GI - Nutrition & Toxic Ingestion
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
obesity
name this condition
- MC nutritional d/o in the US
- uses BMI and waist circumference (>35 F, >40 M)
- population: F>M, black & hispanic > white & asian
- can lead to insulin resistance/DM II, acanthosis nigricans, dyslipidemia, sleep apnea, GERD, cancer, liver dz, OA, and cholelithiasis
- blood glucose
- triglycerides
- HDL
- BP
- waist circumference
name the 5 factors to determine metabolic health
- normal: 18.5-24.9
- overweight: 25-29.9
- obese I: 30-34.9
- obese II: 35-39.9
- severely obese (III): 40+
name the ranges of BMI from normal to Severely obese (obese III)
- leptin
- melanocortin signaling
name 2 genetic causes for obesity
- maternal DM
- fetal malnutrition
name 2 constitutional causes of obesity
- psych meds
- steroids
- OCPs
- insulin
- BBs/alpha blockers
- HIV antivirals
name 6 medications that can be a secondary cause of obesity
- cushing's disease
- insulinoma
- hypothyroidism
name 3 conditions that can be a secondary cause of obesity
PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome)
name this condition related to obesity
- excess androgen production in females that causes hirsutism, irregular menstruation/amenorrhea, and infertility
- at risk waist circumference
- elevated triglycerides/on meds
- low HDL/on meds
- HTN/on meds
- elevated fasting glucose/ on meds
name the 5 factors of metabolic syndrome
- must have 3/5
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP)
what hormone increases energy storage?
- leptin
- peptide YY
- cholecystokinin
- amylin
name 4 hormones that inhibit food intake
Phentermine(Adipex-P)
name this obesity medication
- reduces appetite for 3 months
- avoid in those w/ CVD and/or HTN
Saxenda (liraglutide)
name this obesity medication
- GLP1 agonist that inhibits glucagon release and delays gastric emptying
- given through weekly injection
Wegovy (semaglutide)
name this obesity medication
- mimics GLP1
- titrated to 2.4mg weekly SQ
- avoid in endocrine neoplasia and medullary thyroid cancer
phentermine/topiramate
name this obesity medication
- reduces appetite, increases satiety, and distorts taste
