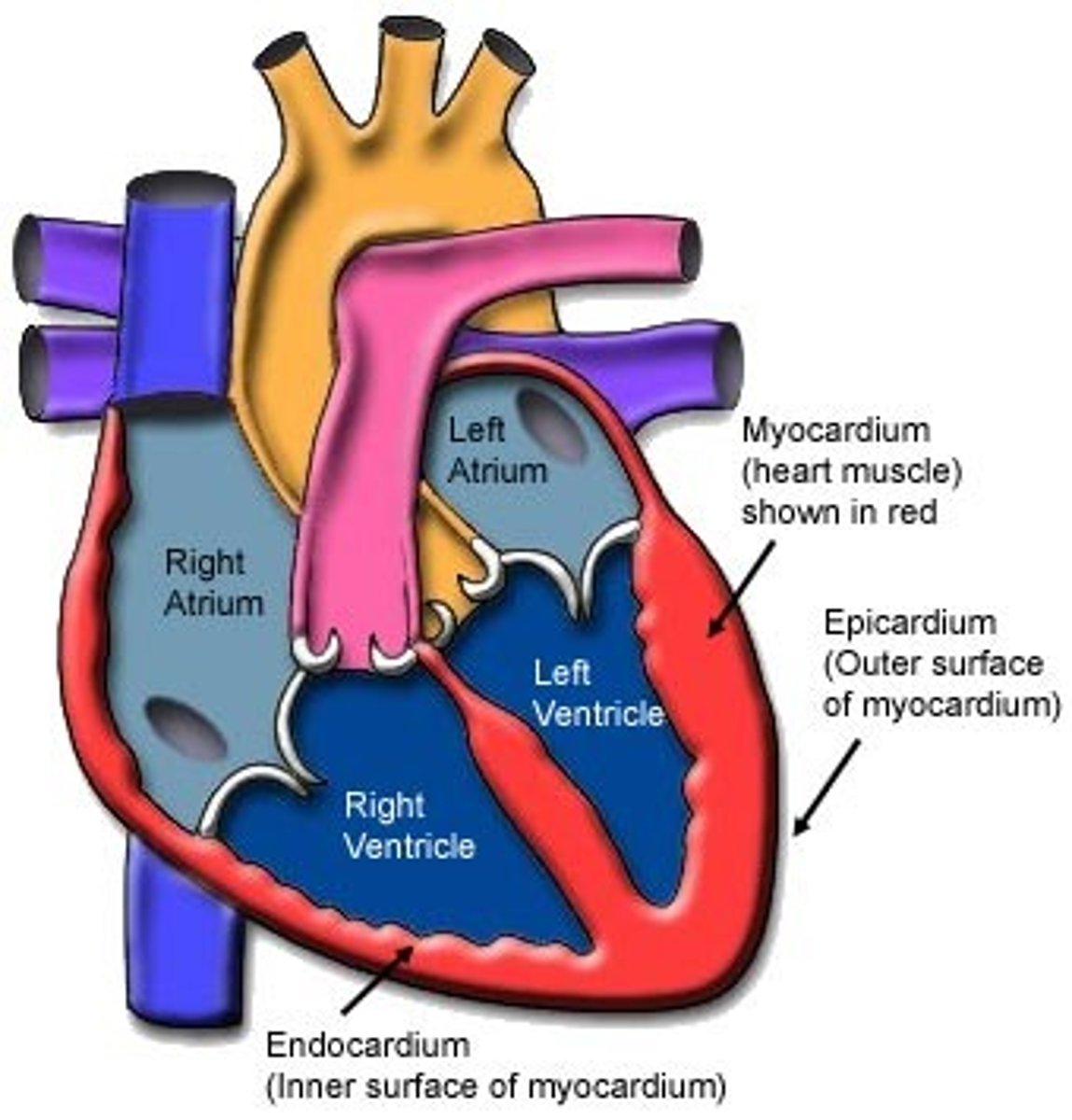
epicardium
thin external layer (most superficial) formed by the visceral layer of serous pericardium
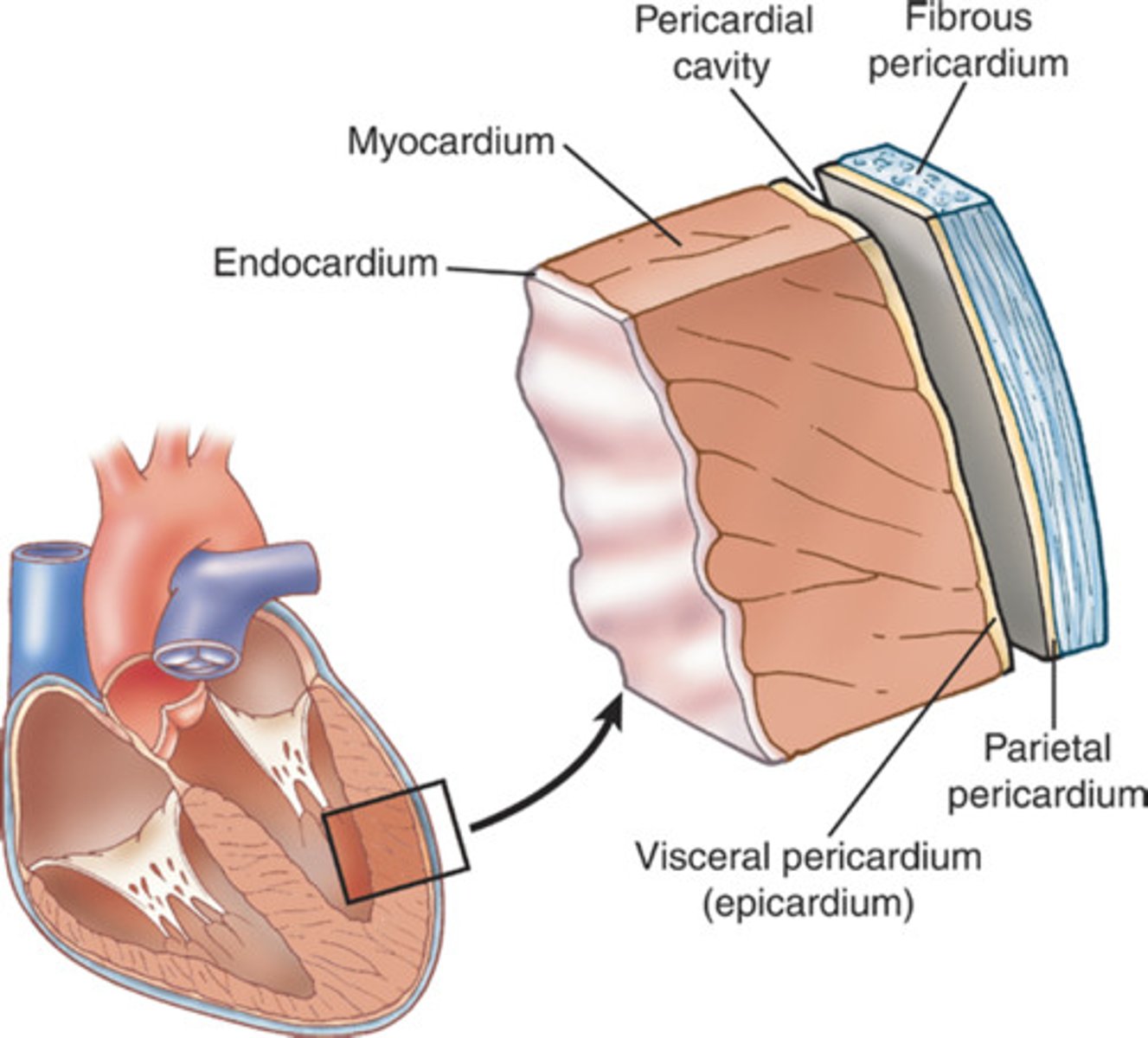
Myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart. cardiac muscle
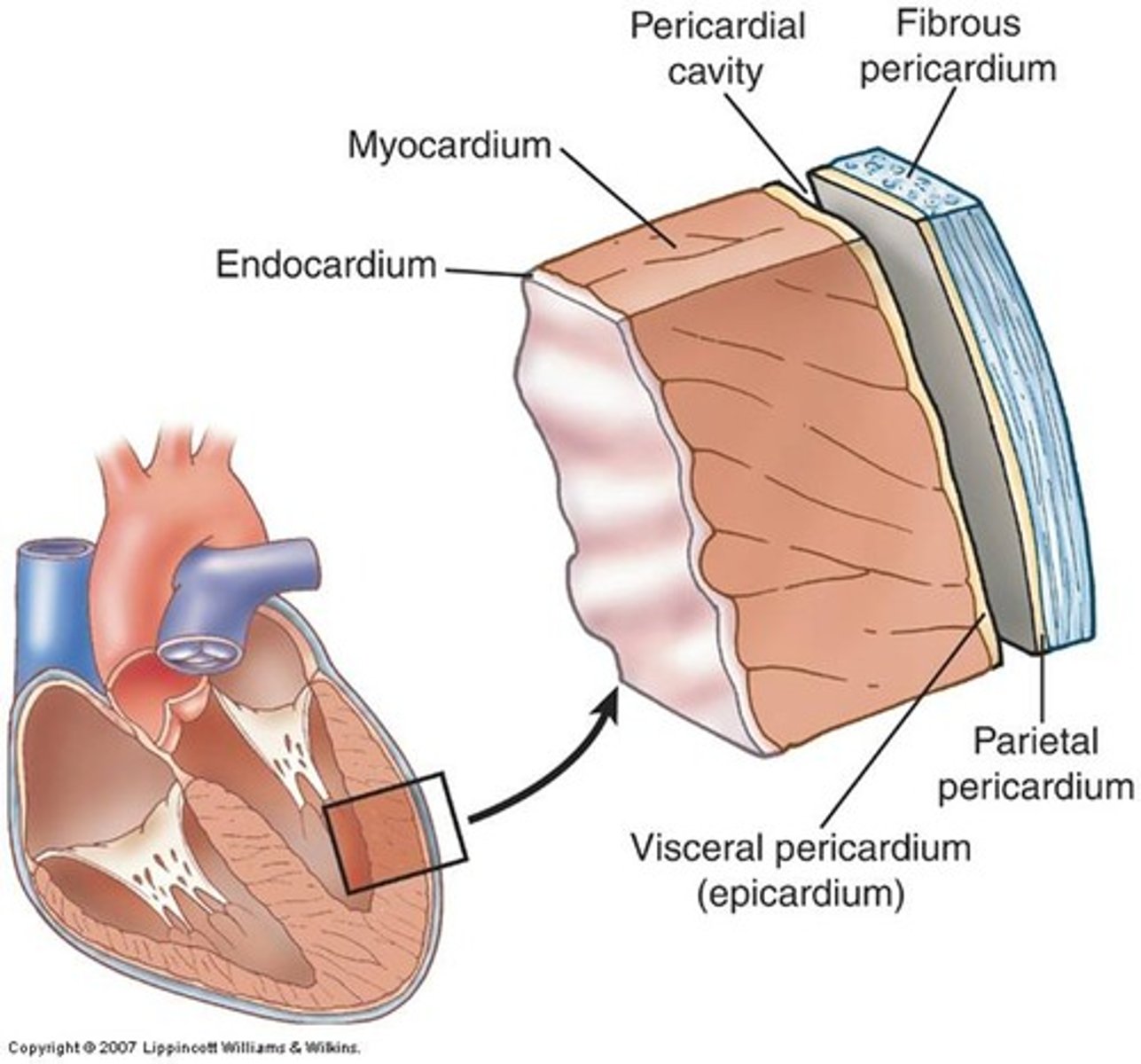
endocardium
inner layer of the heart; lines the heart chambers and valves
heart skeleton (fibrous skeleton)
Is made up of four rings of thick connective tissue which surround the base of the heart and large vessels. Framework formed of dense cartilaginous rings that surround the orifice of the valves
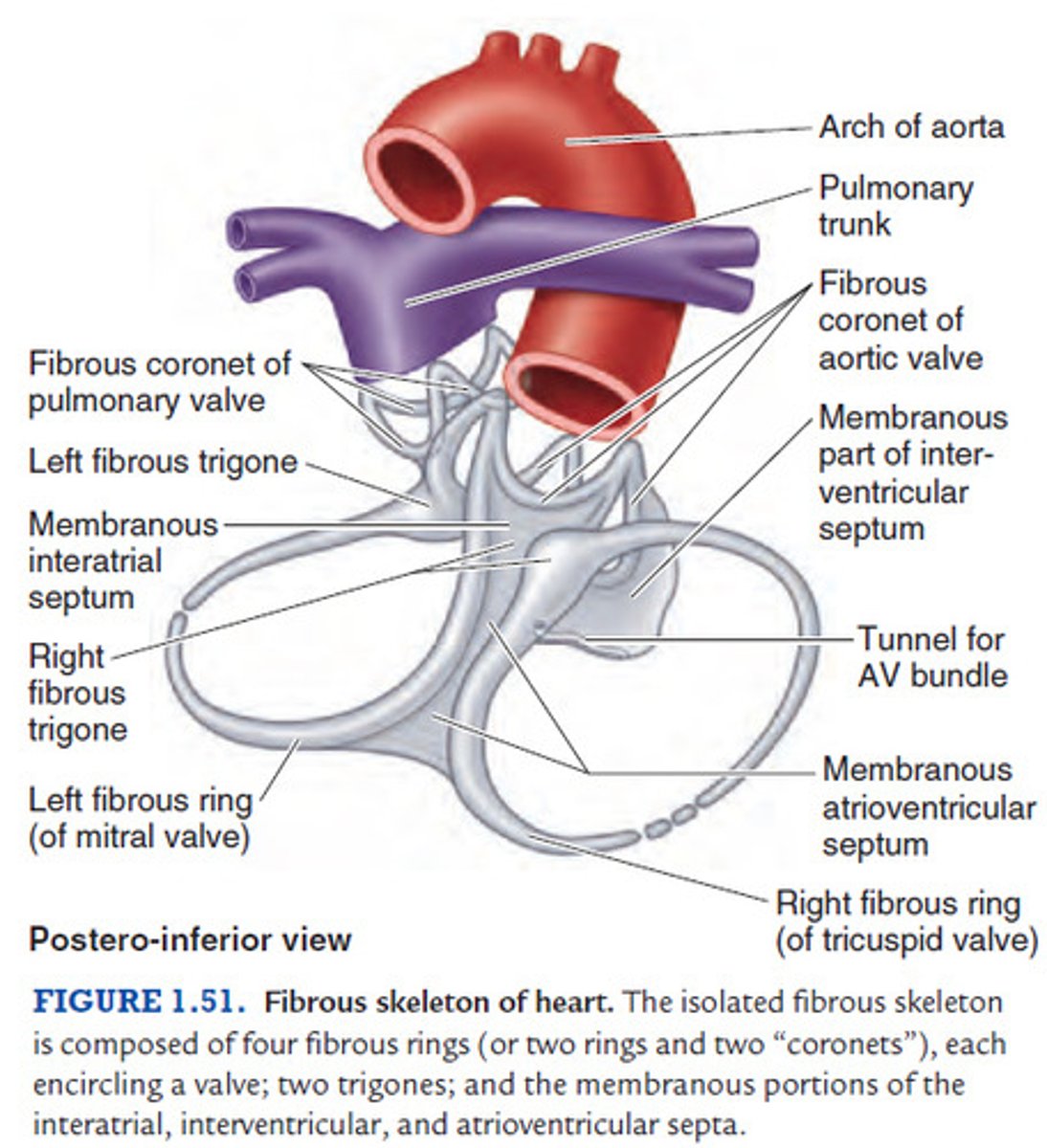
The heart skeleton, a fibrous skeleton, keeps orifices of the valves
patent and prevent their over-distention, and provide attachments for the valves
the heart skeleton, a fibrous skeleton, provides
Provides attachment for the myocardium
the heart skeleton, a fibrous skeleton, forms
an electric insulator for impulses of the atria and the ventricles
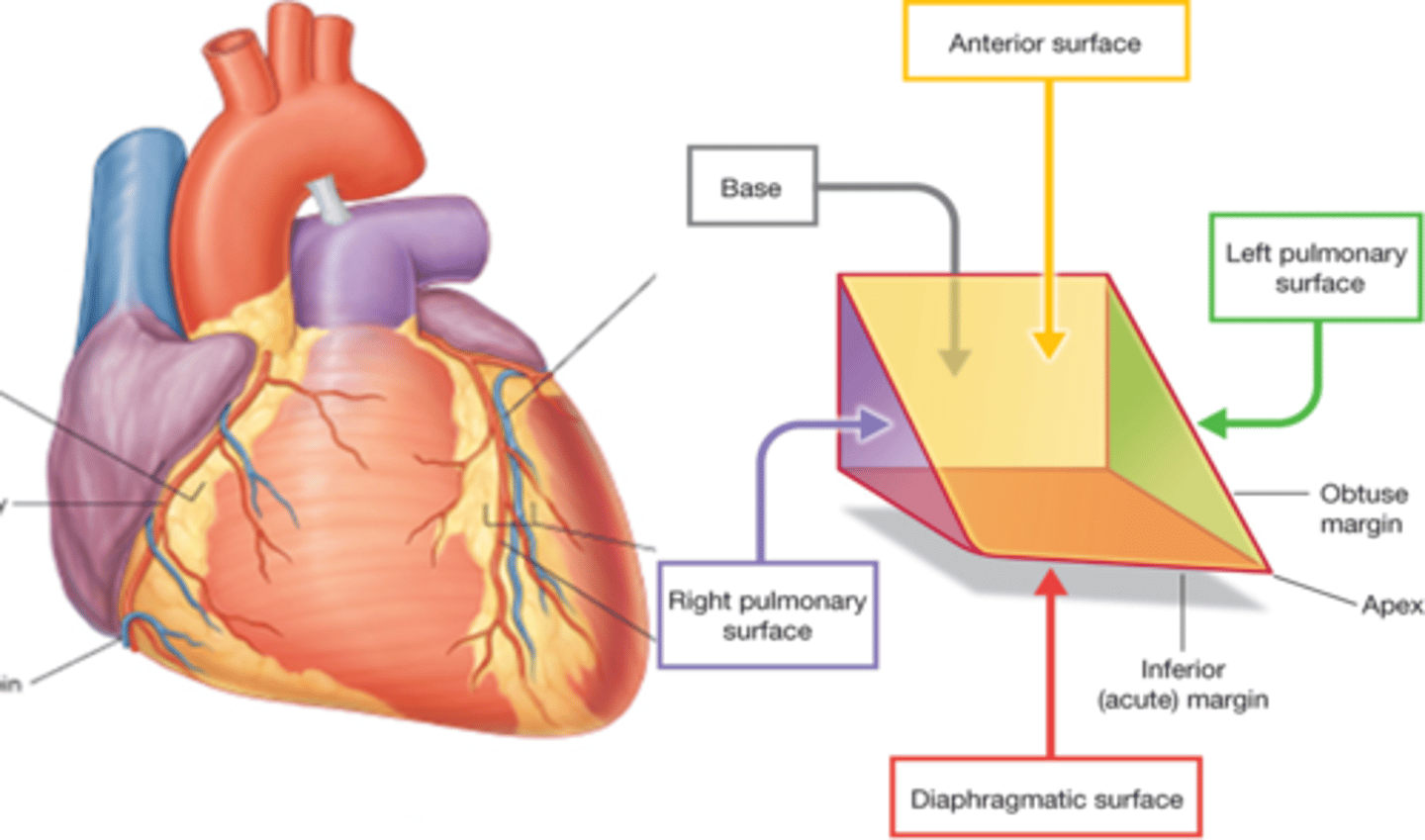
Heart Surfaces
- anterior (sternocostal) surface
- inferior (diaphragmatic) surface
- left pulmonary surface
- right pulmonary surface
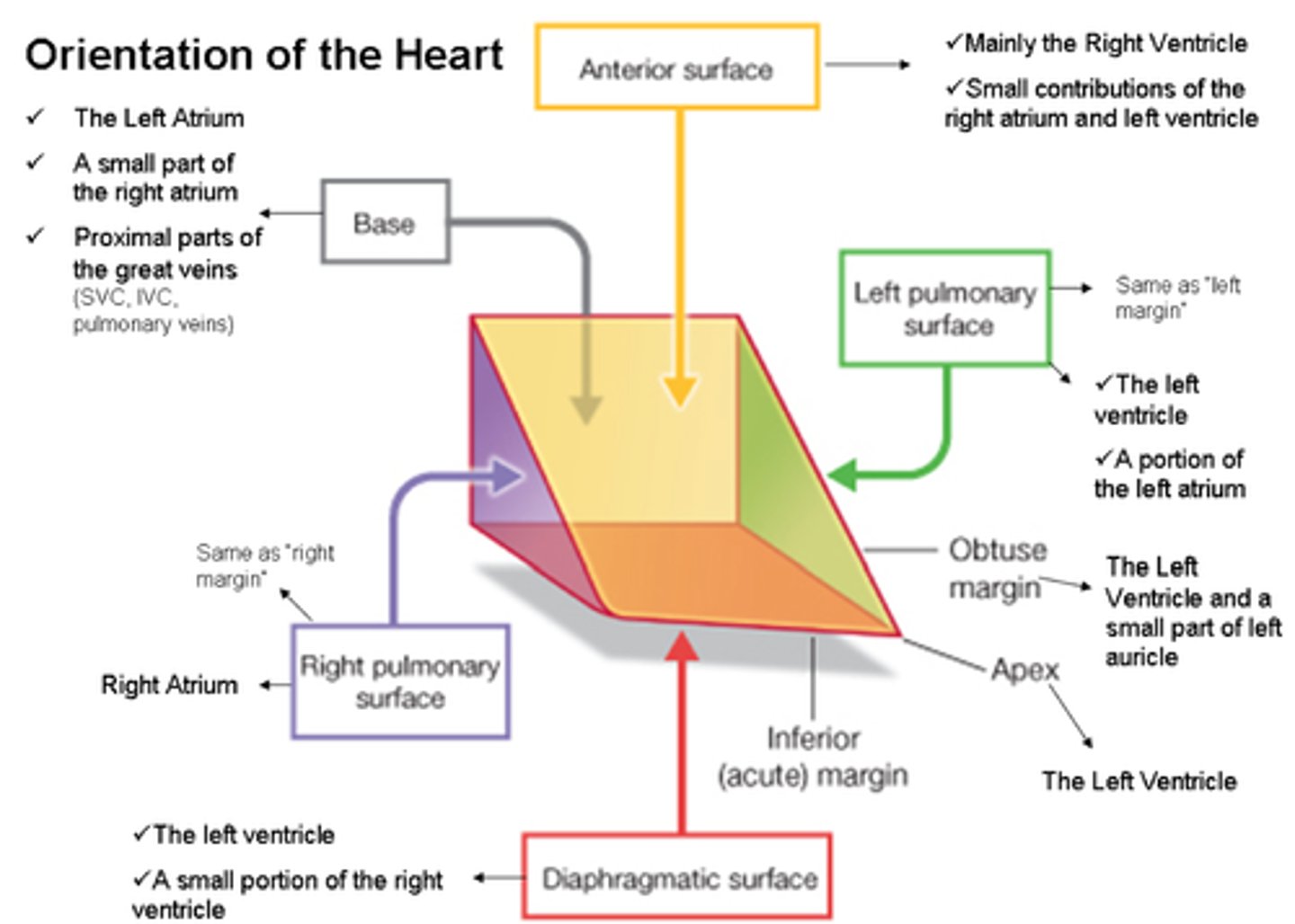
anterior (sternocostal) surface of the heart
