BLG400 - Pedigrees / DEFINITIONS
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Male
Square
Female
Circle
Twins (Dizygotic - nonidentical)
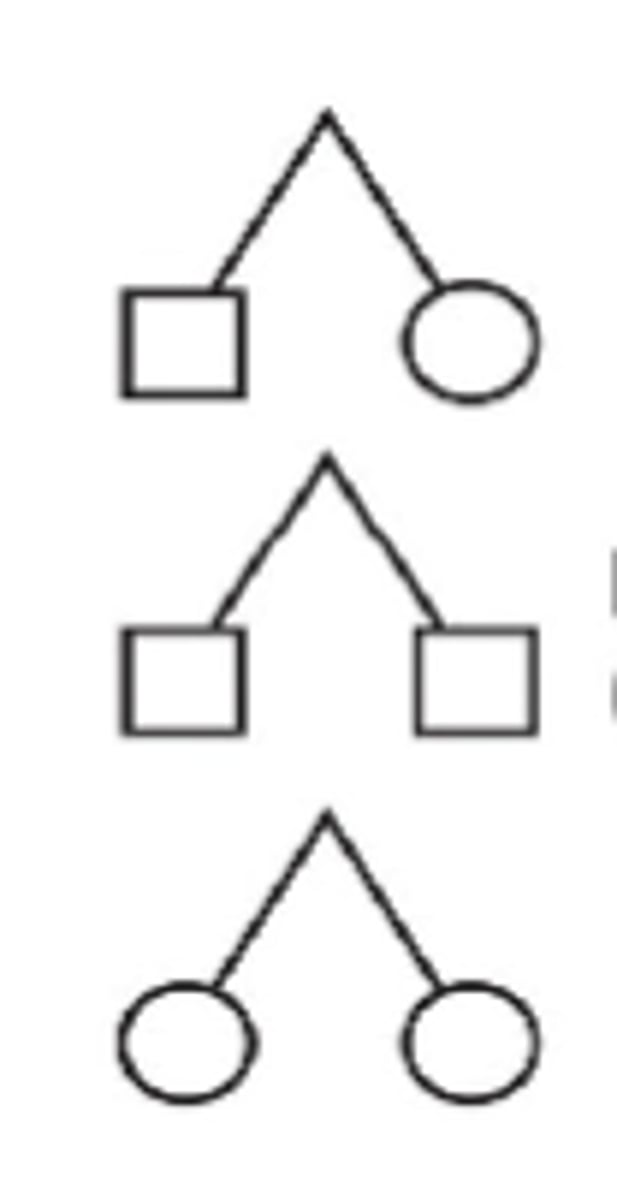
Twins (Monozygotic - identical)
