OPT 217 Lasers
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What does LASER stand for?
light amplification stimulated emission radiation

Laser radiation travels through space as a ___________________.
EMR wave

What are 3 qualities of laser radiation?
1. monochromatic
2. highly directional
3. coherence = light is in the same phase, wavelength, and direction
What are 3 ways we can describe laser output?
wavelength
pulse duration
irradiance

Explain what 2 things the wavelength of a laser determines.
absorption = how well light is captured by the tissue target
transmission = how well light penetrates overlying media to reach a tissue target
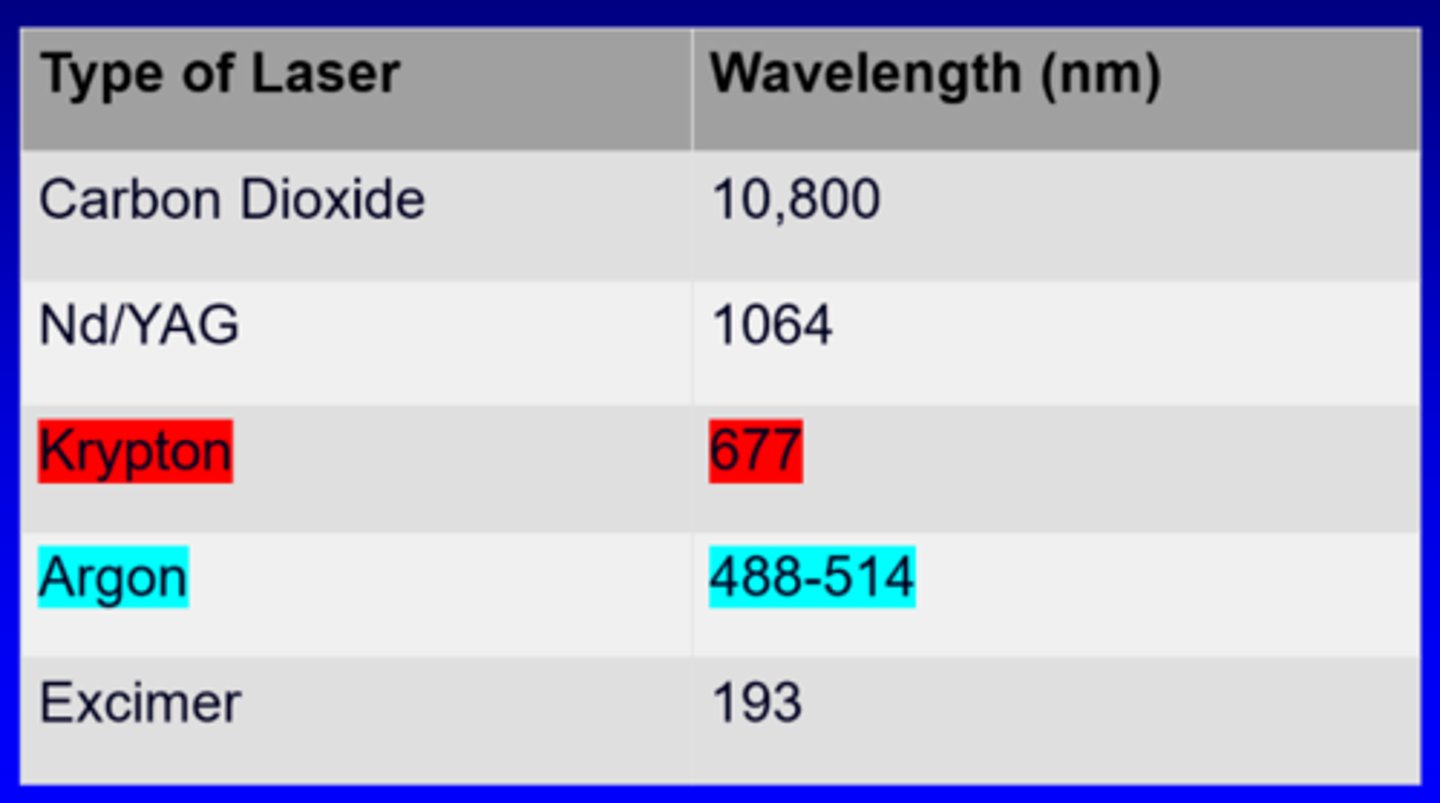
What are 3 categories of ophthalmic laser wavelengths?
UV
visible
IR
What are 2 types of lasers, based on pulse duration?