This heart surface is formed mainly by the right ventricle
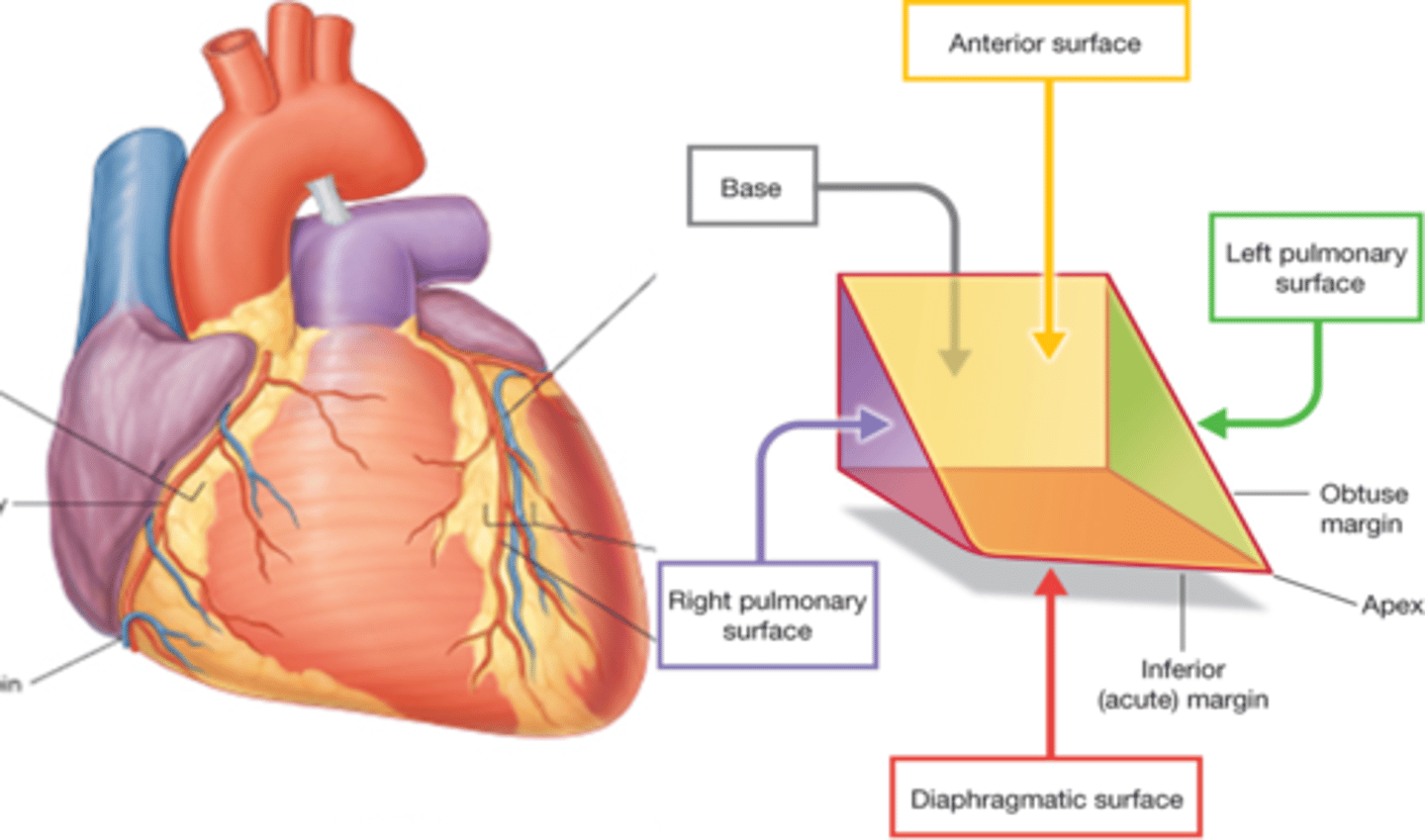
Inferior (diaphragmatic) surface of the heart
-primarily the left ventricle
-lesser contribution by right ventricle
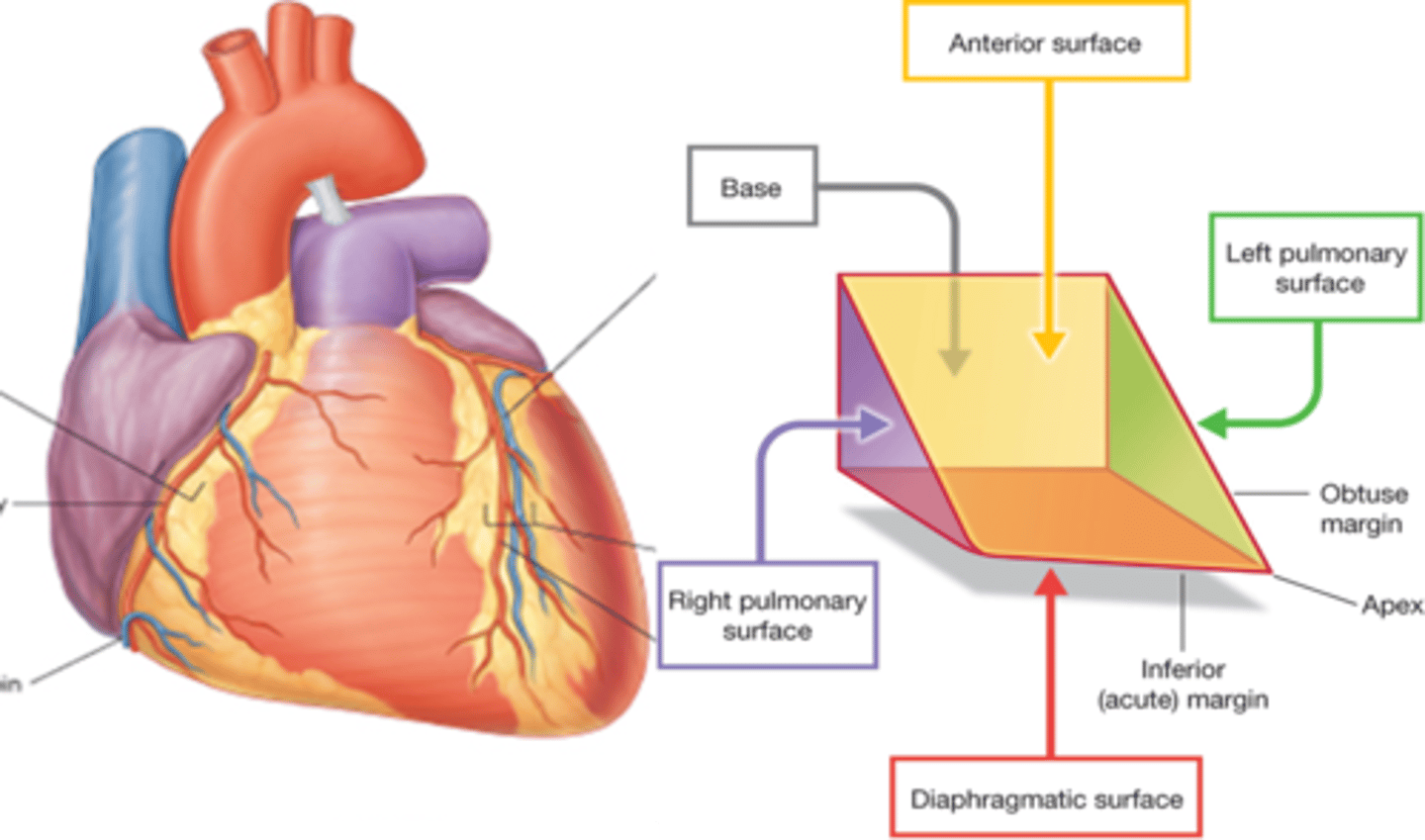
Right pulmonary surface
formed mainly by the right atrium
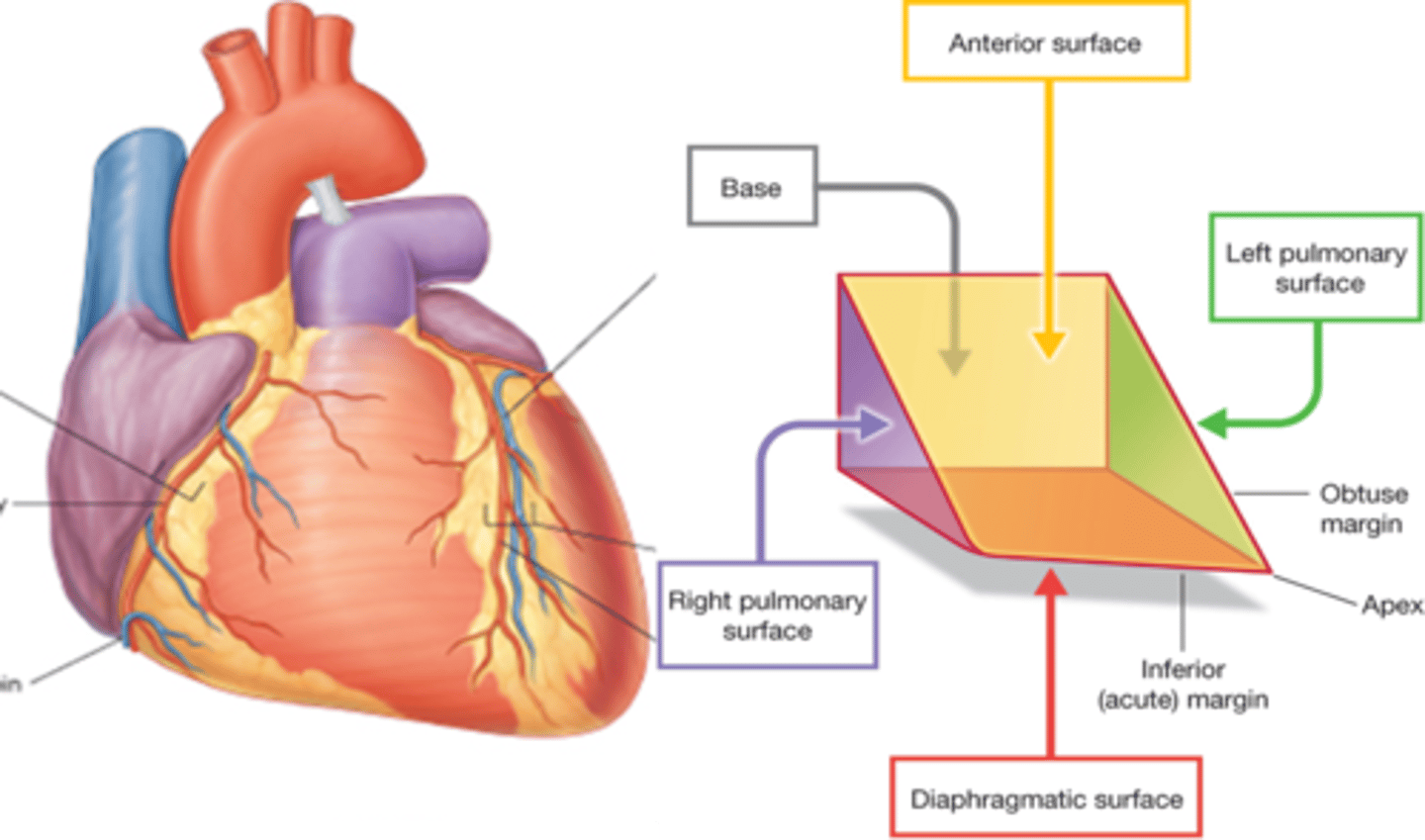
Left pulmonary surface
formed mainly by the left ventricle
heart borders
trapezoid in shape
Superior, right, left, inferior
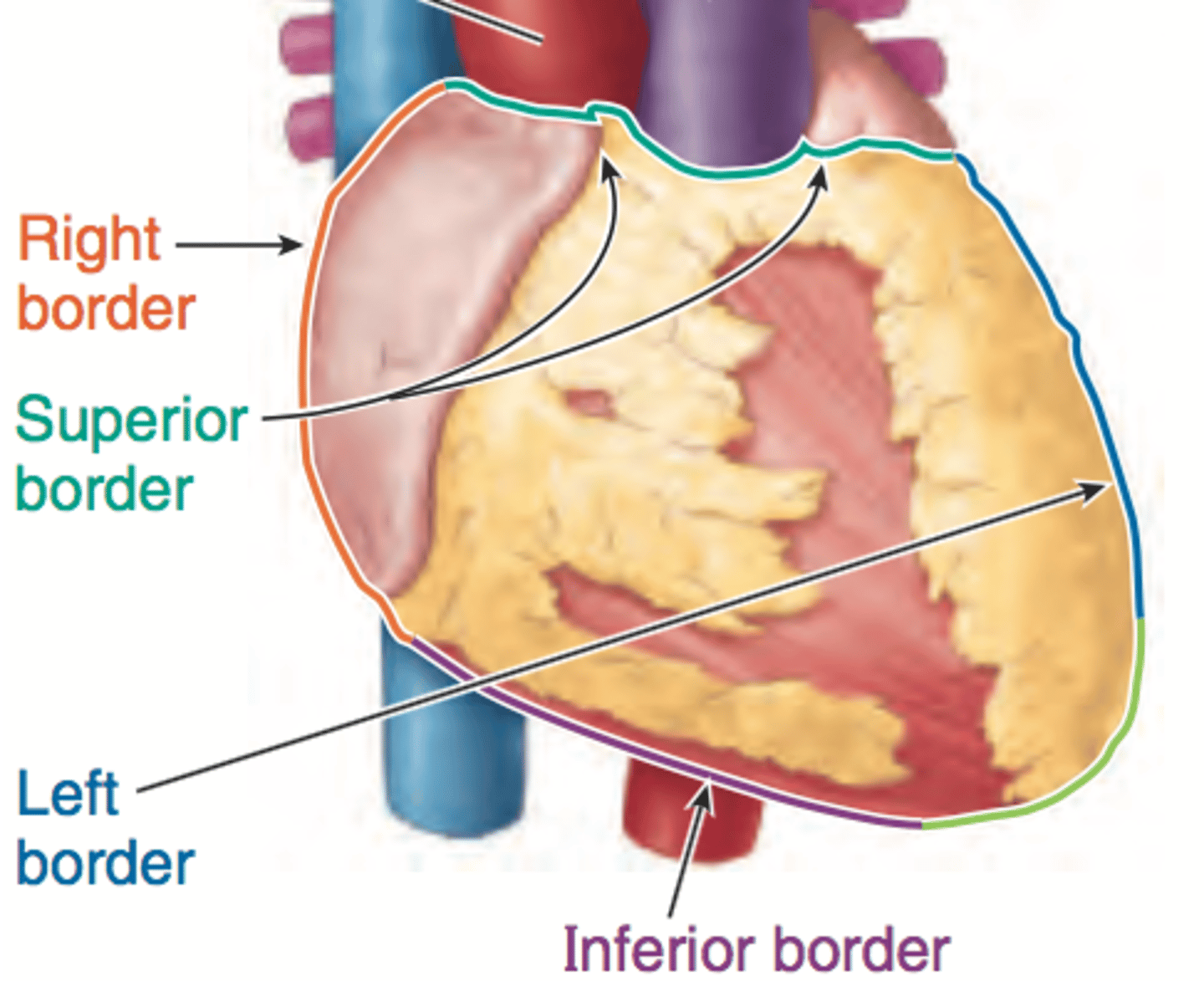
Right border of the heart is formed by
the right atrium and extends between the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava
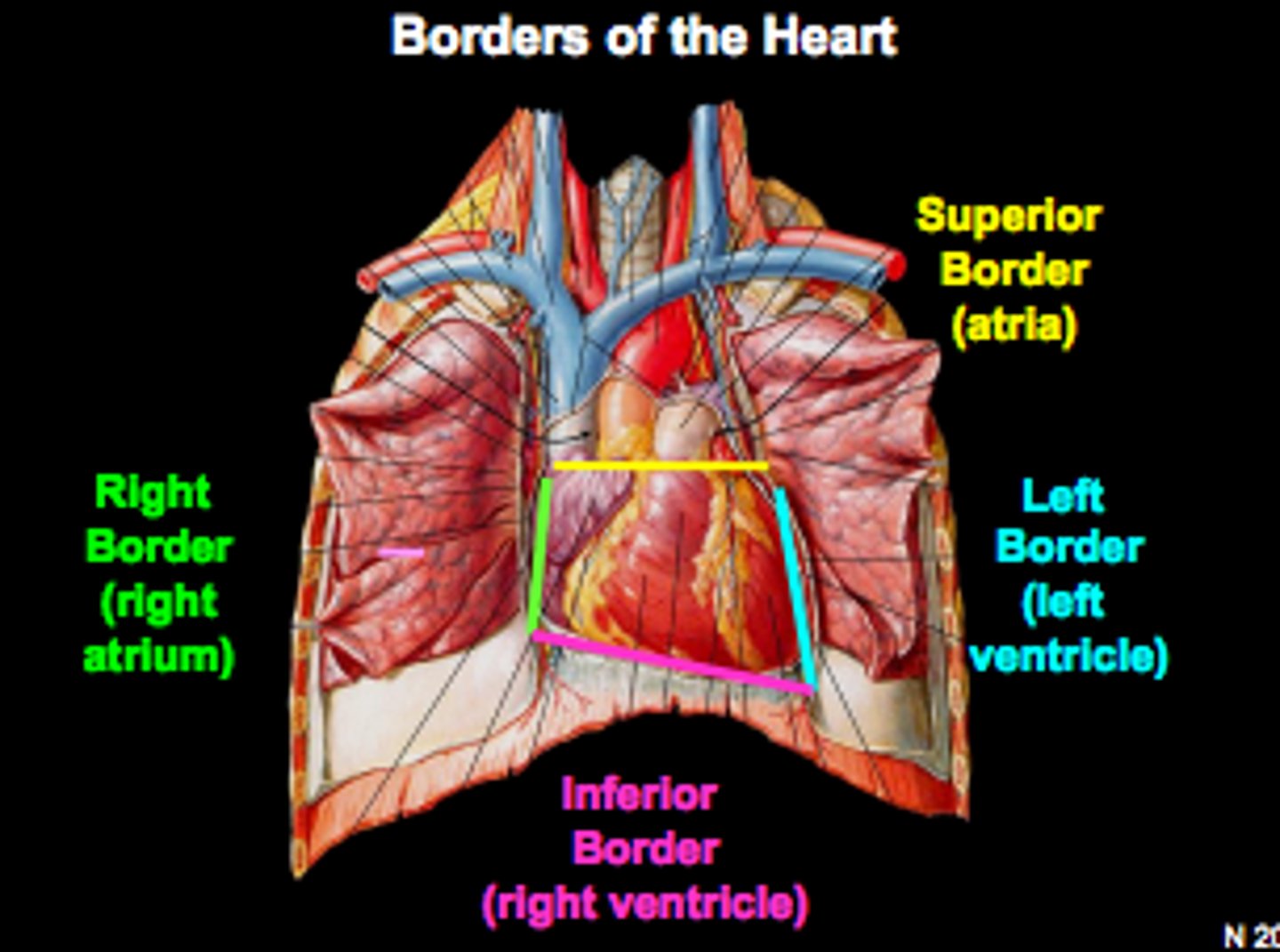
Inferior border of the heart is formed by
Right ventricle and lesser contribution by Left ventricle
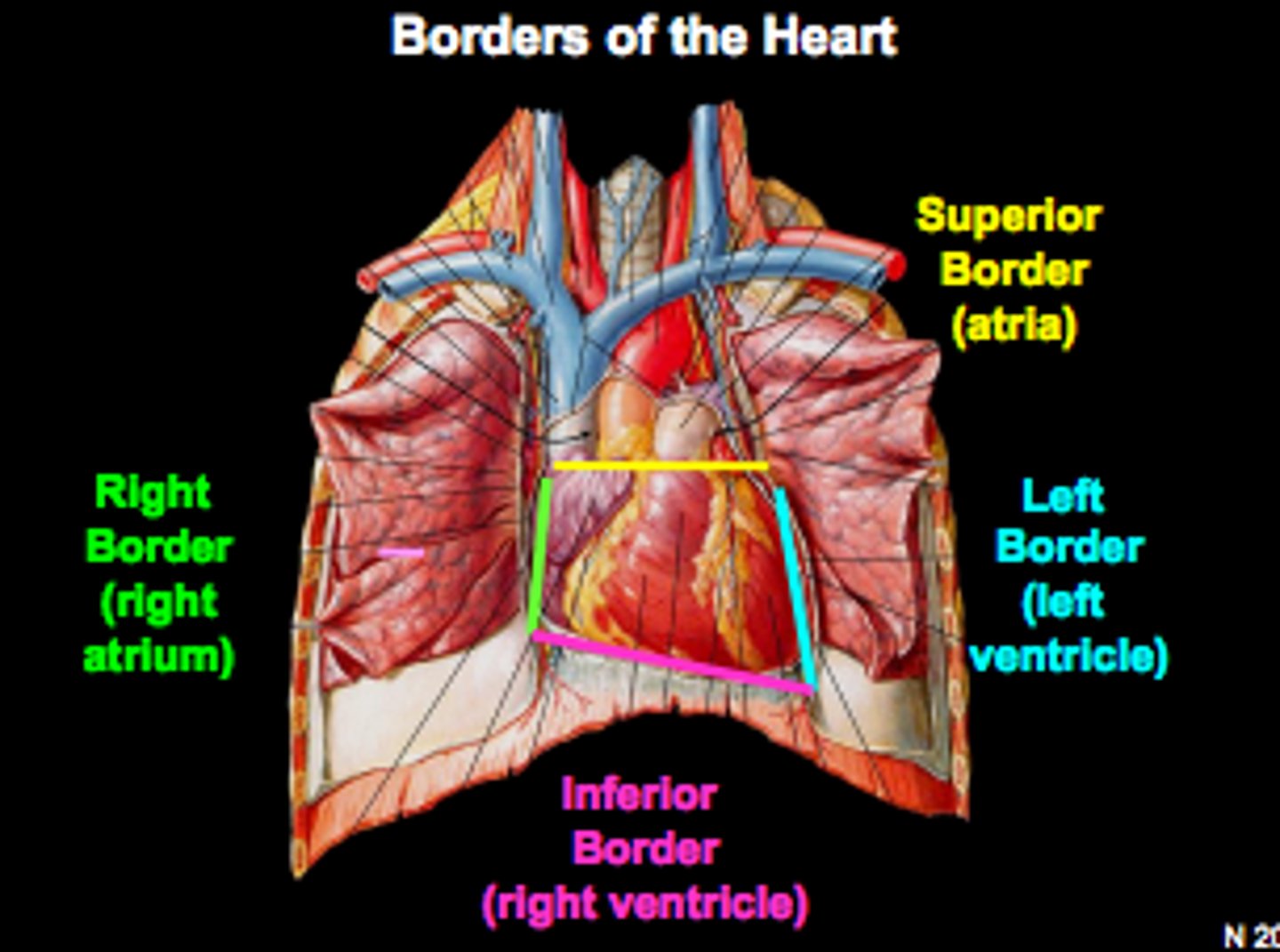
Left border of the heart is formed by
Left ventricle and left auricle
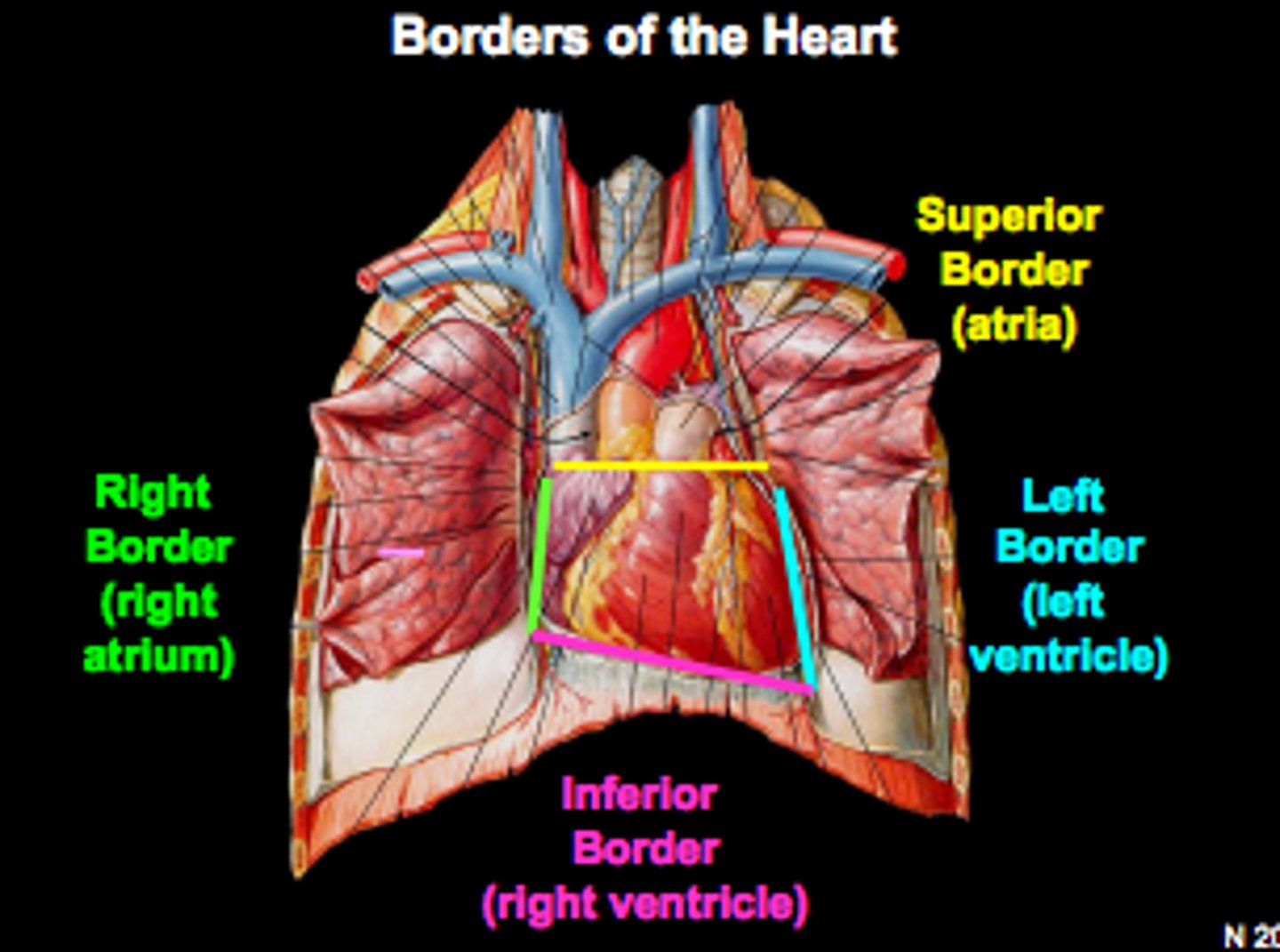
Superior border of the heart is formed by
right and left atria and auricles of the atria
The heart's big vessels have
entrances and exits to and from the heart
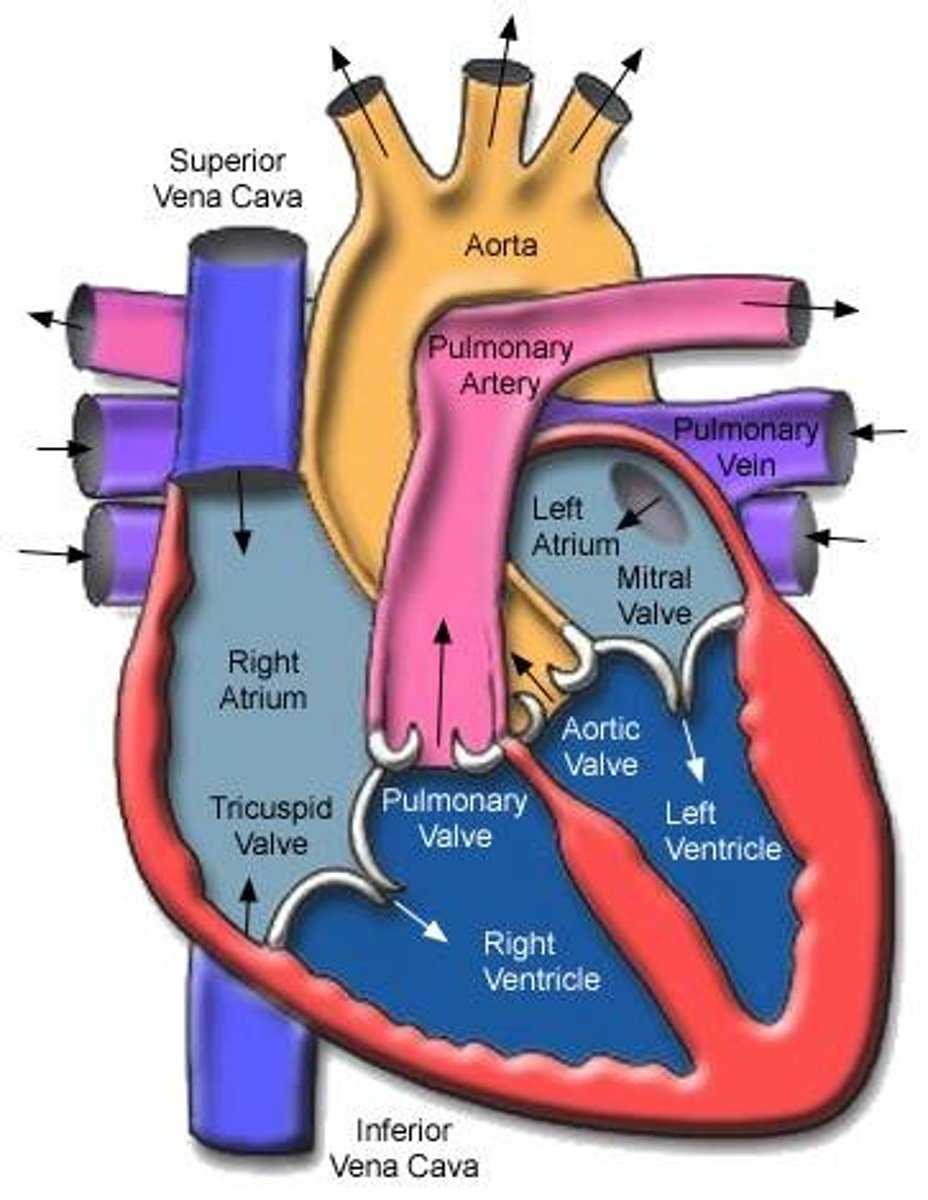
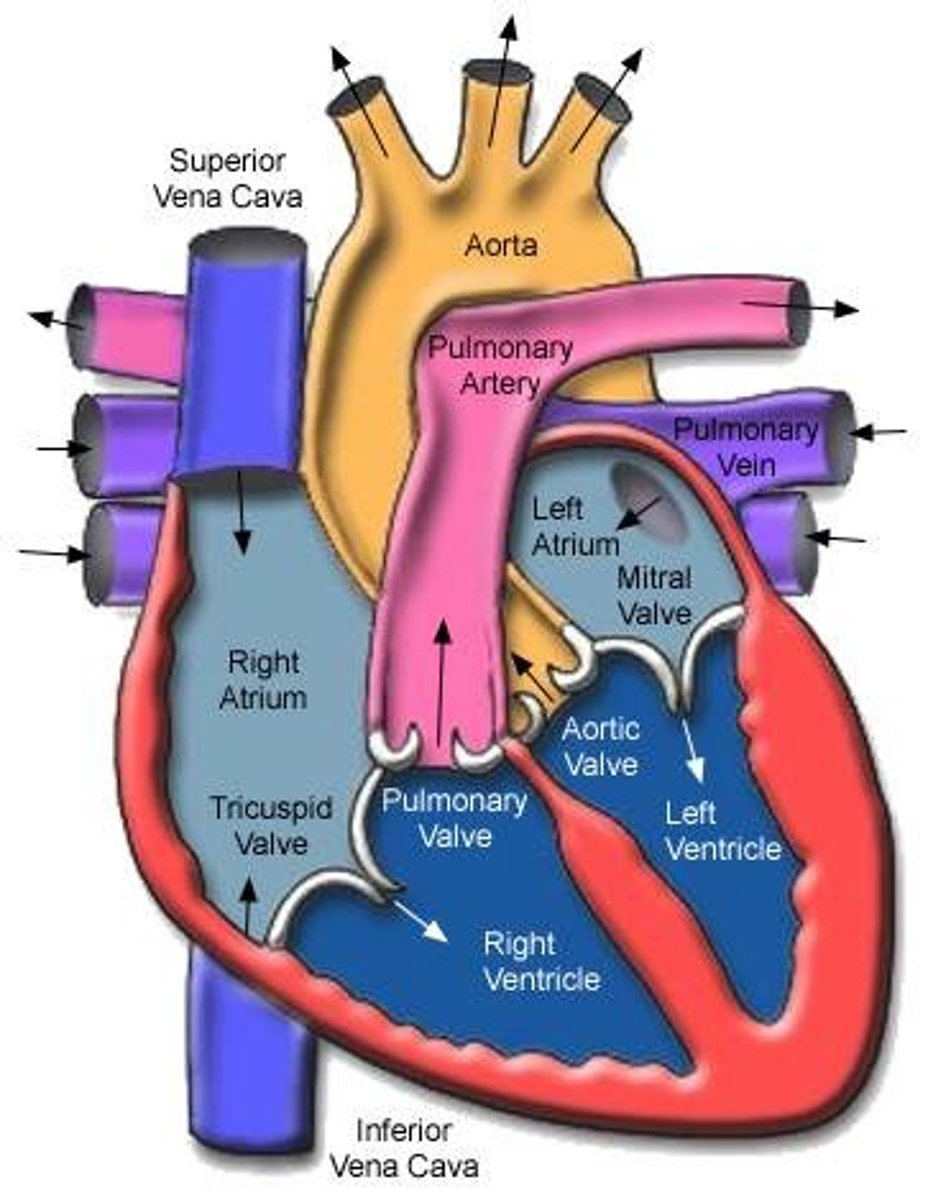
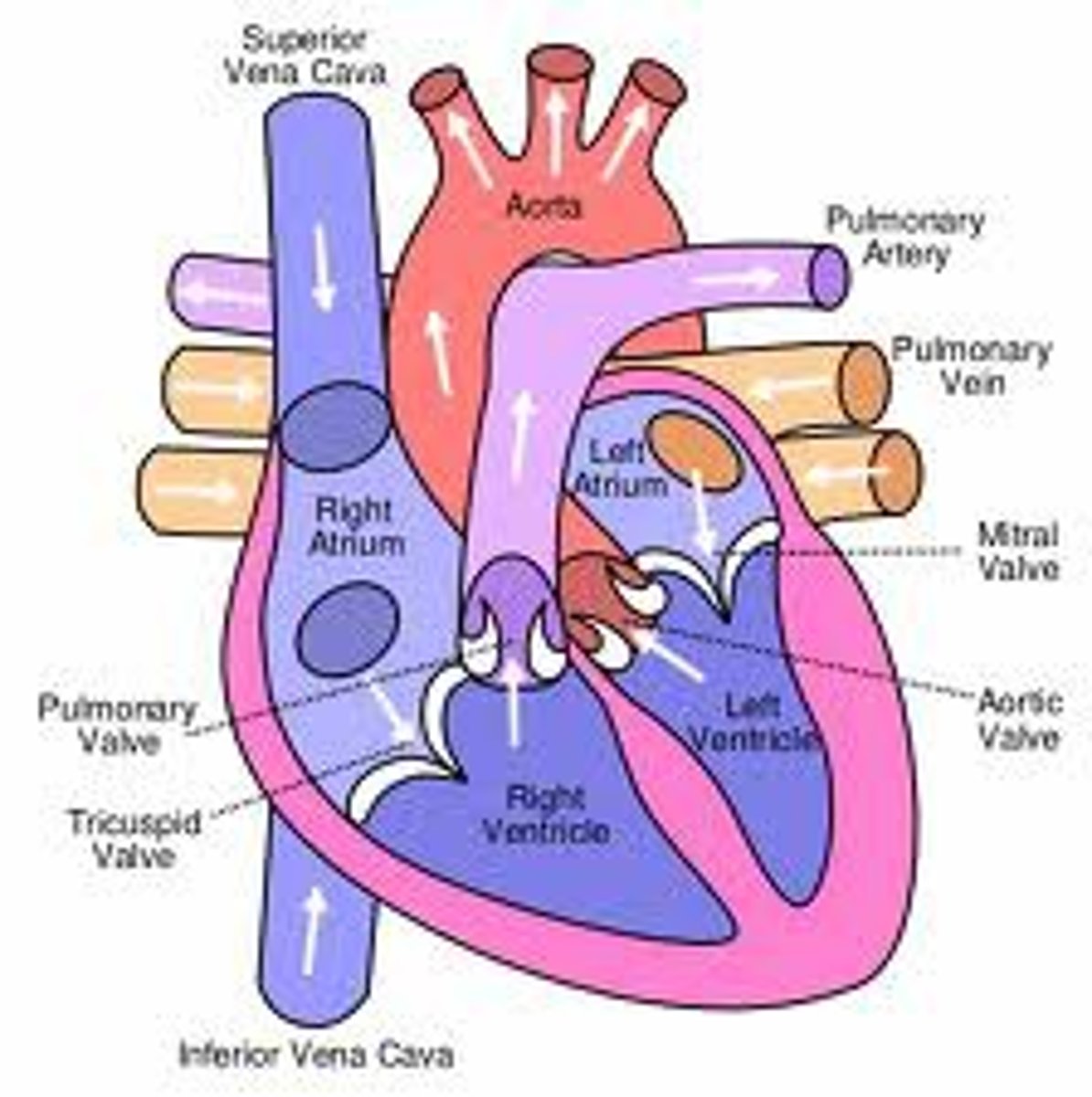