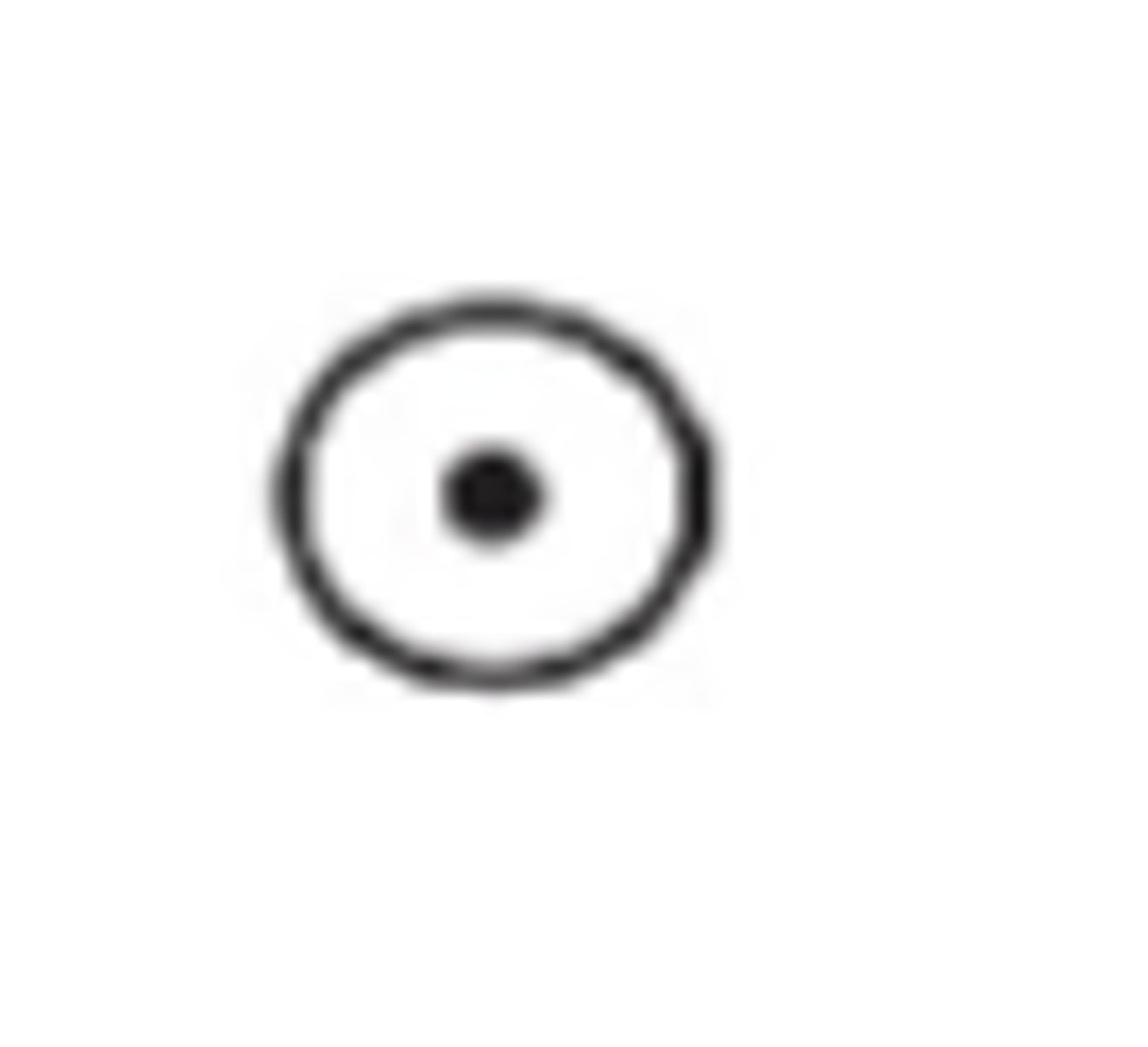
Unspecified sex
rhombus
Heterozygotes for autosomal recessive
Half shaded

Carrier of sex-linked recessive

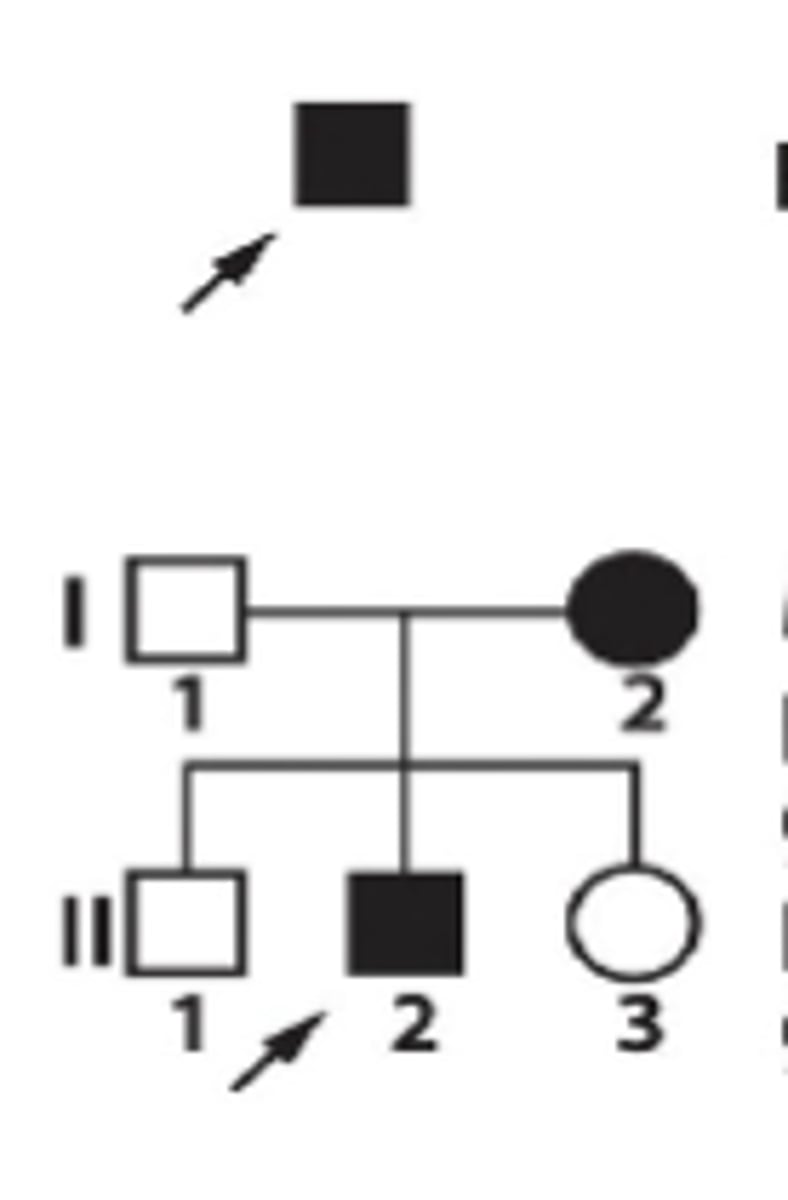
Propositus + meaning
