Vesicular Transport
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
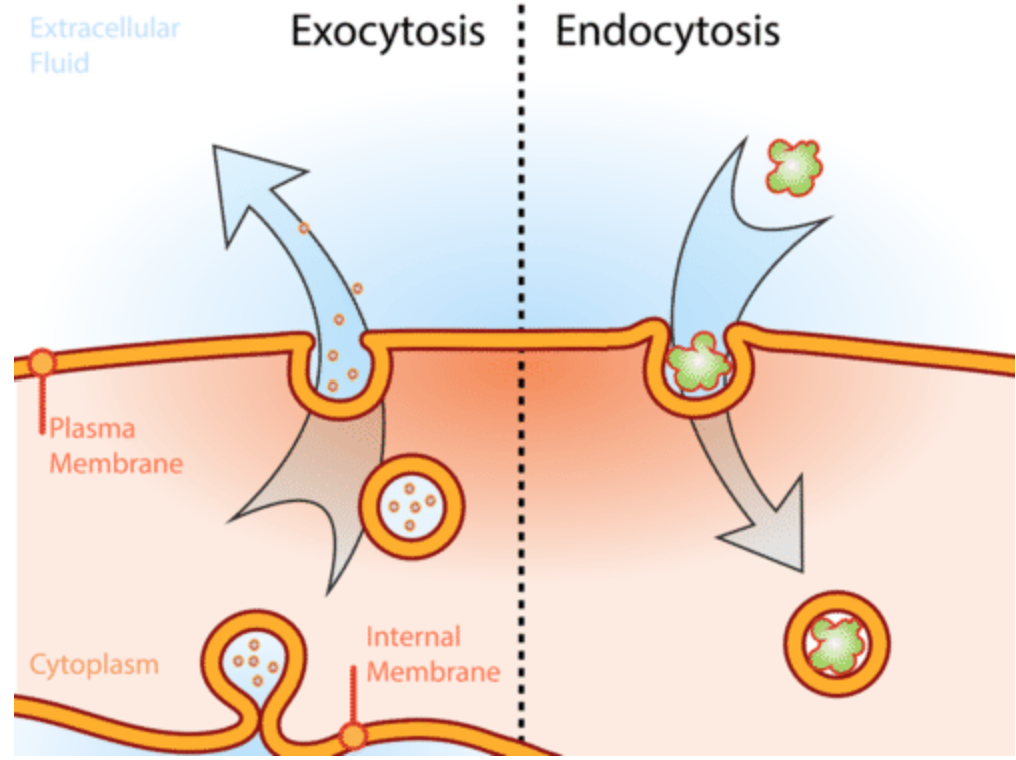
What is endocytosis
The process by which large substances or bulk materials enter the cell without crossing the membrane
How does endocytosis work
The cell membrane invaginates (folds in) to form a flask-shaped pocket that traps extracellular material.
This pocket then pinches off to form an intracellular vesicle containing the material
What are the two main types of endocytosis
Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis
What is phagocytosis
The process by which the cell engulfs solid particles (like bacteria or cell debris). The vesicle is usually sent to a lysosome for digestion
What is pinocytosis
The process by which the cell takes in liquids or dissolved substances. It allows for faster uptake than through individual protein channels
What is receptor-mediated endocytosis
A selective form of endocytosis that uses specific receptor proteins on the membrane to recognise and capture target molecules
What are clathrin-coated pits
Specialised membrane regions lined with the protein clathrin, which help form vesicles during receptor-mediated endocytosis
Why is receptor-mediated endocytosis important
It allows the cell to control what enters, ensuring specific substances (like hormones or nutrients) are taken in.
What is exocytosis
he process by which large substances (or bulk amounts of smaller ones) exit the cell without crossing the membrane.
How does exocytosis occur
Vesicles (usually from the Golgi apparatus) fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents into the extracellular environment
What happens to the vesicle membrane after exocytosis
The vesicle’s phospholipids become part of the cell membrane, replacing those lost during endocytosis
Why is exocytosis important
It allows the cell to secrete materials (like hormones, enzymes, or waste) and helps maintain the cell membrane’s surface area