Advanced Chest Exam
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Bacteria
Complex, single-celled organisms that reproduce on their own; can survive, even adapt, to various environments including the human body
Virus
Small, simple organism consisting of a core of genetic material and a protein shell; can only survive and reproduce when attached to a host cell
Pneumonia
Infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus.
What is the radiograph appearance of pneumonia?
Patches of white density
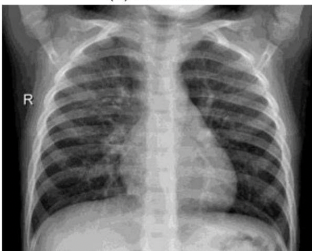
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
Pneumonia
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Common, very contagious virus which attacks the lower respiratory tract
What is the radiograph appearance of RSV?
Hyper inflated lungs with diffuse interstitial markings. More severe cases – focal areas of atelectasis are present.
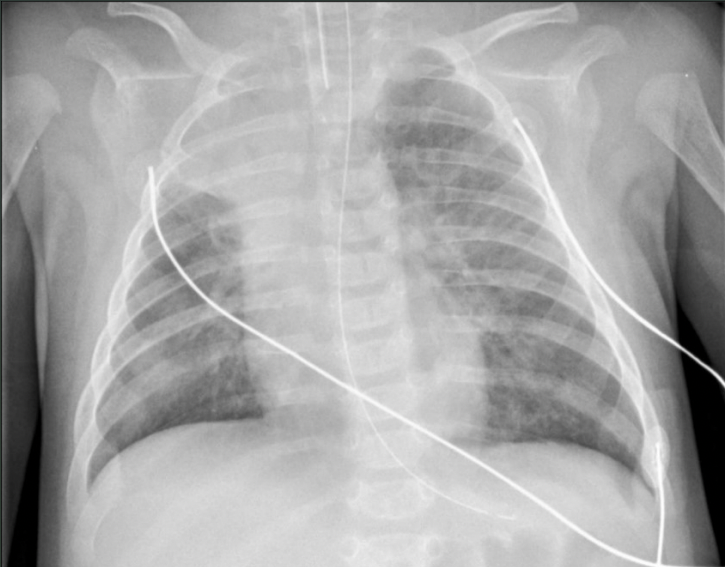
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
RSV
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (C.O.P.D.)
Inefficient exchange of respiratory gases causing difficulty to breath
What is the main cause of COPD?
Smoking
What is the radiograph appearance of COPD?
Bronchial scarring, prominent interstitial markings, lungs hyperaerated
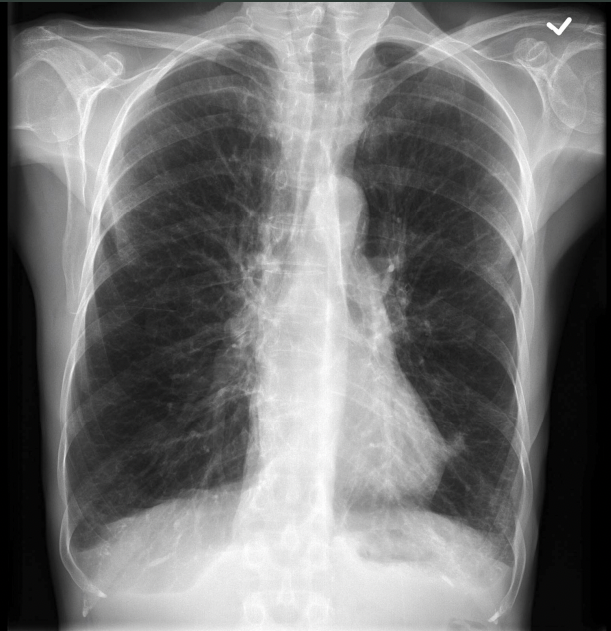
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
COPD
Cystic Fibrosis
Disease that causes thick, sticky mucus to form in the lungs, pancreas and other organs
What is the radiograph appearance of cystic fibrosis?