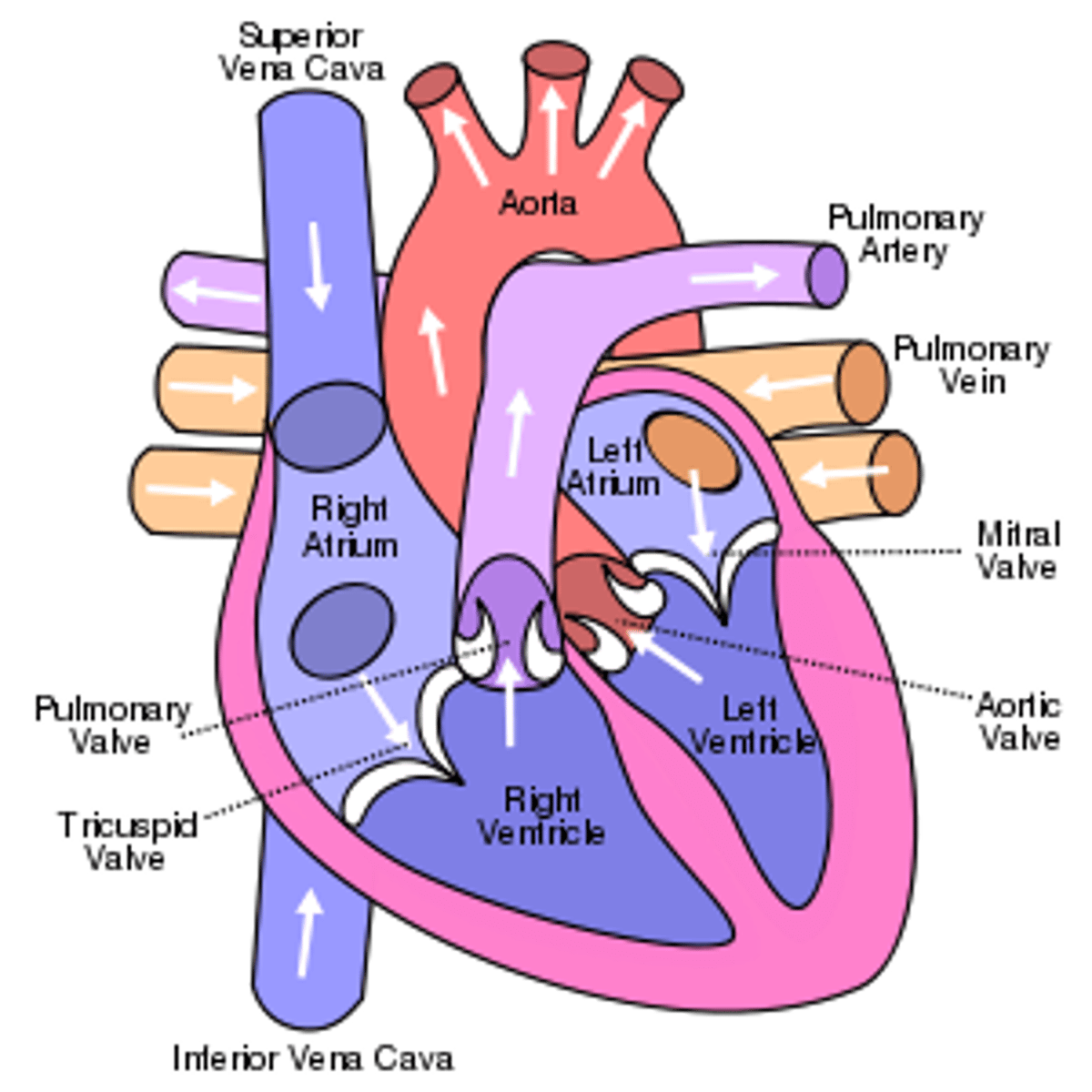
Heart Entrances
Right atrium and left atrium
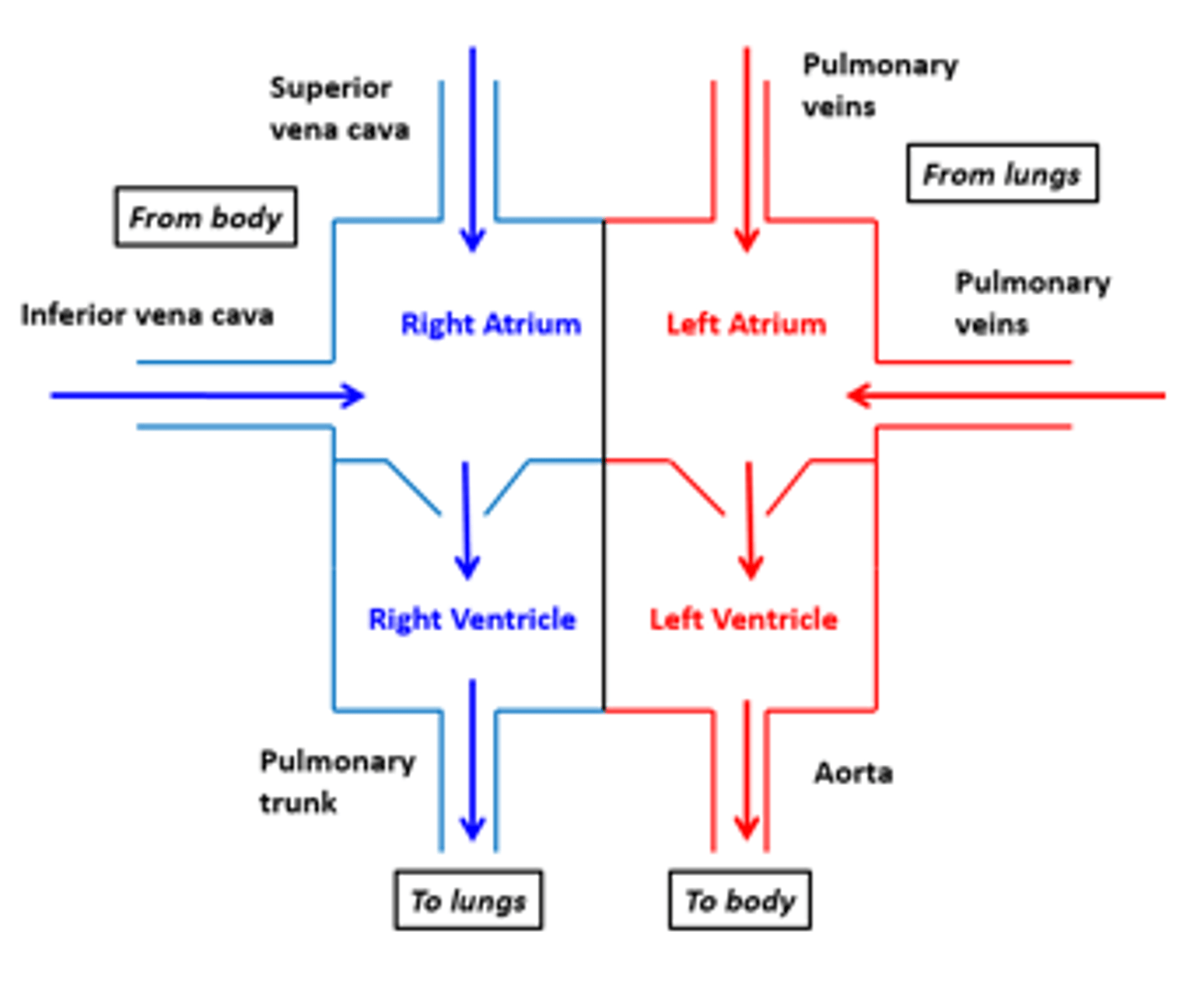
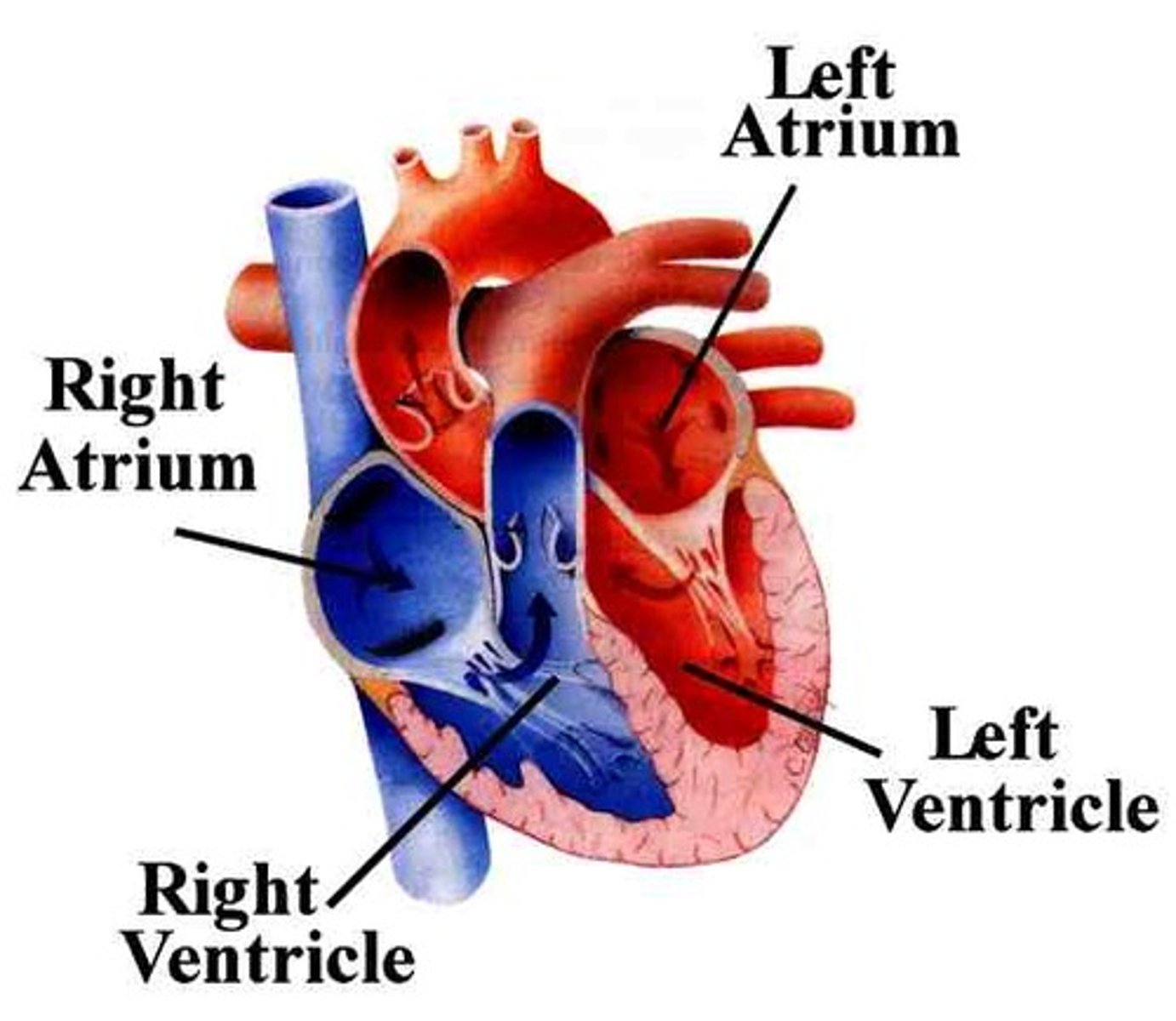
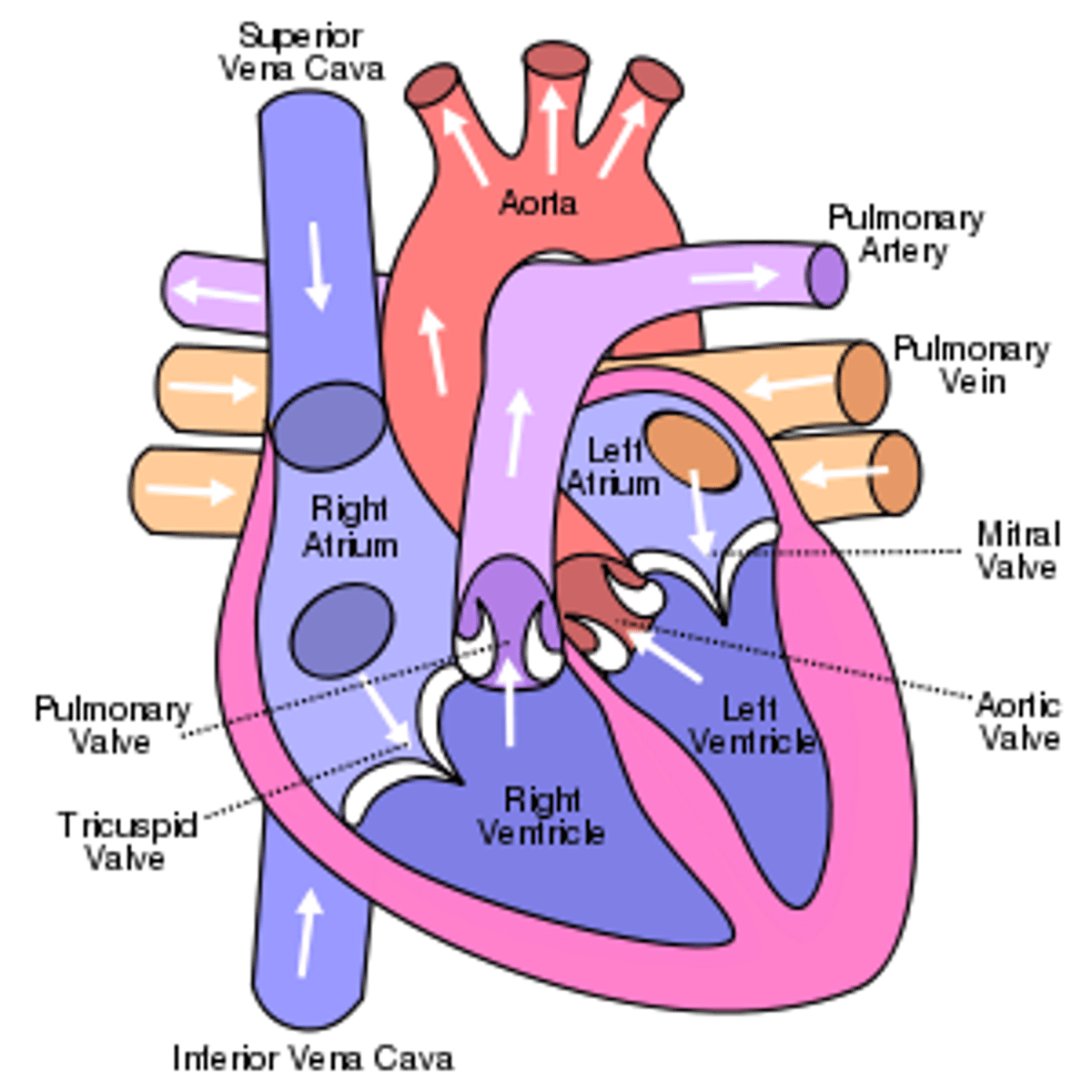
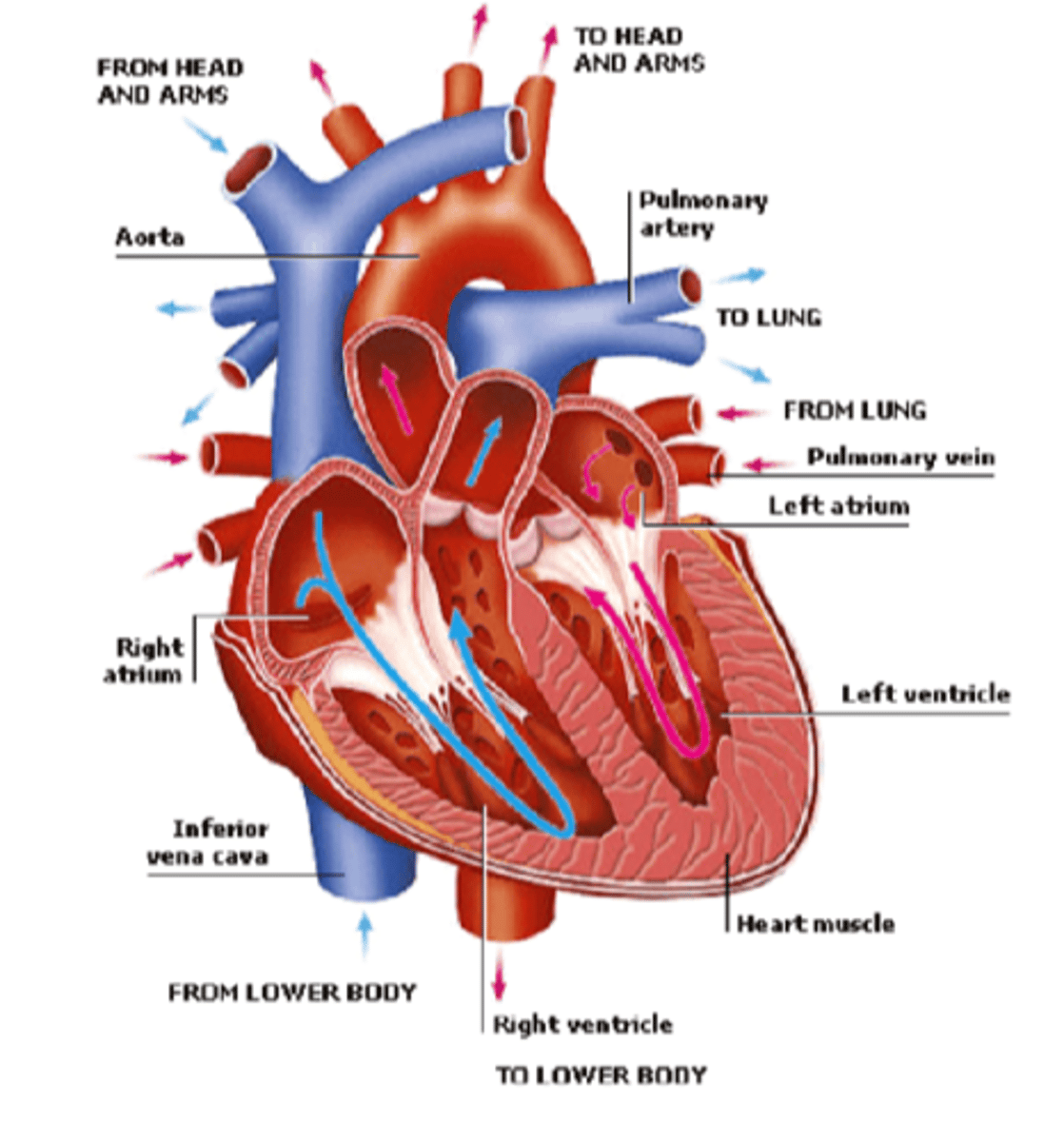
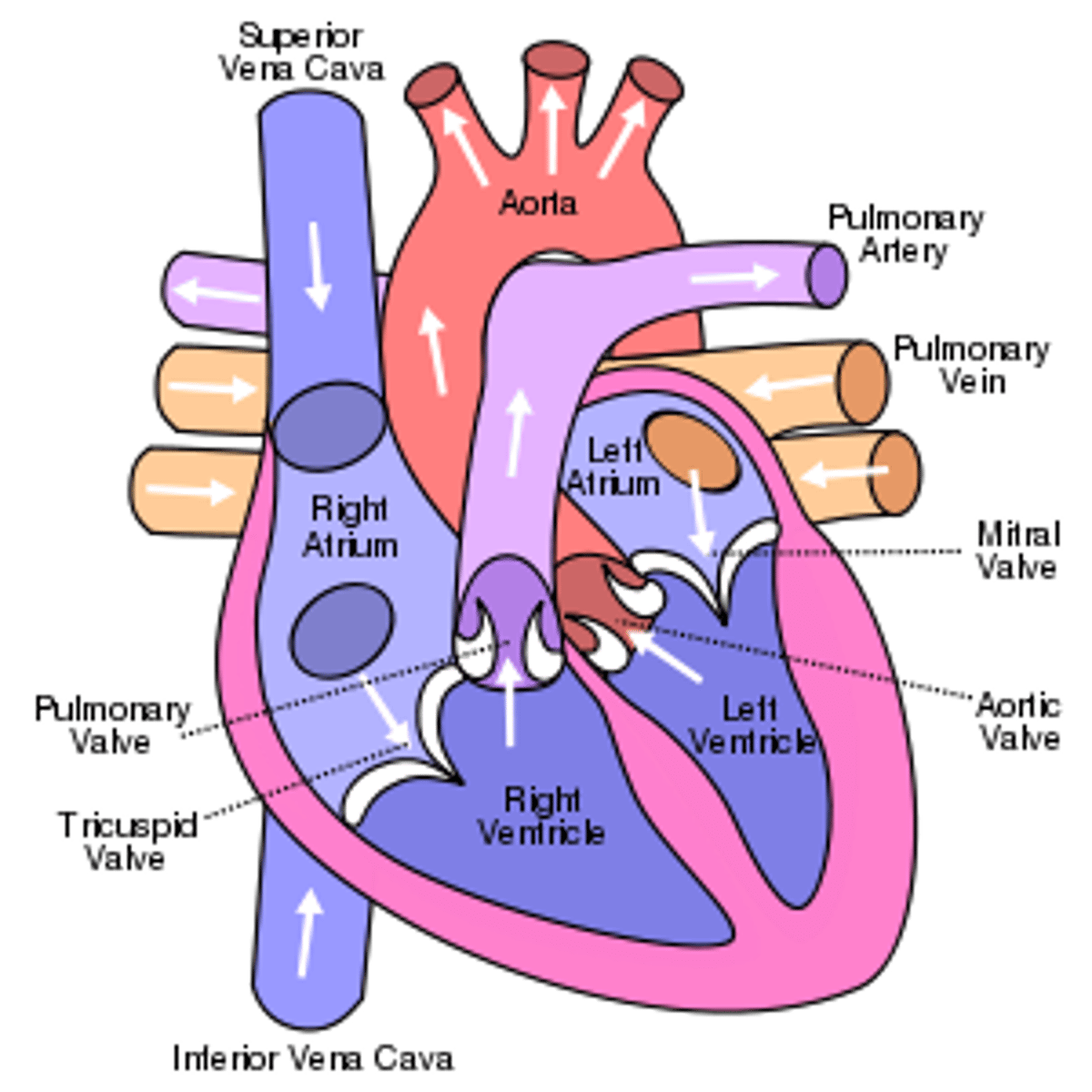
Right atrium
Superior Vena Cava (SVC), Inferior Vena Cava (IVC), and coronary sinus. Receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
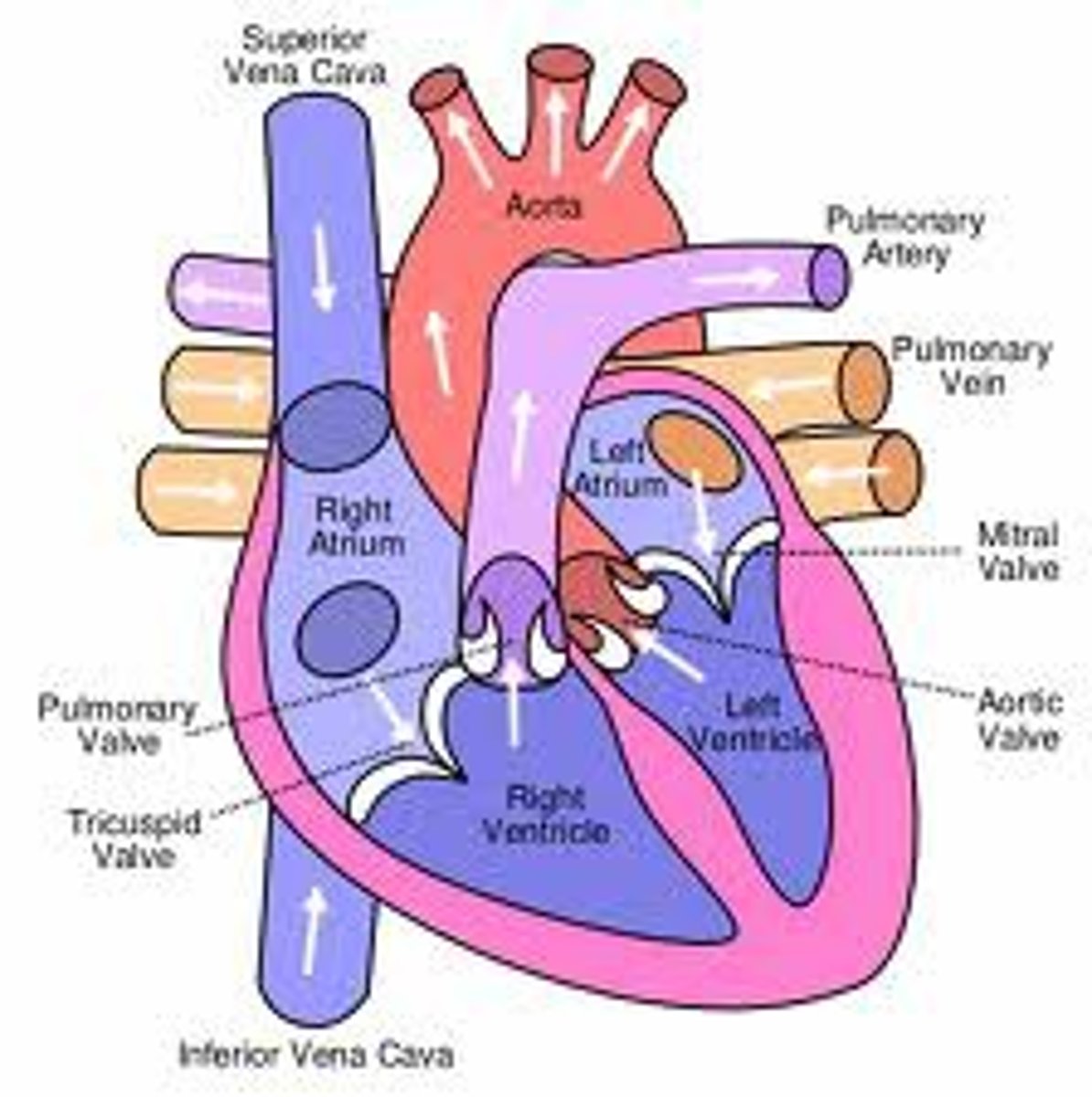
Left atrium connects to the
right and left pulmonary veins
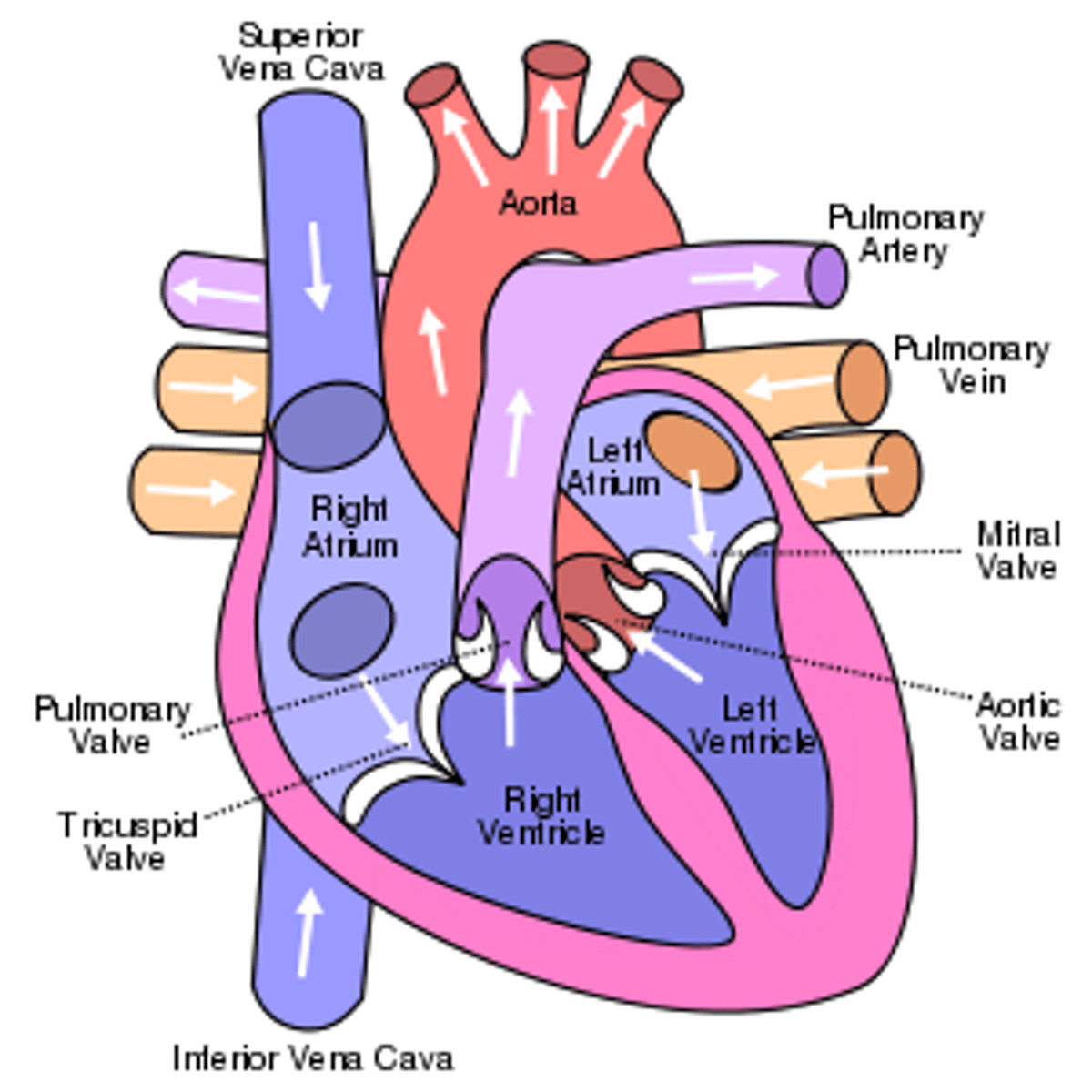
Heart exits
right ventricle and left ventricle
Blood exits the right ventricle from the
pulmonary trunk
left ventricle pumps
oxygen-rich blood into the aorta (the largest artery in the body)
Heart chambers: right atrium
-Forms R. border of the heart
-Receives blood from the SVC, IVC, and coronary sinus
-Auricle
Auricle:
conical muscular pouch projecting from the R. atrium, and increasing its capacity
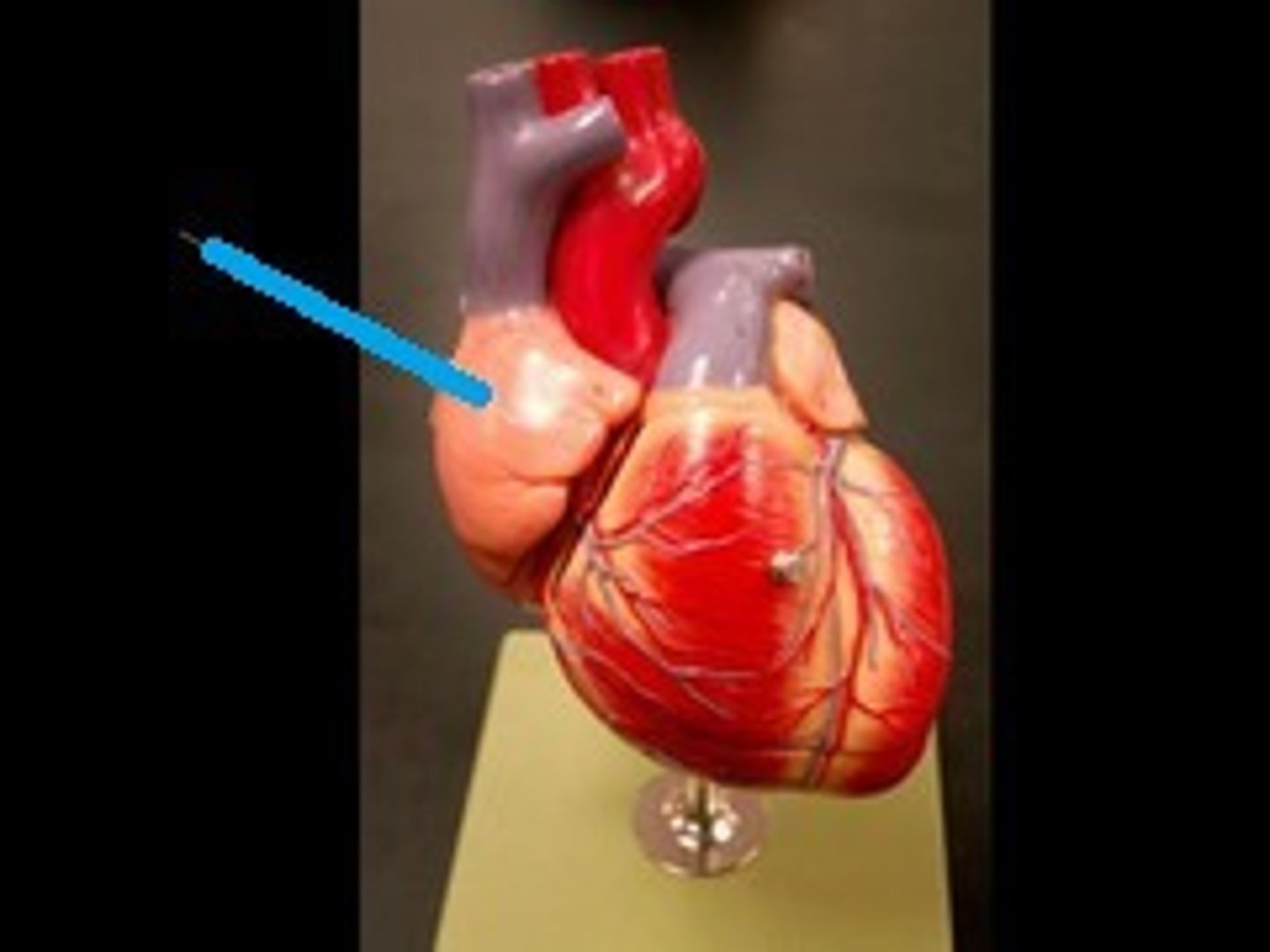
Right atrium (location)
upper right chamber of the heart and overlaps the ascending aorta
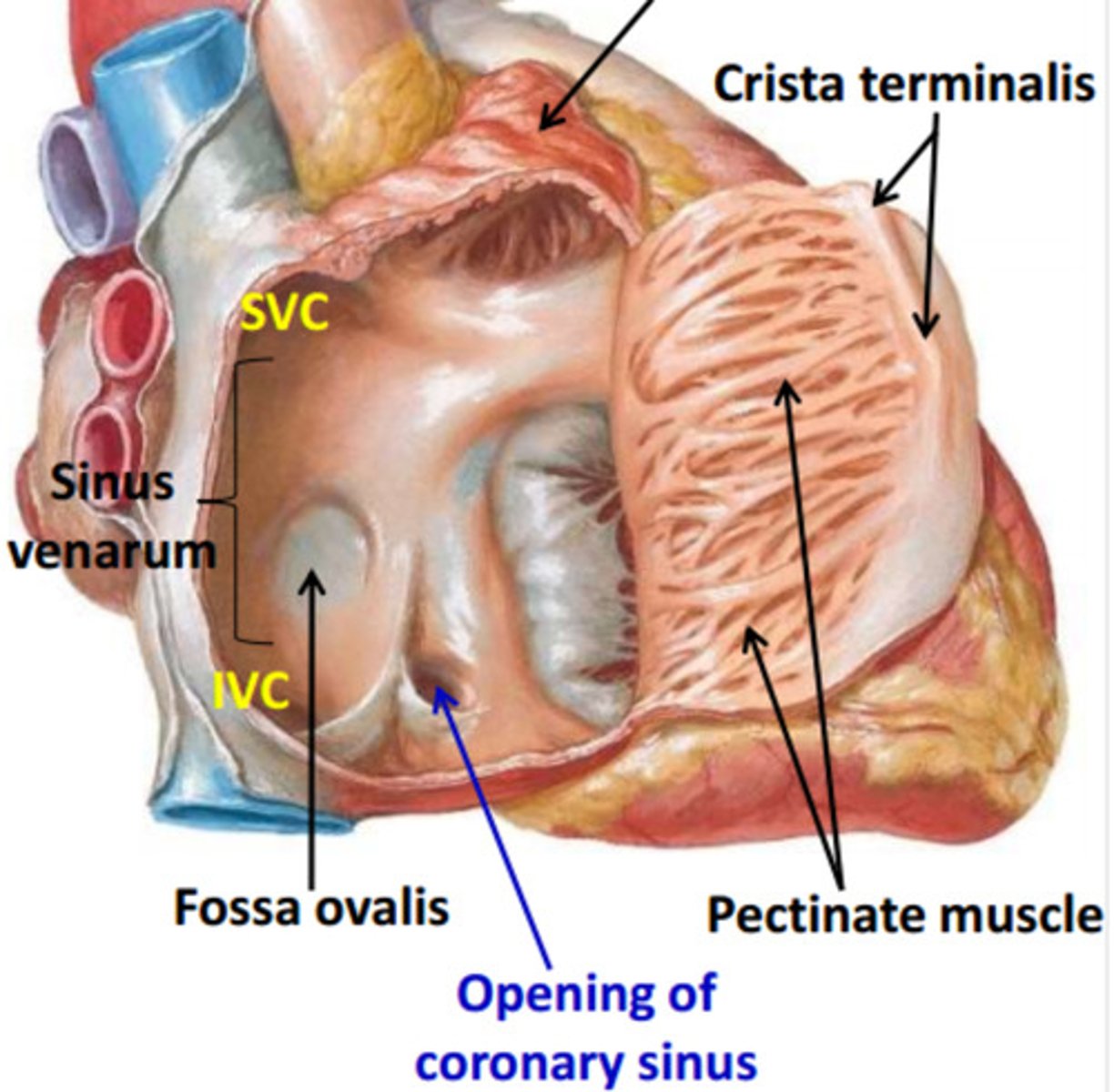
The interior of the right atrium
- Sinus Venarum
- Pectinate muscles
- Right AV orifice