- avoid in CVD and pregnancy
Bupriopion/Naltrexone
name this obesity medication
- used commonly in smokers
- has risk of suicidal ideation
- avoid w/ drug/alc use
orlistat
name this obesity medication
- causes fat metabolism which leads to steatorrhea
- BMI >30 or BMI >27 w/ 1+ complications
- must be compliant w/ diet/exercise and behavior mods
describe the indication for obesity medication
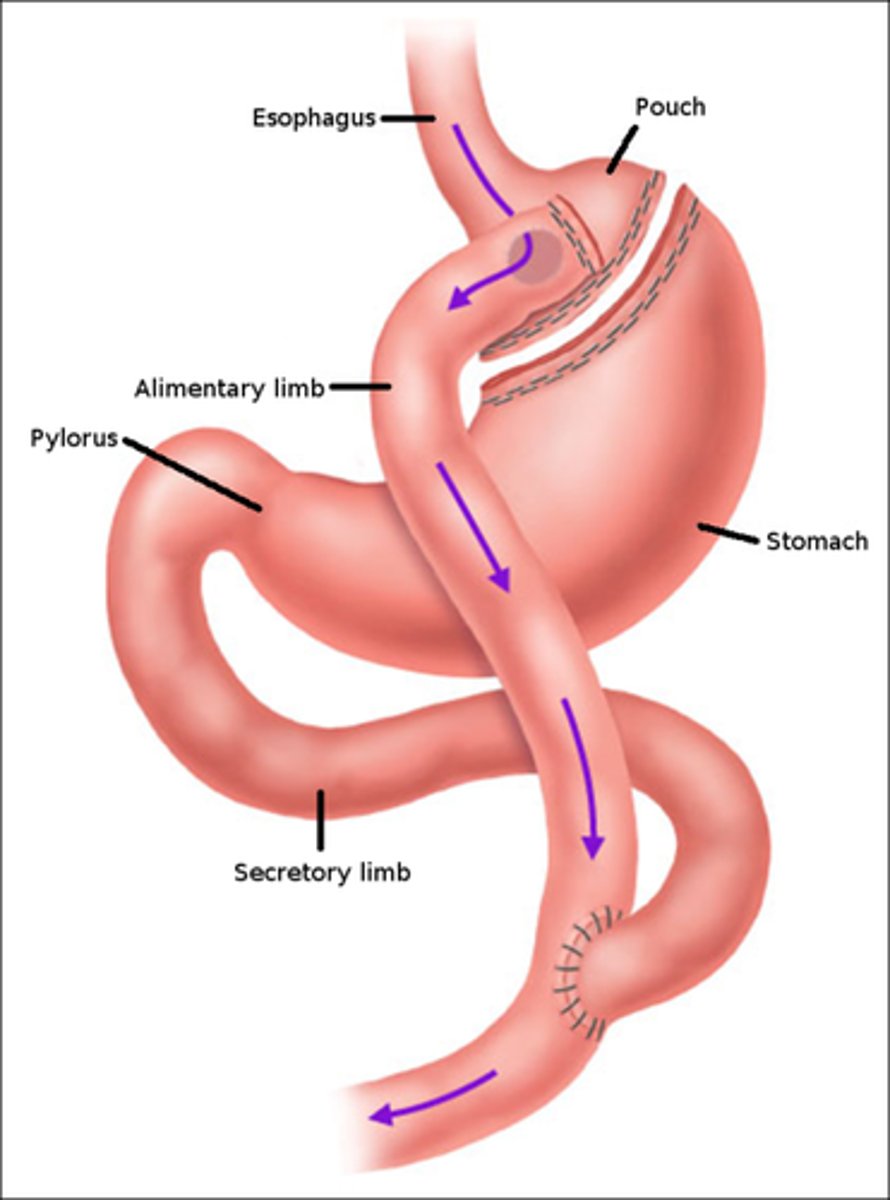
Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y)
name this obesity procedure
- gastric pouch is reduced to the size of an egg
- makes ERCP difficult
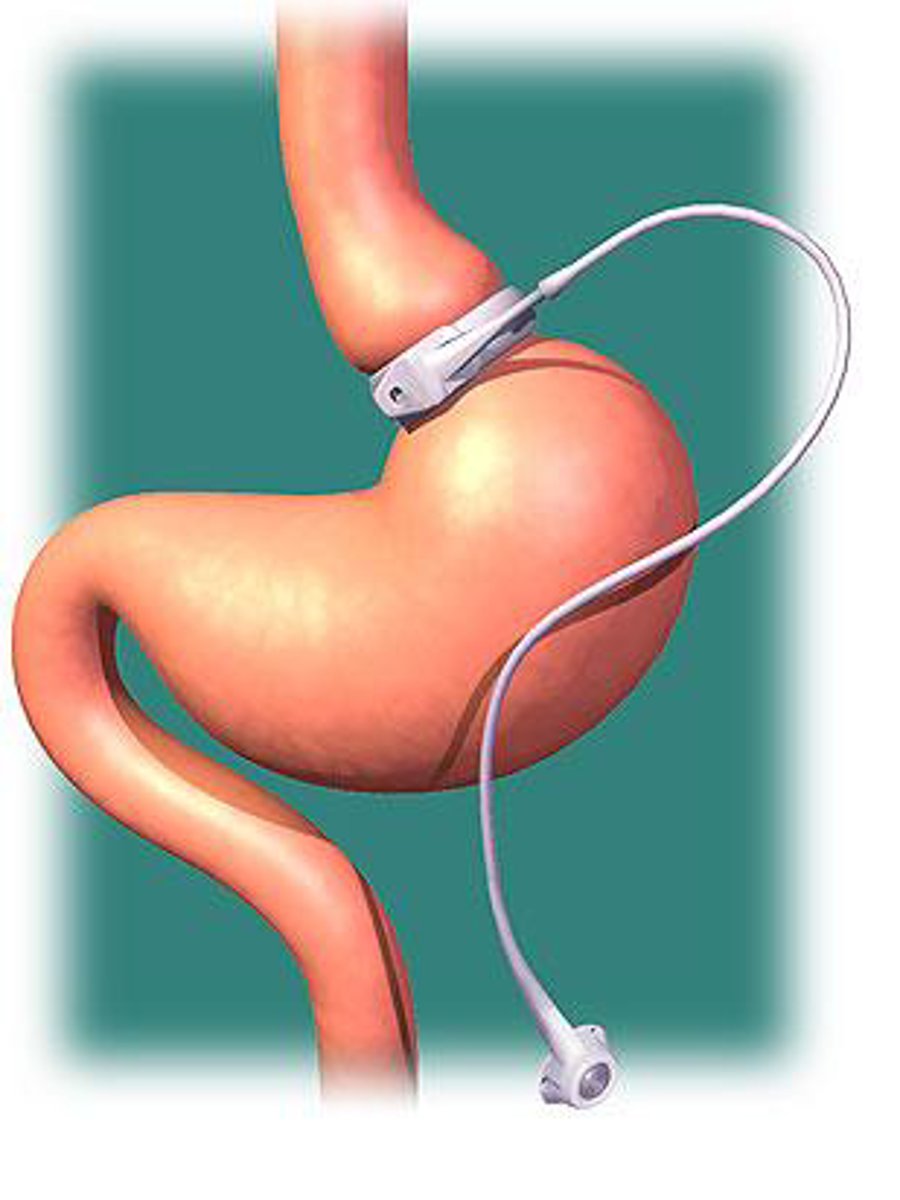
lap band
name this obesity procedure
- an inflatable silicone device placed around the top portion of the stomach
- intended to slow consumption of food and thus reduce the amount of food consumed
obesity endoscopy
name this obesity procedure
- occupies gastric lumen to provide satiety
- removed after 6 mo to allow pt to adjust to lifestyle
- has different types: obalon, orbera, and reshape
- safety concerns: pancreatitis and death
NG tubes
name this enteral feeding
- a tube placed in the proximal bowel
- standard feeding tubes
- two types: keofeed tube and dobhoff tube (weighted)
PEG Tubes (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy)
name this enteral feeding
- more prolonged enteral feeding systems (usually placed if greater than 2-6 wks)
- bowel obstruction
- perforation
- ischemia
- peritonitis
name 4 contraindications for enteral feeding
- sinusitis
- aspiration
- diarrhea
- bowel ischemia
- fluid overload
- refeeding syndrome
name some compilations of enteral feeding
parenteral nutrition
name this type of feeding
- aka TPN
- used for pts who cannot have PO or EN
- contains dextrose, AA, lipids, electrolytes, vitamins, minerals, and meds
- requires PICC or central venous cath
- short bowel syndrome/intestinal failure
- severe IBD
- obstruction
- EN feeding unlikely for 7-10 days
- severe catabolic stress
name some indications for TPN
- functional GI tract
- fluid intolerance
- glucose/electrolyte disruption
- severe bacteremia
- hemodynamic instability
name some contraindications for TPN
