FINAL EXAM - Renaissance - Modern Art History
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Neo Classism - Post Impressionism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
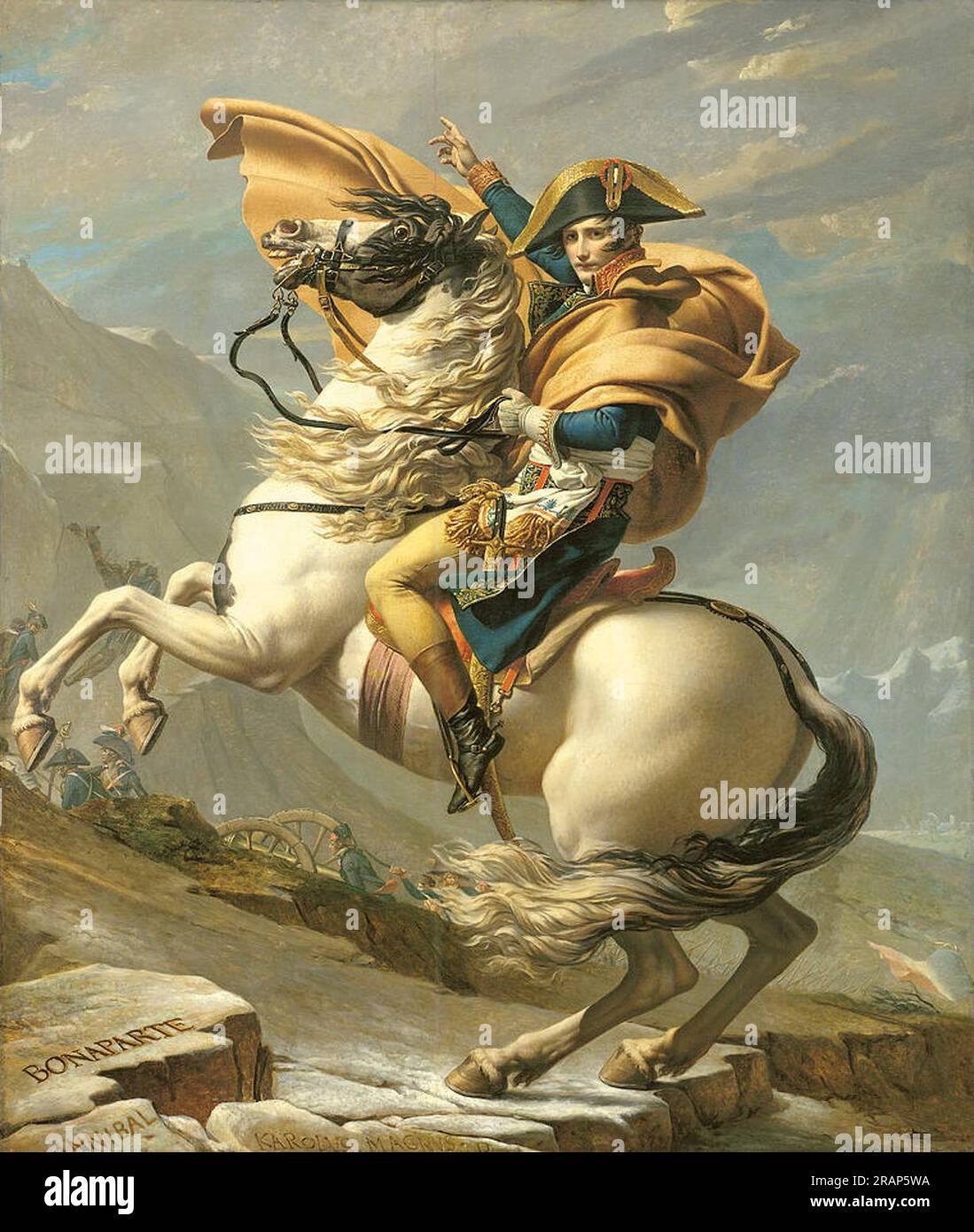

David, Napoleon Crossing St. Bernard’s Pass
Neo-Classicism
David is hired by Napoleon to make several portraits of Napoleon.
Grand dramatic lighting shining upon him
Vivid red cloak that pops out and swirls around him
puts his name in the rock.
Grand Gesture, “Onward, we go.”
Napoleon’s cloak adds in more sizeto him, horse looks small
Napoleon complex, short man complex
the reality, Napoleon crossed this mountain on a clear sunny day on a donkey.
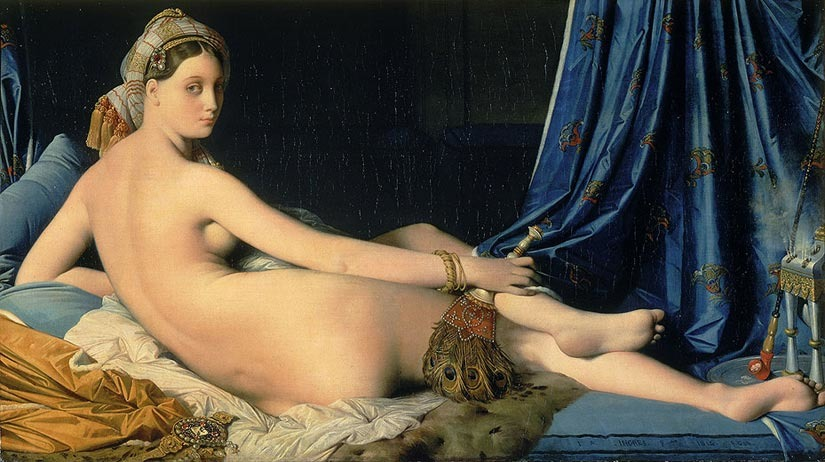
Ingres, Grand Odalisque
Neo-classicism
controversial: wealthy people do NOT want to see that
sex-slave in a harem
turned away to tempt the viewer, pulling the curtain to cover herself
average Turkish/Middle Eastern woman but depicted as a more European for his wealthy European audience.
wanted to emulate Raphael
borrowing a little from mannerism
very long back
inaccurate portrayal
strongest example of orientalism
popular at the time to be interested in exotic cultures
She is seen as an exotic creature from a foreign land.
peacock feathers, turban, jewelry, hooker
hard to read face, often believed the audienece is viewing her as a captive animal in a zoo.
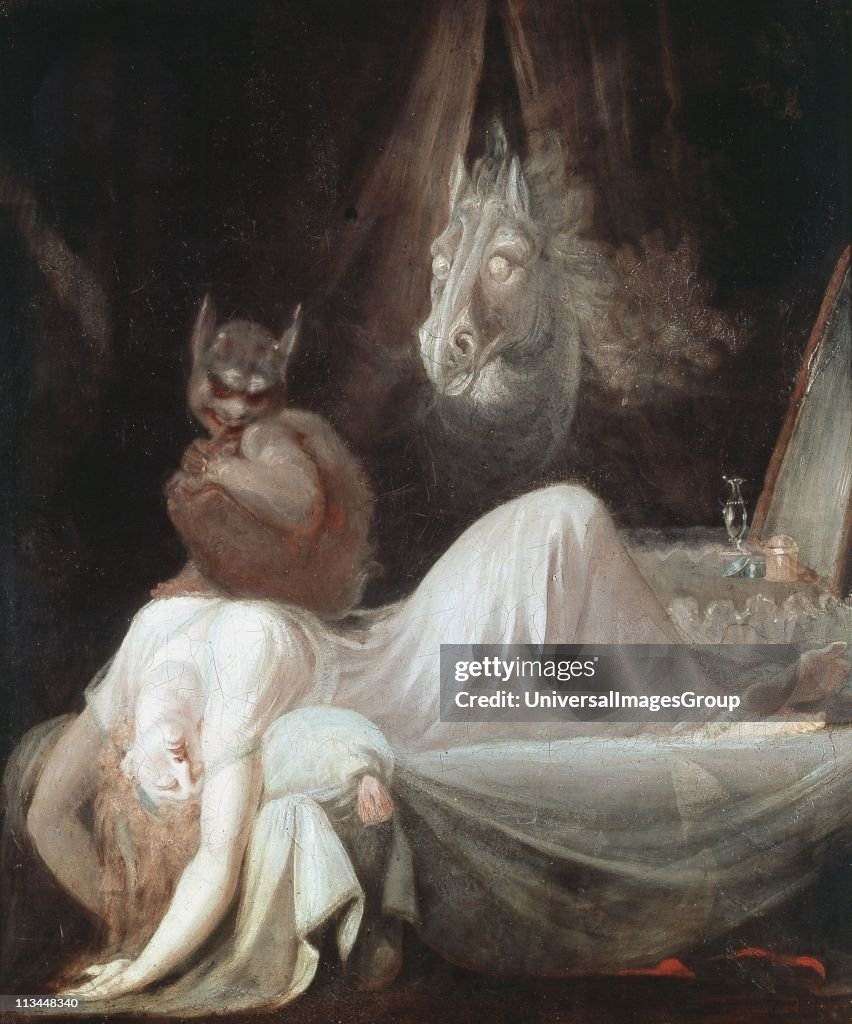

