MUSCULOSKELETAL EXAMINATON HIP AND PELVIS (P2: HIP Objective Exam)
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
If the hip is affected, the weight is lowered carefully on the ___________ side and the knee _______ slightly to absorb the shock.
If the hip is affected, the weight is lowered carefully on the affected side and the knee bends slightly to absorb the shock.
The length of the step on the affected side is (shorter/longer?)
The length of the step on the affected side is shorter
True or False:
If the hip is stiff, the entire trunk and affected leg swing forward together.
True
In standing, the patient commonly has the hip slightly _______ if there is pain in the hip
In standing, the patient commonly has the hip slightly flexed if there is pain in the hip
What muscles are tight when there is pathology of the hip?
adductors
iliopsoas
piriformis
tensor fasciae latae
rectus femoris
hamstrings
What muscles are weak when there is pathology of the hip?
gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus
Weak abductors lead to what gait?
In this gait deviation there is a lateral pelvic shift of how many centimeters?
The lateral pelvic shift is toward which side (WB/NWB)?
This gait may be accompanied by trunk ____________
Trendelenburg gait / Abductor lurch / May West gait
2 cm (0.8 inches)
Toward weight bearing side
This gait may be accompanied by trunk inclination
Internal hip pathology or a flexion contracture may lead to a ____________
pelvic wink or butt wink
It may be due to muscle tightness (i.e., iliopsoas) or structural change (e.g., anteversion angle of acetabulum or femoral neck, diameter of femoral neck, or depth of acetabulum)
Pelvic Wink / Butt wink :
excessive (anterior/posterior?) pelvic rotation in the axial plane
toward the affected hip as the patient flexes the hip and knee in an attempt to obtain terminal hip extension in the opposite leg
How many degrees of pelvic rotation
Pelvic Wink / Butt wink :
excessive posterior pelvic rotation in the axial plane
toward the affected hip as the patient flexes the hip and knee in an attempt to obtain terminal hip extension in the opposite leg
more than 40°
Compensation of the trunk for hip conditions:
(B) Hip flexion contracture = Excessive Trunk ________
Weak hip extensors = Trunk moves (backward/forward?)
Compensation of the trunk for hip conditions:
(B) Hip flexion contracture = Excessive Trunk extension
Weak hip extensors = Trunk moves backward
If the lateral rotators are significantly stronger than the medial rotators, as is normally the case what is the result?
Excessive toe-out
If the patient uses a cane, it should be held in the (opposite/same?) side as the affected hip
Proper use of the cane can decrease the load on the hip by how many percent
If the patient uses a cane, it should be held in the opposite side as the affected hip
40%
Posterior rotation of the innominate bone causes what type of leg rotation?
Lateral Rotation
True or False:
Tightness of the iliopsoas can cause deviation of the spine to the opposite side.
False:
Tightness of the iliopsoas can cause deviation of the spine to the same side
True or False:
Symmetrical skinfolds may indicate anatomical variations such as pelvic obliquity, leg-length discrepancy, developmental dysplasia of the hip, or muscle atrophy.
False:
Asymmetrical skinfolds may indicate anatomical variations such as pelvic obliquity, leg-length discrepancy, developmental dysplasia of the hip, or muscle atrophy.
Traumatic posterior hip dislocation:
Limb is shortened/lengthened?
Limb is adducted/abducted?
Limb is medially/laterally rotated?
What femoral bone structure is prominent?
Traumatic posterior hip dislocation:
Limb is shortened
Limb is adducted
Limb is medially
Greater Trochanter
True or False:
If the piriformis (or other lateral rotators) is in spasm, then the affected leg will be laterally rotated when the patient is standing.
False:
If the piriformis (or other lateral rotators) is in spasm, then the affected leg will be laterally rotated when the patient is relaxed and lying in supine.
Anterior hip dislocation:
Limb is adducted/abducted?
Limb is medially/laterally rotated?
Increased pressure in what triangle?
