BIOL 2302 Ch 26: Reproduction, Fetal Development and Heredity
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
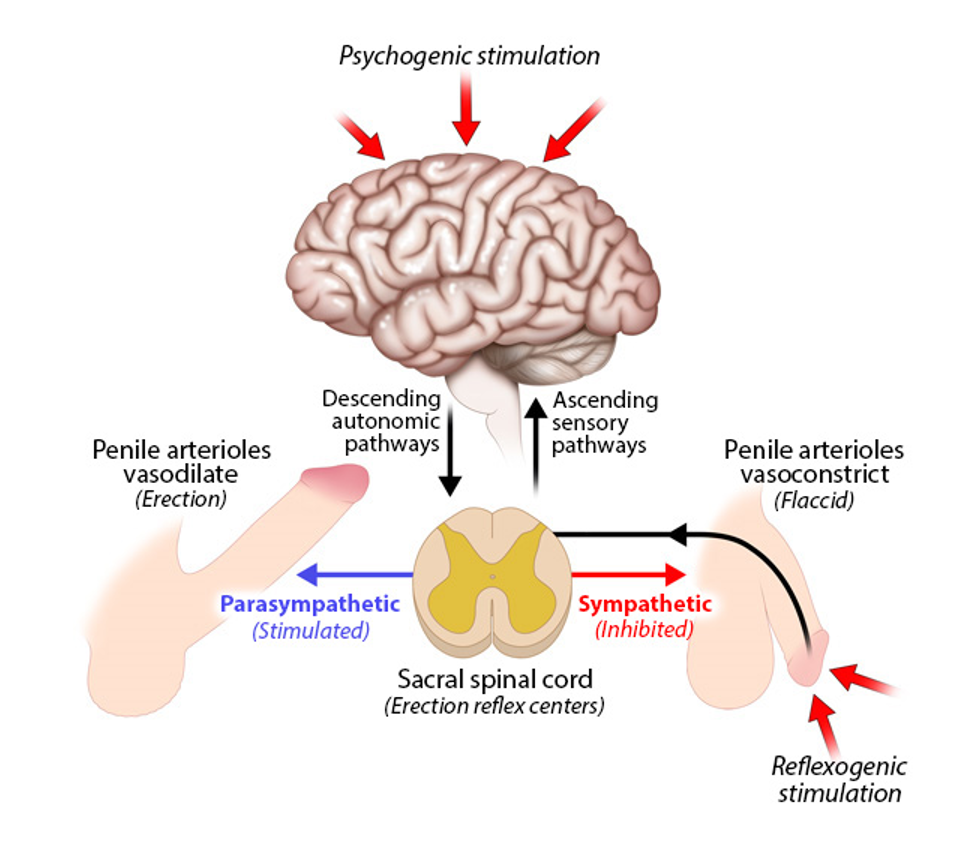
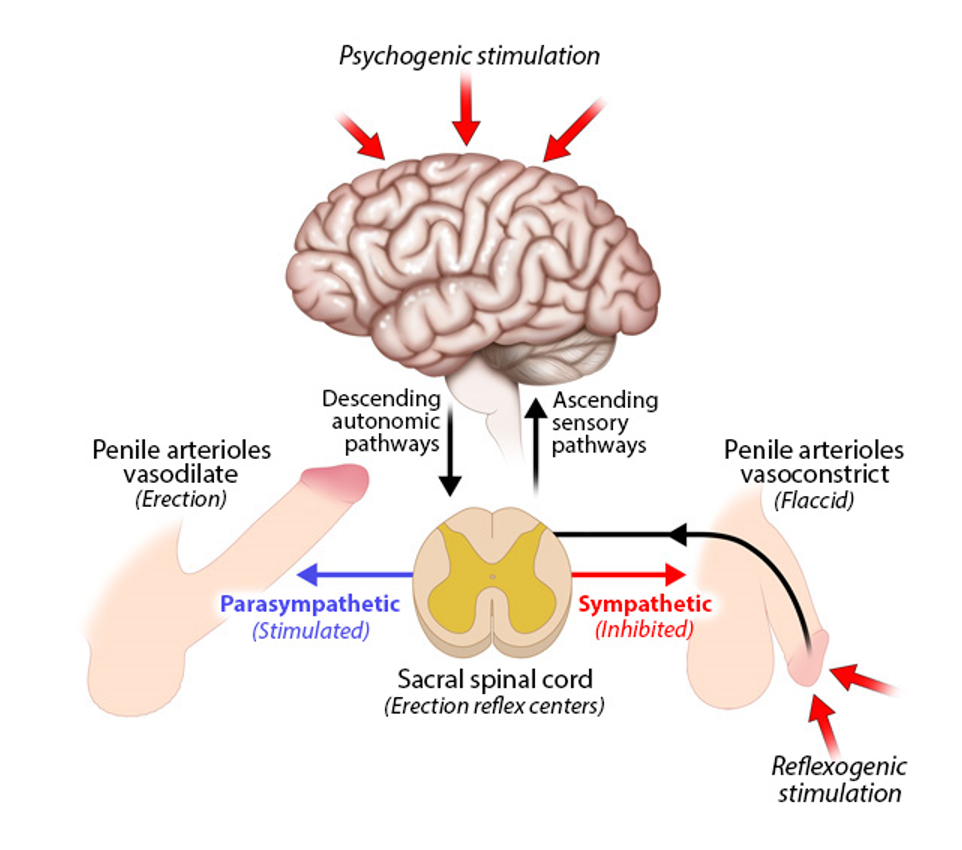
erection reflex
a spinal reflex influenced by the brain
triggered by
psychogenic stimulation
thoughts, sights, etc.
reflexogenic stimulation
physical touch
both types activate autonomic pathway from brain→ sacral spinal cord (? reflex centers)
parasympathetic stimulation
vasodilation of penile arterioles→ erection
sympathetic inhibition
vasoconstriction of penile arterioles→ flaccid state
sexual arousal
reflexogenic or psychogenic trigger
can incorporate all the senses
4 stages
excitement
plateau
orgasm
resolution
male specific
urethra opens and widens (for ejaculation)
scrotum skin thickens
cremaster muscle elevates testes
common to M and F
increased heart rate
increased blood pressure
increased breathing rate and depth
erect nipples
sex flush (reddening of skin, often on chest/face)
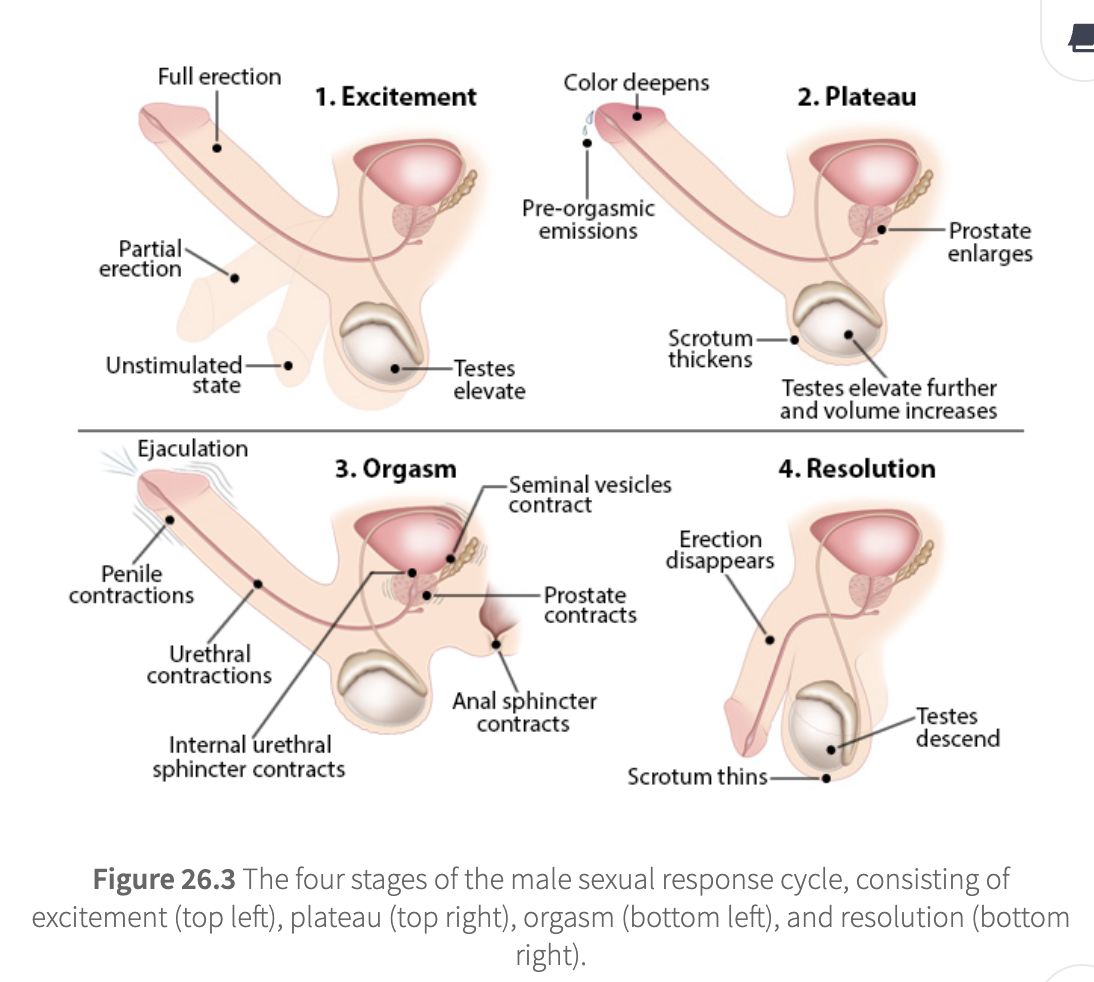
male sexual reponse
excitement
originates in erection reflex center of sacral spinal cord
erection can be reflexogenic (physical) or psychogenic (mental)
penis goes from unstimulated→ partial→ full erection
testes elevate
plateau
requires continual erotic stimulation
pre-orgasmic emission begins
prostate enlarges
scrotum thickens
testes elevate further and increase in volume
orgasm
loss of voluntary muscle control
ejaculation (emission + expulsion of semen)
penile and urethral contractions
internal urethral sphincter contraction
seminal vesicle and prostate contractions
anal sphincter contraction
followed by refractory period (no new erection/orgasm possible for a while)
resolution
reproductive tissue return to their resting state
erection disappears
scrotum thins
testes descend
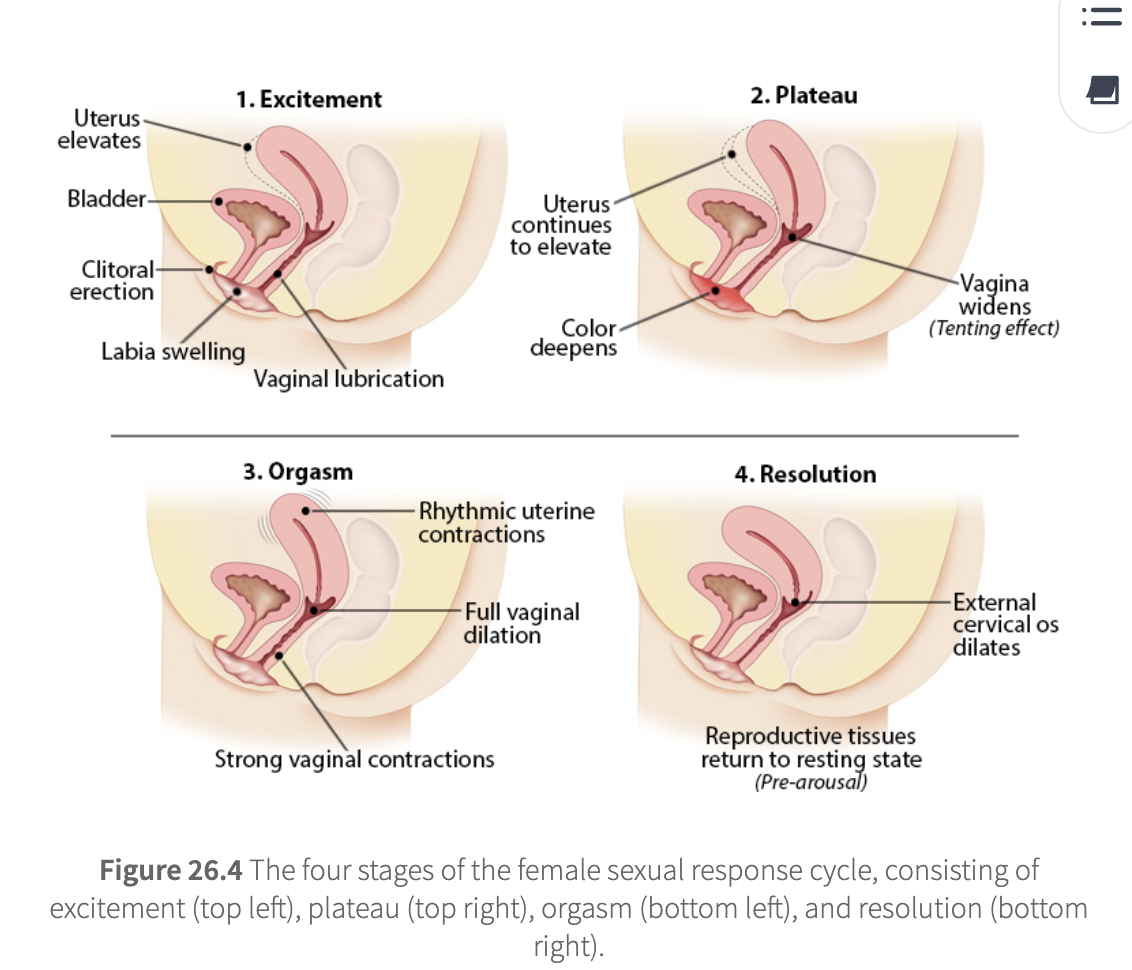
female sexual response
excitement
vaginal lubrication
uterine fibrillations (minor contractions)
clitoris becomes erect
labia swell
uterus elevates above bladder
plateau
external indicators of sexual arousal continue to increase
labia deepen in color
uterus continues to elevate
vaginal walls widen (tenting effect)
sexual arousal signs intensify
orgasm
strong vaginal muscle contractions apply greater pressure on the penis
vaginal dilation to receive ejaculate