- electrolyte abnormalities
- line issues (pneumothorax, sepsis, thrombosis)
- refeeding syndrome
- hepatic steatosis
- cholestasis
- gallstones
name some complications of TNP
Rickets (osteomalacia)
name this condition
- pediatric condition defined as changes at the growth plate d/t deficient mineralization of bone
- occurs before the closure of the growth plate
- presentation: delayed fontanelle closure, parietal/frontal bossing, enlarged costochondral junction, widened wrists, and bow legs
- tx: vit D/sunlight and calcium
vitamin E
name this vitamin
- a fat soluble antioxidant found in seeds, nuts, spinach, beets, mango, and avocado
- deficiency: very rare, but can be seen in premature infants; causes hemolysis and neuropathy
- toxicity: leads to impaired wbc function, hemorrhagic CVA, and coag disruption
vitamin B1 (thiamine)
name this vitamin
- water soluble vitamin involved in the metabolism of AA and sugars
- found in yeast and pork
- deficiency: Beriberi, wernicke's encephalopathy, jorsakoff's psychosis, and alcoholism
dry beriberi
name this thiamine/B1 deficiency
- presents w/ peripheral neuropathy, paralysis, sensory loss, guillian barre, and sensory ataxia
Wernicke's encephalopathy
name this thiamine/B1 deficiency
- presents w/ nystagmus, opthalmoplegia, and ataxia
Korsacoff's psychosis
name this thiamine/B1 deficiency
- presents w/ hallucinations, impaired short term memory, and confabulation
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
name this vitamin
- a water soluble vitamin that is a coenzyme in oxidation reduction pathways
- found in beef, lamb, milk, yogurt, eggs, and salmon
- deficiency: usually isolated to the mouth, skin, or hematologic issues; presents w/ hyperemia, edema, cheilosis, glossitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and normo/normo anemia
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
name this vitamin
- a water soluble vitamin that aids in neurotransmitter production
- found in beef, fish, cereal , and starchy vegetables
- isoniazid can cause deficiency
Vitamin B9 (Folate)
name this vitamin
- a water soluble vitamin that aids in RNA/DNA production and controls homocysteine levels