Anterior hip dislocation:
Limb is abducted
Limb is laterally rotated
Femoral Triangle
With what type of fractures is the limb is shortened and laterally rotated?
Intertrochanteric Fractures
Conditions that cause structural changes at the hip:
Hip Angulation Deformity
Congenital Hypoplasia
Femoral growth plate problems
developmental disorders
Normal ROM values for the HIP (NORKIN)
Hip flexion = 0-120
Hip extension = 0-20
Hip abduction = 0-40
Hip adduction = 0-20
Hip medial rotation = 0-45
Hip lateral rotation = 0-45
Lumbar Flexion = 0-80
Lumbar Extension = 0-25
Lumbar Lateral Flexion = 0-35
True or False:
normal pattern of contraction = gluteus maximus followed by the erector spinae on the same side and the hamstrings
False:
normal pattern of contraction = gluteus maximus followed by the erector spinae on the opposite side and the hamstrings
If sharp anterior groin pain that may refer to the gluteal or trochanteric region is elicited on full flexion, adduction and medial rotation, the pain may be the result of
Anterolateral impingement of the femoral neck on the anterior acetabular rim (FAI)
If medial rotation is limited relative to other movements, it is predictive of mild to moderate ___________
If medial rotation is limited relative to other movements, it is predictive of mild to moderate osteoarthritis
Cam-type impingement:
also called an _____________ injury as the bony deformity at the femoral head-neck junction enters the joint when the hip flexes
commonly due to impingement of a large aspherical head in a tight ___________
common in young adult (males/females?)
Age range:
Increased stress at the ___________
precursor to ____________
Cam-type impingement:
also called an inclusion type injury as the bony deformity at the femoral head-neck junction enters the joint when the hip flexes
commonly due to impingement of a large aspherical head in a tight acetabulum
young adult males
20 to 30 years of age
Increased stress at the symphysis pubis
precursor to athletic pubalgia
Femoral head abnormality = cam type
Pincer type (rim) impingement
Also called a _____________ -type
Abnormal (femoral head/acetabulum)
Commonly seen in older (females/males)?
Age range
overcoverage/undercoverage of the femoral head?
prominent ____________?
Pincer type (rim) impingement
Also called a impaction -type
Abnormal acetabulum
Commonly seen in older females
40+ y/o
overcoverage of the femoral head
prominent acetabular rim
In the presence of acetabular retroversion or decreased femoral anteversion,
hip flexion in the neutral line is limited to as little as how many degrees?
full range is accomplished if the hip is allowed to rotate _________ and __________
__________ rotation may exceed 60°, with _________ rotation limited
In the presence of acetabular retroversion or decreased femoral anteversion,
hip flexion in the neutral line is limited to as little as 90°
full range is accomplished if the hip is allowed to rotate laterally and abduct
Lateral rotation may exceed 60°, with medial rotation limited
True or False:
Pincer and cam types of FAI may occur in isolation or more rarely together
False:
Pincer and cam types of FAI may occur in isolation or more commonly together
If Pincer and cam types of FAI are not combined, which type of FAI is more common?
Cam-type FAI
Signs and symptoms of FAI:
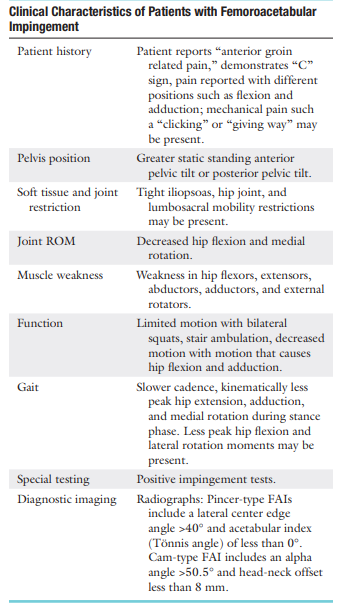
True or False:
In the presence of FAI, the ASIS moves early due to limited hip flexion as the lumbar spine flexes to allow more movement
True
For patients with FAI, If medial rotation is measured at ______ of flexion, medial rotation in the FAI patient will be limited
For patients with FAI, If medial rotation is measured at 90° of flexion, medial rotation in the FAI patient will be limited
Excessive end-range repetitions into medial rotation causes what type of FAI?