no refractory period (can have multiple orgasms)
rhythmic uterine contractions
resolution
reproductive tissues return to their resting state
external cervical os dilates to aid sperm migration
male ejaculate
seminogelin
from seminal vesicles
coagulates semen, sticks sperm to vaginal wall after ejaculation
motility inhibitor
prevents sperm from struggling in the coagulant, wasting energy
PSA (prostate specific antigen)
breaks down seminogelin within 20-40 mins, freeing sperm
liquefant
prostaglandins
induce reverse peristalsis in uterus to draw sperm inwards
reduce cervical mucus viscosity (ease sperm entry)
hCAP-18
anti-microbial protein that prevents bacterial growth in female reproductive tract
factor III
coagulation/clotting and healing of vaginal microabrasians
PSAP (prostate specific acid phosphatase)
potent anti-nociceptive
reduces pain perception during/after sex
seminogelin
From: Seminal vesicles
Function: Coagulates semen, sticks sperm to vaginal walls
motility inhibitor
Prevents sperm from wasting energy while trapped in the coagulate
PSA prostate specific antigen
From: Prostate
Function: Breaks down seminogelin (20–40 mins later), frees sperm
prostaglandins
Induce reverse peristalsis in uterus (pull sperm inward)
Reduce cervical mucus viscosity to ease sperm entry
hCAP 18
Anti-microbial protein
Protects against bacterial growth in female tract
factor III
Promotes clotting and healing of vaginal microabrasions
PSAP prostate specific acid phosphatase
reduces pain perception (anti-nociceptive) during/after sex
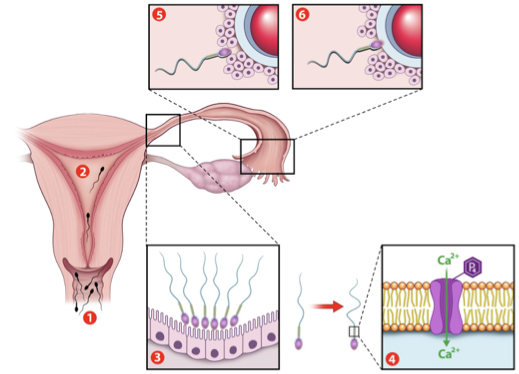
fertilization
sperm deposited in vagina
sperm travel thru cervix→ uterus→ uterine tube
reaches egg in 30 mins- 2 hrs
1 sperm binds egg membrane
egg blocks other sperm (polyspermy prevention)
sperm and egg nuclei fuse→ zygote (1 cell)
capacitation
final maturation step; reqd for fertilization
sperm shed protective layers and gain ability to swim forcefully
prostasomes fuse to sperm head, adding survival and guidance factors
Ca2+ influx increases motility
insemination
sperm enters vagina
initial capacitation
last step of sperm maturation
sperm activate and start swimming
sperm reservoir
sperm rest in uterine tube isthmus until ovulation
hyperactivation
activity of sperm
triggered by progesterone from the oocyte