- found in grains, leafy greens, and asparagus
- deficiency: seen MC in women of childbearing age and alcoholics; causes megaloblastic anemia, diarrhea, and glossitis
- needed supplemented when pregnant
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
name this vitamin
- a water soluble vitamin that aids in the brain, NS, RBC formation, DNA synthesis, and fatty acid and AA metabolism
- found in fish, meat, poultry, eggs, and milk
- deficiency: seen MC in vegans, but overall rare; causes pernicious anemia, AMS, depression, psychosis, megaloblastic anemia, and pancreatic insufficiency
PKU (phenylketonuria)
name this condition
- an autosomal recessive dz of protein metabolism d/t the deficiency of an enzyme that causes toxic levels of phenylalanine
- presents w/ musty breath, urine, and/or skin, seizures, light skin color, and microcephaly
- can lead to intellectual development issues
- tx: low protein diet, no aspartame, special formula, fish oil, Kuvan (med)
G6PD deficiency
name this condition
- an x-lined recessive disorder of RBCs that leads to oxidative stress and hemolysis
- MC presents in black males
- sx: neonatal jaundice, HA, nausea, back pain, chills, and hemoglobinuria (only present during hemolysis)
- usually asymptomatic in females
- tx: folate and transfusions
- antimalarials (dapsoone, glyburide, primaquine, glipizide)
- henna
- mothballs
- fava beans
name some triggers of G6PD deficiency
Esophageal foreign body
name this type of foreign body
- managed w/ glucagon to relax smooth mm anf endoscopy to remove
- f/u to tx underlying cause and assess healing
gastric foreign body
name this type of foreign body
- endoscopy not always necessary; pts w/o sx can be observed w/ radiographs to see passage
- emesis not recommended
- case by case basis for endoscopy or surgical removal
anorectal foreign body
name this type of foreign body
- spontaneous passage is likely, btut can use laxatives and/or enimas
- evaluate/observe for perforation risk (extraction needed)
Toxic ingestion
name this type of foreign body
- MC alkaline materials such as lye or bleach
- can cause severe esophageal injury, necrosis, strictures, cancer risk