Fuseli, The Nightmare
Romanticism
when you sleep, the rational thinking side of your brain subsides and your other side roams free.
ideas of what’s lurking when your rational side goes to sleep.
The horse is an incubus that got rejected by a beautiful woman and has sex with sleeping women and various other acts.
Exploring what happens when someone is not rational.
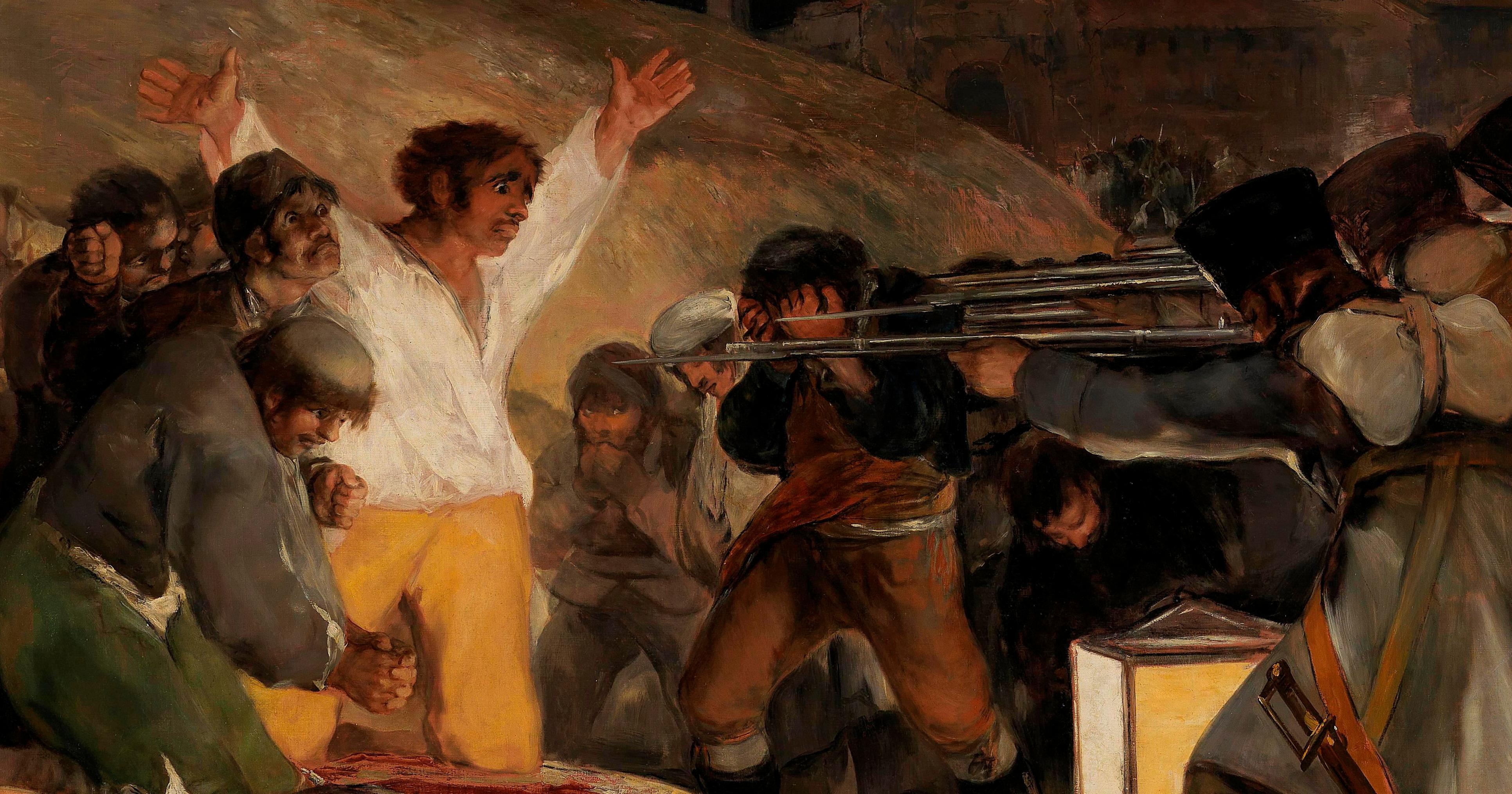

Goya, The Third of May 1808
Romanticism
most famous romanticism painting
based on an actual event, when Napoleon is trying to invade and attack Spain. Tried to capture and murder the Spanish Royal family in Madrid.
Huge uprising of Spainards citizens trying to stop them.
On the 3rd of May, those who were arrested by Napoleon’s troops were ordered to be rounded up and shot.
Evils, what one man can possibly do to another.
Doesn’t have crisp or clear definition of the details.
Loose brushstrokes ex.) white shirt and Hill
Like “the Jolly Toper” by Hals
very dark painting like Rembrandt
back to more expressive, emotional faces
some Spainards are hiding their faces, afraid of what is going to happen to them.
Doesn’t give us the crisp look at it like Gentileschi; as it was a scene of revenge
Central figure is Christ-like, typically the brightest figure, Christ-like sacrifice
soldiers are painted together as a blob as if they are one solid piece. No faces depicted purposefully
Goya was accused of heresy of the Spanish Inquisition, lost faith and moved to France and stopped making art.
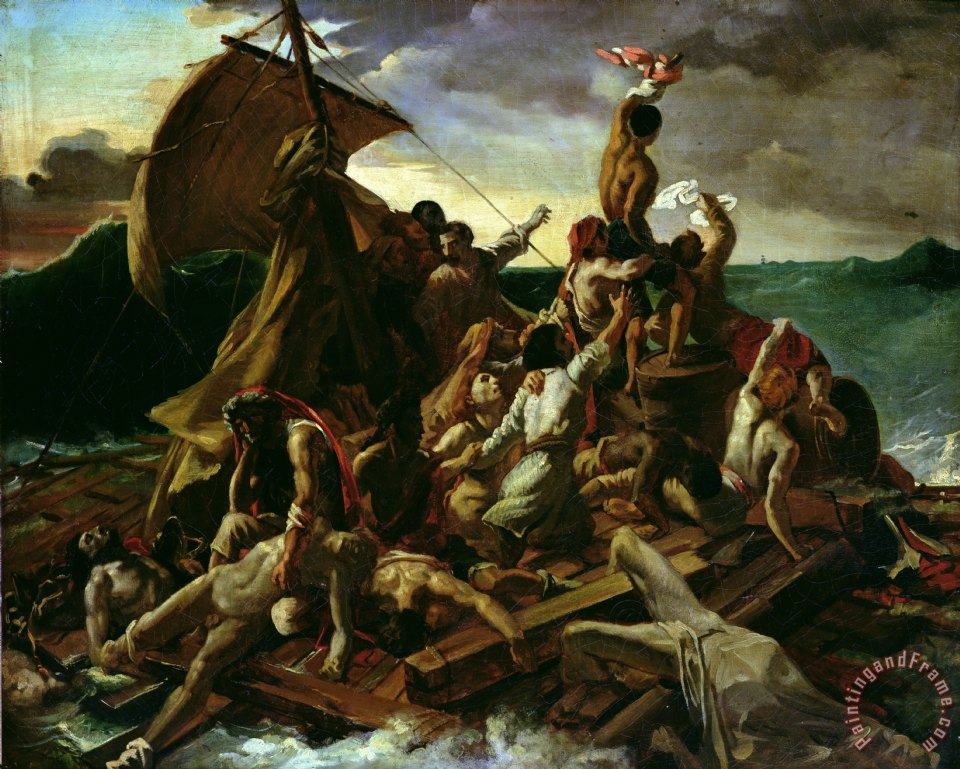

