8 - ANATOMY OF THE HEAD AND NECK (BRS) 2025
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
What laryngeal muscle is innervated by the external laryngeal nerve? What is its function?
-Cricothyroid muscle
-Tensing the vocal cords
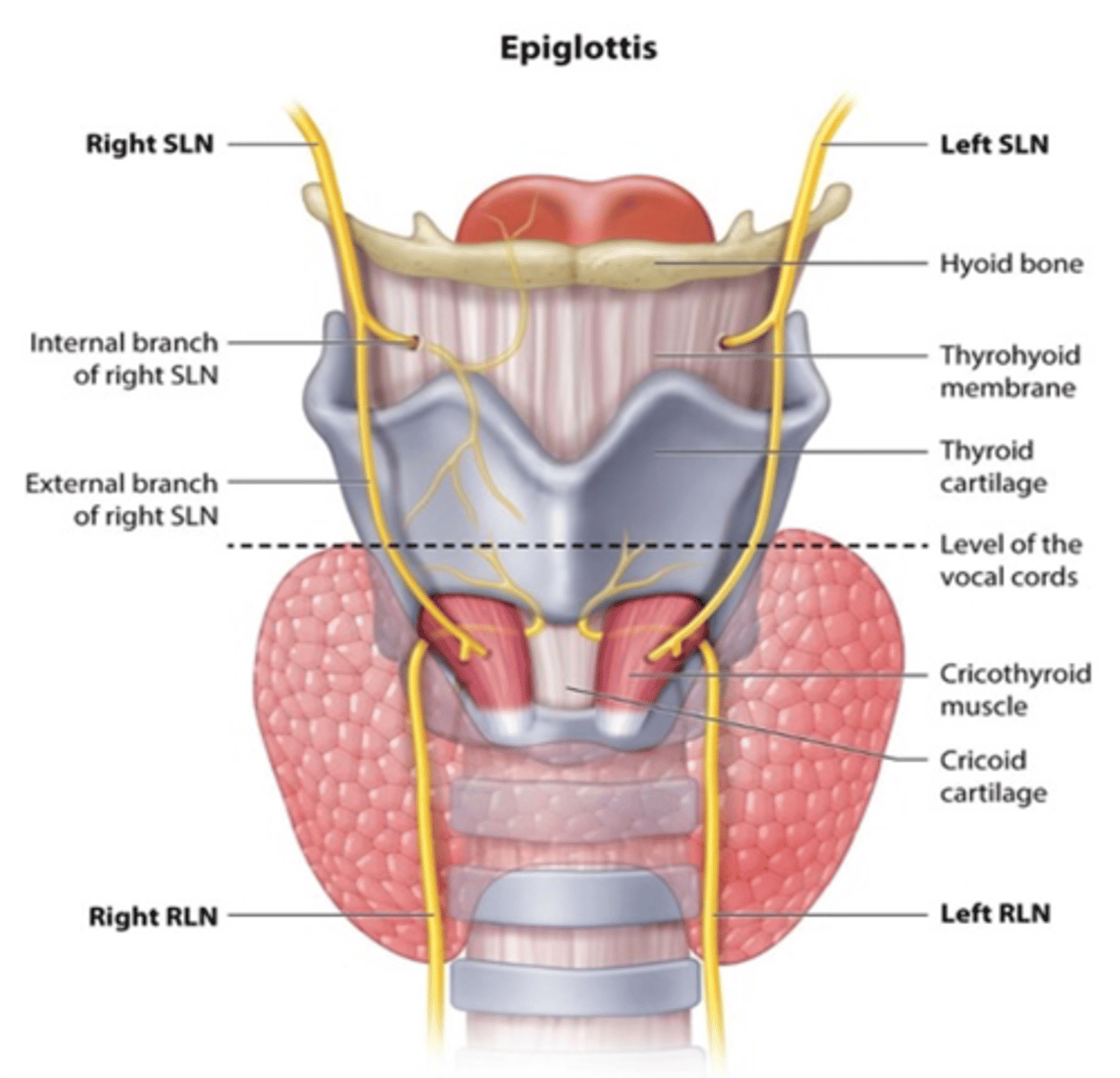
