Unit 1: Water and Life
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
does everything have water in its composition? why is it important?
yes, everything is tied to water
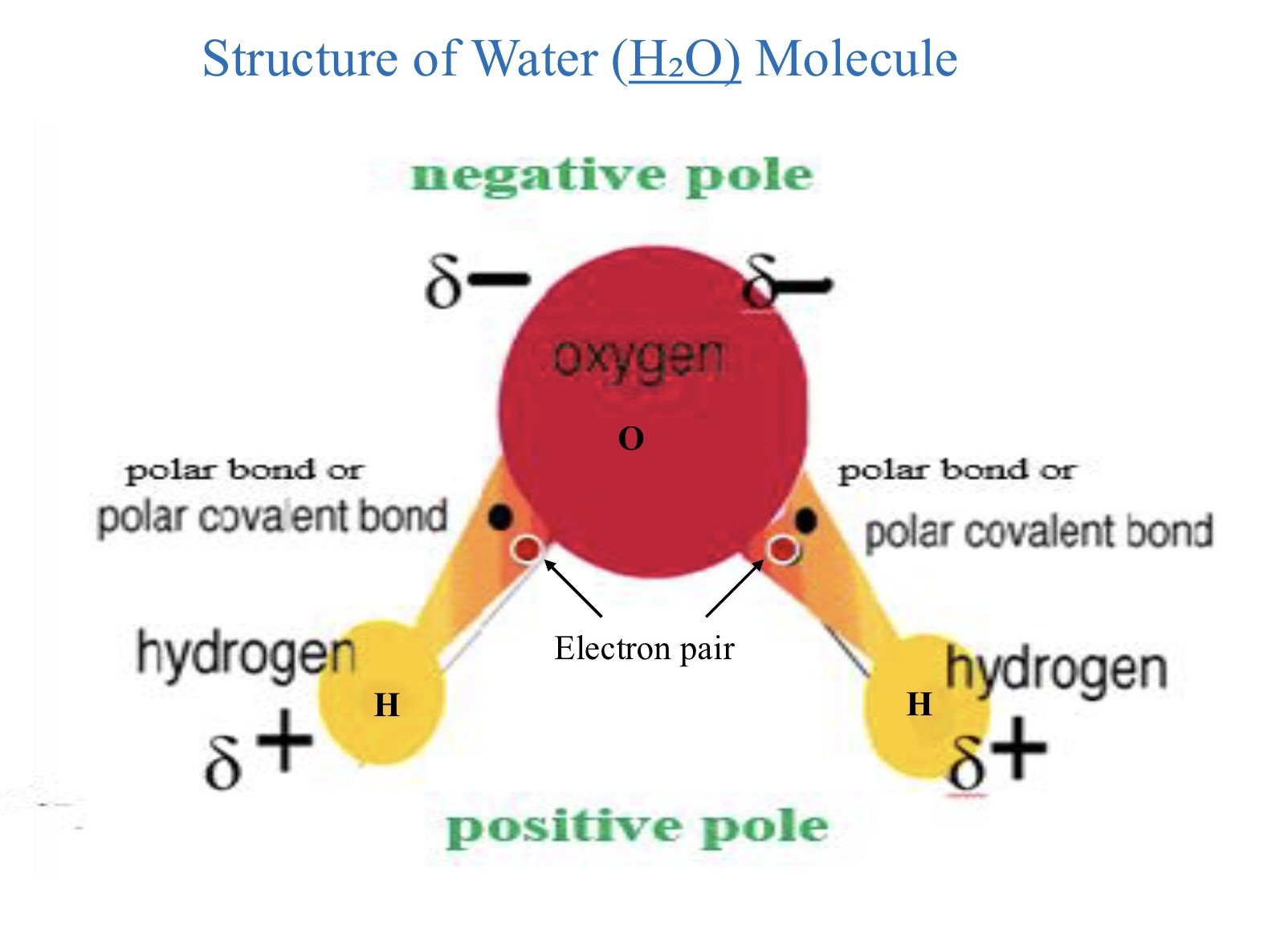
why is water a polar molecule?
bonded together by two polar covalent bonds.
aproximate number of water in animals/humans
animals 60-70%
humans 80-90%
75% infant, 65% children, 55% women, 60% men
hypertonic vs hypotonic
hypertonic: not enough water cause cells to shrink
hypotonic: too much water cause shells to swell up
stay in the middle, neutral, isotonic, normal
what happens during dehydration? hypertonic
loss of water from body, body fluids become hypertonic, thrist, dark urine, small volume of urine, lagargy, raised pulse, low bp, extreme brain damange, seizure, death
what happens during over hydration? hypotonic
extra intake of water, body fluids become hypotonic, clear large volumes of urine, confusion, drowsiness, delirium, nausea, extreme seizures, coma, death
characteristics of O-H molecule
covalent bond bc sharing of one electrons
single bond bc one pair of electrons is shared between O and H
polar bond bc unequal sharing of electron pair; oxygen more electromagnetic & has stronger pull on electron pair
explain
there is one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms.
the oxygen atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms via covalent bonds which means the atoms share electrons. sharing is unequal
oxygen is more electromagnetic than hydrogen meaning it pulls the shared electrons closer to itself resulting in a partial neagtive charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms.
the molecule is not linear but it is bent. due to the repulsion between the pairs of unshared electrons on the oxygen atom which pushes the hydrogen atoms closer together.
unequal sharing of electrons so it is a polar molecule.