Gericault, Raft of the Medusa
Romanticism
16ft x 23ft
life-sized figures
reminiscent of mannerism, twisted positions
unsettled, lots of movement, in turmoil, uncomfortable
perfected Greek and Roman bodies
based on a real event, there was a government ship from France, hit bad weather and had a shipwreck. Govt. officials and wealthy were the only ones saved. The rest were out there for at least 2 weeks. When rescue came to save the little amount of people who survived.
disturbing
very political, but still art aimed for the rich
legends of mutiny and cannibalism
possibility of the dark things that lurk in our minds and what one man can do to another.
Violent portrayal of the sea, violence of nature is one level and then the level of human violence on the ship
Very dramatic like baroque
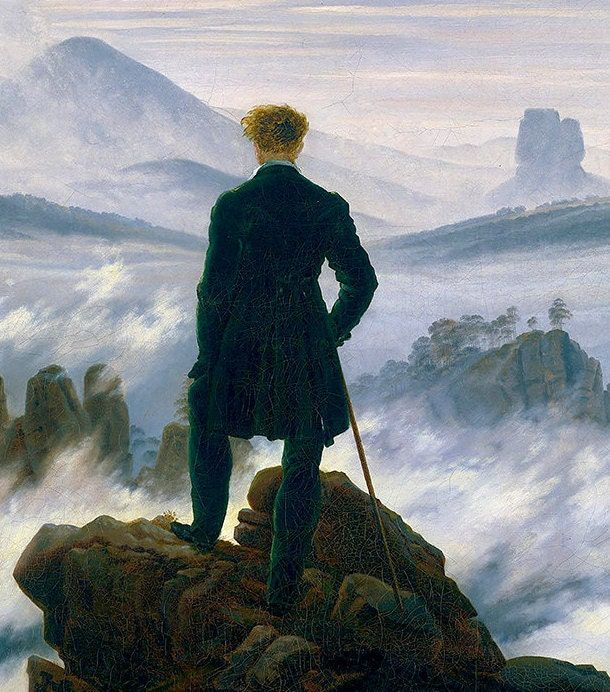

Freidrich, Wanderer Above a Sea of Mist
Romanticism
another well-known ex. of romanticism
Man deep in nature, looking over a mountain-scape or shores
Sublime: refers to the awe or beauty of nature. OR awed by the possible power and/or danger of the nature arond you.
could be inspired by the beauty or dangers of power of nature, could slip and fall

Courbet, The Stone Breakers
Realism
stone breakers made the gravel for roads and railroads
Avant garde: military term “front guard” in French. Considered to be radical and new, often politically engaged as well and first associated w/realism
pushing boundaries
sledgehammers and only a tuff of hay to rest his knee. Everyday breaking big rocks into smaller rocks
This job considered one of the lowest of the low
Courbet purposefully chose this profession to portray
the painting was deemed as repulsive by viewers and critics
The clothing was shabby, the old man was wearing what seems to be his best clothes at some point, vest specifically. Old fashioned pants and shoes. The younger man has tattered but contemporary clothing.
Artists made the paintings in hopes that the wealthy would buy it, yet Courbet chose the lowest of the low
Not planned or displayed poses, real scene in their lives and not crisply rendered
limited color palette, very brown
looks unfished and unskilled
purposefully doesn’t portray their faces, as that is what the wealthy views them, unimportant but common people paving the way for their luxuries.
If the wealthy saw a stonebreaker, they would’ve viewed them as anonymous unseen workers
un-thanked and unthought of, force the wealthy to see them. Roads aren’t magically made.
the roads and modernizing of the city is on the backs of people like this.
Shows both a younger and older man to show the trap or circle of the poor, the old man used to be the younger man at some point and vice-versa, working until you die or get sick.
Often critiqued on being very confrontational, no foreground
Purposefully using techniques that the Art Academy doesn’t like, limited color palette, loose brushstrokes, dark blob background, very flat, using space badly.
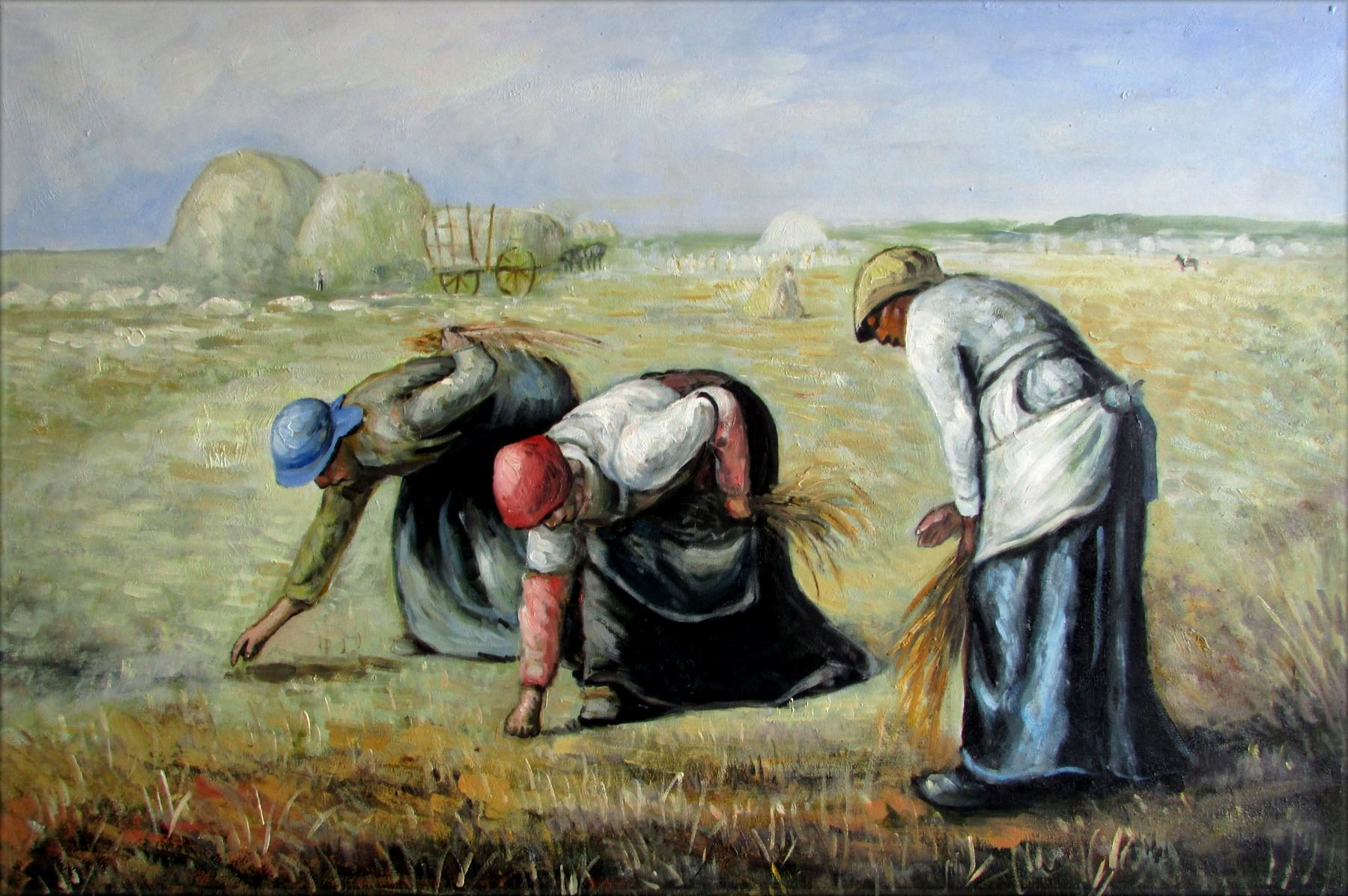

