unit 14 bio -Coordination and Response
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What do electrical impulses travel along?
Neurones
What is the mammalian nervous system made of?
CNS: brain and spinal cord; PNS: nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
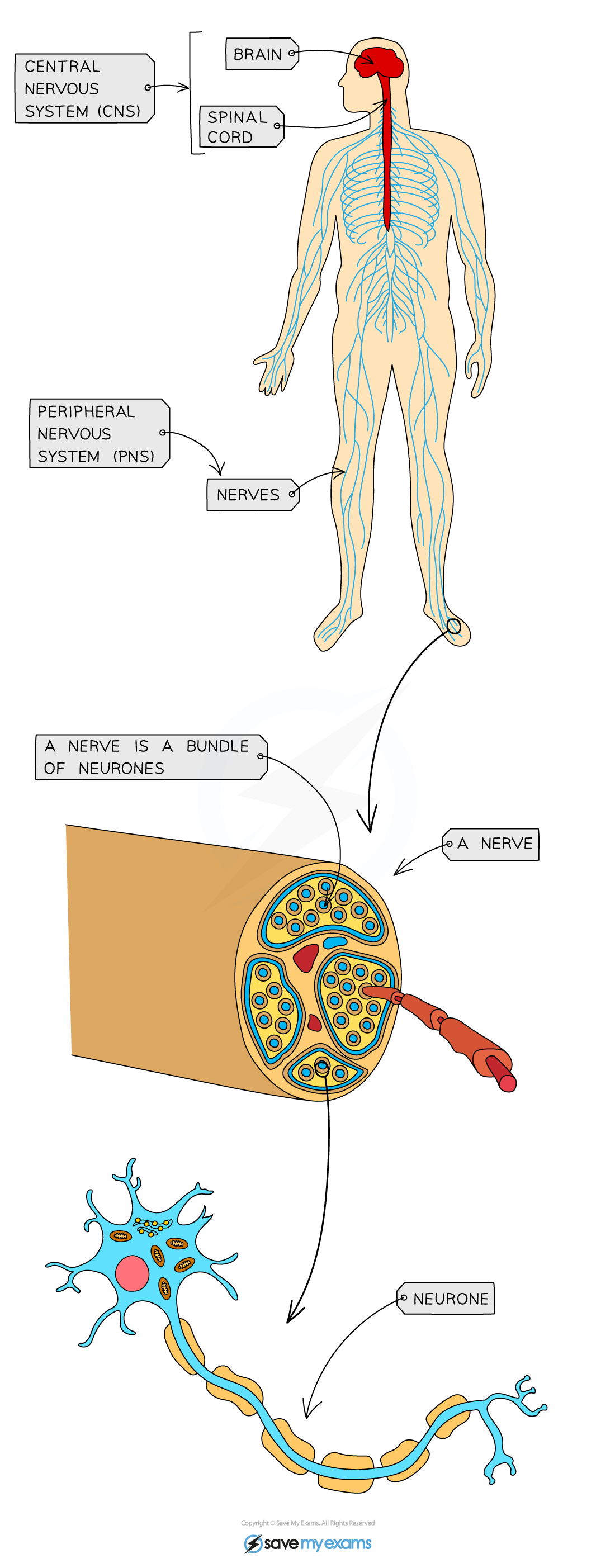
What is the role of the nervous system?
Coordination and regulation of body functions
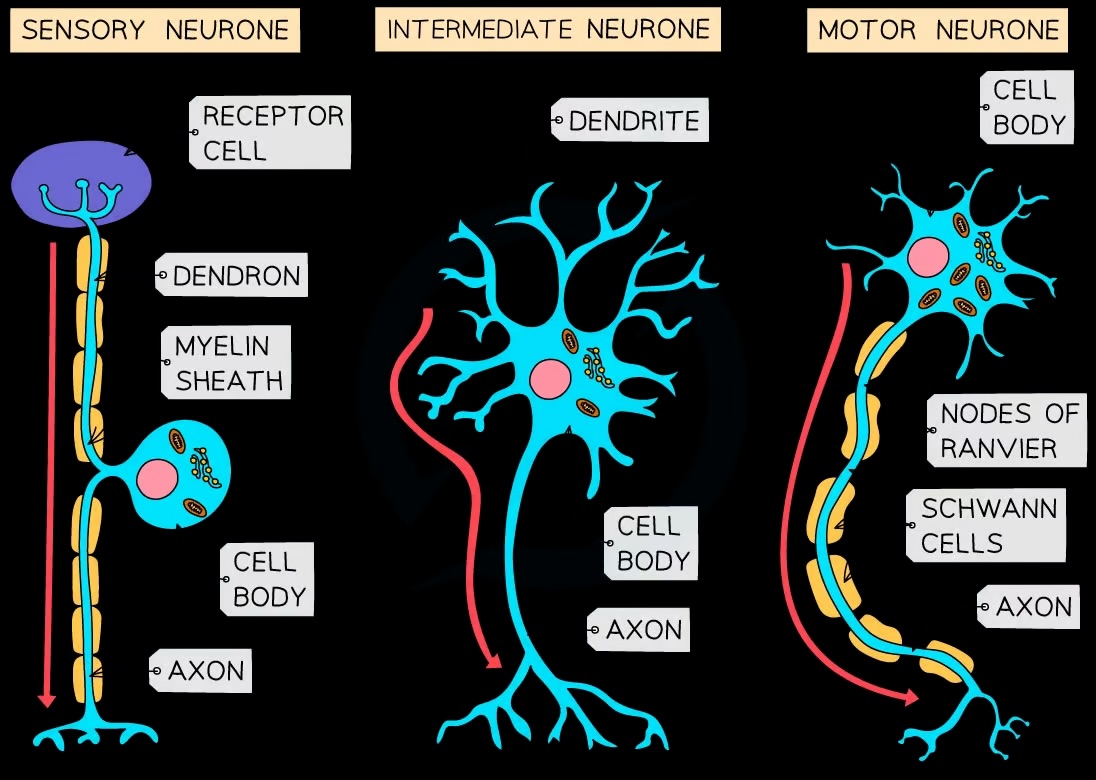
What types of neurones should you identify in diagrams?
