B3.2 Transport in plants
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Two types of vascular tissue found in the roots, stem and leaves
- xylem
- phloem
xylem
transports water and dissolved minerals
phloem
transports glucose and amino acids
Water can move through very long distances against gravity due to...
- transpiration
-capillary action
Why capillary action allows water to move through very long distances against gravity?
- Cell walls contain cellulose which is hydrophilic and forms hydrogen bonds with water (adhesion)
- Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other (cohesion)
Why transpiration allows water to move through very long distances against gravity?
As the cell walls of the leafs draw water our of the xylem. this genetates tension- pulling forces (transpiration pull)
Adaptations of xylem vessels
- They lack cell contents (anucleated, no cytoplasm, etc). Meaning there is minimal resistance to the flow of the xylem sap
- Incomplete/absent cell walls to create long, continuous tubes.
- Thick, lignified walls to prevent the xylem vessel from collapsing under low-pressure
- Non- lignified pits for entry and exit of water
Explain how water is transported from the roots to the leaves during transpiration.
- Roots: absorb water and minerals and contain root hairs, which increase the surface area, for efficient absorbtion
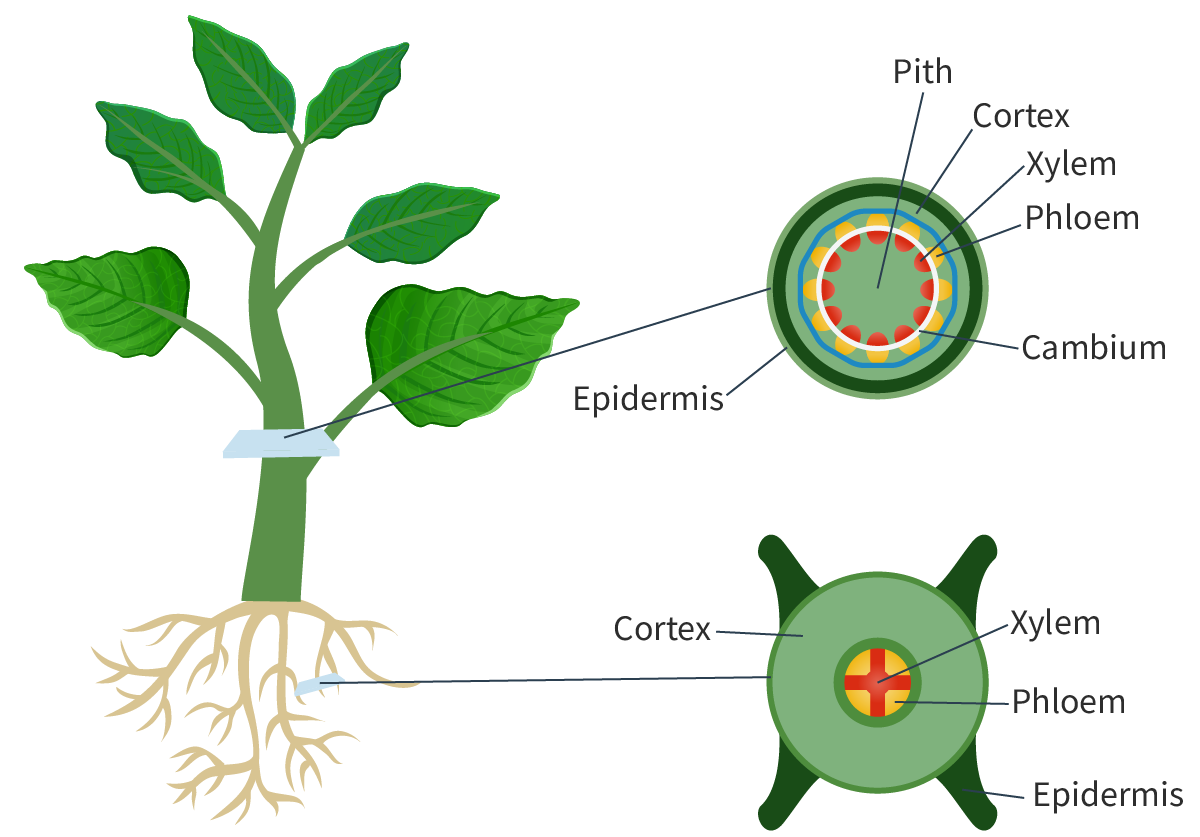
- Cortex: Located between vascular bundes and the epidermis. Provide structural support to the stem and roots, maintaining their shape
- Xylem and pholem: Trasnport substances. In stem, they form a ring, in the roots, they are arranged in the middle.
stem vs roots plan diagram