the oxygen end of the molecule is slightly negative, and the hydrogen ends are slightly positive. this polarity allows water to interact strongly with other polar substances and gives it unique properties like high surface tension and the ability to dissolve many substances.
why is earth habitable?
the abundance of water
where does the metabolism occur?
water medium
cytoplasm is
water based
a molecule is
2 or more molecules connected by bonds
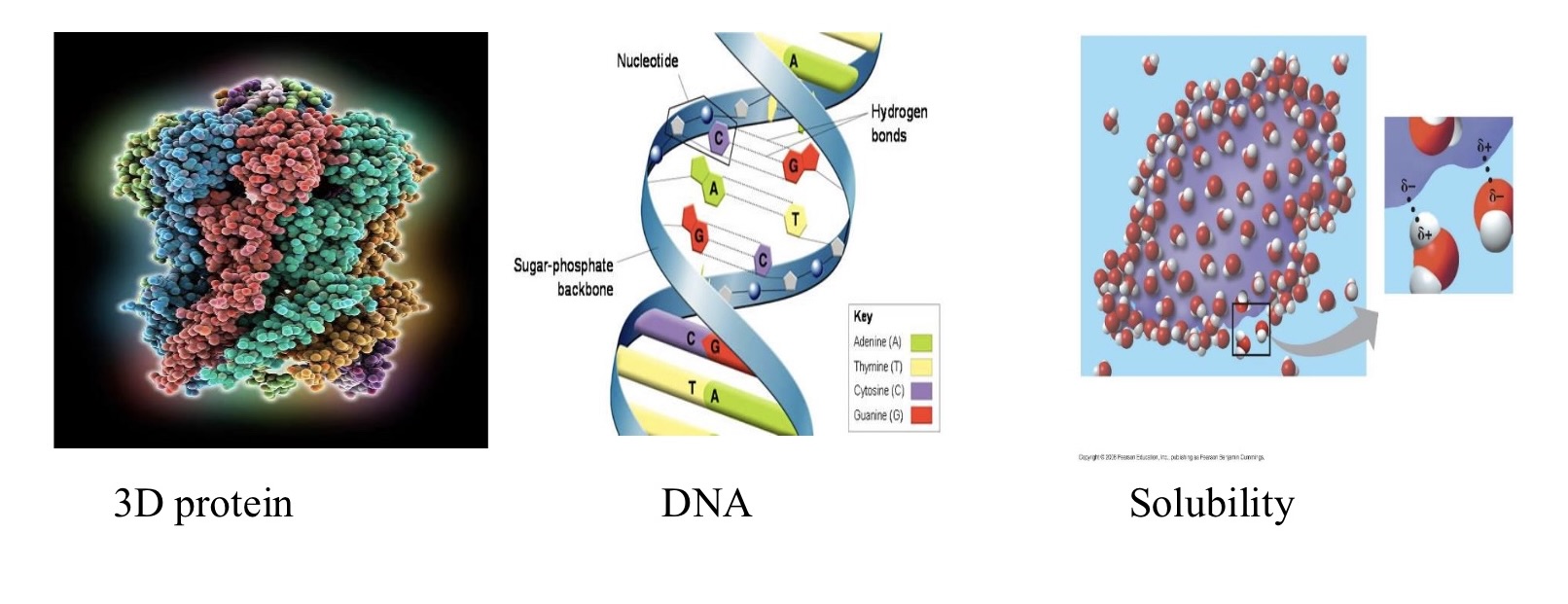
what holds dna together?
hydrogen bonds
water molecules can
form hydrogen bonds with themselves/with other molecules
characteristics of the O-H bond in a water molecule
H-O-H bonded together by 2 polar covalent bonds. therefor water is polar.
covalent bond bc electrons are shared
single bond bc 1 pair of electrons is shared between H & O
polar bond bc unequal sharing of electron pair so oxygen is more electronegative and has a stronger pull on the electron pair
delta negative charges on oxygen
delta positive charges on hydrogen
water molecule is neutral (net charge=0) bc the delta negative and elta positive cancel each other out
hydrogen bond is a weak attraction between
delta negative and delta positive
bonds from strongest to weakest
covalent, ionic, h-bond
h-bonds in water
holds water molecules together
bc h-bonds are weak attractions, they break and reform with great frequency in liquid water.
bc of their large numbers in water, the h-bond determines many properties of water
why is the h-bond important in biology?