progesterone binds catsper channel→ Ca2+ rushes in
sperm swims vigorously, follows chemical signal
cumulus penetration
sperm pushes thru cells around eggs
zona pellucida penetration
sperm breaks thru egg’s outer shell
fertilization! (1 sperm fuses w/ egg)
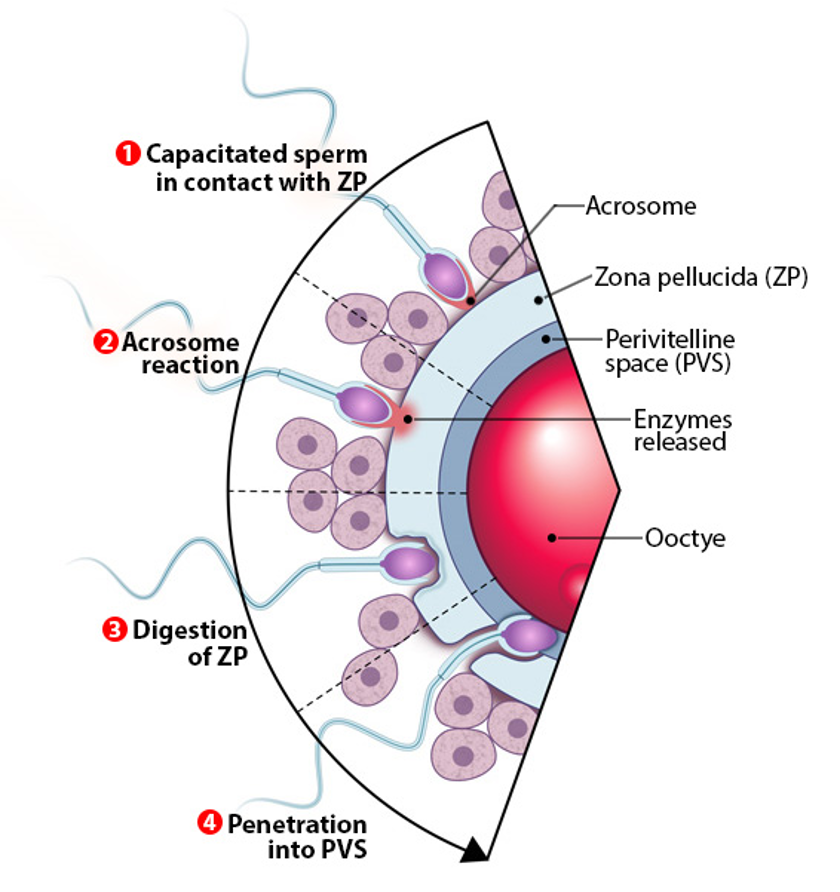
fertilization
capacitated sperm contacts zona pellucida ZP
ZP= species-specific barrier
only sperm of same species can bind
acrosome rxn
acrosome (enzyme sac on sperm head) ruptures
released proteases digest zona pellucida so sperm can pass thru
also rearranges sperm plasma membrane for fusion
digestion of zona pellucida
sperm uses enzymes + hyperactive movement to burrow through
penetration into perivitelline space PVS
sperm enters space btw ZP and oocyte
must find area w/ microvilli to bind and fuse
sperm-oocyte membrane fusion
triggers Ca2+ release in oocyte
activates oocyte→ completes meiosis II
blocks polyspermy, starts development
fusion of egg and sperm
oocyte has microvilli all over its surface, except for overlying the oocyte’s pronucleus
microvilli serve as docking site for sperm, ensuring they dock away from pronucleus
oocyte is activated after sperm-egg fusion
PLCz (a component of the sperm’s plasma membrane) triggers release of Ca2+ from oocyte’s ER
Ca2+ oscillations trigger
block polyspermy
complete meiosis II
recruitment of maternal mRNA
activation of zygotic genome
blocking polyspermy
cortical rxn happens immediately after oocyte activation
cortical granules migrate towards the oocyte plasma membrane and release their contents into the perivitelline space PVS
these materials form a new barrier against further sperm fusion
prevents extra DNA (euploidy issue)
syngamy- 2nd meiotic division
Ca2+ release triggers meiosis II
second polar body is expelled
oocyte has haploid female pronucleus
sperm pronucleus is unpacked
packaging proteins in sperm pronucleus replaced with maternal histones
paternal mitochondria destroyed
maternal mitochondria activated
only maternal mitochondria passed to embryo
maternal RNA destroyed
male+ female pronuclei fuse= diploid zygote (1 cell)
early embryogenesis
initial cleavage (day 1)
zygote (1 cell) divides → 2 cell stage
mitosis begins within 24 hrs
maternal RNA degraded
zygotic genome takes over control
morula stage (day 2-3)
continued cleavage→ 4 cell→ 8 cell→ 16 cell morula
