BI 230 - L7-8(Female sexual behavior I&II)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Exam 2 starting @ “Interspecies variation in the female reproductive cycle“
X
What are 3 characteristics that distinct human females from other female mammals?
no stereotypical mating position
in comparison to female mice who stereotypically display lordosis in estrus
NO estrous cycle
NO breeding season
can mate anytime year-round
Typical length in days of the human menstruation cycle?
(about) 28
What are the 2 types of female reproductive cycles in mammals?
spontaneous ovulation
where a female's ova are released without the need for copulation
induced ovulation
where ovulation is stimulated by copulation
In humans, what is menstruation? When does it occur?
shedding of the uterine endometrium that occurs each cycle
occurs when blood concentrations of estrogens and progesterone is low
endometrial tissue no longer supported by steroid hormones
In some mammalian species besides humans (ex: dogs), what is menstruation? When does it occur?
discharge of blood from the vagina
occurs prior to estrus
results from estrus induced stimulation of the uterine wall, which causes rapid growth of the endometrium and many tears in the supporting blood vessels
Why are there so many kinds of reproductive cycles?
from an ecological perspective, each species’ pattern can be seen as an adaptation for increasing its reproductive success
increases probability that mating will occur when female is fertile
increases probability that offspring will be produced and will survive
Why do female prairie voles display IRREGULAR estrus cycles?
behavior estrus is induced by the presence of fertile male conspecific or his urine
behavioral influence on reproductive cycle → if females don’t engage in anogenital investigation, she WON’T enter estrus
females houses with related males (ex: father or brothers) don’t engage in this behavior and WON’T enter estrus
Urine detected via the VNO → signal sent to accessory olfactory bulb
triggers the release of GnRH → anterior pituitary releases FSH and LH (occurs within 1 hr of exposure)
ovulation is induced and occurs ~12 hrs after mating
Social and environmental effects on reproductive cycle
Lee-Boot effect
Whitten effect
Bruce effect
Vandenbergh effect
3 factors that adversely affect ovarian cycles
lack of proper nutrients
stress
stressful life events in women have been found to impact the reproductive cycle
one study found that perimenopausal women on death row were not experiencing any menstrual cycles
illness
chemical messengers called cytokines (released by activated macrophages) are how the immune system affects neuroendocrine processes in the hypothalamus and pituitary
administration of one such cytokine causes female rats to reduce their receptivity and proceptivity
How do birth control pills work?
combination pills work by keeping estrogen and progesterone concentration at a stable level
suppresses the secretion of LH and FSH by the pituitary
no ovulation occurs because follicles don’t mature
thickens the mucus of the cervix (progestin has this effect) which makes it a more effective barrier for sperm
thins uterine lining which makes it less likely to support a pregnancy
mini pills work by delivering a low dose of progestin
thickens the mucus of the cervix (progestin has this effect) which makes it a more effective barrier for sperm
thins uterine lining which makes it less likely to support pregnancy
may suppress ovulation, but this effect is more variable
Ovulatory vs. uterine cycle
Ovulatory
follicular phase (days 1-14)
ovulation (day 14)
luteal phase (days 14-28)
Uterine
menstrual phase (days 1-5)
proliferative phase (days 6-14)
secretory phase (days 14-28)
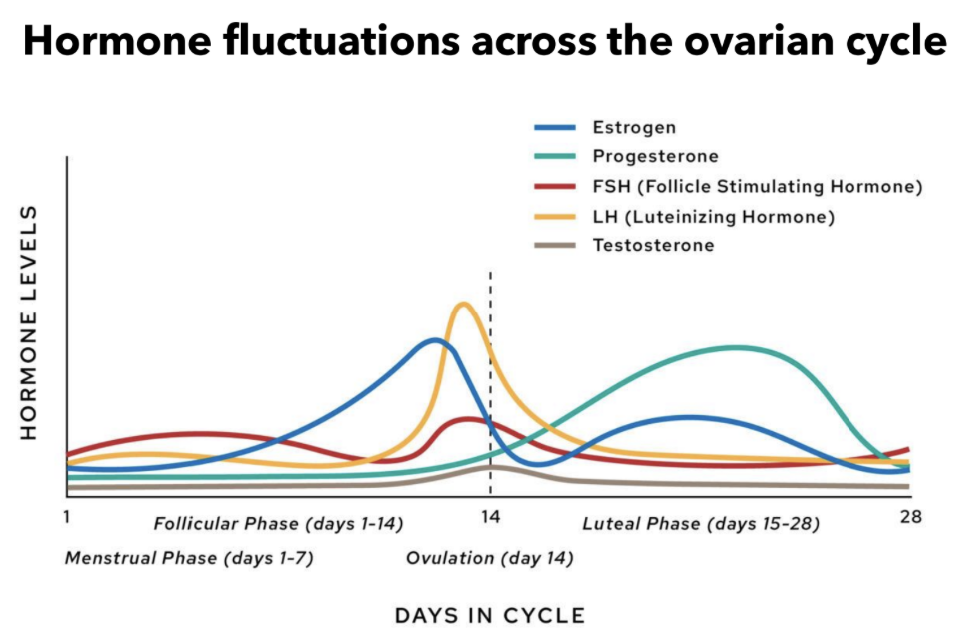
Hormone fluctuations across ovarian cycle: what