- avoid NG, emesis, and neutralizing agents
- tx: endoscopy within 24 hrsl, NPO, surgery consult, abx
Activated Charcoal
name this GI decontamination agent
- used within 1 hour of toxin ingestion in alert pts w/ no bowel obstruction
- not useful for mineral acids, alkalis, highly dissociated salts
ipecac
name this medication
- used to induce emesis, but not recommended d/t risk of aspiration
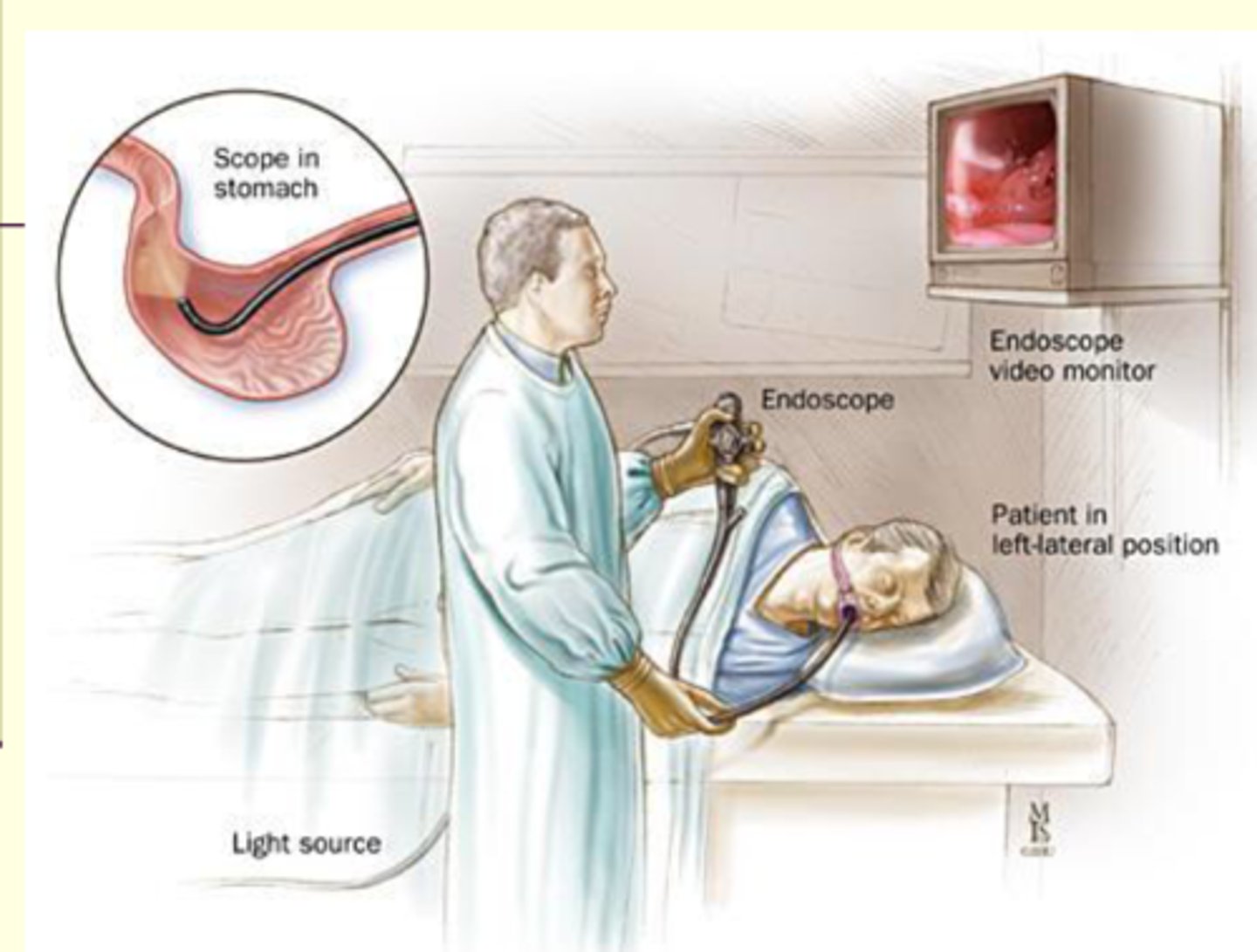
EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)
name this procedure
- a flexible, fiberoptic endoscope under conscious sedation
- pt must be NPO after midnight
- pts in LLD for 10 mins
- used for dilation, biopsy, and tissue removal
- risk of aspiration, perf, bleeding, and infection
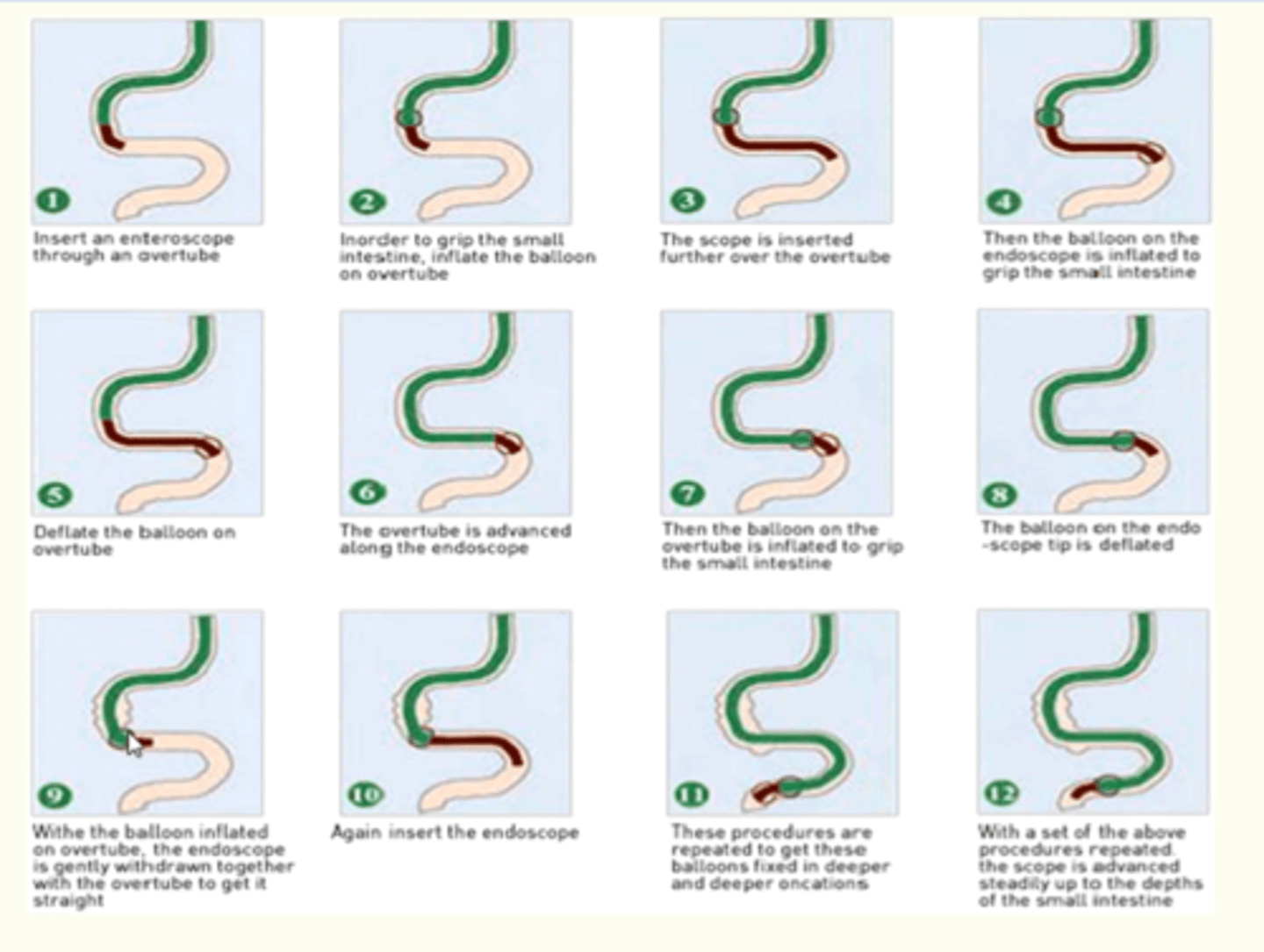
enteroscopy
name this procedure
- a longer, more complex procedure to visualize the mid-small bowel
- balloons used to anchor the endoscope
- can be done antegrade or retrograde
Manometry
name this procedure
- used to measure contractions and pressure gradients in the GI tract
- no sedation is given
- MC is esophageal and anorectal
ultrasound
name this diagnostic imaging
- a transabdominal study that is first line for liver and gallbladder
- useful for doppler exams, but is limited by bowel gas
CT
name this diagnostic imaging
- uses radiation and oral contrast (barium) to visualize structures
- MC used for obstruction, perforation, cancer staging, angiography, and enterography
- caution in those w/ renal issues, shellfish/iodine allergies, insulin pumps, or implanted glucometers
MRI
name this diagnostic imaging
- useful for visualization of viscera and soft tissues
- no radiation needed and image is enhanced w/ gadolinium
- MC used for MRCP, liver, enterography, and angiography
- caution in those w/ renal failure and metallic hardware
nuclear imaging
name this diagnostic imaging
- uses radioactive metal (technetium-99)
- MC used for bleeds (identifies location), gastric emptying tests, and gallbladder scans
- KUB
- CXR
name these two noncontrast images
- evals retained stool, FB, dilated bowels, and pneumoperitoneum
endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)
name this advanced imaging
- combines endoscopy w/ US transducer
- internal is great for staging tumors and for interventional procedures
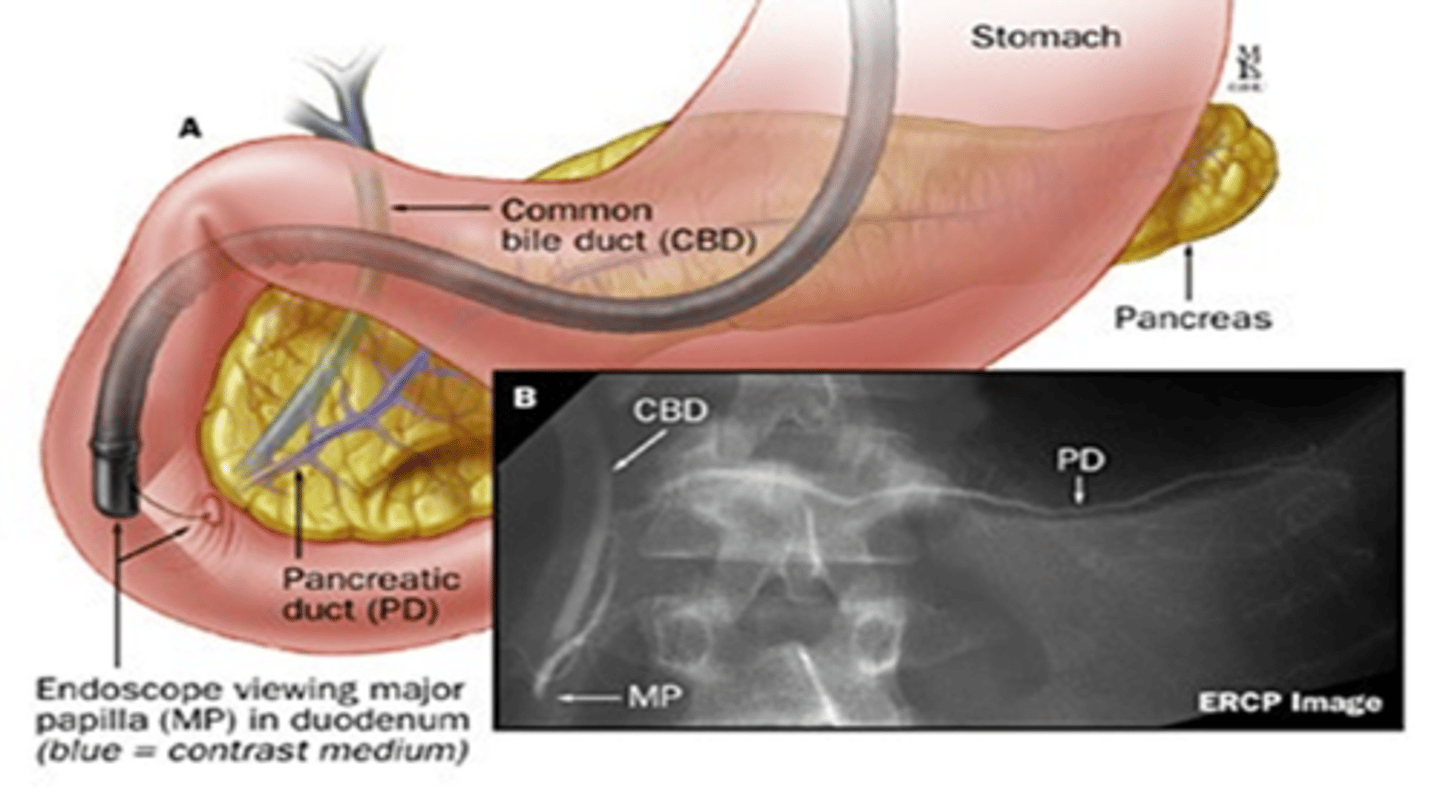
ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
name this advanced imaging
- pt is prone and intubated
- uses fluoroscopy
- good for visualization and intervention of the biliary tree
Elastography
name this advanced imaging
- uses vibration to enhance MRI and/or US of the liver
- measures liver stiffness
- elevated values suggest fibrotic liver disease or cirrhosis
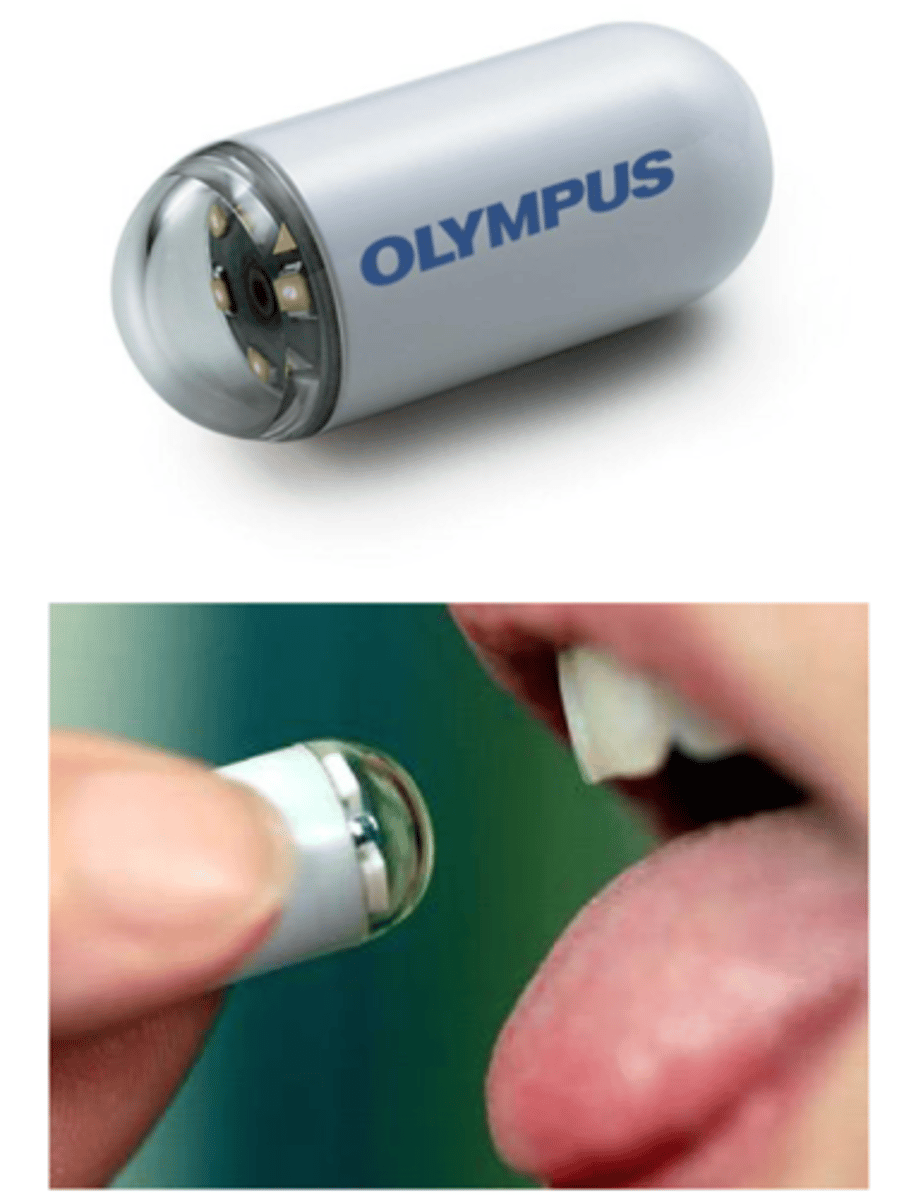
wireless capsule endoscopy (pillcam)
name this advanced imaging
- uses to visualize the mid small bowel for bleeding and tumors for dx purposes
- in pts w/ strictures, may need patency capsule
- caution in pts w/ pacemakers, strictures, and those getting an MRI

luminal biopsy
name this type of biopsy
- uses snare or forceps to obtain tissue
- used to eval inflammation, dysplasia, malignancy, infection
- may be used w/ electocautery
visceral biopsy
name this type of biopsy
- tissue obtained through fine needle aspiration or core
- 45-65%
- 10-35%
- 20-35%
carbs should make up ____ - ____% of the diet
protein should make up ____ - ____% of the diet
fats should make up ____ - ____% of the diet
albumin
name this protein
- standard serum lab test to assess nutritional assessment
- has half life of 18-20 days
stunting
name this energy malnutrition
- pt is short statured and underweight during the first 2-3 yrs of life
Kwashiorkor
name this protein energy malnutrition
- aka edematous malnutrition
- pt has sufficient calories but inadequate protein
- occurs after cessation of breast feeding
Marasmus
name this protein energy malnutrition
- insufficient caloric intake and protein intake
protein energy malnutrition
name this type of malnutrition
- presents w/ ketosis, bradycardia, cachexia, hair loss, skin breakdown, immune suppression, hepatomegaly, ascites, and cerebral atrophy (late)
- has different types (Kwashiorkor, marasmus)
Refeeding syndrome
name this condition
- aggressive re-initiation of feeding