Excessive end-range repetitions into lateral rotation causes what type of FAI?
Cam-type
Pincer-type
True or False:
Iliopsoas impingement may also occur with extension and has been linked to acetabular labral tears.
False
Iliopsoas impingement may also occur with flexion and has been linked to acetabular labral tears.
This impingement is between the AIIS and the femoral neck can occur with knee flexion and hip extension and can lead to avulsion of the AIIS
Subspine Impingement
Subspine impingement results from an overactive ___________ in an ____________ patient
Subspine impingement results from an overactive rectus femoris in an adolescent patient
Iliopsoas impingement average age and gender preference =
Subspine (AIIS) impingements average age and gender preference =
Ischiofemoral impingement average age and gender preference =
Iliopsoas impingement average age and gender preference = 25-35 y/o , females more than males
Subspine (AIIS) impingements average age and gender preference = 14-30 y/o males more than females
Ischiofemoral impingement average age and gender preference = 51-53 y/o females more than males
Most common types of extra-articular impingements:
ischiofemoral impingement (IFI)
deep gluteal syndrome (DGS)
greater trochanteric-pelvic impingement
psoas impingement
This impingement occurs during extension in the narrow space between the ischial tuberosity and the lesser trochanter
may involve what muscle?
ischiofemoral impingement (IFI)
quadratus femoris
Pinching of contractile or neurological tissue can also occur between the lateral aspect of the ischium and the lesser trochanter of the proximal femur by 3 combined movements:
extension, adduction, and lateral rotation
These patients have chronic groin or lower buttock pain with no history of injury
Syndrome caused by limitation hip extension which can lead, over time, to increased load on L3-L4 and L4-L5 lumbar facets, leading to back pain
hip-spine syndrome
True or False
most end-range movements are painful and there may be a snapping sensation, crepitation, or locking. The mean femoral anteversion is lesser in patients with this problem.
False:
most end-range movements are painful and there may be a snapping sensation, crepitation, or locking. The mean femoral anteversion is greater in patients with this problem.
If the sciatic nerve is trapped along its course through the hip area, the patient will demonstrate an inability to sit for more than how many minutes?
more than 30 mins
Activities that hold the hip in _____ degrees of hip flexion can produce sciatic symptoms when the hamstrings are activated.
This is present in what syndrome?
Activities that hold the hip in 30 degrees of hip flexion can produce sciatic symptoms when the hamstrings are activated.
hamstring syndrome
True or False:
Patients with DGS are comfortable sitting, while long-stride walking can exacerbate the pain.
False:
Patients with IFI are comfortable sitting, while long-stride walking can exacerbate the pain.
Short stride or hip abduction alleviates the pain.
True or False:
Patients with IFI may also present with low back pain
True
With IFI there is _____ gluteal pain and distal pain _____ to the ischium
With IFI there is deep gluteal pain and distal pain lateral to the ischium
The condition is caused by narrowing between the ischium and the lesser trochanter, increased neck-shaft angle, or coxa breva
True or False:
If the foot is medially rotated and if the hip adducts during gait, the pelvic tilt associated with the rotary motion may contribute to greater trochanteric impingement against the ischium.
False:
If the foot is medially rotated and if the hip adducts during gait, the pelvic tilt associated with the rotary motion may contribute to lesser trochanteric impingement against the ischium.
Rare impingement in which a high greater trochanter (decreased neck-shaft angle—coxa vara) abuts against the ilium during hip abduction in extension.
greater trochanteric-pelvic impingement
greater trochanteric-pelvic impingement:
typically caused by what condition?
morphological change of what femoral structures?
leading to contact between the ilium and greater trochanter when the hip is extended in __________.