Millet, The Gleaners
Realism
after the main crop is harvested, the Gleaners come through picking up even the grains of wheat, whatever is left behind.
lowest of the low agricultural job
some usage of space, more of a foreground compared to other Realism paintings
Millet’s paintings are more hopeful depictions of the lower class. Showing more dignity as they are depicted less harshly.
Unseen faces, to show how the wealthy view the lowest class, cannot emotionally connect w/them. just viewed as workers.

Degas, Place De La Concorde
realism
new social type of person, Flaneur - to stroll in French, someone strolling around the city, way they experience life, slowly like a stroll.
Flaneurs were typically wealthy men, well-dressed and well-mannered but detached observer of city life, check it all out at a leisurely pace.
At this time it is popular to have exotic pets, likes monkeys and turtles, flaneurs are sometimes described as if they were walking their pet turtle.
There is a flaneur on the far left, barely in the painting, has a walking stick, gloves, ascot, etc.
The family and the dog depict mental vacancy, none of them are looking at the same place, have a glazed overlook.
Background: lack of details, loose brushstrokes, flattens the space.
no true foreground, figures are in our space, confrontationally close to us.
no focal point, nothing in the center, figures are on the side.
gets the audience into the sense of mental vacancy, as we are simply another person in the street not looking at anything.
unfinished, looks like a sketch, goes against the Art Academy, especially the coats, very smooth.

Manet, Luncheon on the Grass
Impressionism
Immoral, indecent
2 women are seen as prostitutes
prostitutes, lowest of the low being shown in art
hints at other well-known paintings Giorgione and Renaissance’s Best painters, critics believes he was too bold to even think about inserting himself into the same level as them.
Piles of clothes in the foreground, implies that the women were wearing clothes as well.
The look of the women’s face, not ashamed of her nudity and boldly looks at the viewers, “I’m nude, so what?”
Not a perfect goddess body, regular women’s body, not crisply rendered.
weird scale, does not go together, not a good perspective.
2nd lady in the background, too close to fore-figures and too large compared to the water.
2nd lady is also too crisp compared to the background
unfinished and unskilled
Manet was thrilled w/ the scuttlebutt, but was hurt that the critics didn’t understand how he did all those techniques on purpose.
The pants of the man on the right, very unfinished, black brush strokes for the folds.
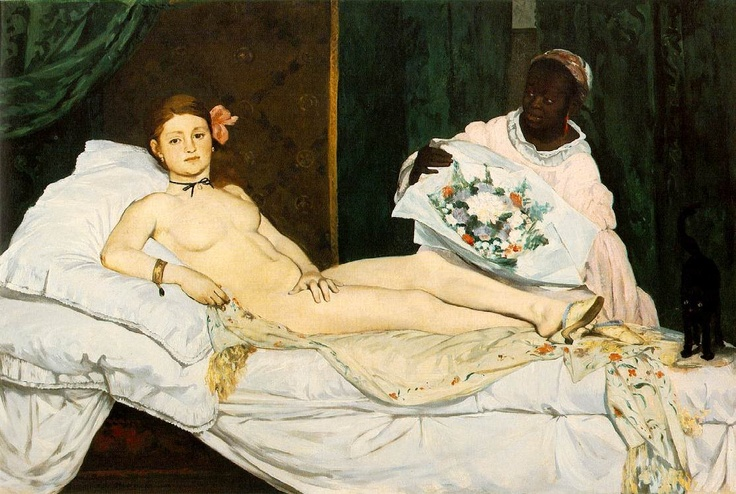

Manet, Olympia
Realism
prostitute at work, lowest of the low shown to us at work.
“Olympia” super popular novel, character that’s a prostitute.
accepted into a salon, a little less sketchy, but very controversial
borrowing from Titian Venus of Urbino & Ingres Grande Odalisque
not a goddess, not a nymph
nude w/ jewelry, flower, and shoes, more nude than without.
awkward position, short proportions
black cat, fading into the background, cats represent sexuality.
Bouquet from a client, represents sexuality, fertility
confrontational positioning of characters, very in our face
very flattened painting, especially the background
body not idealized enough, hypocritical, don’t like how she’s nude, but if she is going to be nude, must be depicted like a goddess.
puts us, the audience, as the next client, her face has a bit of seduction but mainly like “next,”
clothes woman of color, depicted as her servant more below her. Manet could’ve intentionally depicted the social hierarchy in Paris.
Courbet said that the painting was like the Queen of Spades is getting out of the bath, very good.
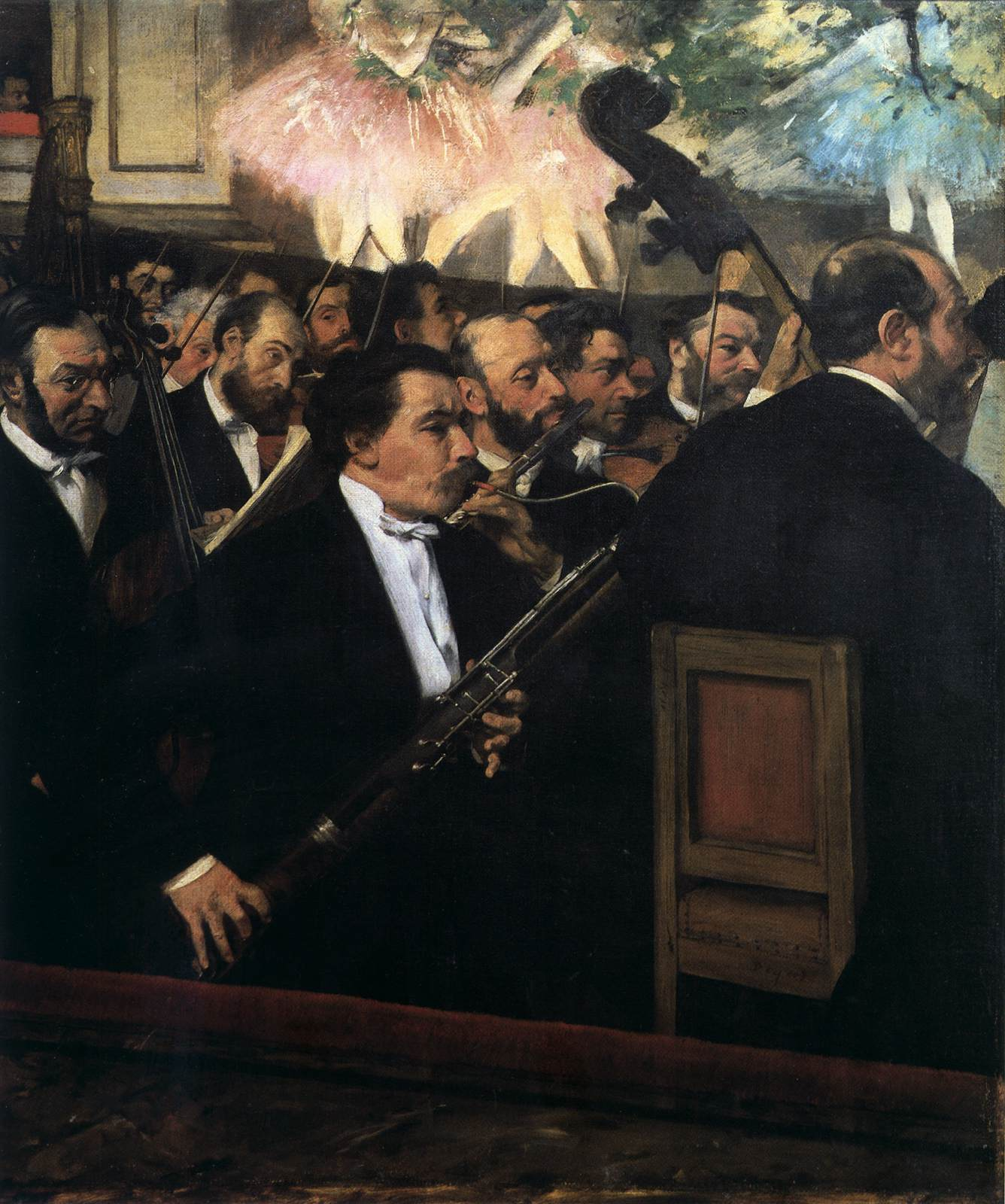