plays an important role in holding water molecules together/solubility of water
found in proteins, nucleic acids…
shape of dna, proteins & water determined by h-bonds
the polar nature of water contributes to earth’s
suitability for life
waters life supporting properties
cohesion, adhesion, crucial solvent of life, frozen water floats, high specific heat
cohesion
holding hands together, cling to one another, can form large bodies
surface tension
surface of water body: stronger bonding enable us to float things on water
resistance of water to spill from glass, formation of water droplets
adhesion
water molecules cling to other polar surfaces: plants
water climbs up because of , clings together by __
adhesion, cohesion
for all life the dissolving agent is
water, water is the solvent of life
solute
dissolves in water
sugar, salt
solution
homogenous mixture of solvent & solute
2 types of sulute
hydrophilic: love water, dissolve easily, ionic compounds NaCl, polar molecules sugar
hydrophobic: dislie water, does not dissolve in water, nonpolar molecules - fats, oils, O2
hydration shell
water molecules form a sphere around ions & polar molecules as they dissolve
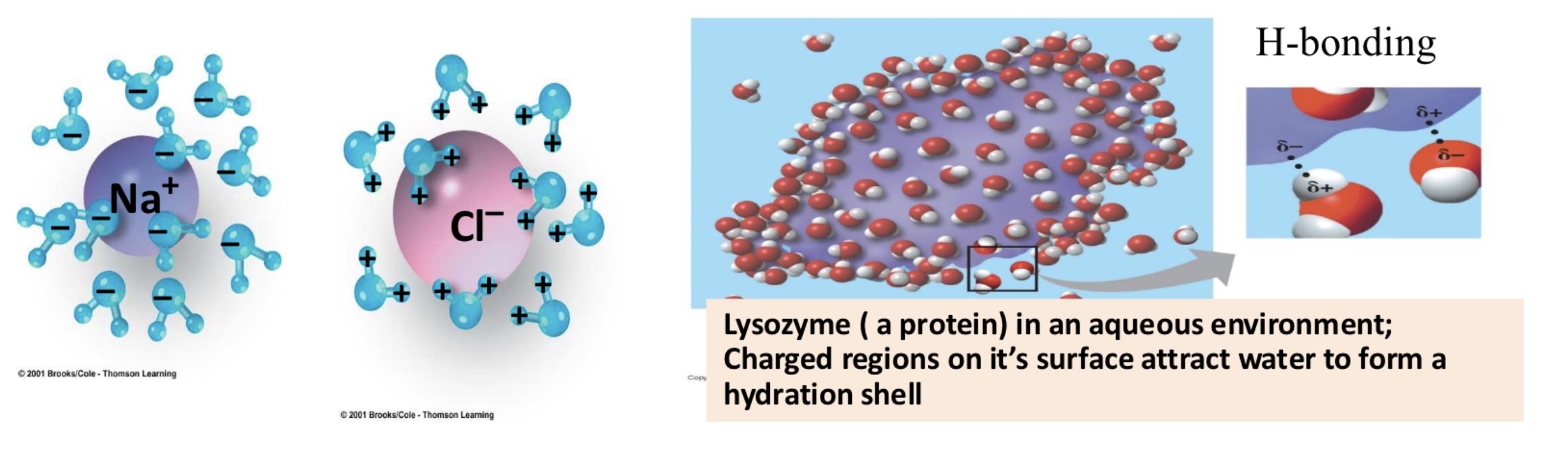
hydrophilic material _ while hydrophobic materials _ absorb water
absorb, do not
is water attracted to molecules with no charge?
no, only charged molecules
is ice denser than water?
less dense, has to do with h-bonding
liquid water
water molecules tightly packed in liquid water making it more dense
heaviest at 4 degrees celcius
h-bonds constantly break & reform in liquid water
density
mass over volume: mass/volume
why does ice expand?
water molecules expand (spread out) & locked in place by stable hydrogen bonds as water molecules freeze at 0 degrees celcius
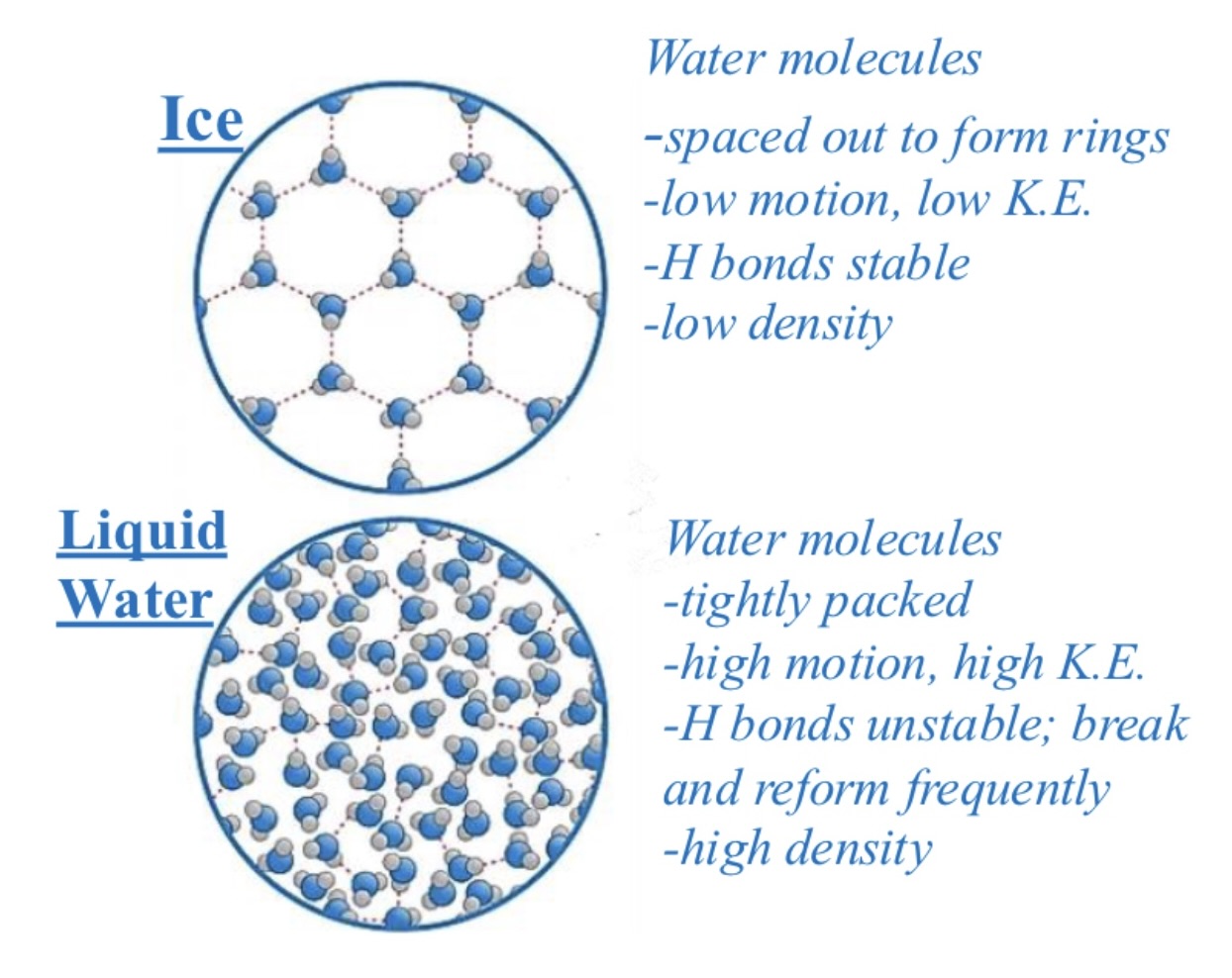
most dense water all the way at the bottom because
more dense so it is heavier
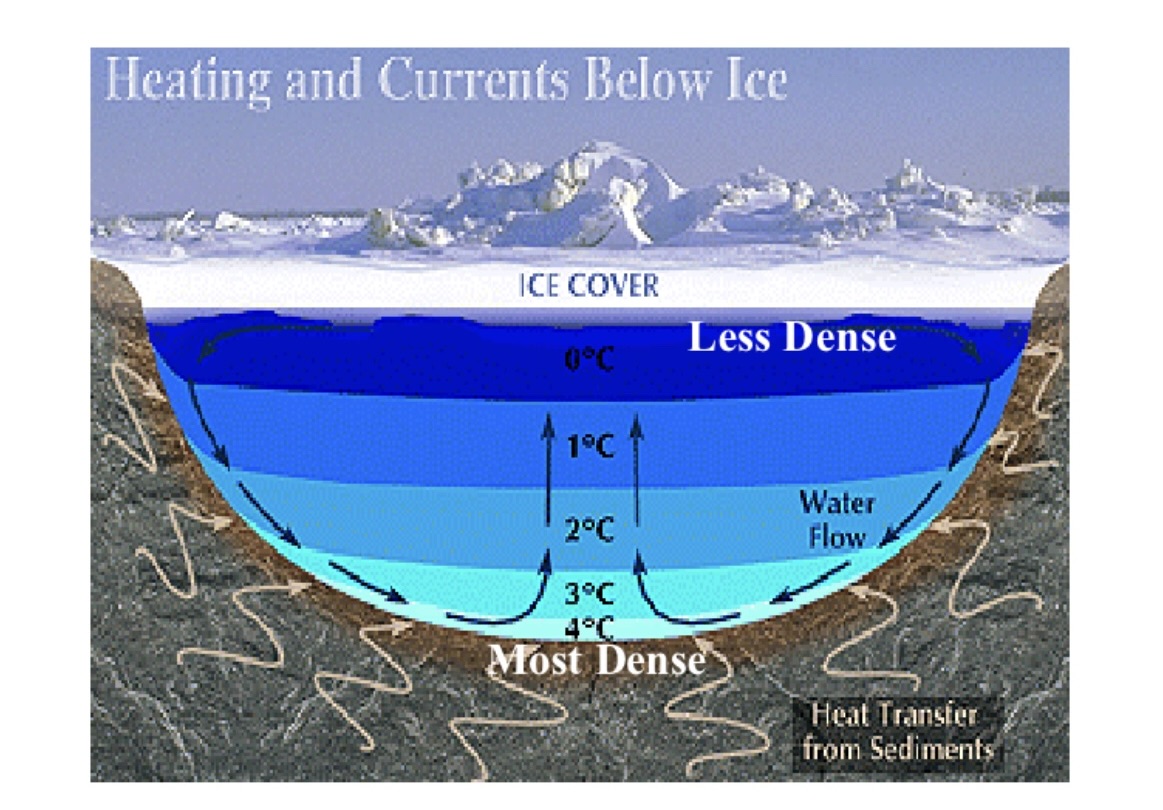
what would happen if ice was heavier than water?