the person immediately concerned
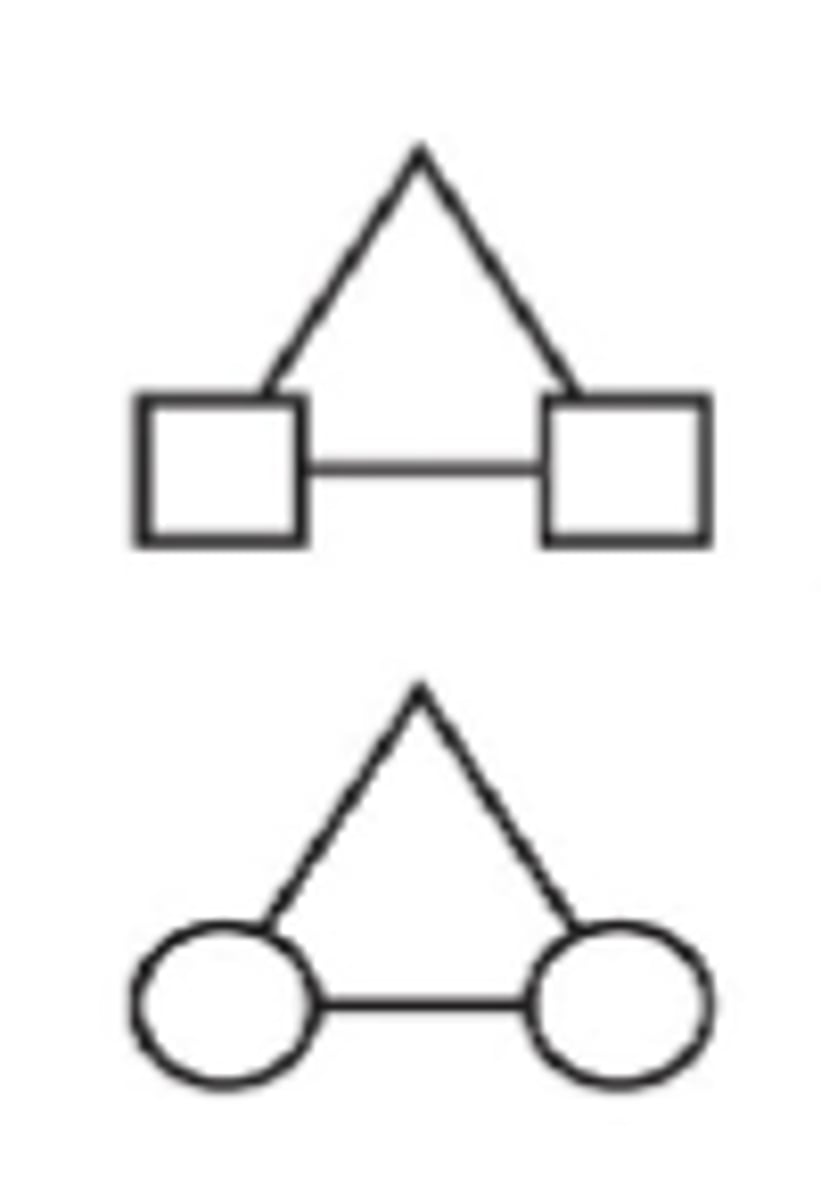
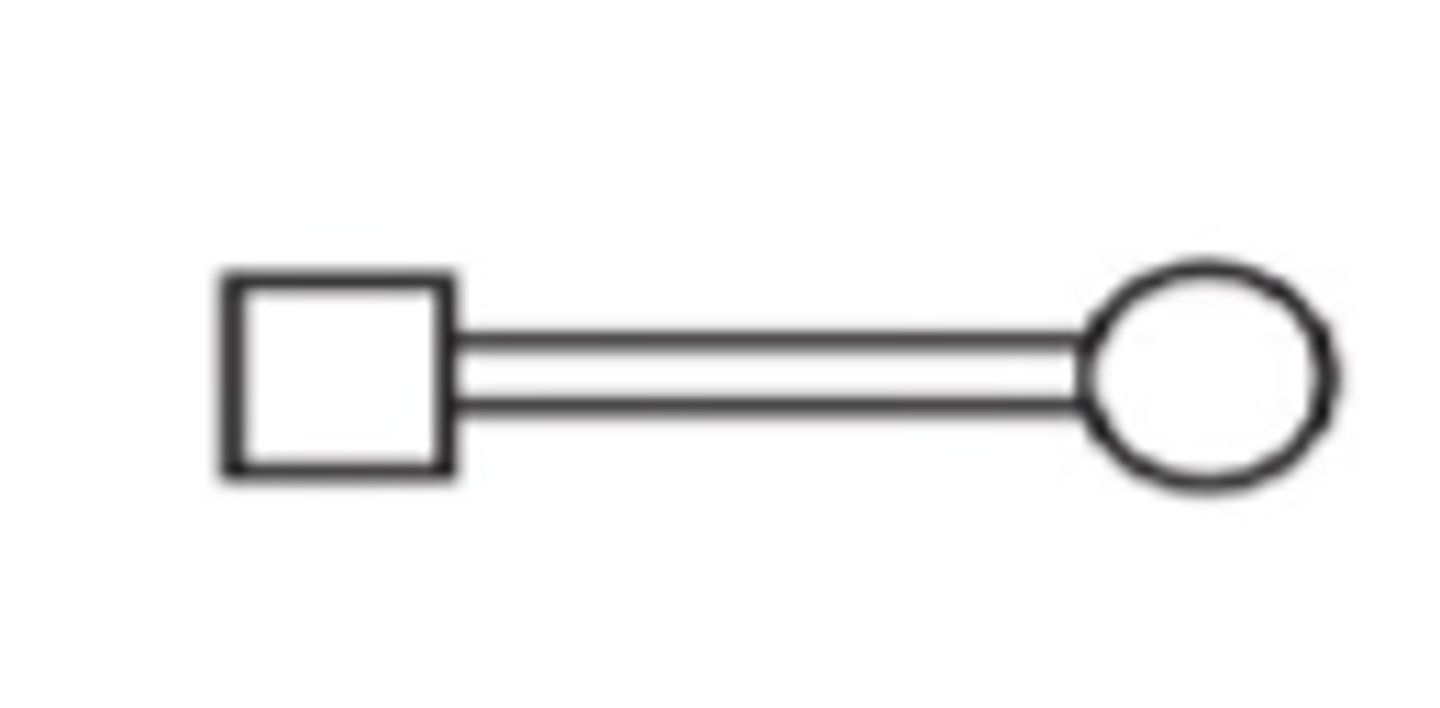
Consanguineous marriage + meaning
individuals closely related
What can human autosomal traits be inherited as?
