Macro Final Exam
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What is glycolysis used for
Breakdown of glucose to do ATP synthesis by substrate-level phosphorylation
starting products for glycolysis
glucose
end products of glycolysis
pyruvate
enzyme responsible for glucose release from the liver (not the muscle)
glucose-6-phosphatase
end products of carbohydrate oxidation
CO2 and water
How to name fatty acids
count the carbons, put a colon, count the double bonds, and write, then what carbon from the omega side did it start on
How many moles of ATP are formed from a fatty acid
cutting phase (generating 4 ATP), feed acetyl coa into TCA (generating 10 ATP), determine cuts (N/2-1) (multiply by 4) and acetyl coa (n/2) (multiply by 10), subtract 2 for the ATP used at the beginning.
The hormone that affects lipolysis
insulin
functions of glycerol
a backbone for triglycerides. Substrate for gluconeogenesis.
end products of lipid oxidation
CO2 (from 2 steps in the Krebs cycle) and water (from the ECT)
The enzyme that hydrolyzes blood triglycerides
lipoprotein lipase
chylomicron
carries dietary fat, made in the small intestine
VLDL
the endogenously derived triglycerides that move away from the liver
LDL
made from VLDL once it loses its triglycerides (chopped off by lipoprotein lipase)
HDL
dumps to the liver by LCAT.
Where are triglycerides used
in the liver
What enzyme allows us to store cholesterol in tissues
ACAT
What enzyme is rate limiting in cholesterol synthesis
HMG coa reductase
What does a statin do
inhibit HMG coa reductase
Purpose of conjugated bile acids
more polar, can form micelles
bile acids
cholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid.