still inside zona pellucida
moves slowly thru uterine tube toward uterus
uterine tube contractions pause morula to sync with uterus readiness
compaction and polarization (day 4-5)
blastomeres compact→ form tight ball
asymmetric division begin→ polarity established
morula enters uterus
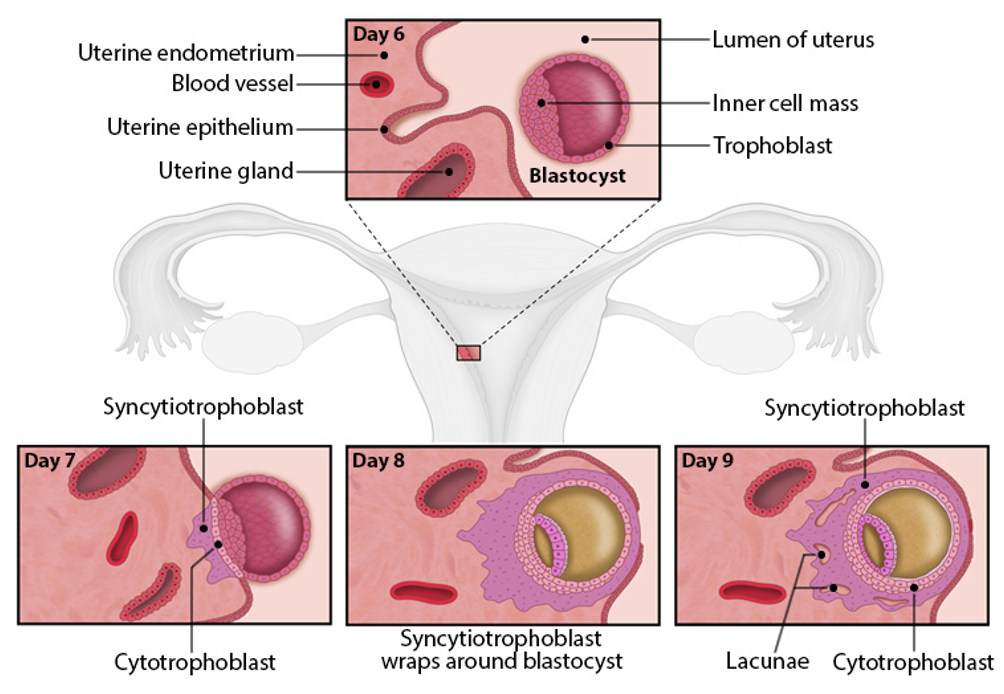
blastulation (day 6-7)
fluid enters morula→ forms hollow blastocyst
trophoblast (outer layer)→ forms placenta
inner cell mass→ forms embryo
blastocoel→ fluid filled cavity
zona pellucida is shed→ embryo ready to implant
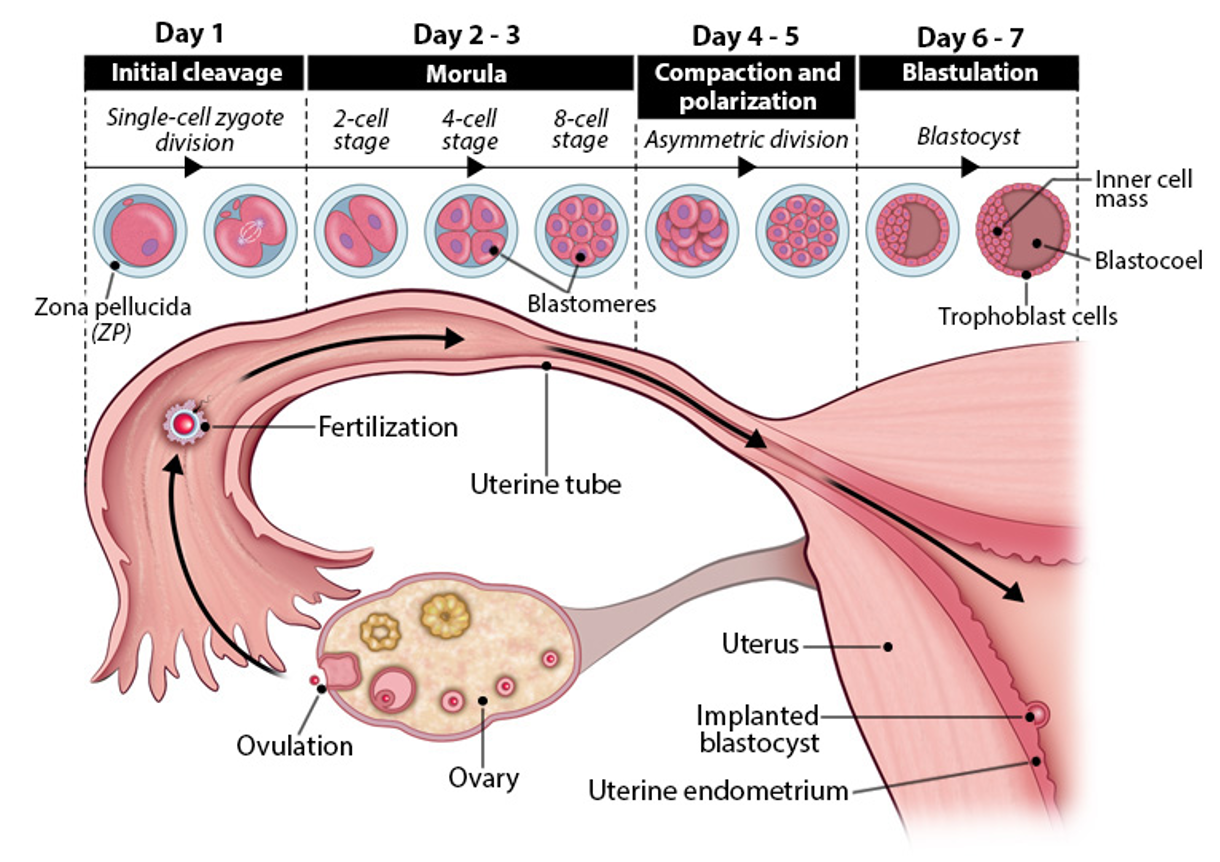
initial cleavage
day 1 embryogenesis
zygote (1 cell) divides → 2 cell stage
mitosis begins within 24 hrs
maternal RNA degraded
zygotic genome takes over control
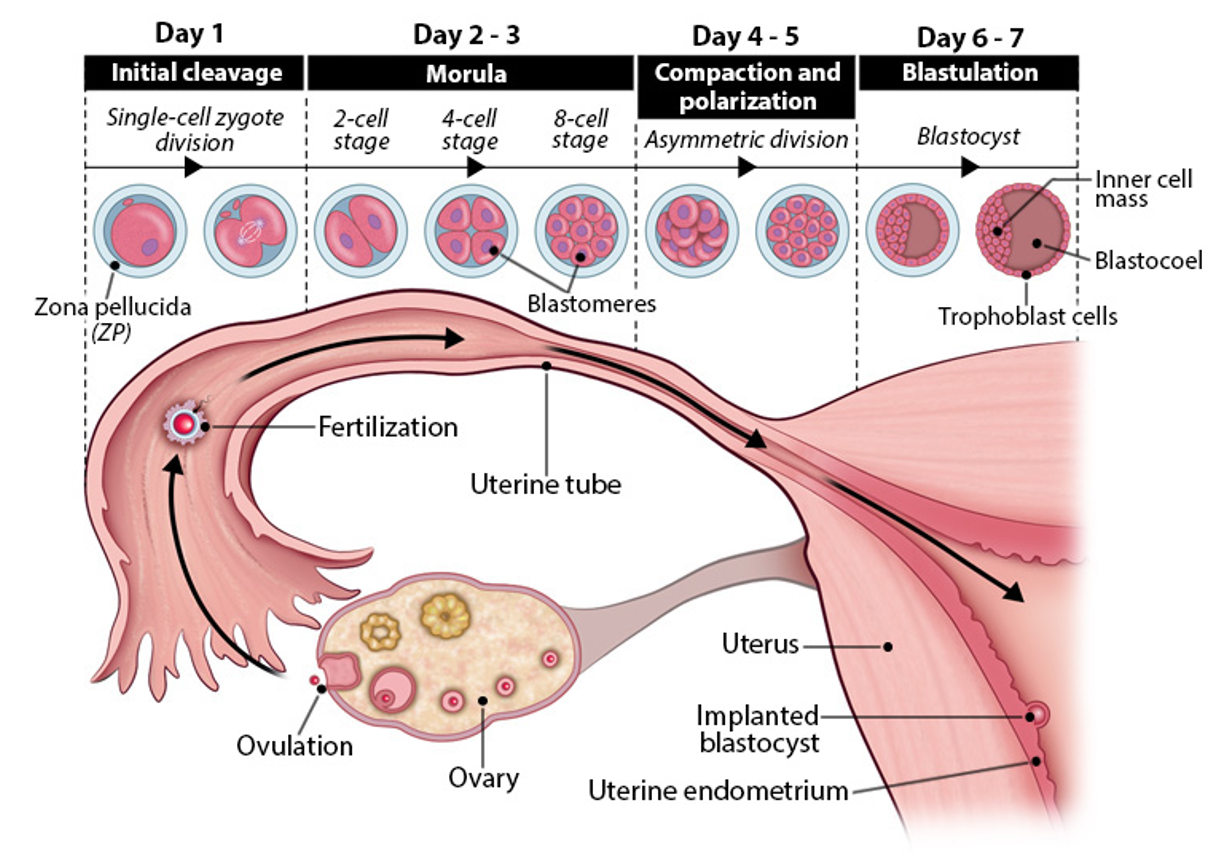
morula stage
day 2-3 embryogenesis
continued cleavage→ 4 cell→ 8 cell→ 16 cell morula
still inside zona pellucida
moves slowly thru uterine tube toward uterus
uterine tube contractions pause morula to sync with uterus readiness
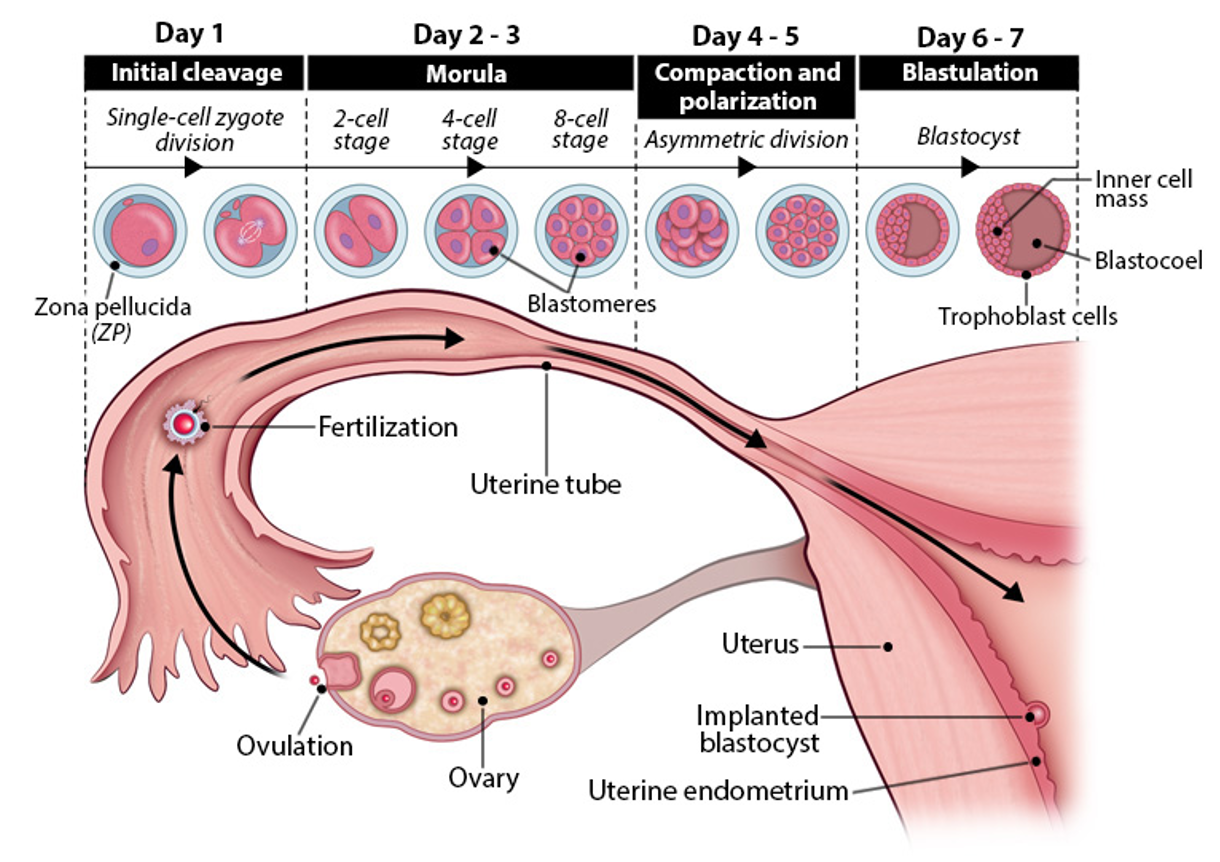
compaction and polarization
day 4-5 embryogenesis
blastomeres compact→ form tight ball
asymmetric division begin→ polarity established
morula enters uterus
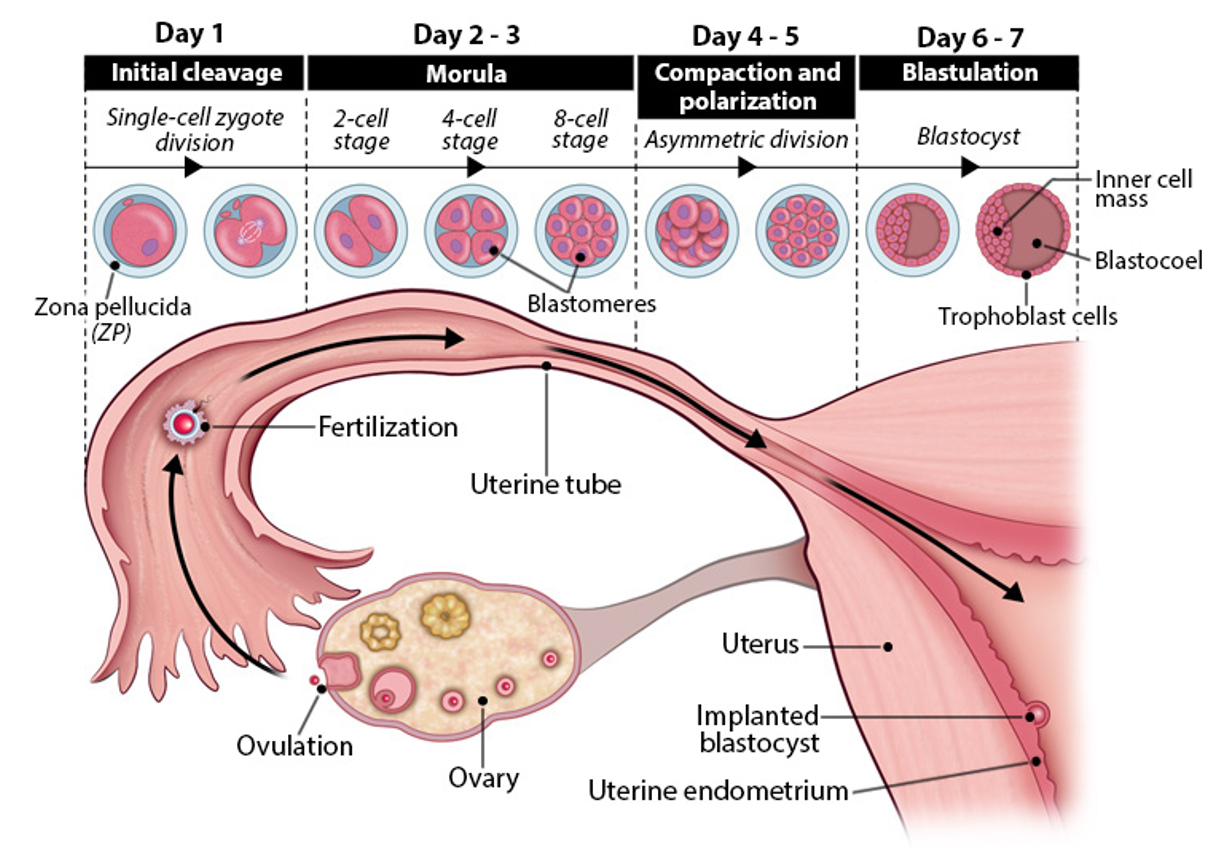
blastulation
day 6-7 embryogenesis
fluid enters morula→ forms hollow blastocyst
trophoblast (outer layer)→ forms placenta
inner cell mass→ forms embryo
blastocoel→ fluid filled cavity
zona pellucida is shed→ embryo ready to implant
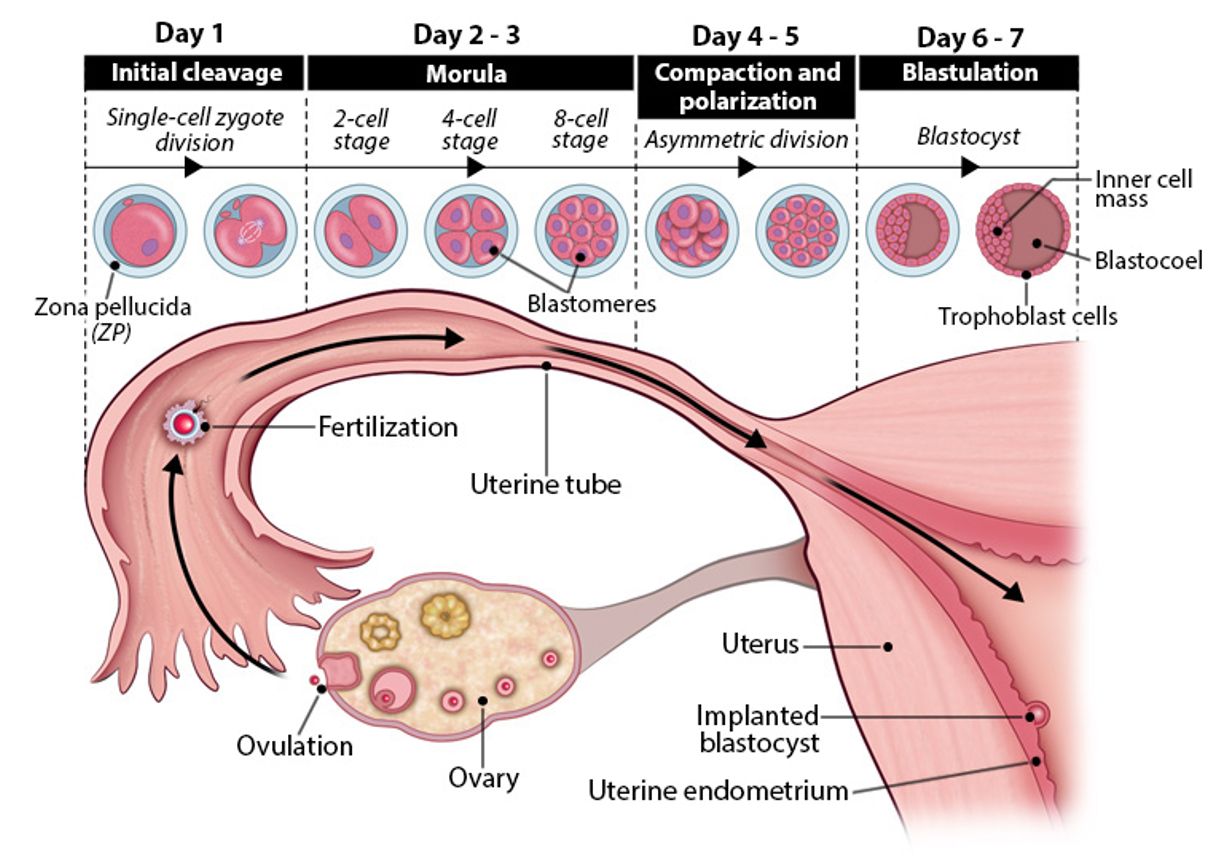
prep for uterine implantation
apposition
uterine walls swell (stromal edema) to bring blastocyst and endometrium closer
helps incoming blastocyst make initial, weak contact with uterine lining
attachment
blastocyst attaches with inner cell mass facing uterus (polarity matters)
trophoblast cells contact uterine epithelium→ differentiate into
cytotrophoblast (retains structure)
syncytiotrophoblast (invades uterus)
penetration
blastocyst burrows into endometrial stroma for access to uterine nutrients
syncytiotrophoblast forms a barrier btw blastocyst and maternal cells
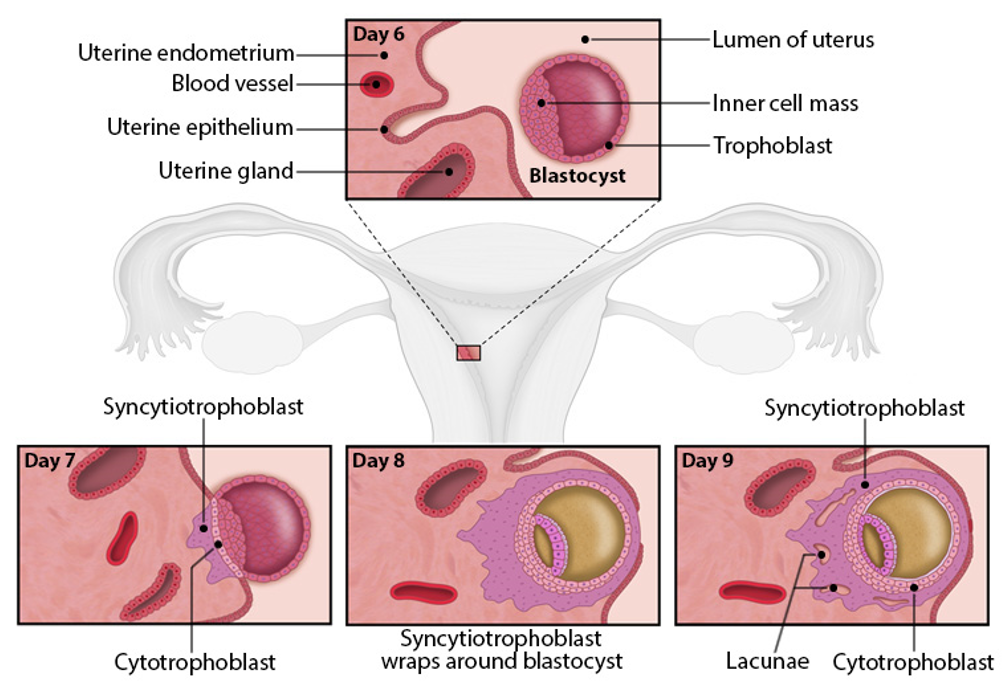
apposition
stage of implantation
Uterine walls swell (stromal edema) to bring blastocyst and endometrium closer
Helps blastocyst make initial, weak contact with uterine lining
