GCSE AQA Equilibrium & Haber Process
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
dynamic equilibrium
rate of the forward reaction = rate of the back reaction
LeChatelier's Principle
whatever is changed in a reversible reaction, it will shift in the direction to oppose that change
Reversible Reaction
Reactants change to products, but the products can also change back to the reactants
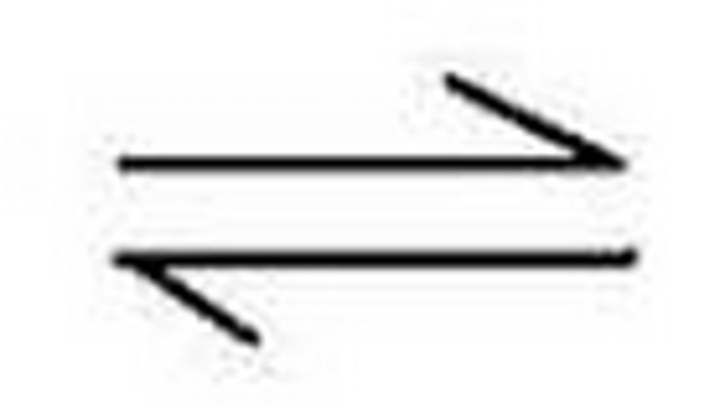
Adding Products
shift to left making more Reactants
Removing Products
shift to right making more Products
An increase of pressure
Only effects Gases! Causes a shift to the side with the fewer moles of gas
A decrease in pressure
Only effects Gases! Causes a shift to the side with more moles of gas
Catalyst
Does not alter the Equilibrium! Only speeds up the time it takes to achieve the equilibrium
+ΔH Positve Enthalpy Value
Endothermic reaction
-ΔH Negative Enthalpy Value
Exothermic reaction
Adding reactants
shift to the right
Removing reactants
shift to the left
Solute
substance being dissolved
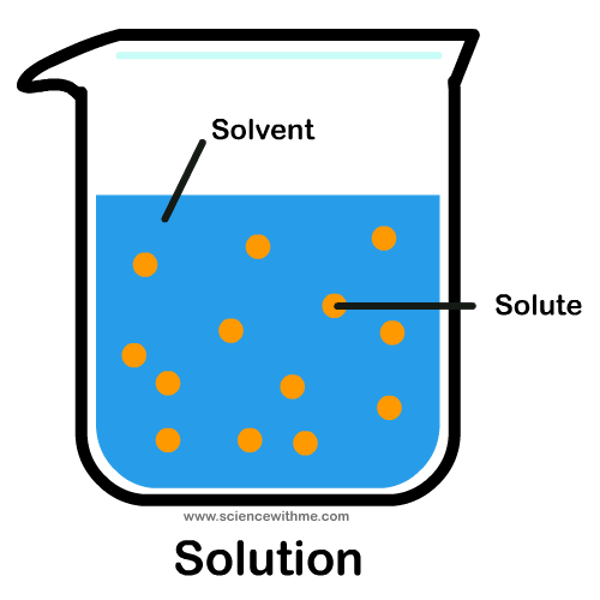
Solution
combination of solute and solvent
Rate of Reaction
Not to be confused with Equilibrium, the determines the speed of a reaction. How quickly the Equilibrium is achieved
What is made in the Haber process?
Ammonia (NH3)
What are the uses of ammonia?
Fertilisers, making nitric acid
What is the equation for the Haber Process?
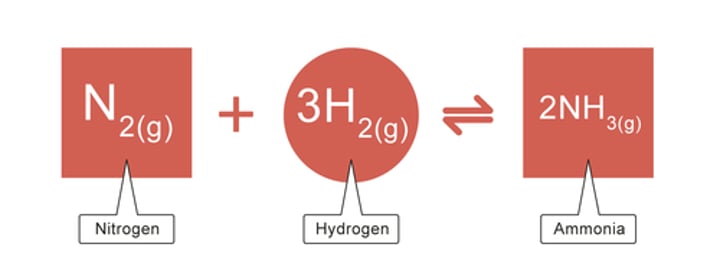
Where are the raw materials in the Haber Process obtained from?
Nitrogen from the air, hydrogen from natural gas
Why is the ammonia removed from the process as it forms?
Because the process is reversible, so removing ammonia reduces the backward reaction
How do we make sure the reactants are not wasted?
Unused nitrogen and hydrogen are recycled.
Is the Haber Process and exothermic or and endothermic process?
Exothermic
What are the compromise conditions required for the Haber Process?
200atm
450 degrees celcius
Iron catalyst
Why is the temperature a compromise condition?
Low temperature required as process is exothermic, but low temperature would make the reaction occur very slowly
Why is the pressure a compromise condition?
To produce the most ammonia a high pressure is required but a high pressure is dangerous and expensive