Sensory, relay, motor neurones
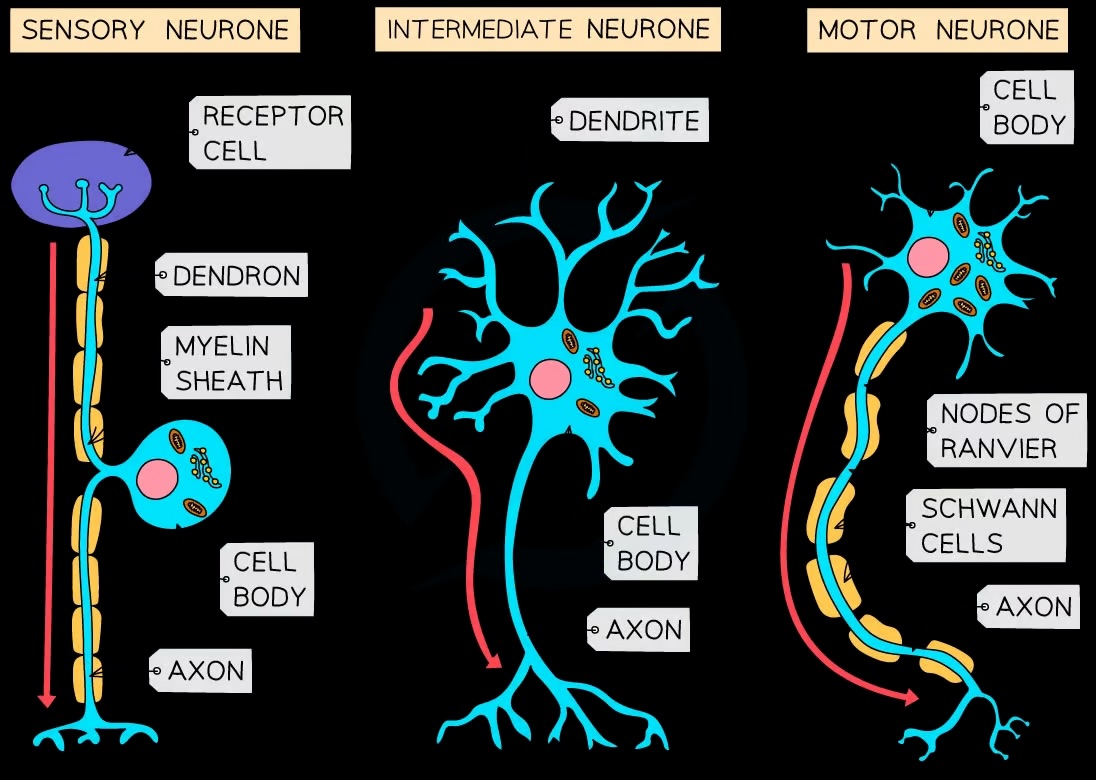
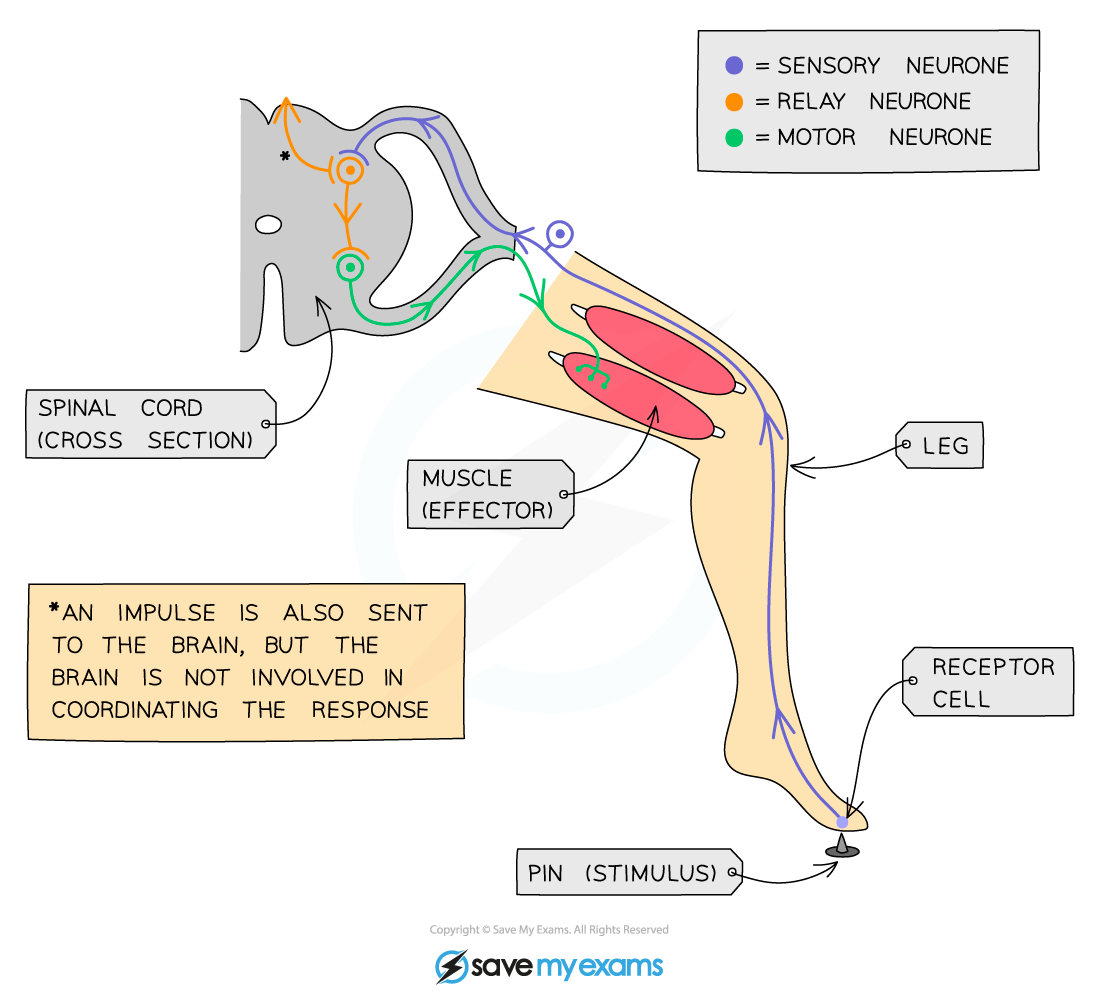
What are the components of a simple reflex arc?
Receptor, sensory neurone, relay neurone, motor neurone, effector
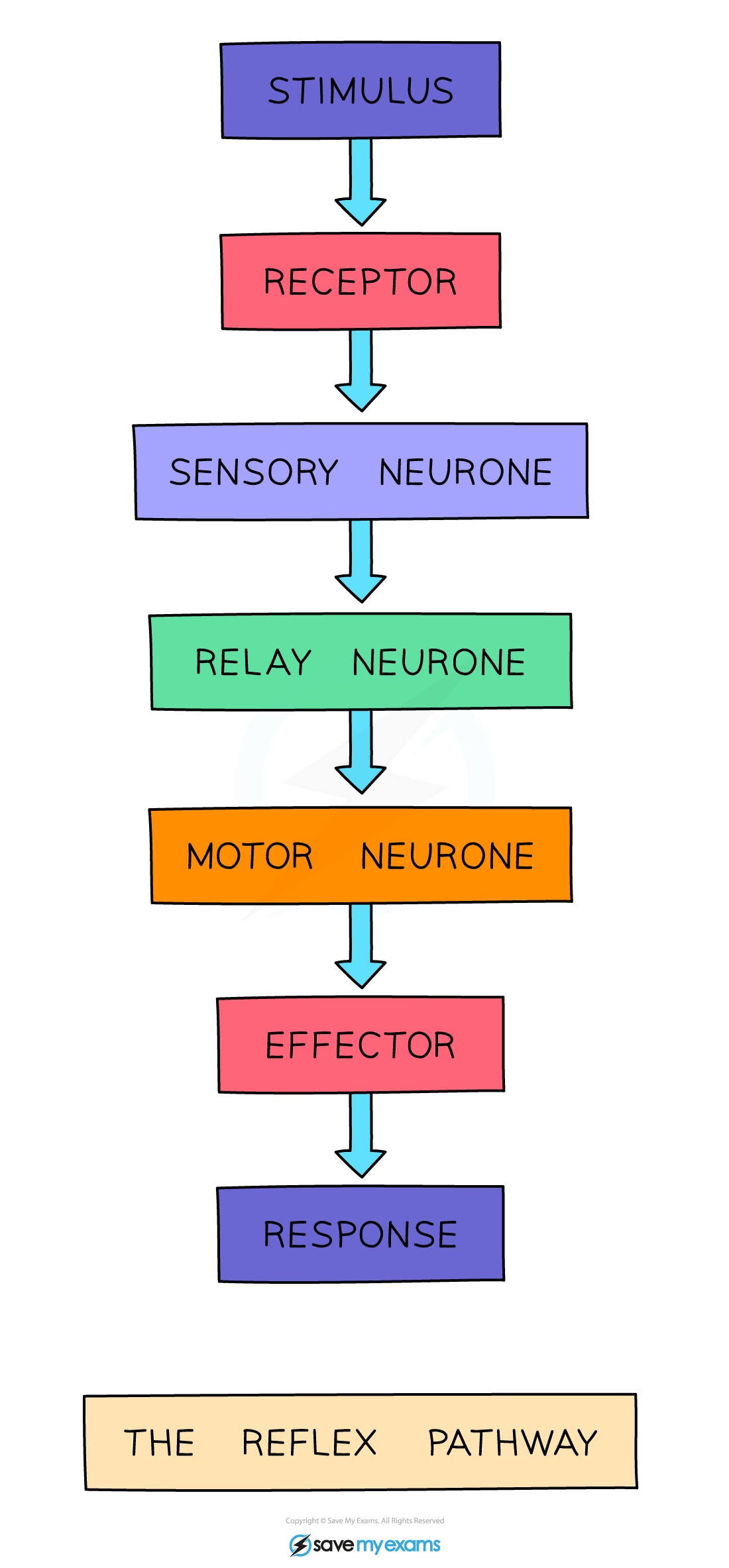
What is a reflex action?
An automatic, rapid response to stimuli involving effectors
What is a synapse?
A junction between two neurones
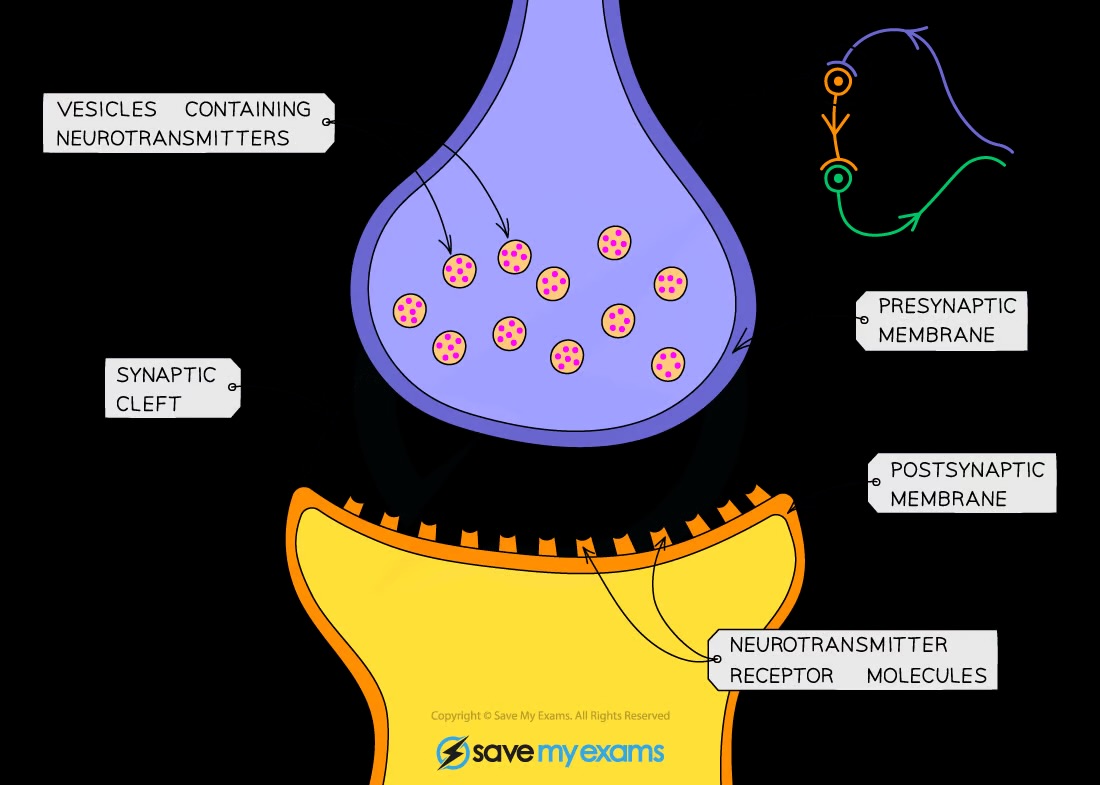
What is the structure of a synapse?