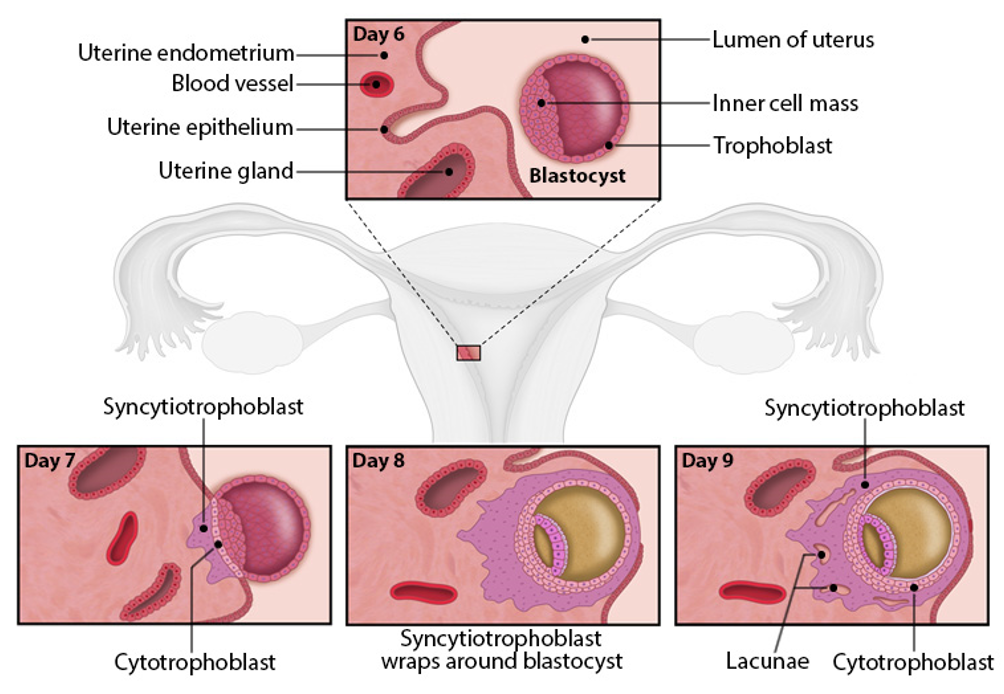
attachment
stage of implantation
Blastocyst attaches with inner cell mass facing uterus (polarity matters!)
Trophoblast cells contact uterine epithelium → differentiate into:
Cytotrophoblast (retains structure)
Syncytiotrophoblast (invades uterus)
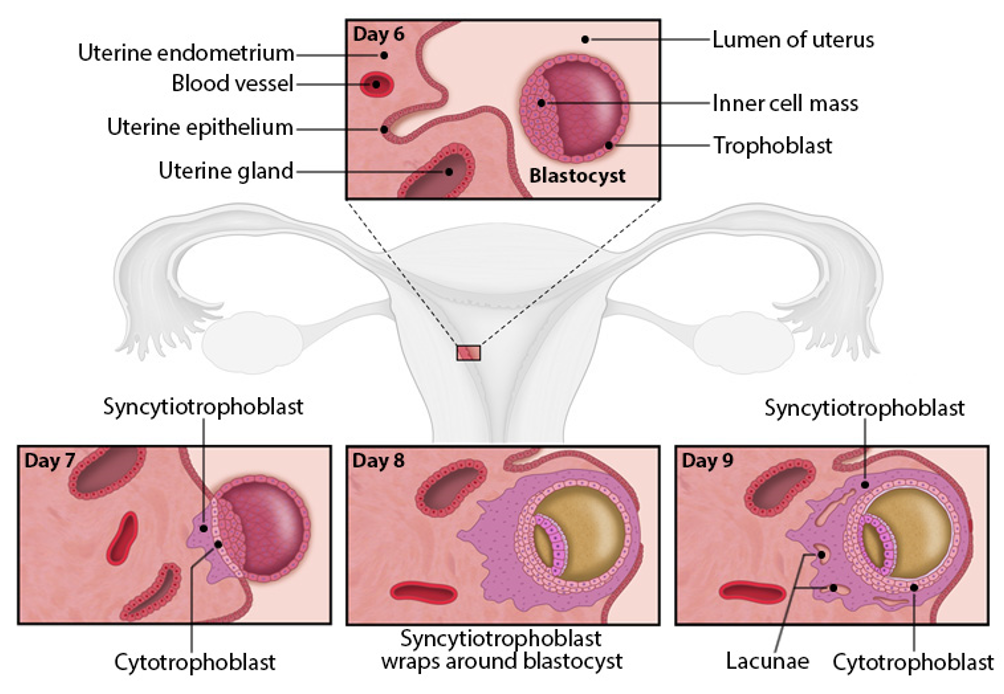
penetration
stage of implantation
Blastocyst burrows into endometrial stroma to access uterine nutrients
Syncytiotrophoblast forms a barrier between blastocyst and maternal cells
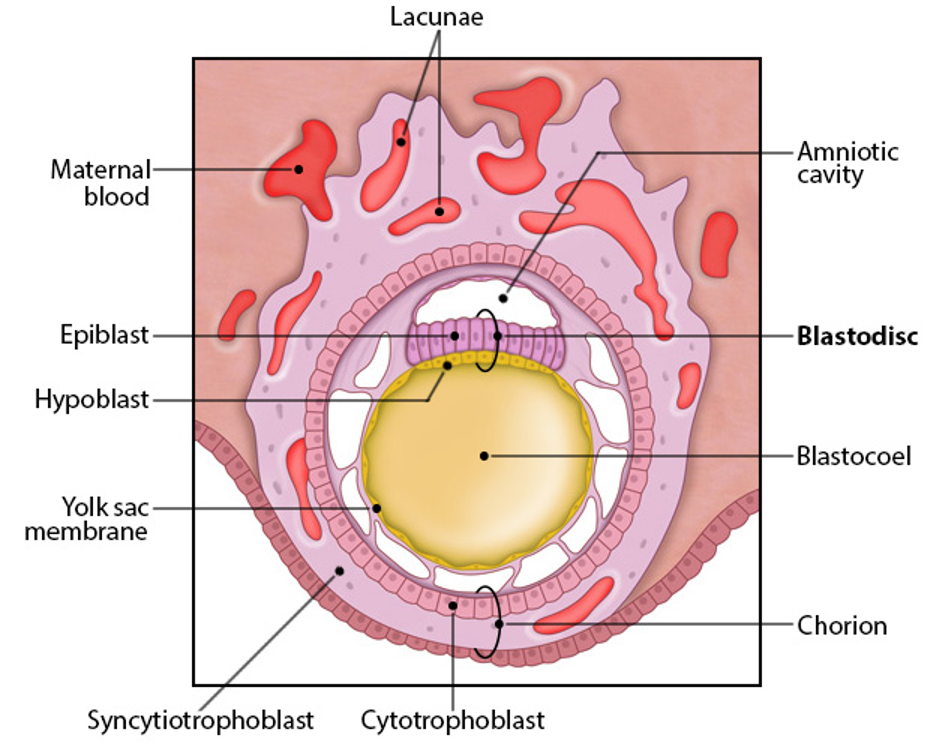
hypoblast
layer of inner cell mass closest to blastocoel
will eventually form the extraembryonic endoderm
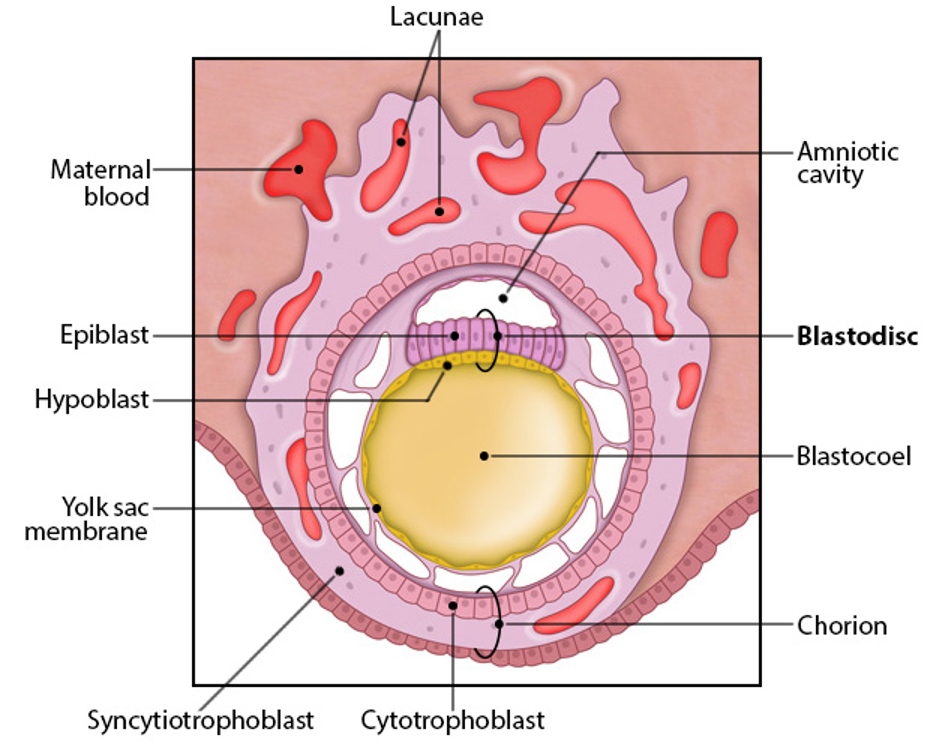
epiblast
layer of inner cell mass farther from blastocoel
gives rise to embryo proper
extraembryonic tissue origin
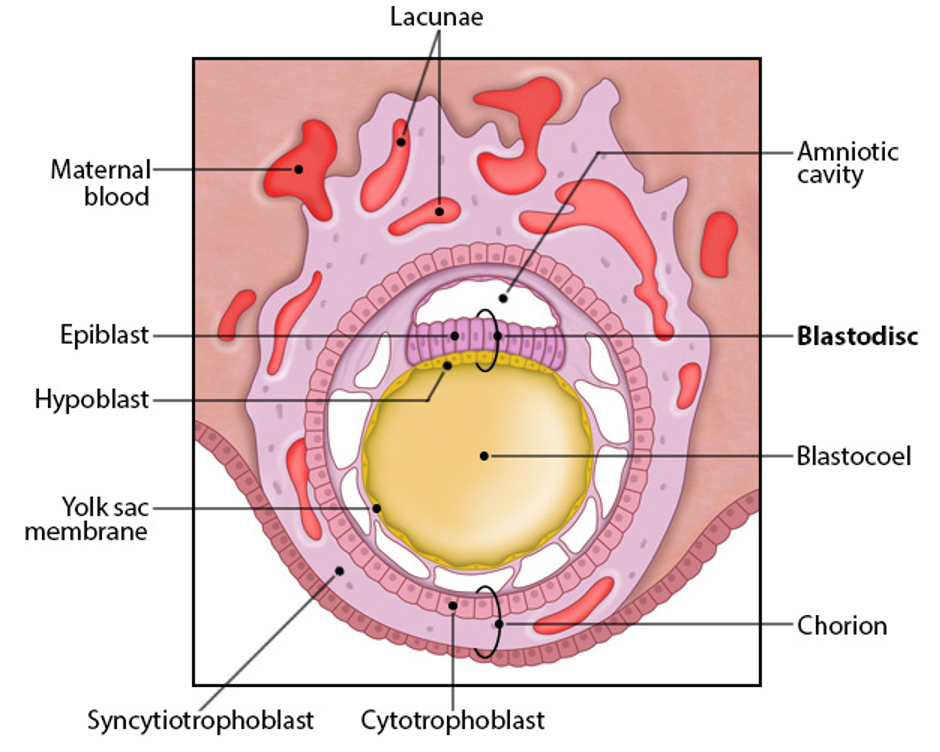
blastodisc
hypoblast + epiblast layer
gives rise to yolk sac, amnion, chorion
yolk sac- early hematopoesis, derived from hypoblast
amnion- surrounds fetus as fluid-filled sac, derived from epiblast
chorion- placenta, derived from cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast
extra embryonic tissue
gastrulation
process where epiblast forms the 3 primary germ layers (blastocyst becomes an embryo)
ectoderm
forms from the remaining epiblast cells (outer layer)
mesoderm
forms btw the ectoderm and endoderm, from migrating epiblast cells
endoderm
forms from epiblast cells that replace the hypoblast (inner layer)
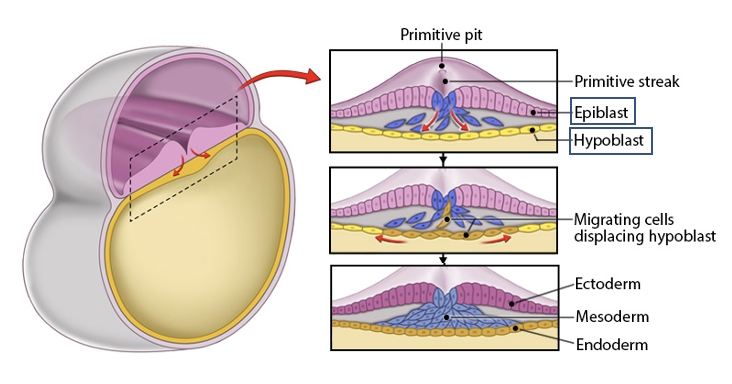
primitive streak
the region where migration of cells occurs to form these layers
epiblast cells migrate inward
endoderm forms from cells that replace the hypoblast
mesoderm orms btw endoderm and epiblast
ectoderm forms from remaining epiblast cells
result: 2 layers (epiblast and hypoblast)→ 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
these 3 layers give rise to all tissues and organs in body
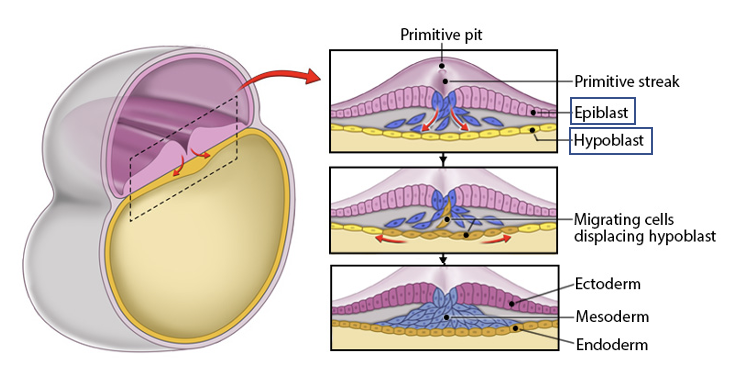
ectoderm
Forms from the remaining epiblast cells (outer layer).
a primary germ layer
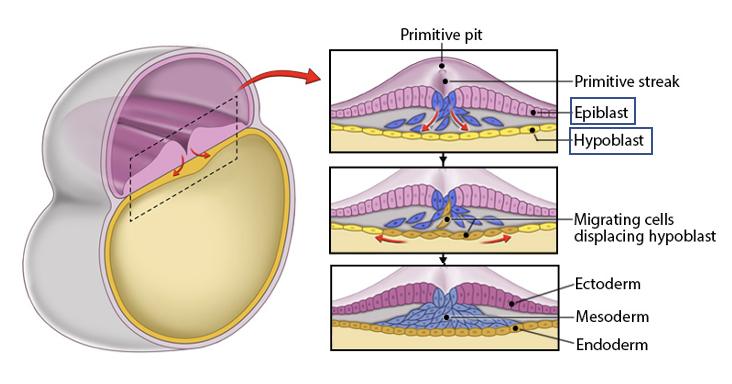
mesoderm
Forms between the ectoderm and endoderm, from migrating epiblast cells.
a primary germ layer
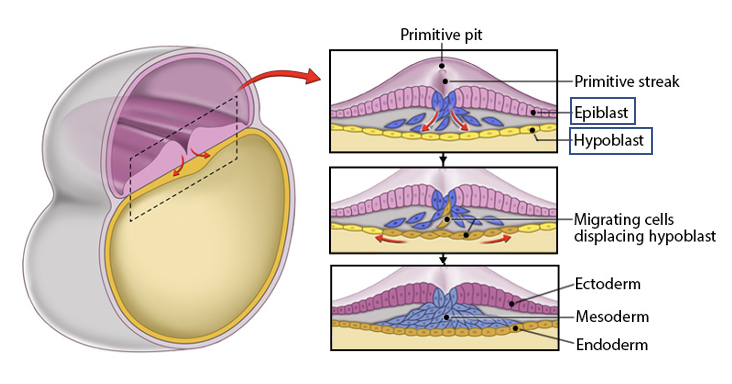
endoderm
Forms from epiblast cells that replace the hypoblast (inner layer).