continuous wave = longer exposures, technically pulse duration of 0.25sec or longer
pulsed = exposures range from femtoseconds to milliseconds
What is laser irradiance?
incident laser power per unit area delivered to a target surface
= power / area
A smaller spot size will _____________ irradiance for a given laser power.
increase
What is direct viewing as a laser eye hazard?
direct intrabeam viewing, straight from source into eye
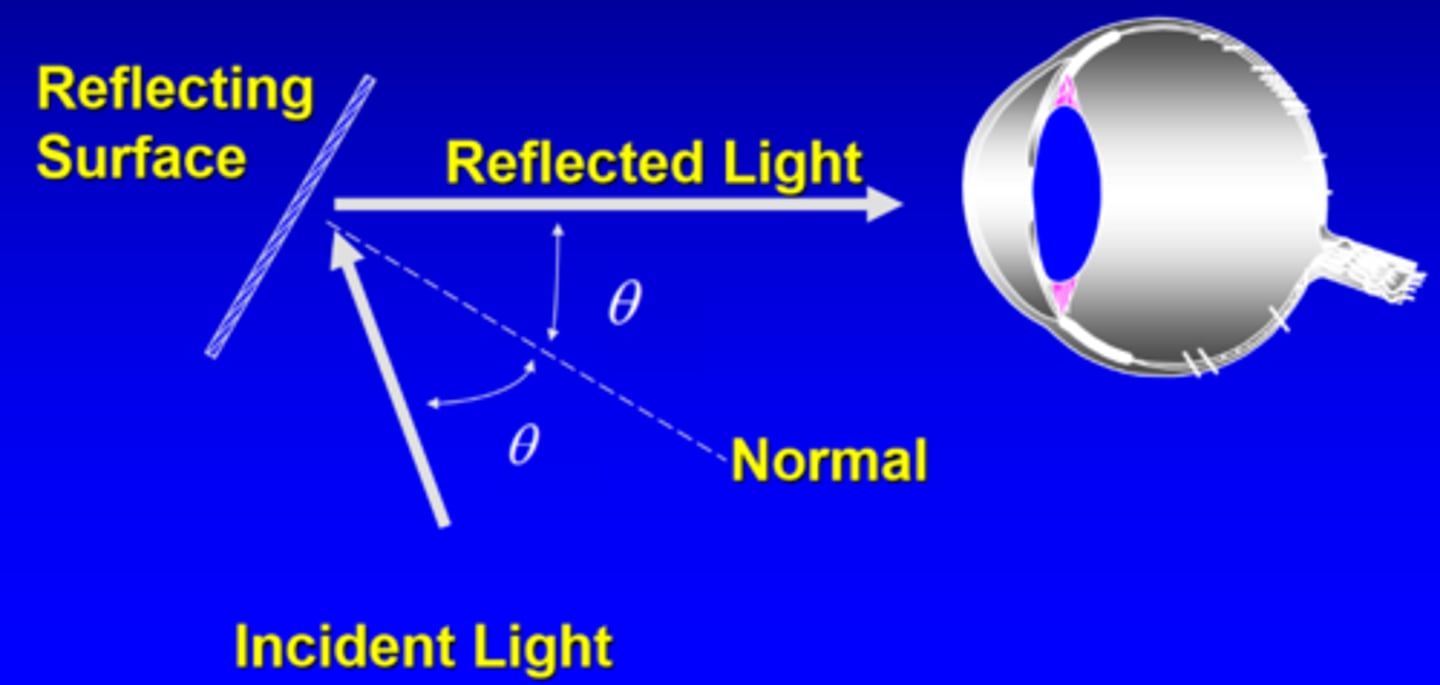
What is specular reflection as a laser eye hazard?
reflects off a surface first before entering eye
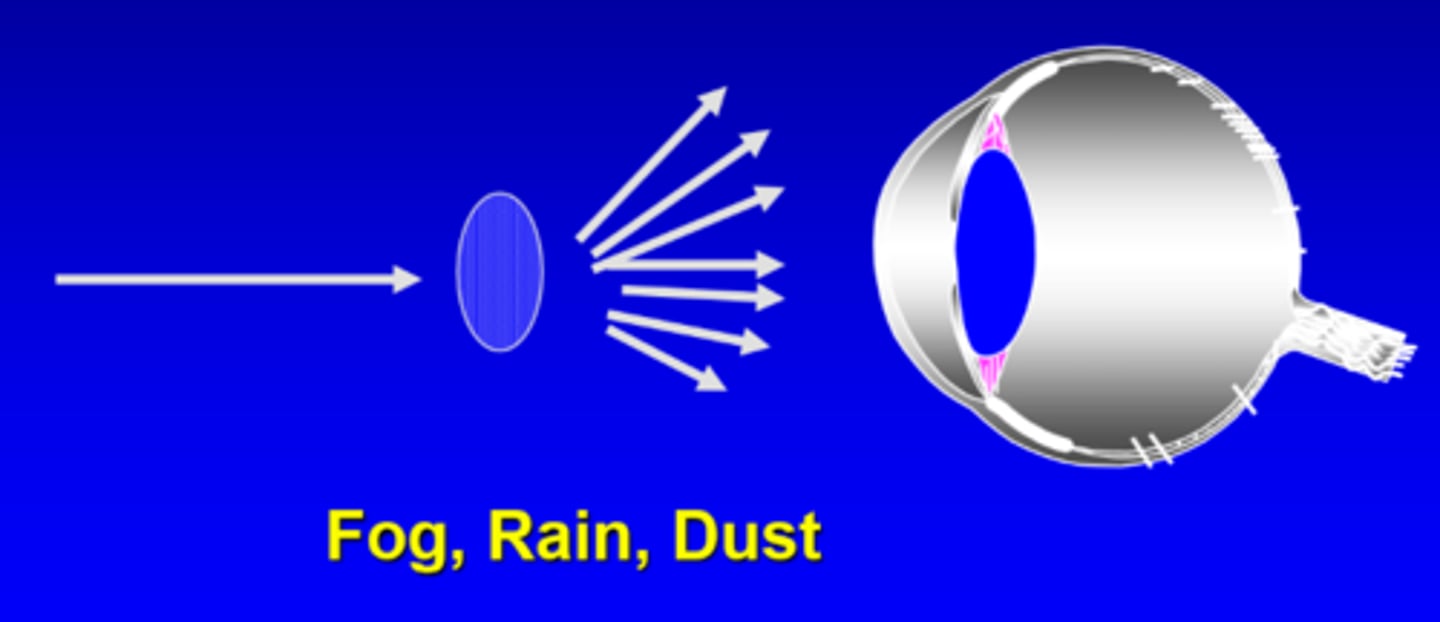
What is diffuse viewing as a laser eye hazard?
something in the way disrupts the beam
BUT not necessarily safe still
Which ANSI standard sets out the safe use of lasers?
Z136.1