Located on non-sex chromosomes (1-22)
- autosomal dominant
- autosomal recessive
What can human sex-linked traits be inherited as?
Located on sex chromosomes (X,Y)
- X-linked dominant
- X-linked recessive
- Y-linked
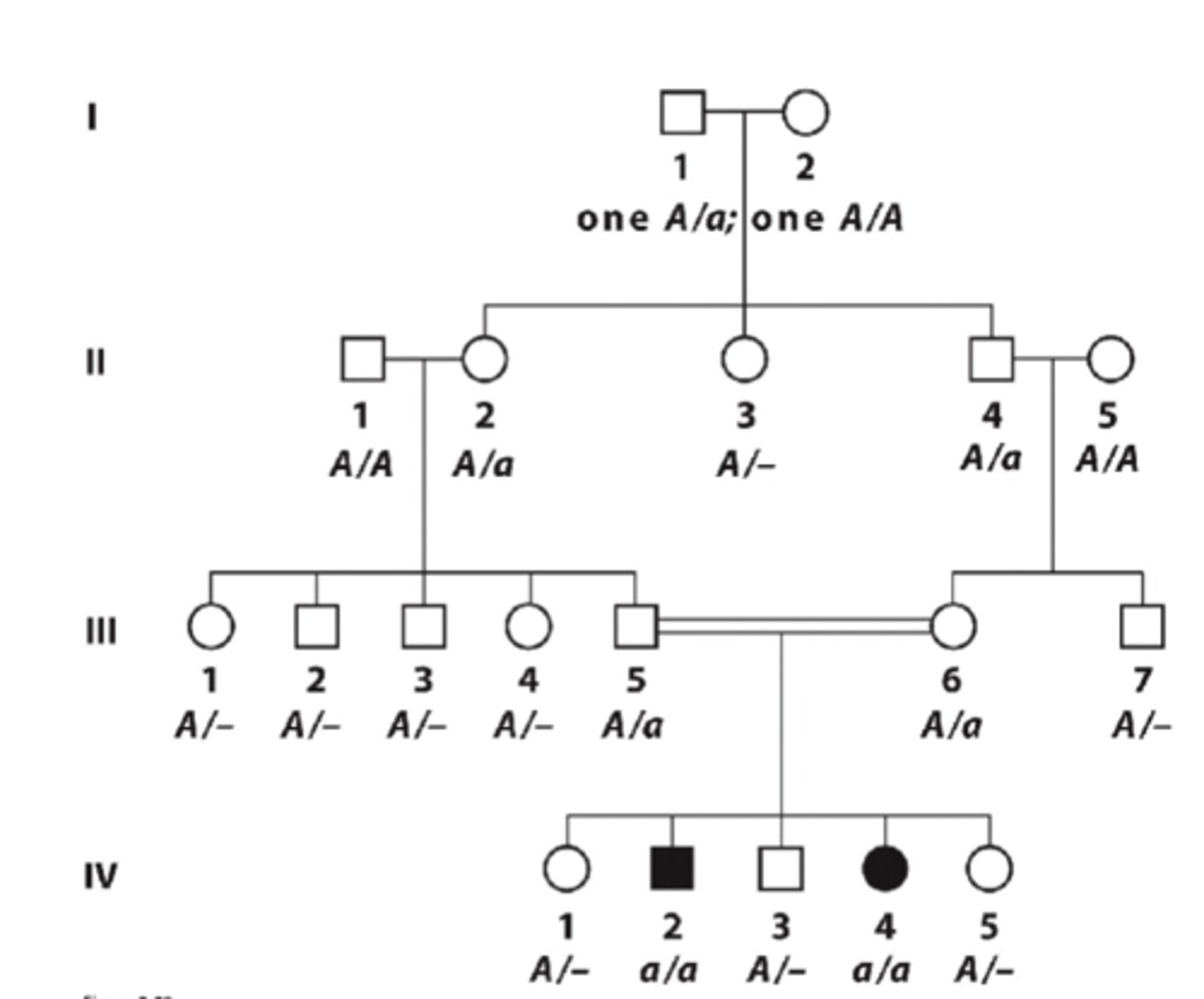
How to recognize autosomal recessive traits in pedigree
- Affected individuals are a/a
- For affected parents: all children affected
- For unaffected parents: If heterozygote, half of children will be affected, appearing equally in both sexes CAN BE RESULT OF CONSANGUINEOUS MATING
- Rare recessive traits show horizontal pattern of inheritance (spread among unrelated individuals)