a primary germ layer
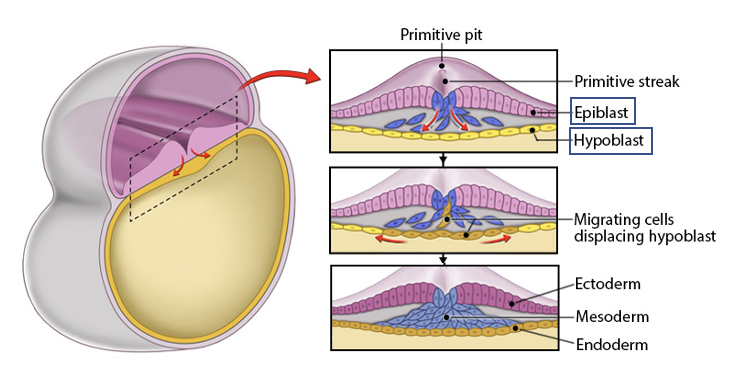
primitive streak
the region where migration of cells occurs to form these layers
epiblast cells migrate inward
endoderm forms from cells that replace the hypoblast
mesoderm orms btw endoderm and epiblast
ectoderm forms from remaining epiblast cells
result: 2 layers (epiblast and hypoblast)→ 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
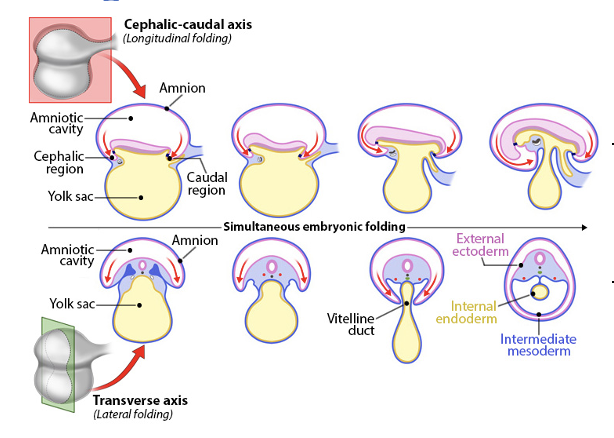
embryo folding
embryo folds along 2 axes
cephalic-caudal (longitudinal) axis
forms head (cephalic) and tail (caudal) ends
embryo bends toward the endoderm and folds back on itself
transverse (lateral) axis
sides of embryo fold inward and fuse at midline
pinches off most of yolk sac, leaving vitelline duct
caused by rapid growth of embryo and amnion, slower growth of yolk sac
result
cylindrical embryo with defined body shape
embryo divided into cephalic and caudal regions
embryo divided into 3 distinct layers
external ectoderm
intermediate mesoderm
internal endoderm
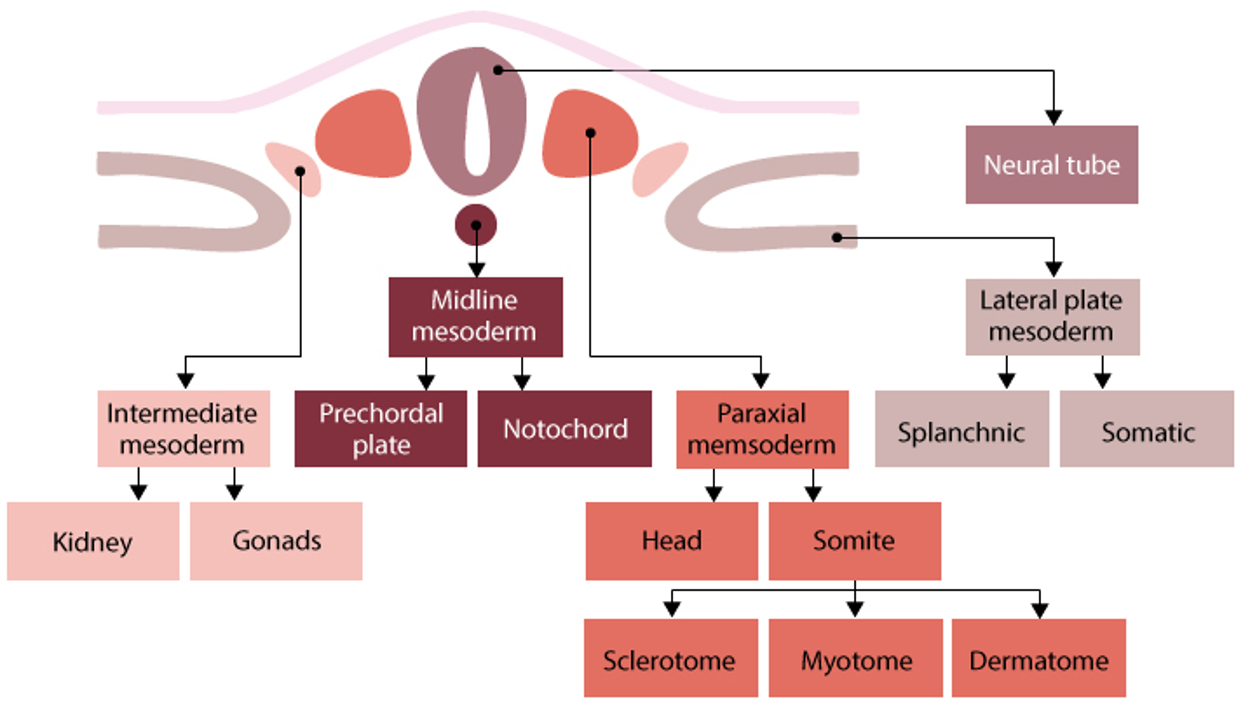
mesoderm fate
depends on location after migration during gastrulation
4 types
chordamesoderm (midline)
forms notochord→ induces neural tube formation
establishes anterior-posterior axis
forms prechordal plate→ gives rise to mouth
paraxial mesoderm (next to midline)
forms somites and head mesenchyme
somites→
sclerotome: cartilage, tendons
myotome: skeletal muscle
dermomyotome: dermis, connective tissue
intermediate mesoderm
forms urogenital system- kidneys, ureters, gonads
lateral plate mesoderm
forms circulatory system, body cavity linings, spleen, adrenal glands, appendicular skeleton cartilage
intermediate mesoderm
forms urogenital system- kidneys, ureters, gonads
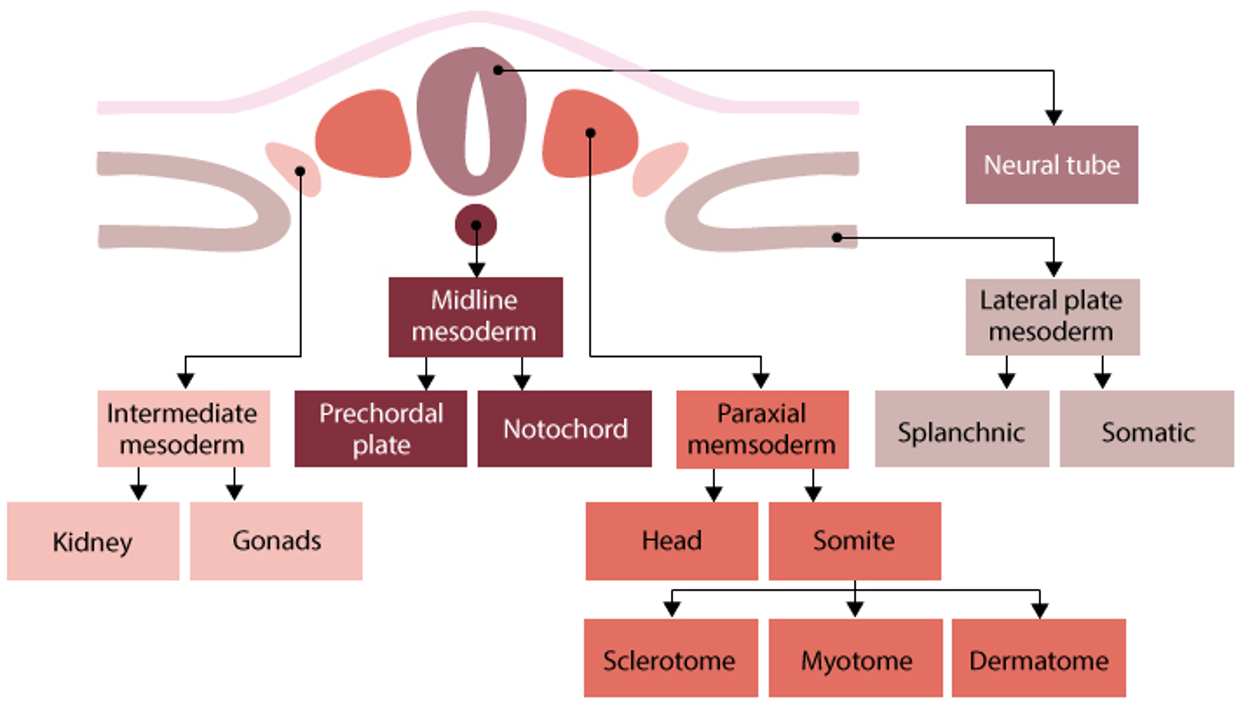
midline mesoderm
forms notochord→ induces neural tube formation
establishes anterior-posterior axis
forms prechordal plate→ gives rise to mouth
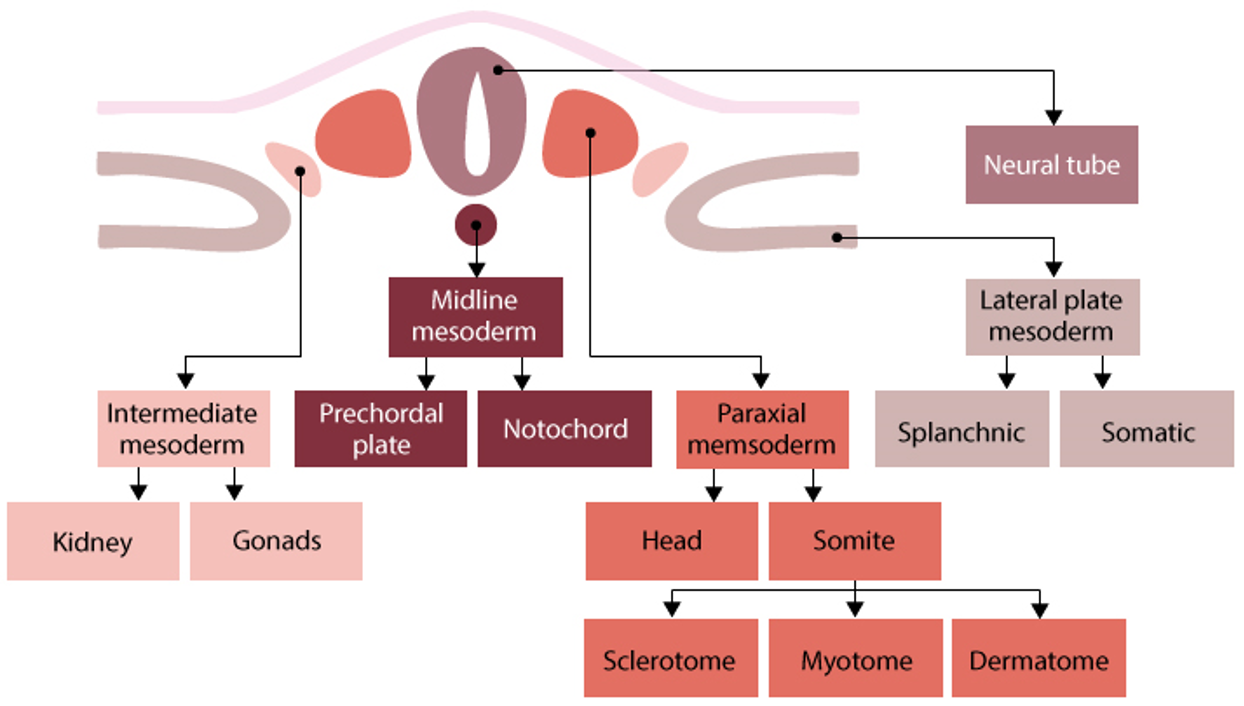
paraxial mesoderm
forms somites and head mesenchyme
somites→
sclerotome: cartilage, tendons
myotome: skeletal muscle
dermomyotome: dermis, connective tissue
lateral plate mesoderm
Splanchnic mesoderm (inner layer) → forms:
Circulatory system
Visceral lining of body cavities
Somatic mesoderm (outer layer) → forms:
Body wall lining
Appendicular skeleton cartilage
Spleen and adrenal glands
ectoderm
nervous tissue
epidermis and derivatives
sense organs
lens of eye
teeth enamel
mouth and anus
pituitary and adrenal glands
endoderm
internal lining of respiratory, GI, urinary and reproductive tracts
portions of liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
palantine tonsils
thyroid and parathyroid glands
thymus
placenta
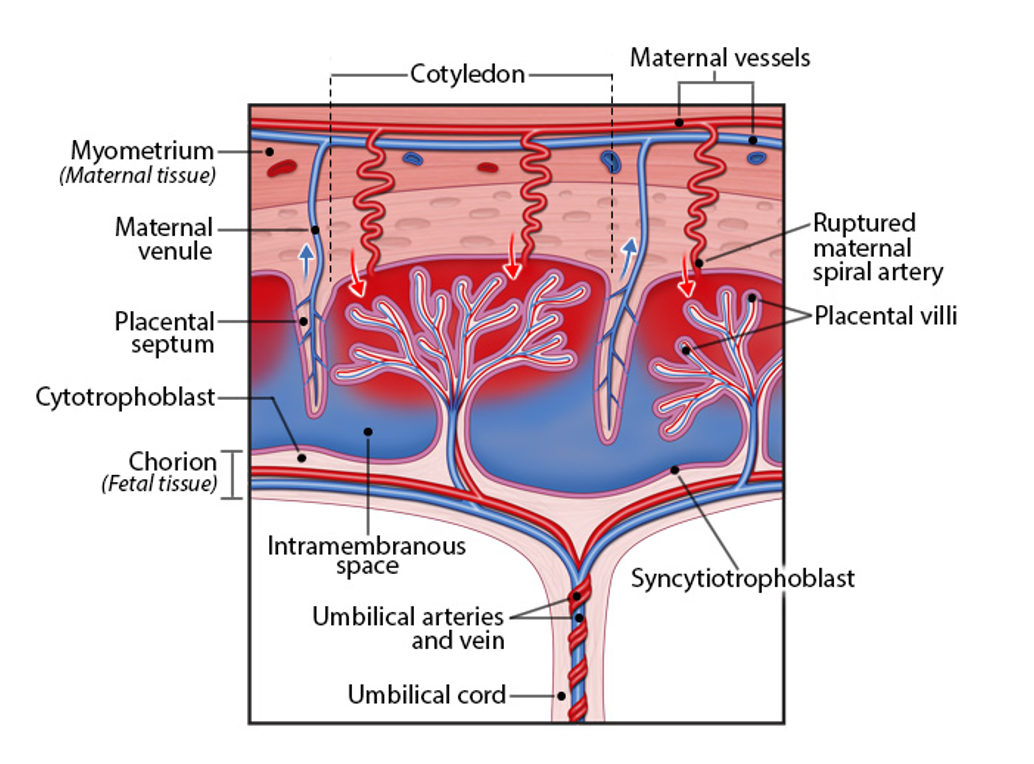
structure
chimeric organ (2 genetically diff tissue sources)
consisting of maternal (uterine) and embryonic (chorion) tissue
several lobes (cotyledons), fed by umbilical vessels
covered in villi sitting in maternal blood-filled spaces
fx
material exchange btw mother and developing embryo/fetus
nutrients, gases, wastes
endocrine organ
produces hormones required for pregnancy (hCG, progesterone, etc)
hemochorial type
embryonic tissue directly contacts maternal blood
minimizes barrier for efficient exchange
ectopic pregnancy
development of the embryo or fetus outside of the uterus
occurs when something blocks the passage of the fertilized ovum
placenta previa
the placenta implants in the inferior uterus, near to/covering the internal os of the cervix, leading to spontaneous abortion or premature birth
preeclampsia
sudden pregnancy induced hypertension
dystocia
difficult labor due to an abnormal fetal position or inadequate vaginal canal
may lead to cesarean section
deliver of physiologically immature baby
