bio lecture 19 polymerase I cell cycle mitosis
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
what direction do both dna polymerase III and dna polymerase I add nucelotides and remove nucleotides in
5’ to 3’ direction
which dna polymerase removes nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction (primer removal)
dna polymerase I
dna polymerase III processivity (length of dna synthesized
high
dna polymerase I processivity (length of dna synthesized
low
chromatin
double stranded eukaryotic dna coiled around histones
chromatid
double stranded eukaryotic dna coiled around histones
histones are tightly packed in …
chromatids
histones are loosely packed in ….
chromatin
chromatin condense into
chromatids
chromatids relax into
chromatins
2 different forms that a chromosome can take
chromatins and chromatids
after replication, each sister chromatid has a
centromere and kinetochore
sister chromatids become highly condensed when
cell is preparing to divide
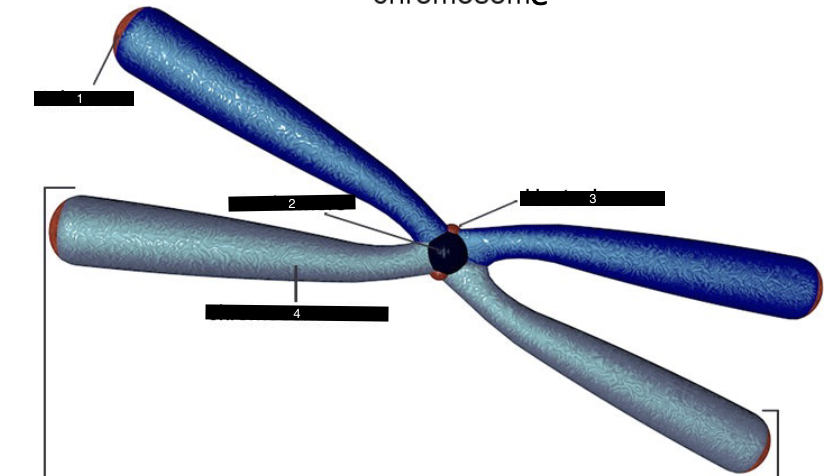
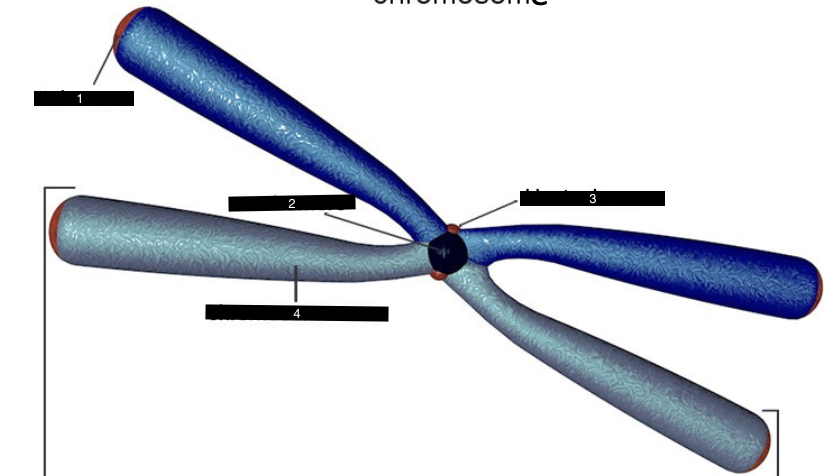
what does this represent
a chromosome
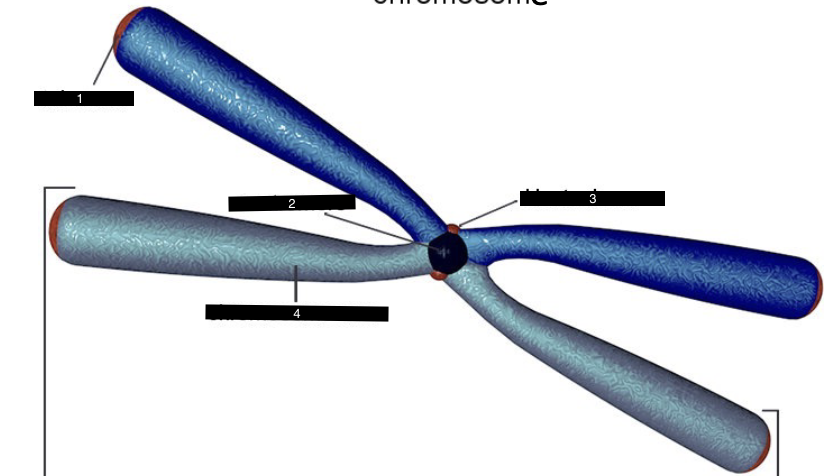
what is #1
a telomere
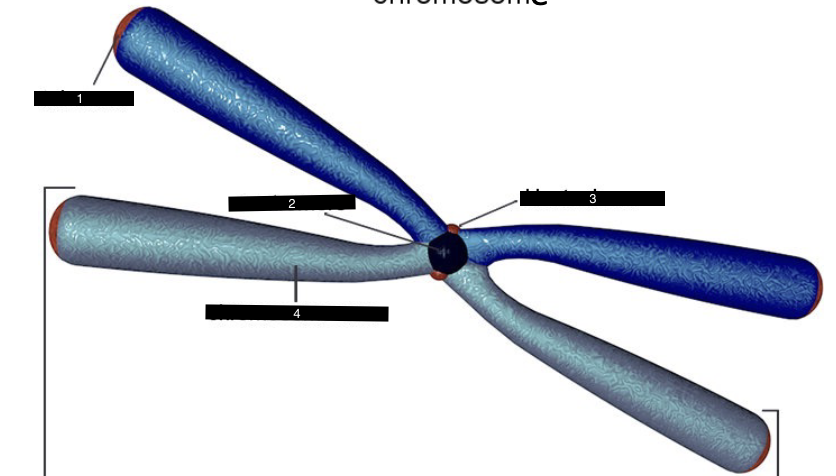
