Therapy ED Other Systems NPTE
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
True or False
CFS (Chronic Fatigue Syndrome) is associated with hypothyroidism.
False
hyperthyroidism via increases hormone production (substance P, etc)
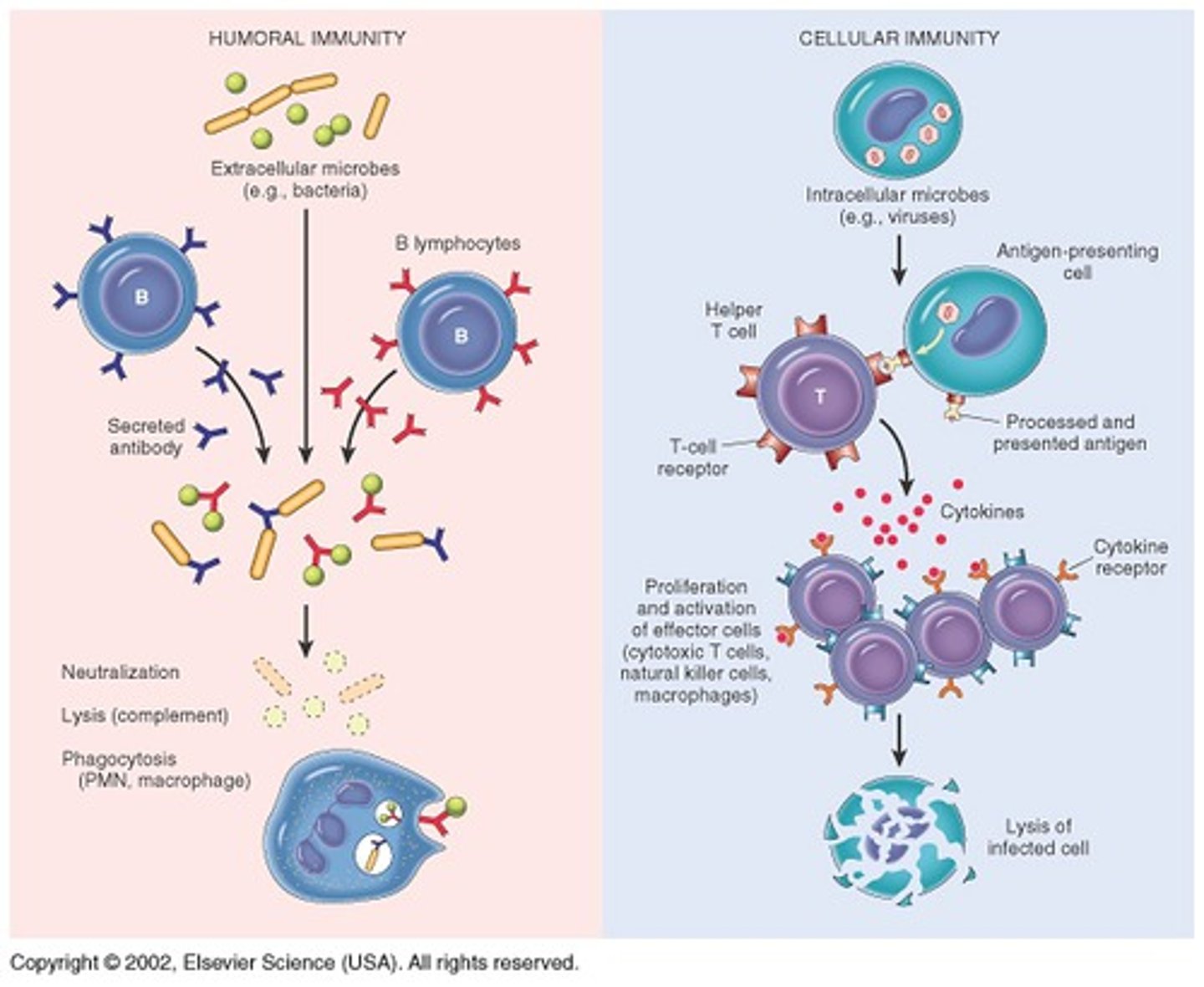
list the different types of immune cells
1. antigen (immunogen)
2. lymphocytes (T and B)
3. macrophages
4. cytokines
5. CD molecules (i.e. CD4 helper cells)
6. major histocompatibility complex (MHC) membrane molecule
CALM CD-M
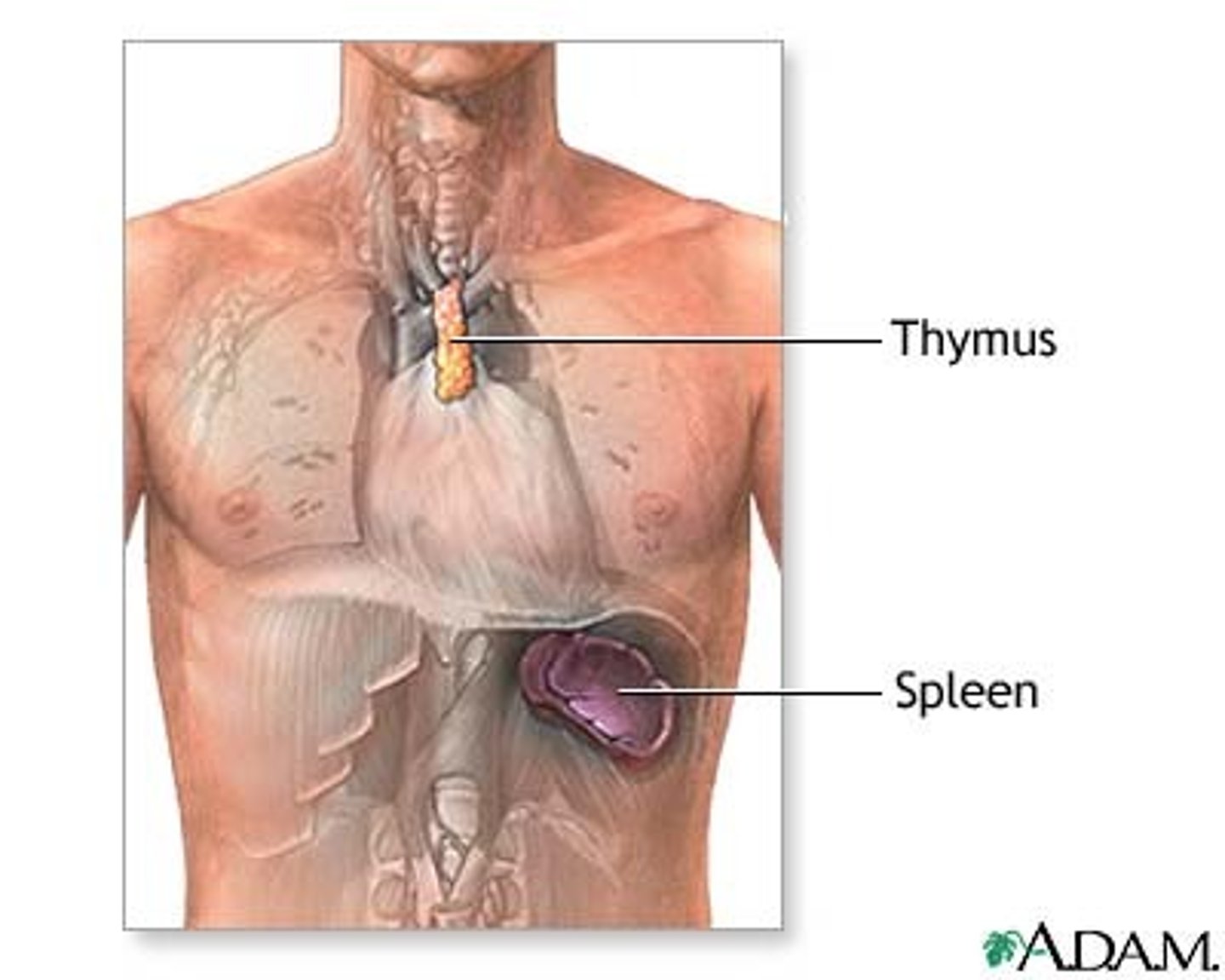
(fully developed at birth) Primary central gland of the immune system located behind the sternum and above the heart
thymus
S&S of
AIDS-related complex (ARC),
Precurser to full-blown AIDS
Recurrent fever
chills
night sweats
swollen lymph glands
loss of appetite
weight loss
diarrhea
persistent fatigue
infections
apathy
depression.
Febrile S&S & GI S&S
HIV-AIDS symptoms (middle to late stage of disease)
All/some ARC symptoms and:
HA
Blurred vision
Dyspnea
Dry cough
Oral/skin lesions
Dysphagia
Dementia
Seizures
Focal neurological signs
AIDS: Adverse effects of anti-viral therapy
Rash
Nausea
Headaches
Dizziness
Muscle pain
Weakness
Fatigue
Difficulty sleeping
With hepatotoxicity signs of CARPAL TUNNEL may be seen
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): Major criteria (3 things)
1. New onset of persistent or relapsing fatigue
2. Must be present for at least 6 months
3. Does not resolve with rest and reduces daily activity by at least 50%
Exclusion of other chronic conditions
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): Symptoms
1. Inability to recover from normal exercise
2. Low-grade fever or chills
3. Sore throat: Non-exudative pharyngitis
4. Lymph node pain and tenderness
5. Muscle weakness
6. Muscle discomfort or myalgia
7. Sleep disturbances (insomnia or hypersomnia)
8. Headaches
9. Migratory arthralgias without joint swelling or redness
10. Cognitive impairments: Photophobia, inability to concentrate, irritability, confusion
Treatment of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Examine exercise tolerance - may show fluctuations in HR, BP, orthostatic hypotension is common
If decondition - dyspnea with exercise
Modified fatigue impact scale
Treatment:
Reduce activities when fatigue is maximal - avoid overexertion
BEDREST CONTRAINDICATED other than for sleep
Graded ex program - short duration, gradually increasing intensity
Activity pacing, energy conservation
Address posture
Teach stress management
Support group
Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) and Sxs (what temperature intolerance?)
Chronic pain syndrome affecting muscles and soft tissues
SXS: Myalgia, generalized aching, persistent fatigue, sleep disturbances, generalized morning stiffness, trigger points
Visual problems, mental/physical fatigue, spasm, cold intolerance, headaches, irritable bladder or bowel, cognitive problems (impaired memory, decreased concentration), restless legs, atypical patterns of numbness and tingling (sensitivity amplification)
Women>men
PT Treatment for Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS)
Pt typically demonstrates exercise intolerance
Daily exercise is important
Protection strategies to avoid overuse syndromes
Focus on aerobic training, mild-moderate intensities
Aquatic therapy ideal to decrease pain and increase cardiovascular conditioning and strength
stachylococcal infections
-localized bacterial infection that enters through the skin (wounds, ulcers, burns)
-spreads through the blood stream or lymphatic system to almost any body location
-infection produced suppurations (pus) and abscess
-can develop into antibiotic resistant strains
Medical management for staphylococcal infections
-antibiotic therapy
-drainage of abscesses
-skin infections that are untreated can become systemic; septic; lethal
Methicillin-resistant stachylococcal aureus (MRSA) - precautions
-MRSA resistant to all penicillins
-hospital patients with MRSA infections are isolated and standard mask-gown gloves precautions required
Which is acute liver inflammation that is mostly transmitted via fecal -oral route
HEP A
HEP B
HEP C
HEP D
HEP A (A =acute)
HEP B= chronic, transmitted bodily fluid via STD
HEP C = most common; transmitted bodily fluid via STD (no vaccine)
HEP A
Transmitted primarily through fecal-oral route or close personal contact
Contracted through contaminated food or water, infected food-handlers
Acute infection with flu-like symptoms, does not progress to chronic disease or cirrhosis. Pts usually recover in 6-10 weeks.