Vesicles with neurotransmitters, synaptic gap, receptor proteins
How do synapses work?
Impulse triggers neurotransmitter release into the gap, diffusion across the gap, binding to receptors, new impulse in next neurone
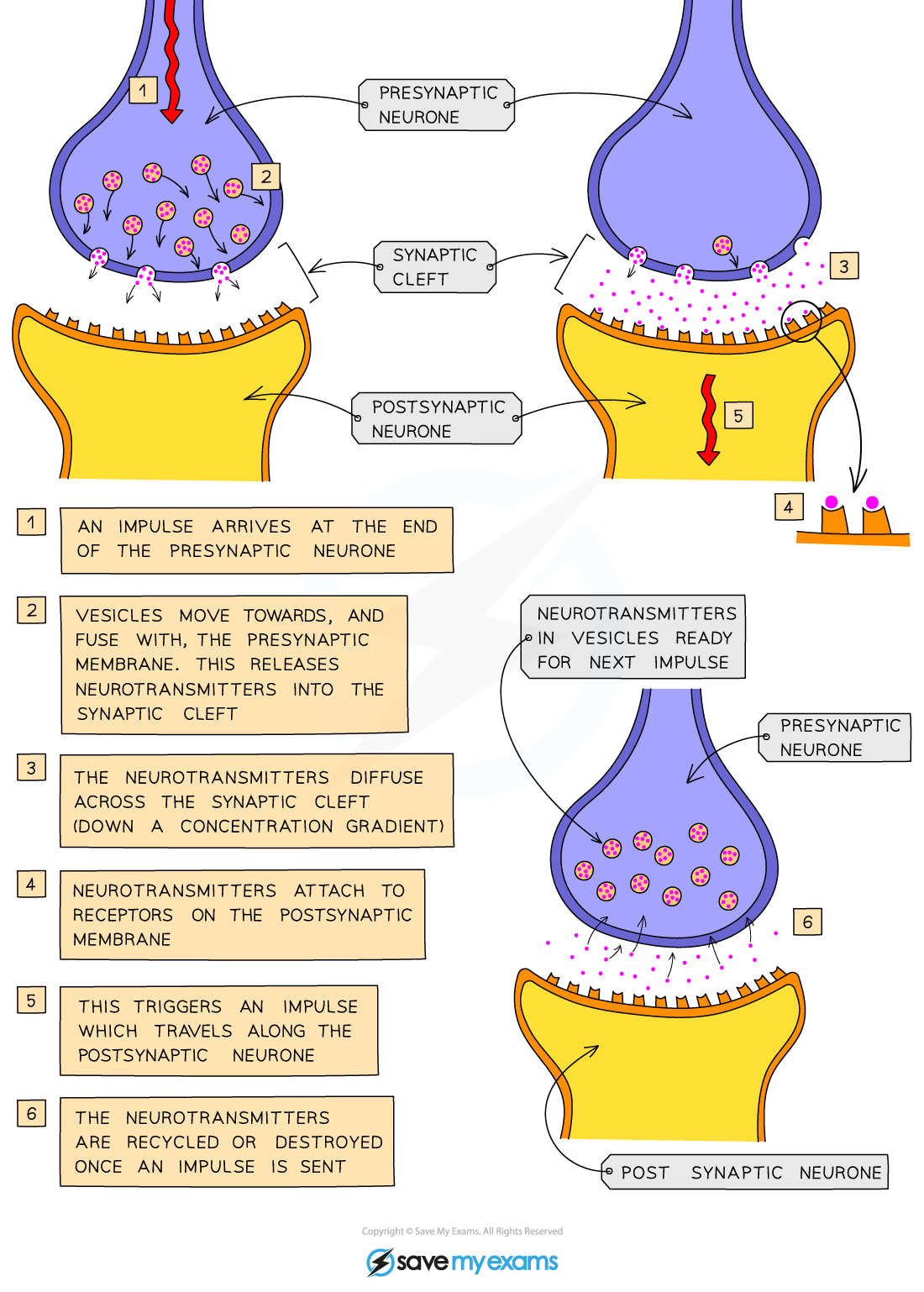
Why do impulses only travel one way at synapses?
Because neurotransmitters are only released from one side
What are sense organs?
Groups of receptor cells that detect light, sound, touch, temperature, and chemicals
What parts of the eye should you identify in diagrams?
Cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve, blind spot
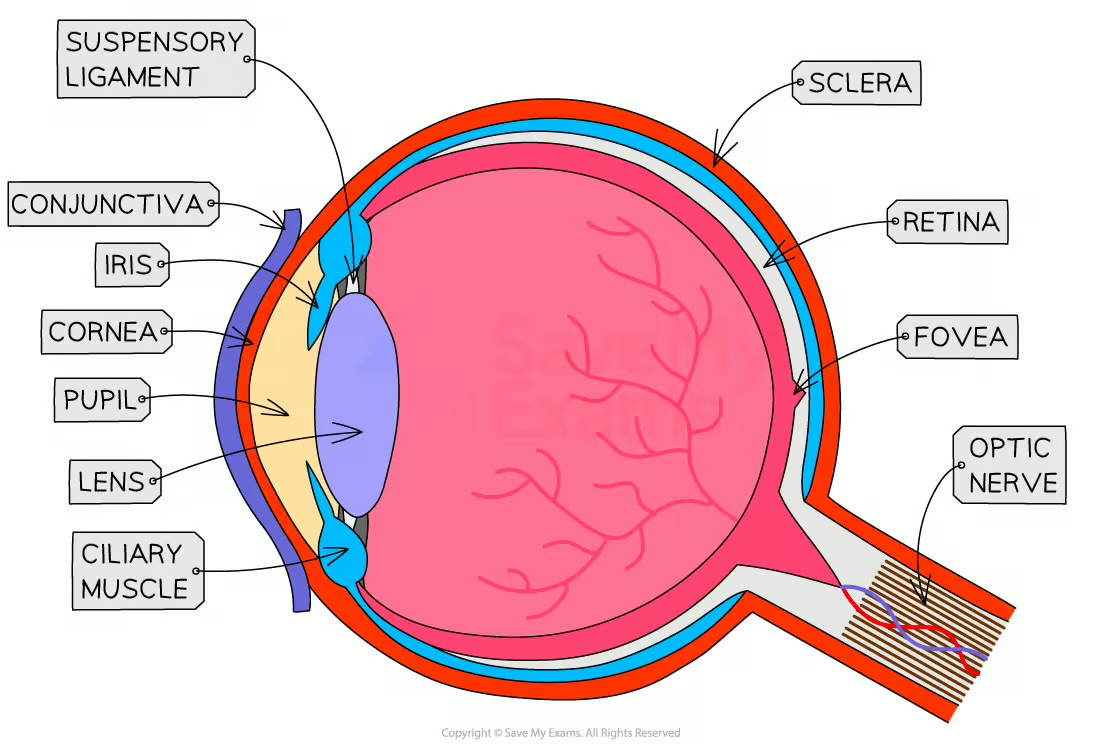
Functions of the eye parts?
Cornea refracts light; iris controls light entry; lens focuses light; retina detects light and colour; optic nerve sends impulses
What is the pupil reflex?
Pupil changes size with light intensity
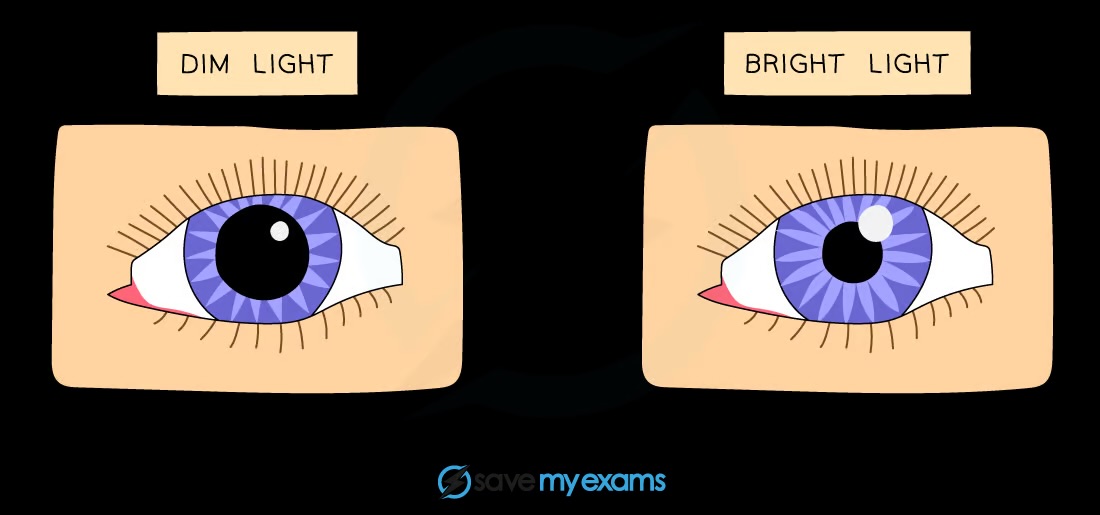
How does the pupil reflex work?