what is #2
a centromere
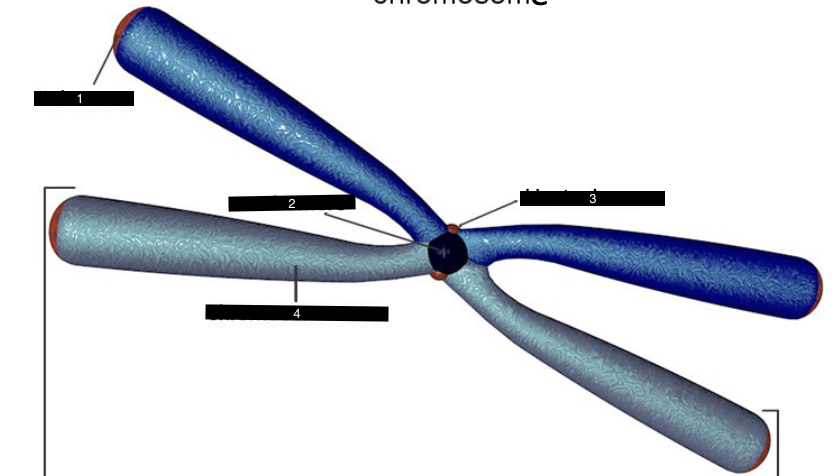
what is #3
a kinetochore
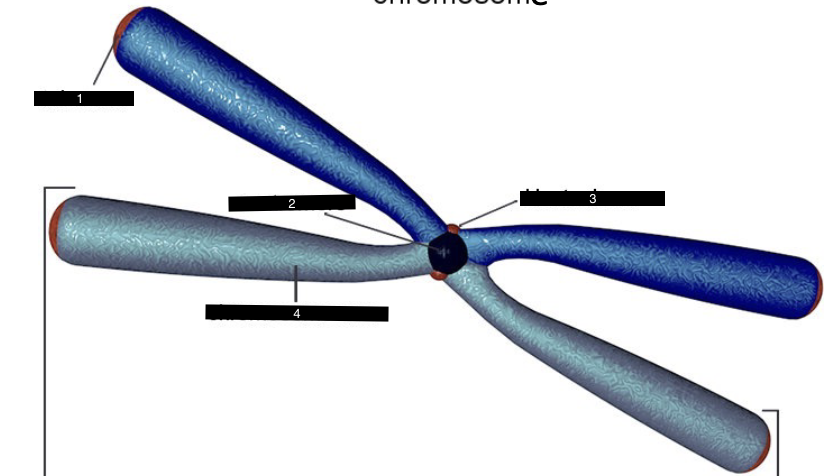
what is #4
a chromosome arm
what makes up a chromosome
chromatids
chromatid
one of two identical halves of replicated chromosomes
how many chromatids make up a pair of sister chromatids
2
centromere
region where sister chromatids are joined
chromosome arm
short vs long arm
kinetochore
proteins that bind to the centromere
what are kinetochores necessary for
sorting chromosomes
telomere
a region at the end of a chromosome
homologous chromosomes are
similar but not identical
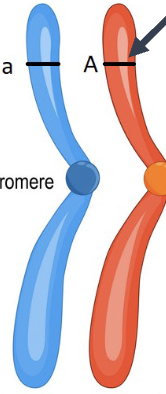
what are these an example of
homologous chromosomes
true or false: dna replication doesn’t change chromosome number
true
how many homologous chromosomes do humans have
23
how many total chromosomes do humans have
46
what are the phases of the cell cycle
G1, S, G2, M
what phases of the cell cycle make up interphase
G1, S, G2
G1 phase
primary growth phase, usually the longest, cell becomes divided
S phase
Synthesis of dna, each chromosome replicated
what does the S phase form
sister chromatids
G2 phase