HEP B
Transmission from blood, body fluids or body tissues
Rx: Hepatitis immunoglobulin (HBIG) for unvaccinated pt within 24 hrs of exposure. Pt should then receive vaccination series.
HEP C
Transmission from blood, body fluids or body tissues
One of the primary causes of chronic liver disease and eventual liver failure. Accounts for 90% of hepatitis post transfusion.
No vaccine
Tuberculosis (TB) - signs & sxs, precautions
Airborn infection
Most commonly affects respiratory system
Sxs: Fatigue, low-grade fever, night sweats, anorexia, weight loss
-Cough, rales, dyspnea
Respiratory droplets or sputum - use tissues to cover nose/mouth when coughing/sneezing; disposable containers for sputum and tissues
If a pt is in Shock should he/she be placed in semi fowler/reclining position or supine/trendelenburg position?
Shock = Inadequate blood flow to body tissues
Associated with hypotension, inadequate CO, changes in peripheral blood flow and resistance
Vital functions must be carefully monitored and restored as quickly as possible
Patient should be placed supine or in a modified Trendelenburg position to aid venous return
List the types of hematological disorders
1. Anemia
2. Sickle cell disease
3. Hemophilia
Anemia signs/sxs
Fatigue
weakness
dyspnea on exertion
yellow skin, tachycardia, bleeding of the gums
Severe: hypoxic damage to the liver and kidneys
What are the signs and symptoms of a sickle cell anemia crisis?
-Acute abdominal pain from visceral hypoxia
- painful swelling of soft tissues of the hands and feet
-persistent headache dizziness confusion
-nystagmus, coughing
What PT modality is contraindicated for sickle cell disease tx?
Cold is contraindicated because it increases vasoconstriction
Cancer: Malignant tumor: Connective tissues
General: Sarcoma
Blood vessels: Hemangiosarcoma
Bone: Osteosarcoma
Fat: Liposarcoma
SMC: Leiomyosarcoma
Fibroblasts: Fibrosarcoma
Originates in connective and mesodermal tissues (muscle, bone, fat)
Cancer: Malignant tumor: Hematopietic tissues (4)
What is Leukemia?
What is Myelodysplasia?
What is polycythemia?
What is myeloma?
Myleo = marrow
Leukemia: Blood/bone marrow, abnormal increase in immature cells (usually leukocytes), crowding, unable to make healthy cells
Myelodysplasia: Group of marrow diseases. Poorly formed/dysfunctional blood cells, underproduction.
polycythemia: Increased cellular proliferation of one or more cell types, increased fibrous marrow tissue that an result in scarring and underproduction of cells.
Multiple myeloma: Cancer of plasma cells in marrow - increased growth, tumor, decreased RBCs/WBCs/platelets
Cancer: Malignant tumor: Staging
What does T stand for ?
What does N stand for ?
What does M stand for ?
Primary tumor (T)
Regional lymph node involvement (N)
Metastasis (M)
Numbers used to denote extent (stage 0-IV)
Cancer Stages (0-4)
stage 0 = early malignancy in layer of cells
1 = Limited to tissue origin (no metastasis)
2 = spread to adjacent tissue (maybe metastasis)
3 = likelihood of lymph metastasis
4 = bones and other organs
Cancer: Radiation therapy adverse effects
Radiation sickness, immunosupression, fibrosis, burns, delayed wounds healing, edema, hair loss, CNS effects.
Cancer pain syndrome
Nerve/nerve root compression
Ischemic response to blockage of blood supply
Bone pain
Mod-severe pain may be accompanied by tachycardia, HTN, tachypnea, nausea, vomiting
Pain at side distal to initial site may suggest metastasis
Iatrogenic pain may result from surgery, radiation or chemo
Adverse side-effects of CA treatment
MSK symptoms
Muscle atrophy and weakness (high steroid doses in many chemo protocols)
Weakness from disuse/tumor compression.invasion
ROM deficits (radiation)
Hematological symptoms
Decreased WBCs (leukopenia), increased susceptability to infection
Platelet suppression (thrombocytopenia) increased bleeding
RBC supression (anemia) diminished aerobic capacity
Cancer: PT precautions- low platelet counts (<20,000), bony metastases, osteoporosis
AROM, ADL only
Weight bearing may be restricted - provide aids/orthoses
High risk of vertebral/other compression #'s - light ex only
Cancer: Thermal agent contraindications
Do not use:
Directly over tumor
Over dysvascular tissue
Over tissue exposed to radiation therapy
Increased bleeding/hemorrhage (corticosteroids)
Cancer: Cryotherapy red flags
Do not use:
Insensitive to cold
Delayed wound healing
Dysvascular tissue
Tissue exposed to radiation therapy
Cancer: Hydrotherapy with agitation red flags
Do not use:
Dysvascular tissue
Tissue exposed to radiation therapy
Decreased temp sensitivity
Pain in affected area
Areas of increased bleedingg/hemorrhage/open wounds
Risk of cross infection is high with immunosupressed pts
Early signs of pancreatic cancer
vague during the initial stages of the disease which often results in delayed diagnosis
common symptoms include weight-loss, jaundice and epigastric pain that can radiate to thoracic region
Cancer: describe basal cell carcinoma vs squamous cell
Basal Cell
- Raised
-Low growing form of skin cancer that rarely metastasizes
-most common form of skin cancer
-prognosis is good
SquamousCell
-Flat
-Uneven edges
-malignant
-various colors (dark)
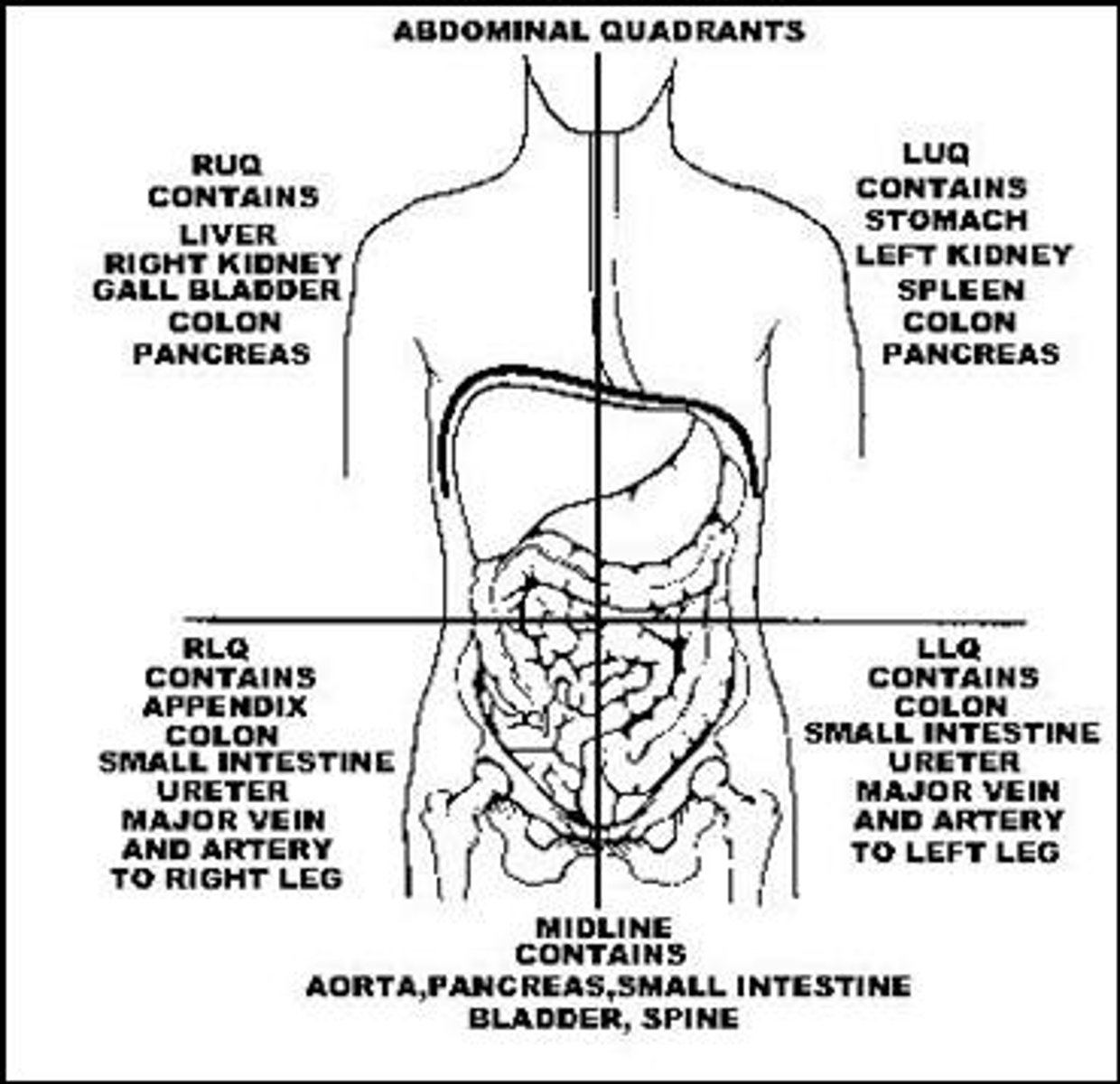
Function of GI gland organs
Gall bladder (RU):
Liver (RU):
Pancreas (LU/RU):
Gall bladder (RU): Stores and releases bile into the duodenum
Liver (RU): Produces bile, assists with RBC and vit K production, regulates serum level of carbs, proteins and fats
Pancreas (LU/RU): Exocrine secretes bicarbonate and digestive enzymes into duodenum; Endocrine secretes insulin, glucagon and other hormones into blood (Balance PH)
Esophageal varices
-Abnormal enlargement of veins in the lower part of the esophagus (most often follows serious liver disease)
-esophageal varices develop when blood flow to liver is obstructed by scar tissue and blood flows into smaller blood vessels that are not designed to carry large volumes of blood
Pain referral pattern for the liver, diaphragm, pericardium
Shoulder
Pain referral pattern - Gall bladder, stomach, pancreas, small intestine
Mid-back
Scapular region
Pain referral patterns - Colon, appendix, pelvic viscera
Pelvis
Low back
Sacrum (Colon)
GERD - PT
Positional changes from full supine to modified, more upright positions is indicated
Recumbency (lying down) will induce symptoms
Left-sidelying is preferred (R sidelying may promote acid flowing into esophagus)
VALSALVA CONTRAINDICATED
GI disorders: Peptic ulcer
Disruption/errosion in GI mucosa. Imbalance between protective mechanisms of the stomach and the secretion of acids within the stomach. Many ulcers are caused by H. Pylori and chronic NSAID use. Irritants which increase risk include alcohol, stress, particular meds, foods and smoking.