What nerve accompanies the superior laryngeal artery
Internal laryngeal nerve
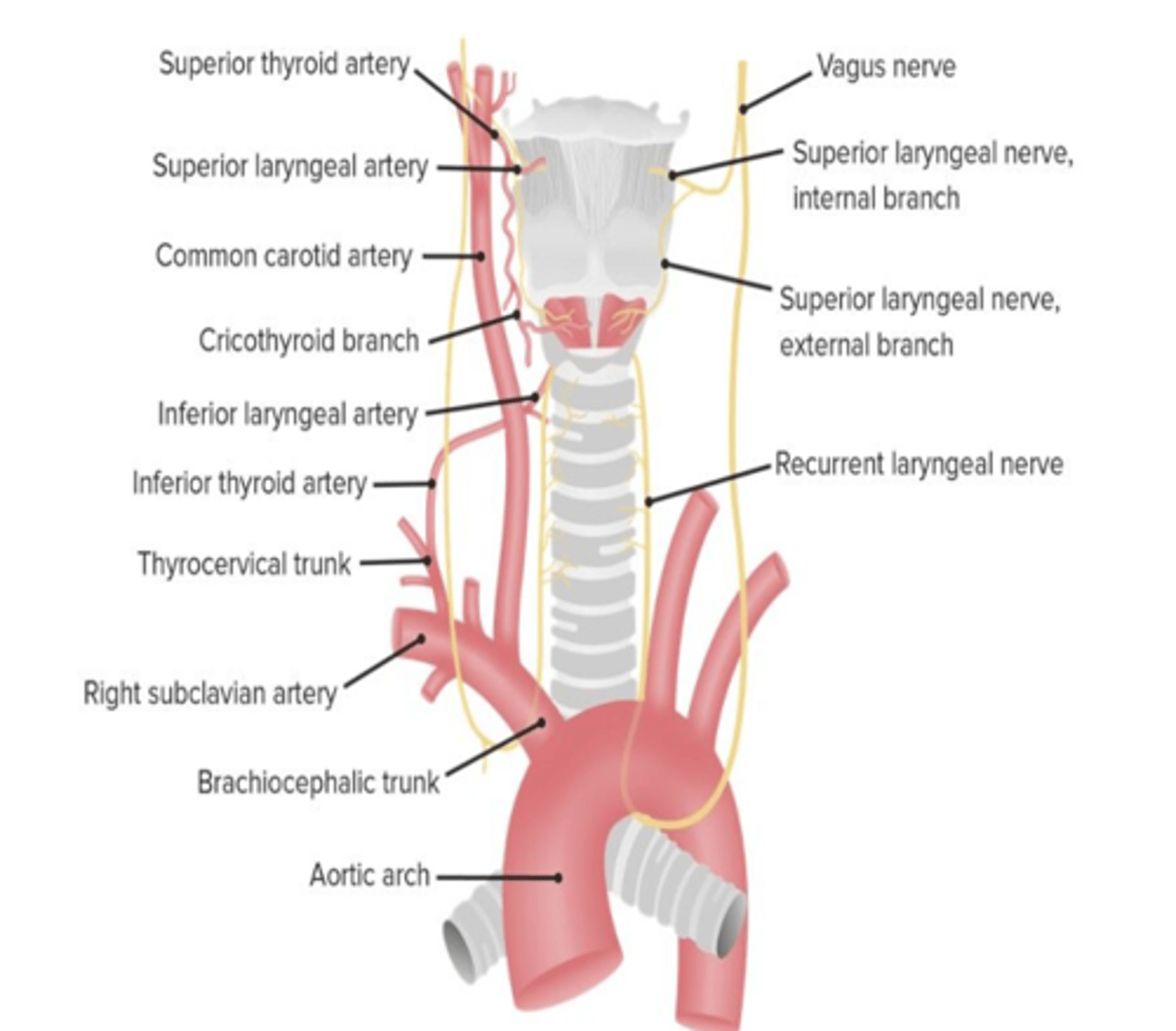
What nerve accompanies the superior thyroid artery
External laryngeal nerve
What division of the trigeminal nerve conducts sensation over the forehead?