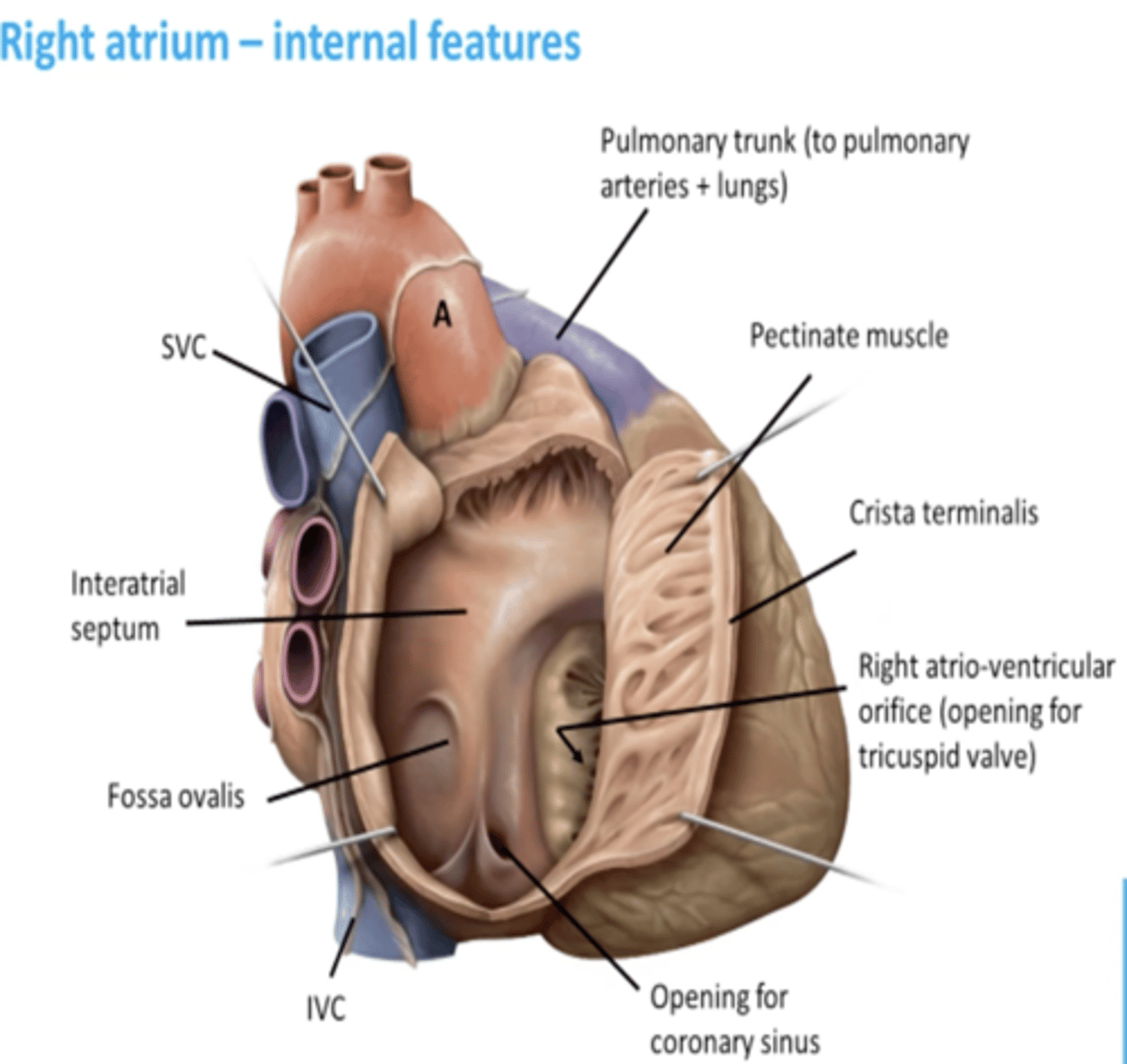
Sinus venarum
smooth, thin-walled, posterior part; where SVC, IVC, and coronary sinus open
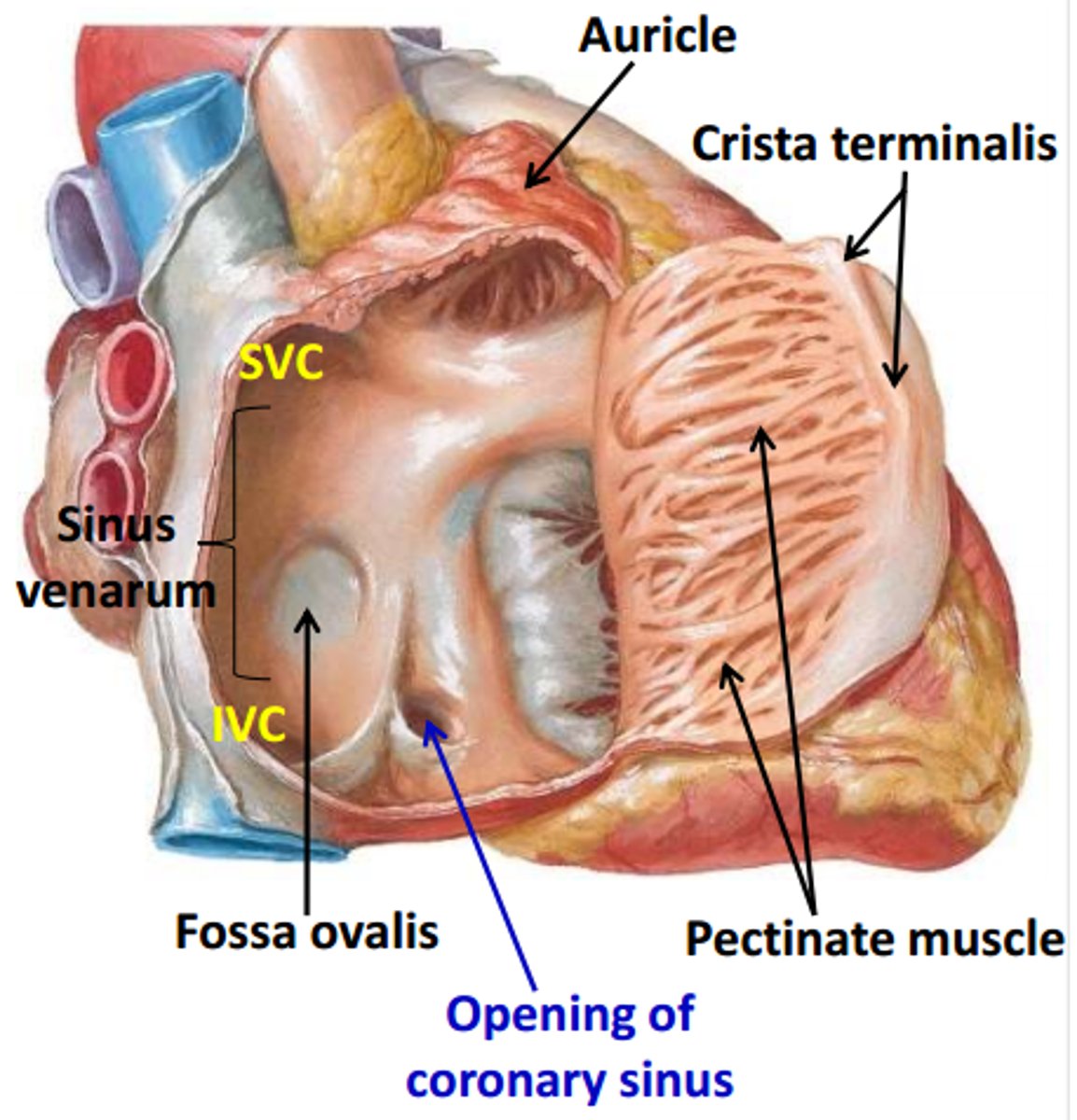
Pectinate muscles:
rough, muscular anterior wall
Right atrioventricular orifice:
R. atrium discharges the low-oxygen blood into R. ventricle
Sulcus terminalis
external vertical groove separating the smooth and rough parts of the R. atrium
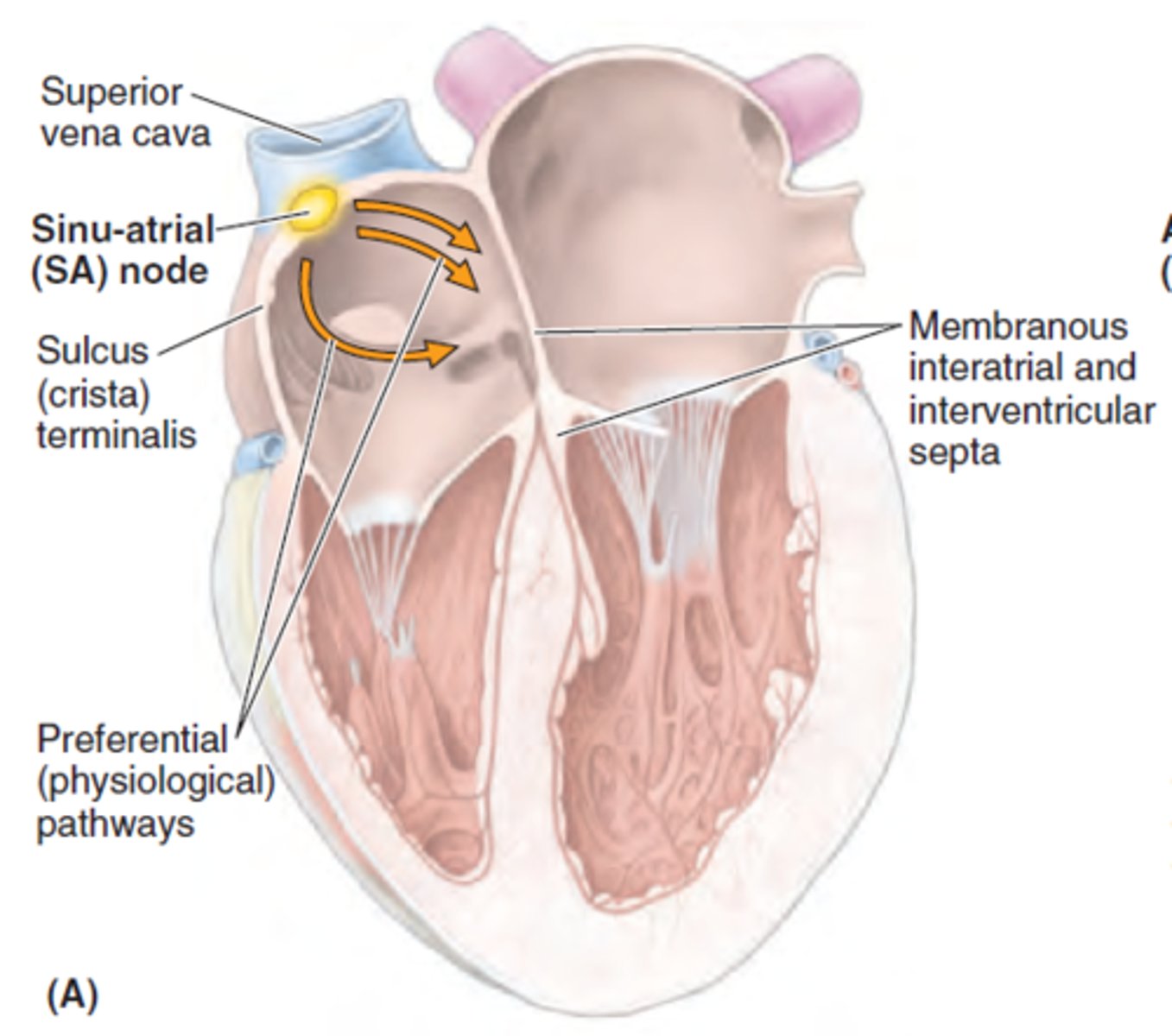
Crista terminalis:
internal vertical ridge separating the smooth and rough parts of the R. atrium
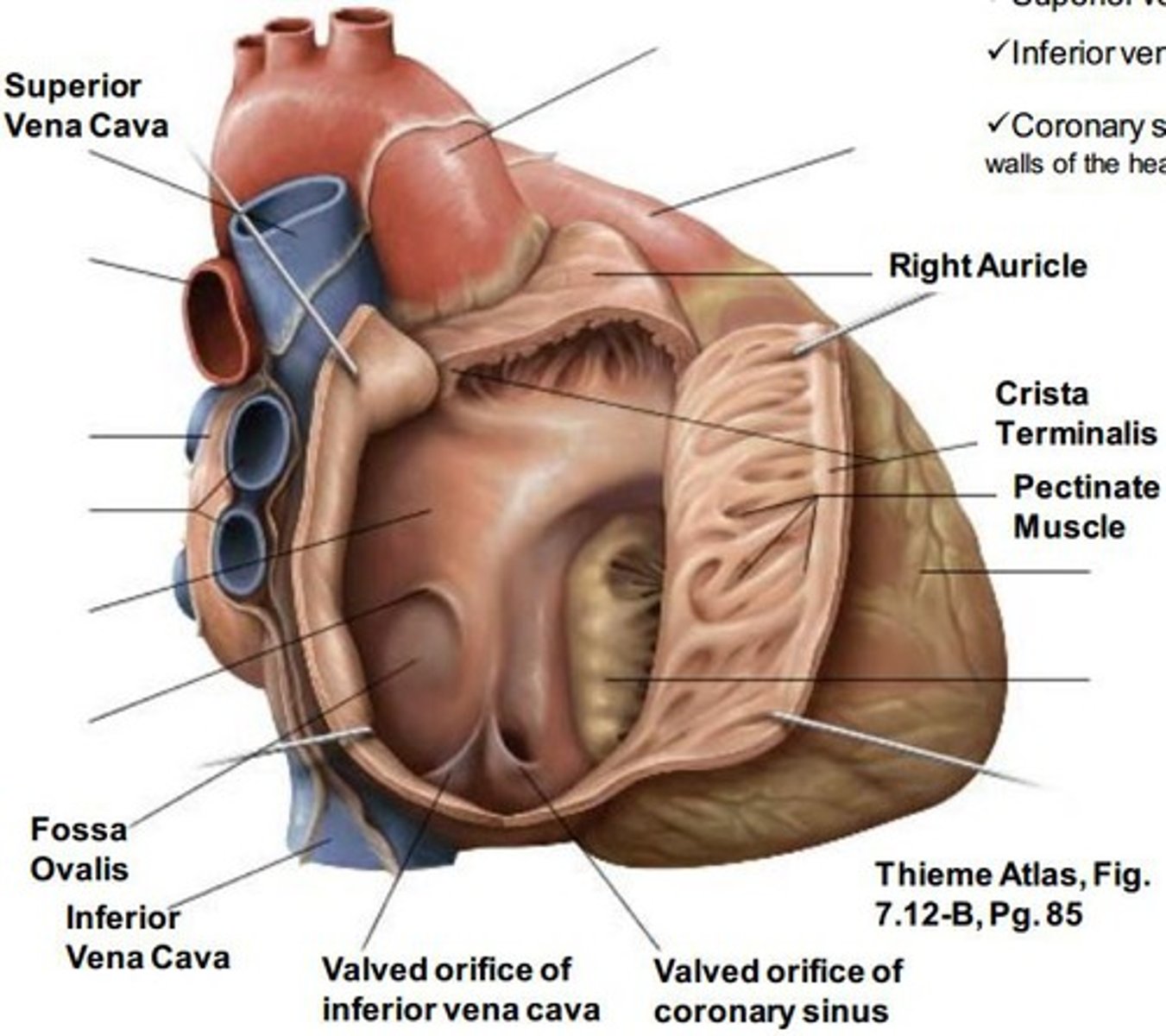
superior vena cava
opens into superior part of R. atrium, at the level of the 3rd costal cartilage
inferior vena cava
opens into the inferior part of R. atrium, at the level of 5th costal cartilage
Opening of the coronary sinus:
short trunk receiving most cardiac veins, between the right Atrioventricular. orifice and the Inferior vena cava orifice
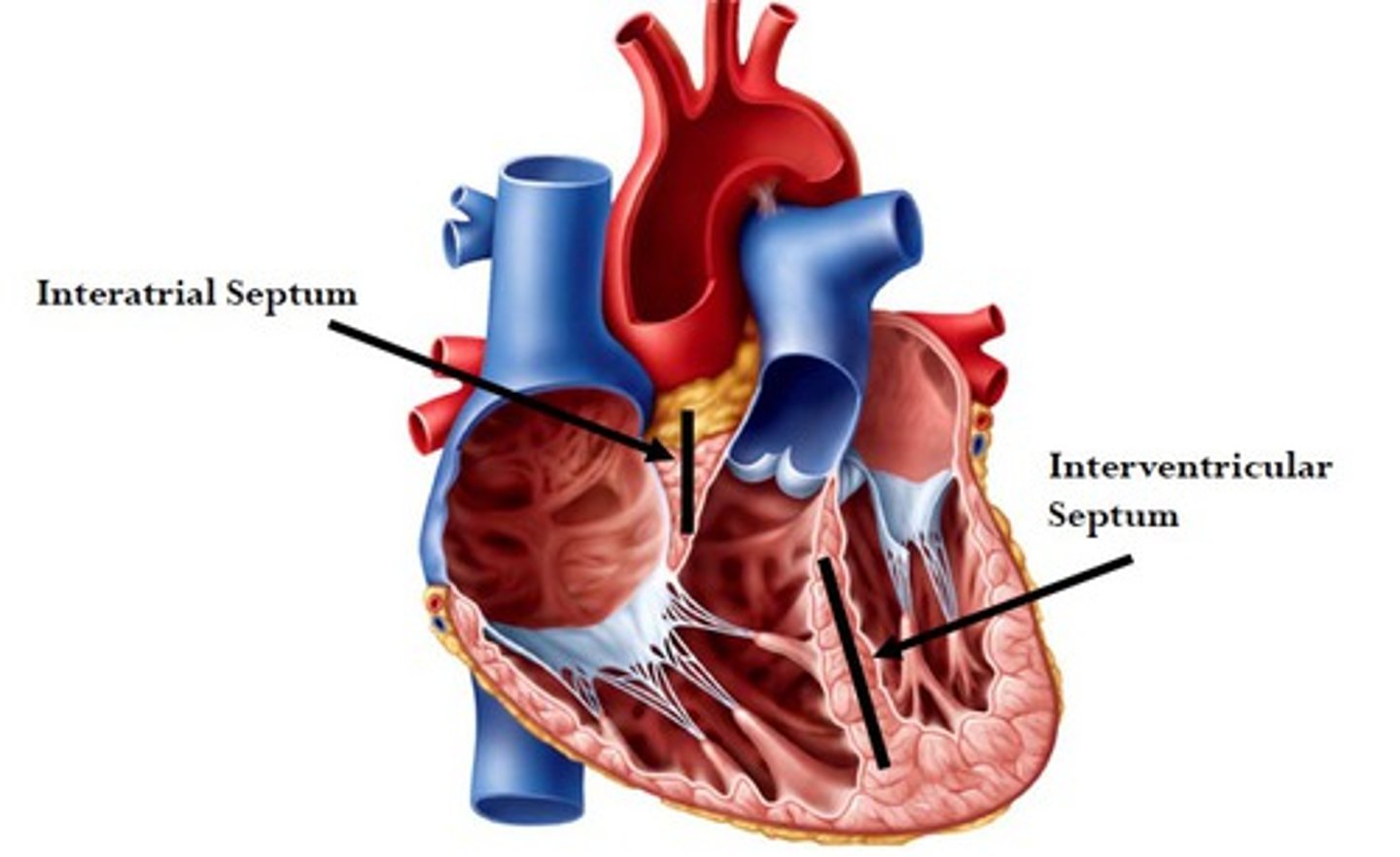
Interatrial septum:
separate atria
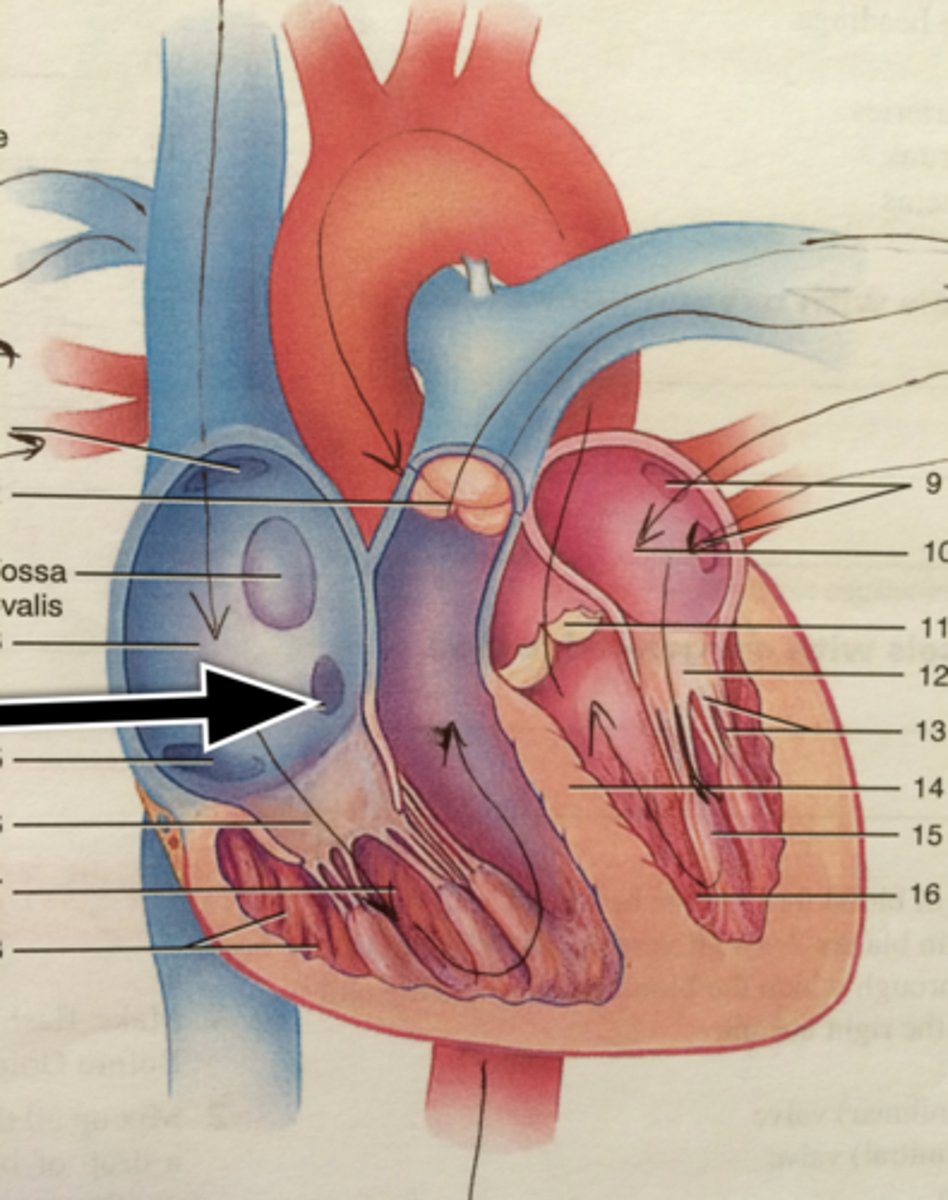
Oval fossa
oval depression on right side of interatrial septum, and it is the remnant of the foramen ovale in the fetus
right ventricle