Degas, Orchestra of the Paris Opera
Realism
The musicians of the Orchestra aren’t shown much attention, unlike the ballerinas, dancers, etc.
Blob of tuxedos, very crowded, not one focal point
depicted tiredness

Caillebotte, Paris Street: Rainy Day
Realism
life sized fore-figures
photography starts being more readily available
W/rising popularity w/photography, artists were worried about their jobs, so they started making paintings like photographs
No focal point or focus, no poses, mainly walking like a snapshot, no one looking in the same direction
Cobblestones painted like actual wet cobblestones, shadows being depicted
Very wet scene

Monet, Impression Sunrise
Impressionism
entire movement of impressionism started from this painting
his version of a sunrise. general idea
laborers working even before the sun rose. Industry is happening even in this hour of the day.
limited color palette, tended to use paint straight from the tube
very visible loose brushstrokes

Renoir, The Boating Party
Impressionism
Start to see places w/a mixing of social classes (in Paris)
2 men in tank tops and straw-hats w/ well-dressed ladies and a flaneur
2 men w/ straw-hats are the people running the boat
white on white, glass, “hard to paint” subjects
the background is full of brushstrokes, made the painting off the rails. “Ruins” the painting according to critics.
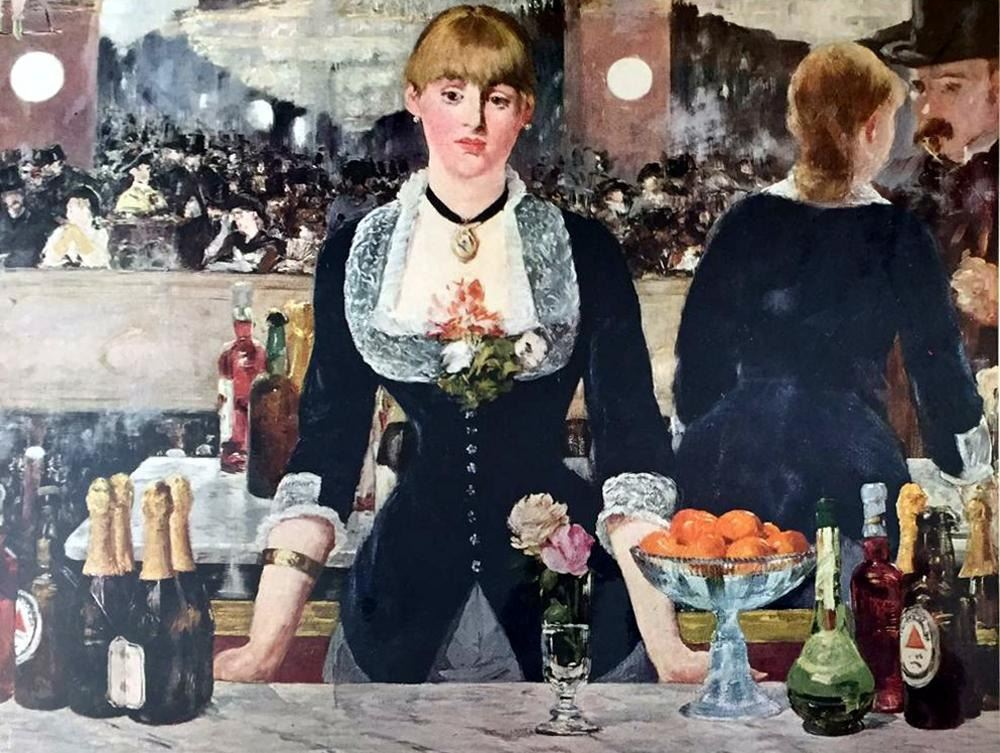
Manet, The Bar at the Follies-Bergere
Impressionism
Manet is dying, at the end of his life while painting this, bc of syphilis
most deaths at the time were either due to syphilis or tubercolocis,
his final work, to go off with a big bang
a debate about whether the waitress is behind a bar or there’s a mirror behind her.
mental vacancy, glazed over look of boredom at work
most audience of the day know that bar maidens with a flower on her chest indicate a prostitute
Flaneur client, is us, the next man
mirror or no mirror, Manet wants us to think it through
all modern life in the city is not great or ideal, mental vacancy
One of many in the bustling city life
trapeze in the left upper corner.
darker side to modernism

Seurat, Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jette
Post-Impressionism
brand-new thing to give people Sundays off
people on their day off, near water, beautiful scenery
mixing of social classes, pet monkey w/ a wealthy lady
man w/ a cap and tank top, near wealthy lady and a flaneur
Seurat studied a lot about the eye, the optics of the eyes, and how they perceive, specifically color and color theory + other color studies.
the eye can mis colors together better than physically mixing colors
entire painting made up of dots, pointillism
puts a very light wash of one color, short strokes of other solid colors like shadows, then covers it in dots
8ft x 10 ft
sense of mental vacancy
critics still hate post-impressionism as much as impressionism
not excitingly happy or intimate interactions
wants to show us how modern life has not improves our lives w/ sociability, isolation, or alienation.
critics said that it is “a sea of individual loneliness,” “a landscape of suicides.”