Ophthalmic division (CN V1)
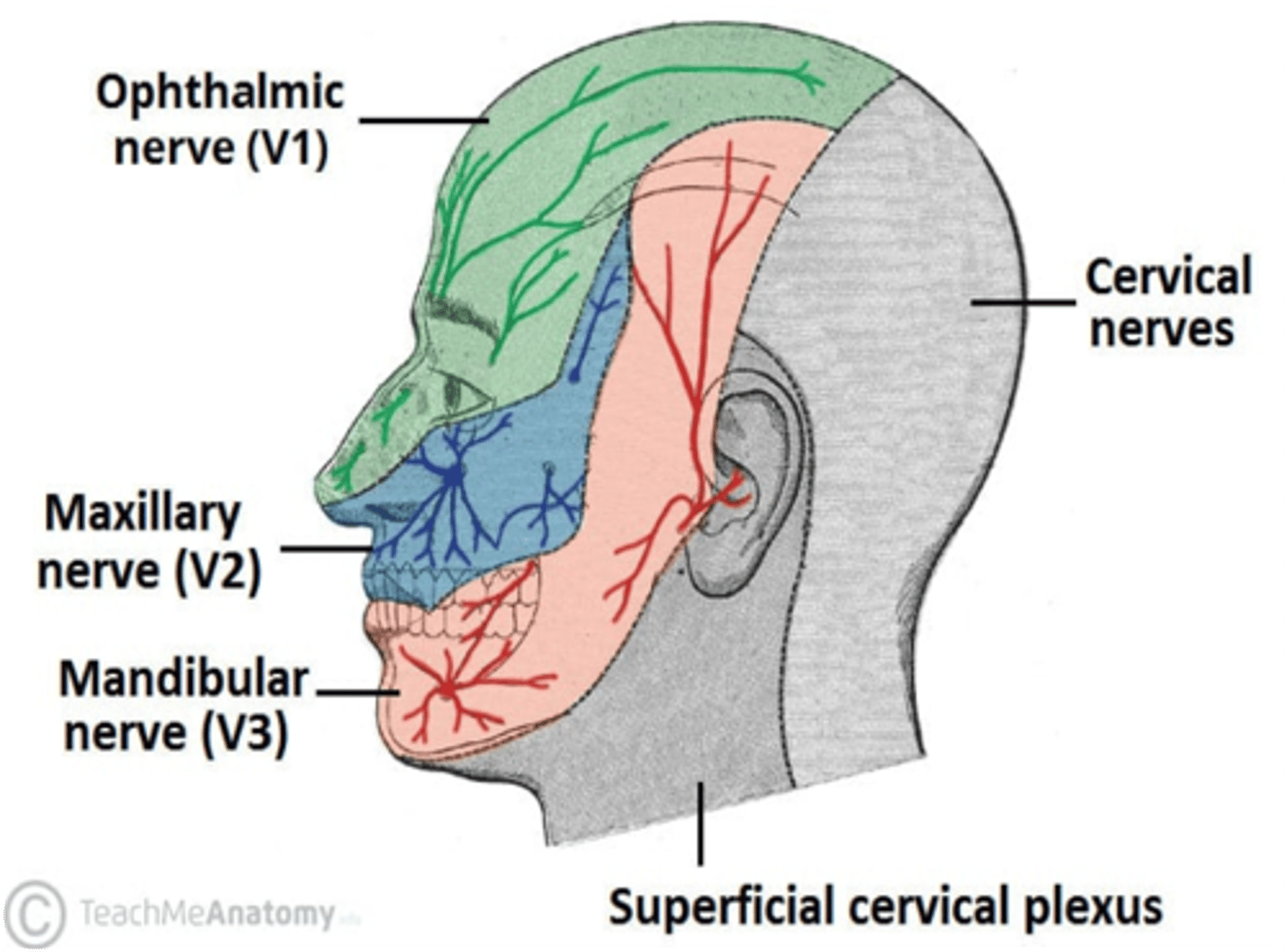
Which division of the trigeminal nerve provides sensation over the tip of the nose?
