Topic 3: Networks
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Server
A computer system or a software application that provides a service to other computer systems on the same network
Client
A computer system or software application that requests a services from a server connected to the same network
A computer network
Formed when 2 or more computers are linked together.
Every computer or device on a network can send and receive data from any of the other computers or devices connected to the network.
Hub
Connection point for devices on a single network
When a network device wishes to send data to another device on the network, it copies the data and sends it to all devices connected to its ports.
This generates a lot of unnecessary traffic on the network, slowing it down.
Switch
Similar to a hub, but can identify which device is connected to which port, allowing a network connected by switches to operate much faster
Data is only sent to the computer that needs it
Router
Can connect multiple networks and serves as an intermediary between them (i.e. home network and Internet)
What is the internet?
Globally connected network system
Uses TCP/IP protocol to transmit data
No centralized governance
Hosts the web pages that make up the World Wide Web
ISPs (Internet Service Providers) run networks that provide internet access
ISPs are “glued together” by internet exchanges (IXPs)
IXPs are the key to connecting all the different ISPs and networks together - usually run and maintained by nonprofits
How does the internet work?
Data travels in the form of packets.
Every file you send or request you make is split up into packets over the internet.
Individual packets often take different routes through exchanges, ISPs, and junction boxes
Ultimately reach the same destination and are reassembled at destination.
Packet Switching
A packet is a unit of information suitable for travel through computer networks.
Data is grouped into packets.
A file being transmitted through packet switching may be divided into multiple packets and each packet could follow a different route to the same destination.
This allows for more efficient data transmission and reduced delays.
What does a router do on the internet?
Used to manage traffic
Controls the flow of data packets
Checks address of data packets
Puts packets on correct path
Secure transmission
The 8 Network Topologies
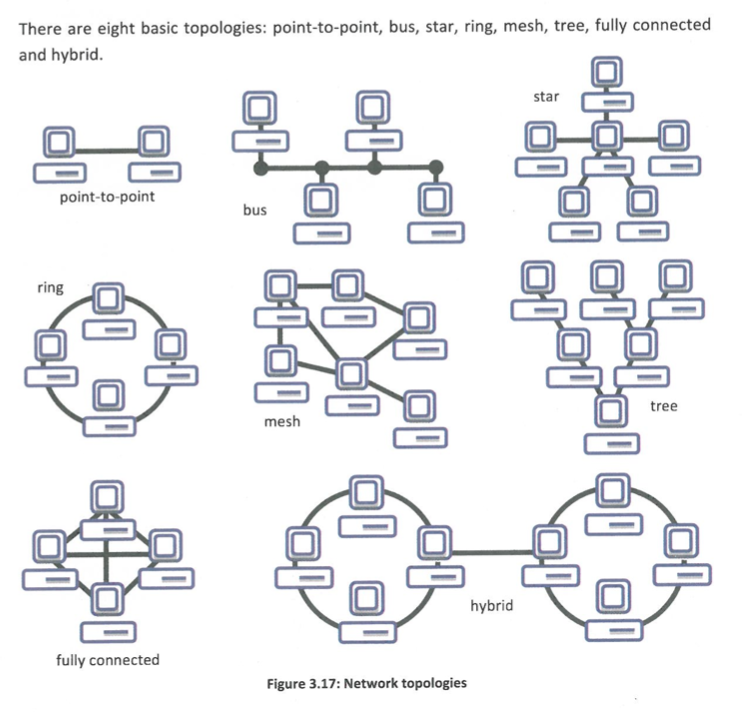
LAN (Local Area Network)
Covers a single building or collection of buildings
Less than 1KM radius
WAN (Wide Area Network)
Covers more distance than LAN
Greater than 1KM radius
Often uses multiple routers
May be several LANs connected together
Examples: Internet, Cellular Network, ATM network
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
1 or more physical LAN (local area network)
Network switch used to divide network
Works as multiple networks
More than the number of physical networks
Each VLAN may have different security requirements
Appears to an outsider as 1 LAN or WAN
WLAN (Wireless LAN)
LAN by which devices are connected by high-frequency data waves
Requests and responses from the internet (internet access) can be made
through WLAN
Uses can move around
“Wifi network”
Uses type of radio waves called Wifi (Wireless Fidelity)
Intranet
Private network
Sort of a “private internet”
Uses TCP/IP
Can view web pages similar to those on the internet
Intranet web pages only accessible from computers on network
North Korea - nationwide intranet
Extranet
Intranet that is accessible by wifi
How does a VPN (Virtual Private Network) work?
It makes a "tunneled" network through the internet or any other public network. It's considered ideal for establishing a secure connection.
What are the hardware and software components of a VPN?
Internet Access
VPN software (client, utilities, and server. Establishes the private connection)
VPN routers
VPN appliances
VPN concentrators (A single device to handle a large number of incoming VPN tunnels)
VPN servers
What does a site-to-site VPN do?
It connects two different locations securely.
What does a remote-access VPN do?
Connects an individual to a private network.
Benefits of a VPN

P2P Networks
Allows 2 or more computers to share resources with each other
Each computer acts as both a client and server
No central point
What are protocols and what are their roles?
A set of rules for data transmission (packets).
Roles:
Maintain Data Integrity - same data that is sent is received
Flow Control - data is sent and received at the same rate
Prevent Deadlock - two packets don’t “block each other”
Prevent Errors - Make sure no errors introduced in transit
wifi vs ethernet
Ethernet faster, more consistent speed, lower latency data transfer
Wifi easier to install and deploy, cheaper
Ethernet more secure, can only be tapped through physical access
Fiber Optics vs Copper Cabling
Fiber - faster, more expensive, lighter, almost impossible to tap, immune to interference, longer range(40 km+)
Copper - Susceptible to electromagnetic interference, shorter range (100m), heavier, thicker
Factors Affecting Transmission of Data
Primary Factors
Traffic
Secondary Factors
Time of Day
Distance
Infrastructure
Tertiary Factors
Environmental Issues (Temperature, Interference)
Financial Factors (Cheaper equipment, etc.)
Type of Data (Size, streaming, etc.)
Lossy Compression
Removes data
Smaller file size - Irreversible
Used when some data can be lost (videos, images, etc.)
Lossless Compression
Uses algorithm to reduce file size
Larger than lossy, but smaller than normal - Reversible
Used when no data can be lost (text, software, etc.)
One Factor Authentication
One factor, just one thing to input (e.g., passwords)
Two Factor Authentication
Something you know (e.g., password) and something you have (e.g., phone)
Three Factor Authentication
Something you know (e.g., password), something you have (e.g., phone) and something you are (e.g., fingerprint)
What is encryption?
A method of encoding data in a way that can only be read by the sender and receiver, and requires a “key”
MAC (Media Access Control) Address
Used to identify network-enabled devices in networks
“Hard-coded” by manufacturer (But can be spoofed)
Network interface controller
Unique, 6 pairs of 2 hexadecimal digits
Check against white list
Firewalls
Can be hardware- or software-based
Analyzes data packets
Controls incoming and outgoing traffic according to predetermined rules
Can filter based on MAC addresses
Physical Security
Locked doors
Cages
Security Guards
Secure Rooms
Hurricane/Earthquake Proof
EMP-Insulated