ponds, lakes, oceans would freeze solid killing life
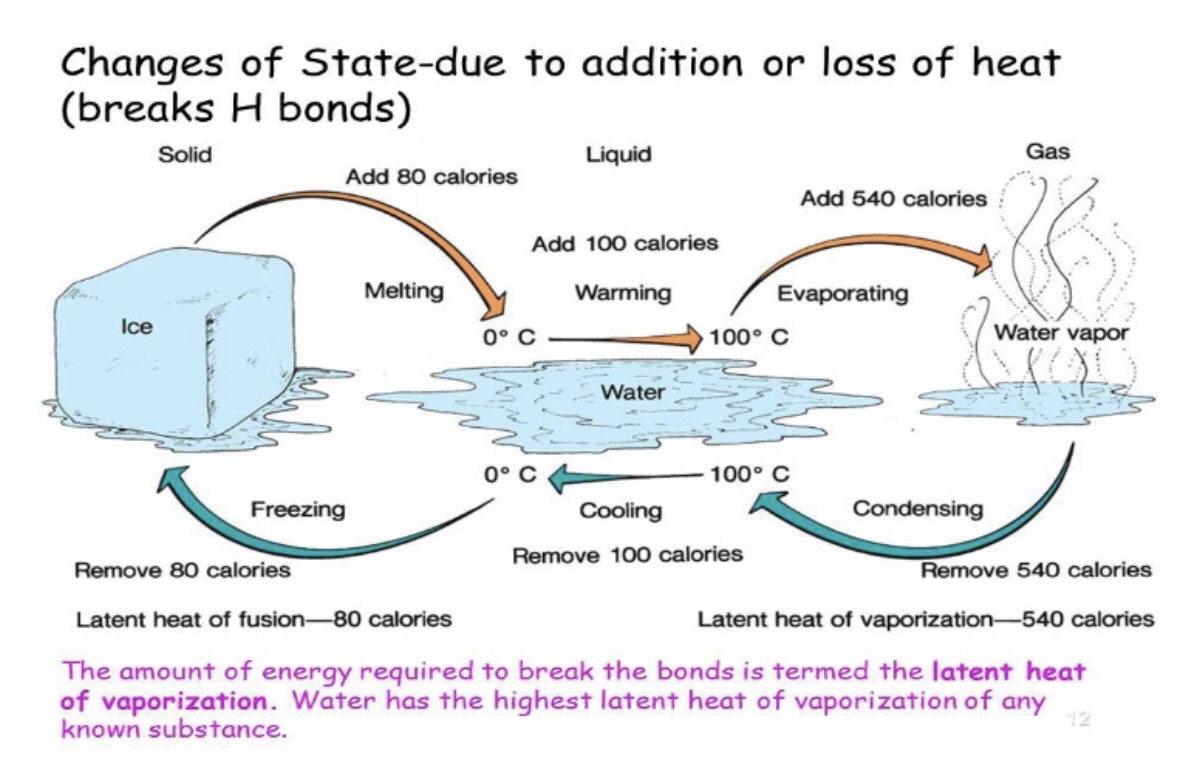
specific heat
amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of. a substance by 1 degree Celcius (or 1 Kelvin).
a substance with high specific heat requires more heat to change its temperature compared to a substance with lower specific heat.
why does water have high specific heat?
due to its molecular structure & strong hydrogen bonds between water molecules
high specific heat of water
water molecules held together by h-bonds
when you add heat to water, instead of the energy increasing the motion of the molecules (which raises the temperature), the energy goes towards breaking/weakening these h-bonds
bc of the h-bonds water can absorb a lot of heat without significant rise of temperature. this gives water a specific heat of 4.18 J/g degree celcius
why is high specific heat of water important?
temperature regulation: water can act as a buffer, absorbing/releasing heat with small changes in temperature. important for stable environments for organisms. large bodies of water (like oceans) help moderate earth’s climate by absorbing heat during the day and releasing it at night
human & animal bodies: our bodies mostly composed of water, high specific heat helps us maintain stable internal temperature. crucial for homestasis: process of keeping our bodies functioning properly despite changes in environment
climate & weather:weather paterns, stabilizes coastal climates preventing extreme temperature fluctuations. between day & night
what is waters high specific heat mainly due to?
h-bonds between molecules which require a lot of energy to break before temperature can rise
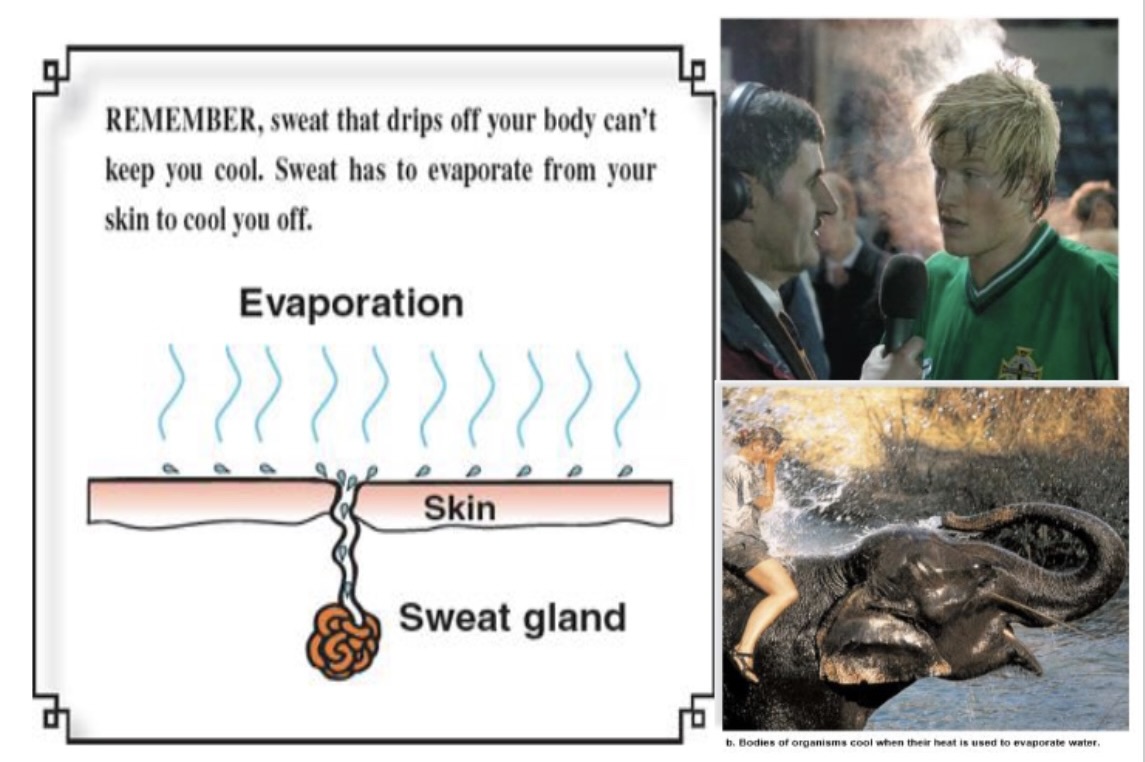
evaporative cooling
evaporation of water from the surface of the body, leaving the body cooler