Ophthalmic division (CN V1)
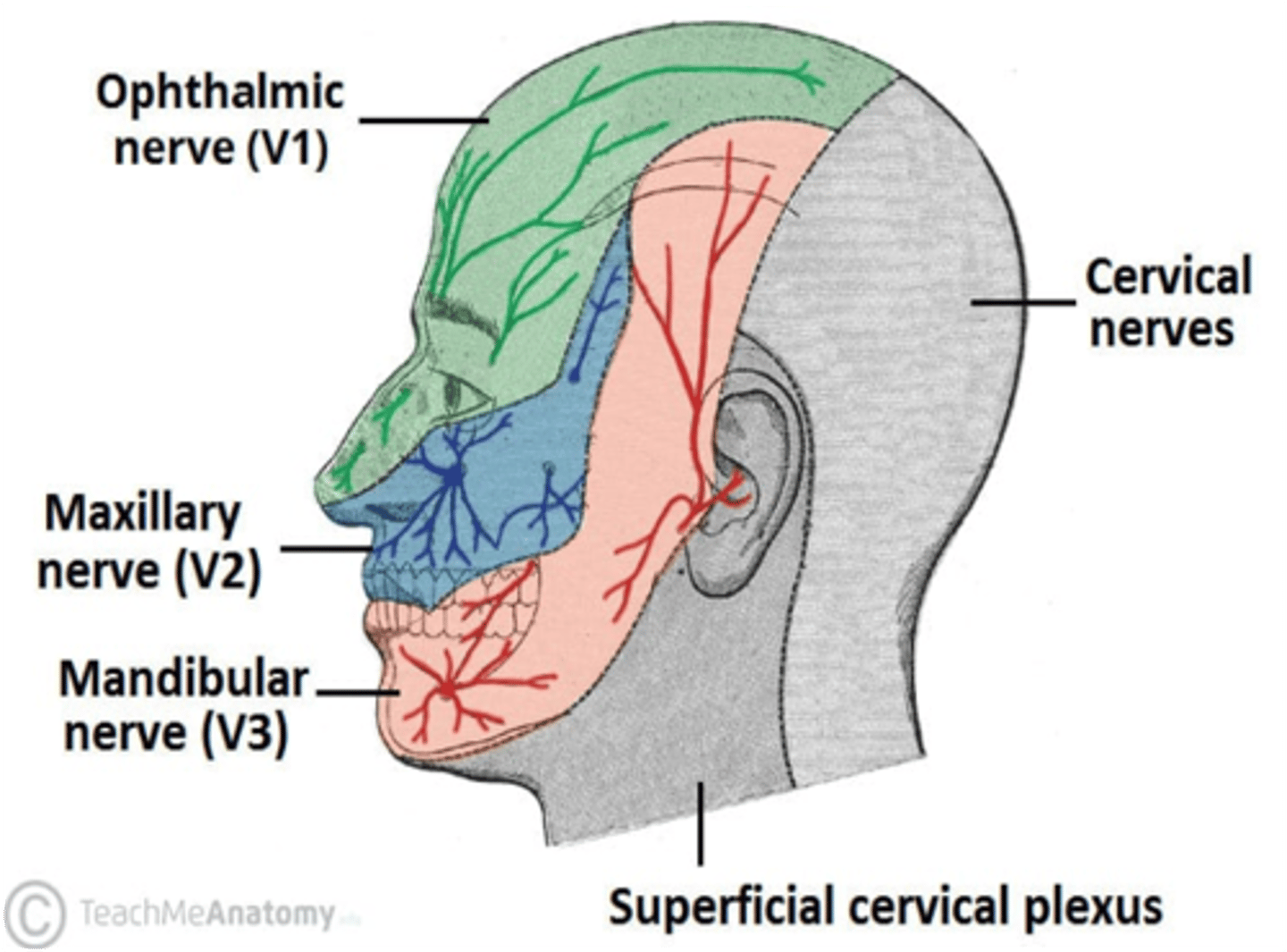
Which division of the trigeminal nerve provides sensation over the angle of the jaw?