Conjugated bile acids
glycocholic acid, taurocholic acid, glycochenodeoxycholic acid, taurochenodeoxycholic acid.
the essential amino acids
phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, histadine, leucine, lysine
the gluconeogenic amino acids
alanine, glycine, serine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, glutamine, valine, methionine, histidine, and arginine
ketogenic amino acids
leucine & lysine
the ammonia-carrying capacity of amino acids
glutamine = 2, alanine = 1
the function of transamination
to make a nonessential amino acid.
the shuttle systems that transfer NADH
glycerol phosphate shunt in the mitochondria in the liver
the shuttle system that transfers acetyl CoA for fat synthesis
citrate shuttle
pathway of the citrate shuttle
citrate synthase produces citrate in the mitochondria. It gets split by citrate lyase and malonyl coa is created from ACC
Substrates for gluconeogenesis
glucogenic amino acids, lactate, pyruvate, glycerol
Brain fuel in starvation
ketones
Metabolism during type one diabetes
no insulin being made, can't get glucose into cells. Need an insulin shot. Other tissues are broken for energy (protein & fat). Is fatal without treatment.
Metabolism during type 2 diabetes
making insulin but it's not responding. Insulin overproduces and the pancreas might eventually stop producing.
Vo2 max
max volume of oxygen that a particular person can utilize (higher the better), indicates fitness level.
Percent vo2 max
how much oxygen you are using, the insensitivity of activity.
Hyperglycemia
high blood glucose
Pathways that require NADPH
alcohol (MEOS system), fatty acid synthesis