Complications: Hemorrhage, perforation, obstruction (secondary to scarring), malignancy.
ULCER AT POSTERIOR WALL CAN PRESENT AS RADIATING BACK PAIN/RIGHT SHOULDER PAIN
GI disorders: IBS symptoms
Persistent/recurrent abdo pain relieved by defecation
Constipation/diarrhea, vomiting
Bloating
Abdo cramps
Flatulence
Nausea
Anorexia
Changes in form of stool, passing of mucus in stool
IBS rehab considerations
Physical activity assists bowel function and can relieve stress
Breathing techniques will assist in stress reduction and with breath-holding patterns
Biofeedback training may be beneficial
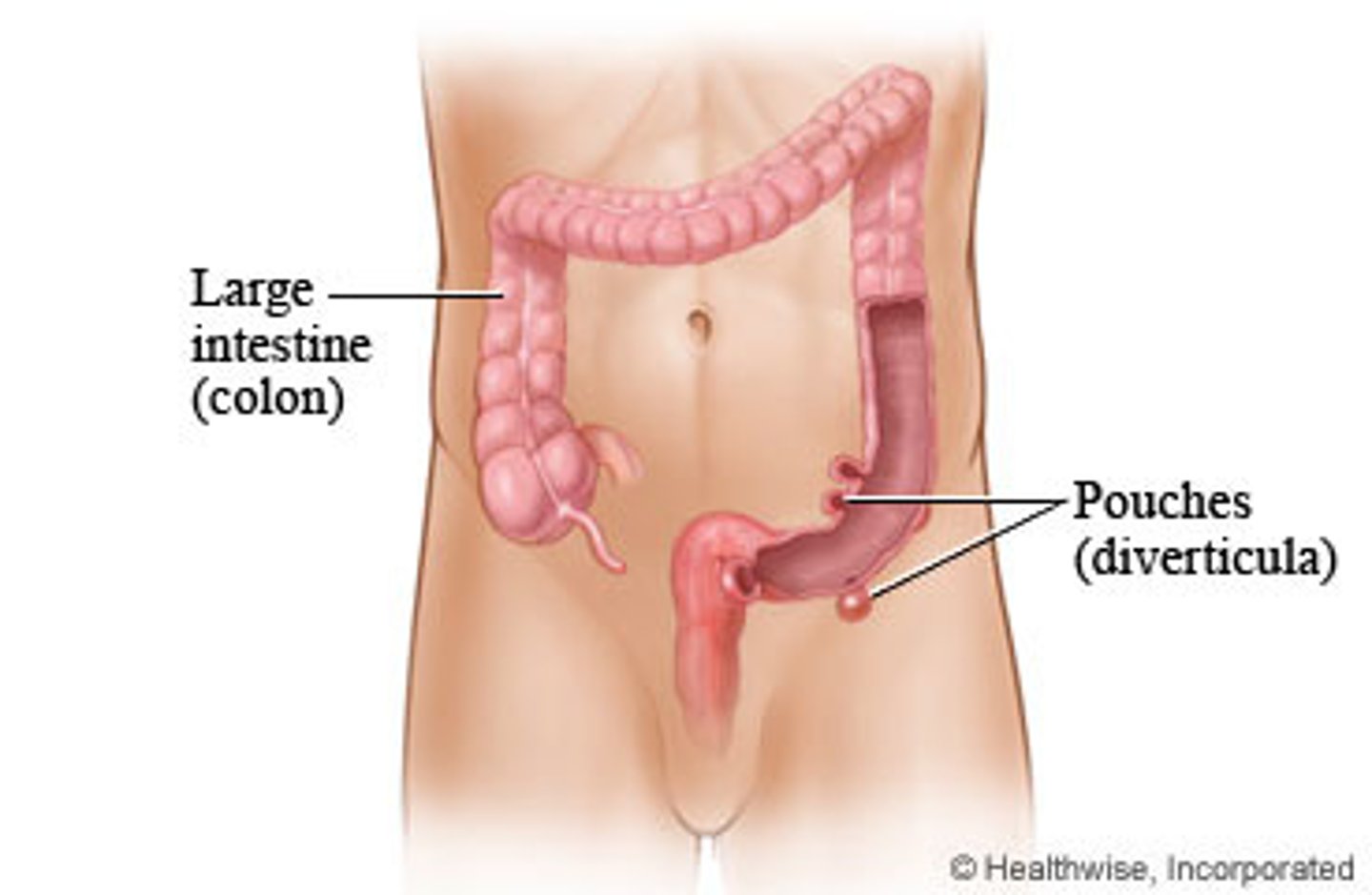
GI disorders: describe Diverticulitis symptoms
Inflamed/infected diverticuli
Pain and cramping in lower left quadrant (primary symptom), Nausea, Vomiting, Slight fever, Elevated WBC, constipation, chills, vomiting
Complications: Bleeding, infections, intestinal blockage, abscess, perforation, tears in colon, fistulas, peritonitis
GI disorders: Appendicitis symptoms
Abrupt onset pain in epigastric/periumbilical area
Increases in intensity over time
Rebound tenderness (Blumberg's sign)
Point tenderness at McBurney's point (site of the appendix located 1.5-2" above ASIS in right lower quadrant
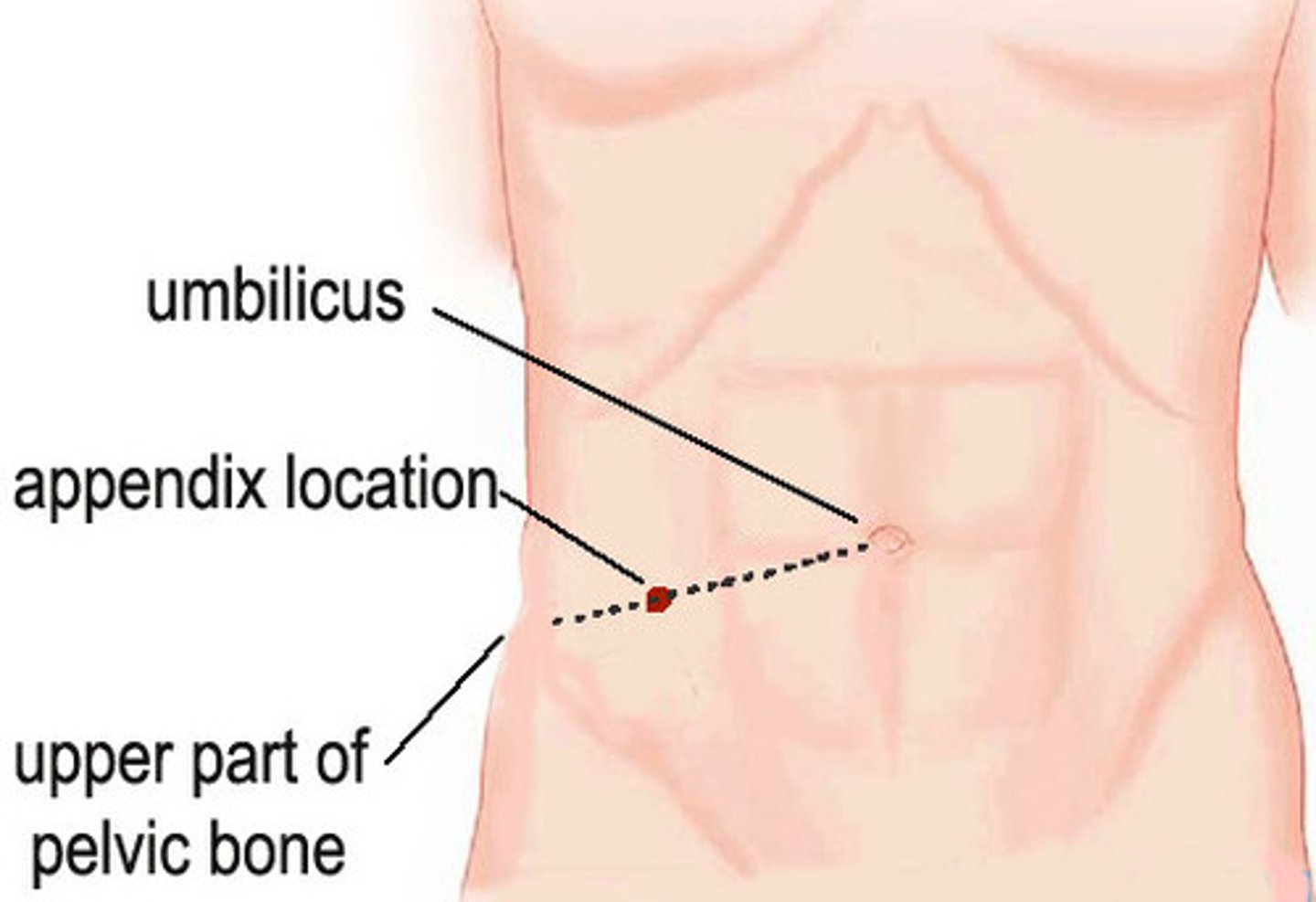
GI disorders: Peritonitis signs and Symptoms
Inflammation of inner lining of stomach
Abdominal distension
Severe abdominal pain
Rigidity from reflex guarding
Rebound tenderness
Decreased/absent bowel sounds
Nausea and vomiting
Tachycardia
Elevated WBC count
Electrolyte imbalance
Fever
Hypotension
Peritonitis is a serious medical condition that can lead to toxemia and shock, circulatory failure, respiratory distress. Requires immediate medical attention
-What is cholecystitis?
-What are Cholelithiasis?
What type of diet is associate with Cholelithiasis?
cholecystitis a: refers to inflammation of the gallbladder that may be acute or chronic
cholelithiasis: are otherwise known as gallstones, -gallstones develop from hypomobility of the gallbladder supersaturation of the bile with cholesterol or crystal formation from BiliRubin salts
High fat Treatment: low-fat diet can decrease gallbladder stimulation
Genitourinary system: describe muscles of the pelvic diaphragm
Levator ani: pubococcygeus, puborectalis, iliococcygeus, and coccygeus
genitourinary system: Symptoms of pelvic floor weakness
Does pelvic floor weakness cause pain to radiate down the anterior or posterior thigh?
Pelvic pain (perivaginal, perirectal, lower abdo quadrant)
Urinary incontinence
Pain on sexual intercourse
Can radiate down posterior thigh
Post-cesarean section PT
TENS (electrodes parallel to incision)
Prevent post-op pulmonary complications (assist breathing, coughing)
Exercises:
Gentle ab exercises - incisional support with pillow
Pelvic floor exercises
Postural exercises (precautions about heavy lifting for 4-6 weeks)
Ambulation
Prevent incisional adhesions (friction massage)
Genitourinary system: uterus: describe endometriosis
Endometrial growth that occurs at the uterosacral ligament is most common
-moderate to severe lower abdominal pelvic or low back pain before or during menstruation
Genitourinary system: uterus: describe uterine prolapse
-The dissent of the uterus and cervix into the vagina
-S&S: pelvic pressure that increases with exertion frequency of urination discomfort and vaginal dryness
-pelvic floor muscle training using biofeedback Keagle exercises core strengthening exercises and lifestyle modifications
Genitourinary system: What is the function of the Kidney?