Mandibular division (CN V3)
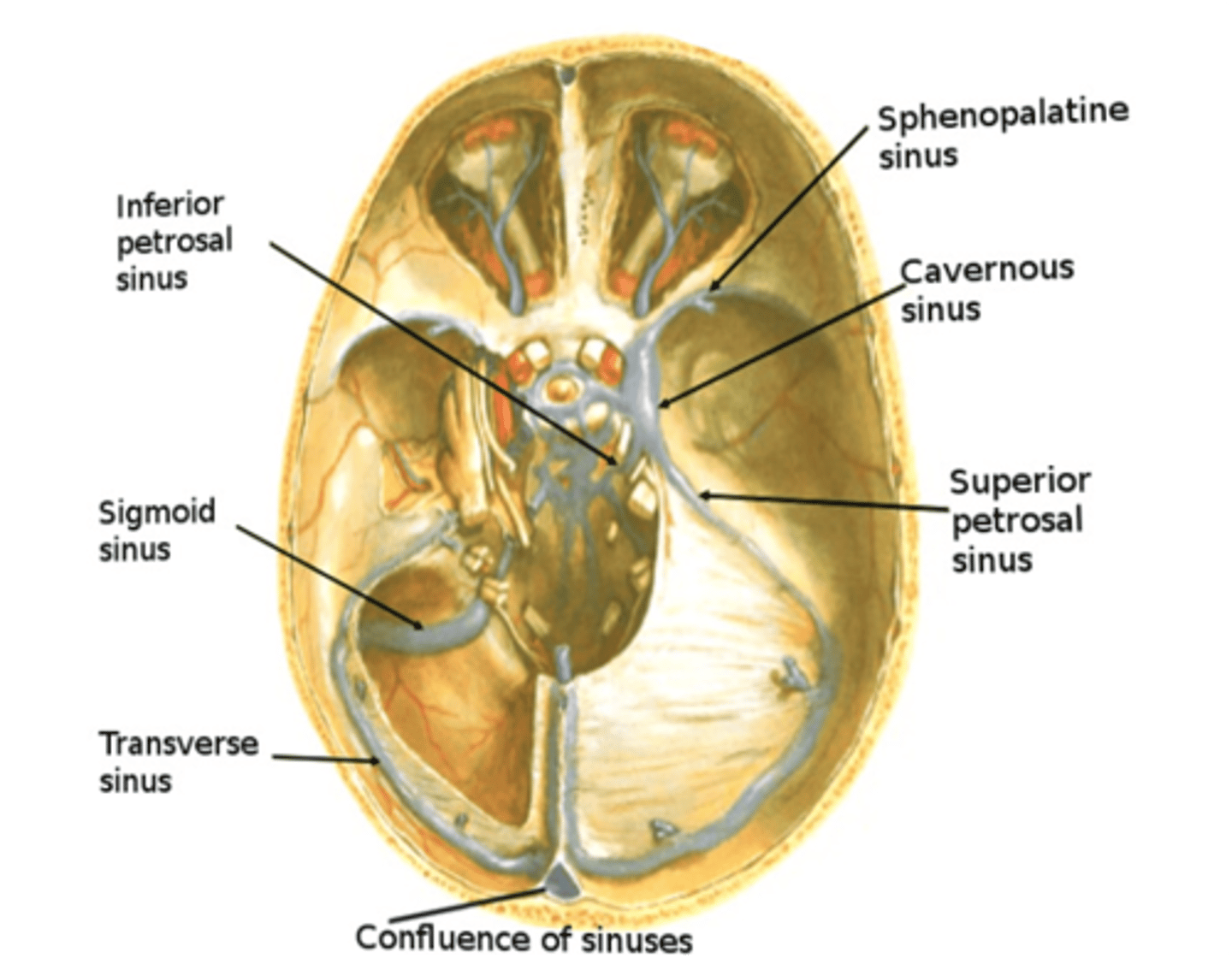
Sinus that lies in the margin of the tentorium cerebelli from the posterior end of the cavernous sinus to the transverse sinus
Superior petrosal sinus
What blood vessel is commonly associated with an epidural hematoma?