Pathways that create CO2
glycolysis, beta-oxidation
Ketone formation substrate
acetyl coa
Substrates for exercise over time at a low intensity
creatine phosphate, then glycolysis, & fat
The function of insulin
Inhibits lipases and regulates blood sugar
Insulin resistance
T1D where you don't respond to insulin properly.
How does insulin regulate blood sugar
by causes glucose to go into the cell when it goes to the blood and tissues and binds to an insulin receptor which moves glucose transporters to the surface of the cell.
Functions of the kidney
Acid-base balance, absorption, excretion of nitrogen in the form of urea, gluconeogenesis in starvation, and amino acid metabolism
Respiratory quotient
co2 produced/o2 consumed
RQ 1
body is metabolizing carbs.
RQ .7 means
body is metabolizing fat.
RQ .85 means
body is metabolizing fat and carbs
RQ .82 means
the body is metabolizing protein
RQ under .8 means
underfed
RQ under .7
starvation/low carb diet
VO2 25-30%
low intensity
VO2 50-75%
moderate intensity
VO2 over 85%
high intensity
ATP mechanisms
substrate level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation
Substrate level phosphorylation
two reactions together (coupling the reactions)
Oxidative phosphorylation
ATP synthase and electron transport
Hyperglycemia
high blood glucose
Substrates used in exercise
higher intensity less fat used. Longer low intensity, more fat used. Longer higher intensity like a marathon, supplemented with carbohydrates.
Why you cannot use 100% fat
all your cells do not have mitochondria (RBC). You need carbs & protein in your diet.
Fatty acid location
cytosol
Beta oxidation location
mitochondria
