Core Concepts-L17- Antigen Recognition by B and T cell Receptors and The Genetics of Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
what is the basic structure of an antibody? how does this relate to T cells differ/similar?
2 heavy chains and 2 light chains and make a Y- heteroteramers
N terminal: variable domain- where antigen ends
C terminal- constant domain- - determines effector function
antibody- 2 beta pleated sheets held by disulphide bonds
CD8- heterodimer- each chain has 1 Ig domain
CD4- 4 Ig domains
types of MHC classes and genes
class I- HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C- makes MHC I(CD8)- a1/2/3, b2 micro globulin
class II- HLA-DR, HLA-DP, HLA-DQ- makes MHC II(CD4)- a1/2, b1/2
TAP1/2, TNF
highly polymorphic!
differences between B and T cell receptors and how they recognise things
TCR
recognises peptide presented by MHC- explains why MHC restriction is needed
needs to be chopped by proteasome or acidified in phago-lysosome
T cell activation and effector function
BCR
recognises the antigen alone
doesn’t need MHC presentation
BCR secretes plasma cells
what is the differences between the antibody responses?
primary: first time exposure
innate: non specific antibodies- IgM and low affinity
adaptive/second exposure- IgG- higher levels of antibodies and higher affinity and memory cells
functions of immunoglobulins
antigen binding/neutralisation- Fab(variable) region binds specific antigens and neutralise viruses and stops them from infecting cells,
agglutination- antibodies with many binding sites can crosslink antigens to make complexes- makes it easier to detect phagocytose. enhances phagocytosis by binding to Fc receptor on macrophages
complement activation- Fc triggers complement cascade. Fc binds C1- C3b, opsonisation, C5-C6C9 lysis by MAC formation and amplification of inflammation
discuss roles of Fab and Fc regions- Fc mediated functions(3)
Fab- antigen binding site and cannot crystallise
Fc region mediates the effector function
Fc receptors on phagocytes- enhances engulfment of antibody coated pathogens
NK cell activation- CD16 binds Fc- releases perforin and granzymes
complement activation- binds C1-Fc- C3 convertase and C5+C6-C9- opsonisation, C3a/5a- inflammatory mediator
how is antibody specificity and diversity achieved? why can multiple antibodies bind the same protein?
each antibody can recognise a unique epitope from Fab region- large proteins have many epitopes so many antibodies can bind
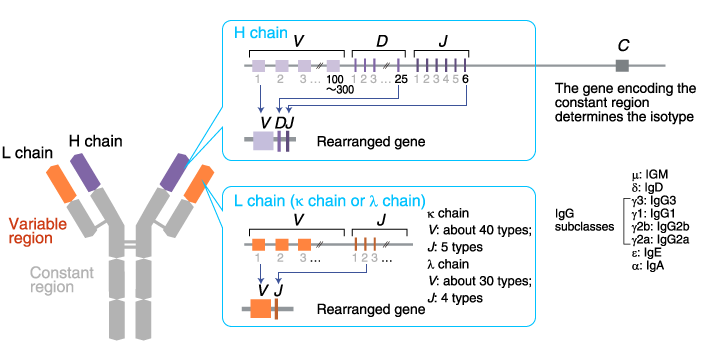
VDJ recombination- for Fab!!!!!!(bone marrow)
heavy chain by VDJ- DJ then V(Pre B cell)- picks RANDOM D!
light chain- V-J- VJ (B cell)
somatic hypermutation- in the VDJ region after antigen activation- germinal centres and gets Tfh- V of heavy and light chain Fab- to get higher affinity
compare IgG and IgM in terms of structure, affinity, function and when they occur
IgM- first exposure
10 binding sites
lower affinity
low specifcity
IgG- secondary/adaptive
monomer
higher affinity
long term protection and high specificity
what are the forces that hold antibodies and antigens?
hydrogen bonds
van der waals
hydrophobic interactions
difference between affinity and avidity? examples
affinity- strength of one Fab-epitope
avidity- combined strength of ALL Fab sites- IgM in primary has low affinity but high avidity as many are produced
how are antibody types distinguished by eachother?
by the constant region