-Forms the largest part of anterior surface of the heart, a small part of the diaphragmatic, and almost entire inferior border
-Outflow into the pulmonary trunk leaves superiorly and to the left, with the blood having a U-shape (140˚) trajectory inside the R. ventricle
interior of right ventricle
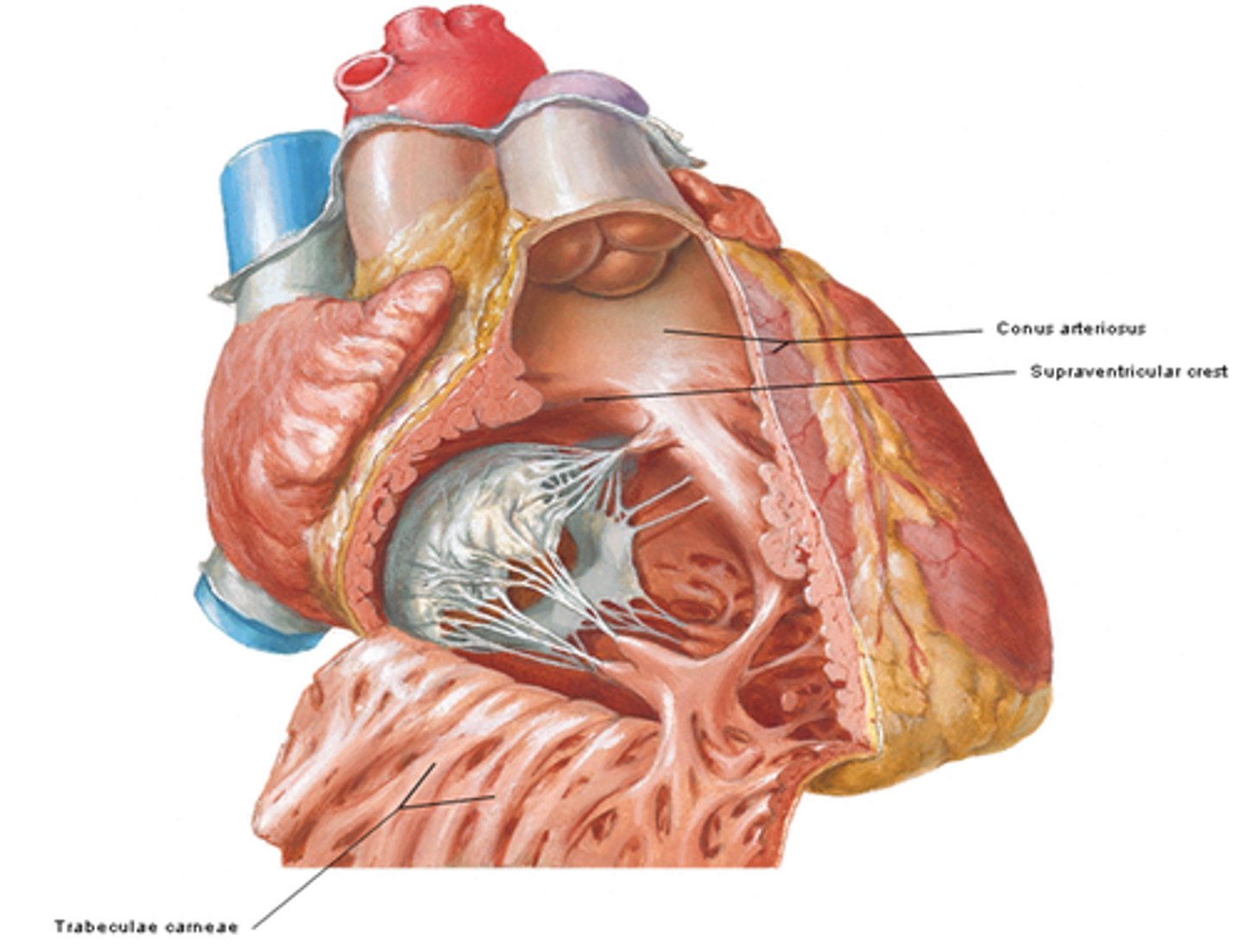
- Conus arteriosus
- Trabeculae carneae
- Supraventricular crest
- Right AV orifice
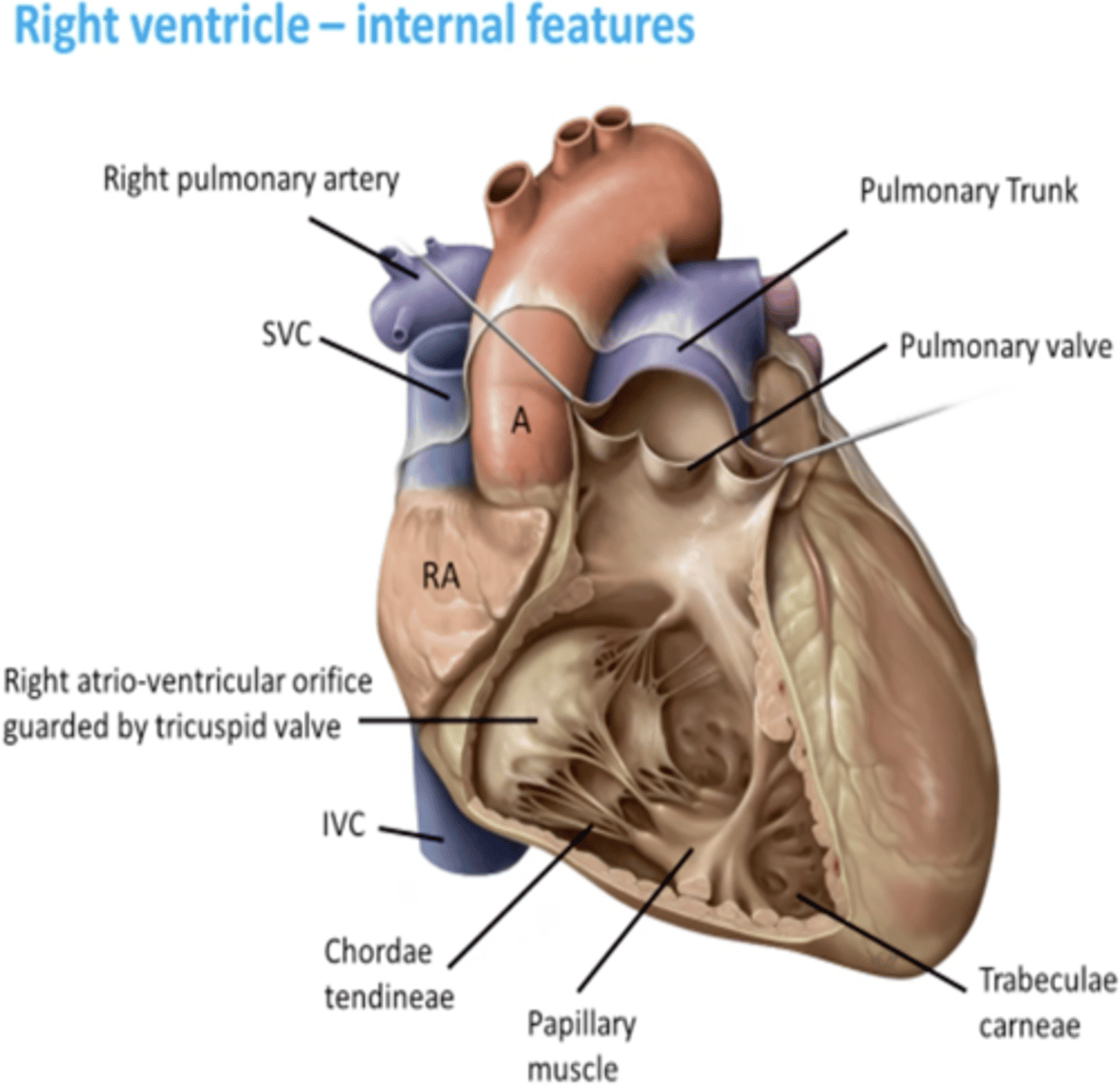
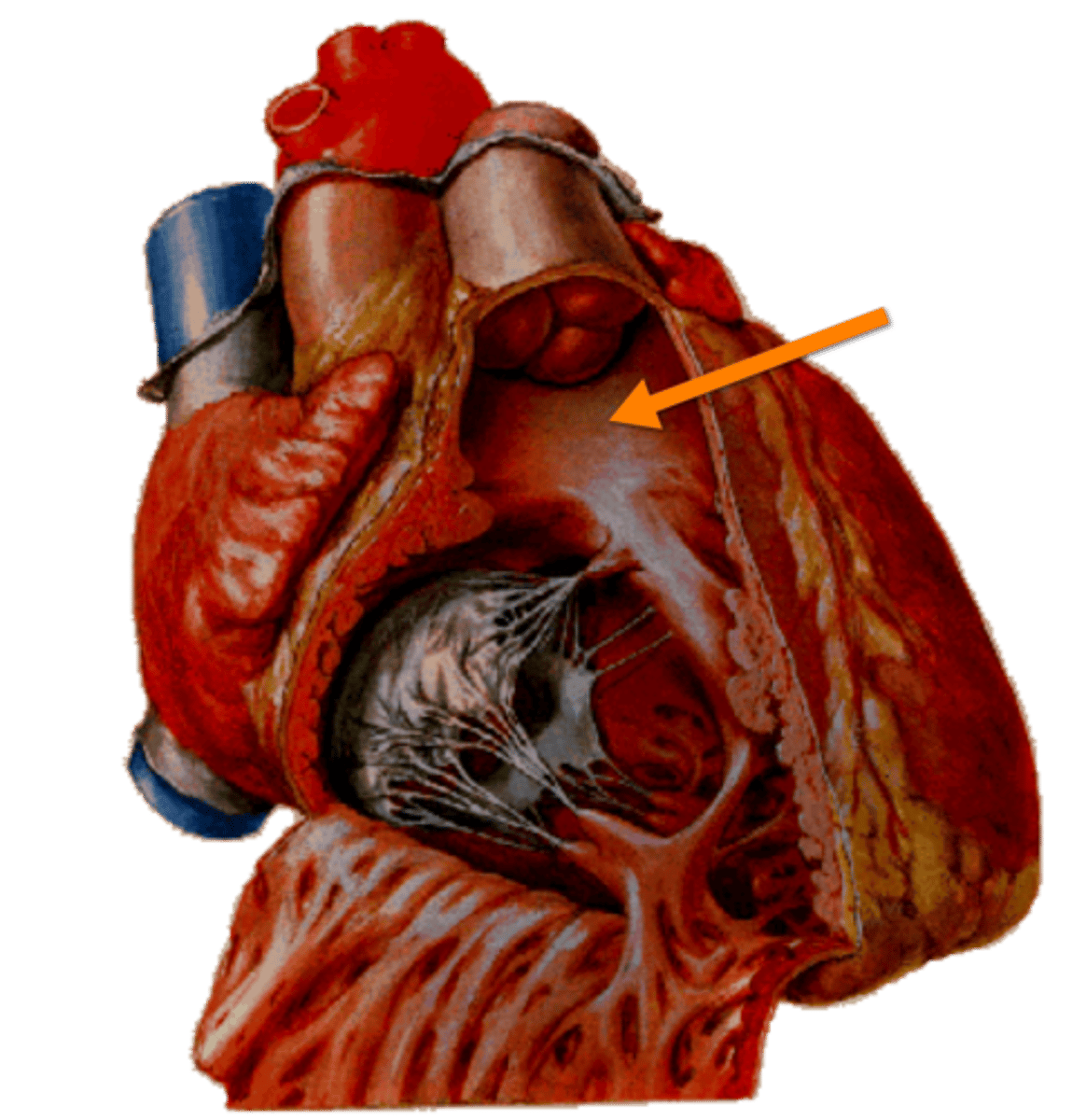
conus arteriosus of the right ventricle
smooth muscle wall, forming a superior narrowing of the ventricle, which leads into the pulmonary trunk
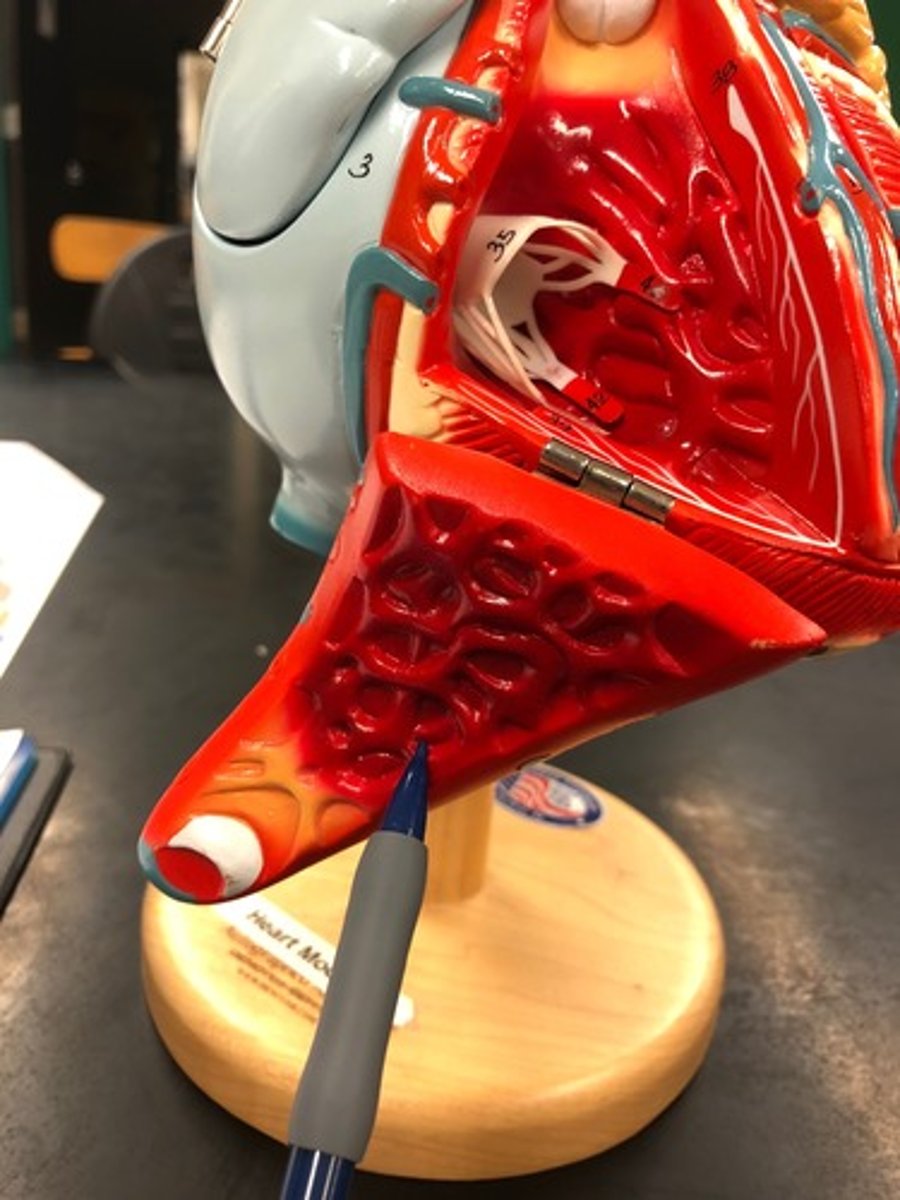
tabeculae carneae of the right ventricle
internal irregular muscular elevations

Supraventricular crest:
thick muscular ridge, separating the ridged muscular wall from the smooth wall of the conus arteriosus
Right AV orifice
receives low-oxygen from the R. atrium, at the level of the 4th - 5th intercostal spaces
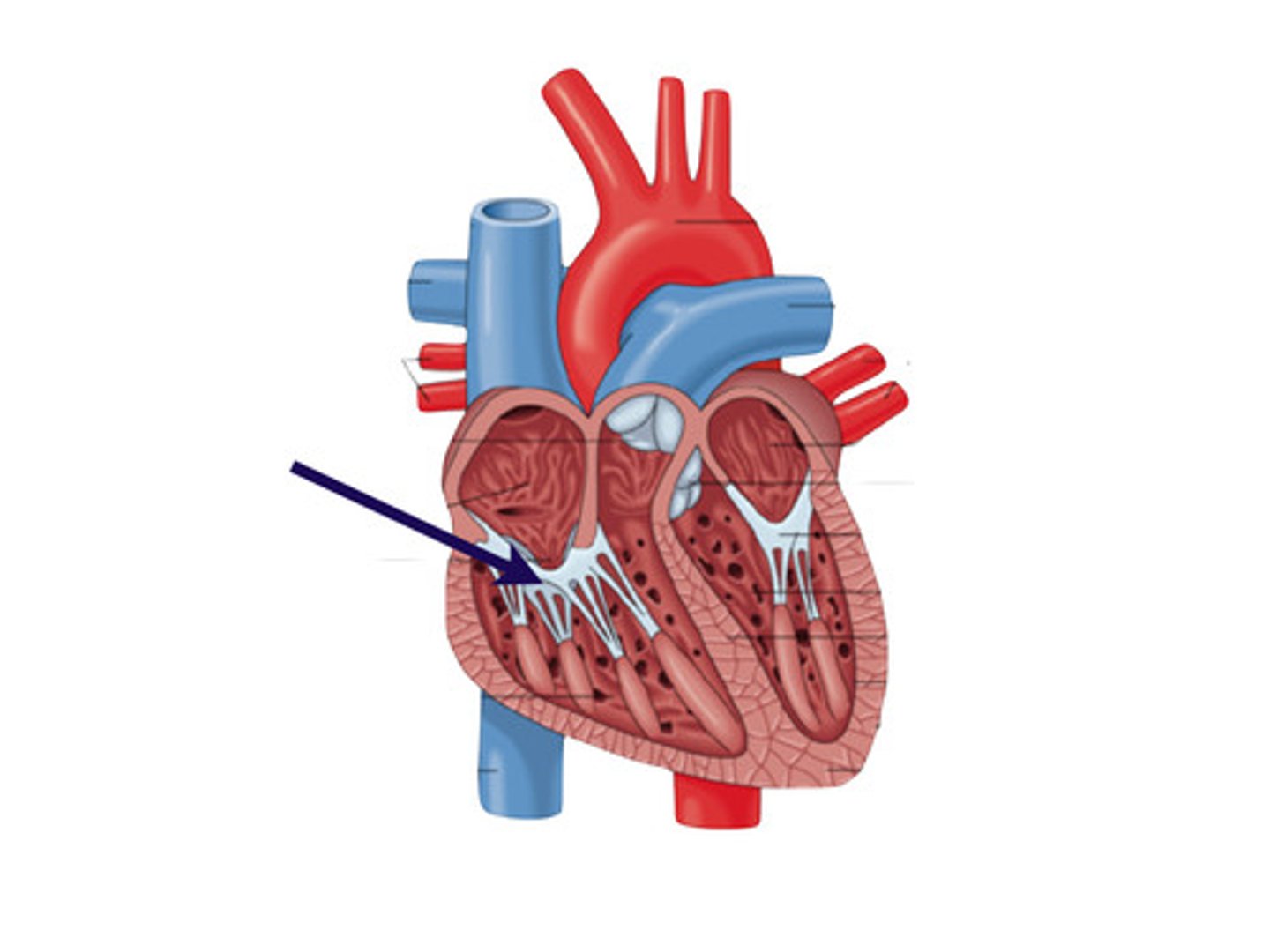
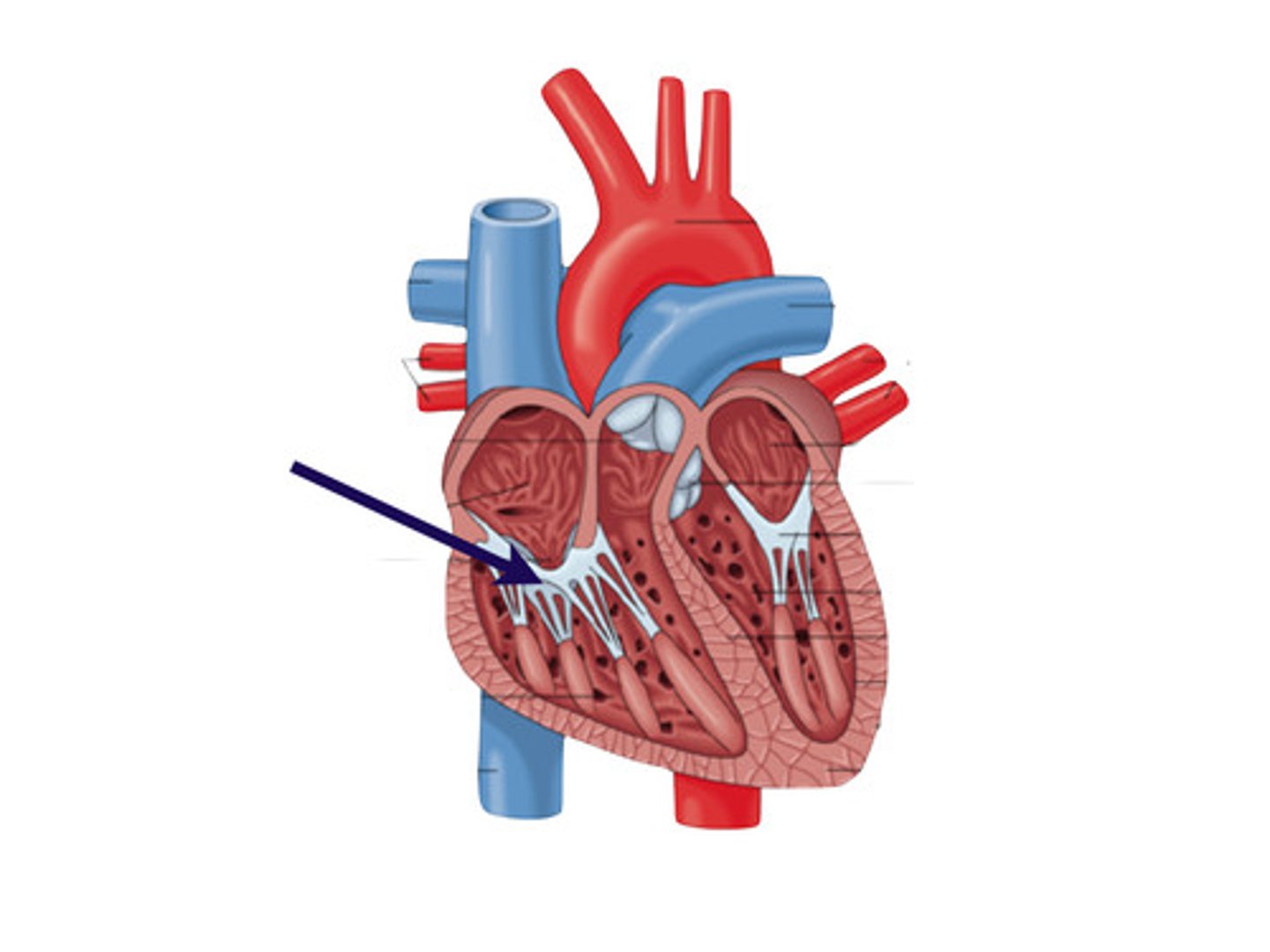
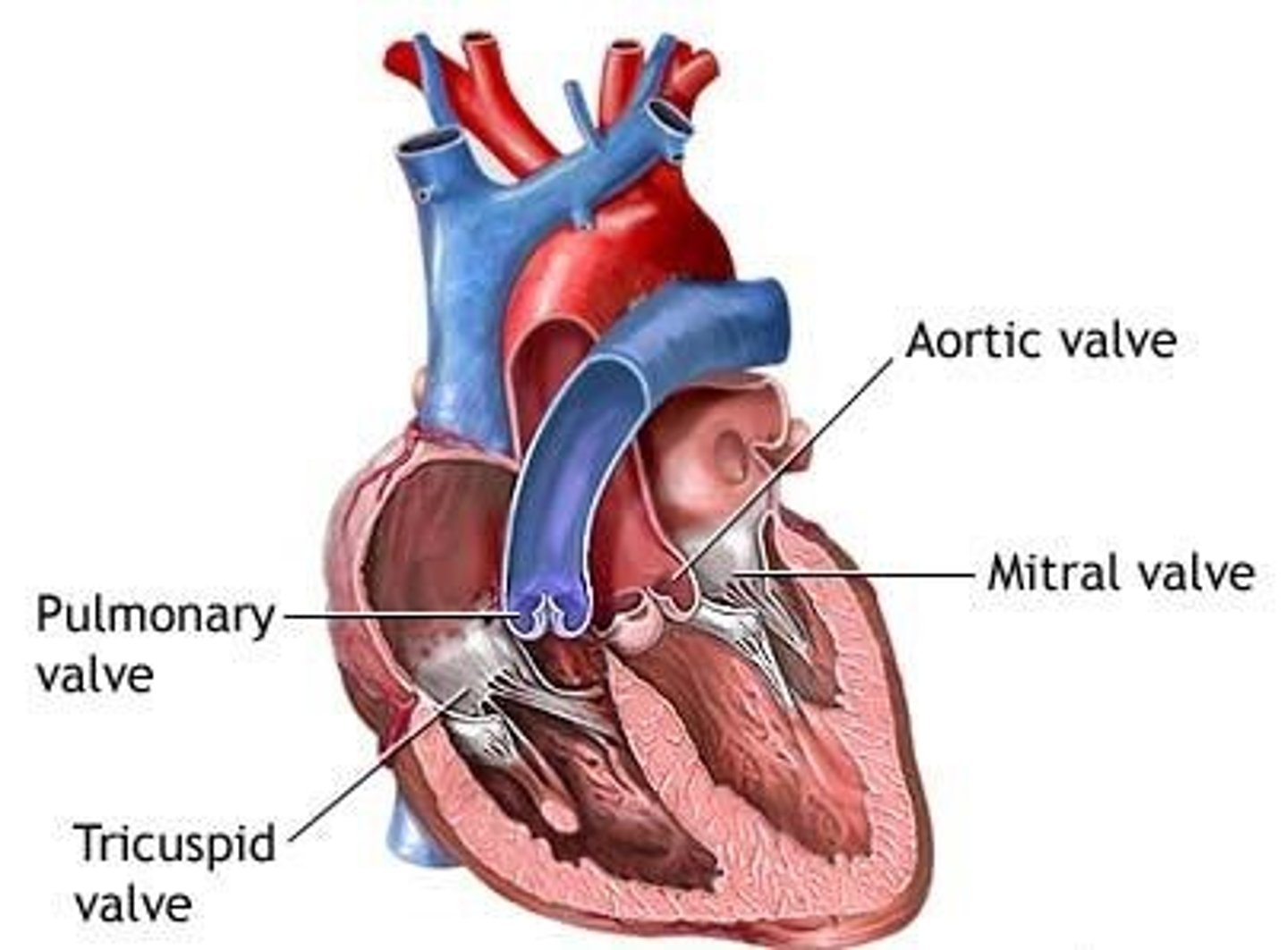
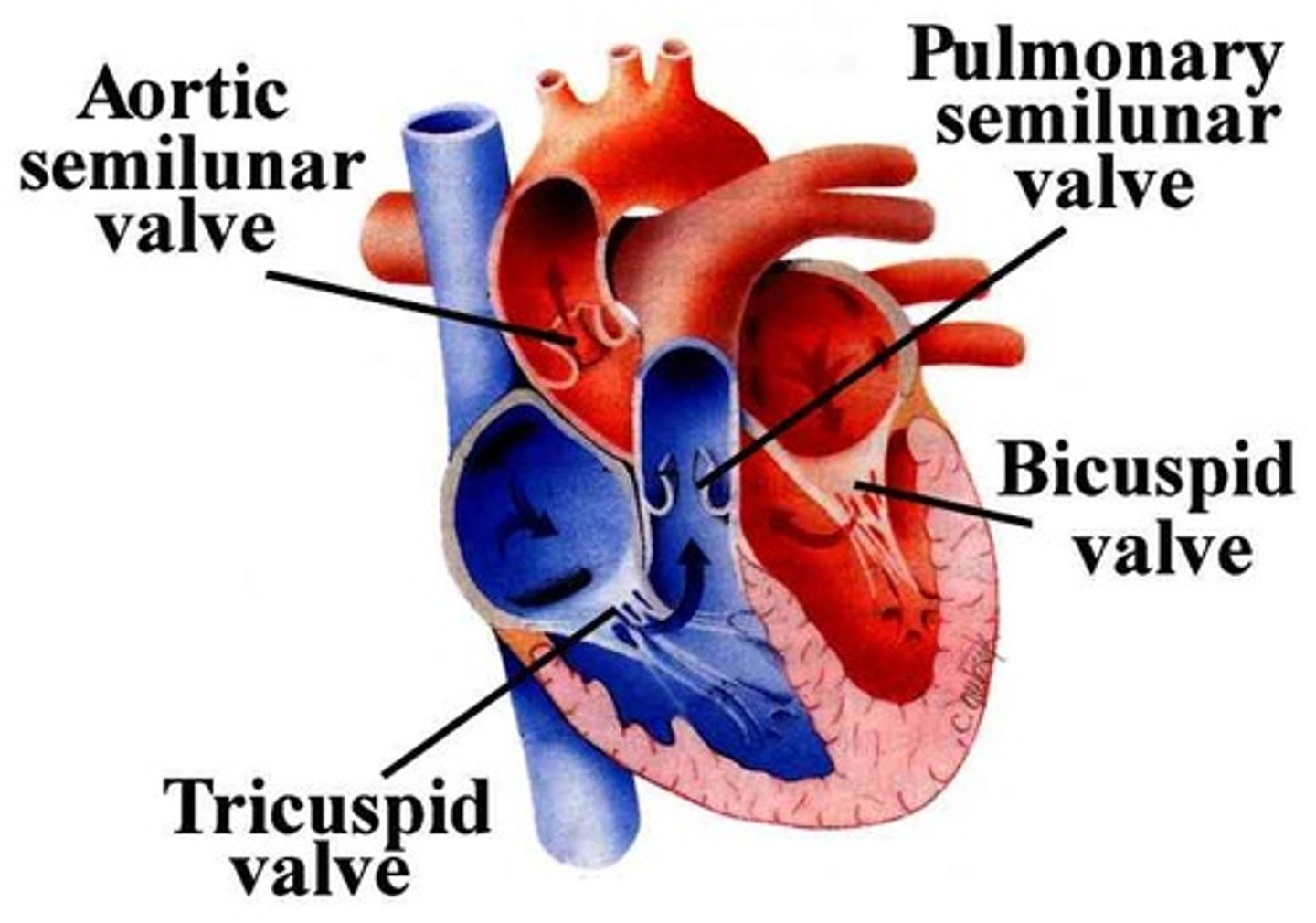
Triscupid valve:
guards the right AV. orifice, attached to the fibrous ring around the right AV. orifice