White, fuzzy patches all over lung fields
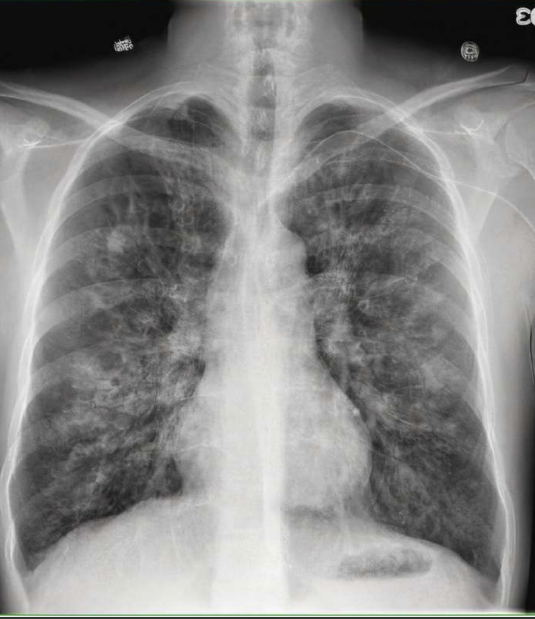
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
Cystic fibrosis
Tuberculosis (TB)
Serious infection affecting the lungs
Latent TB
Person carries the bacteria but is symptom free and not contagious
Active TB
The bacteria is multiplying in the body faster than the immune system can combat, resulting in a dangerous infection that is also contagious
What is the radiograph appearance of TB?
Small opaque spots throughout the lungs (similar appearance to pneumonia) with possible enlargement of the hilar region
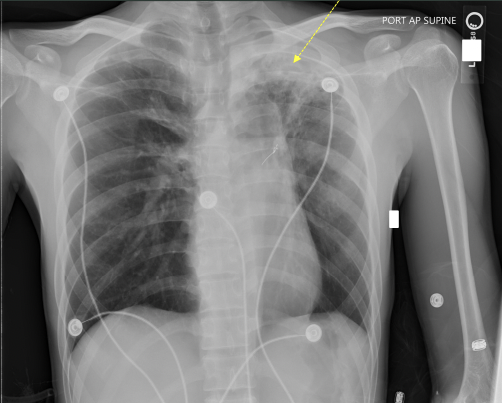
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
TB
Pneumothorax
Presence of air in the pleural cavity (collapsed lung)
What is the radiograph appearance of pneumothorax?
Hyperlucent area with absence of pulmonary markings
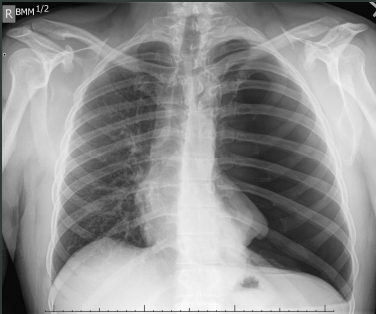
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
Pneumothorax
Pleural Effusion
Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space
What is the radiograph appearance of pleural effusion?
Blunting of the costophrenic angles with upward concave border of the fluid level
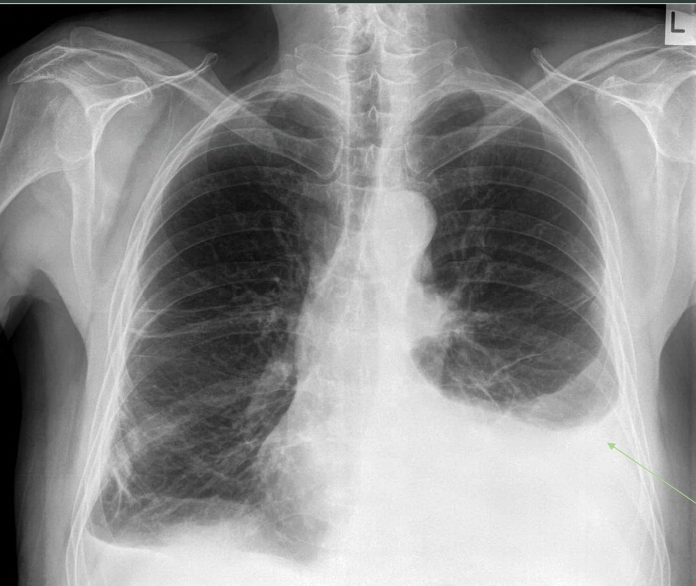
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
Pleural effusion
Atelectasis
Condition in which there is diminished air within the lung, also known as a partial or complete collapse of a lobe or entire lung
What is the radiograph appearance of atelectasis?