organelles replicate, proteins necessary for chromosome sorting are made
G0 phase
nondividing phase
G1 checkpoint
determines if conditions are favorable for cell division and if the dna is damaged
G2 checkpoint
checks for dna damage, determines if all the dna is replicated and monitors the levels of proteins needed for M phase`DC
G1, S, G2
interphase
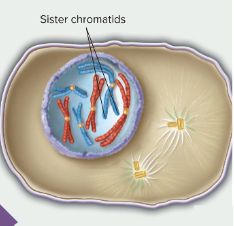
start of mitosis
prophase
mitotic spindle
structure responsible for organizing and sorting chromosomes duing mitosis
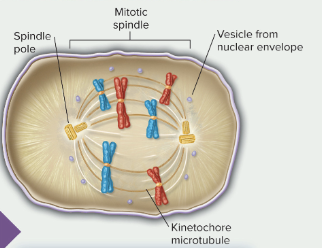
prometaphase
when sister chromatids attach to the spindle
prometaphase
prophase
when sister chromatids condense and the mitotic spindle starts to form
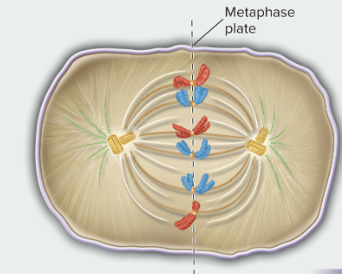
metaphase
metaphase
sister chromatids align along the metaphase plate
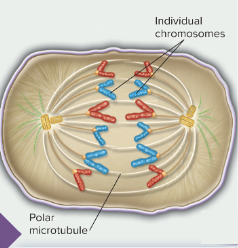
anaphase
anaphase
sister chromatids separate and individual chromosomes move toward the poles a
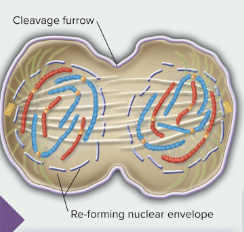
chromosomes condense and the nucelar envelope reforms
telophase
what quickly follows mitosis and the two nuclei separate into daughter cells
cytokinesis
mitosis makes
body cells
meiosis makes
gametes (sperm and egg cells)