Which ANSI standard sets out the safe use of lasers in healthcare?
Z136.3

What 2 things determine the classification of lasers?
1. capability to cause eye injury
2. maximum output power/radiant energy
What is maximum permissible exposure (MPE)?
highest level of laser radiation that an unprotected person may be exposed to w/o adverse biological changes or hazardous effects to the eyes or skin (immediate or LT injuries)
NOTE: based on radiation actually received by eyes/skin
What are 3 assumptions used when calculating MPE?
1. eye is perfectly refracted for the insuling wavelength
2. pupil is 7mm in size
3. aversion response takes 0.25 sec
NOTE: most of these are not typically true
How long is the assumed aversion response?
0.25 sec - even though most can blink or turn head/eyes within 0.1 sec of irradiation
True or False: you can override this 0.25 sec aversion response deliberately.
true
What is the accessible emission limit (AEL)?
max radiation energy level permitted within a particular laser hazard class
NOTE: based on actual laser emission
Who designed the older laser classification system from the 1970s?
FDA and CDRH (center for devices in radiologic health)
How do we know if a given classification is part of the older system?
roman numerals are used
What is class I in the older classification system?
no eye hazard
no control measures
no warning label required
outputs up to 0.4 mW
ex) barcode reader, laser printer
What is class II in the older classification system?
low risk
natural avoidance response (0.25 sec) sufficient
no warning label required
outputs up to 1 mW visible radiation
ex) older laser pointers
What is class IIIa in the older classification system?
eye safe when viewed directly
retinal damage is viewed thru ocular instrument like binoculars
requires caution/danger label
outputs up to 5 mW visible radiation
ex) road survey equipment