Patients may have a (shortened/lengthened?) involved leg and a positive _________ gait
The _______ sign will be positive
greater trochanteric-pelvic impingement:
Legg-Calvé-Perthes
morphological change of what femoral head and neck
leading to contact between the ilium and greater trochanter when the hip is extended in abduction
Patients may have a shortened involved leg and a positive Trendelenburg Gait
The “gear-stick shift sign” will be positive
coxa valga and femoral anteversion, which are associated with hip dysplasia, will also demonstrate limitation in what hip movements?
extension, adduction, and lateral rotation.
True or False:
For the hamstring syndrome (or ischial tunnel syndrome), the pain is lateral to the ischium and pain occurs at heel strike
True
in DGS, tenderness is usually felt over the piriformis muscle and retrotrochanteric area, and sitting for more than _______ minutes is painful.
20-30 mins
True or False
In addition to piriformis syndrome, the DGS may include involvement of fibrous bands, obturator internus/gemellus syndrome, and quadratus lumborum muscle
False:
In addition to piriformis syndrome, the DGS may include involvement of fibrous bands, obturator internus/gemellus syndrome, and quadratus femoris muscle
True or false:
When the patient abducts the leg, the same side ASIS tends to move first with an adduction contracture; this occurs earlier in the ROM.
False:
When the patient abducts the leg, the opposite ASIS tends to move first with an adduction contracture; this occurs earlier in the ROM.
If, during abduction, lateral rotation and slight flexion occur early in the movement what muscle is stronger than the gluteus medius/minimus?
Tensor Fascia Lata
True or False:
If lateral rotation occurs earlier in the ROM, the iliopsoas or piriformis may be overactive
False:
If lateral rotation occurs later in the ROM, the iliopsoas or piriformis may be overactive
If the pelvis tilts up at the beginning of movement, what muscle is overactive.
Quadratus Lumborum
True or False:
When the patient adducts the leg, the ASIS on the same side moves first. This movement occurs earlier in the ROM if there is an abduction contracture
True
True or False:
Asymmetric lateral rotation may indicate acetabular anteversion, femoral retrotorsion, or femoral head-neck abnormalities
False:
Asymmetric lateral rotation may indicate acetabular retroversion, femoral retrotorsion, or femoral head-neck abnormalities
Loss of medial rotation is one of the first signs of ________ hip pathology
Loss of medial rotation is one of the first signs of internal hip pathology
If, in supine lying, the patient demonstrates enough lateral rotation that the lateral border of the foot touches the table, there is probably a lax ________capsule or hip _________
If, in supine lying, the patient demonstrates enough lateral rotation that the lateral border of the foot touches the table, there is probably a lax anterior capsule or hip retroversion
opposite for limited lateral rotation
MMT TESTING:
HIIISSLOOOPPP
ROM:
NOOOORKINNN
Test adductors with hip flexed to 30o to 45o = optimal test position
This test is called wat?