Cezanne, Mount St. Victoire
Post-Impressionism
tended to use palette knives to make brushstrokes, leading to patchiness
starts getting more abstracted, farther from representing an actual valley
doesn’t have political commentary like impressionism
Cezanne also studied a lot about human perception. human brains process paintings in 2 ways. 1: simultaneously, as we take in the painting we see a landscape w/a mountain & a tree. 2: consecutively, first we start at the bottom of the painting and we process a landscape, then a valley, then a mountain, sky, and then suddenly hit branch.
Putting the branch so close to the mountain, flattens the painting as your brain is pushing and pulling w/ the information. Slightly irritating
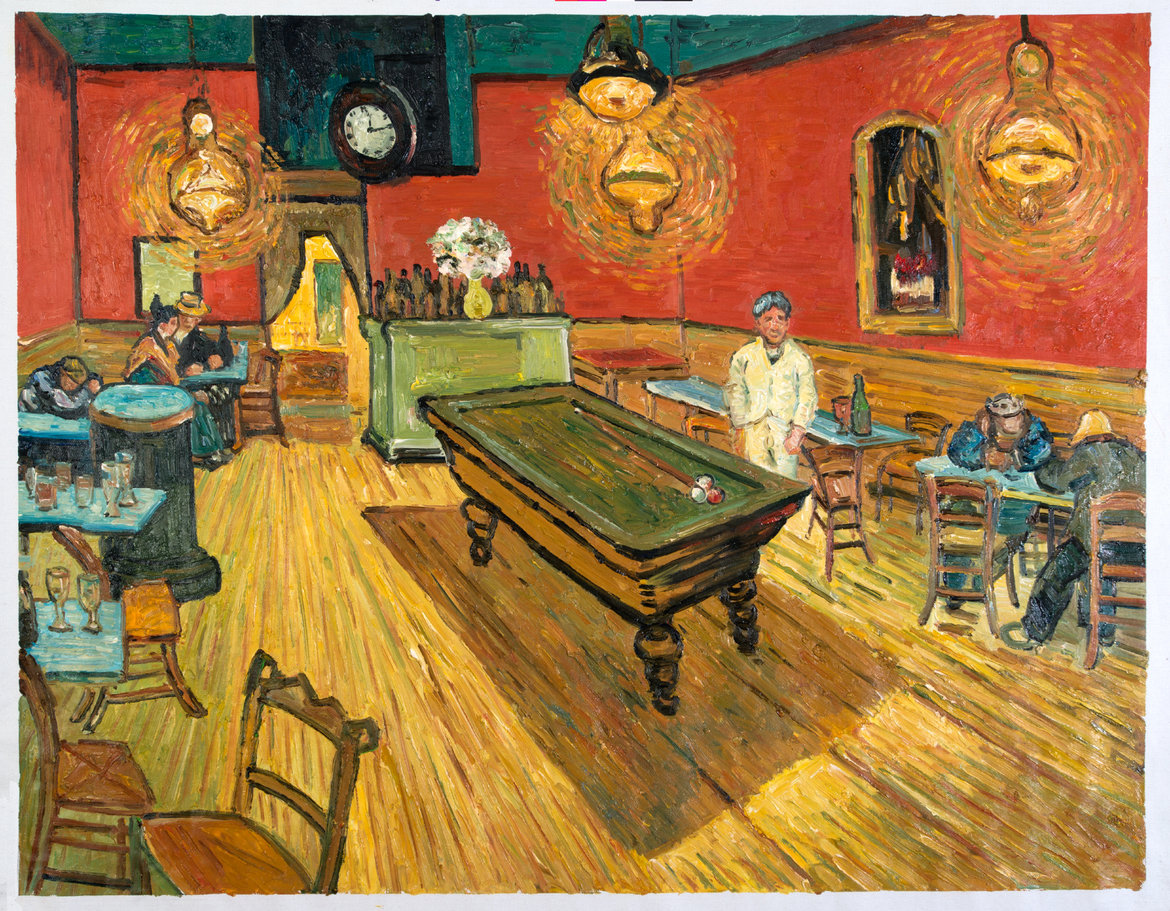

Van Gogh, Night Cafe
Post-Impressionism
Signature brushstroke, described as in motion, or having movement.
uses very thick and heavy application of paint
Van Gogh was a very troubled, sensitive man, suffering from undiagnosed mental conditions and would turn to alcohol like most people suffering at the time
chopped his ear off and also suffered from seizures and medicines for seizures could cause users to see fuzziness to light sources.
cannot 100% prove that he took such medicine, but can also assume that he depicted light as such to show movement
odd angle of the pool table, unsettling vibes, lone men, isolated
night cafes are open all night, for people with nowhere else to go or be
slice of life, interior lives, sense of sadness and melancholy
exaggerated coloration by Van Gogh
remnants of people partying and then leaving to go home.

Van Gogh, Starry Night
Van Gogh often left unpainted canvas showing
Undiagnosed mental illnesses, at the end of his life he was put into a mental asylum in France
One of his last painting of his time, while he was in the asylum
painted it entirely from memory, shown clearly by the town depicted, not a French town. He’s Dutch, but moved to France for his art career.
Dutch style town from his memory
Cypress tree, very common in cemeteries, could be a symbol of death OR a symbol of eternal life.
The whitest and brightest star is believed to be Venus, symbol of love.
beautifully rendered, but unsettling, unstill painting.

Gauguin, Vision After the Sermon
Post-Impressionism
subject matter: their faith is so strong that when they gather to pray they can see Jacob
Borrowed from Mary of Burgundy, praying in her home.
Jacob wrestling w/the Angel, well-known bible story
using unusual colors
blood red grass
painterly technique, very flattened application where you cannot see the brushstrokes.
Dry and Flat applicaiton
very flattened space, no depth, no space
Red isn’t meant to imply blood or war
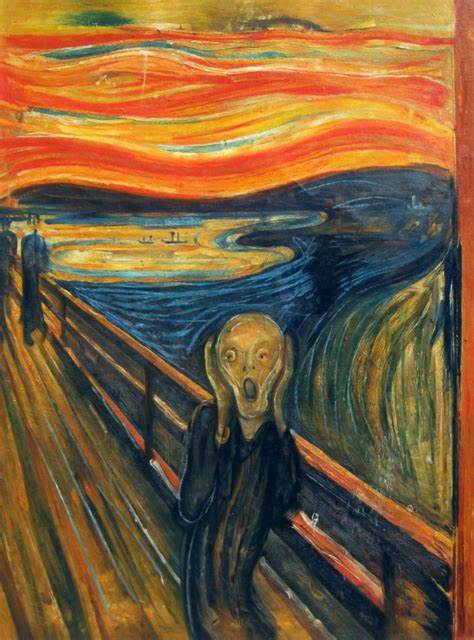

Munch, The Scream
Post Impressionism
subject matter: The internal life of the man
showing us the reality of city life
figure shoved to the bottom of the canvas and traveling/ echoing up
understandable, relatable subject
described that the figure is alien or skull-like
inspiration from Van Gogh, lots of movement in the brushstrokes
odd angle of the bridge, coming right towards us
very particular sky either representative of something
Scientists determined that there was a massive volcanic eruption in Tahiti, and that it was the loudest noise known to man at the time
The ash spread around for months, and changed the color of the sky
Could be an actual representation of the sky
Munch says that he felt a gust of melancholy and the sky turned blood red, as he trembled with anxiety and felt a vast scream
Anxiety brought upon modern life

Klimt, The Kiss
Post-Impressionism
Trying to show us the inner desires of each person rather than the actual kiss
passion and love shown
shiny metallic gold background
known for decorative patches of flowers
man, masculine decorative patches on his cloak
feminine floral patches on the woman’s cloak
critics were a little less harsh, as it doesn’t look as unfinished as others, but very decorative, but still has very bizarre poses.