What is class IIIb in the older classification system?
moderate power/risk
retinal damage in less than 0.25 sec
aversion reflex won't help
danger label required
output up to 500 mW
ex) military range finders

What is class IV in the older classification system?
high power/risk
retinal damage
can cause combustion/fire
danger label required
output > 500 mW

What class are most ophthalmic lasers we use at TEC?
class IV
How do we know if a given classification is part of the newer system?
alphanumeric
Who designed the newer laser classification system?
ANSI Z136.1 / IEC 60825
IEC established it and ANSI incorporated it in 2007
What are 2 major updates with the newer laser classification system?
required “warning” labels on laser equipment
additional triangular warning label required for Class 2 and higher
What is class 1 in the newer classification system?
safe under normal use
exempt from control measures
eye protection not required
What is class 2 in the newer classification system?
safe assuming intact blink reflex
"do not stare into beam"
exempt from control measures except under unusual viewing
eye protection not required
What is class 1M in the newer classification system?
safe under normal use except w/ magnifying optical instruments
exempt from control measures except under unusual viewing
eye protection not required
What is class 2M in the newer classification system?
safe assuming intact blink reflex AND no use of optical instrument
"do not stare into beam or use w/ optical instruments"
exempt from control measures except under unusual viewing
eye protection not required
What is class 3R in the newer classification system?
safe with careful handling, restricted viewing
"avoid direct eye exposure to beam"
exempt from control measures except under unusual viewing
eye protection not usually required
"caution" on laser controlled area warning sign recommended
What is class 3B in the newer classification system?
may be hazardous w/ direct or specular exposure
protective eyewear required
"avoid direct eye exposure to beam"
appropriate control measures required
"warning" on laser controlled area warning sign required
What is class 4 in the newer classification system?
eye damage from direct, specular, diffuse viewing
most dangerous
protective eyewear required
"avoid eye exposure to direct or scattered radiation"
"avoid skin exposure to direct radiation"
appropriate control measures required
"danger" or warning" on laser controlled area warning sign required

