intr 3000 final
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
comparative advantage
need to know opportunity cost to decide which country has more advantage compared to other countries
2
New cards
\
Heckscher-Ohlin trade theory
Heckscher-Ohlin trade theory
relative endowments determine comparative advantage
3
New cards
Trade barriers
tariff, quota, subsidies, prohibitions
4
New cards
Stolper-Samuelson theorem
owners of scarce factors of production favor protectionism, but owners of abundant factors favor trade
5
New cards
Ricardo-Viner (specific factors) approach
most demands for protection come from specific industries, not factors
6
New cards
WTO system
* all members in WTO have equal vote
* generally dominated by the largest trading states
* encourages cooperation by:
* collecting information about trade policies
* monitoring national compliance
* complaints are sent to dispute settlement body in the WTO
* generally dominated by the largest trading states
* encourages cooperation by:
* collecting information about trade policies
* monitoring national compliance
* complaints are sent to dispute settlement body in the WTO
7
New cards
types of foreign investment
1. portfolio investments
* claim on some income but no management
* investors’ interests - the rate of return
* loans, stocks, and bonds
2. foreign direct investments (FDI)
* company owns and controls facilities in another country
8
New cards
problems with foreign investment
* both investors and countries they invest
* interest cooperating but want as much while giving as little
* debt payments can require
* raising taxes
* reducing gov spending services
* restraining consumption and wages
* interest cooperating but want as much while giving as little
* debt payments can require
* raising taxes
* reducing gov spending services
* restraining consumption and wages
9
New cards
what can debt payments require
* raising taxes, reducing government services
* restraining consumption and wages
* restraining consumption and wages
10
New cards
How can a country facing debt negotiate economic policies w/ the IMF?
* IMP will give inexpensive loans to country
* play major part in negotiations b/w sovereign governments and private financiers
* critics
* IMF as tool of international financiers
* doing little to assist poor nations in achieving economic development
* play major part in negotiations b/w sovereign governments and private financiers
* critics
* IMF as tool of international financiers
* doing little to assist poor nations in achieving economic development
11
New cards
Why are most companies multinational corporations?
to gain access to
* local market
* local resources
* local market
* local resources
12
New cards
Problems of MNCs?
* not investing at home
* “outsourcing” jobs to countries w/ lower wages
* looking for pollution-friendly regimes
* seeking ethically relaxed governments
* “outsourcing” jobs to countries w/ lower wages
* looking for pollution-friendly regimes
* seeking ethically relaxed governments
13
New cards
Appreciation (Strengthening)
the dollar goes up in value against some other currency
14
New cards
Depreciation (Devaluing)
the dollar’s value goes down against that of another currency
15
New cards
Lower interest rates
make it easier for people to borrow, allowing the economy to expand
16
New cards
Higher interest rates
make it harder to borrow, restraining demand
17
New cards
Fixed exchange rates
provide stability and facilitate international trade and investment
18
New cards
Floating exchange rates
* offer more freedom to pursue one’s own monetary policy
* However, can make international trade and investment much more difficult
* However, can make international trade and investment much more difficult
19
New cards
Why Is Development So Hard to Achieve?
Three factors
* Geographic location
* Domestic factors (policies, infrastructure, politics, a variety of groups, powerful national goal)
* Domestic institutions
* Geographic location
* Domestic factors (policies, infrastructure, politics, a variety of groups, powerful national goal)
* Domestic institutions
20
New cards
“Resource curse”
initial wealth gives rise to ensuing poverty
21
New cards
Import-substitution industrialization (ISI)
Policies that reduced imports and encouraged domestic manufacturing
* trade barriers
* subsidies to manufacturing
* state ownership of basic industries
* ex: Latin American countries in the 1970s and 1980s
* trade barriers
* subsidies to manufacturing
* state ownership of basic industries
* ex: Latin American countries in the 1970s and 1980s
22
New cards
Export-Oriented Industrialization
* manufacturers to produce for foreign consumers
* Techniques such as tax breaks, low-cost loans, and a weak currency helped make their products
* Ex) East Asian countries
* Techniques such as tax breaks, low-cost loans, and a weak currency helped make their products
* Ex) East Asian countries
23
New cards
Washington Consensus
The transformation towards a general acceptance of market-oriented policies
24
New cards
The Geneva Conventions (1949)
* Appropriate treatment of civilians and captured soldiers during times of war
* Do not kill or injure an enemy who surrenders
* Do not kill or injure an enemy who surrenders
25
New cards
Responsibility to Protect (R2P, 2006)
* protect threatened populations from genocide, war crimes, ethnic cleansing, and crimes against humanity by any means necessary
* the right of states to intervene in the internal affairs of others even without that state’s permission.