Thigh Adductor Squeeze Test
Test bilateral adductors with knees extended
Most diagnostic of the adductor tests
Bilateral Adductor Test
Strength of the hamstrings
Pt in crook-lying, resting on elbows
Pt then lifts buttocks off table maintaing body weight on elbows and heels
Alternately lift good leg and affected leg
(+) pain at ischial origin or hamstrings pr pelvic “collapse” or rotation = weak hamstrings
Supine Plank Test
Special Tests for Hip Pathology
Patrick’s Test
Craig’s Test
Hip Scour (Grind) Test (Flexion- Adduction Test
Lateral FABER Test (yellow)
Log Roll Test
Anterior Labral Tear Test
Honestly the name the test shit was NOT working so the following slides would just be a review of the tests
Patrick’s Test
AKA figure 4 or Jansen’s test
Pt in supine then test leg placed in figure 4 position
PT lowers leg (on top of knee)
(+) pain and test leg remaining on top of opposite knee
If pressure produces lateral pain then it may indicate superolateral and lateral FAI
Groin pain may indicate iliopsoas pathology or psoas impingement
Posterolateral may indicate ischiotrochanteric impingement
Craig’s Test
AKA Ryder method
Pt in prone with knee flexed to 90 degs
PT palpates posterior aspect of greater trochanter then IR and ER hip until greater trochanter is parallel to bed or in most lateral position
Measure the angle of lower leg with vertical line
For femoral anteversion
30 degs at birth; 8-15 degs for adults
Inc anteversion leads to squinting patella and in toeing
2x more common in girls
Hip Scour (Grind) Test (Flexion- Adduction Test)
AKA quadrant or scouring test
Pt in supine, then PT flexes and adducts hip until it reaches opposite shoulder and the resistance is felt
PT maintains slight resistance on the hip while passively abducting the hip (maintain knee flexion)
Look for “bumps”, pain, apprehension
(+) sign not mentioned so just look for abnormalities
causes impingement of the femoral neck against the acetabular rim and pinches the adductor longus, pectineus, iliopsoas, sartorius, and/or tensor
fascia lata, depending on the position of the hip
Lateral FABER Test (yellow)
Pt in sidelying
PT holds upper leg while palpating the hip then abducts the leg while flexing/extending it
(+) if pain; indicates intra articular hip involvement
Log Roll Test (passive supine rotation)
Pt in supine with extended leg
PT then IR and ER leg to end rage
Normally PT just IR leg then let leg passively fall to ER
Pain or restricted ROM = intra articular hip pathology
Click may indicate labral tear
Inc ER = lax iliofemoral lig
Stresses only intra articular tissue NO EXTRA ARTICULAR TISSUES
Anterior Labral Tear Test
AKA fitzgerald, anterior apprehension test
Used to test for anterosuperior impingement syndrome, anterior labral tears,and iliopsoas tendinitis
Pt in supine
PT puts hip into full flexion, ER and abduction then PT extends, IR and adducts hip
(+) if pain, reproduction of sx, or apprehension
Tests for Muscle Dysfunction:
90–90 straight leg raise test
Trendelenburg test
Ely’s test
Ober’s test
Thomas test
Noble compression test
Adductor Squeeze test
Hip Lag sign
Phelp’s test (red)
Piriformis test
Sign of the buttock
Tripod sign (hamstring contracture test)
90–90 straight leg raise test
Pt in supine, hips and knee flexed to 90 deg
Stabilize behind the knees, extend knees as much as possible on each knee
(+) if cant do more than 20 deg
Magee:
Pt in supine flexes both hips to 90 degs with knees flexed
Pt is asked to extend each knee
(+) replication of sx