Circular and radial muscles act antagonistically

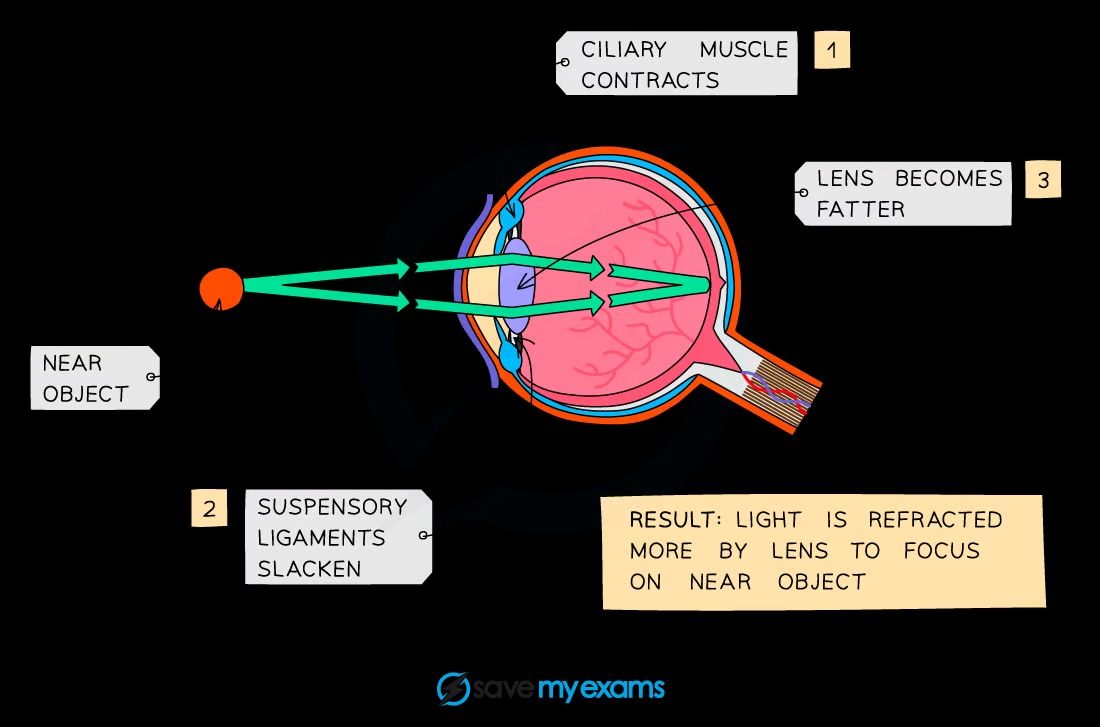
What is accommodation?
Focusing on near or distant objects by changing lens shape using ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments
Where are rods and cones found in the retina?
Rods are spread out; cones are concentrated at the fovea
What are rods and cones for?
Rods: night vision; cones: colour vision
What is the function of the fovea?
Area of sharpest vision with many cones
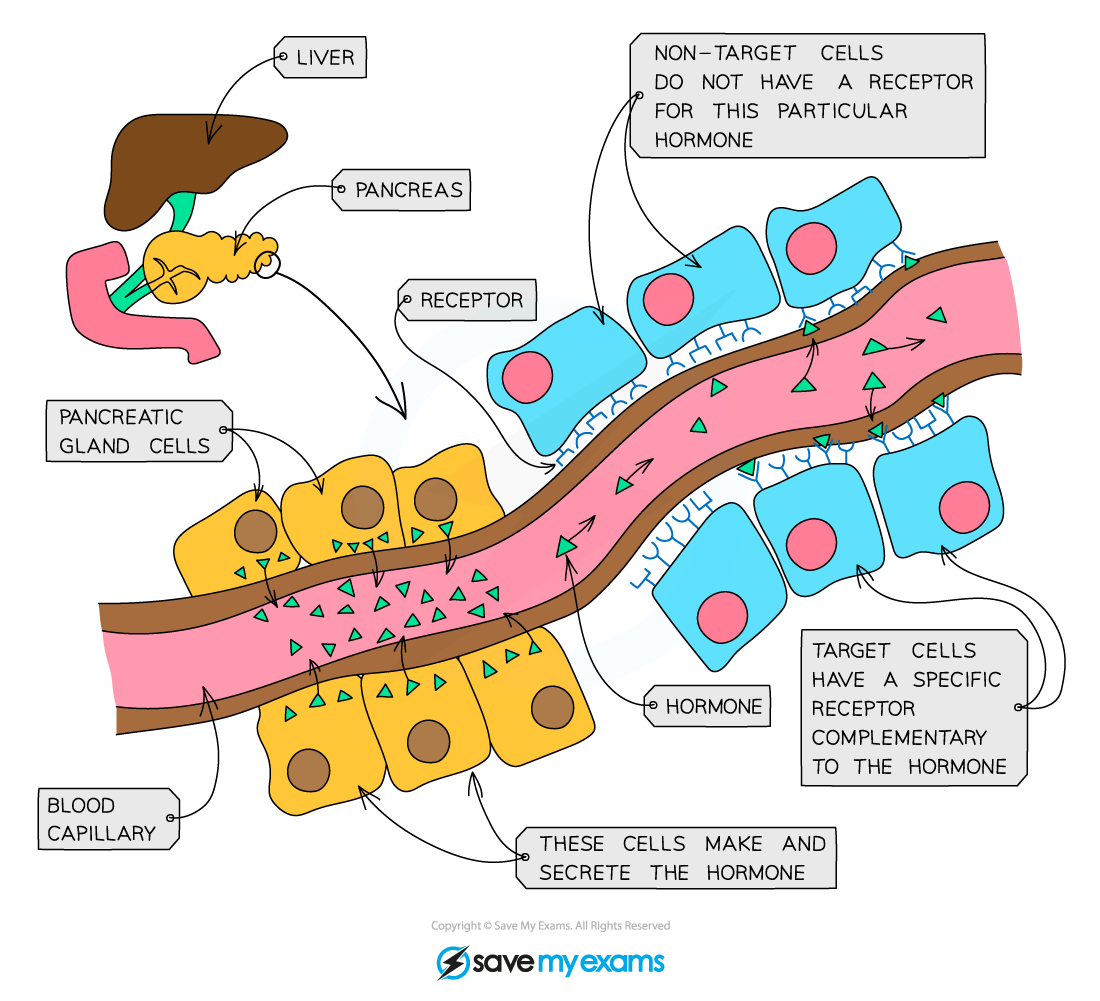
What is a hormone?
A chemical substance made by a gland, carried in the blood, affecting target organs
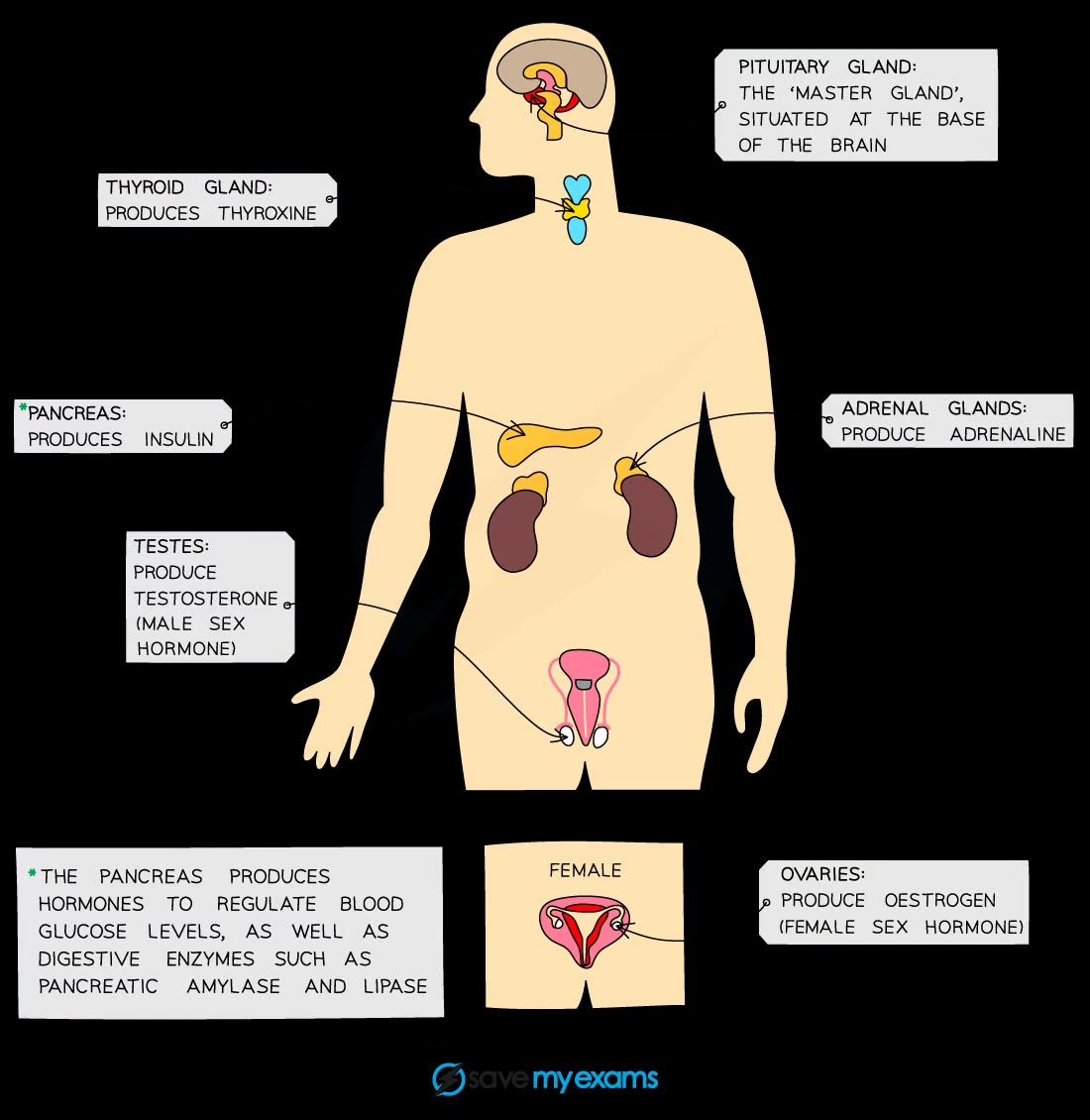
Endocrine glands and hormones to know?