Regulate:
pH
Fluid composition
Mineral and water balance
BP (via renin-angiotensin-aldosterone & salt/water regulation)
Metabolic waste elimination
Bone metabolic function (via PO4- regulation & vit D activation)
RBC production in marrow (via erythropoietin production)
metabolic system: Metabolic acidosis causes, S&S, Rx
Acid gain/bicarbonate loss
Causes - diabetic/alcoholic ketoacidosis, renal insufficiency/failure, severe diarrhea, lactic acidosis, starvation,
S&Sxs: Compensatory hyperventilation (decrease CO2), Deep respirations, Weakness, Muscular twitching, Malaise, Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Headache, Dry skin and mucous membranes, Poor skin turgor, arrhythmias. Left untreated can induce coma and death
Rx: Manage underlying cause, correct any coexisting electrolyte imbalances, administer NaCO3
metabolic system: Metabolic alkalosis causes, S&S, Rx (Think too many metabolic salts so lost via diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics, etc)
Causes: Excess vomiting, excess diuretics, hypokalemia, peptic ulcer, excessive intake of antacids, nasogastric suctioning
Compensatory hypoventilation, Depressed respirations, Dysrhthymias, Prolonged vomiting, Diarrhea, Weakness, nausea, Muscle fasciculations/cramping, neuromuscular excitability, paresthesias, Irritability, Agitation, confusion, Convulsions, coma, death
Rx: Manage underlying cause, correct coexisting electrolye imbalances, administer potassium chloride
Respiratory acidosis
(CO2 retention, impaired alveolar ventilation)
Causes: hypoventilation, drugs/over-sedation, chronic pulmonary disease, hypermetabolism (sepsis, burns)
Dyspnea
Hyperventilation
Cyanosis
Restlessness
Headache
Respiratory alkalosis causes S&S
(diminished CO2, alveolar hyperventilation)
Causes: Anxiety attack with hyperventilation, hypoxia (emphysema, pneumonia), impaired lung expansion, CHF, pulmonary embolism, diffuse liver or CNS disease, salicylate poisoning, extreme stress (stimulation of respiratory center)
Tachypnea
Dizziness
Anxiety
Difficulty concentrating
Numbness and tingling
Blurred vision
Diaphoresis
Muscle cramps
Twitching/tetany
Weakness
Arrythmias
Convulsions
metabolic system: Renal failure
Usually occurs due to DM or HTN
Acute: Sudden loss of renal function with resulting elevation in BUN and creatinine, oliguria, hyperkalemia, Na retention
Chronic
Progressive loss of kidney function leading to end-stage failure
DM, severe HTN, SLE and others
metabolic system: Renal failure S&S
Nausea, vomiting, lethargy, weakness, hiccups, anorexia, GI ulceration, sleep disorders, headache, peripheral neuropathy, anemia, pruritus, osteomalacia, ecchymosis, HTN, dyspnea on exertion, HF, dizziness, pulmonary/peripheral edema, anxiety, inability to concentrate, convulsions, seizures, coma.
Chronic pain: Ischemic leg pain, painful cramps
Muscle weakness: Peripheral neuropathy, cramping, restless legs
Skeletal: Osteomalacia, osteoporosis, bone pain, fracture
Skin: Pallor, ecchymosis, pruritis, dry skin
Anemia, tendency to bleed easily
Decreased endurance, functional losses
Autonomic nervous system dysfunction: decreased HR, BP, orthostatic hypotension
Adrenal cortex
Mineral corticosteroids vs Glucocorticoids vs Adrenal androgens
Mineral corticosteroids (aldosterone): Kidneys - Increases reabsorption of Na ions from kidneys into the blood, increases excretion of K ions by the kidney into the urine
Glucocorticoids (cortisole): GI system - Influences metabolism of food, anti-inflammatory effect in large amounts
Adrenal androgens (dehydroepiandrosterone, androstenedione): Ovaries/testes - Increases masculinization, promotes growth of pubic hair in males and females
Adrenal medulla
Epinephrine vs Norepinephrine
Epinephrine: Cardiovascular and metabolic systems - Increases heart rate, contractility, energy production, vasodilation in skeletal muscle
Norepinephrine: Cardiovascular and metabolic systems - Vasoconstriction in skin, organs and skeletal muscles
Thyroid
Triiodothyronine, Thyroxine: All tissues - Involved with normal cellular development, increases cellular metabolism
Calcitonin: Plasma - Increases Ca storage in bone, decreases blood Ca
Endocrine system: signs and symptoms of endocrine dysfunction
Neuromuscular: muscle weakness, myalgia, arthralgia stiffness, arthritis, muscle atrophy, and adhesive capsulitis
Systemic: growth dysfunction, skin pigmentation dysfunction, polyurea, increased vital signs, hair dysfunction, and nervousness or anxiety
Signs of low blood sugar
Rapid onset (minutes)
Glucose <60mg/dL
CNS changes: Labile, irritable, headache, blurred vision, slurred speech, decreased concentration, confusion, incoordination
Sympathetic changes: Diaphoresis, pallor, piloerection, tachycardia, heart palpitations, nervousness and irritability, weakness, shakiness/trembling, hunger
Hypoglycemic coma: Loss of consciousness that results from abnormally low blood sugar levels
IF PATIENT AWAKE GIVE SUGAR
IF UNRESPONSIVE CALL FOR HELP - IV GLUCOSE REQUIRED
Signs of high blood sugar.
What is the glucose level?
Gradual onset (days)
Glucose >250 mg/dL
Results from untreated DM
CNS changes: Dulled senses, confused, diminished reflexes, paresthesias
Fruity breath odor
Thirst/dehydration
Flushed
Nausea/vomiting
Abdo pain
Deep, rapid respirations
Rapid, weak pulse
Hyperglycemic coma: Caused by hyperosmolarity of ECF and dehydration - can lead to death
Rehabilitation considerations for DM (when not to exercise)
ETT prior to exercise due increased cardiovascular risk
Do not inject short-acting insulin into exercising muscles or sites close to them
DO NOT EXERCISE:
-Without eating at least 2 hours before
-Uncontrolled glucose levels (>250mg/dl)
-Urine test positive for ketones
-Poorly controlled complications (cardio, HTN, retina, renal, neural)
Addison's disease
Adrenal disorder - hypofunctioning - decreased production of cortisol and aldosterone
Sxs -
1. Hypotension
2. Weakness
3. Anorexia
4. Weight loss
5. Altered pigmentation (bronze skin)
6. If left untreated, will result in shock and possible death
Hypoparathyroidism versus hyper parathyroidism
Parathyroid regulates calcium
Hyper: increased bone reabsorption hypercalcemia, gout, hypertension and significant renal damage, decrease neuromuscular irritability
Hypo: decreased bone reabsorption, hypocalcemia cardiac arrhythmias potential heart failure increase neuromuscular activity
Rehab for Thyroid Dysfunction
Are hot environment's tolerable?
NO!!
1. Recognize reduced exercise capacity and fatigue are typical
2. Avoid treatment that exacerbates symptoms
-hot aquatic, hot gym setting
3. Avoid Cardiovascular stress
-due to complications with graves disease and hypotension, goiter
4. Close monitoring of vital signs
Psychological disorders: Side effects of tricyclic antidepressants
Disturbed balance
Postural hypotension
Falls and fractures
Increased HR
Dysrhythmias
Ataxia
Seizures
Tay-Sachs Disease
Inherited Metabolic Disorder
At ~ 6 mos. pt will start to miss developmental milestone and will continue to deteriorate in motor and cognitive skills. Will develop significant mental retardation, paralysis and will usually die by age 5.
Currently no effective treatment
Wilson's disease
Defect in the body's ability to metabolize copper - copper accumulates in brain (esp the BG), liver, cornea, kidneys and other tissues.
Symptoms begin ~ 6 yrs: hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, athetoid movements, ataxic gait patterns, may be emotional/behavioral changes as copper accumulates. Over time there will be musculoskeletal deformities, pathological fractures, osteomalacia, muscle atrophy, contractors.
Osteomalacia
Bones become soft due to calcium or phosphorus deficiency
S&S: Vague presentation of aching, fatigue, weight loss. Myopathy & sensory polyneuropathy may also occur along with periarticular tenderness and pain, thoracic kyphosis deformity and bowing of the LLs. Pt may struggle with transfers and STS
Paget's disease
Excessive bone formation without structural integrity. Bone is enlarged and lacks strength
S&S: Musculo pain, bony deformity, vertigo, hearing loss, mental deterioration, increased CO leading to HF.