Trendelenburg test
Pt has to balance on one leg then PT observes
+) if pelvis on non stance leg drops
Weakness of Gmeds or instability
Ely’s test
Pt in prone
PT flexex pt’s knee maximall; compare
(+) if hip flexion occurs in knee flexion
Magee:
Pt lies in prone, while PT flexes knee
(+) if ipsilateral hip flexes
Ober’s test
Pt in sidelying, lower leg and hip flexed for stability
PT passively abducts upper leg and bring it to slight extension
Stabilize pelvis then slowly lower upper leg to table
(+) upper leg stays in the air and does not fall down on table
Magee:
Pt in side lying with lower leg and hip flexed
PT abducts and extends upper leg while knees are extended
(+) if during hip extension, upper leg stays abducted
Thomas test
Pt in supine; check for excessive lordosis
Ask pt to bring knee to chest and hold it
(+) extended leg is lifted off the Muscle table with yan ty
``J-sign or stroke - if extended leg abducts = tight ITB
Magee:
Pt lines supine while PT checks for excessive lordosis
PT flexes one hip towards chest while pt holds that position with hands
(+) if the other hip lifts off the table
Noble compression test
For checking if pt has ITB friction syndrome near knee (chronic inflammation of ITB near insertion / femoral condyles)
Pt in supine with knee flexed to 90 degs with hip flexion
PT extends the knee while applying pressure on lateral femoral condyle
(+) if at 30 degs knee flexion of pt feels pain on lateral femoral condyle
Same pain pt feels when running
Adductor Squeeze test
AKA fist squeeze test
Pt in supine with hips flexes to 45 degs, knees at 90 degs
PT puts his fist in between the knees (dynamometer or sphygmomanometer if you want numbers)
Pt has to squeeze the fist
(+) if reproduces sx; indicates adductor pathology
May also be used for determining symmetry of symphysis pubis
Hip Lag sign
Tests hip abductors
Pt in sidelying, then PT abducts and IR the extended leg to 45 degs
Pt holds that position for 10 secs
(+) if pt cannot hold position, leg drops 4 inches(10cm) or IR decreases
(+) sign indicates Gmeds tear
Phelp’s test
Pt in prone with knees extended
PT abducts both legs as far as possible
At maximum abduction PT flexes knee to 90 degs and try to abduct the hip further
(+) gracilis contracture if abduction increases
Sign of the buttock
Pt in supine then PT does an SLR test
If present limitation, flex knee
(+) If hip flexion does not increase = lesion is in buttock or hip not the hamstrings or sciatic nerve
(+) sign may indicate ischial bursitis, neoplasm, abscess in ass, fx, hip pathology
Tripod sign (hamstring contracture test)
Pt sitting with both knees flexes to 90 degs over edge of bed
PT extends the knee
(+) if pt extends spine (extending spine relieves tension in hamstrings)
Straight Leg Raising Test or Lasegue's Test
Hello Again
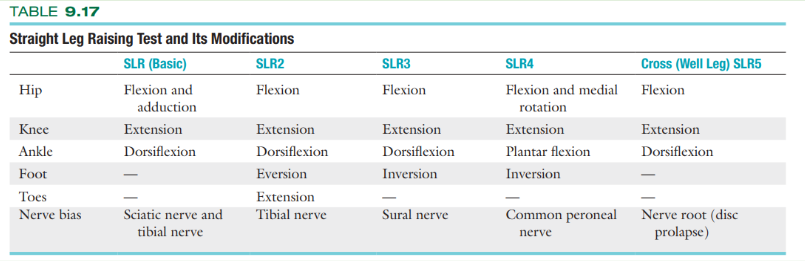
Pain referral:
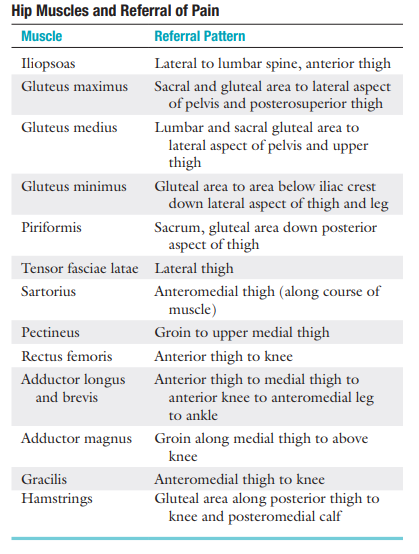
Sites of Entrapment, Key Signs and/or Symptoms with Nerves in the Anterior and Posterior Hip Region:
Tests For Balance Assessment
Timed- Single Leg Stance
Ask the patient to balance first on one leg (good leg) and then the other
first with the eyes open and then with the eyes closed
Stork Standing Test (proprioception)
SI jt, knee, ankle, foot
Y-Balance Test
Star Excursion Balance Test
Postero-medial/lateral = measures FAI and susceptibility to injury
Dislocation from hip trauma with FADIR?
Posterior hip dislocation
Dislocation from hip trauma with EABER
Anterior hip dislocation