Suppositories, Inserts, Medication Sticks
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
_____________: a solid dosage in which 1+ APIs are dispersed in a suitable base and molded or otherwise formed into a suitable shape for insertion rectally or vaginally
suppository
Suppositories are medicated, _________ preparations
used in … (3) routes of administration
T or F: they provide only systemic activity
semisolid
rectal, vaginal, urethral
F (local and/or systemic)
Why would a drug need to be administered rectally when oral route is the most convenient? (advantages)
rectum is considered relatively _______ and ______
has low ________ _______ in comparison to other sections of GI tract
drugs can partially bypass the liver following systemic absorption, which reduces the hepatic _________ effect
achievement of a ______ drug effect systemically
constant, stable
enzymatic activity
first pass
rapid
Rectal suppositories uses: (3)
systemic effects → antiemetics (anti N/V), analgesics, hormones
treat anorectal diseases/local effects → hemorrhoids, anal fissures, infections, ulcerative proctitis, inflammation
promote defecation (laxatives)
Rectal suppositories DISADVANTAGES:
not __________ by patients and may be ________
some may _______ or are ________ after insertion
absorption may be ________
the “bullet shaped” suppository can _______ the anorectal site after insertion → ascend to recto sigmoid and descending colon
___________ may interrupt absorption process
area of absorption in the rectum is _________ (_________)
small rectal ________ content may cause problems w drug dissolution or absorption
preferred, inconvenient
leak, expelled
erratic
leave
defecation
small, 200-400 cm²
fluid
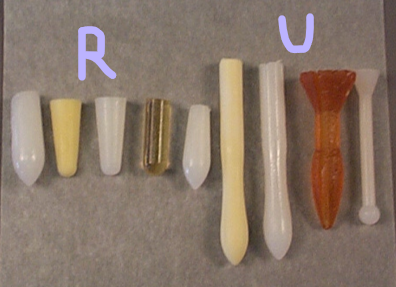
Rectal suppositories shape = ________ or _______ and tapered/pointed at one end
T or F: infant rectal suppositories weigh about half as much as adult supp
Vaginal suppositories shape =
Urethral inserts/bougies shape =
cylindrical, conical
T
ovoid, globular, cone shaped
slender, pencil-shaped
_________ _________: designed to give an extended-release of medication (________ hrs)
Treatment of internal and external _________ simultaneously
rectal rocket, 4-6 hrs, hemorrhoids
Systemic action
The ________ _________ of the rectum permit the absorption of many soluble drugs
Suppositories may be used in the treatment of … (6)
mucous membranes
N/V, pain, fever, migraines, provide sedation, hormone replacement
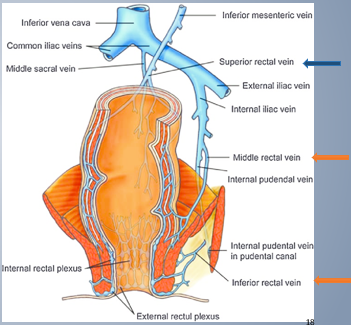
Rectal Drug absorption
_______________________ → enters hepatic portal system → first-pass effect
_______________________ → enter systemic circulation
superior rectal vein
middle and inferior rectal vein
_______ ___________: severe and often fatal disease, characterized by acute onset of encephalopathy, liver dysfunction, and fatty infiltration of the liver and other viscera
Contraindication: aspirin and other salicylates in ___________ and ___________ w viral illness-associated fever due to possible association w ^
Reye syndrome
children, young adults <20 yo
Vaginal Suppositories and Inserts
systemic effect →
local effect →
hormone
infection, dryness, contraception, urethral inserts
Physiological factors that affect rectal drug absorption:
__________ __________: generally accepted that ________% of active ingredients bypass the liver and avoid the first pass effect
__________________
pH of rectal fluid ___________ and lack of ________ capacity
circulation route, 50-70%
colonic contents
6.8-7.4, buffering
Physiochemical Factors that Affect Rectal Drug Absorption:
__________ _______
^ Oil-soluble drug + oily base = __________ release
^ Water-soluble drug + oily base = __________ release
^ oil-soluble drug + water base = ____________ release
^ water-miscible drug + water base = __________ release
___________ _______ →
lipid-water solubility
slow
rapid
moderate
moderate → based on diffusion
particle size (smaller = faster dissolution)
Types of suppository bases (2):
fatty/oleaginous → melt
water-soluble/miscible → dissolve
Desirable properties of suppository bases:
_________ and _________ to mucous membranes
_________ w a variety of drugs
chemically and physiologically ________
_______ or __________ in presence of mucous secretions at body T
allow ________ of API
remain ________ on storage
nontoxic, nonirritating
compatible
inert
melt, dissolve
release
stable
Fatty or Oleaginous Bases
Melt in ________ minutes
_________ MPs than water miscible bases
MUST BE KEPT AT controlled _________ or __________
Example →
^ melts at _________℃
3-7
lower
room T, refrigerated
cocoa butter/theobroma oil
30-36 (86-97F)
__________________: ability of a solid material to exist in different crystalline forms which differ in their physical properties
Cocoa butter must be slowly and evenly melted to avoid formation of unstable crystalline form
polymorphism
Water-soluble and water-miscible bases:
Example 1 =
freq used as base for ____________ suppositories for __________ local action
dissolves slowly in the mucous secretions in about ______ mins
Due to __________ (water absorbing) of glycerin → dehydrating effect and irritate tissues, thus supp should be …
may be used w a _________ range of drugs
glycerinated gelatin
vaginal, prolonged
30-40
hygroscopicity, dipped in water before insertion
wide
Water-soluble and water-miscible bases:
Example 2 =
Dissolves in body’s _______ and do _________________