- leads to low potassium, magnesium, and phosphate
- causes elevated glucose, fluid overload, mm weakness, arrhythmias, diarrhea, and confusion
- opiates
- cannabis
name two drugs that decrease gut motility and appetite
>5% loss in 6-12 mo (w/o intent)
when is weight loss a concern?
Ghrelin
what hormone stimulates appetite?
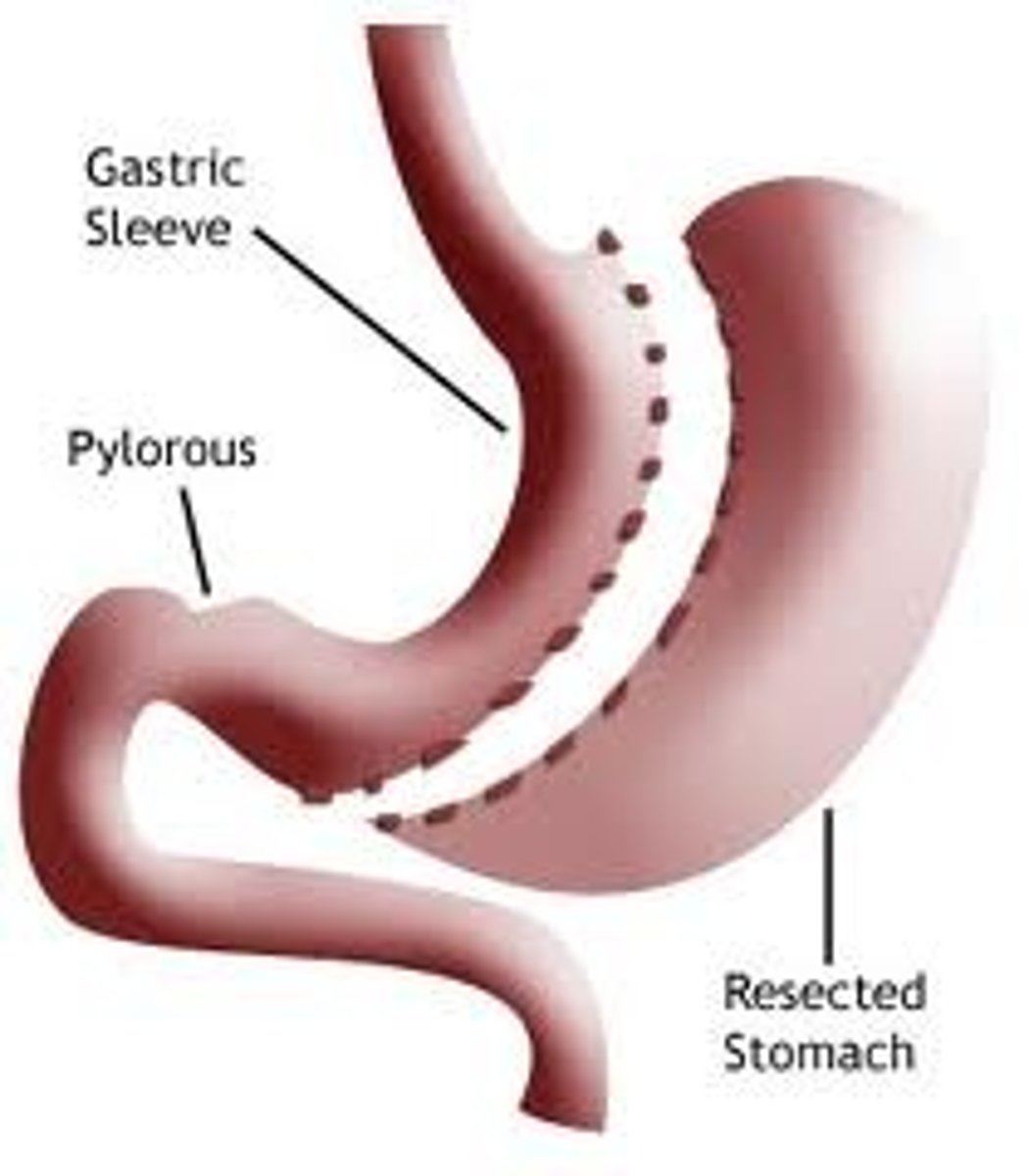
gastric sleeve
name this obesity procedure
- portion of stomach is removed, leaving a banana-shaped stomach pouch
enteral feeding
name this type of feeding
- given is 5-7 days NPO
- reduces infection rates and complications such as organ failure and mortality
- maintains nutrition and gut integrity
- increases contractility and intestinal blood flow
vitamin A
name this vitamin
- fat soluble vitamin that plays a role in immunity and contains light sensitive proteins
- found in sweet potatoes, carrots, leafy greens, bell peppers, and fish
- precursor is beta carotene
- deficiency: night blindness
- toxicity: hepatotoxicity, intracrtanial HTN, teratogenic, atacia, pseudotumor cerebri, retinopathy
vitamin D
name this vitamin
- fat soluble vitamin found in various foods (dairy, fish, eggs) and is formed in the skin when exposed to UVB
- deficiency: demineralized bones, growth plate expansion, replacement of normal bone, osteomalacia
- toxicity: metastatic calcifications, renal failure, altered mentation
paget disease of bone
name this condition
- aka osteitis deformans
- focal d/o of bone metabolism that occurs in the aging skeleton (pts usually over 55)
- mostly asymptomatic, but can have bone pain/arthritic complaints and/or deformity
- tx: nitrogen containing bisphosphonates, calcitonin, hearing aids, PT/OT, and NSAIDs
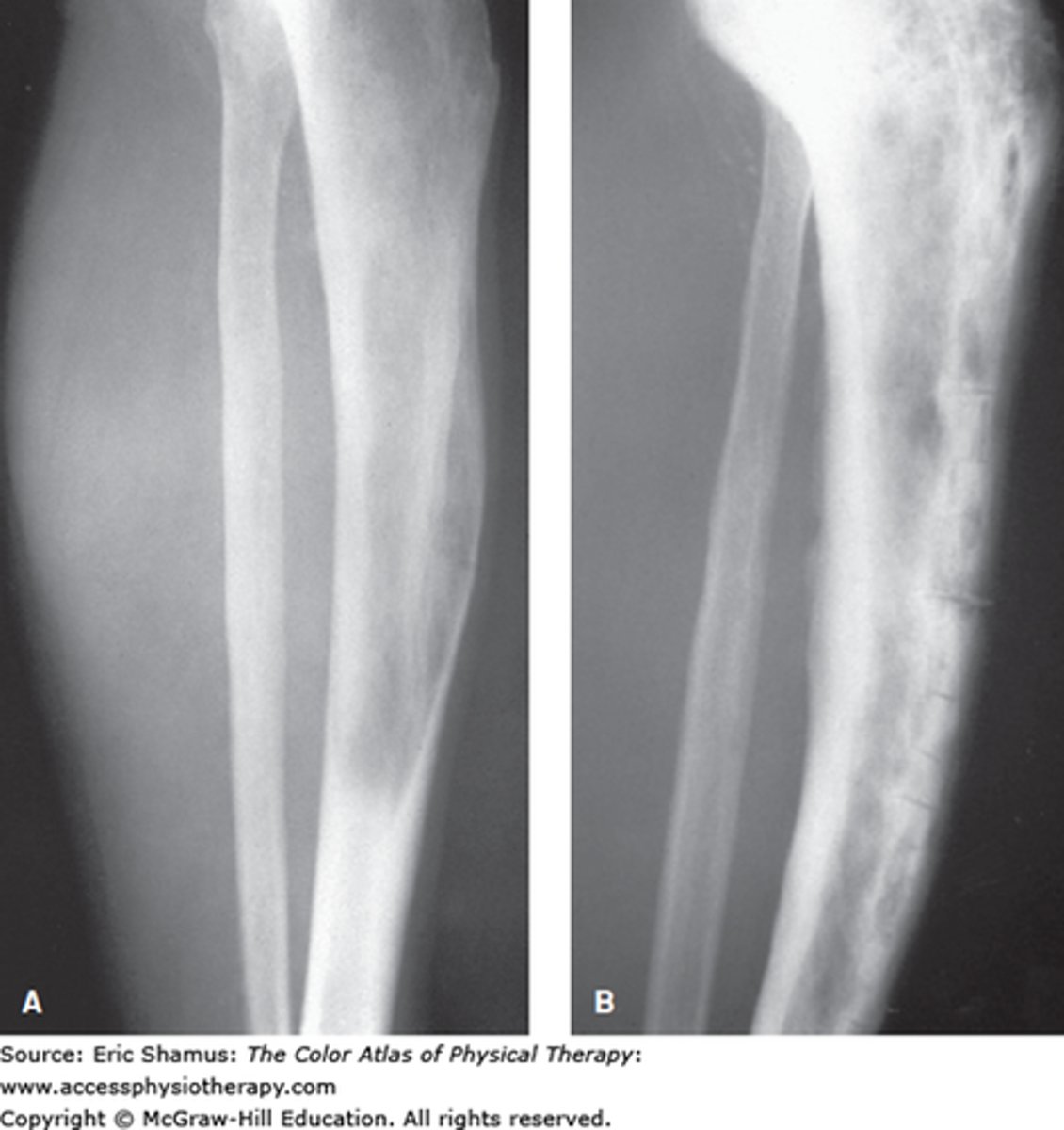
vitamin K
name this vitamin
- a fat soluble vitamin dependent on clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X (have procoag and anticoag roles)
- type 1 found in plants and type 2 found in animal products
- deficiency: hemorrhage
- toxicity: anticoag interference
wet beriberi
name this thiamine/B1 deficiency
- presents w/ confusion, muscular atrophy, edema, tachycardia, cardiomegaly, CHF, and peripheral neuropathy