Localized increase in density
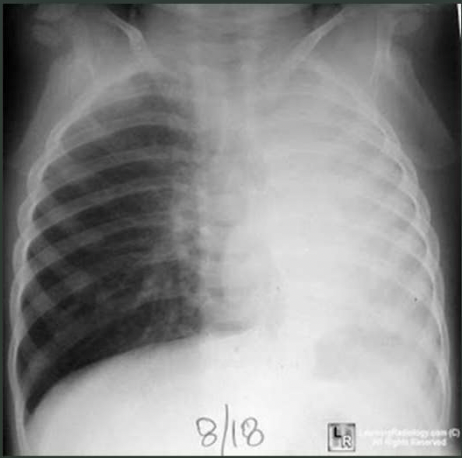
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
Atelectasis
Cardiomegaly
Enlarged heart
What is the radiograph appearance of cardiomegaly?
Very large heart, widened in appearance from typical
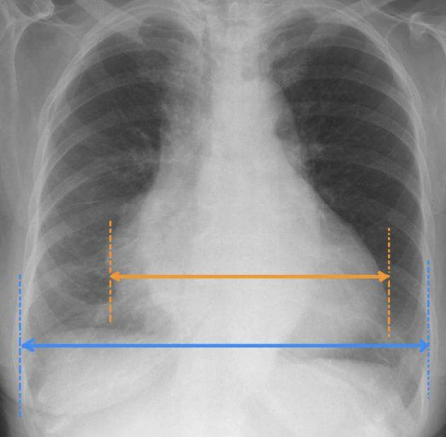
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
Cardiomegaly
Congestive Heart Failure (C.H.F.)
Inability of the heart to pump the blood at a rate/volume that is sufficient to provide adequate supply to the tissues
What is the radiograph appearance of left side heart failure?
Cardiomegaly, increased interstitial markings due to edema and pleural effusions
What is the radiograph appearance of right side heart failure?
Right atrium & ventricle and maybe the SVC are dilated, edema of lower extremities
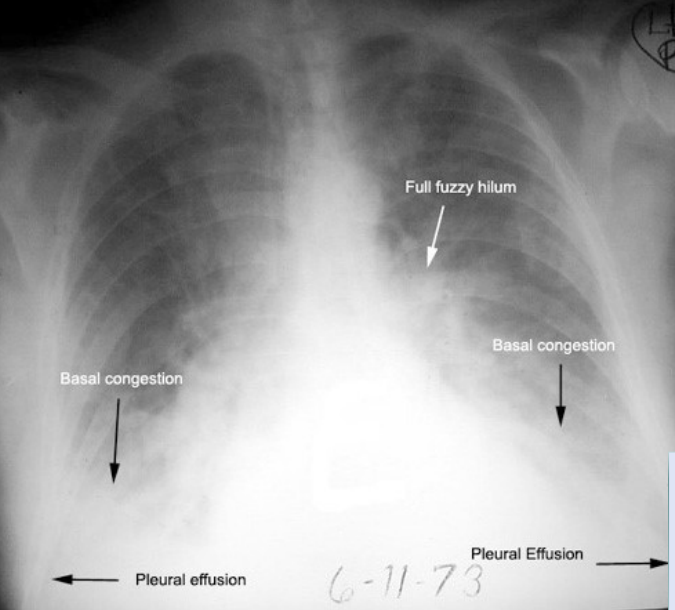
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
CHF
Dextrocardia Situs Inversus
Abnormal positioning of the heart and other internal organs
What is the radiograph appearance of dextrocardia situs inversus?
