Lecture 6: Postmortem Changes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are postmortem changes the result of?
autolysis (decomposition)
What changes occur prior to death and take minutes to hours to weeks to develop?
antemortem
What is autolysis?
the decomposition of cells which occurs due to loss of cellular integrity or breakdown of cells which occurs after death
How is autolysis minimized?
performing a post mortem evaluation and collection of tissues as close to the time of death as possible and fixing tissues in a fixative such as formalin at the time of collection
What tissues will autolyze quickly?
intestinal mucosa, brain, and spinal cord
What tissues has the ability to contract after death which can lead to artifacts?
striated muscle
When does rigor mortis set in and how long does it persist?
1-6 hours after death and persists for 1-2 days thereafter
Why should you cool a carcass and not freeze it?
cooling of the carcass slows autolysis, but freezing destroys tissue architecture and cellular integrity due to ice crystal formation
How can abundant adipose tissue in overweight or obeswe animals or thick wool cause rapidly progressing autolysis?
heat retention in the body longer
Why do febrile animals autolyze faster?
higher body temp
How can microbial flora affect post mortem decomposition?
gas production causing bloat of tissues and organs which can result in post mortem prolapse of the rectum, uterus, or protopsis of the eyes, even diaphragm can rupture
What are the variables in post mortem decomposition?
tissue
type of animal
cause of death
environmental temp
body temp
microbial flora
What is liver mortis/hypostatic congestion?
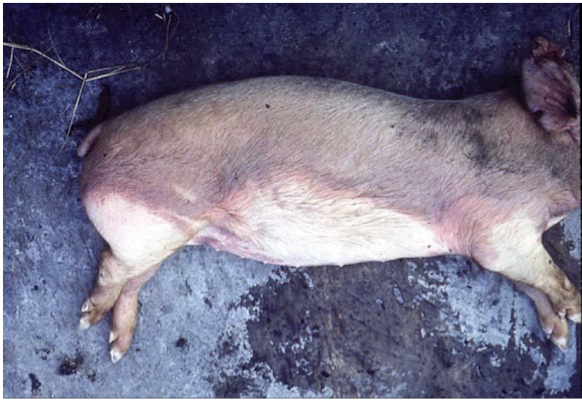
the gravitational pooling of blood after death which results in discoloration of tissues (can also be present in organs like the lungs)
True or false: postmortem lesions are differentiable from antemortem lesions.
false: postmortem lesions can mask antemortem lesions