Adrenal glands: adrenaline; pancreas: insulin; testes: testosterone; ovaries: oestrogen
What are the effects of adrenaline?
Increases breathing rate, heart rate, pupil diameter
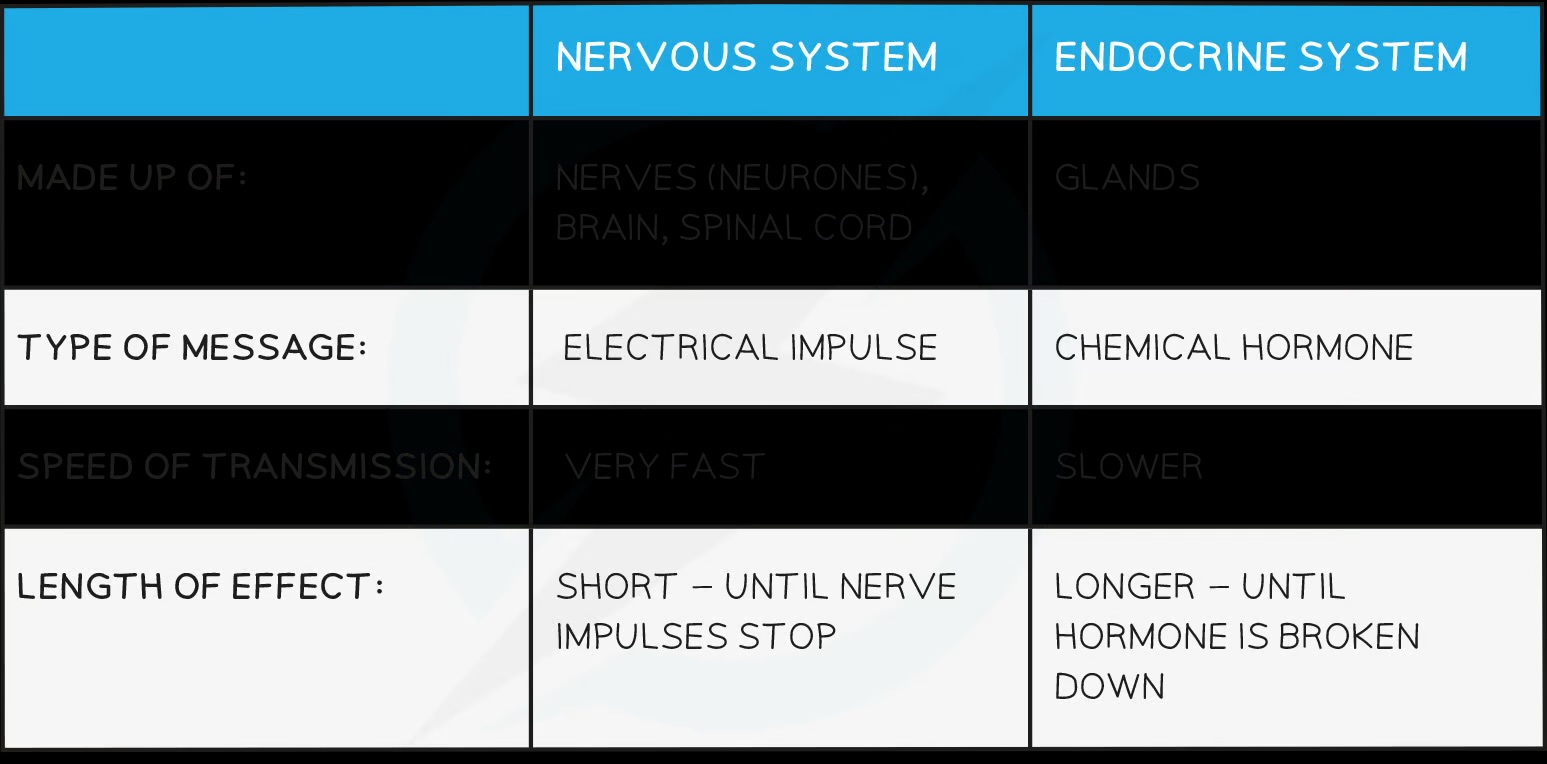
Compare nervous and hormonal control