Tip of the heart points towards the right side of the chest instead of the left side; the mirror-image reversal of the organs in the chest and abdominal cavity
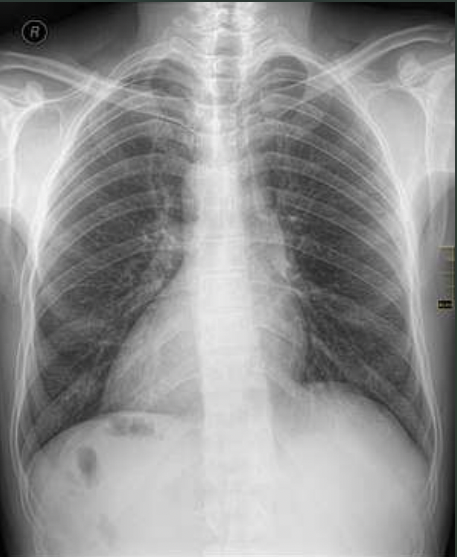
What pathology is seen on this x-ray?
Dextrocardia situs inversus
Pulmonary Embolism
Sudden blockage of a pulmonary artery in the lung
What is the radiograph appearance of pulmonary embolism?
Rarely demonstrated on radiographs; severe cases can demonstrate a wedgeshaped opacity (Hampton’s Hump) or a Westermark’s sign
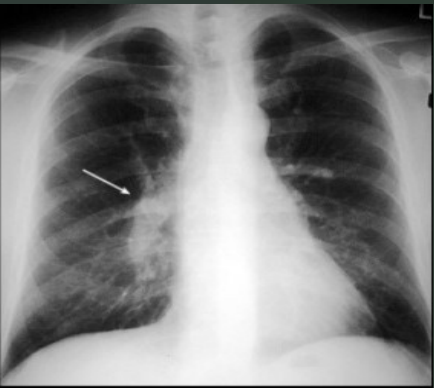
What is the arrow pointing to on this PE?
Westermark’s Sign
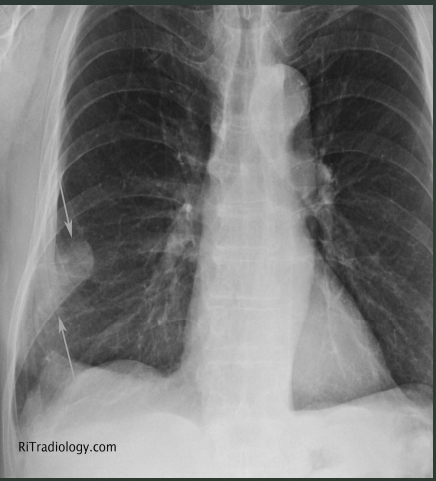
What is the arrow pointing to on this PE?
Hampton’s Hump
What is the technique for an adult lateral chest x-ray?
120 kVp and center cell
What is the fixed technique for an adult lateral chest x-ray?
120 kVp @ 3.6 mAs
What is the fixed technique for an adult AP erect chest x-ray?
90 kVp @ 1.6 mAs
What is the technique for an adult lateral decubitus chest x-ray?
120 kVp and varying cells
What is the fixed technique for an adult lateral decubitus chest x-ray?
120 kVp @ 2.0 mAs
For every 1 cm of thickness.. how do you change the kVp?
+/- 2
What is the technique for a pediatric PA and lateral chest x-ray?
80-90 kVp and center cell
What is the fixed technique for a pediatric PA chest x-ray?
80-90 kVp @ 1 mAs
What is the fixed technique for a pediatric lateral chest x-ray?
80-90 kVp @ 2 mAs
AP axial (lordotic) chest x-ray
Done to view the apices without superimposition from the clavicles; used to see lung nodules in the apices
AP supine chest x-ray
Alternative for any patient that cannot sit or stand erect