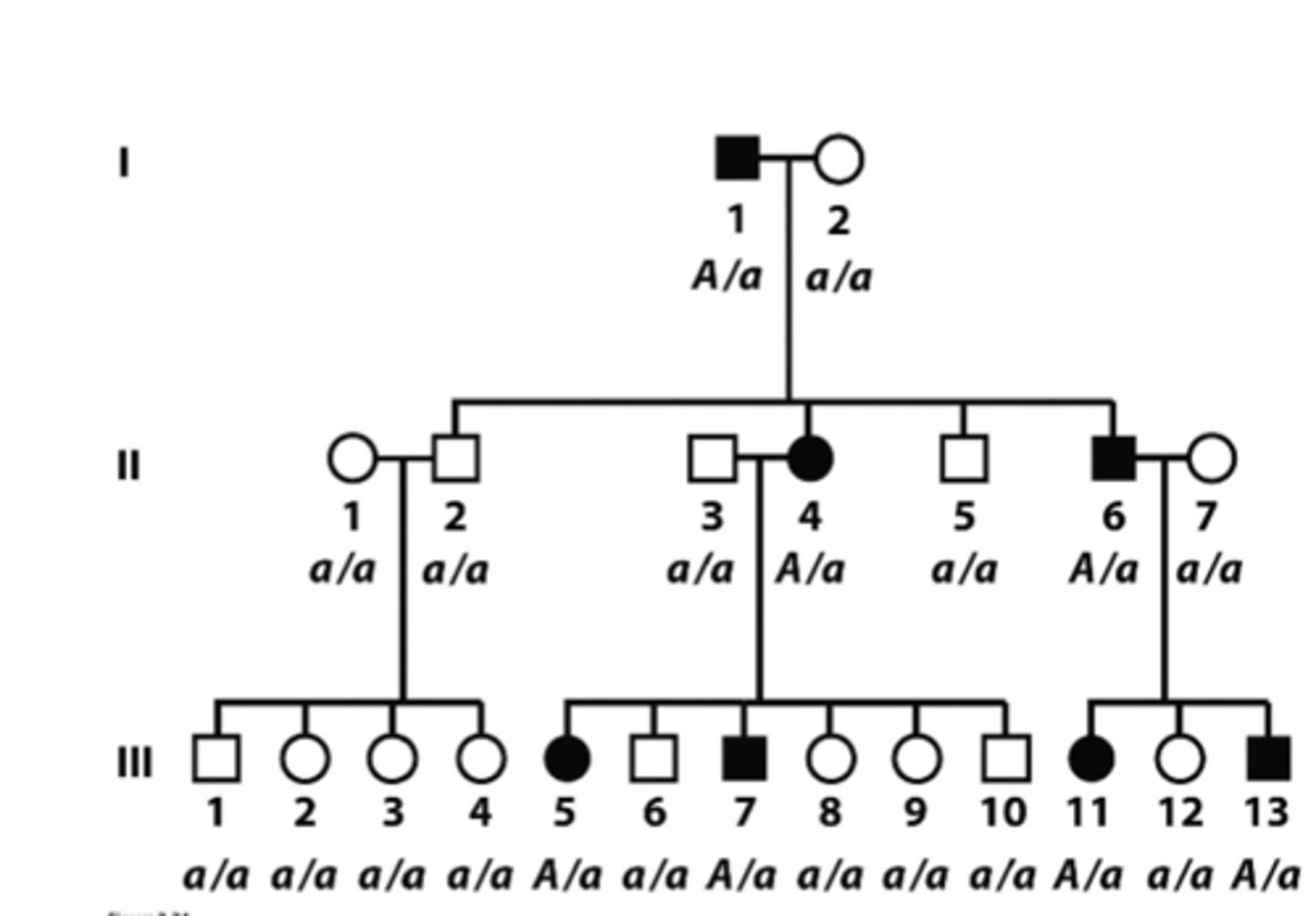
How to recognize autosomal dominant traits in pedigree
- Affected individuals are A/A or A/a
- Affected children will ALWAYS have at least one affected parent
- Vertical pattern of inheritance (parent to offspring)
- Two affected parents CAN have unaffected progeny if both are heterozygotes
- Appear equally in both sexes
Autosomal polymorphism
Co-existence of two or more common phenotypes of a character/trait
Morph
the alternative phenotype
Dimorphism + example
simplest polymorphism with just two morphs