Nervous: fast and short-lived; hormonal: slow and long-lasting
What does the pancreas also secrete (besides insulin)?
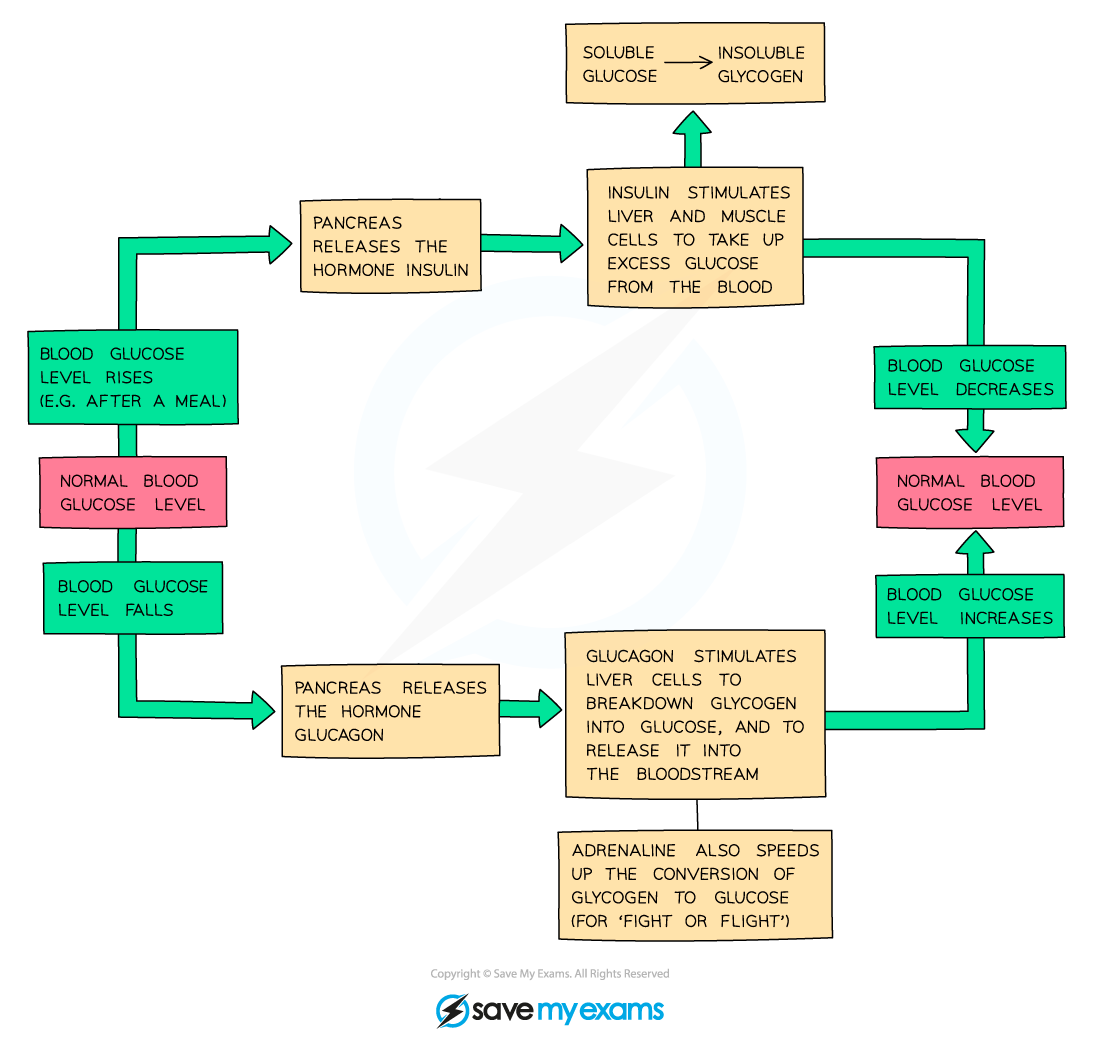
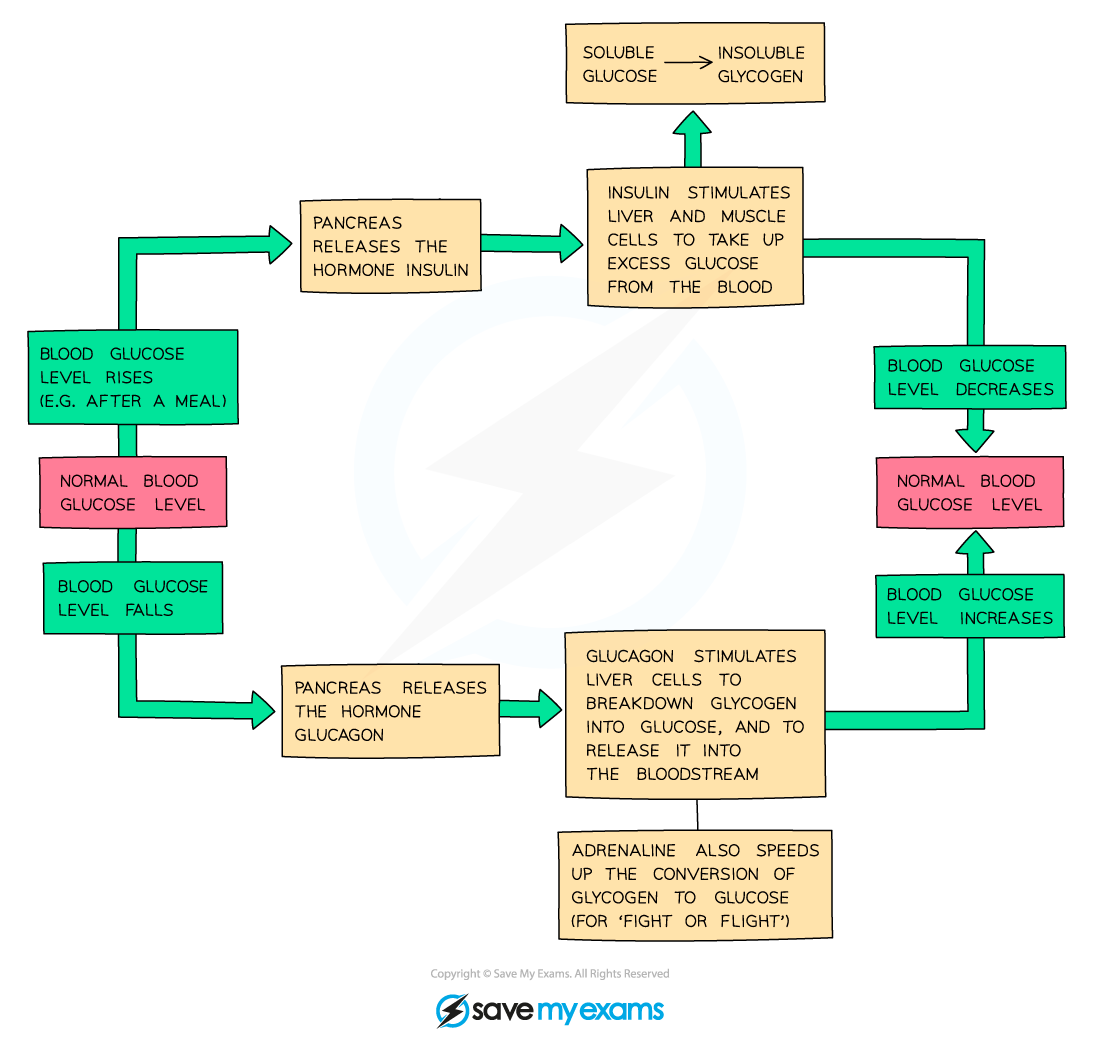
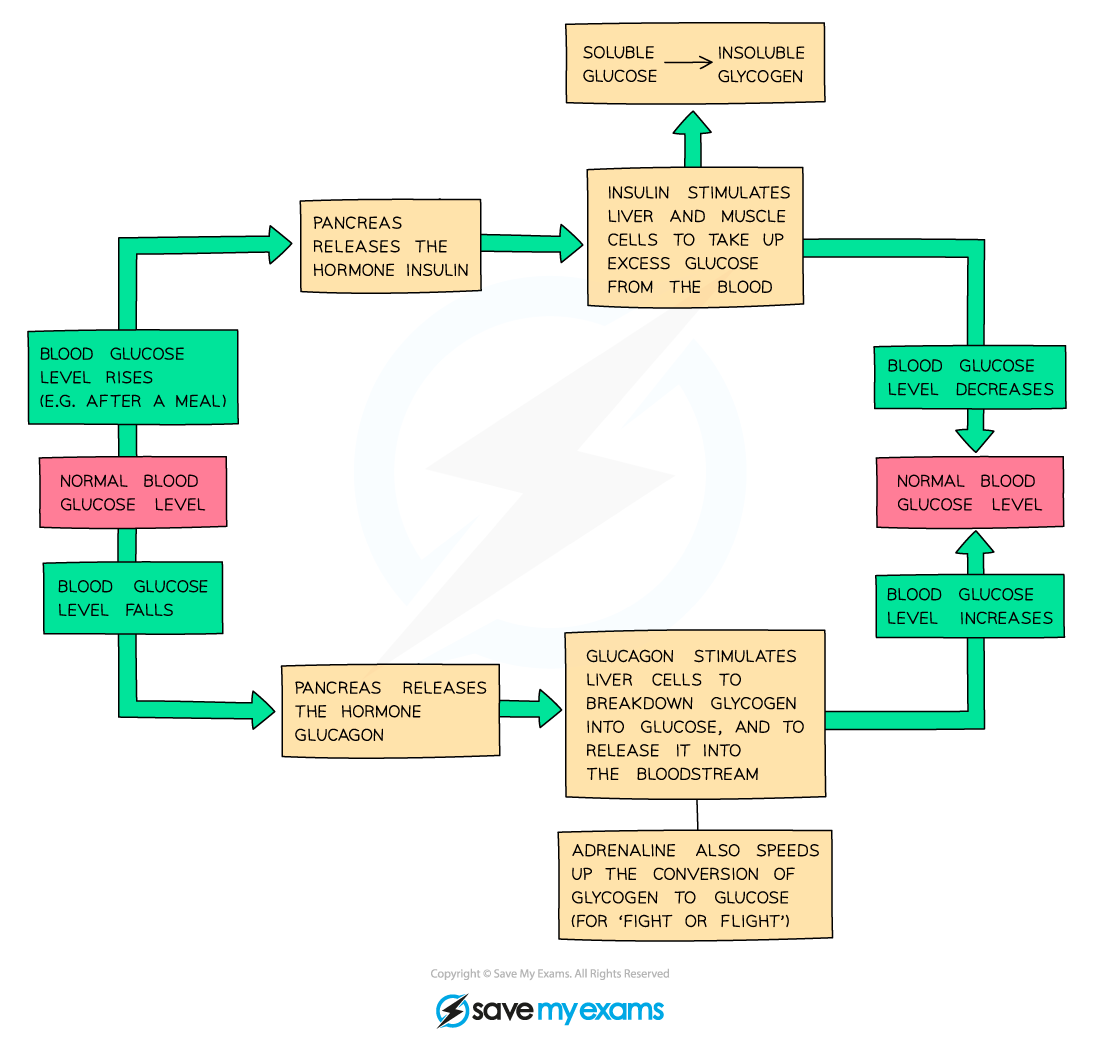
Glucagon
How does adrenaline affect metabolism?