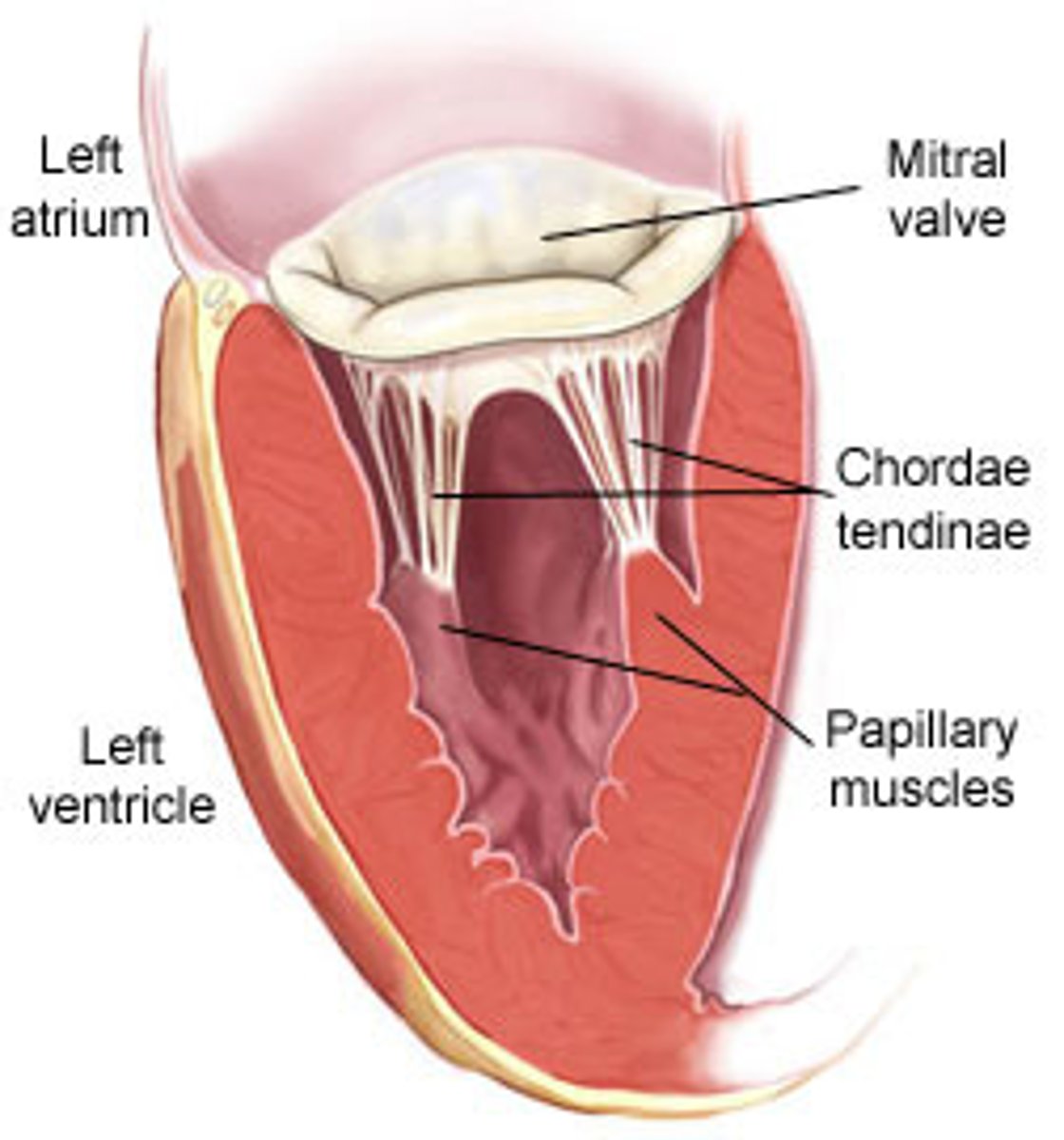
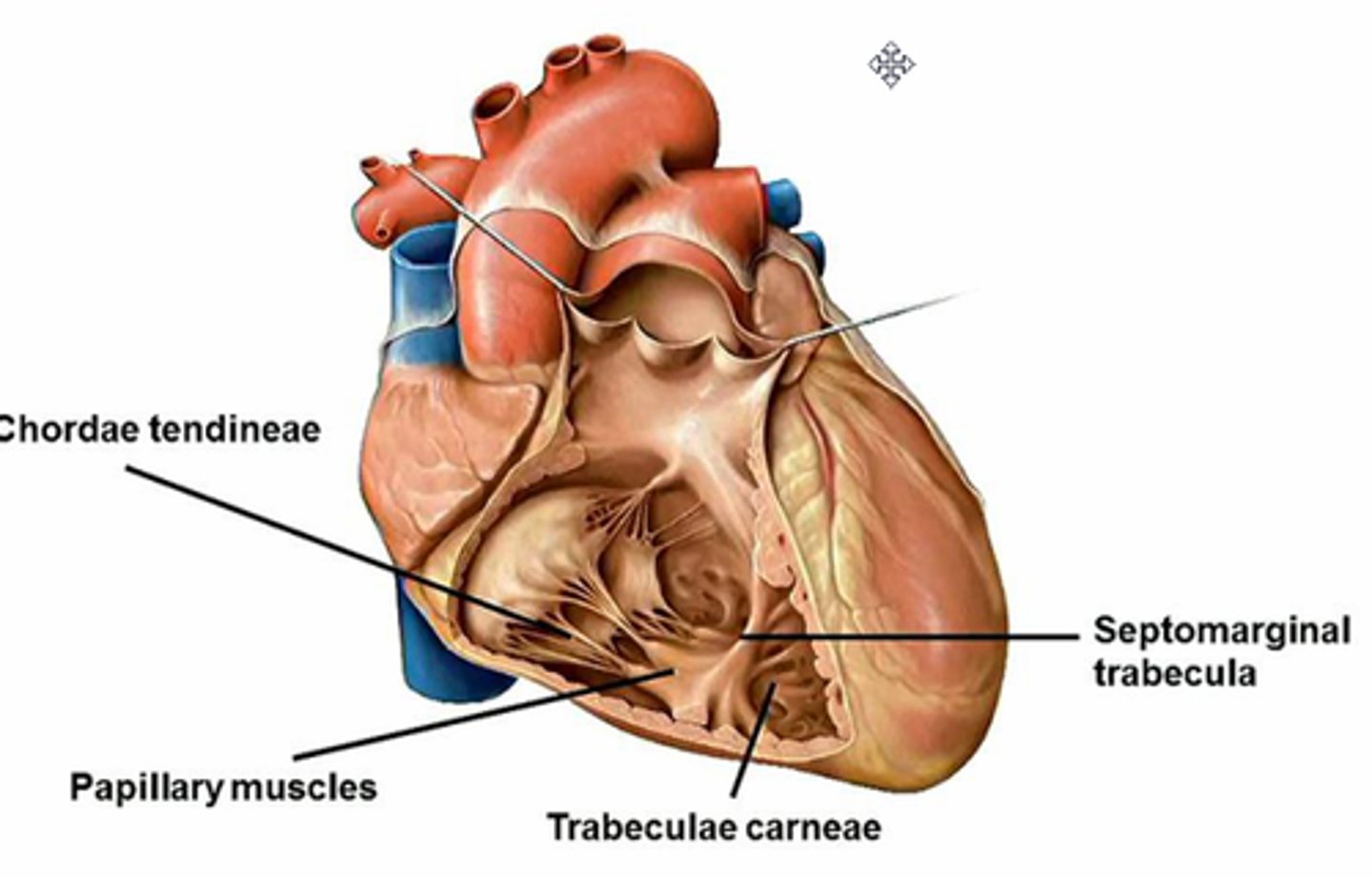
Tendinous cords:
attach to free edges and ventricular surface of the anterior, posterior, and septal cusps, and to the apices of the papillary muscles
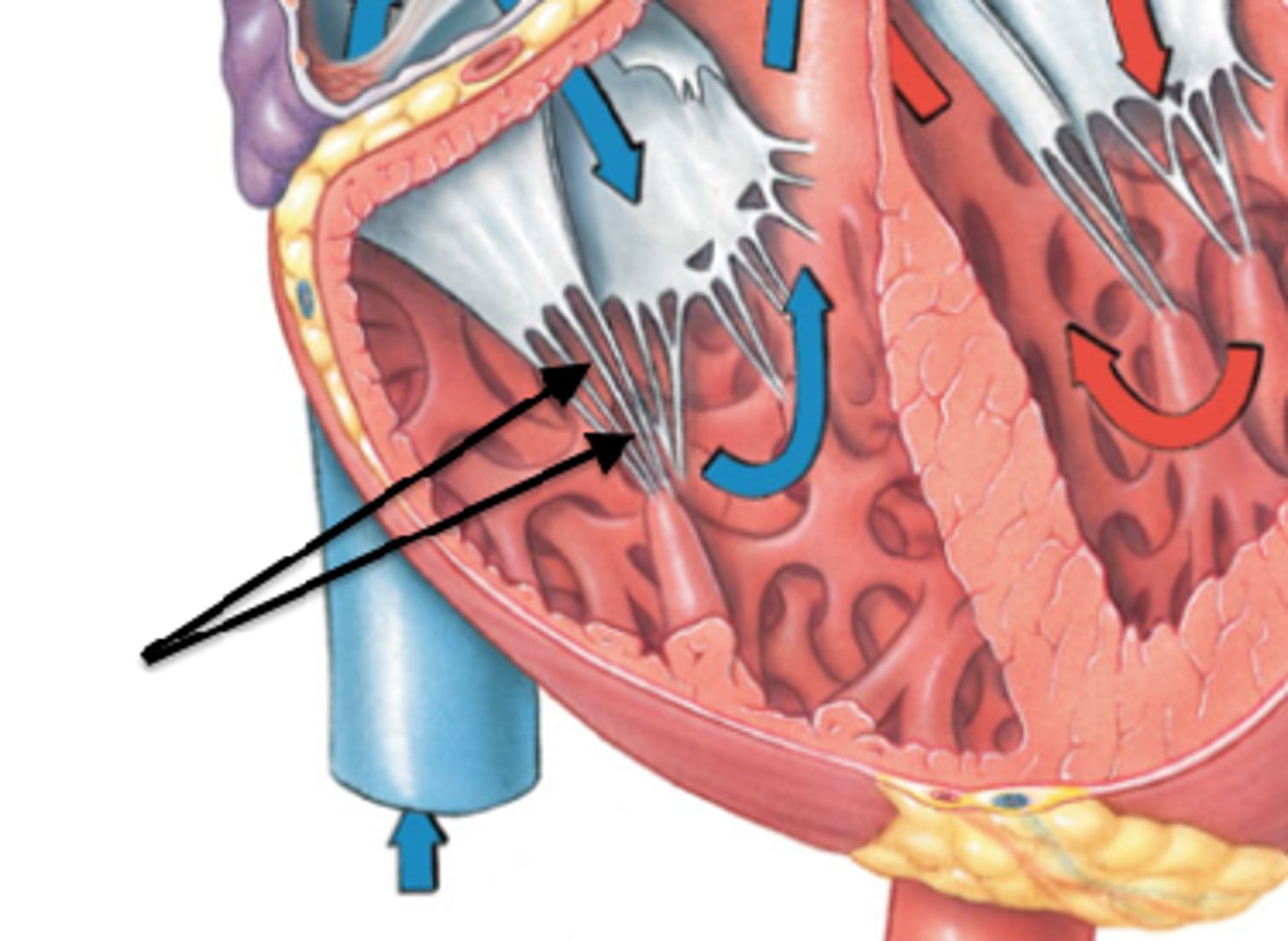
Papillary muscles:
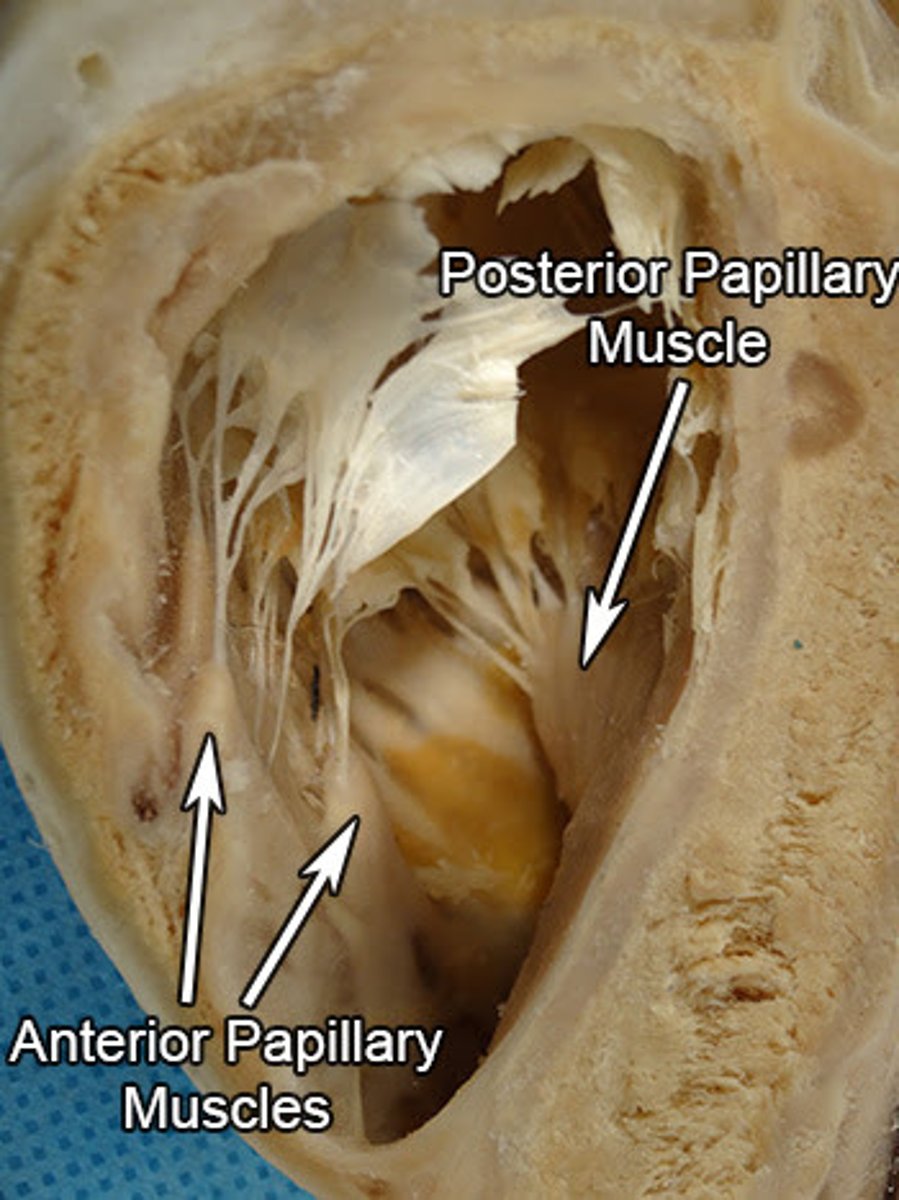
conical muscular projections, with base on the ventricular wall
-Anterior: largest and most prominent, arises from anterior wall and attaches to anterior and posterior cusps
-Posterior: arises from inferior wall and attaches to posterior and septal cusps
-Septal: arises from interventricular septum and attaches to anterior and septal cusps
anterior papillary muscle of right ventricle
largest and most prominent, arises from anterior wall and attaches to anterior and posterior cusps
Posterior papillary muscle of right ventricle
arises from inferior wall and attaches to posterior and septal cusps
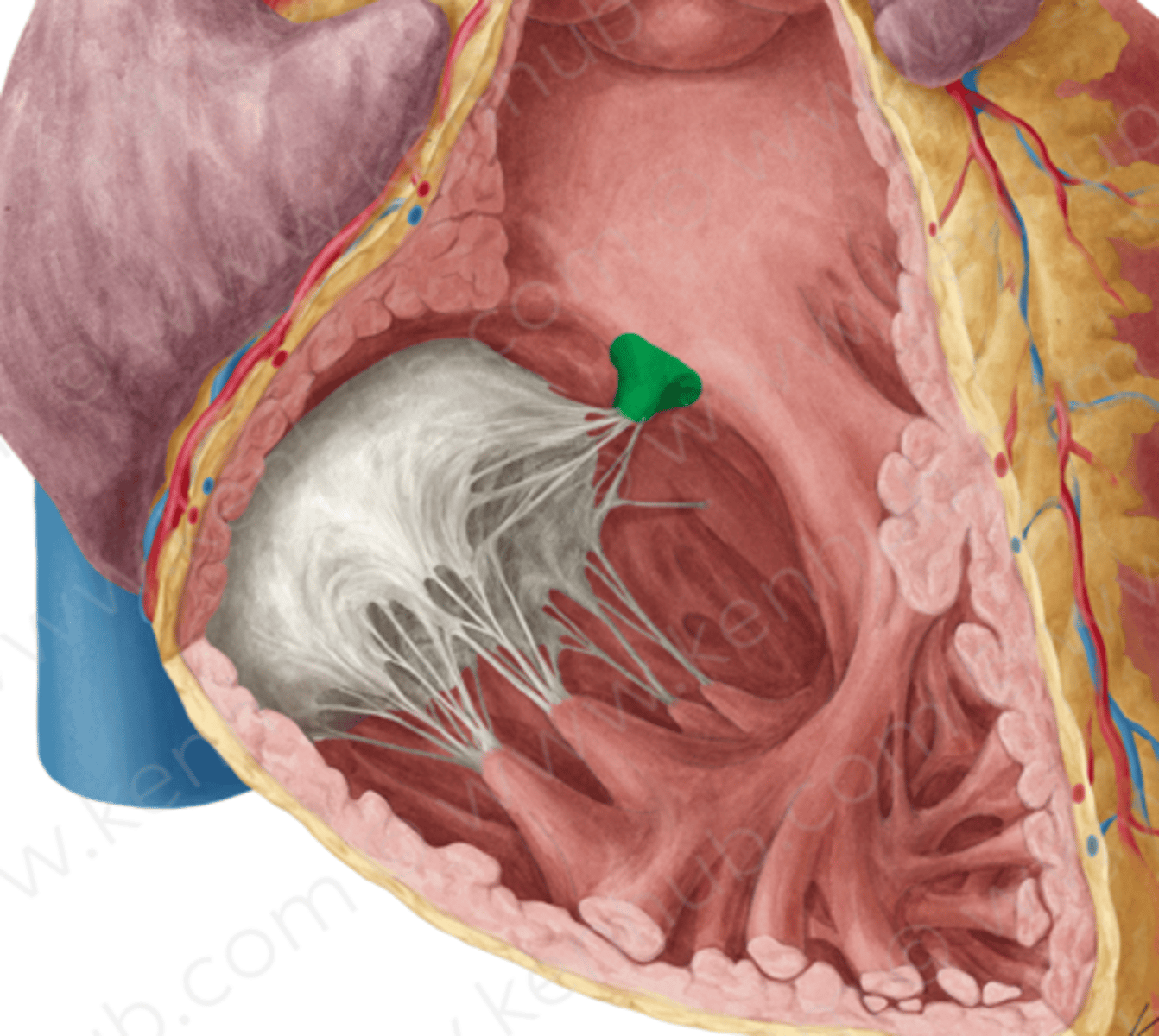
Septal muscle of right ventricle
arises from interventricular septum and attaches to anterior and septal cusps
Interventricular septum:
muscular and membranous parts located between the R. and L. ventricles
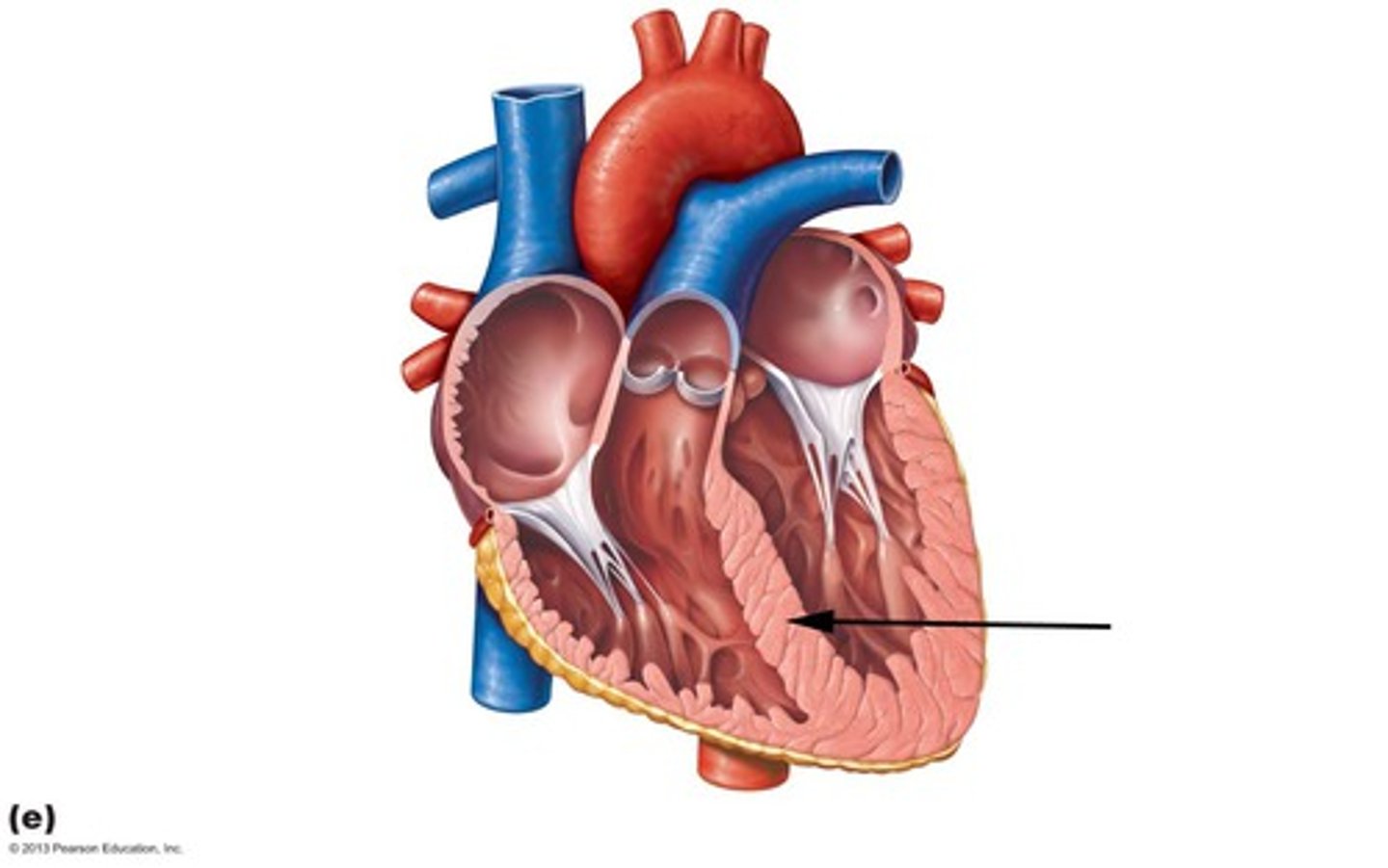
Septomarginal trabecula (moderator band):