Hexose monophosphate shunt/pentose phosphate location
cytosol
Glycogen synthesis location
cytosol
Glycogen lysis location
cytosol
TCA cycle location
mitochondria
Pyruvate carboxylase pathway
gluconeogenesis
Acetyl coa carboxylase pathway
fatty acid synthesis
The two parts of the fatty acid synthase complex are
condensing enzyme and acyl carrier protein.
Functions of acetyl coa
makes ketones, fatty acids, and cholesterol, feeds the TCA cycle to make ATP.
Harris-Benedict/Mifflin St. Jeor measures this type of energy
basal.
EER measures this type of energy
total.
How reactions are inhibited by alcohol
they can go backward or stop completely. The NADH/NAD ratio gets thrown off and enzymes begin to compete with one another. Alcohol generates NADH and NAD is used in alcohol metabolism.
phenylalanine

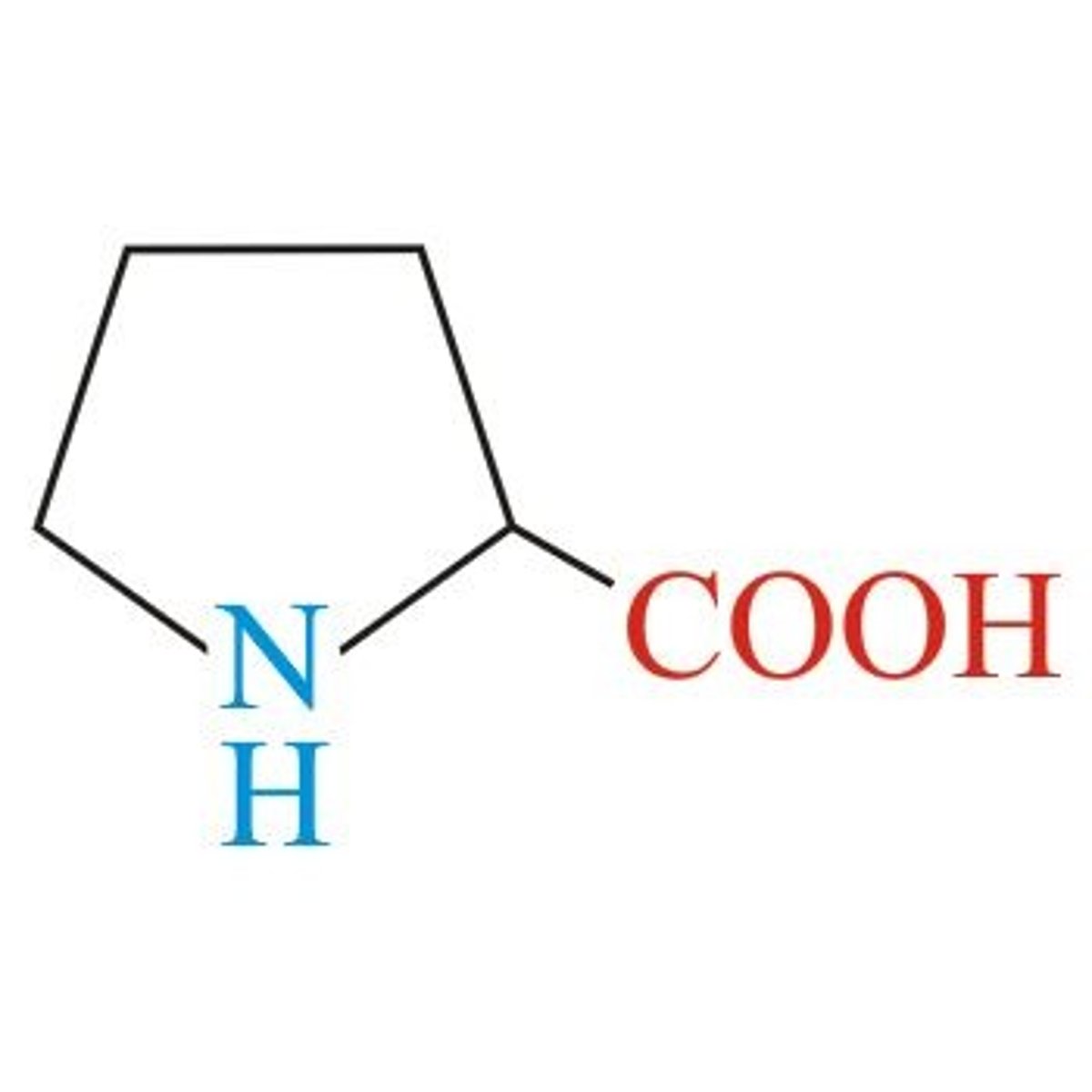
proline