What is the lowest class of laser that requires laser eye protection?
3B
What 5 things are required on the laser equipment warning label?
1. class of laser
2. emitted wavelength
3. pulse duration
4. maximum output power
5. precautionary statement
Lasers newly classified by IEC as "1M", "2M", or "3R" require same control measures as the older Class ________________ lasers.
"IIIa/3A"
Given the extremely small power output of lasers in Classes 1 - 3R, how could an eye injury ever occur?
laser light demonstrates coherence = eye can focus this light to be 100,000x stronger at the retina than it was at the cornea
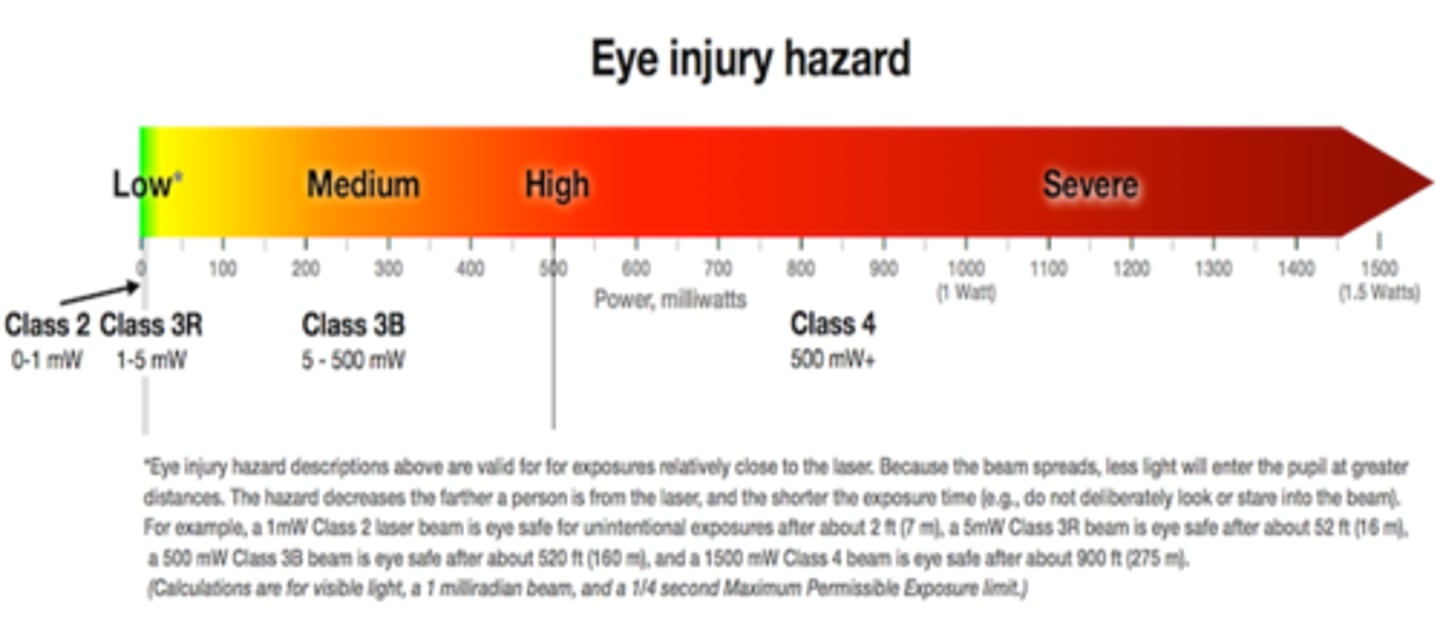
True or False: jumps between power for laser classes are uniform.
false = not uniform
Describe the wavelength and clinical use of a YAG laser.
neodymium: ytrrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG)
1064nm laser
used to vaporize PCO (fibrotic haze on the back of IOL implant)
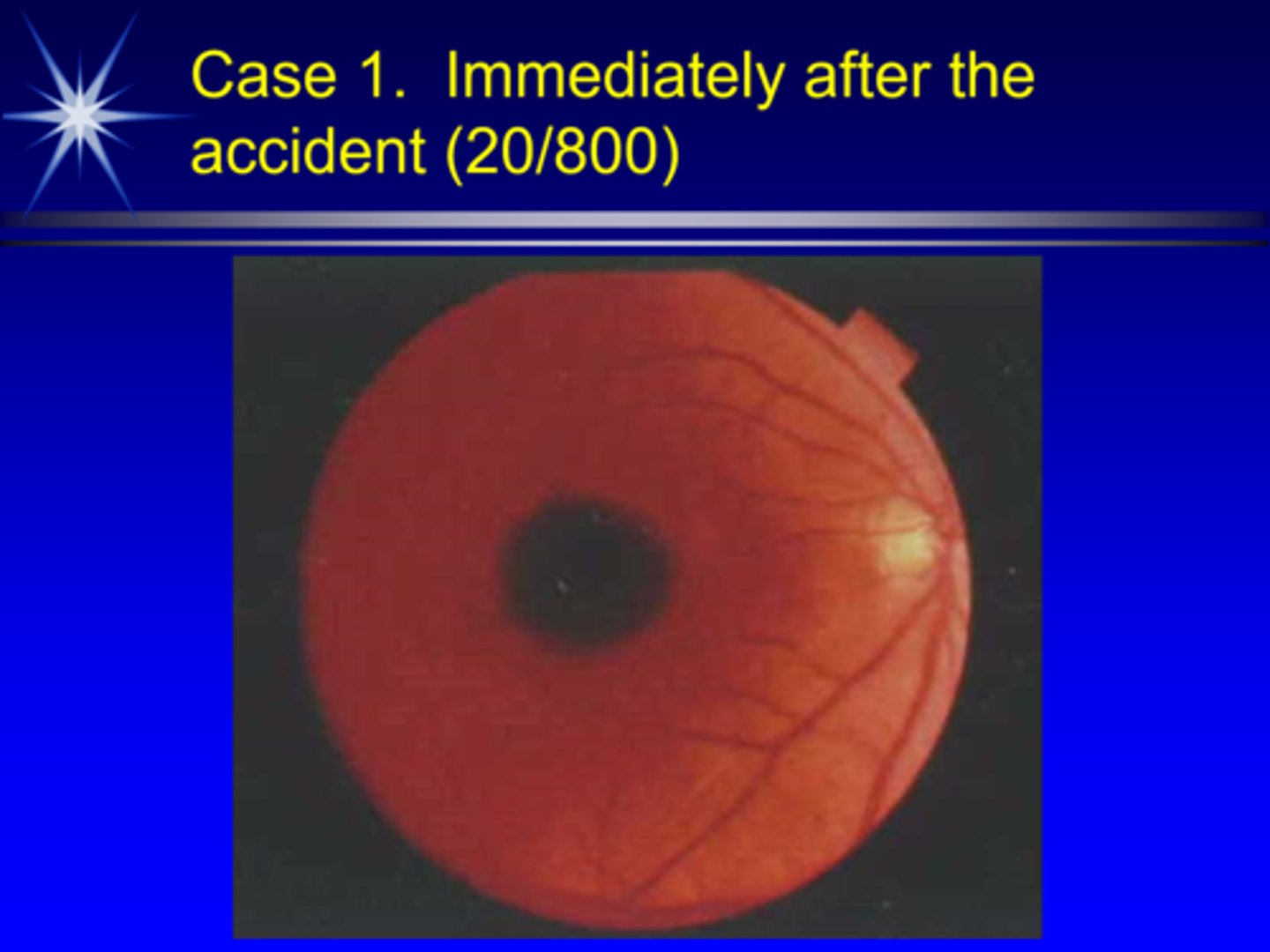
True or False: laser injuries from a YAG laser can never heal to 20/20.
false = just takes roughly 6 mos with likely some contrast, colour vision issues (not a great 20/20)