Increases blood glucose and heart rate
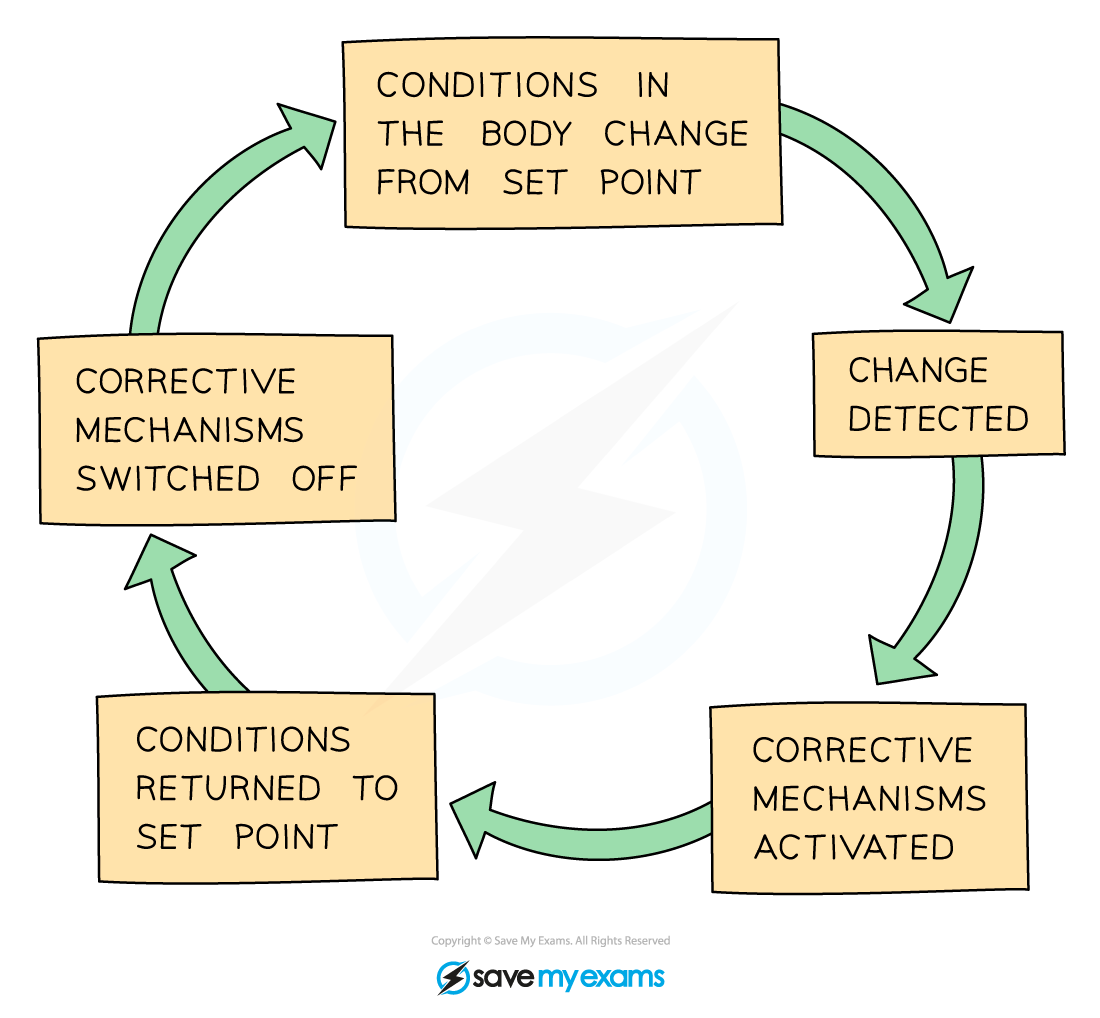
What is homeostasis?
Keeping the internal environment constant
What does insulin do?
Lowers blood glucose levels
How does negative feedback maintain balance?
Detects changes, triggers responses to return to set point
How is blood glucose controlled?
Liver stores/releases glucose; insulin lowers, glucagon raises
How is Type 1 diabetes treated?
Insulin injections
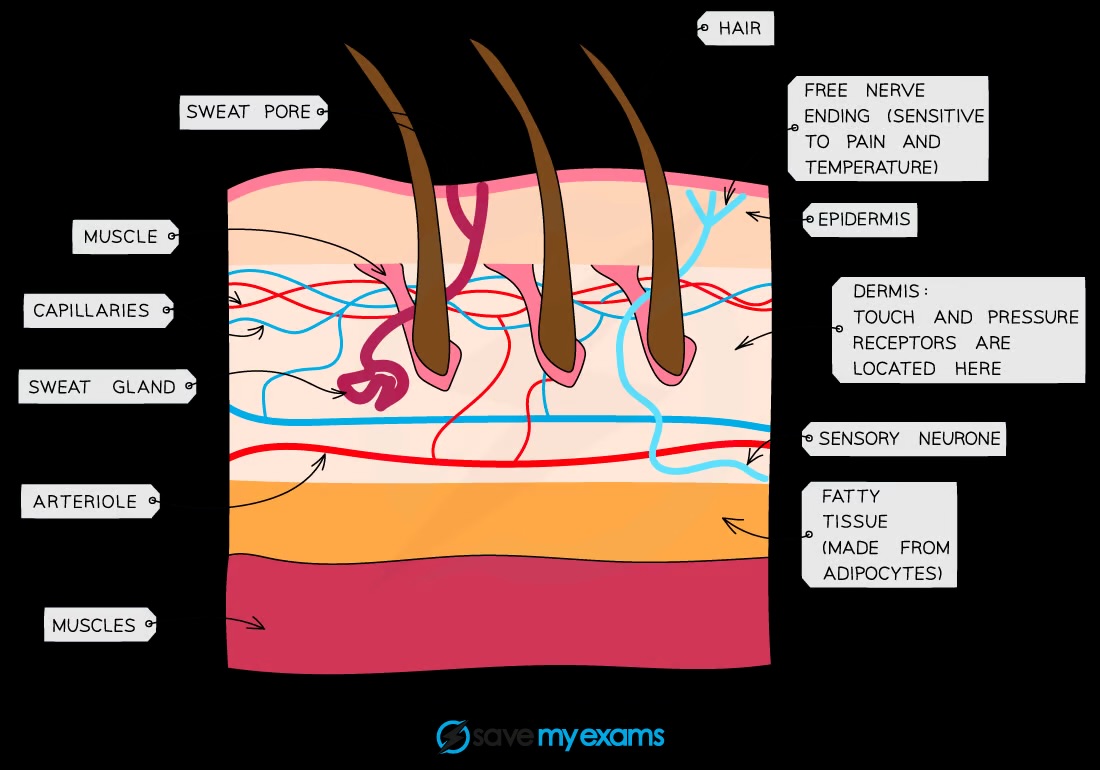
What skin structures should you identify in diagrams?
Hairs, erector muscles, sweat glands, receptors, sensory neurones, blood vessels, fat
How is body temperature maintained?