as sweat evaporates it removes excess heat, helps mamals from over heating
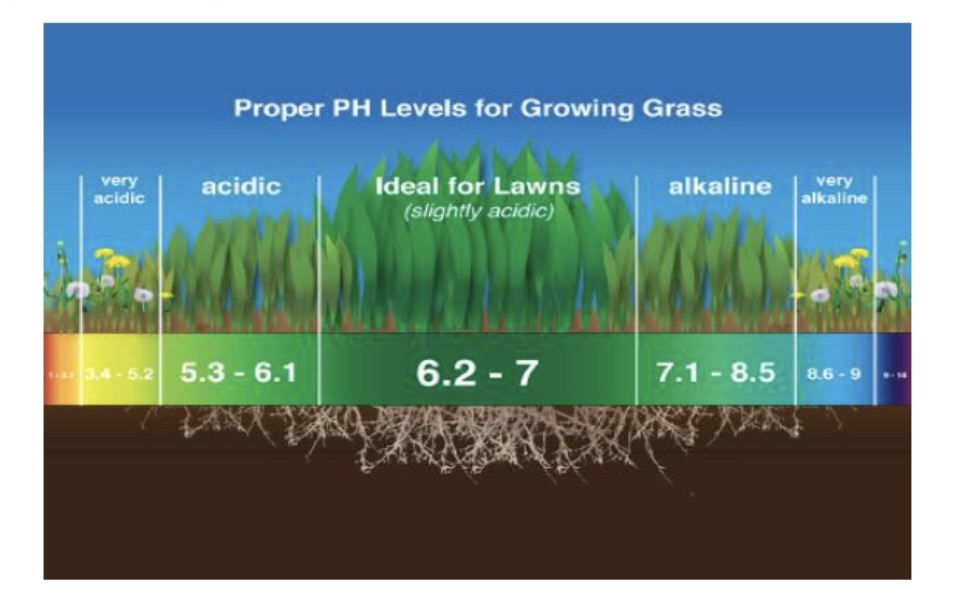
importance of ph
plants depend on soil to have right ph level for proper growth
our bodies must maintain proper ph level to function properly
soft drinks, medicine, cosmetics are “ph balanced”
ph informs us of
the power of hydrogen in life
stomach acid
ph of 2 or 3, very acidic, lots of hydrogen ions H+
most living things can not live in the presence of strong acid so it is important stomach acid stays in the stomach
the cells in stomach lining replace themselves continually bc it is a rough environment in which to live.
chemical composition of water
H2O
H3O+ (H+) ion
OH- ion
naturally undergoes a dossiciation (ionization) producing hydorgen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in equal amounts.
neutral ph of 7, 10^-7 mol/L with an equal concentration of of H+ and OH- ions
H+ and OH- are very reactive
H+ acidity
OH- alkalinity (basic)
acidity
acidic content in solution, determined by concentration of H+ ions or protons in that solution
high concentration of H+ ions
ph less than 7
more H+ ions more acidic
alkalinity
ability of a solution to neutralize acids
measure of a solutions capacity to resist changes in ph when acids are added
considered alkaline (basic) if it has high concentration of OH- ions
ph greater than 7
often associated with the precense of substances like bicarbonate ions (HCO3-), carbonate ions (CO3²-) and hydroxide ions (OH-) which can act as buffers to neutralize acids
acids
H+ (proton) donors
increase H+ concentration
hydrolic acid HCL ~ H+ + Cl-
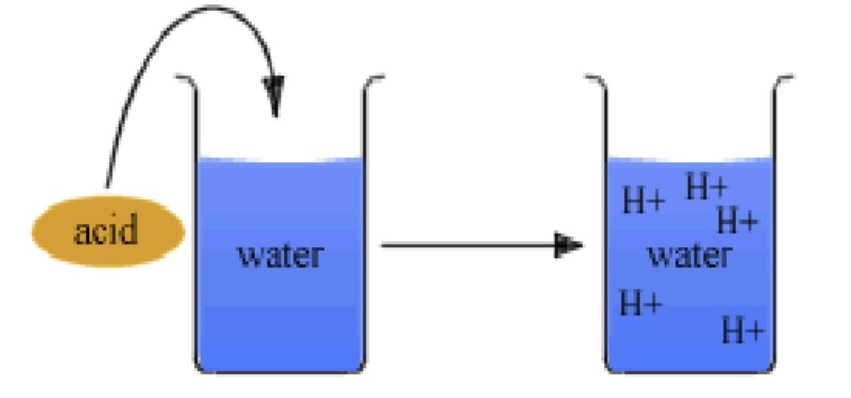
acidosis
high levels of free H+
stop cell reactions, denature proteins, nucleic acids, coma, death
bases
H+ (proton) acceptors