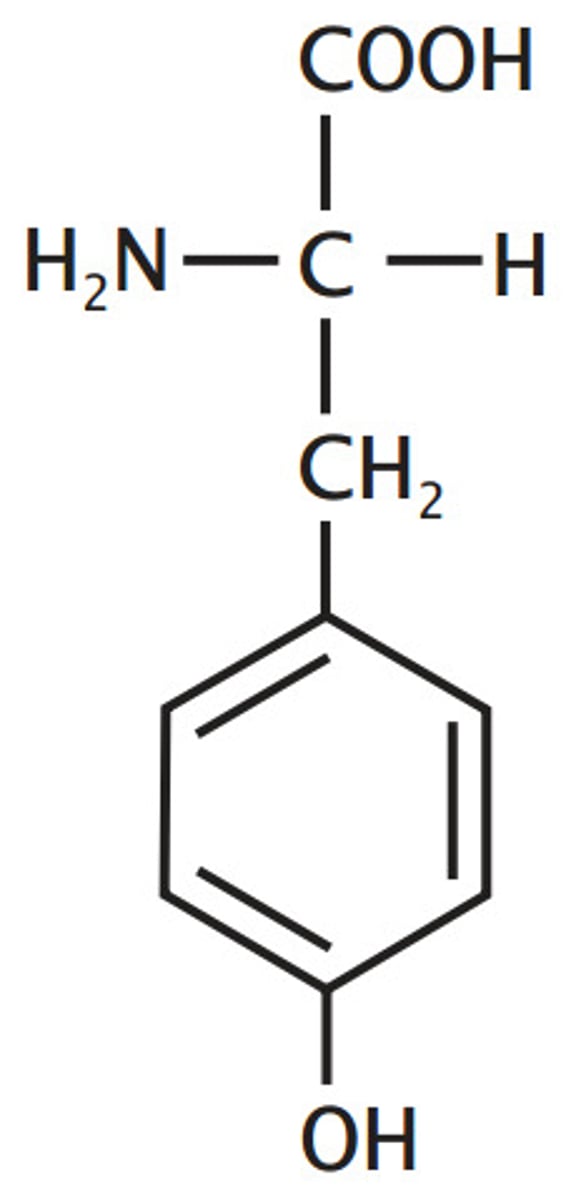
tyrosine kinase
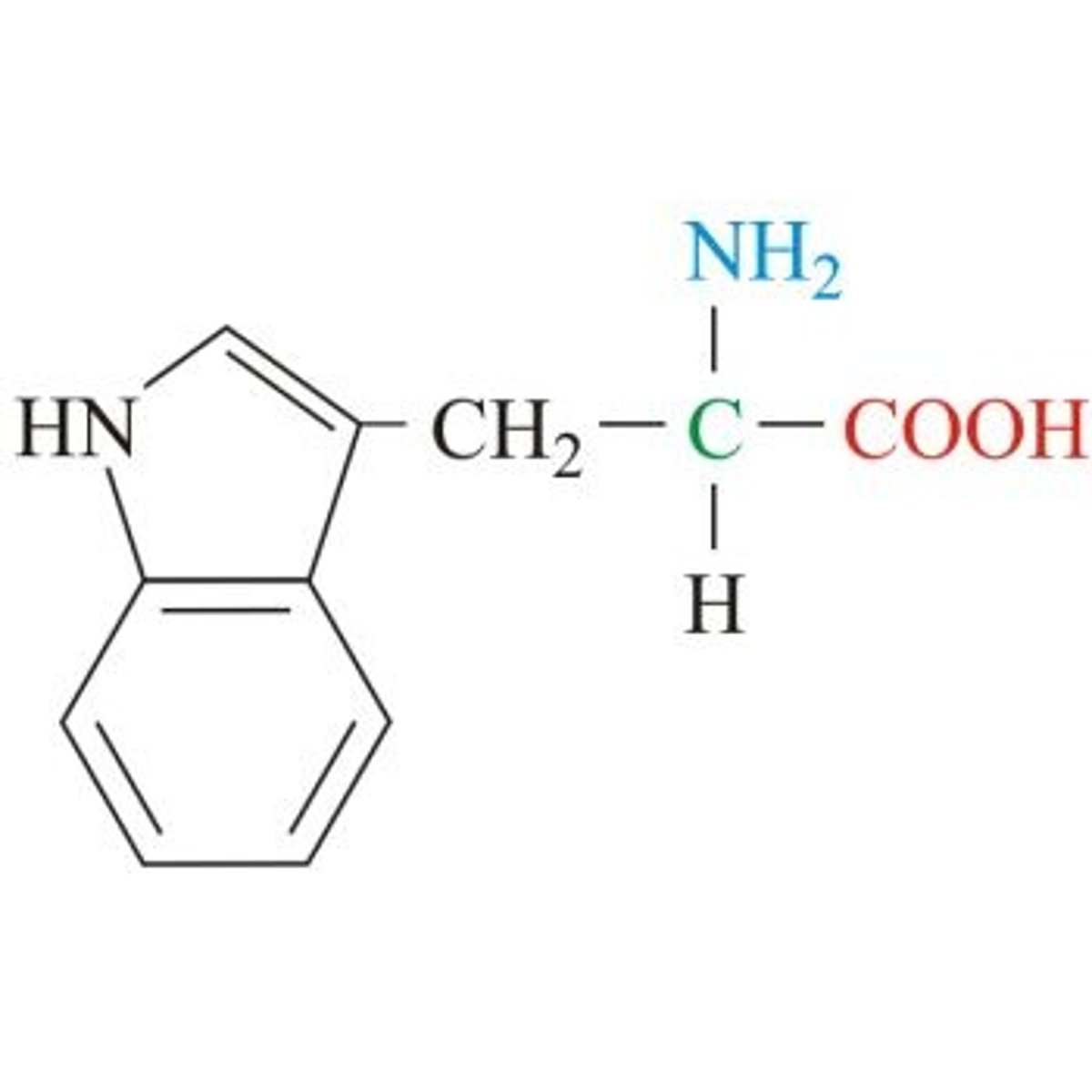
tryptophan
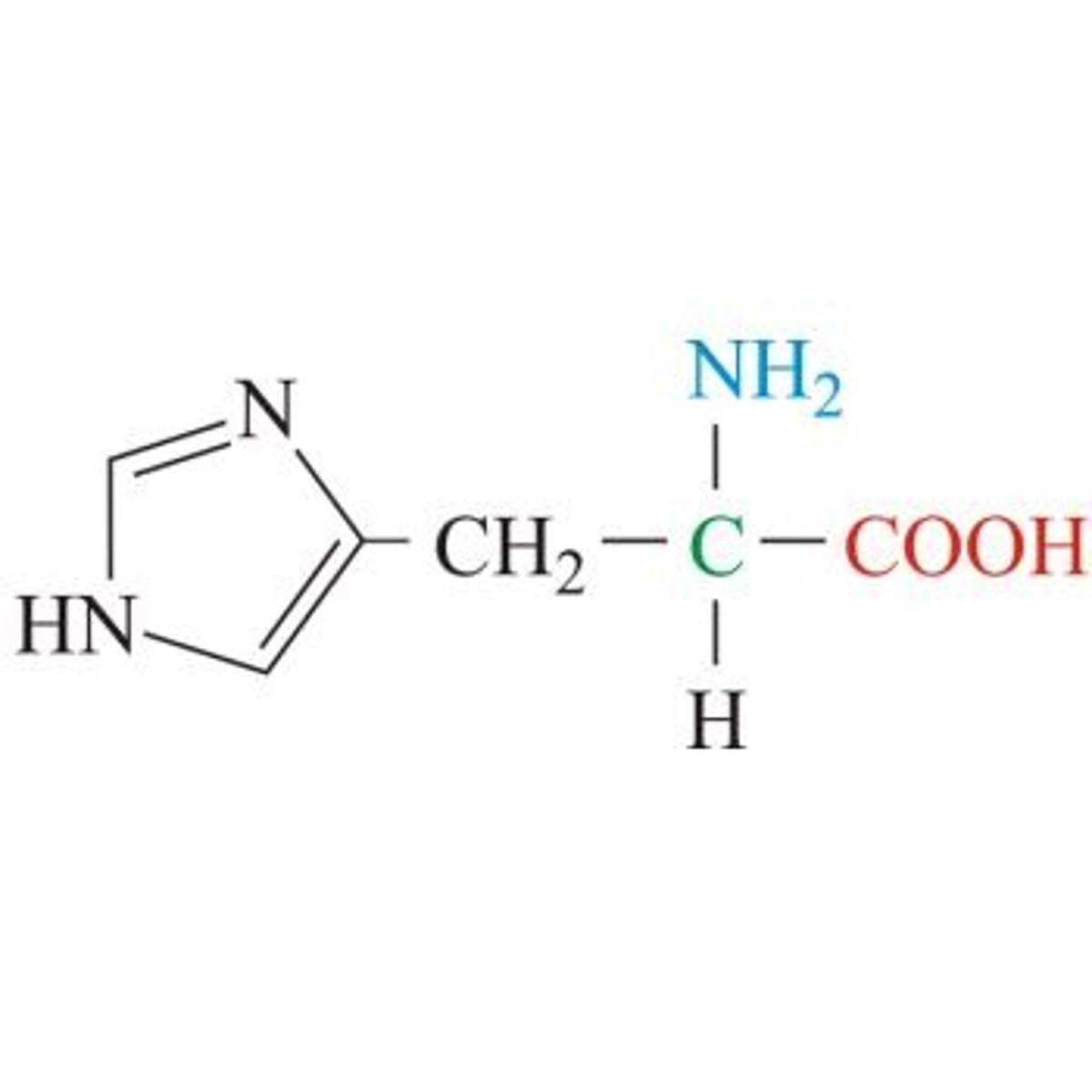
histadine
methionine
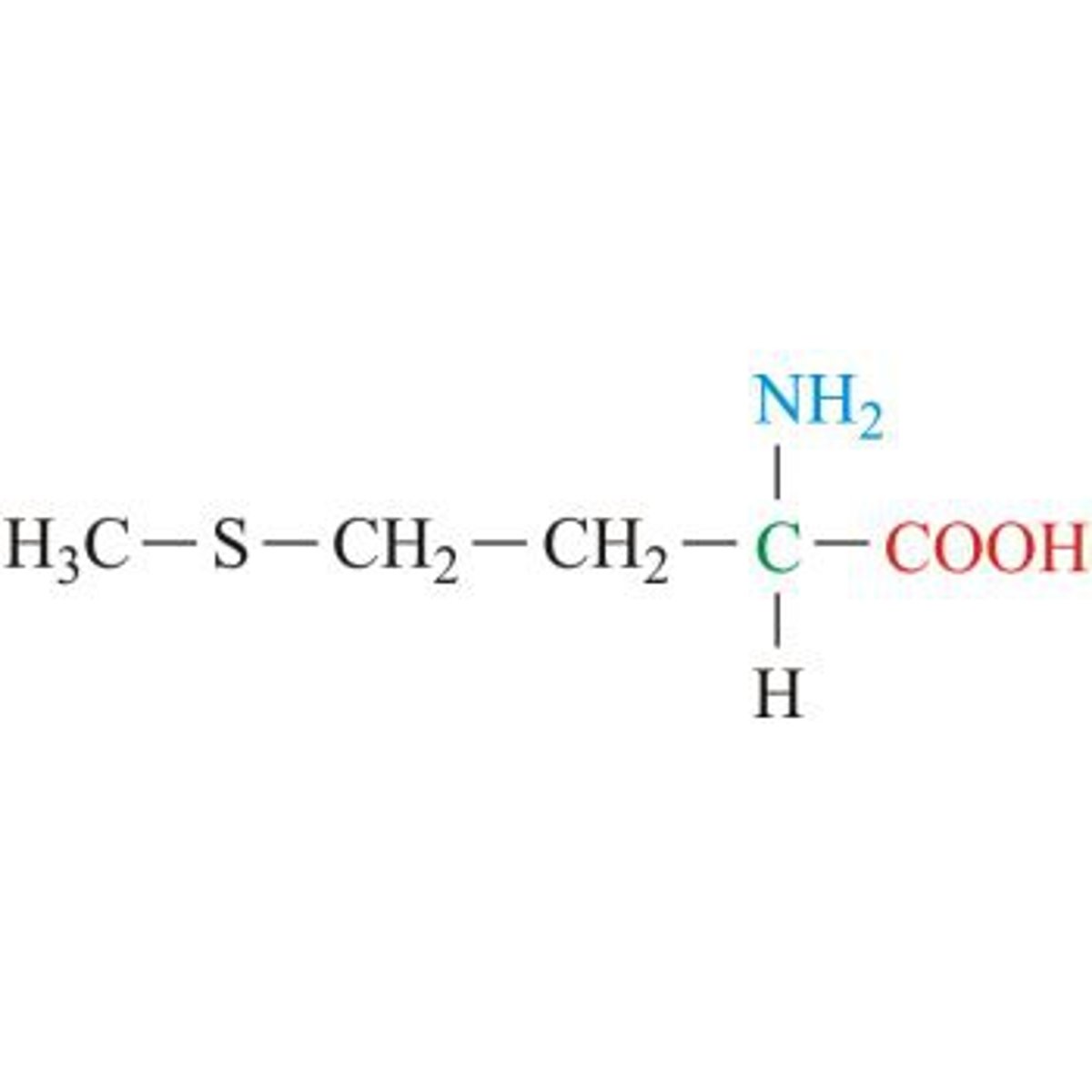
alanine
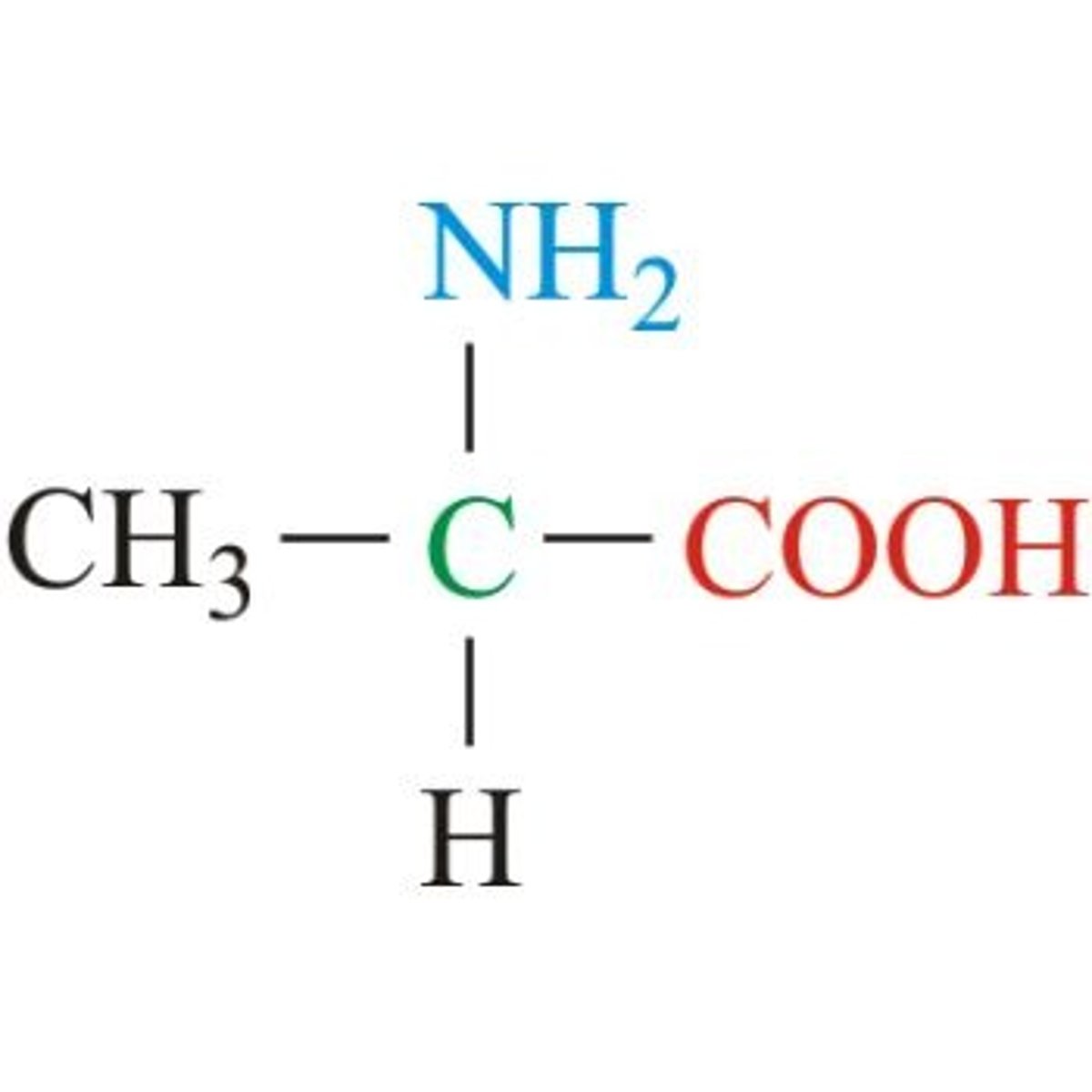
leucine
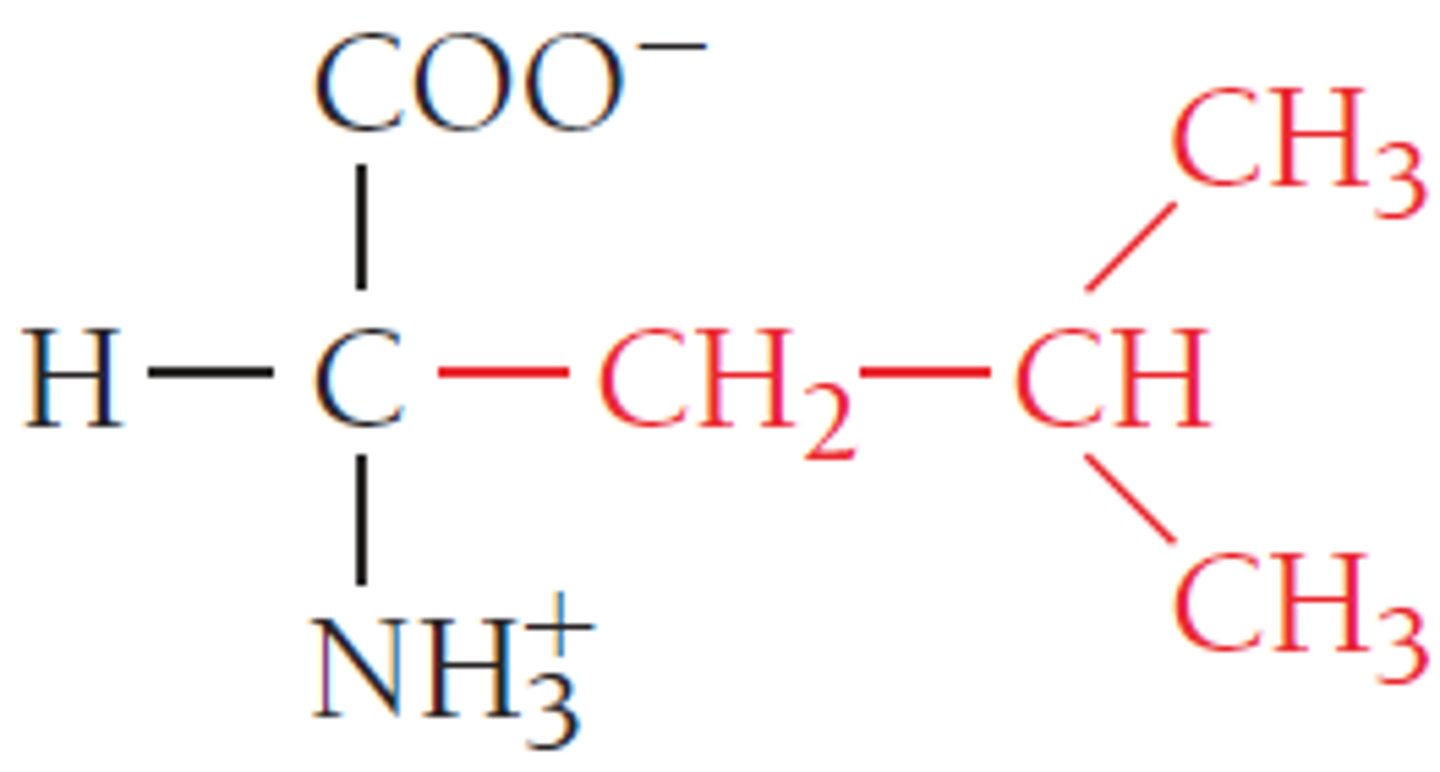
valine
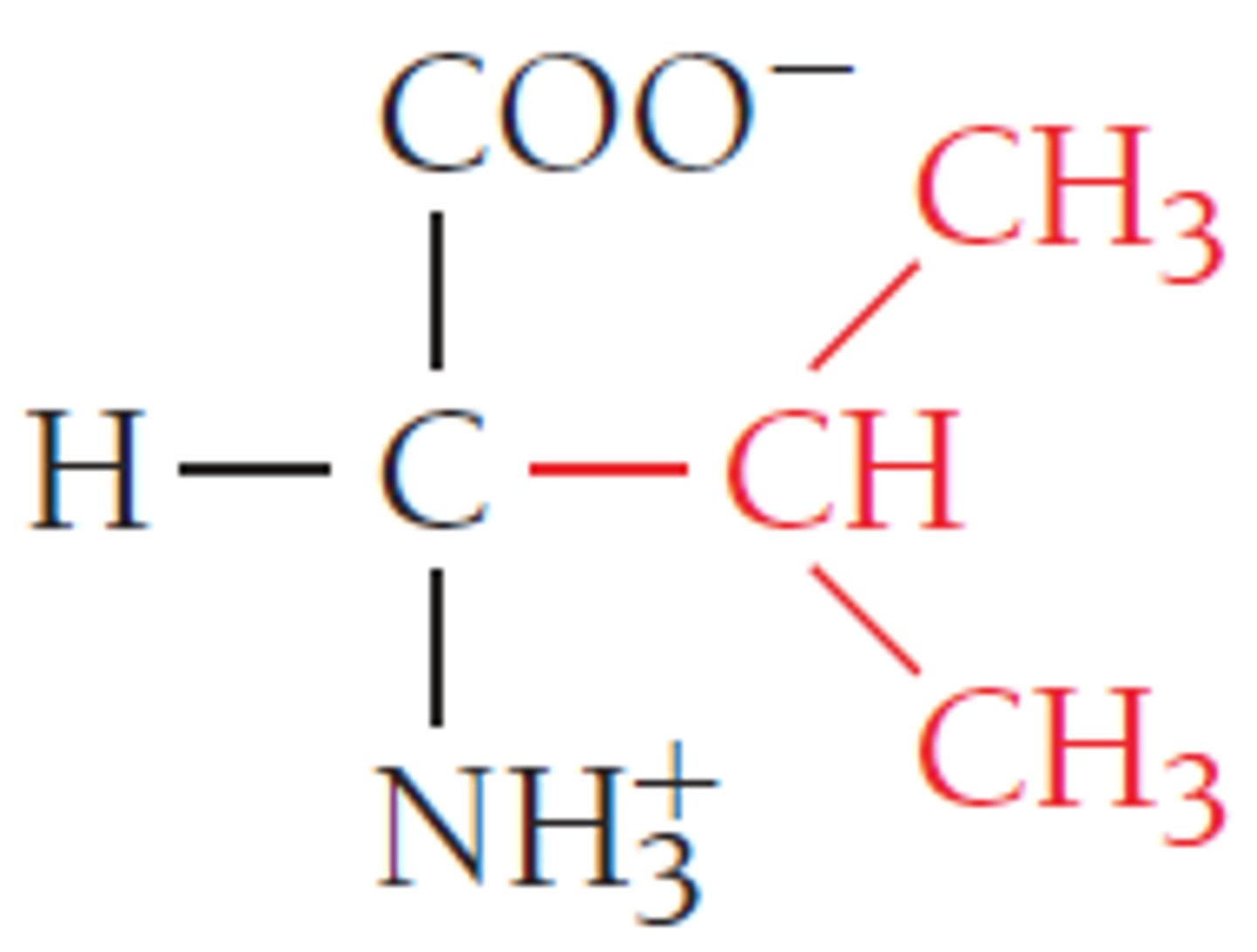
glutamine
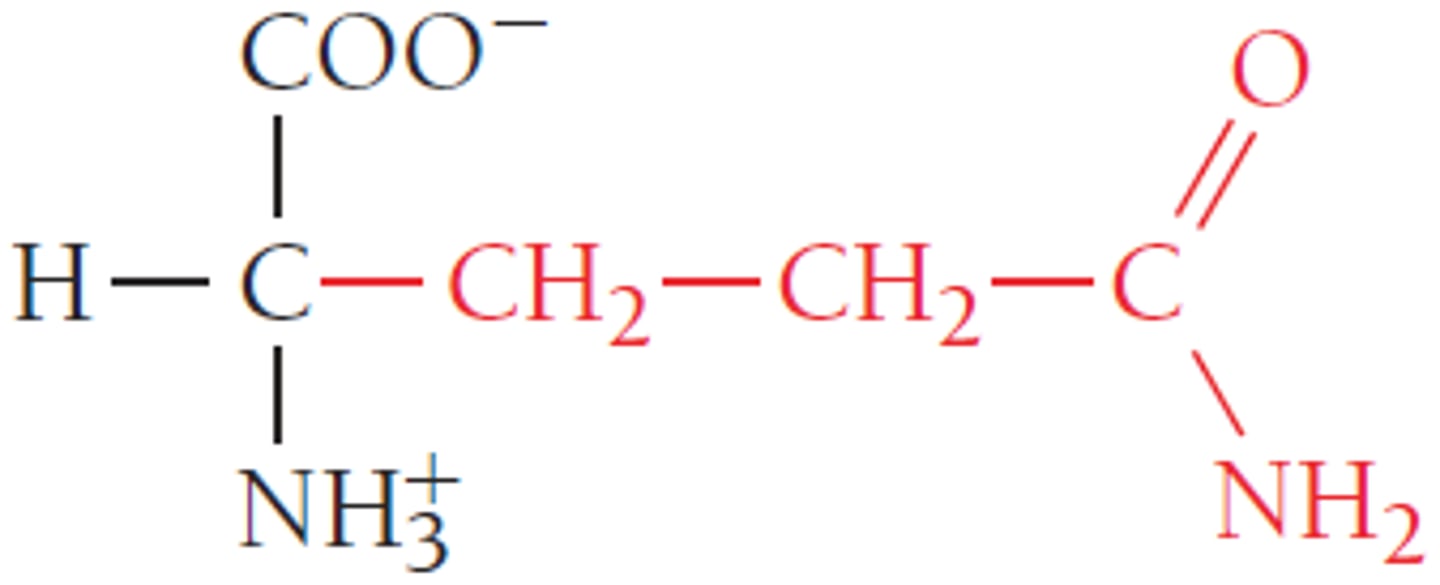
aspartic acid
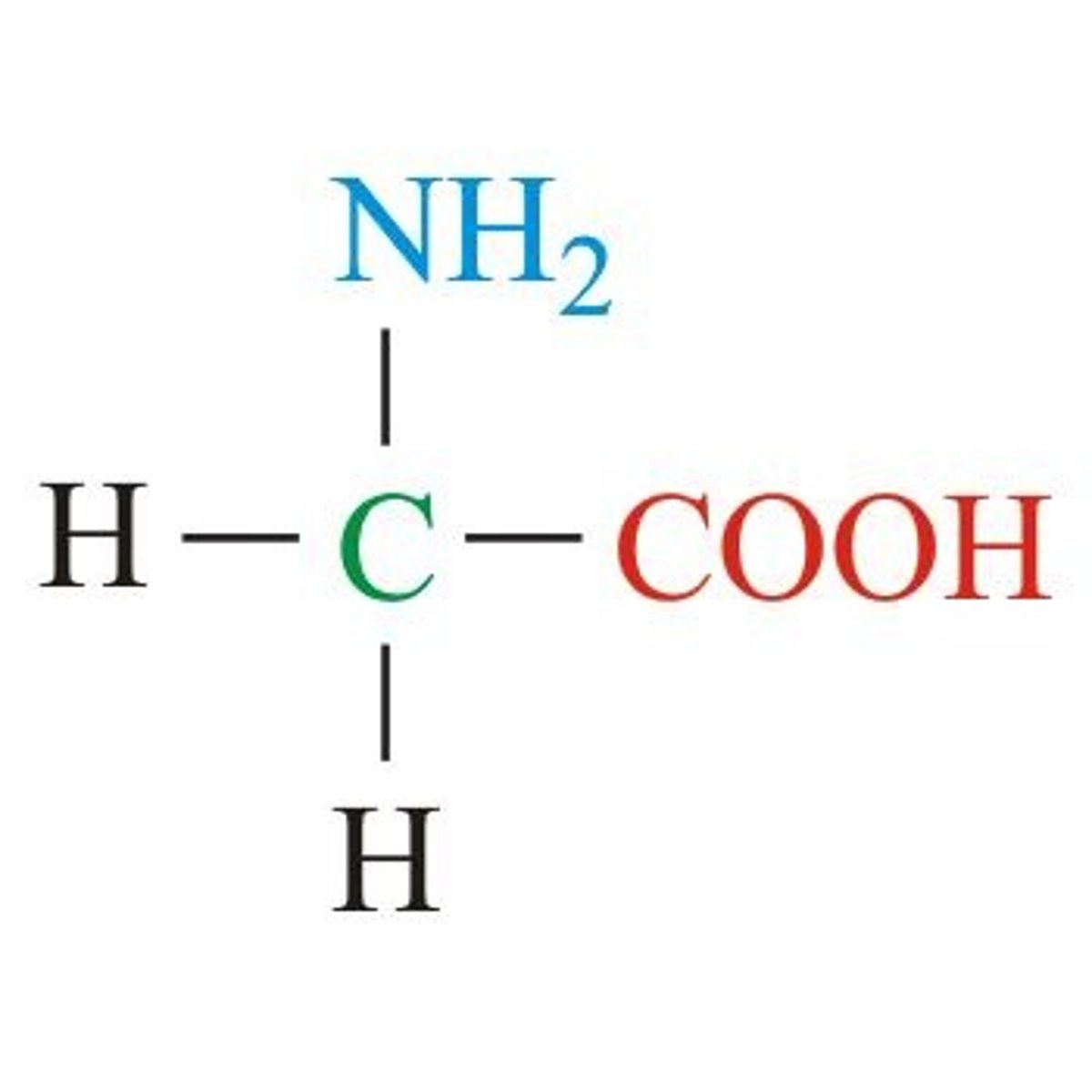
glycine
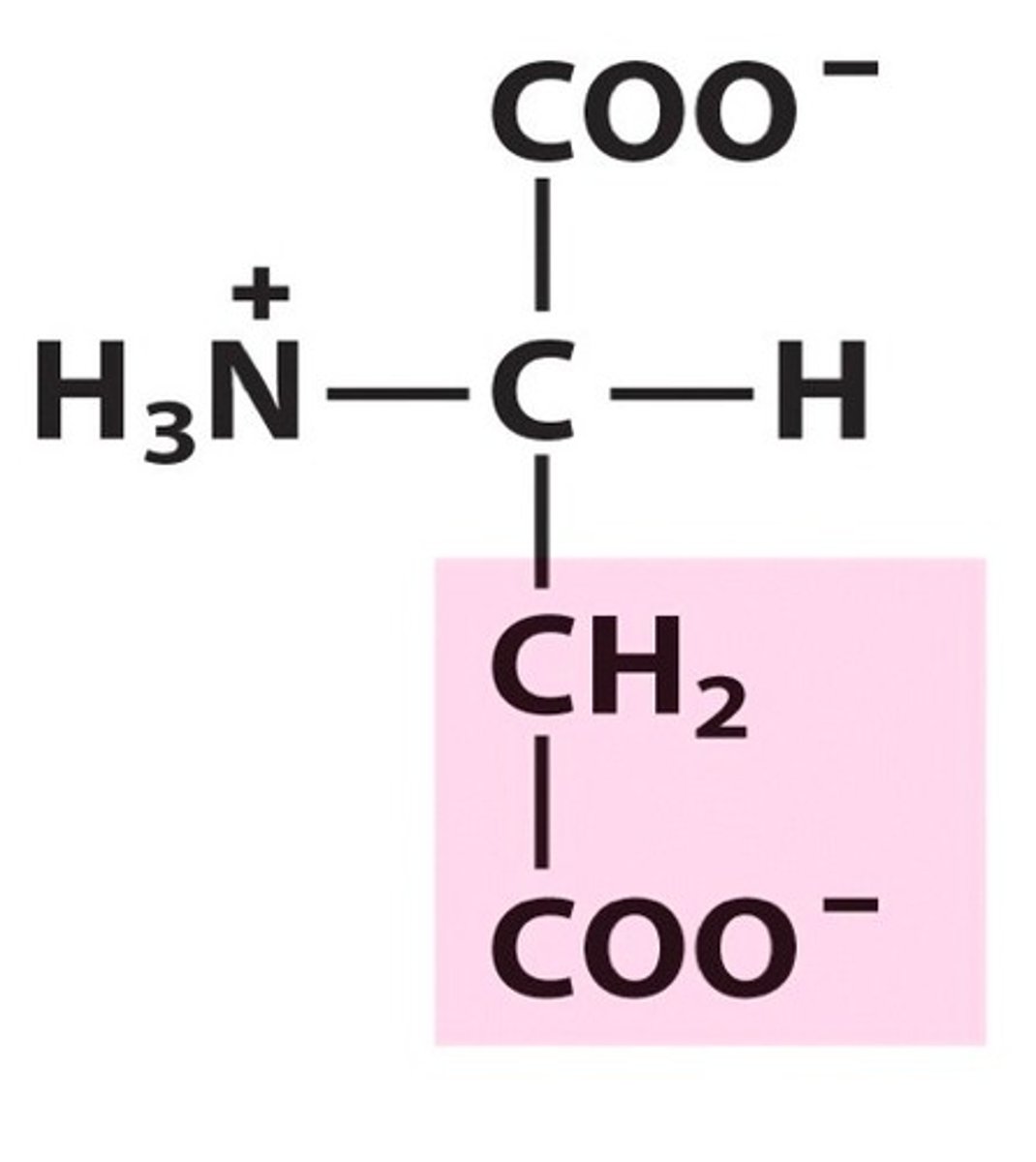
glutamic acid

isoleucine
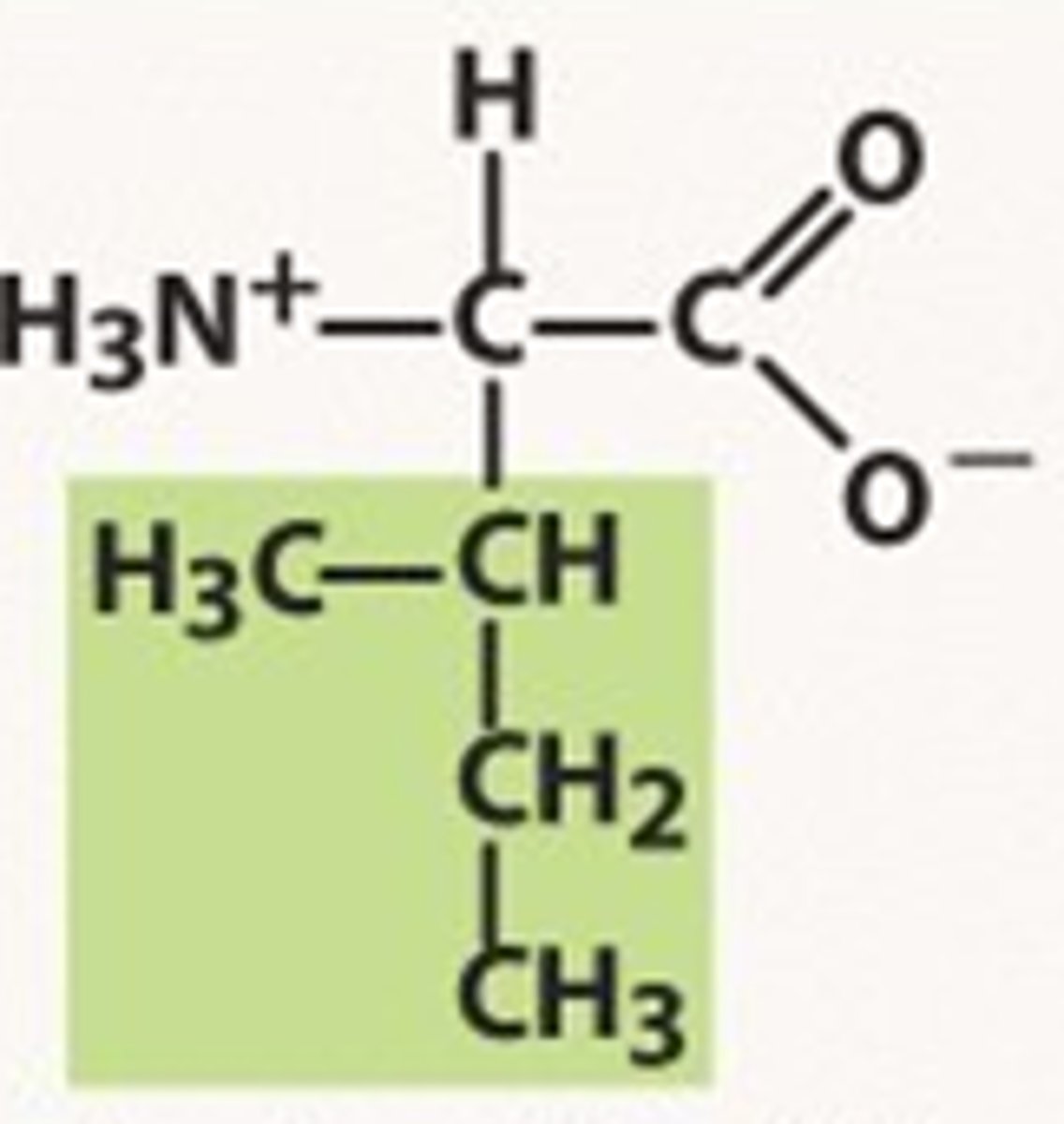
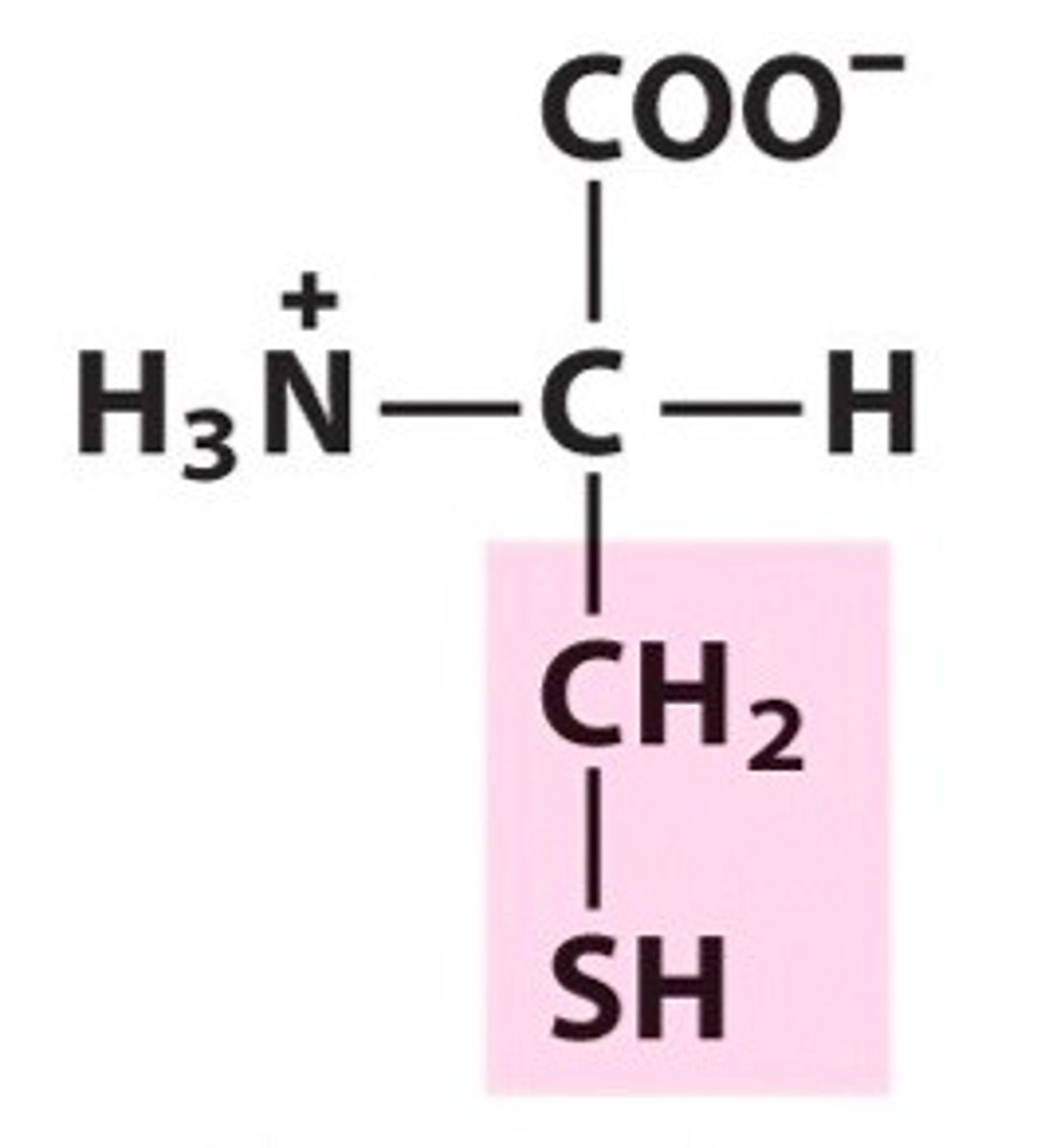
cystine
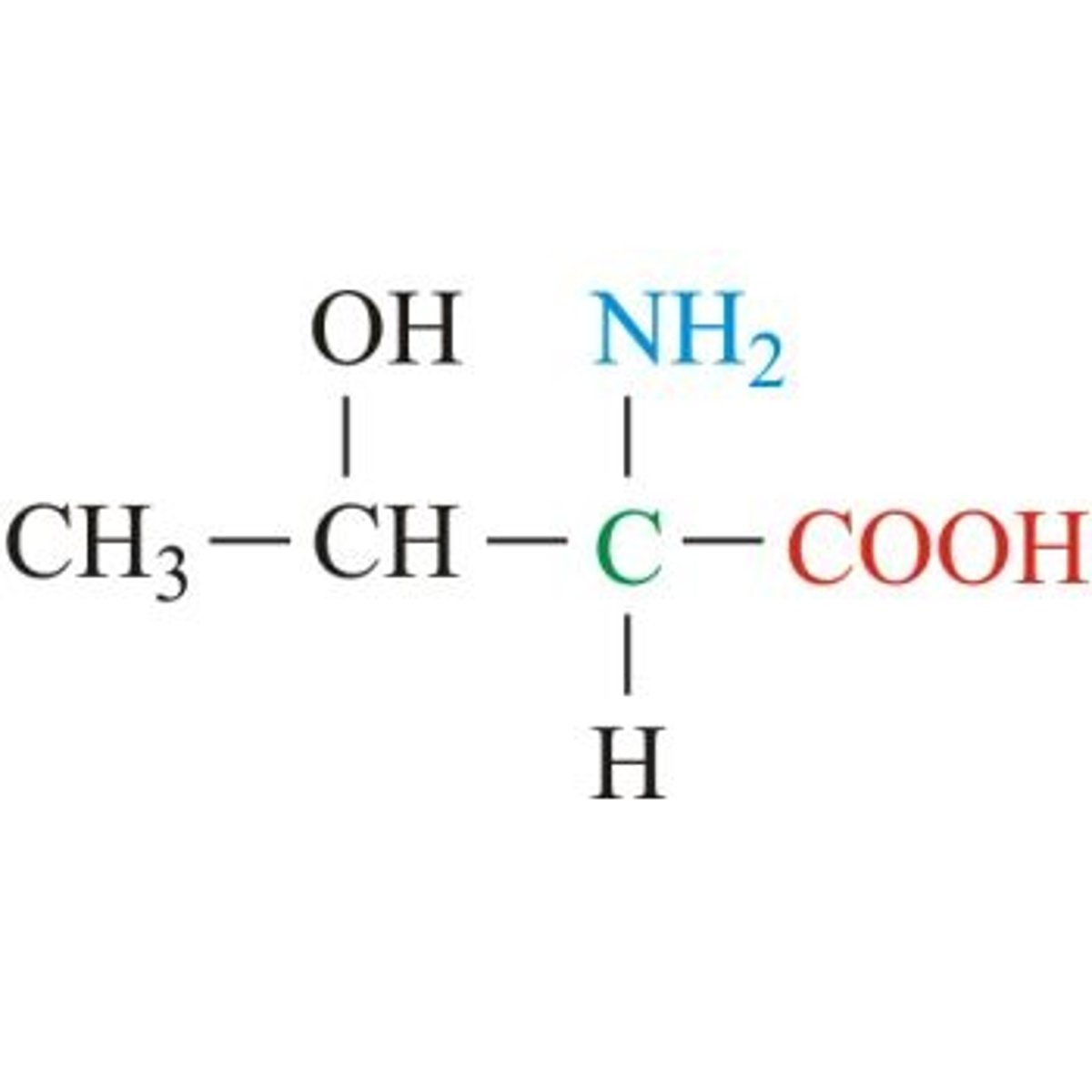
threonine
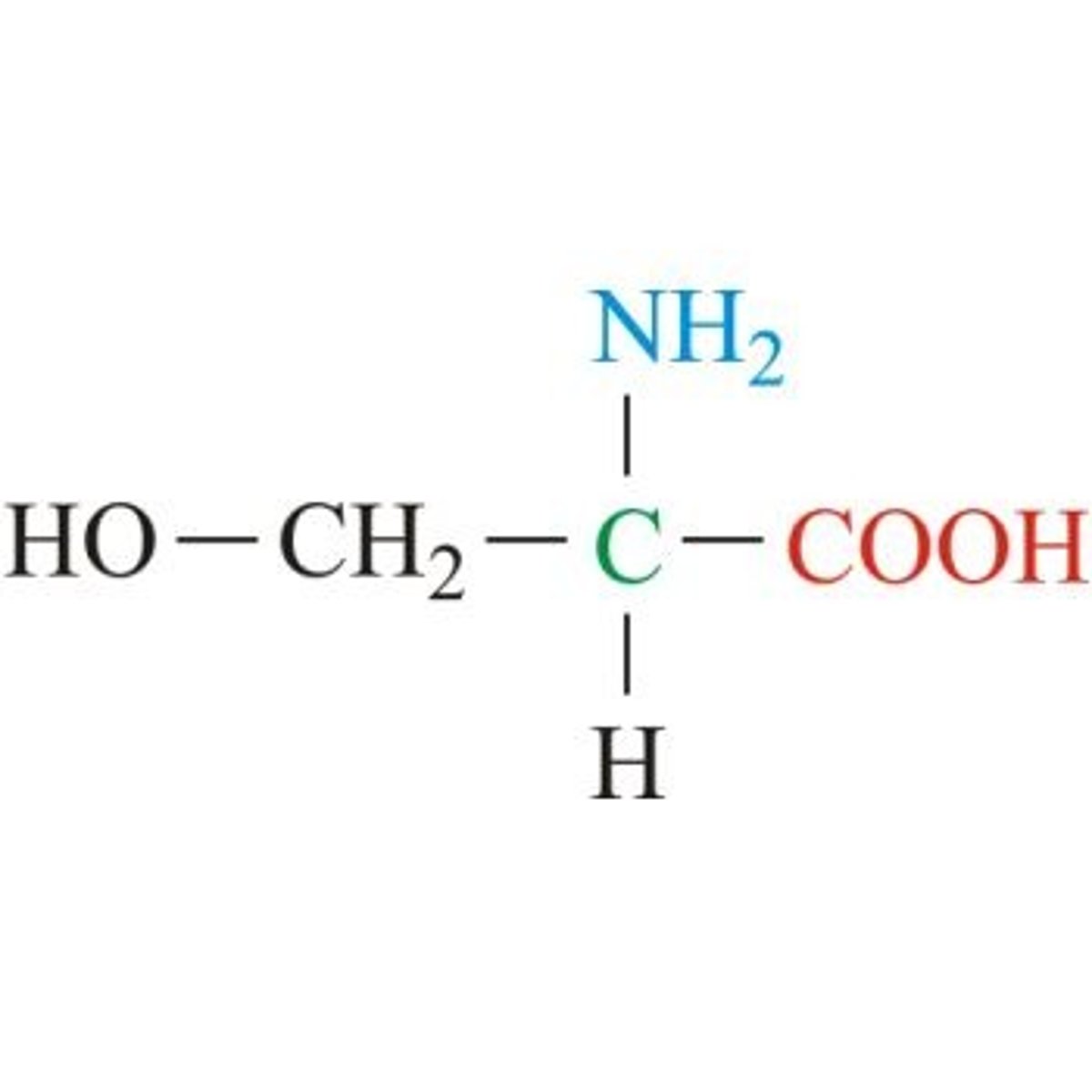
serine
arginine
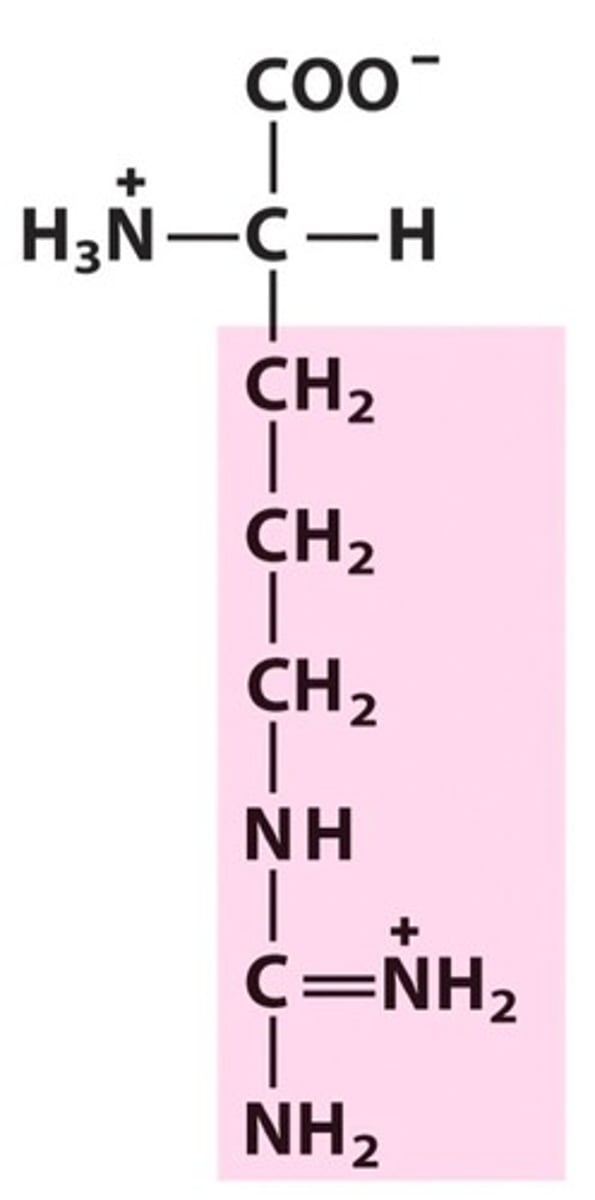
lysine
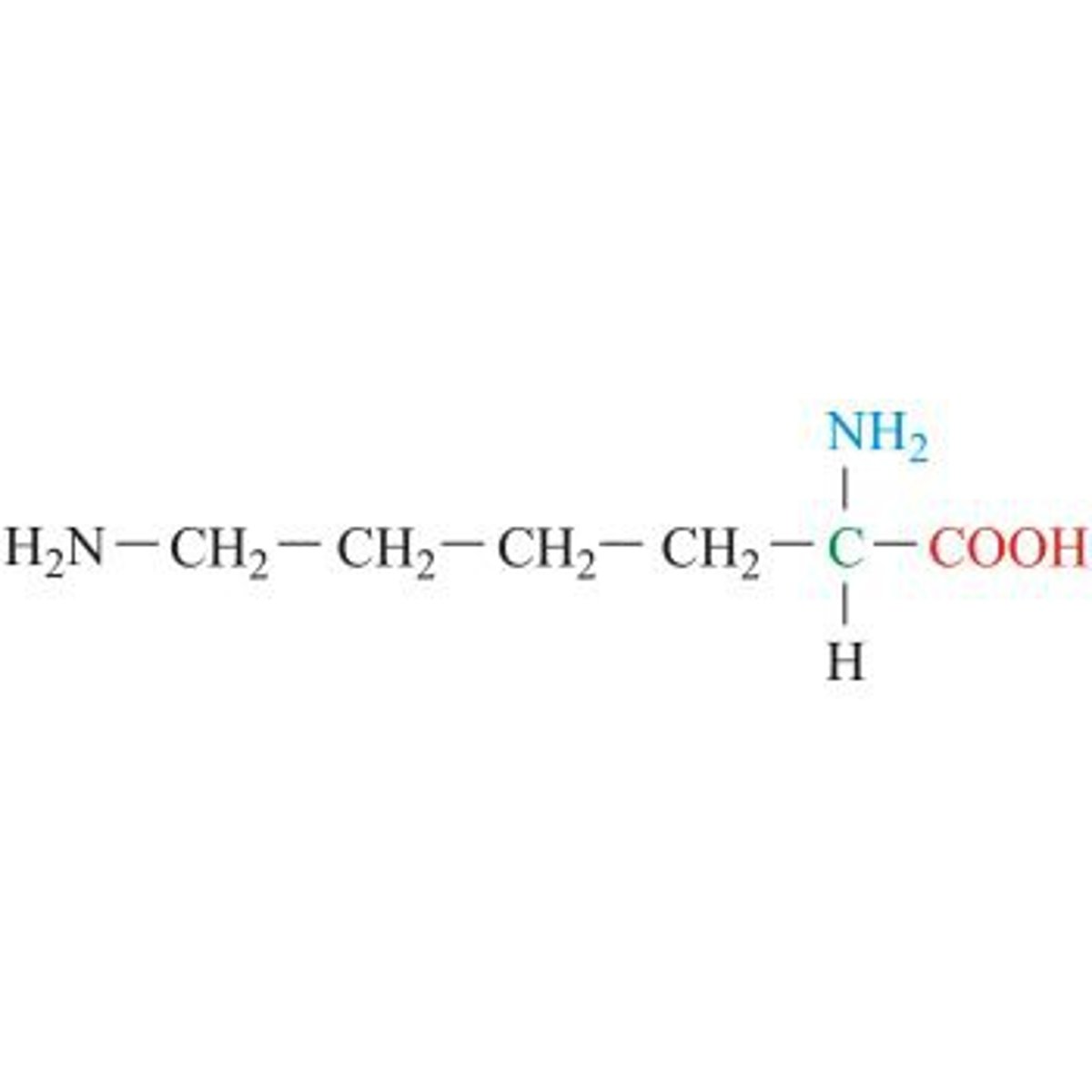
asparaginine