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
name this vitamin
- a water soluble vitamin that facilitates numerous metabolic processes and has a role in lowering LDL and TGs, and elevating HDL
- found in meat and peanuts
- deficiency: pellegra 3-Ds (diarrhea, dementia, dermatitis); glossitis, vertigo, and stomatitis
- toxicity: flushing, hyperglycemia, hepatotoxicity, and hyperuricemia
vitamin C
name this vitamin
- a water soluble vitamin that is a cofactor in collagen synthesis, an antioxidant, and aids in iron absorption
- found in citrus fruit and liver
- deficiency: very rare but can cause scurvy; presents w/ fatigue, depression, inflamed gingivae, petechiae, and impaired wound healing
lactose intolerance
name this condition
- MC cause of selective carbohydrate malabsorption
- highest prevalence in asian pts, black pts, and native pts
- presents w/ gas, bloating, and osmotic diarrhea w/o wt loss
- tx: lactase or dairy free diet
Nut allergies
name this condition
- an IgE mediated response to proteins that causes urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis, and severe GI sx
- 1-2% of the population has
- RF: FHx of atopy, egg allergy, late introduction
- tx: Epi-Pen, desensitization oral immunotherapy w/ Palforzia (ages 4-17)
Button battery ingestion
name this type of foreign body
- severe esophageal perforation occurs within 2 hours of ingesting; medical emergency (needs endoscopy ASAP)
- pts should take honey after ingestion and Carafate in the ER
- must call national battery ingestion hotline
whole bowel irrigation
name this type of GI decontamination
- flushing the ingested poison from the entire GI tract
- used for drug packets, heavy metals, and enteric coated drugs
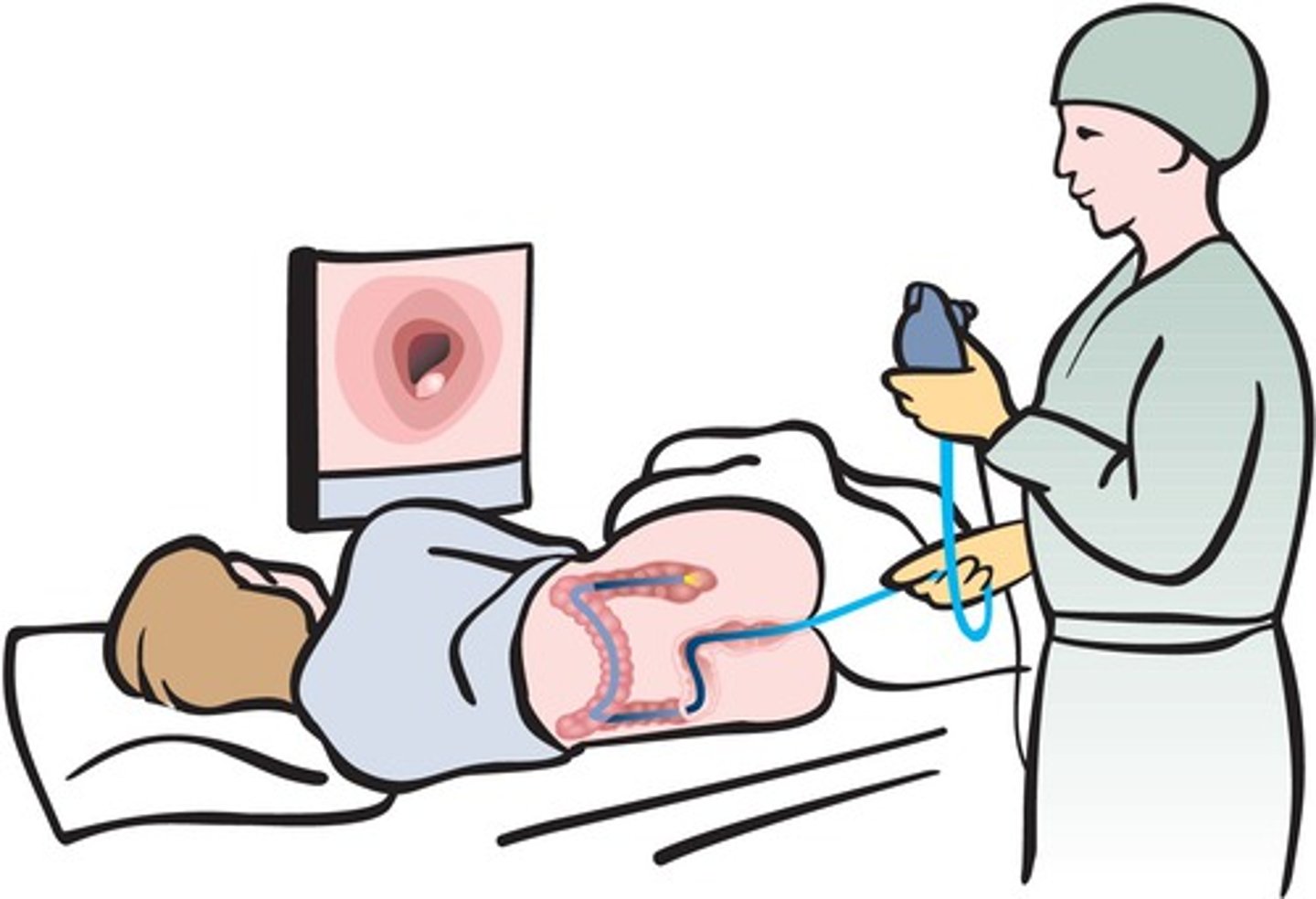
colonoscopy
name this procedure
- visual examination of the colon done under conscious sedation
- done to biopsy, dilate, and remove polyps
- can visualize terminal ileum via ileocecal valve
- risks of perforation, bleeding, and infection
barium
name this conventional contrast
- can swallow for an esophagram or given in enema for colon
- can visualize obstructions, inflammation, strictures, and motility issues