Matisse, Woman with a Hat
Fauvism
doing something new and interesting with color
liberating and freeing color from rules and restrictions
seen in Gaugain’s painting w/red grass
no perspective at all with the different blotches of paint in the background, weird nowhere space
no details at large
just the color alone is mapping out the painting
portraying his wife
critics were losing their minds, believing that the artists are lost it.
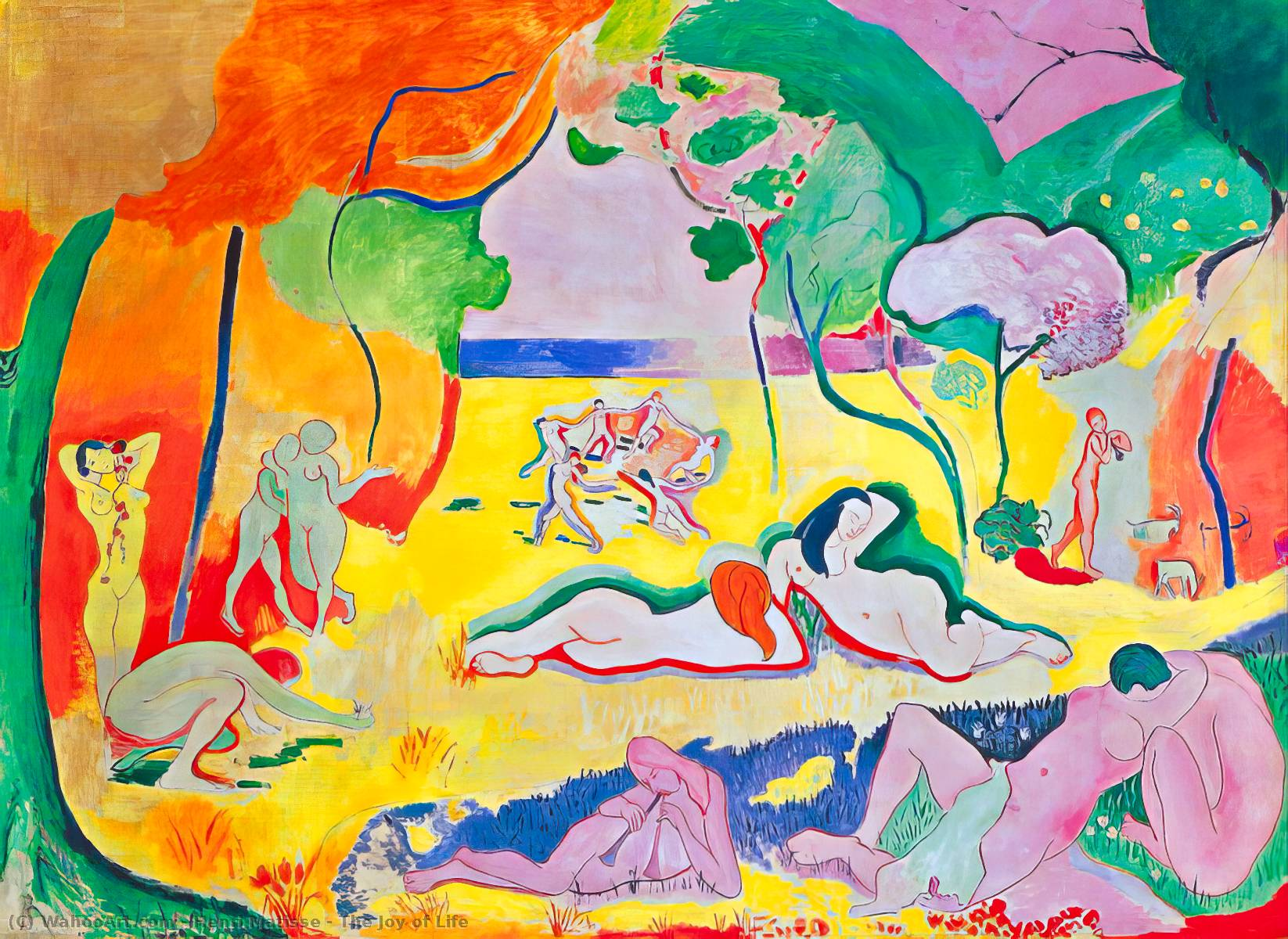

Matisse, The Joy of Life
Fauvism
very simple trees
crazy perspective, figures dancing in the background, doesn’t fit in scale
conflicting scale of figures
very simple outlines of figures
critic says that this represents an orgy of colors and called these artists wild beast, which is “Fauv” in French.
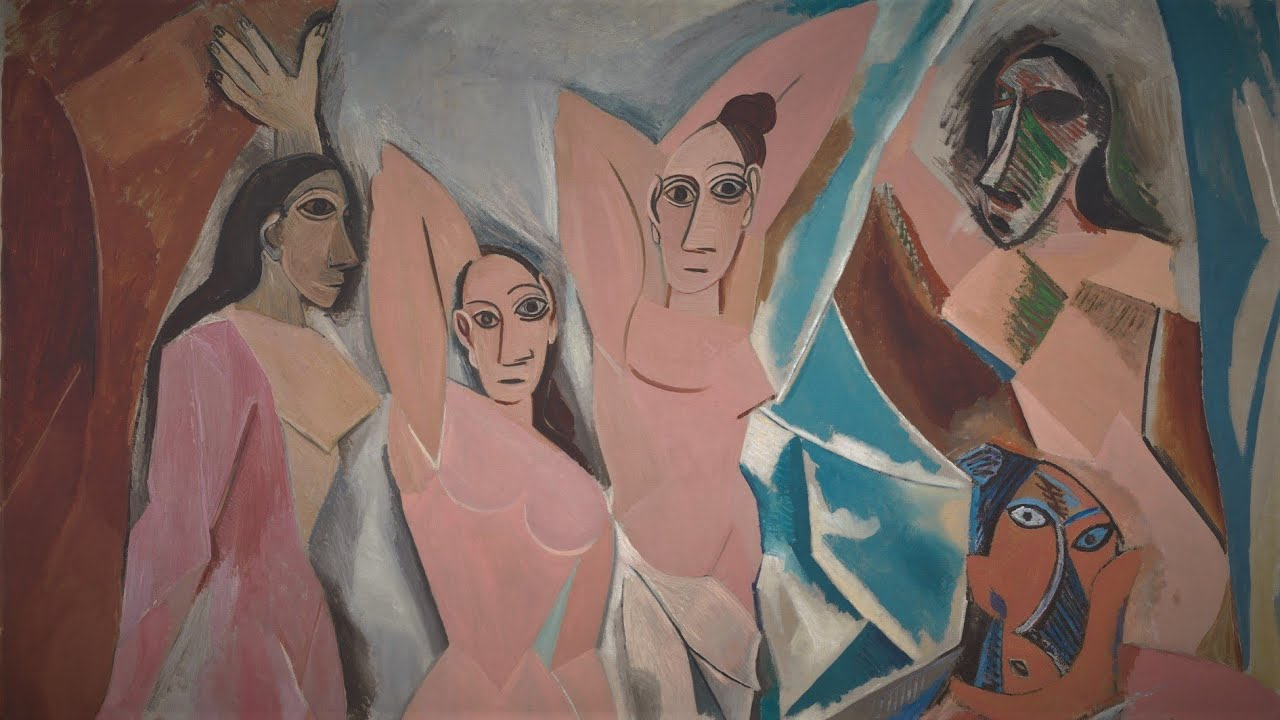
Picasso, Demoiselles D’Avignon
Cubism
D’Avignon Red light district in Barcelona
showing low class workers
showing the same prostitute at 5 different angles
side view, top down viewing (laying down on the bed), other side view, and head spinning around on back view
sneaks in fruit, represents female sexuality, fertility, fruit for sale, women for sale.
Picasso saw a traveling exhibit of African masks, added to these figures possibly.
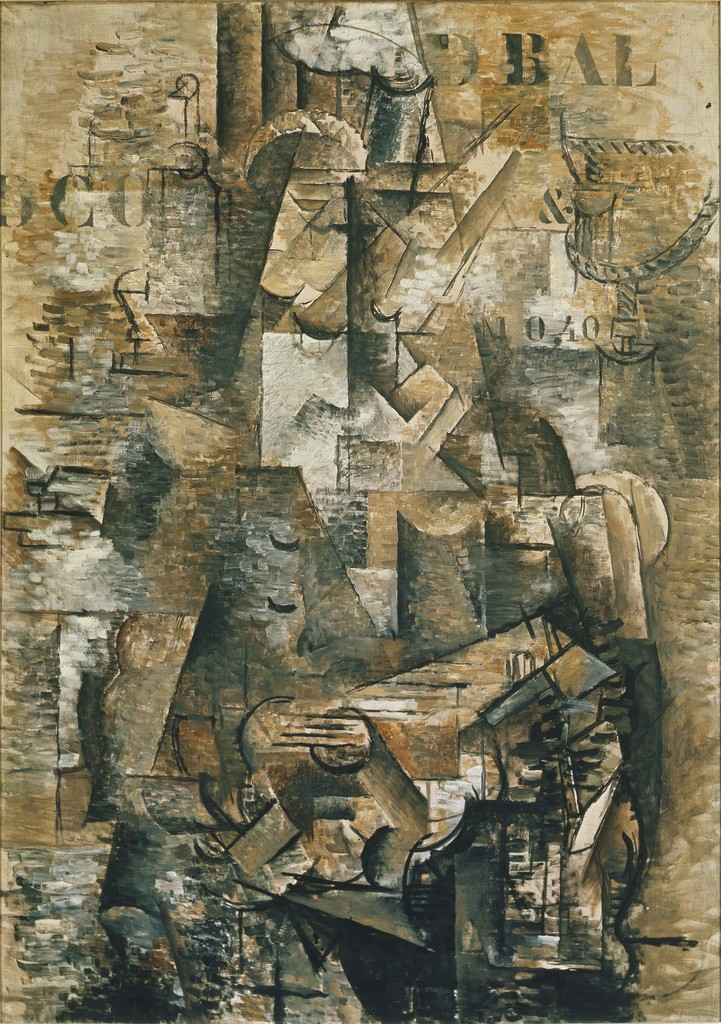