classified as a baby that weighs less than 2500g at birth
carries substantial risk to the baby
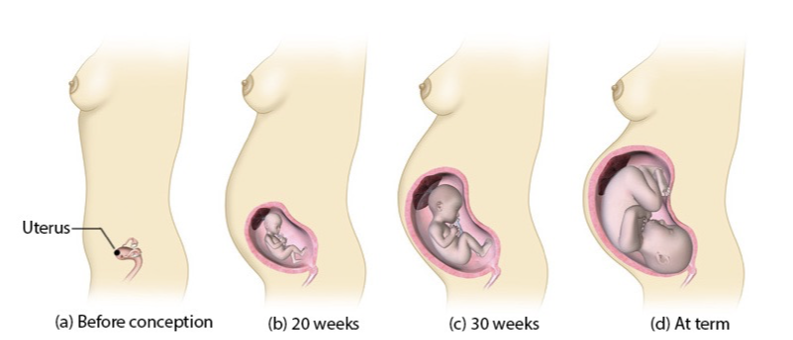
uterus growth during pregnancy
mostly from hypertrophic and hyperplastic growth of the uterine myometrium
starts growth around week 4
doubles in size by end of first trimester
by week 20, fundus (top of uterus) reaches umbillicus
in 3rd trimester, grows beyond umbillicus
by term, reaches xiphoid process of sternum
displaces and compresses nearby organs- often causes discomfort
grows all the way xiphoid process of the sternum by term
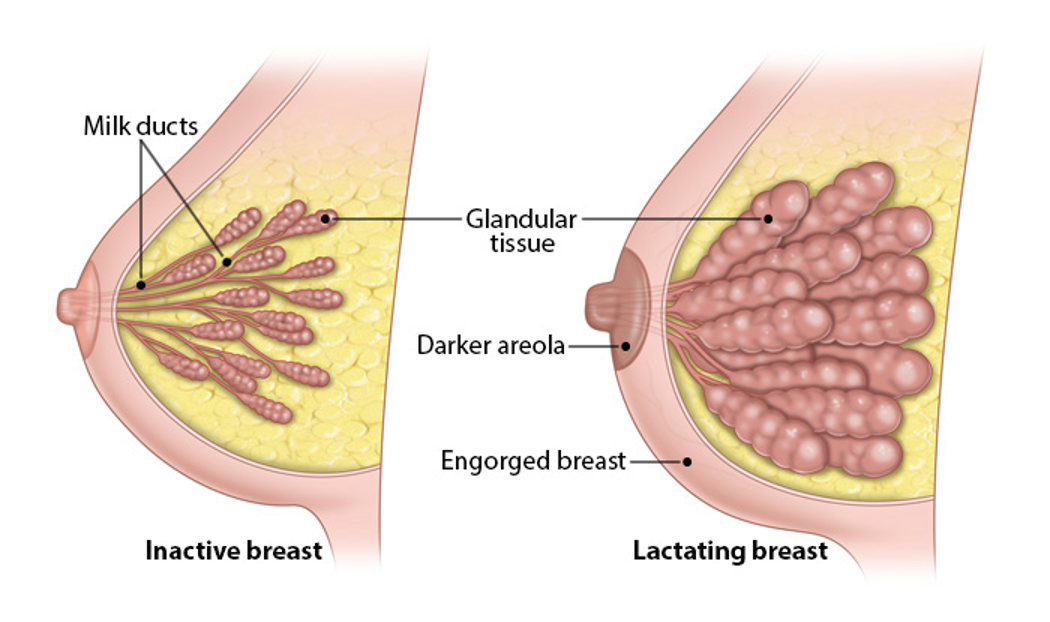
mammary glands during pregnancy
grow in response to placental hormones
areola and nipple become darker in response to melanocyte-stimulating hormone MSH
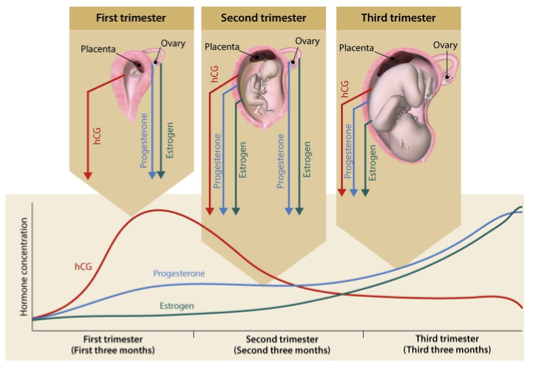
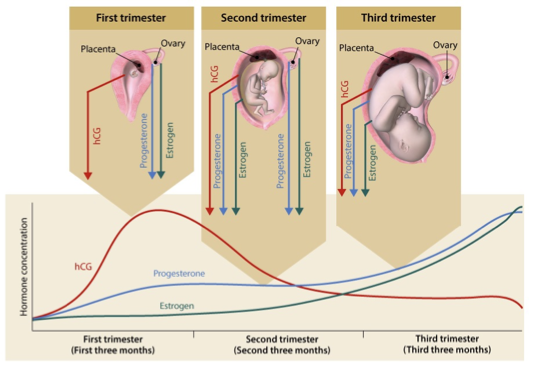
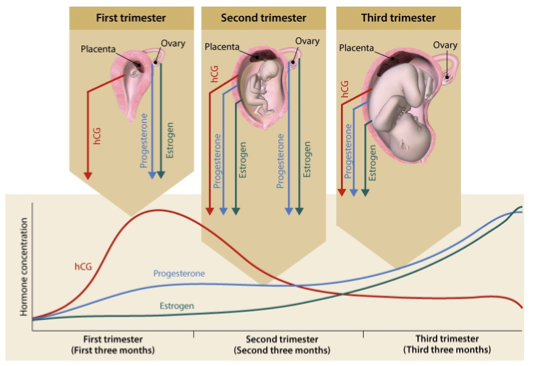
pregnancy hormones
1st trimester
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) peaks early
progesterone and estrogen produced by ovary
2nd trimester
ovary and placenta produce hormones, with placenta taking over production of progesterone and estrogen
3rd trimester
placenta produces hCG, progesterone, and estrogen
progesterone and estrogen rise throughout pregnancy and reaches peak towards end of 3rd trimester
estrogen peaks right before labor
other hormones:
placental lactogen PL
prolactin PRL
relaxin
corticotropin releasing hormone CRH
human chorionic gonadotropin hCG
produced by chorion (syncytiotrophoblast cells)
fx
maintains corpus luteum
stimulates progesterone production
enhances implantation
regulates trophoblast differentiation
promotes maternal-fetal immunological balance
detectable around 10 days after ovulation (home pregnancy test detects)
peaks around 2k 10 of pregnancy, then declines and plateaus
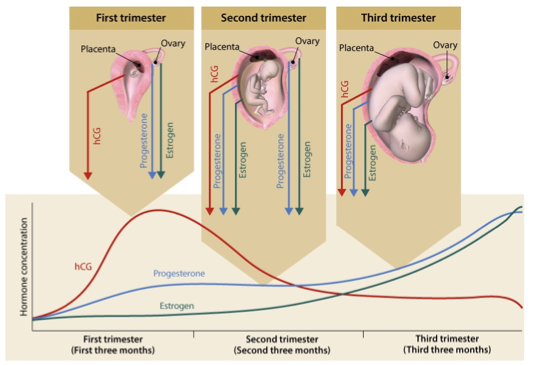
progesterone
produced by corpus luteum (1st trimester), then placenta (2nd and 3rd trimesters)
fx
prevents uterine contractions
supports uterine and mammary enlargement
maintains pregnancy by inhibiting maternal gonadotropins and suppresses parturition (giving birth)
estrogen
produced by corpus luteum (1st trimester), then placenta (2nd and 3rd trimesters)
fx
promotes uterine and mammary enlargement
relaxes pelvic ligaments
facilitates uterine contractions to support parturition
placental lactogen PL
produced by syncytiotrophoblast cells
shifts fuel away from mother→towards fetus
increase maternal blood glucose and lipolysis
anti-insulin effect: decreases maternal insulin sensitivity
prolactin PRL
produced by placenta and mother’s anterior pituitary gland
shifts fuel towards mother in periods of insult/stress/illness
helps protect maternal survival in adverse conditions
relaxin
produced by syncytiotrophoblast cells
plays important roles in osmoregulation and cardiovascular adaptation
opposes parturition (birth) and supports fetal growth
reduces uterine contractions
corticotropin releasing hormone CRH
produced by syncytiotrophoblast cells
increases DHEA production→ synthesize estrogen
serves as an initial signal for parturition around wk 34-35
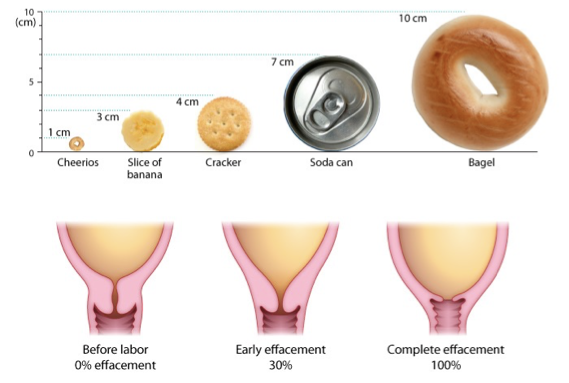
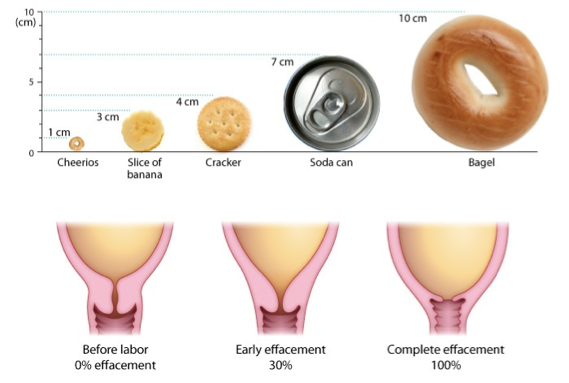
cervical effacement, dilation
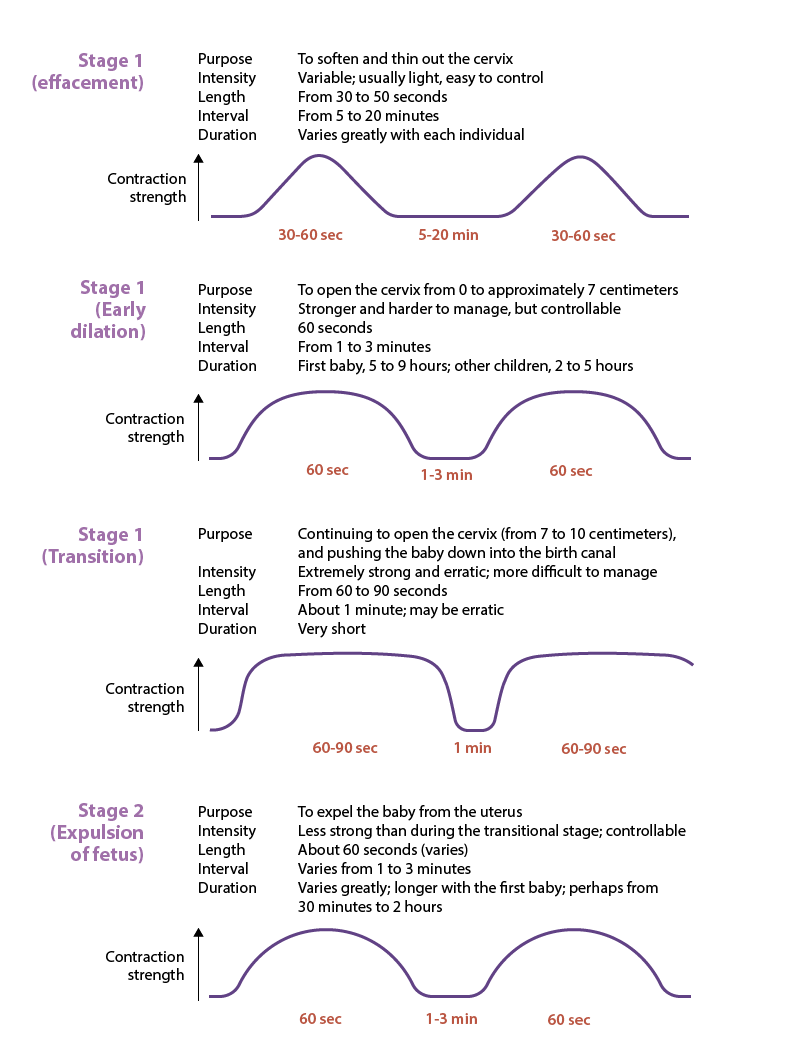
stage 1 of parturition
prep birth canal for fetal passage
phase 1: effacement
effacement= thinning of cervix
0→100% effacement of cervix
preps cervix to start dilating
phase 2: dilation
cervix dilates from 1→ 7cm
1 cm= cheerio
4 cm= cracker
7 cm= soda can
contractions become longer, stronger, more frequent
lasts 5-9 hrs (1st baby birth) or 2-5 hrs (subsequent births)
phase 3: transition
cervix dilates from 7→ 10 cm
10 cm= bagel
most intense and painful phase
contractions last 60-90 secs, very close together