No _________ after insertion and preferred base for vaginal + urethral
Counseling →
Major disadvantage is their __________ w a large number of drugs
300-600 Mw = _____________
1000+ Mw = ____________
increasing Mw = ________ MP
polyethylene glycol PEG
fluids, not require refrigeration
leaking
dip in water before insertion, rectal use may cause defecating reflex
incompatibility
clear liquid
white waxy solid
inc
What bases can you use for
Vaginal supp =
rectal supp =
glycerinated gelatin or PEG (preferred)
oleaginous bases or PEG
PEG vs fatty bases
compatibility and stability
patient comfort
rectal suppositories
fatty less reactive than PEG (more stable and compatible)
fatty more comfortable
fatty preferred
Max amount of solid material that can be incorporated in a suppository is approx _______ of the blank weight (weight of one supp that contains only the base)
30%
Methods of Preparation of Suppositories
________________ → most common (molding)
________________ → for small number of supp to be prepared in cocoa butter base
________________ → heat labile components (NOT heat stable)
fusion method
hand rolling
compression
Advantages of Molding
less __________ skill
____________ and professional appearance
Disadvantages of Molding
_________ molds are required
caution when incorporating ______ _______ components
__________ calculations, mold ___________, or ______________ procedures are required to give accurate dose
Supp molds may require ___________ w ___________
technical
elegant
special
heat labile
density, calibrations, double-casting
lubrication, mineral oil
_________ ____________: when an API is added to a supp base, it will displace an amount of base as a function of its density
DF = weight of API/weight of base displaced
density factor
Compounding Suppositories
General Rule: calculate the amounts of materials needed for the preparation of one or two more suppositories than the number prescribed to compensate for the inevitable loss of some material. Alternatively, many compounding pharmacists prepare an extra ______%
10%
PACKAGING suppositories
Suppositories made in disposable _________ or __________ molds may be dispensed directly in the mold
Glycerin + PEG base supp should be packaged in __________ containers to protect from moisture
Oleaginous base supp not dispensed in mold usually individually ________ or _______ in compartmented boxes
Supp containing light sens drugs are individually wrapped in an ________ material (e.g. foil)
plastic, rubber
airtight
wrapped, separated
opaque
STORAGE temps
Oleaginous base suppositories =
Glycerinated gelatin or PEG suppositories =
cold T = 2-8 C / 36-46 F
room T = 20-25 C / 68-77 F
Physical instabilities of suppositories (7)
softening
hardening
drying
cracking
separation
polymorphs when MP is affected
odor of rancidity
Chemical instabilities of suppositories (7)
hydrolysis
decarboxylation
dehydration
oxidation
photochemical decomposition
pH effect
solid state stability
T or F:
Suppositories must contain preservatives/antioxidants because water is present in the formulations (which may support growth of microorganisms)
F (not needed, water is usually excluded)
Patient Counseling → Suppositories:
When supp are dispensed in foil or plastic wrapping, instruct patient to __________ wrapping before inserting supp
__________ conditions
____________________ if compounded
remove
storage (fatty = cold, water sol = room T)
beyond use date
How to insert a rectal suppository
Insert into rectum until it passes the sphincter (how far in for infants vs adults?)
close legs and sit OR lie still for __________
avoid emptying bowels for at least ___________ (unless supp is a laxative) and avoid excessive movement/exercise
0.5-1 in for infants, 1 in for adults
15 min
1 hr
Prescription Only Products
Rectal suppositories
→ hemorrhoids
→ hemorrhoids
→ ulcerative proctitis
→ anti-inflammatory
→ antiemetic (prevent N/V)
→ antiemetic
→ migraine
→ pain associated w ureteral spasm
→ pain
→ pain
Anusol HC - hydrocortisone acetate
Proctocort - hydrocortisone acetate
Canasa - mesalamine
Indocin - indomethacin
promethazine
prochlorperazine
Migergot - ergotamine+caffeine
Belladonna/Opium
morphine sulfate
hydromorphone
Prescription Only Products
Suppositories and Inserts
→ vulvovaginal candidiasis/yeast infection
→ bacterial vaginosis
→ progesterone
→ erectile dysfunction
Terconazole
Cleocin ovules - clindamycin
Endometrin insert
Muse Uretheral pellet - alprostadil
Medication Sticks
2 types →
provide what kind of activity?
Easily ____________ and convenient dosage form for administering ________ medications
_________ and __________ purposes
What may be administered by medication sticks? (5)
soft sticks, hard sticks
local OR systemic
transportable, topical
cosmetic, medical
local anesthetics, sunscreens, oncology drugs, antivirals, antibiotics
SOFT medication sticks:
Prepared similarly to __________
clear sticks made from …
opaque sticks made from …
examples =
suppositories
sodium stearate, glycerin, and/or propylene glycol
petrolatum, cocoa butter, PEG
lip balm, deodorant, makeup
HARD Medication Sticks
Prepared from _______ powders that are _______ together OR fused by a _________ such as …
Must be _________ to be activated
Example =
crystalline, heated, binder → cocoa butter, petrolatum
moistened
styptic pencil
What rectal drug + base pair has rapid absorption?
water-soluble drug + fatty base