Braque, The Portuguese
Cubism
Analytic Cubism, where the title doesn’t help you decipher the painting
person playing guitar at different angles
critics not happy w/cubism
limited color palette because color doesn’t have add anything to their ideas and goals
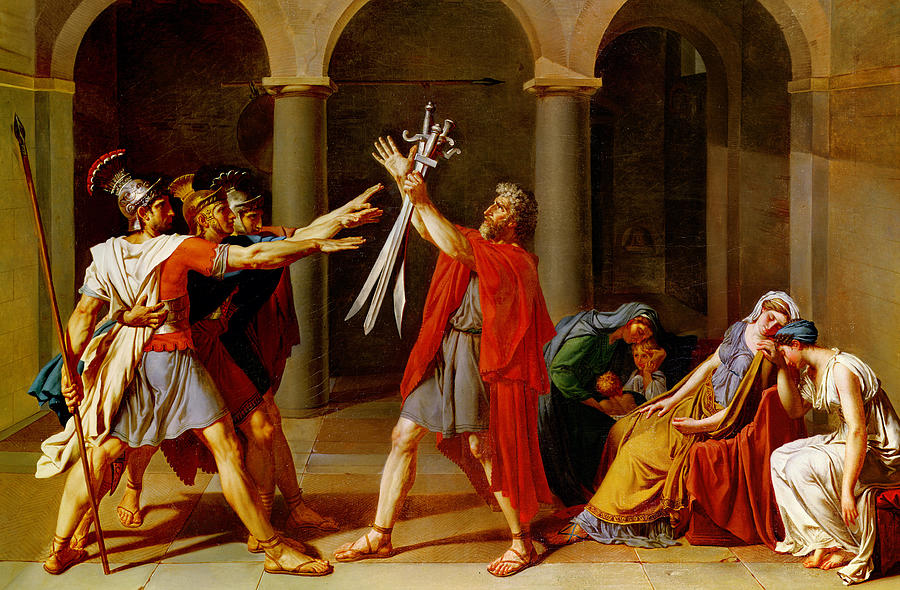

David, The Oath of the Horatii
Neo-classicism
France
David: most well-known painter of N-C
linear perspective, lines in the floor
roman clothing, known roman story
perfected body, very muscular arms and legs, extremely detailed
David, very political man, and apart of the French Revolution
Horatii, the father asked his three sons to fight to the death in battle, wives and mother of the sons are on the right, full of grief.
A time concerned about morals and making the right choice
David cleverly uses linear perspective and the building to divide the painting into thirds.
Orientalism
Western fascination with the culture of the Muslim world of North
Africa and the Near East
• Resulting in reductive and racist imagery, overly sexualized (exotic,
erotic, desired)
• Emphasizing the “primitive” Otherness of Arab/non-Western/non-Christian people
Avant Garde
Military term--‘Front guard’ in French
“At the forefront”Movements in art and literature considered to be radical and new,
often politically engaged as well
Symbolism
Addresses fears, desires, and impulses of the human mind
• “A turn inward”—focus on internal or mind, the psyche, emotion, the
spiritual
• Not replicating reality but actually observation plus imagination and feeling
Fauvism
A relatively short-lived movement (ca. 1905-08)
• Not an organized group per se but a label given
to the exhibiting artists by an art critic who
found the “orgy of pure colors” so outrageous
that he called the artists “Fauves” (Wild Beasts)\
• 3 key elements:
• 1) Flattening
• 2) Simplified forms
• 3) Arbitrary, anti-naturalistic color
Cubism
Rejection of traditional perspective.
Instead, Cubists embrace of simultaneous
viewpoints, and the use of collage.Interest in the 4th dimension and SIMULTANEITY
Post-Impressionism (Neo-Impressionism)
push beyond loose brushstrokes and style + realism, worker’s life and such
take loose brushstrokes to a new extreme in their own individual styles
the political subject matter will still talk about their harsh lifestyles of the industrial age, but focuses on their inner lives, how they psychologically effect people.
Modernity, city life.
Big four artists: Seurat, Cezanne, Van Gogh, and Gaugin
Impressionism
audience of the day and critics hated impressionism
borrowing realism subject matter like laborers
paintings were made even MORE against the Academy
Impressionist painters considered themselves Anarchists
Very political
Realism
separate from realistic painting styles
realist artists want to get to the truth/reality of life at this moment
showing depictions of the poor, political movements, like Bruegel w/the Hunter & Peasant Wedding
many moved from poor small towns to the city in hopes of making more money, but instead many got more poor.
Beaux Art Academy, often referred to as The Academy becomes a school for artists to learn the “correct” way to make good paintings and what they look like. They decide which art belongs in a gallery or salon.
Because of this, artists start adding things that go against the Academy and what good art is.
Political in style and technique artists use.
Romanticism
Not about romance or Rome at all
Artists who followed this style, thought that the Enlightenment didn’t make things better for everyone, cities are now overcrowded, poor got poor-er. Unhappy with the results of Enlightenment, not all their ideas were good
wanted to bring attention to the parts of the mind that did not have reason, dark aspects, darkness of humanity, and the human mind.
examples: romantic literature, Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein
Neo-Classism
The Enlightenment: “Age of Reason”
finally out of the hold of Church having most of the art themes.
Neo, New, Revival, Re-visiting
Revival of Humanism
Renaissance were the new ideas of classism (Greeks and Romans)
Return of linear perspective, mastering Greek and Roman Bodies
“Age of Reason,” the reasoning of the mind
Big time of Scientific Discovery, importance of Knowledge, Democracy, Science, and Philosophy.
Philosophers and Thinkers of Enlightenment begin to question religion, driving a wedge w/religion and the Church
*Empiricism: Issac Newton → Scientific method: facts/data/observation.
John Locke: “Natural Rights of Man” → rights of life, liberty, and property were protected by the government
Beyond religion → morals, civic duties for the greater good
Problems of the world solved through reason
Purposefully trying to be divergent from Baroque and Rococo.