Describe hydrocolloids
-gel-formed polymers (carboxymethylcellulose, gelatin, pectin)
-film or foam adhesive
-does not attach to wound but anchors to the intact surrounding skin
-dressing absorbs excudate by swelling into a gel-like mass
-used for partial thickness wounds, full-thickness wounds, and granular or necrotic tissue
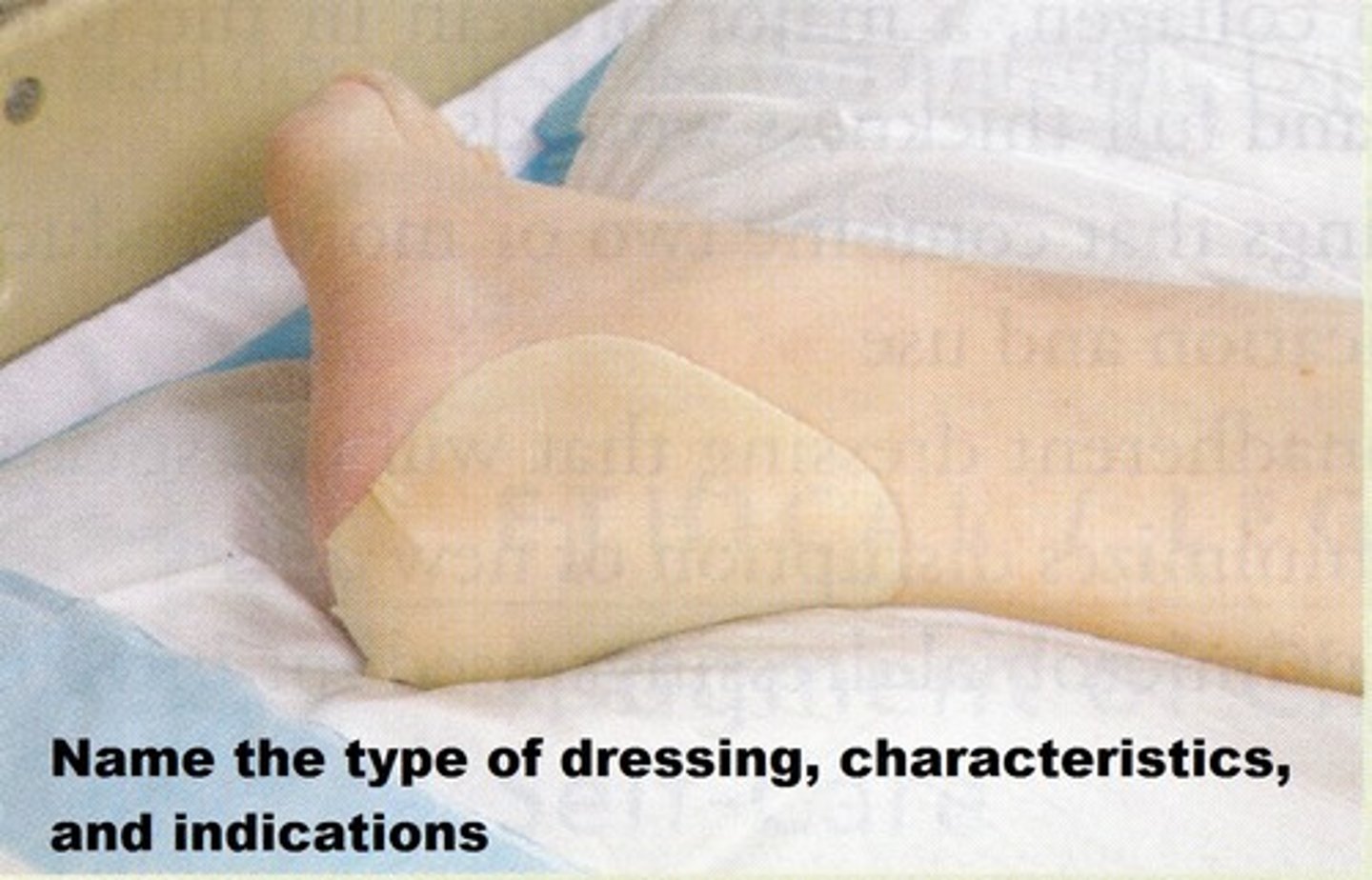
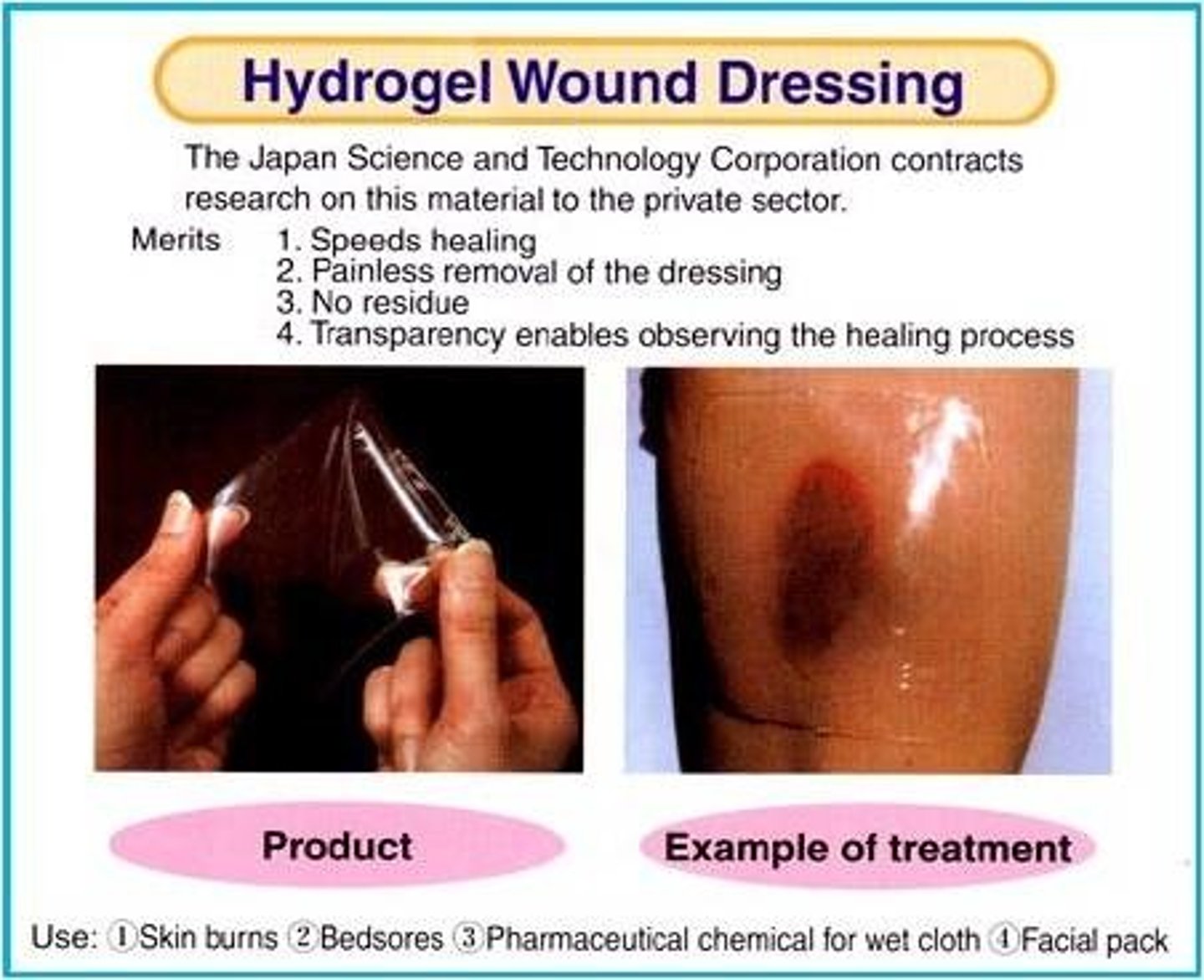
Describe hydrogels
-water and gel-forming materials such as glycerin
-commonly used on superficial and partial thickness wounds (abrasions, blisters,. pressure ulcers) that have MINIMAL DRAINAGE
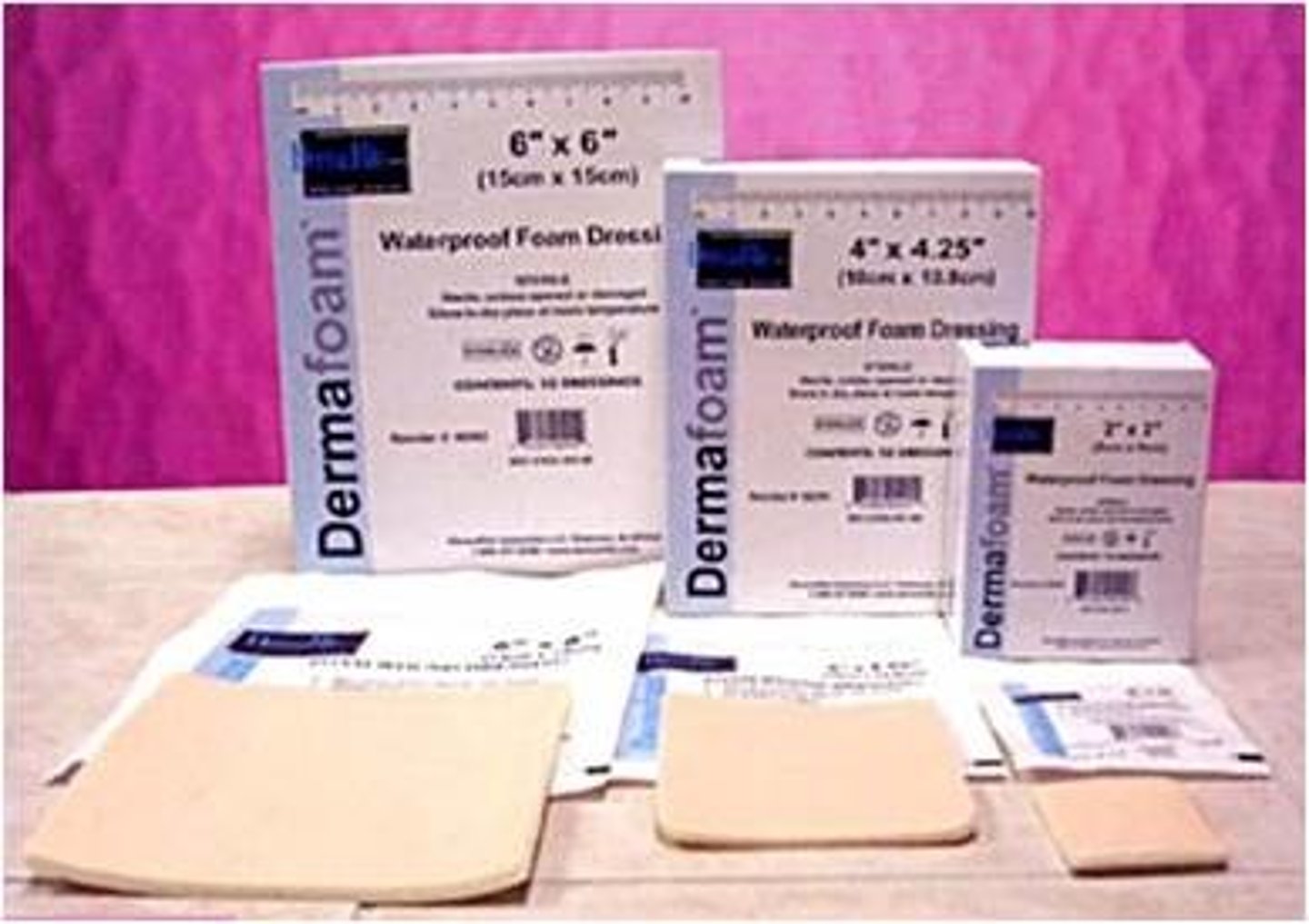
Describe foam dressings
-hydrophilic polyurethane base that contacts the wound surface and a hydrophobic outer layer
-allows exudate to be absorbed into the foam through the hydrophilic layer
-most commonly available in sheets and pads with varying degrees of thickness

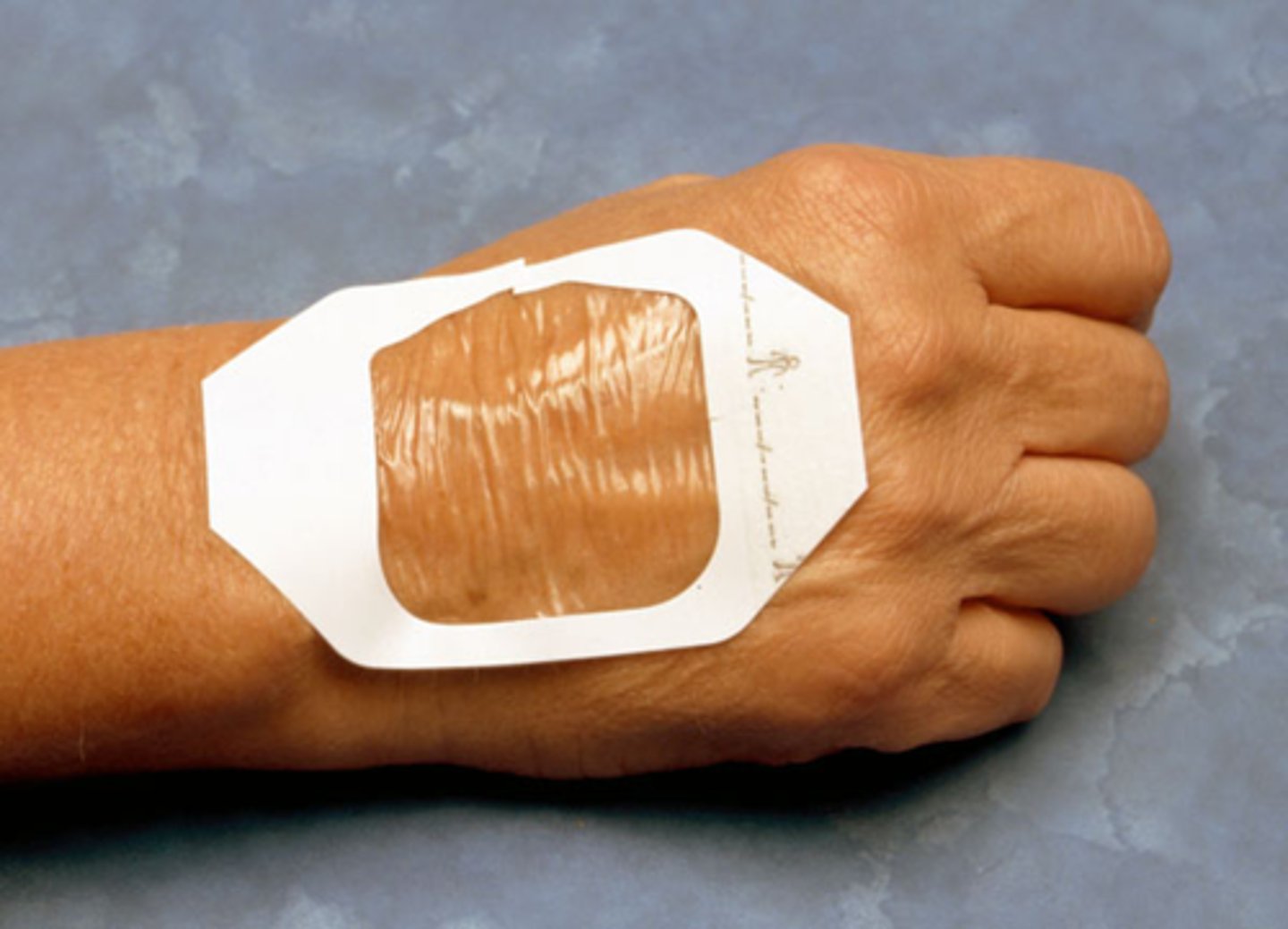
Describe transparent film
-thin membrane from transparent polyurethane with water-resistant adhesives.