OH- donors
decrease H+ when added to water
stronger the base, greater decrease in H+
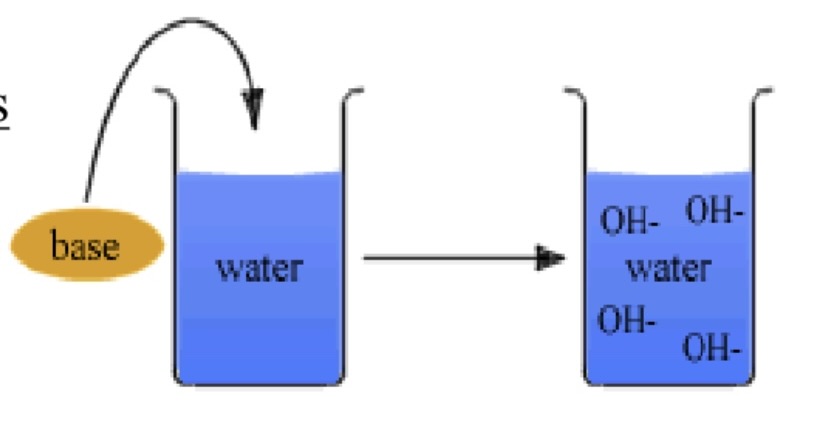
acids & bases
when added to water, change the concentrations of H+ and OH-
ph scale
ranges from 0-14
ph stands for
potential hydrogen
a measure of H+ concentrations in moles per litr
calculate ph of distilled water
ph = -log[H+] -log[10^-7]= -[-7] =7
ph is 7
calculate pOH- of distilled water
pOH= -logOH-] -log[10^7] = -[-7] = 7
pOH is 7
ph scale
classifies substances as neutral, acidic, alkaline 0-14
ph 7 neutral
ph 0-6.9 acidic
7.1-14 alkaline
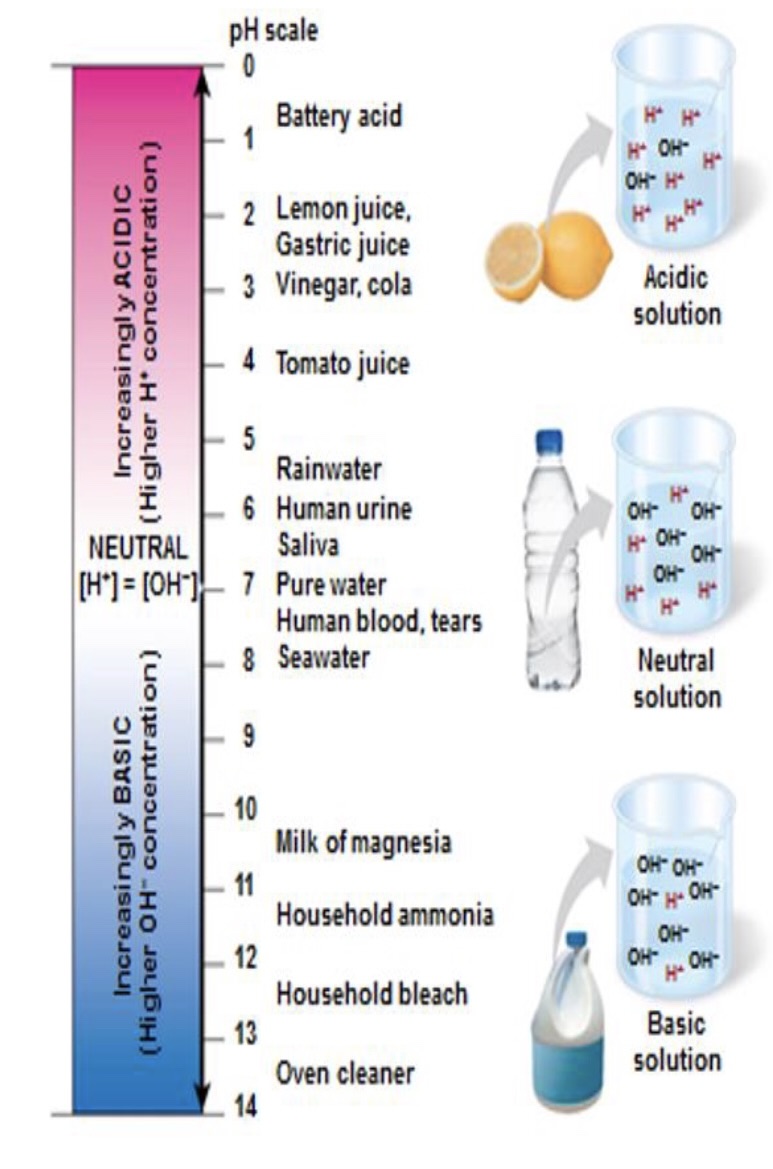
2 important constants on the ph scale
ph + pOH = 14
[H+] x [OH-] = 10^-14
![<p>ph + pOH = 14</p><p>[H+] x [OH-] = 10^-14 </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0fe3c520-e8f6-42d0-88c6-57c444954c12.jpg)
change in ph vs change in [H+]
if ph drops by 1 unit more acidic; [H+] is 10-fold higher
if ph rises by 1 unit less acidic; [H+] is 10-fold lower
each unit change on ph scale represents a 10-fold change in [H+]
![<p>if ph drops by 1 unit more acidic; [H+] is 10-fold higher</p><p>if ph rises by 1 unit less acidic; [H+] is 10-fold lower</p><p>each unit change on ph scale represents a 10-fold change in [H+]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d05767cd-a86f-4b3c-9d23-158f155f702a.jpg)
buffers
helps maintain constant ph ph by neutralizing acids or bases
minimize changes in ph when acid or base is added
minimizes [H+] and [OH-]
weak acid + conjugate acid
weak acid: neutralizes alkalinity; H+ donor
conjugate acid: neutralizes acidity; H+ acceptor
buffers are crucial for
normal cell function, metabolism, homeostasis
bicarbonate buffer system in the blood is one of the most important examples of how buffers maintain a stable internal environment in organisms.
