Management of Allergic Rhinitis
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Allergic Rhinitis
IgE-mediated nasal disorder from allergen exposure.
Rhinorrhea
Medical term for runny nose symptom.
main symptoms
rhinorrhoea
nasal itching
congestion
sneezing
how many people suffer gobally
400 million
geographical high prevalance
Australia
new Zealand
uk
What is chemotaxis?
Movement of immune cells towards allergen sites.
What is activated during chemotaxis?
Chemocytes.
What type of antibody is synthesized in response to allergens?
IgE.
What happens when IgE cross-links with an allergen?
It triggers hypersensitivity.
What substances are released during an allergic reaction?
Histamine, tryptase, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes.
Eosinophils
White blood cells involved in allergic reactions.
Histamine Release
Chemical causing allergic symptoms like itching.
IgE Synthesis
Production of immunoglobulin E in response to allergens.
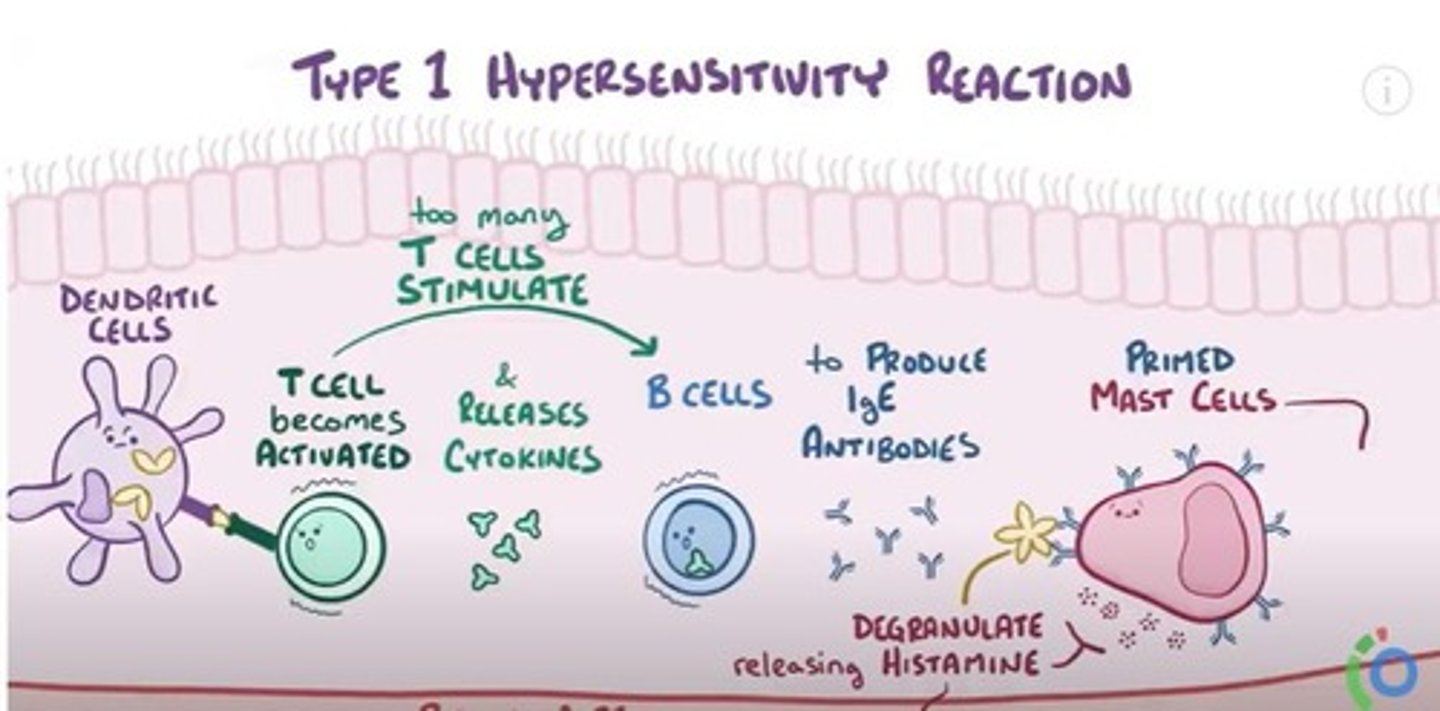
Sensory Nerve Activation
Triggers sneezing and nasal itch during allergies.
Mucus Cell Production
Increased mucus secretion during allergic reactions.
other causes
infectious
drug induced
hormonal
idiopathic
Persistent vs Intermittent
majority of a week vs less than 4 days a week
Rhinoscopy
Examination of nasal passages for diagnosis.
Socrates
Site
Onset
Character
Relieving factors
Associated symptoms
Timing
Exacerbating features
Severity
taking a history
age
sex
socrates
Differential Diagnosis
Identifying other conditions mimicking allergic rhinitis.
Other diagnostic tests
rhinoscopy
allergy tests
cytology of nasal secretion
CT scan
Mast Cell Stabilizers
Medications preventing histamine release from mast cells.
Sodium Cromoglicate
Mast cell stabilizer used for allergic symptoms.
OTC
eyedrop
6+
no contacts
Antihistamines
Drugs blocking histamine effects, alleviating symptoms.
Nasal Irrigation
Saline solution used to clear nasal passages.
Beclomethasone
Corticosteroid nasal spray for allergy symptoms.
corticosteroid
topical
18+
2 sprays each morning and night
blow nose before use to clear mucus
Corticosteroid
Anti-inflammatory medication effective for nasal symptoms.
Topical effect
Localized action at the site of application.
H1 Receptor Antagonists
Block histamine effects, alleviating allergic symptoms.
1st Generation Antihistamines
Sedating; include diphenhydramine and chlorphenamine.
not usually given for allergic rhinitis
chlorphenamine is the drug of choice
2nd Generation Antihistamines
Non-sedating; include loratadine and cetirizine.
commonly sold for allergic rhinitis
other uses of first generation H1 antagonist
sedating
can be useful if patients symptoms are disturbing sleep
Antiemetic (nausea and vomiting associated with conditions)
general properties of 1st generation H1 antagonists
lipid soluble
well absorbed
metabolized in the liver
half life around 5-6 hours
clinically relevant interactions of antihistamines
sedative effect
- opioids and alcohol
anti-muscarinic effect
- TCAs
-oxycontin
azoles
- increase exposure of antihistamines
- QT prolongation
QT prolongation
Potential heart rhythm issue with certain antihistamines.
general properties of 2nd generation H1 antihistamines
- lipid structure with highly ionised functional group
-less CNS penetrations
-well absorbed
- metabolized in the liver
- half life 6+
- lower incidence of adverse effects
Cetirizine
Common non-sedating antihistamine; 10mg OD for adults.
mast cell stabilizer and anti-muscarinic
Azelastine
Nasal spray formulation for allergic rhinitis.
Insomnia preparations
Contain diphenhydramine for sleep disturbances.
Antiemetic
Medication for nausea and vomiting relief.
Loratadine
Most commonly used non-sedating antihistamine.
GSL and P
10mg once daily 6+
Mast cell stabilizer
Prevents release of histamine from mast cells.
Fluticasone
Another corticosteroid nasal spray option.