example: in humans, brown vs. blue eyes, pigmented vs. blond hair, sticky vs. dry earwax, attached vs. free earlobes
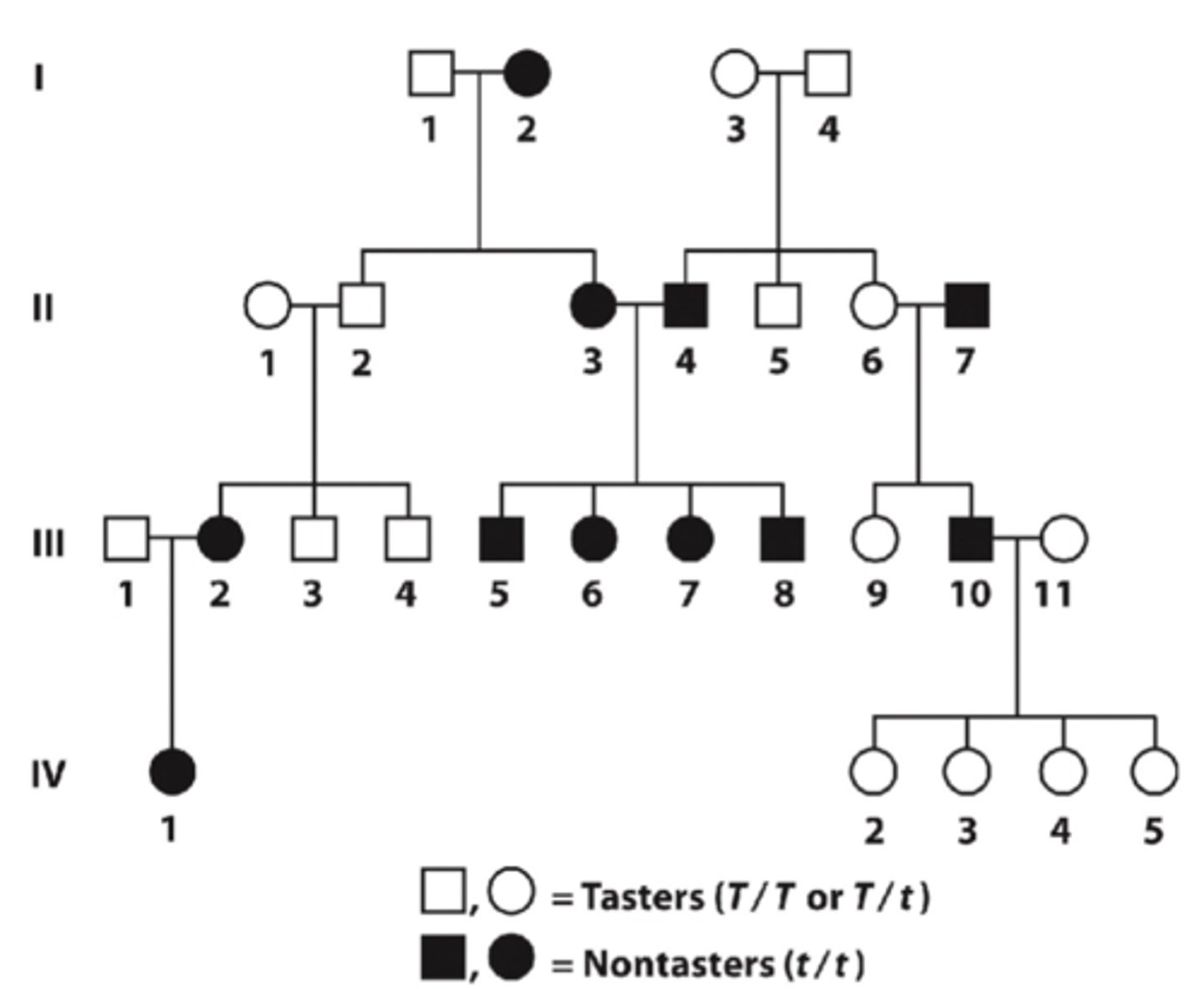
Pattern of inheritance for common recessive traits
Example of autosomal polymorphism as two common phenotypes can exists (the common recessive trait + dominant trait)
- the recessive train can show vertical pattern of inheritance IF the train is very common in the population
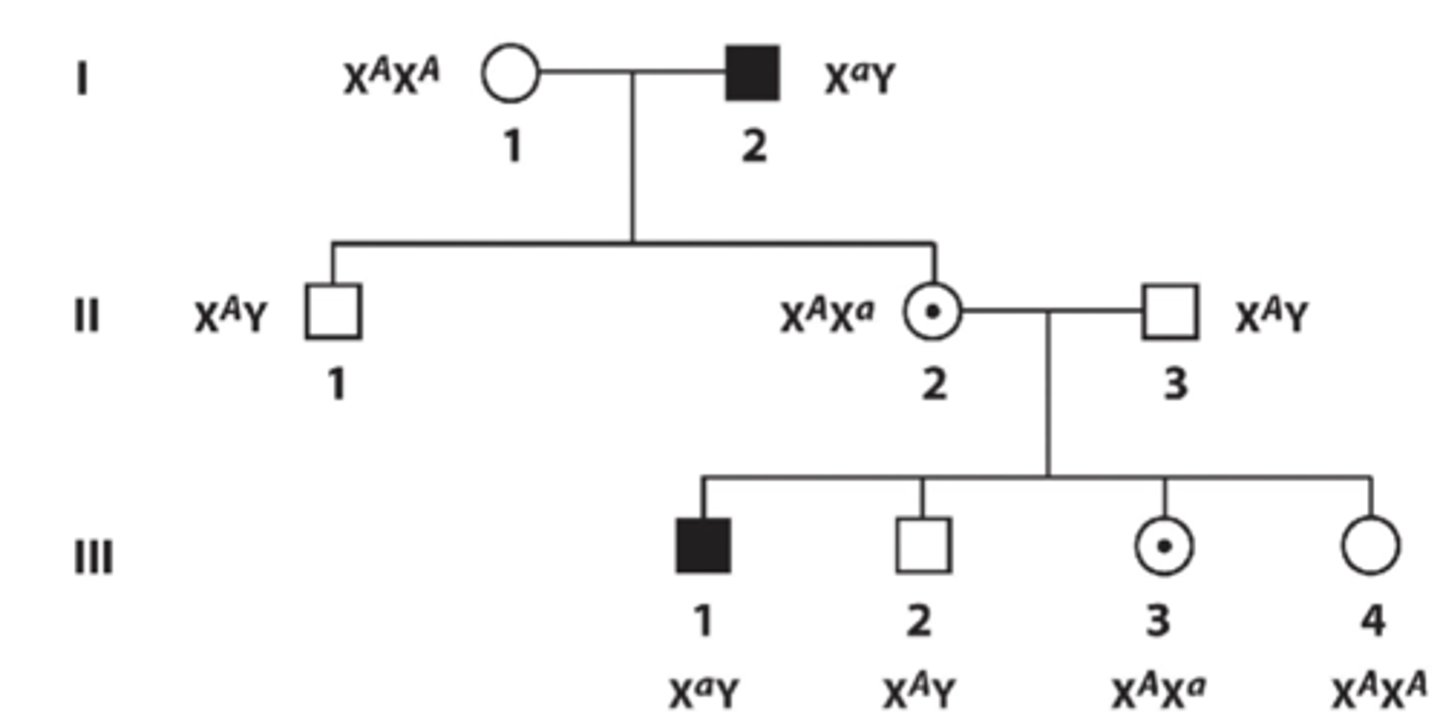
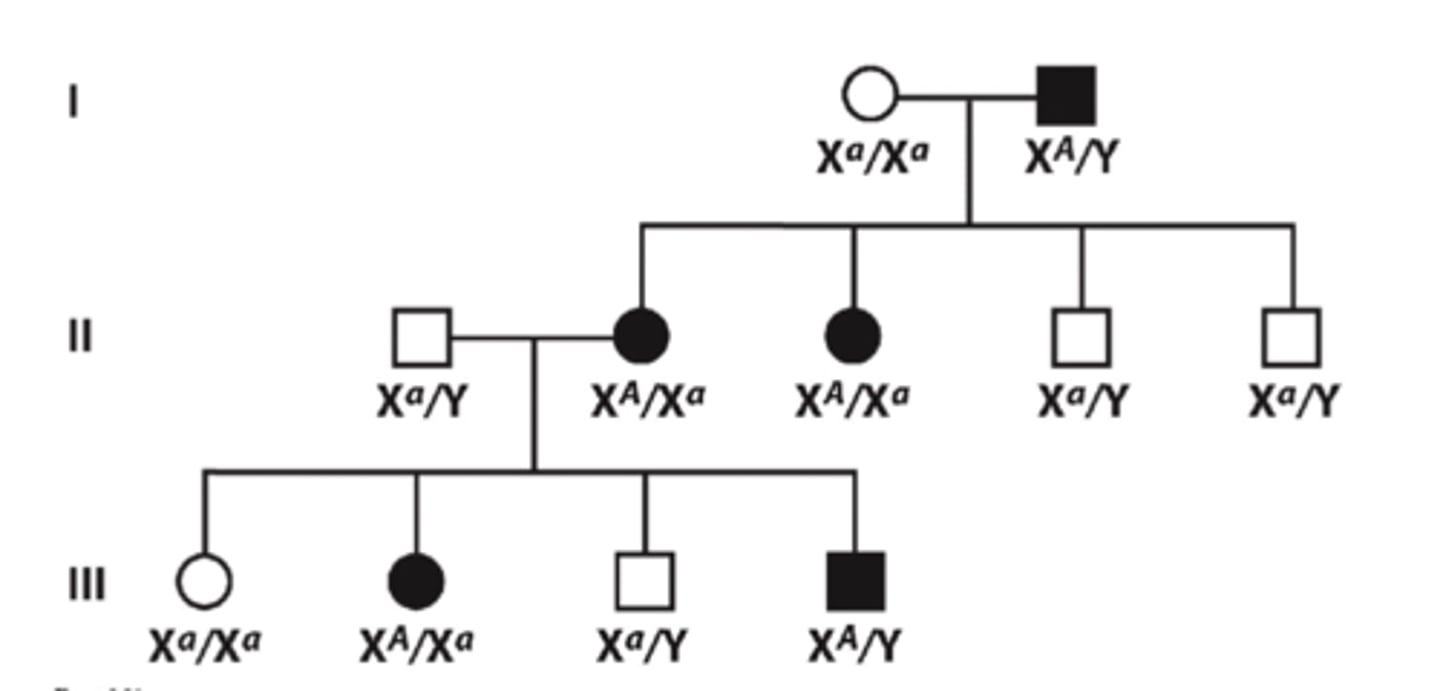
X-linked recessive disorders relationships between parent and offspring