fetus moves into pelvic basin, creating urge to push
ends when full dilation (10 cm) is reached→ ready for delivery
effacement contractions→ dilation of cervix→ transition
effacement
phase 1, step 1 of parturition
effacement= thinning of cervix
0→100% effacement of cervix
preps cervix to start dilating
dilation
phase 2, step 1 of parturition
cervix dilates from 1→ 7cm
1 cm= cheerio
4 cm= cracker
7 cm= soda can
contractions become longer, stronger, more frequent
lasts 5-9 hrs (1st baby birth) or 2-5 hrs (subsequent births)
transition
phase 3, step 1 of parturition
cervix dilates from 7→ 10 cm
10 cm= bagel
most intense and painful phase
contractions last 60-90 secs, very close together
fetus moves into pelvic basin, creating urge to push
ends when full dilation (10 cm) is reached→ ready for delivery
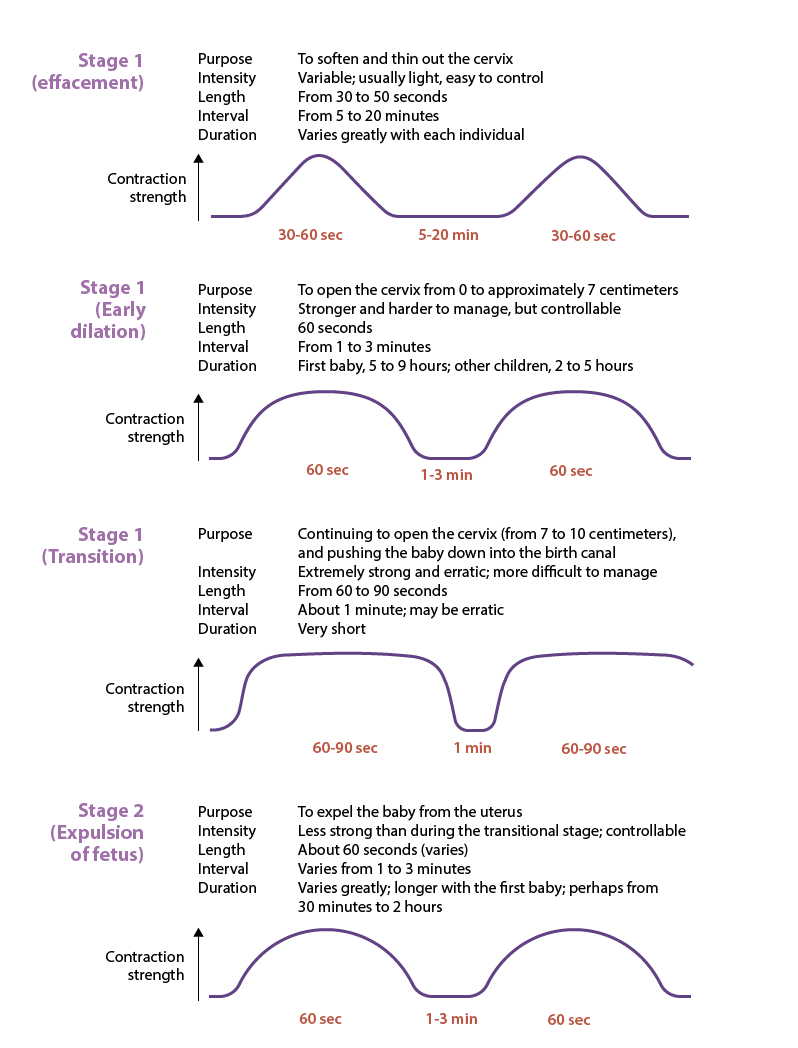
fetal expulsion
to expel baby from uterus
contractions less strong than during transitional stage; controllable
contracts last around 1 min, every 1-3 mins (variable)
generally 30 min-2 hrs w/ first baby, usually shorter in subsequent births
active pushing helps move fetus thru birth canal
crowning (baby’s head visible at vaginal opening) → birth is near
baby usually emerges face down, then rotates to align shoulders
final pushes completely deliver baby
stage 2 of parturition
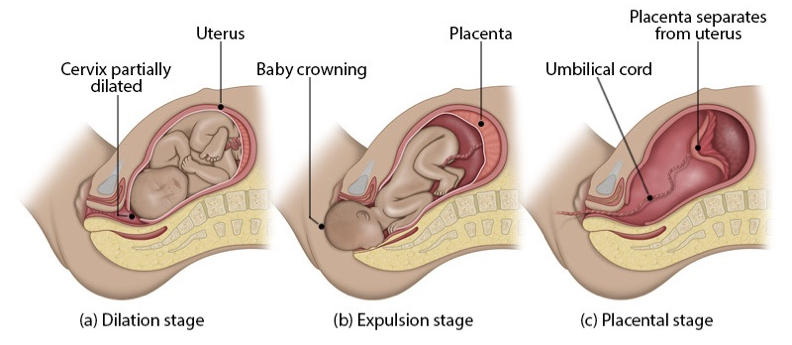
placental expulsion
3rd and final stage of labor
occurs 15-30 mins after birth
uterine contractions help detach and expel placenta
around 200 mL blood loss is normal
marks delivery completion
afterward, uterus begins involution (shrinking back to pre-pregnancy size), which takes up to 6 weeks postpartum
stage 3 parturition
parturition
cervical effacement
cervical dilation
transition
expulsion of fetus
expulsion of placenta
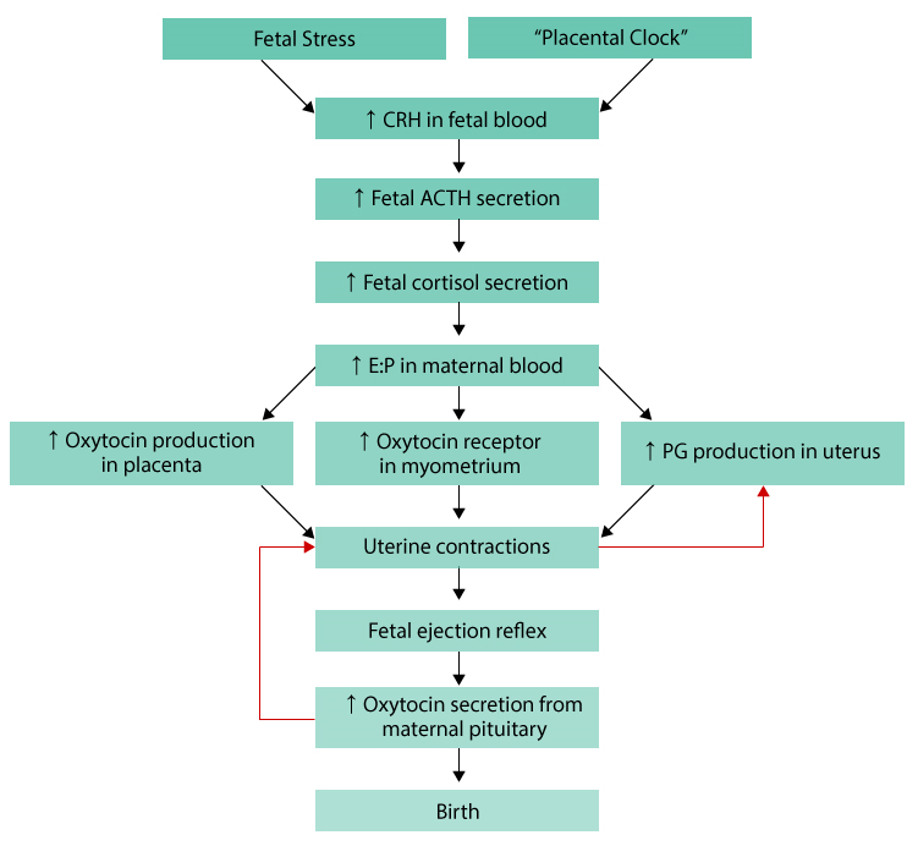
fetal stress or “placental clock” triggers labor
this increases corticotropin-releasing hormone CRH in fetal blood
CRH causes fetus to release adrenocorticotropic hormone ACTH, increasing fetal cortisol
fetal cortisol
increases estrogen levels in mother
decreases progesterone
higher estrogen
boosts oxytocin production in placenta
increases oxytocin receptors in uterus
stimulates prostaglandin PG production in uterus
oxytocin + prostaglandins cause uterine contractions
contractions press fetus against cervix→ triggers fetal ejection reflex
fetal ejection reflex makes mom’s pituitary release more oxytocin
more oxytocin=stronger contractions→ positive feedback loop
strong contractions continue until birth occurs
sexually transmitted diseases
infections that spread thru sexual contact
ex.,
nongonococcal urethritis
chlamydia
syphillis
gonorrhea
vaginitis
herpes simplex
human papilloma virus
AIDS
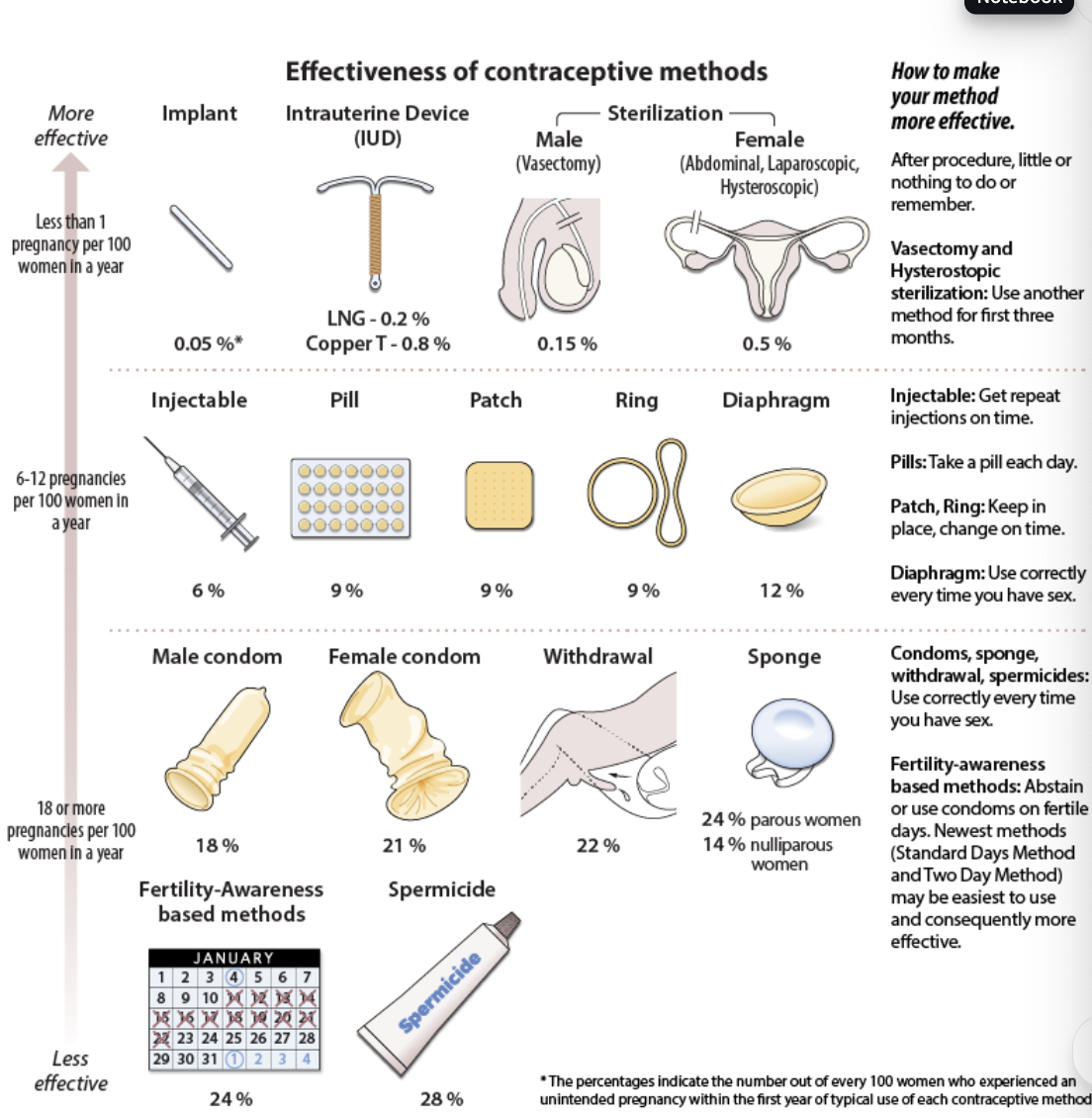
contraceptive devices
Most Effective (<1 pregnancy per 100 women/year)
Implant: 0.05%
IUD (LNG): 0.2%
IUD (Copper T): 0.8%
Male sterilization (vasectomy): 0.15%
Female sterilization: 0.5%
Tip: After procedure, little or nothing to remember
Vasectomy & hysteroscopic sterilization: use backup method for first 3 months
Moderately Effective (6–12 pregnancies per 100 women/year)
Injectable: 6% → Get repeat shots on time
Pill: 9% → Take daily
Patch: 9% → Change weekly, use as directed
Ring: 9% → Replace monthly
Diaphragm: 12% → Use every time you have sex, correctly
Less Effective (18–24+ pregnancies per 100 women/year)
Male condom: 18%
Female condom: 21%
Withdrawal: 22%
Sponge: 24% (parous women), 14% (nulliparous women)
Tip: Use correctly every time you have sex
Least Effective (>24 pregnancies per 100 women/year)
Fertility-awareness methods: 24%
Spermicide alone: 28%
Tip:
Fertility-awareness: Abstain or use condoms on fertile days
Standard Days & Two-Day Methods = easier, possibly more effective