Insulation, sweating, shivering, brain control
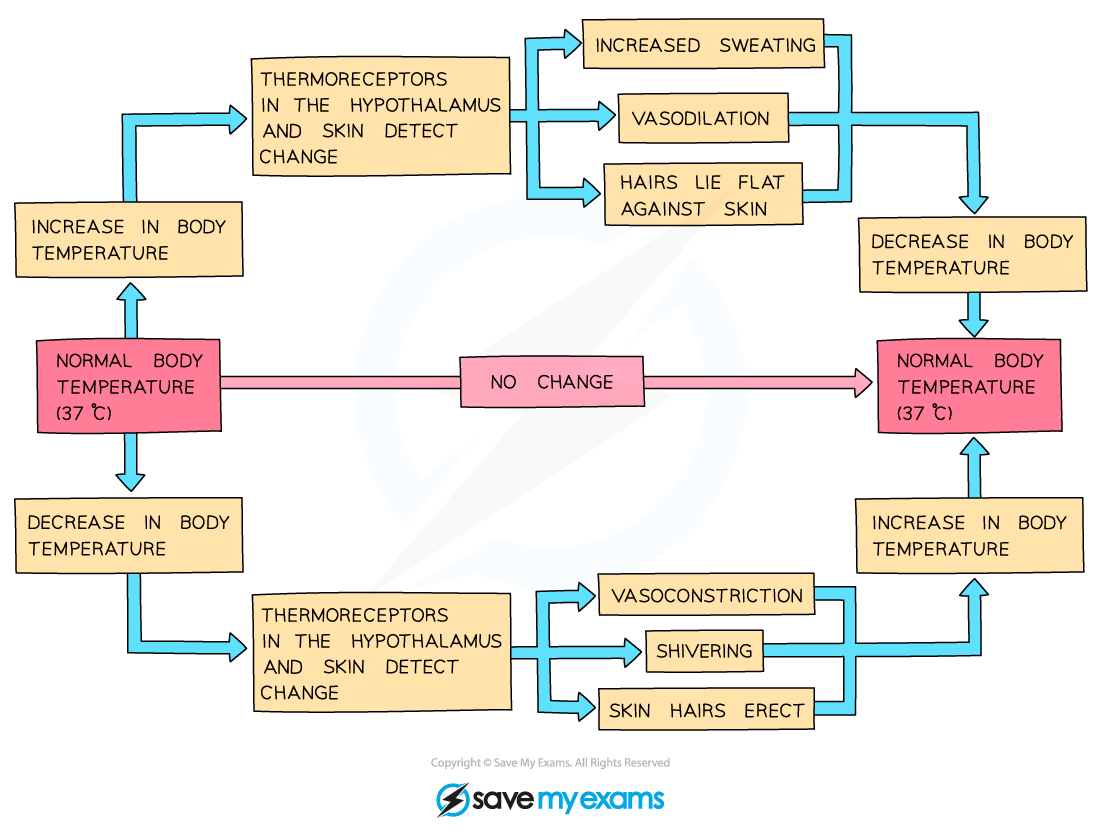
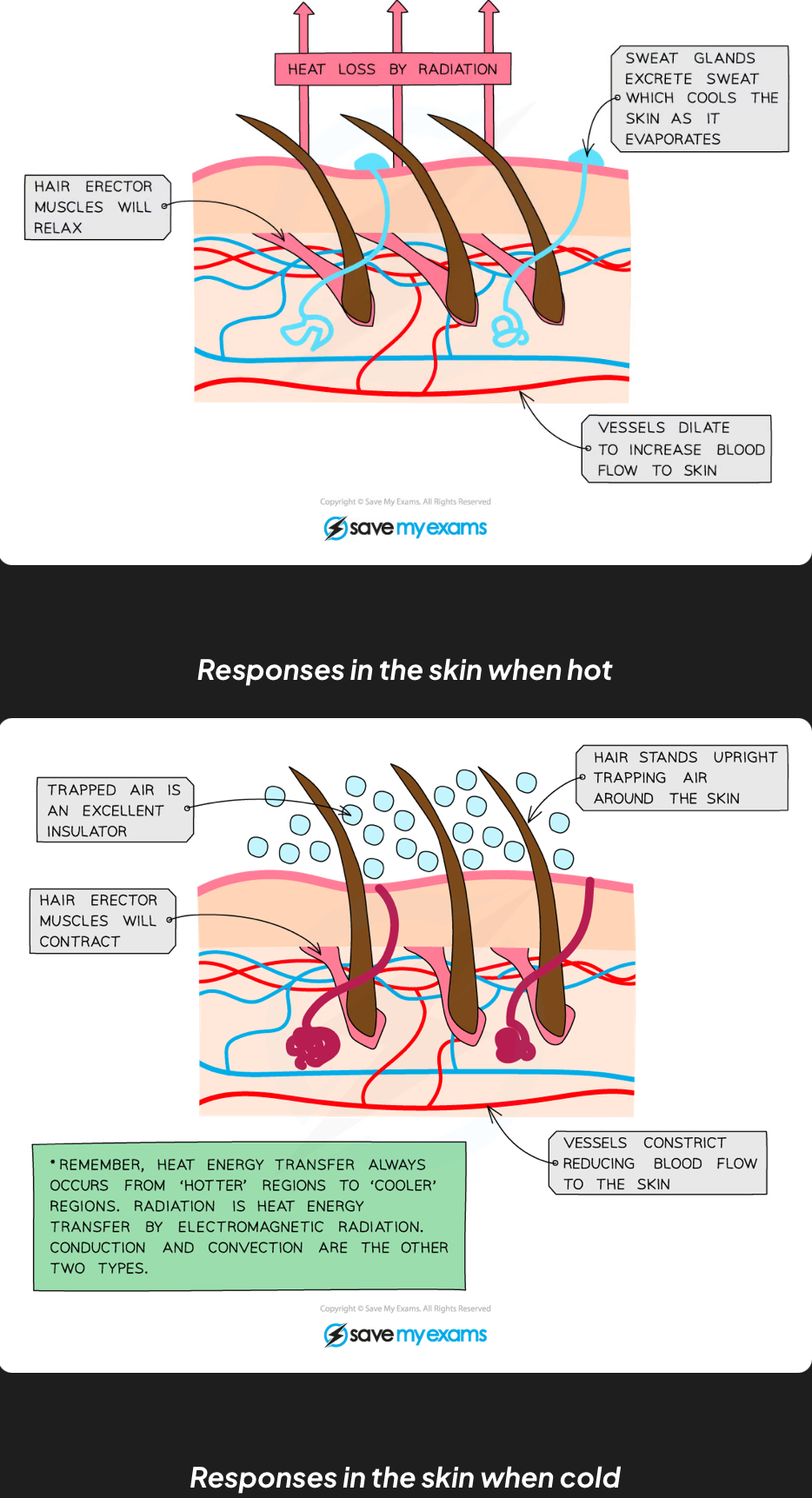
What are vasodilation and vasoconstriction?
Vasodilation increases heat loss; vasoconstriction reduces it
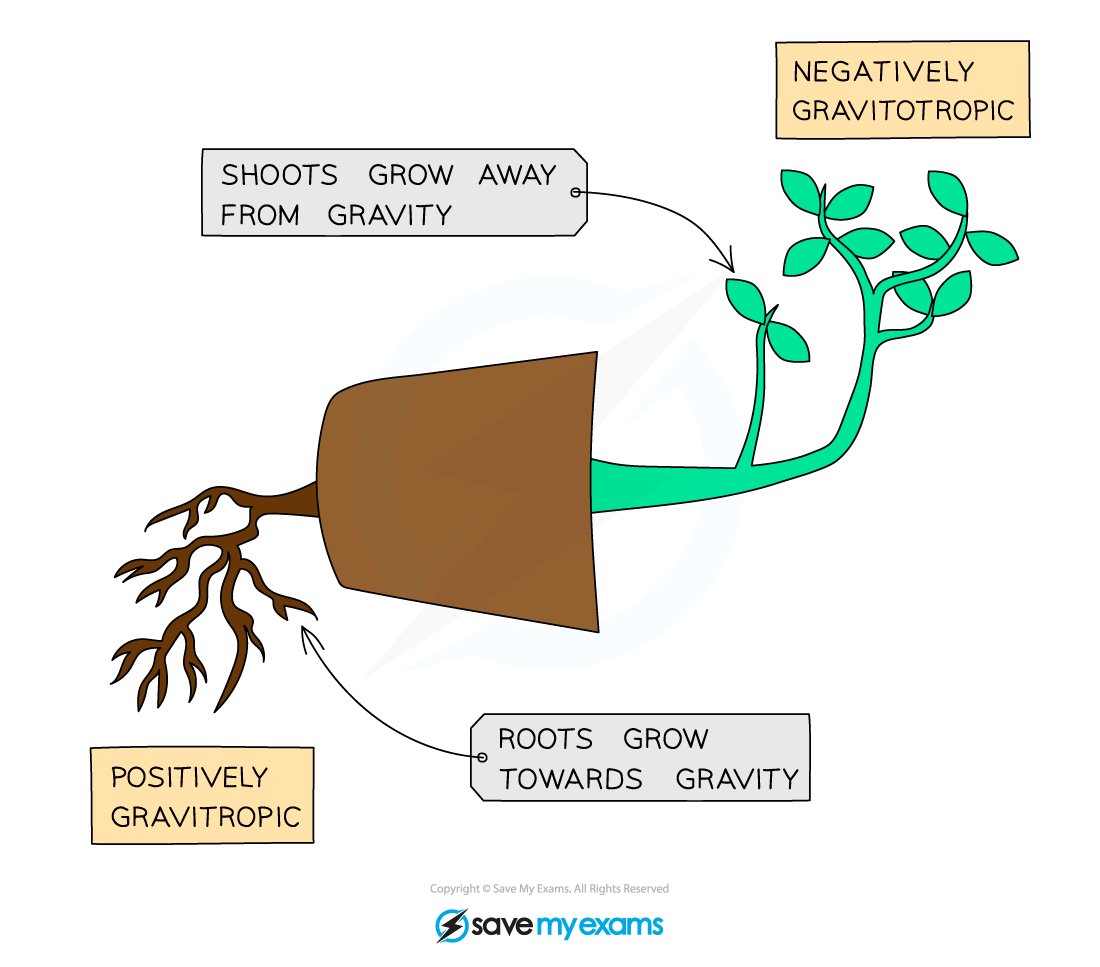
What is gravitropism?
Growth response to gravity
What is phototropism?
Growth response to light
How can you investigate tropisms?
By observing growth direction in shoots and roots
How are tropisms controlled?
Chemically, using hormones like auxin
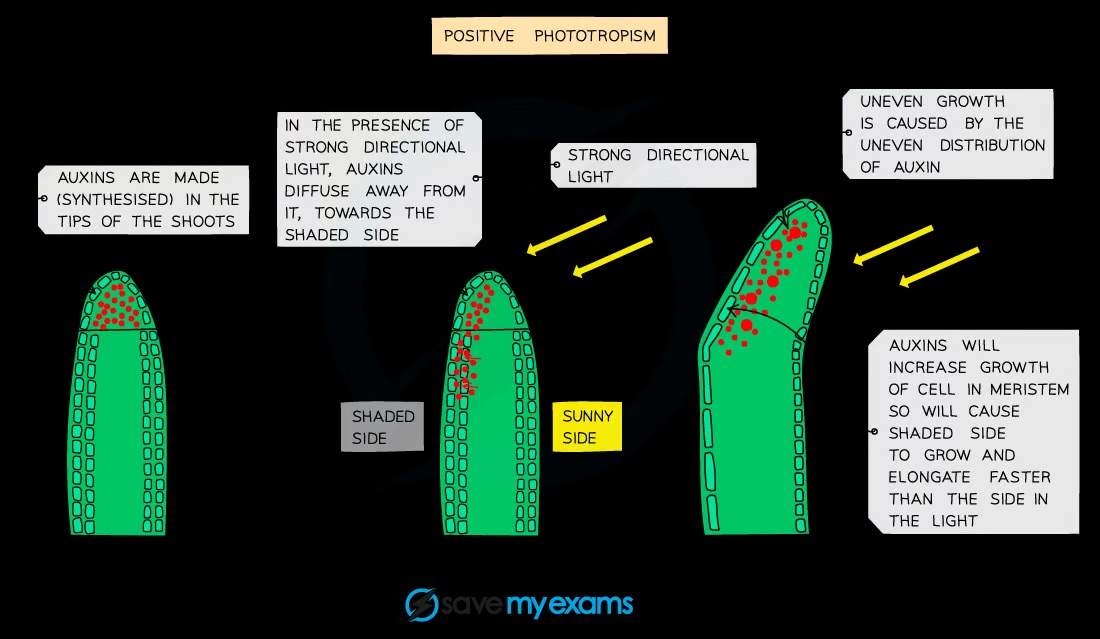
What does auxin do?
Made in the shoot tip; diffuses through plant; uneven distribution due to light or gravity; stimulates cell elongation