curved muscular bundle running from inferior part of interventricular septum to base of anterior papillary muscle. Carries part of the right branch of the AV bundle and prevents overdistension
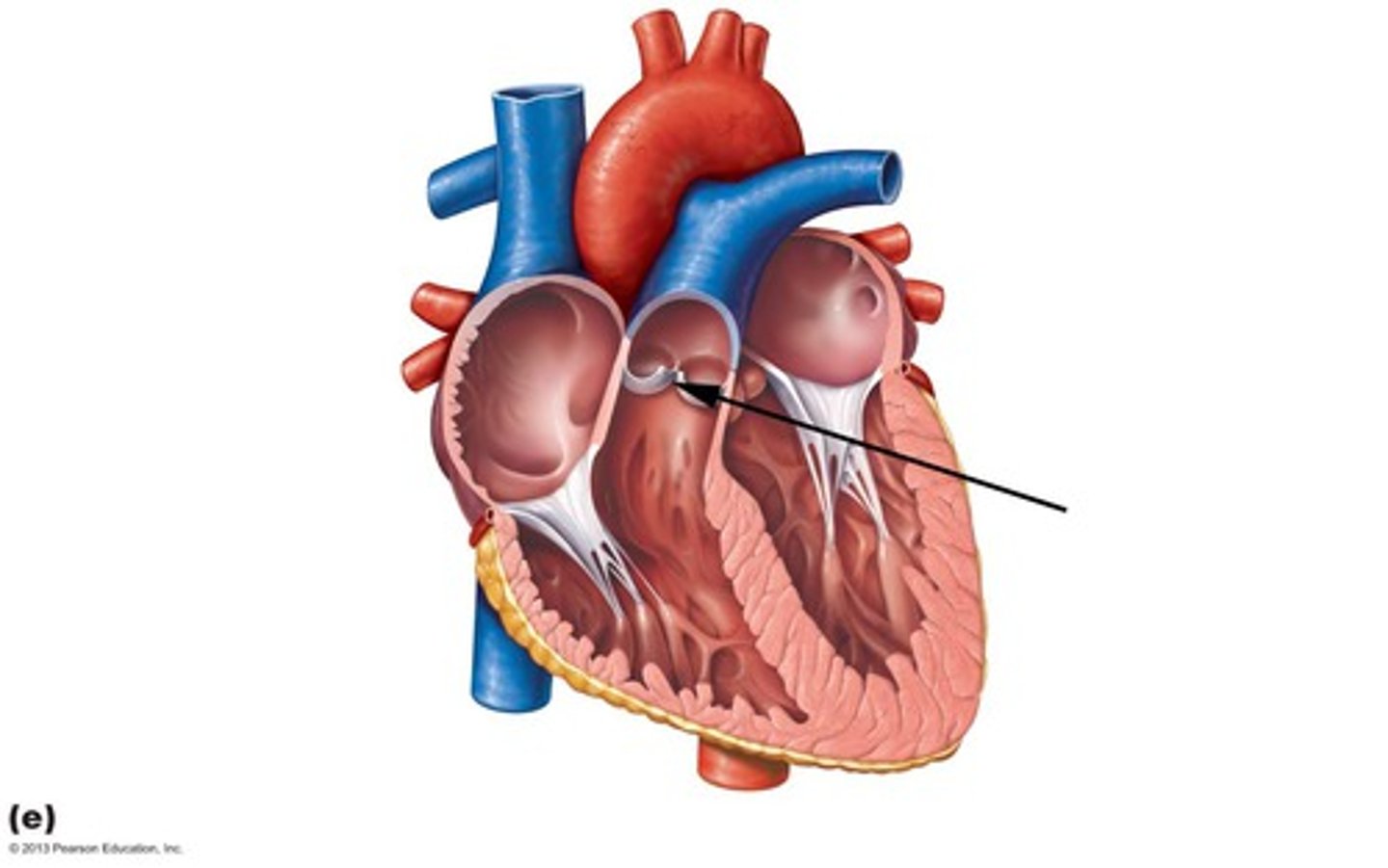
Pulmonary valve:
at the apex of the conus arteriosus and at the level of the 3rd costal cartilage, separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk during filling of the ventricle.
left atrium
-Forms most of base of heart
-Receives the pairs R. & L. pulmonary veins in its smooth muscle wall
-Auricle
-Left AV. orifice: L. atrium discharges into the L. ventricle high-oxygen blood
left atrium (auricle)
trabeculated wall with pectinate muscles, and extends the L. atrium, overlapping the root of the pulmonary trunk
left ventricle functions
-Forms apex of heart, almost all of the pulmonary surface and border, and most diaphragmatic surface
-Performs more work than R. ventricle because of higher arterial pressure
-Outflow into the aorta leaves superiorly and to the right, with the blood having a U-shape (180˚) trajectory inside the L. ventricle
interior of left ventricle
- Walls 2-3 times thicker than right ventricle
- Covered with mesh of trabeculae (finer and more numerous)
