2.5.6 catalysts
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
what is a catalysts
increases rate without being used up
by providing an alternate route with a lower activation energy
what is a heterogenous catalyst
in a different phase from reactants
what is a homogenous catalyst
in the same phase as reactants
where do reactions of heterogenous catalysts occur
at active sites of the surface
what may lead to catalytic action
adsorption of reactants
what does a support medium do to heterogenous catalysts
maximises surface area
minimises costs
name the heterogenous catalysts in the contact process
V2O5
overall equation and steps in the Contact process
overall equation: 2SO2 + O2 —→ 2SO3
step 1: SO2 + V2O5 —→ SO3 + V2O4
step 2: 2V2O4 + O2 —→ 2V2O5
what is used as a heterogenous catalyst in the Haber process
Fe
how can catalysts become poisoned
by impurities that block active site and has reduced efficiency - cost implication
when catalysts and reactants are in the same phase what happens
the reaction proceeds through an intermediate species
why are transition metals able to act as homogenous catalysts
they have variable oxidation states
able to oxidise and reduce
partially filled d orbital so can easily lose and gain electrons
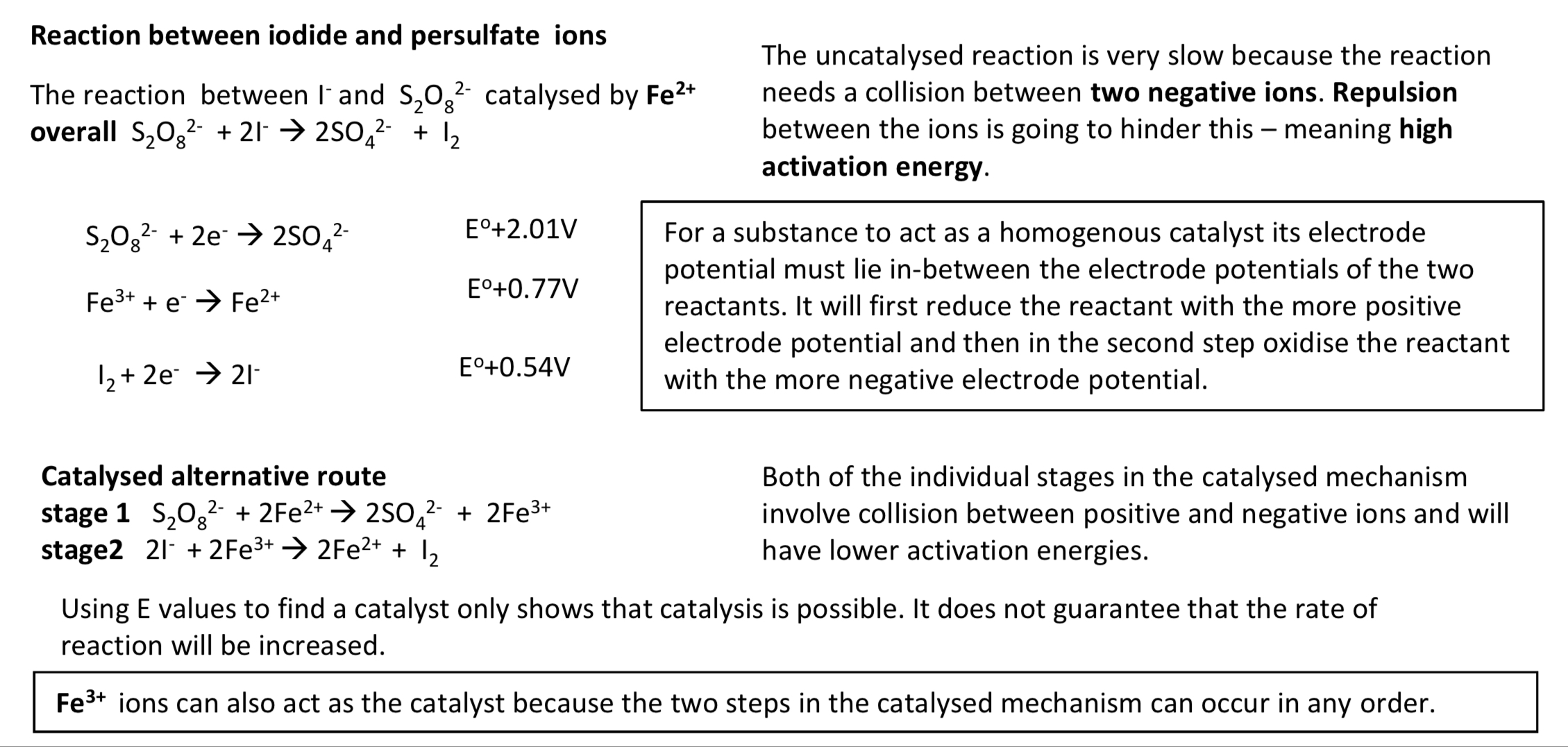
reaction between iodide and persulfate ions
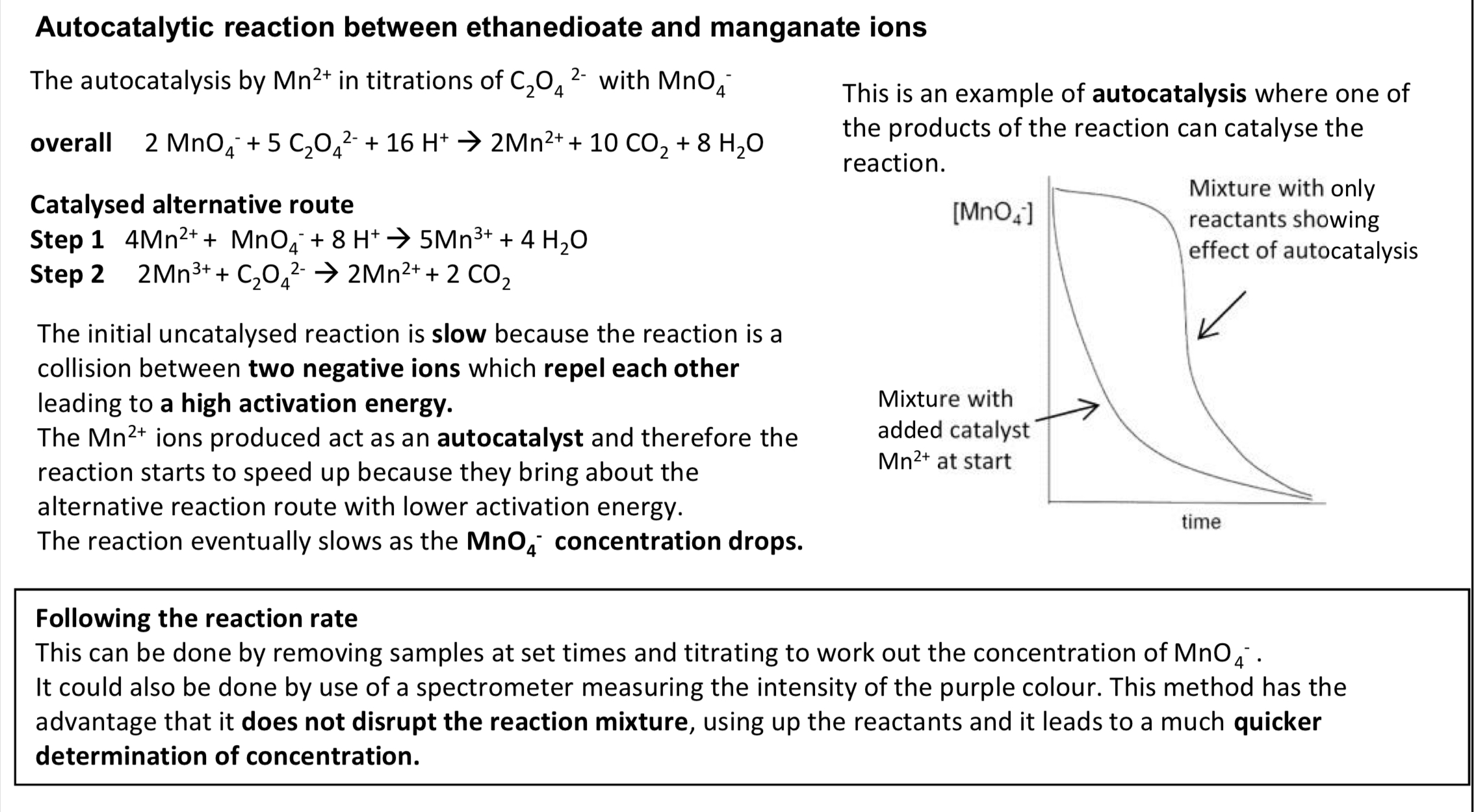
autocatalytic reaction between ethanedioate and manganate ions