what is the ph of pure water
7
if water has the ability to buffer it should
resist change even if you add acid or base to it
ph should resist change
ph should be maintained for a good buffer/resist change
if ph goes down it is now a good buffer
the composition of buffer is
acid and conjugate base
you can neutralize acid and base if
buffer is present
if something is very alkaline
ph level will be above 7, more OH- ions, low H+ proton (inverse so acidic is the opposite)
how does the acid neutralize the base
raise H+ levels
buffer capacity
once it gets used up the system will no longer buffer
in the human, tissue fluid and blood what is the common buffer
carbonic acid, sodium bicarbonate system HCO3
if it does not have an H+ it will pick up another positively charged ion
base neutralizes
acid
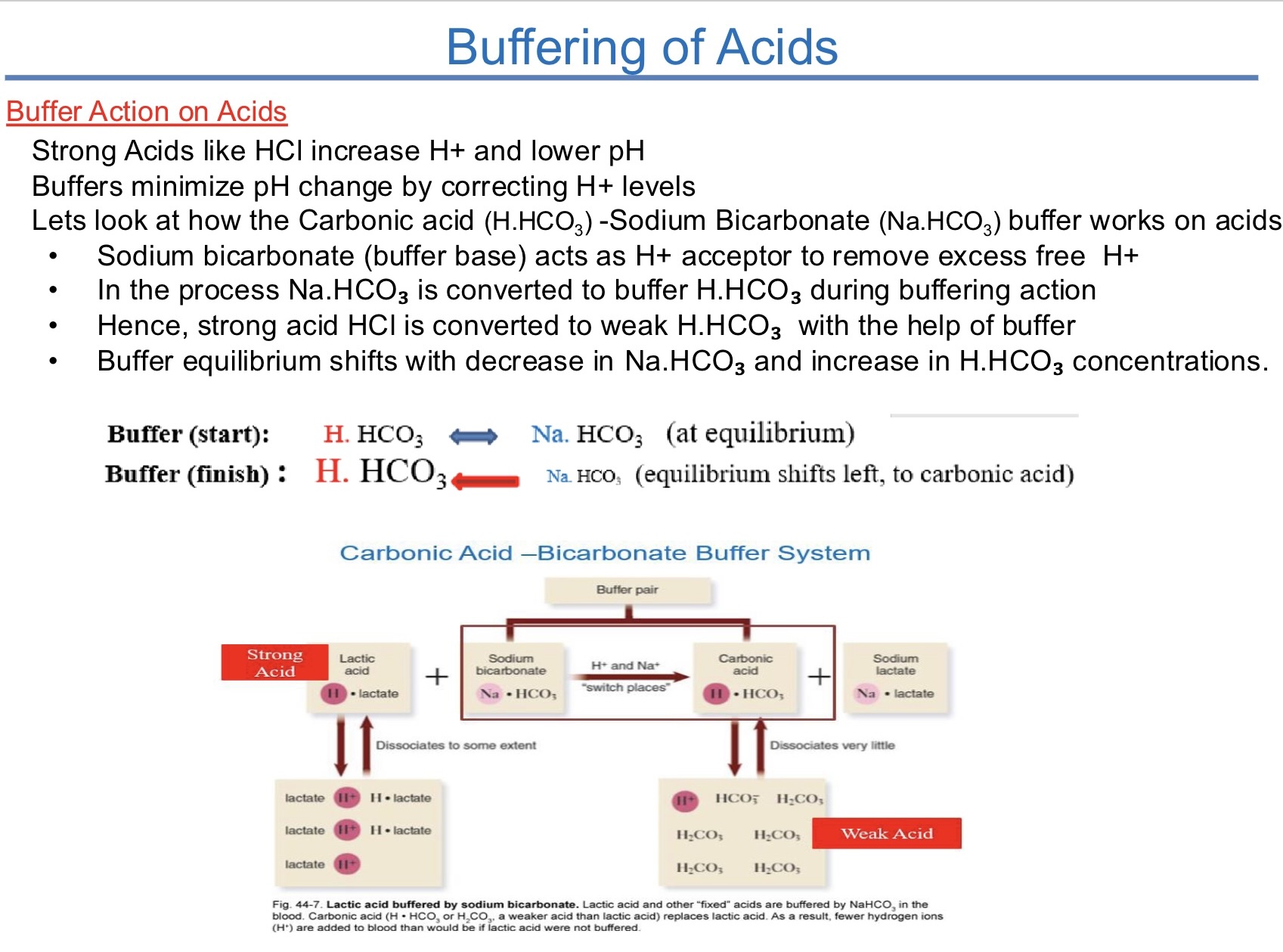
human buffer system as a ph regulator
carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer
H.HCO3 (back and forth) Na.HCO3
buffer capacity
once weak acid or conjugate base of buffer is depleted solution can no longer buffer and rapid changes in ph occur
how many bonds hold the atoms of a water molecule together? What type of bonds?
2, 2 polar covalent bond
what element is more electronegative and has a partial negative charge in water
oxygen
anything with high specific heat
can not change the temperature easily
why is it hard to change the temperature in water
the kinetic energy does not increase bc the water molecules are held together by the h-bonds, so break the h-bonds
when removing h-bonds
involves removal of heat
acids are
H+ donors, raise H+ levels (associated with acidity)
bases are
OH- donors, lower H+ levels (associated with alkalinity)
H+ acceptors
OH- + H+ =
H2O