-permeable to vapor and oxygen
-impermeable to bacteria and water
-highly elastic
-easy to visually inspect
-used for superficial and partial thickness wounds with minimal drainage
Describe gauze
-manufactured from yard or thread and are the most readily available dressing used in inpatient
-many shapes and sizes
-used for infected and non-infected wounds of any size

Describe alginates
-dressing derived from seaweed extraction specifically the calcium salt component of alginic acid.
-highly absorptive but highly permeable and non-occlusive
-used for partial and full thickness draining wounds such as pressure or venous insufficiency ulcers or infected wounds with EXCESSIVE DRAINAGE
Define occlusion
ability of a dressing to transmit moisture vapor or gases between a wound bed and the atmosphere
Splinting type for burns to the elbow
-gutter splint
-conforming splint
-three-point splint
-air splint
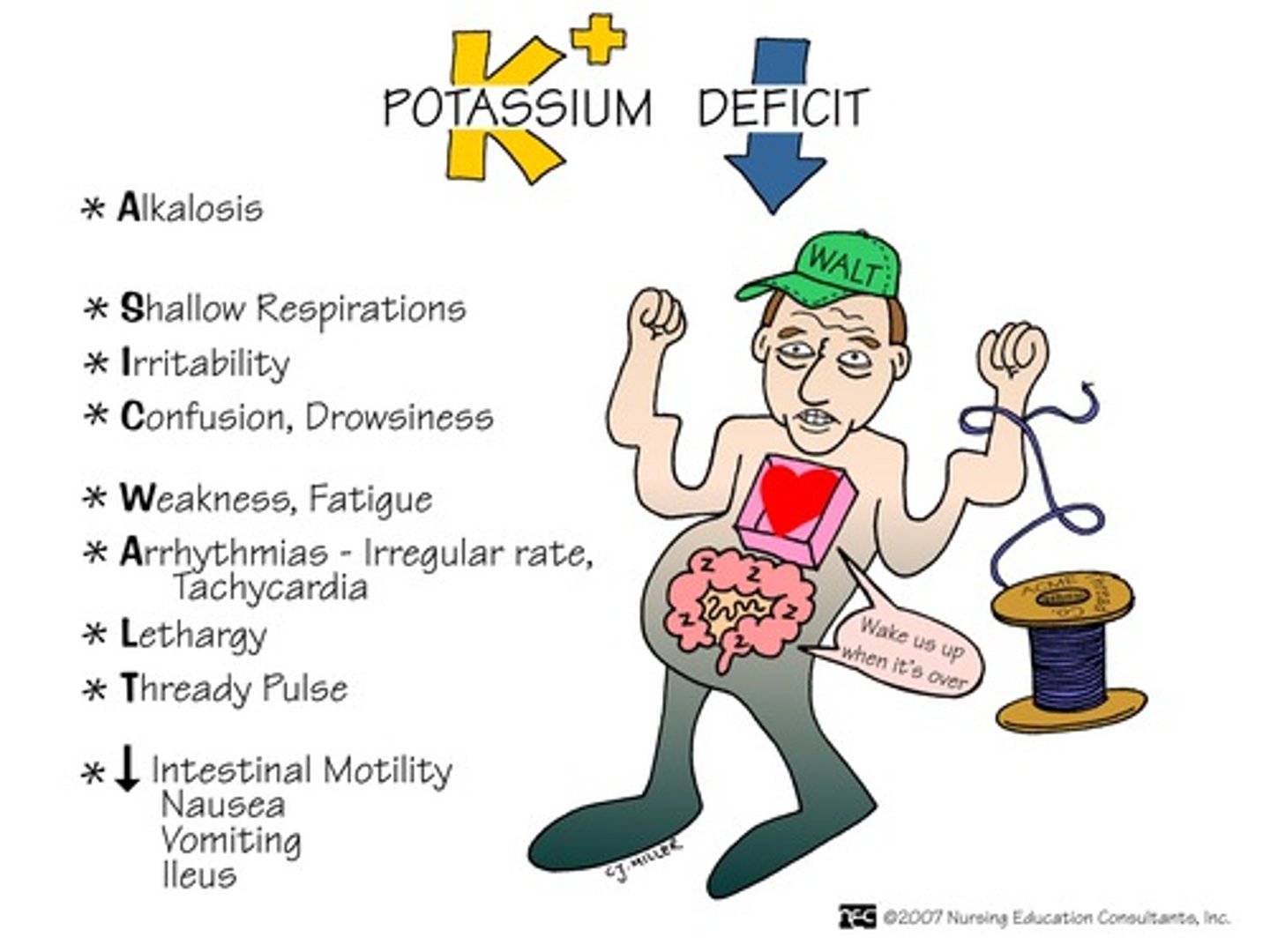
Hypokalemia
refers to abnormally low potassium levels in blood. This condition can be caused by vomiting, diarrhea, burns, uncontrolled DM, diuretic therapy and steroid therapy.