What are the 3 types of control measures in place for laser protection? List them in order from highest to lowest priority.
1. engineering
2. administrative
3. PPE
What are engineering control measures?
control measures designed or incorporated into the laser or laser system
ex) interlocks, shutters, watch-dog timer
What are administrative control measures?
control measures incorporating “administrative” means
ex) training, safety approvals, “Laser Safety Officer (LSO)” designation, standard operating procedures (SOP)
What are PPE control measures?
control measures incorporating personal safety protective devices
ex) laser protective eyewear (LPE), protective clothing, gloves
What are 2 features that must be designated on laser protective eyewear?
1. wavelength specific = designated wavelength(s) or band of wavelengths
2. optical density that must be appropriate to laser output power

What is optical density?
OD = log(opacity)

Ex) OD of 3 means you're going to dampen that particular wavelength by how much?
1000x = out of 1000 rays, 999 are going to be blocked

What OD level is likely "enough" to be considered safe?
OD 7 for that particular wavelength/range

What form of filtering devices are acceptable as laser protective eyewear?
goggles are best
spectacles
visors
windows
viewing screens

What 2 things must be labeled on all laser protective eyewear?
optical density / OD
wavelength(s)

What is the %VLT that is also present on most laser safety glasses markings?
the % of visible light transmitted

What is the minimum %VLT that ensures the wearer can see through the eyewear?
20%

Higher OD means a _____________ lens (in the visible range).
darker

Higher VLT means a _____________ lens (in the visible range).
lighter

What was the class, wavelength, and output power of early laser pointers?
class II
wavelength of 632nm
very bright
< 1 mW output
inconvenient power source

What was the class, wavelength, and output power of later laser pointers?
class IIIa
wavelength of 670nm (eye less sensitive)
very bright
3-5 mW output

What did the laser pointer injury study find about the risk of using laser pointers?
risk to the human eye from transient exposure to light from commercially available class 3A laser pointers having powers of 1, 2 and 5 mW seems negligible
Historically, most cases of eye injury from laser pointers have appeared to have been from what?
intentional exposure = staring into the laser beam on purpose
Are red or green laser pointers potentially more dangerous to the eye?
green
maybe due to the way the retinal pigment absorbs it
currently made with 532nm wavelength = eye is more sensitive
can be altered to become more powerful
What are some things that make laser pointers a possible public health issue?
ease of internet purchasing
manufacturing quality control issues = labeled power may not be actual power, or may emit alternate wavelengths
marketed as toys
Does the FDA have the authority to regulate lasers?
yes

True or False: The light energy from a laser pointer aimed into the eye can be more damaging than staring directly into the sun.
true
don't aim laser pointer at people
shouldn't be used by children
ensure product is properly labeled