* the right of states to intervene in the internal affairs of others even without that state’s permission.
26
New cards
Transnational advocacy networks (TANs)
* Important roles in changing behavior by promoting normative values
* Actors
* NGOs
* social movements
* foundations
* media
* churches
* trade unions
* other organizations.
* Actors
* NGOs
* social movements
* foundations
* media
* churches
* trade unions
* other organizations.
27
New cards
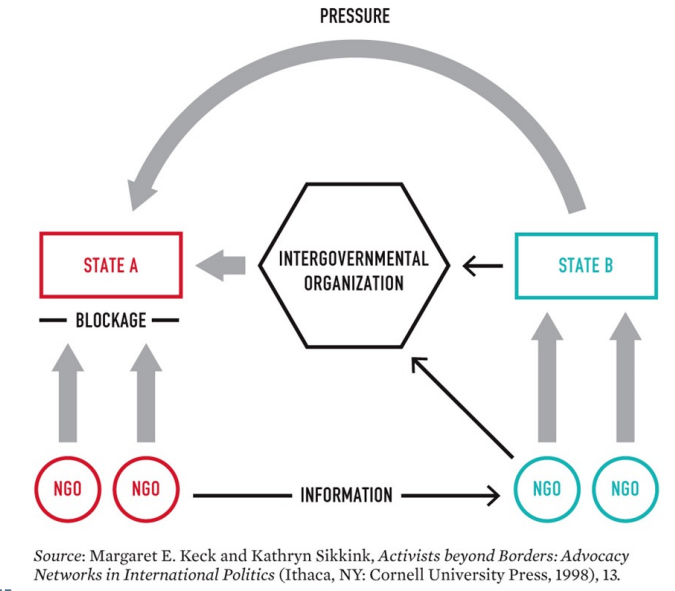
Boomerang Model
28
New cards
The International Bill of Rights
* Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)
* International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR)
* The International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights (ICESCR)
* International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR)
* The International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights (ICESCR)
29
New cards
Why are human rights controversial?
* States have different interests in human rights
* Human rights: human-created institution, evolving over time
* acceptable to use on terrorist suspects?
* Human rights: human-created institution, evolving over time
* acceptable to use on terrorist suspects?
30
New cards
The most frequent form of violence
by governments against their own citizens
31
New cards
What are the effects of international human rights institutions?
may have a beneficial effect in the long run
32
New cards
Public good
nonexcludable and nonrival in consumption, free-rider, collective action problem
33
New cards
Cap-and-Trade
Firms may purchase credits from other. (Ex: Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS), Kyoto P.
34
New cards
Common pool resources
non-excludable but are rival in consumption
35
New cards
Joint Products
public goods bundled with private goods to facilitate cooperation
36
New cards
How much CO2 do developed states emit?
70 % of the world’s CO2 (US: 23 %)
37
New cards
How much does China’s greenhouse gases grow?
rapidly and dramatically
38
New cards
What are framework conventions?
general principles that states often negotiate and agree on
39
New cards
What are current issues?
* Weapons of mass destruction (WMD)
* The Rise of China
* Economic Globalization.
* The Rise of China
* Economic Globalization.