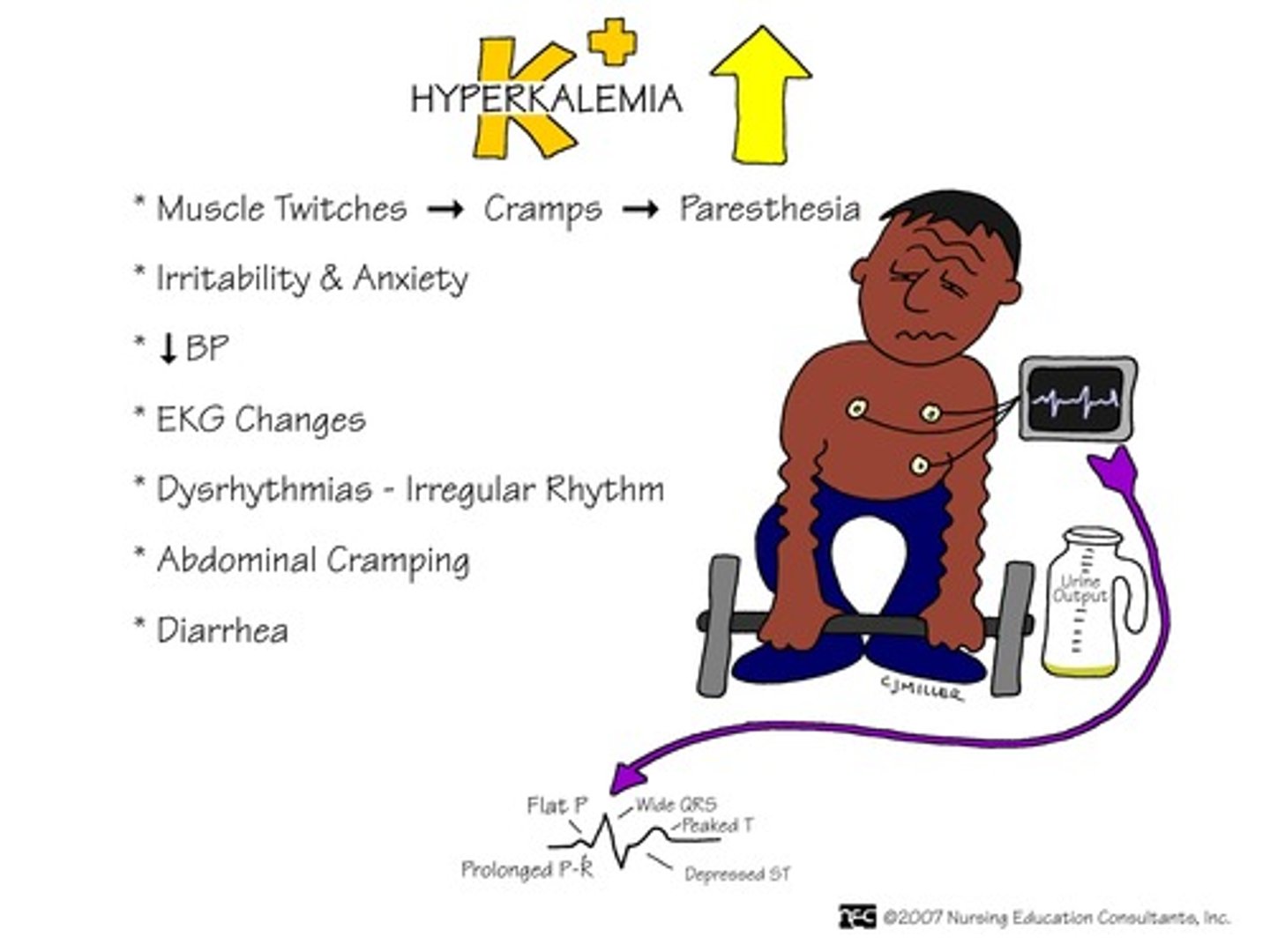
Hyperkalemia
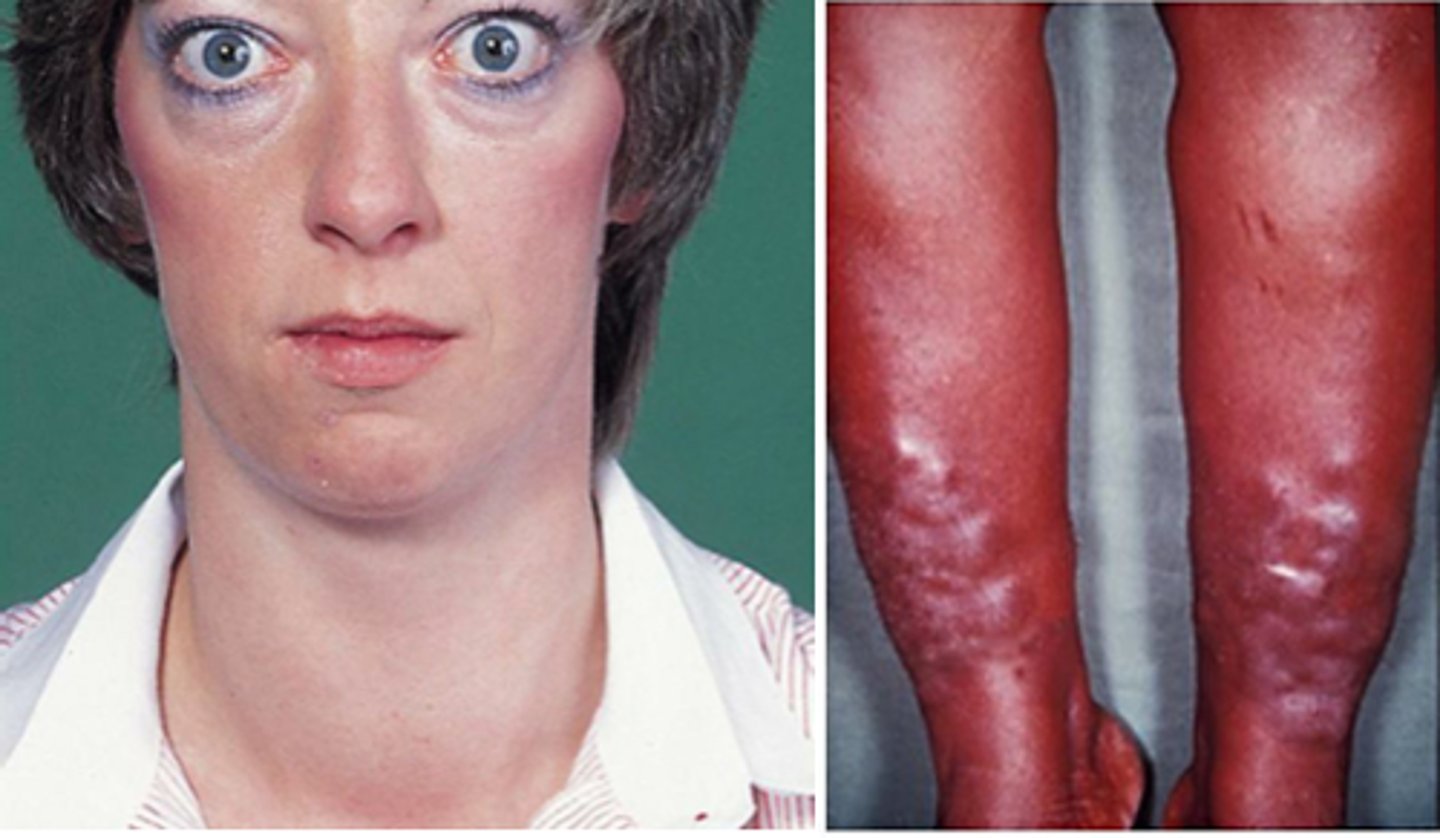
Grave's disease
Excess secretion of thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism).
Classic signs include difficulty eating, mild facial edema, and abnormal protrusion of eyes.
Other symptoms include heat intolerance, weight loss, nervousness, muscle weakness/fatigue, tremor and palpations.
Increased DTRs
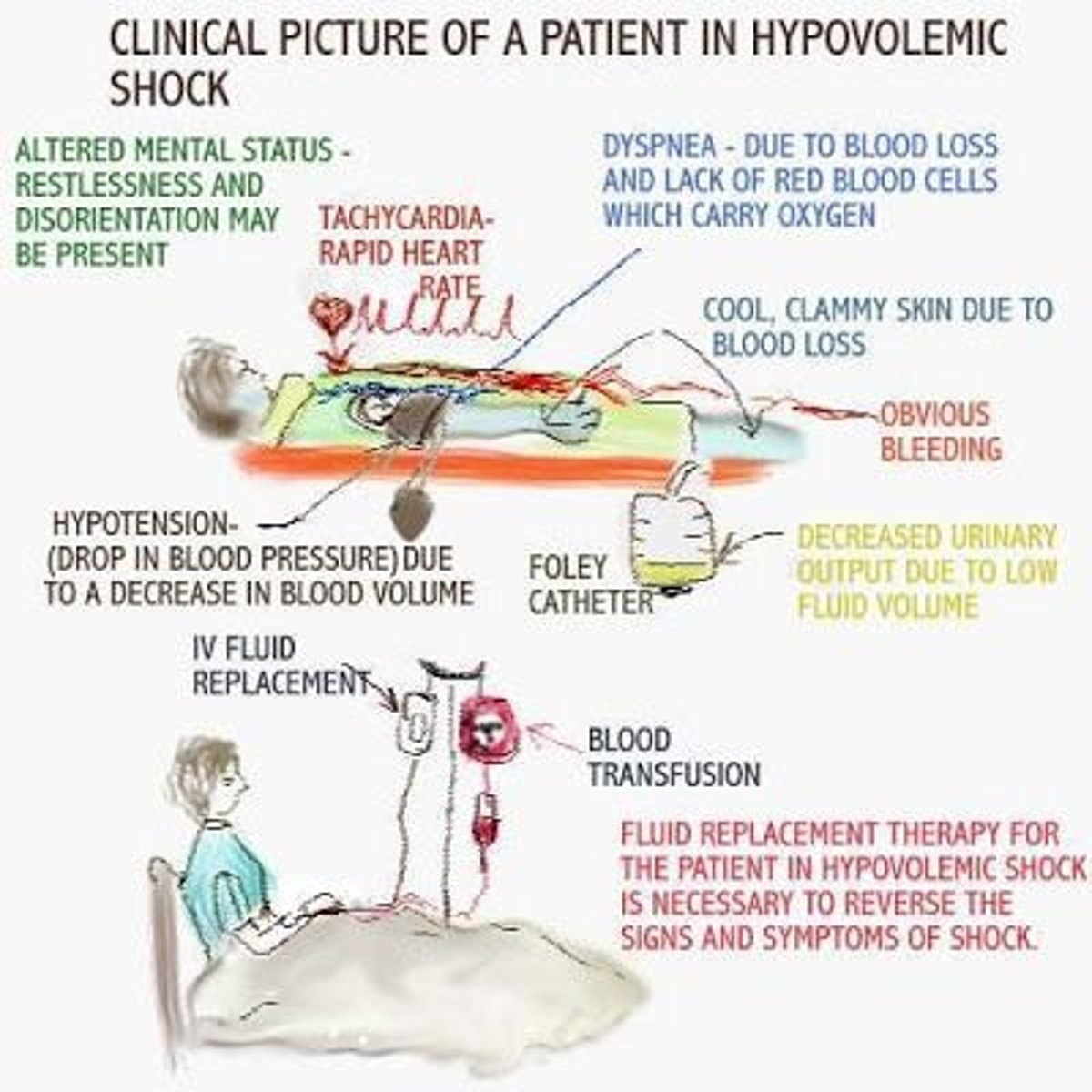
Hypovolemic shock
Dehydration, pulse and respirations are increased; BP may decline. Restlessness, anxiety and confusion may all be present.
Caused by hemorrhage, vomiting, diarrhea
OCCURS IN: Addison's disease, burns, pancreatitis, peritonitis
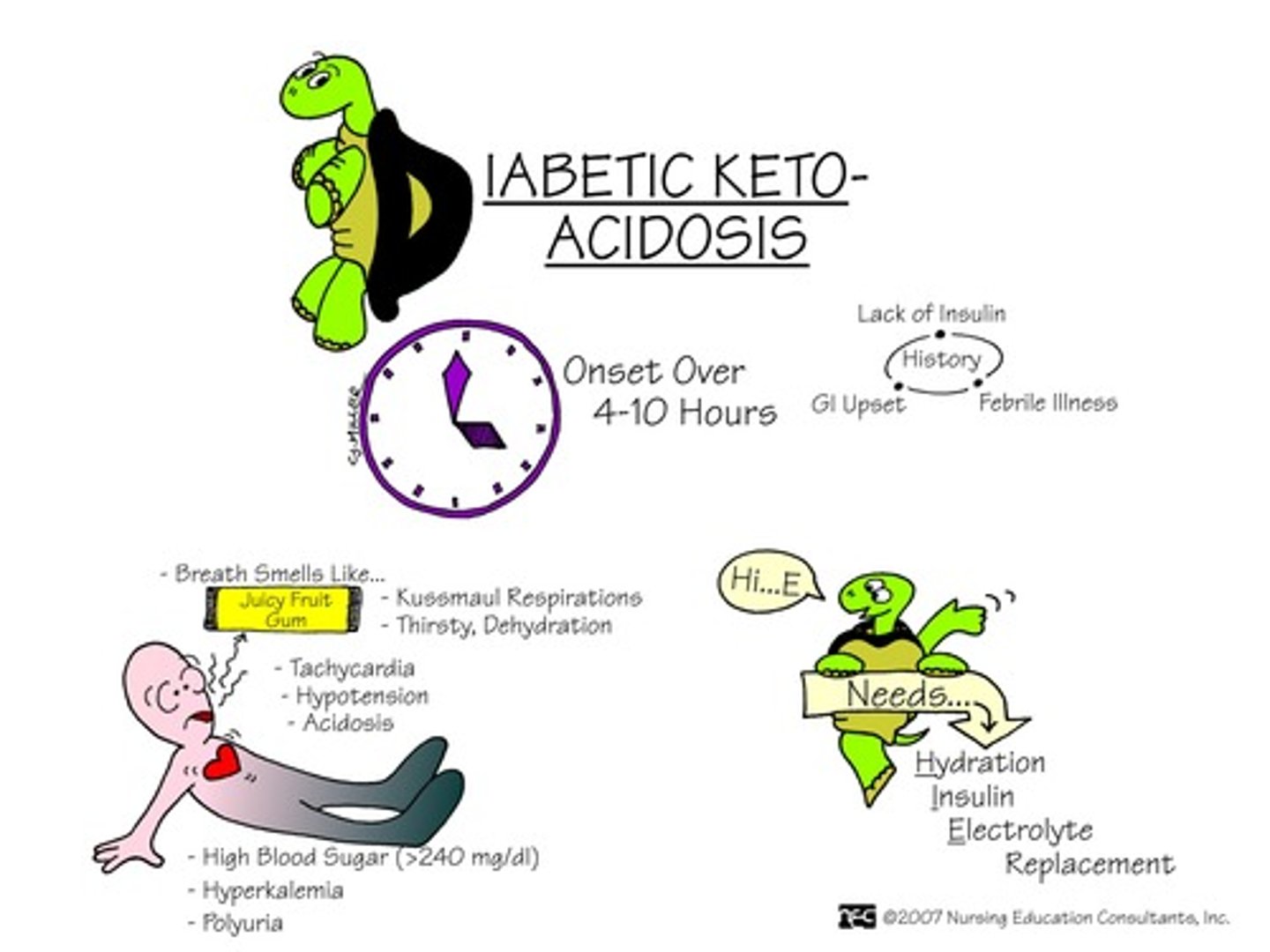
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Production of excess ketones by the liver
S/S
-Altered GI: (anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain),
-neural function (weakness, lethargy, malaise, confusion, stupor, coma, depression of vital functions)
-CV function (peripheral vasoildation, decreased HR, cardiac dysrhythmias, skin (warm and flushed); and increased rate and depth of respiration.