- Larger conical cavity than right ventricle
- Anterior and posterior papillary muscles: more developed than in right ventricle
- Tendinous cords and papillary muscles attach to the anterior and posterior cusps
-Aortic vestibule
-Mitral valve
-Aortic orifice
-Aortic valve
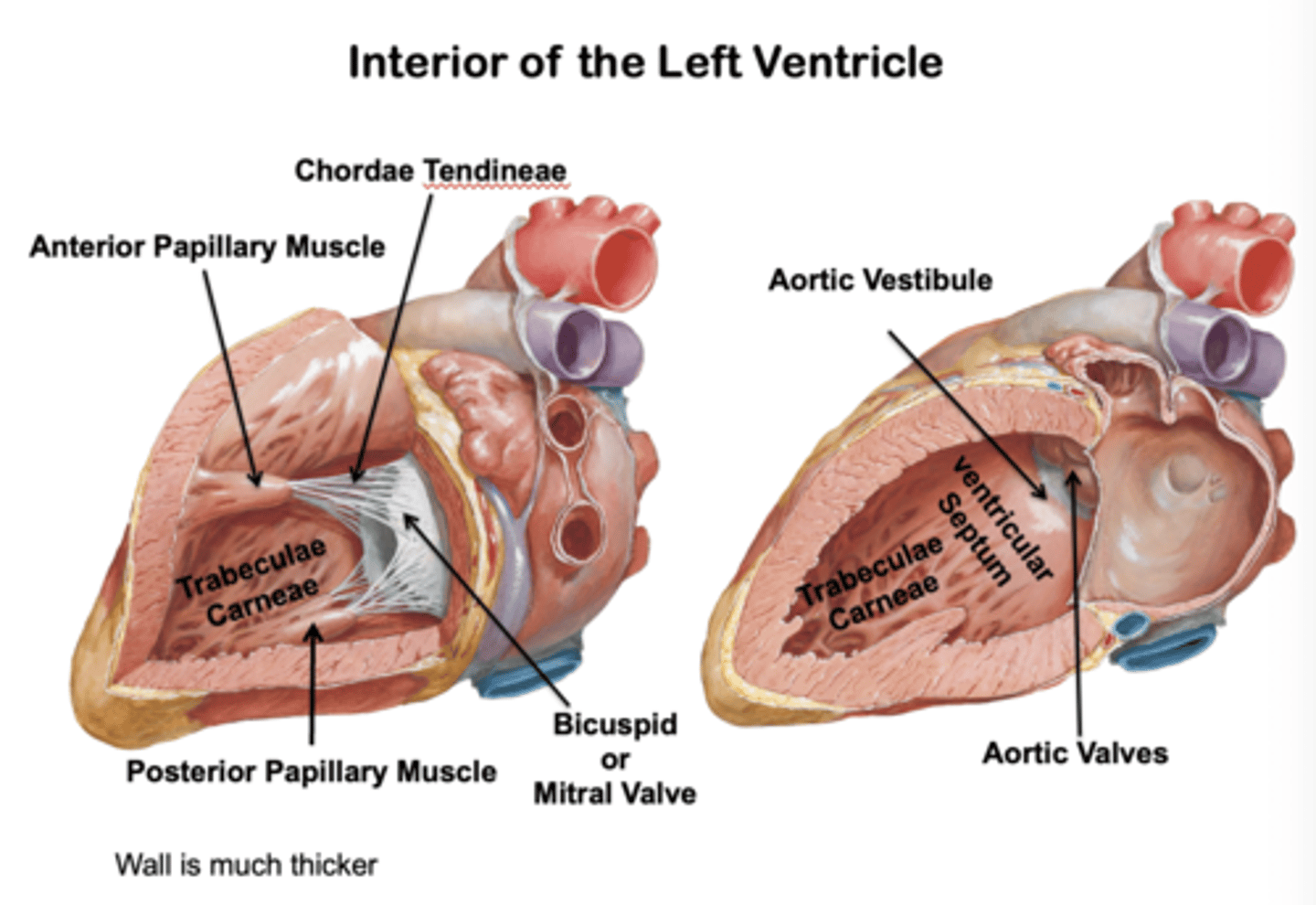
Aortic Vestibule (Left Ventricle):
smooth-walled, leading to the aortic orifice and aortic valve
Mitral valve (left ventricle):
guards the right AV. orifice. Located posterior to sternum at the level of the 4th costal cartilage, with anterior and posterior cusps only
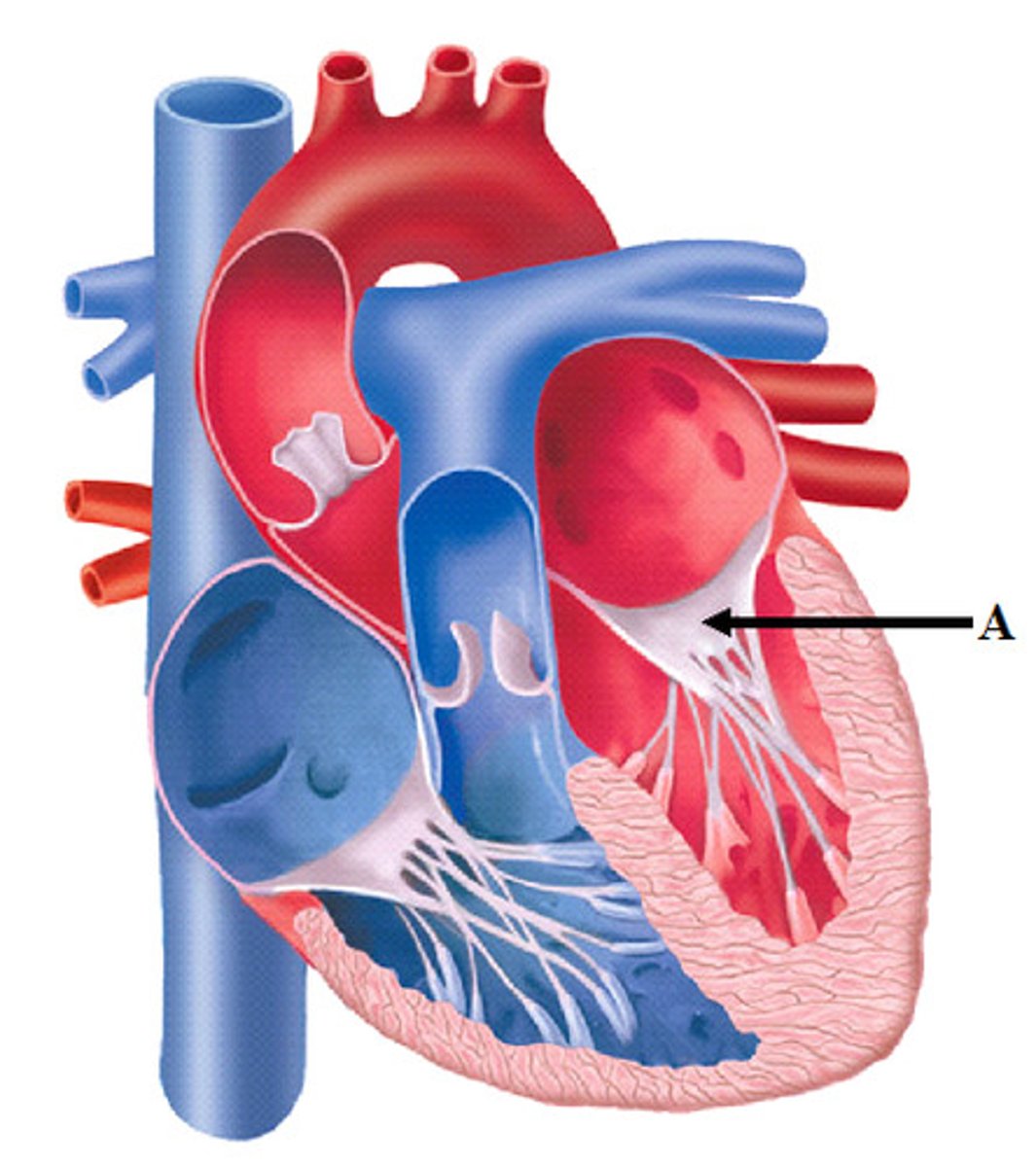
Aortic orifice
lies in the right posterosuperior part
Aortic valve
between L. ventricle and ascending aorta at the level of the 3rd intercostal posterior to left side of stern
Heart Vasculature
-Formed by coronary arteries and cardiac veins
-Blood exchange of the myocardium
-Run across the surface of the heart just deep to the epicardium (visceral layer of serous pericardium)
-Anastomoses
-Regulated by sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
anastomoses
the potential exists between the arteries -> potential collateral circulation in the heart, but the coronary arteries are terminal end arteries