- Daughters of affected male are always carriers of recessive trait
- Mutation NEVER passes from father to son (since son gets Y chromosome from father, never affected X)
- More males than females show rare trait since they only need one affected recessive allele to express trait
Examples of X-linked recessive disorders
red-green colour blindness
hemophilia
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
X-linked dominant disorders relationships between parent and offspring
- affected males pass condition to ALL daughters and NONE of their sons
- Affected heterozygote females mating with unaffected males pass trait to half their sons and daughters (both sexes equally affected)
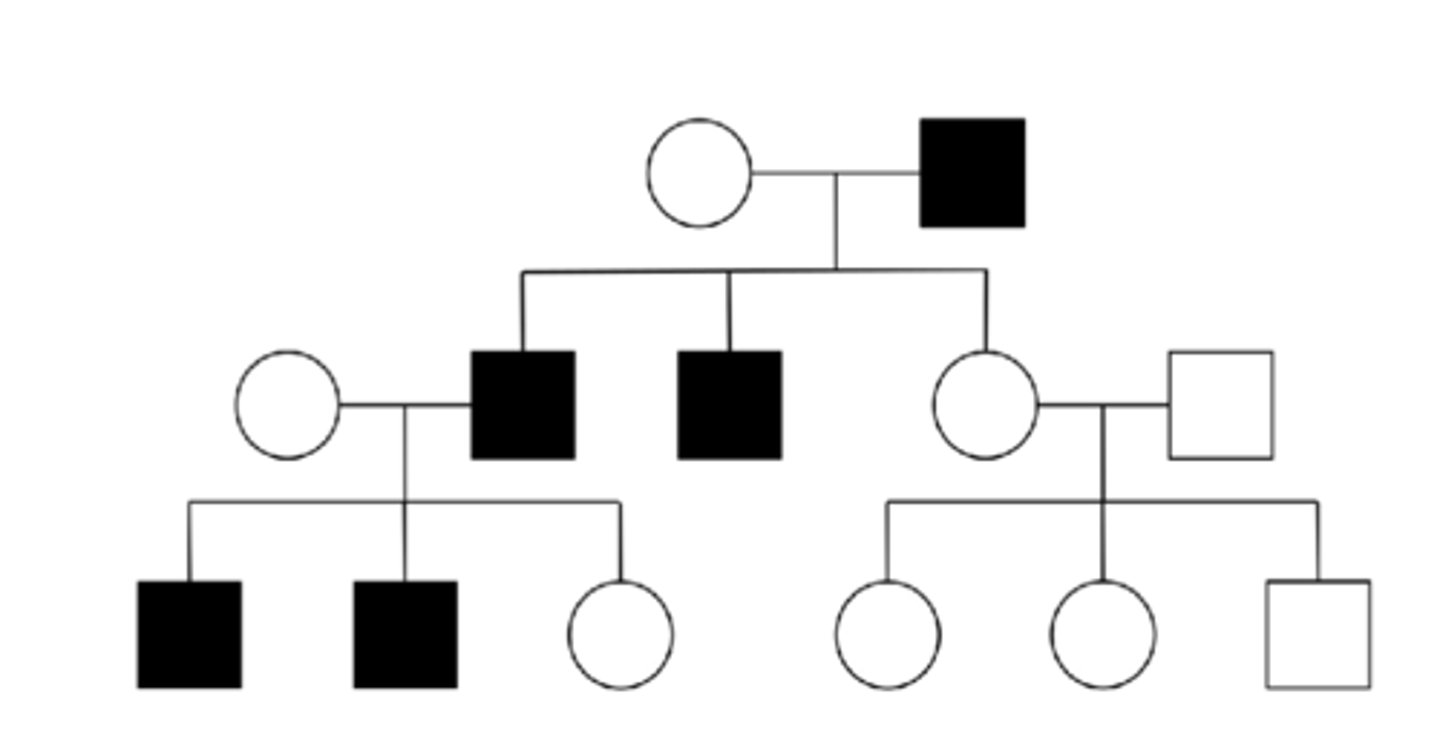
Y-linked disorders relationships between parent and offspring
Trait only observed in males (male to male transmission)
- All male descendants of affected male will have trait
Tay-Sachs Disease
Severe, rare autosomal recessive disease caused by malfunction of the enzyme hexosaminidase A
Product rule
The probability of two independent events both occurring is the product of their individual probabilities
Probability of Event 1 and Event 2 = Probability of Event 1 x Probability of Event 2