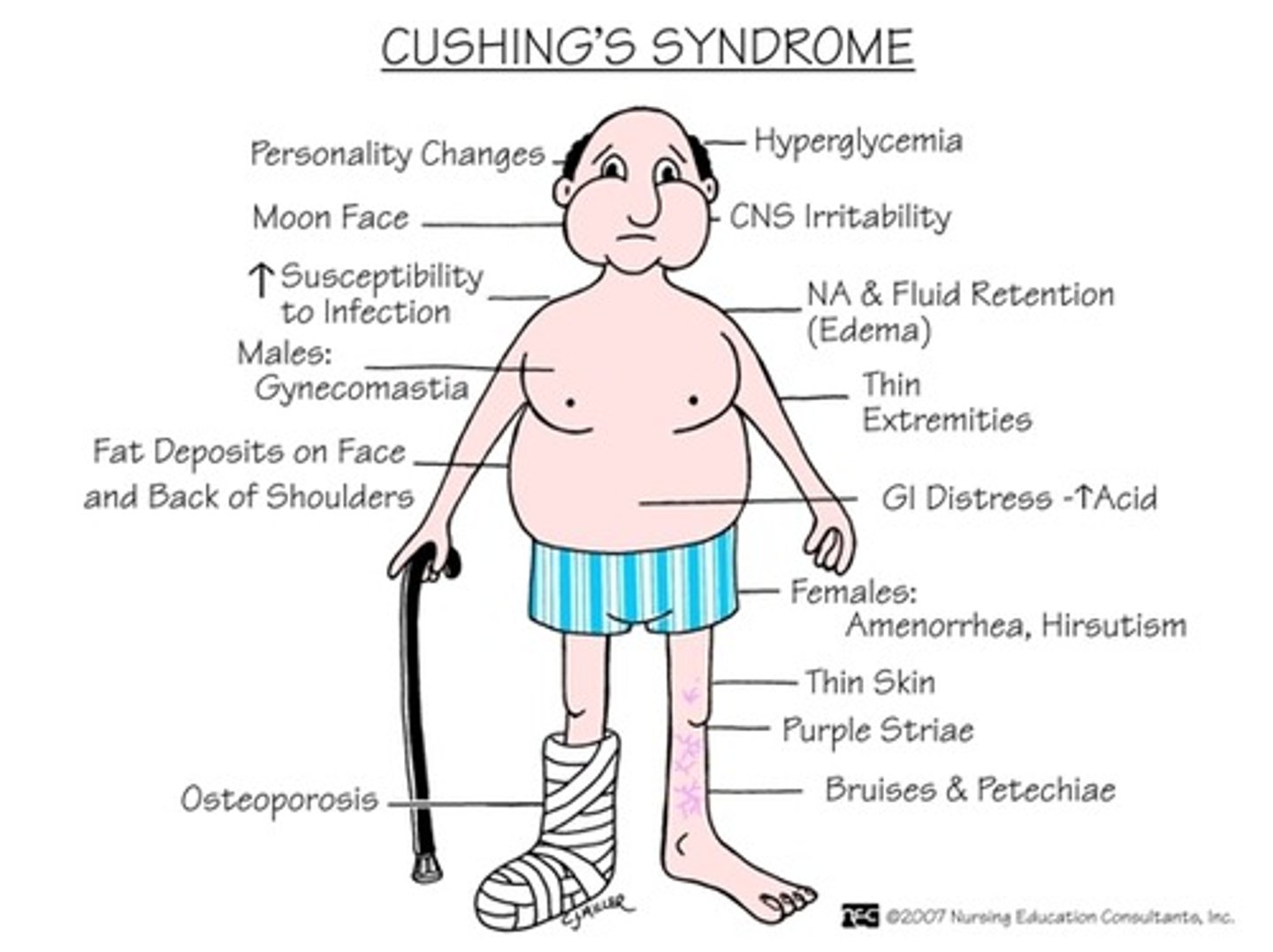
Cushing's syndrome
Adrenal disorder - TOO MUCH cortisol
Causes hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, HTN, muscle weakness and wasting.
S&S: Evolve over years and include hyperglycemia, round "moon face", weakness, acne, HTN obesity (fat pads on chest, abdomen, buffalo hump), depression, poor concentration, memory loss
Metabolic syndrome w/ multiple CV disease risk factors, initial exercise prescription should be
AKA DM
Moderate intensity (40-60%), exercise 30 min per day, most days of the week.
Inherited Metabolic Disorders: Phenylketonuria (amino acid metabolic disorders)
Autosomal recessive trait
Consists of mental retardation as well as behavioral and cognitive issues as a result of elevation of serum phenylalanine
Presents within a few months of birth
Shows signs of gait disturbances and hyperactivity
Parathyroid dysfunction
Hyper: Excessive levels of horomone production
leading to distribution of calcium, phosphate, and bone metabolism.
Symptoms: Renal stones, kidney damage, memory loss, bone deformity,
Hypo: Symptoms include hypocalcemia , neurological symptoms such as seizures, cognitive defects, muscle pain, cramps
Thyroid Dysfunction: Hypothyroidism - Signs & Symptoms
1. Fatigue
2. Weakness
3. Decreased Heart Rate
4. Weight Gain
5. Constipation
6. Delayed Puberty
7. Retarded Growth and Development
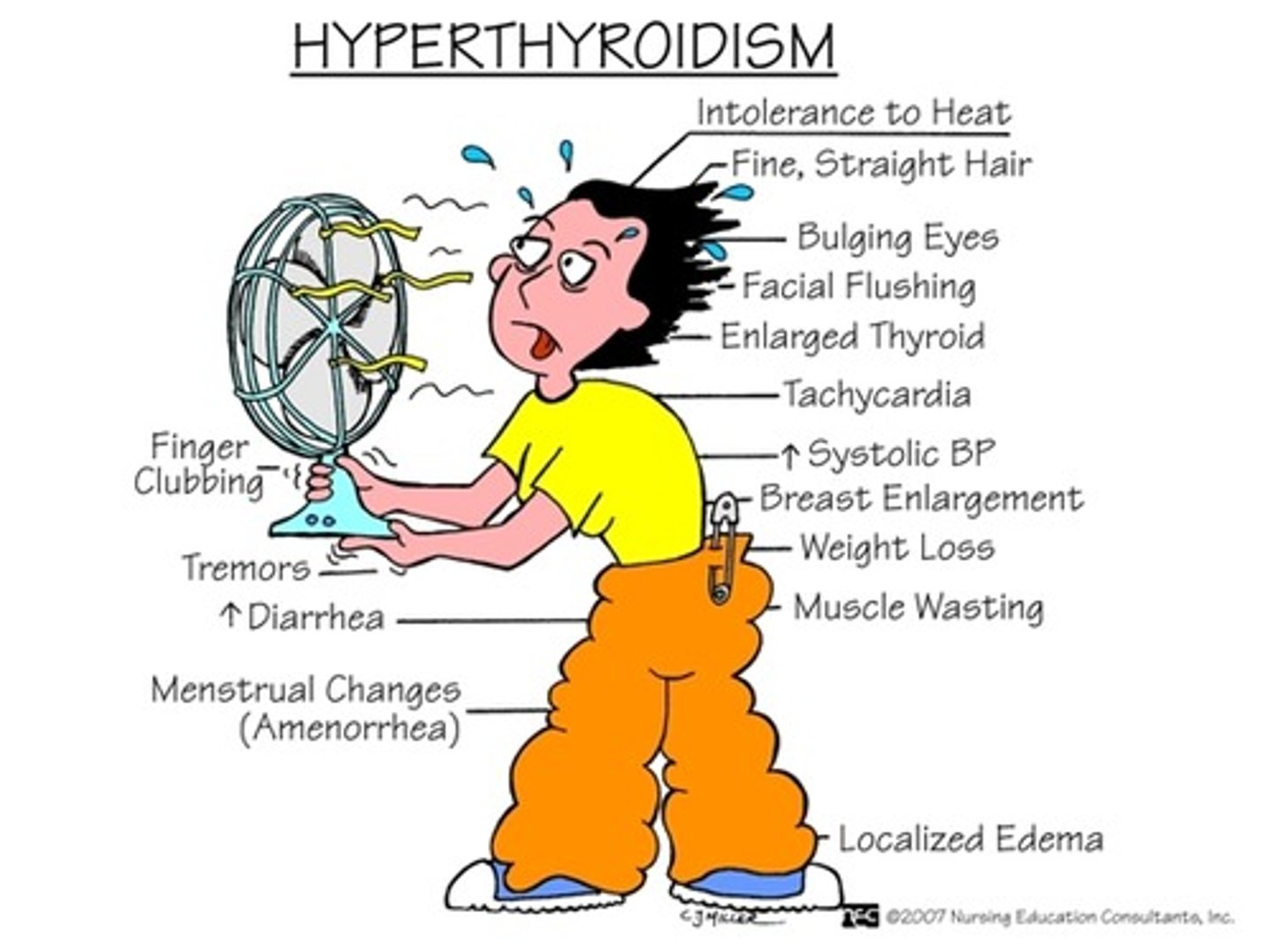
Thyroid Dysfunction - What is Hyperthyroidism?
Occurs when there are excessive levels of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream.
Hyperthyroidism - Signs & Symptoms
Think ^ metabolism - Grave's Disease
1. Increase in nervousness
2. Excessive sweating
3. Weight loss
4. Increase in blood pressure
5. Exophthalmos (bug eyes, eyes protrude)
6. Myopathy
7. Chronic peri-arthritis (frozen shoulder)
8. Enlarged thyroid gland
A physical therapist observes that a patient with end-stage renal disease has significant exercise intolerance. Which factor is the MOST likely cause of the exercise intolerance?
Anemia - kidneys no longer releasing EPO to stimulate RBC production (which carry O2)
Persons with end-stage renal disease have limitations to exercise due to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity associated with anemia.
A patient who has been receiving corticosteroids over the past 3 months is MOST likely to experience which side effects?
Increased risk of infection
The risk of infection is increased because cortisol or corticosteroids dampen the body's inflammatory response
Herpes Zoster
(shingles) Acute viral infection; painful vesicular eruptions on the skin following along the nerve pathways of underlying spinal or cranial nerves.
usually has a symptom distribution in the nerve root pattern