Middle meningeal artery
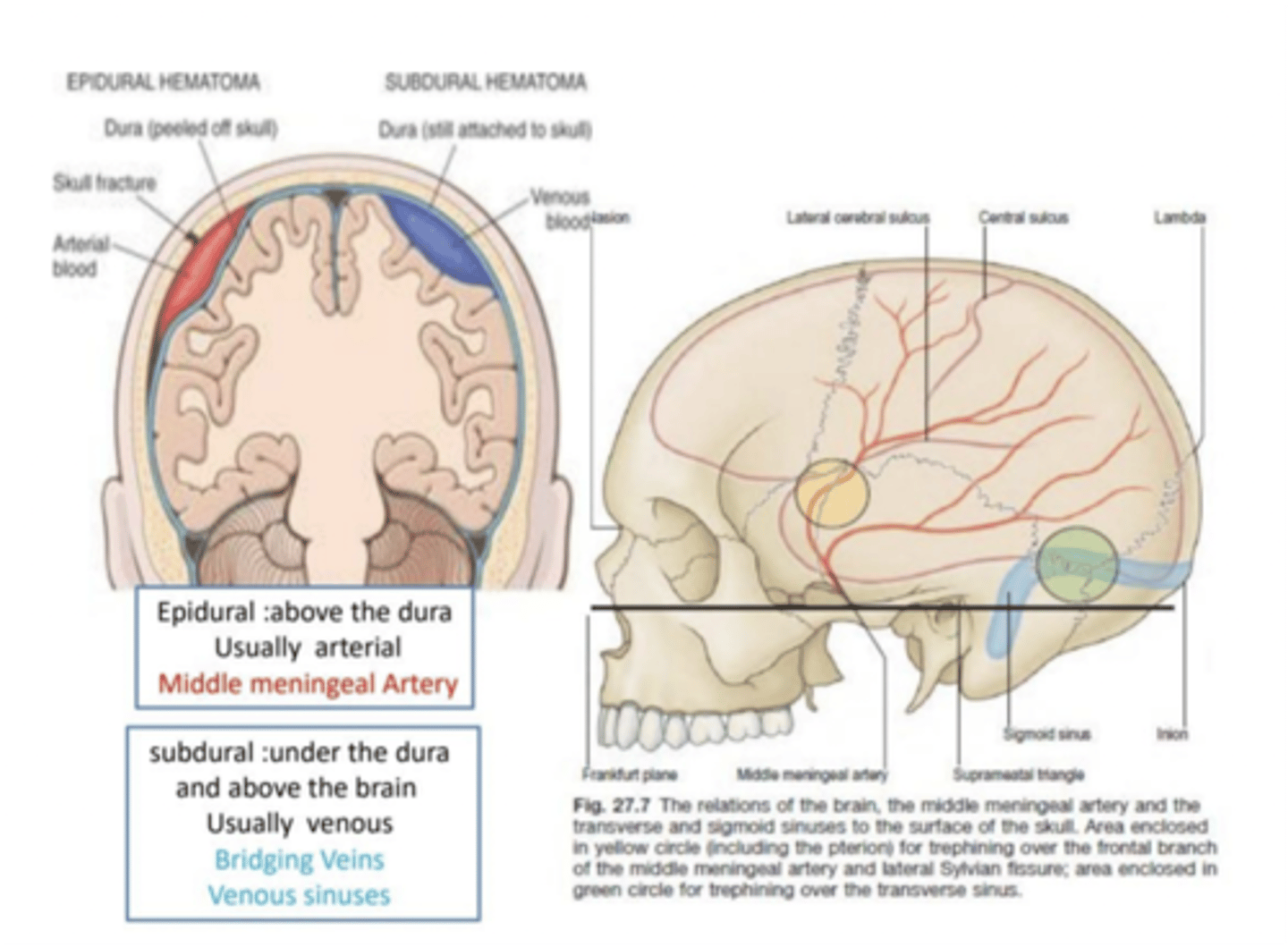
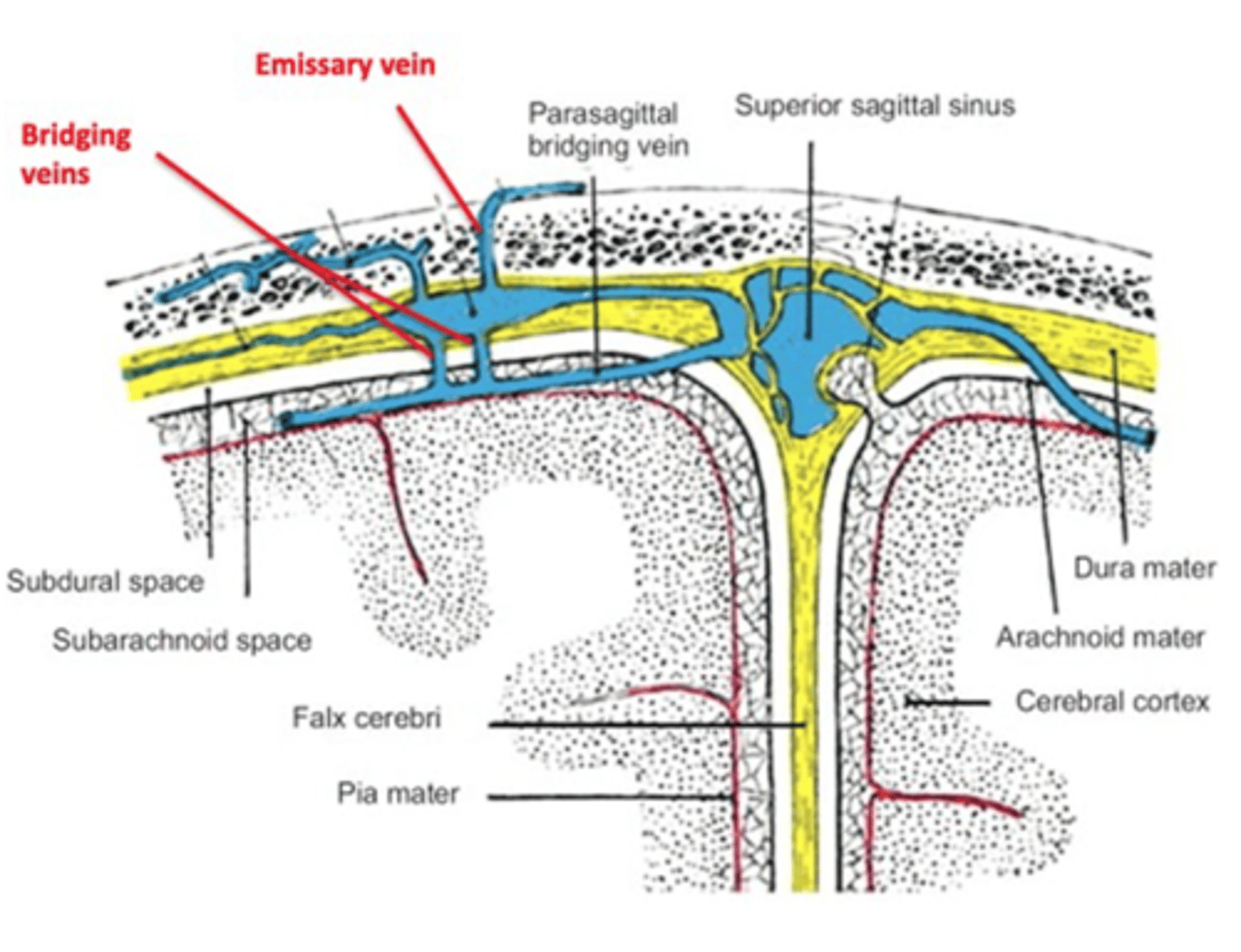
What blood vessel is commonly associated with a subdural hematoma?
Cortical bridging veins
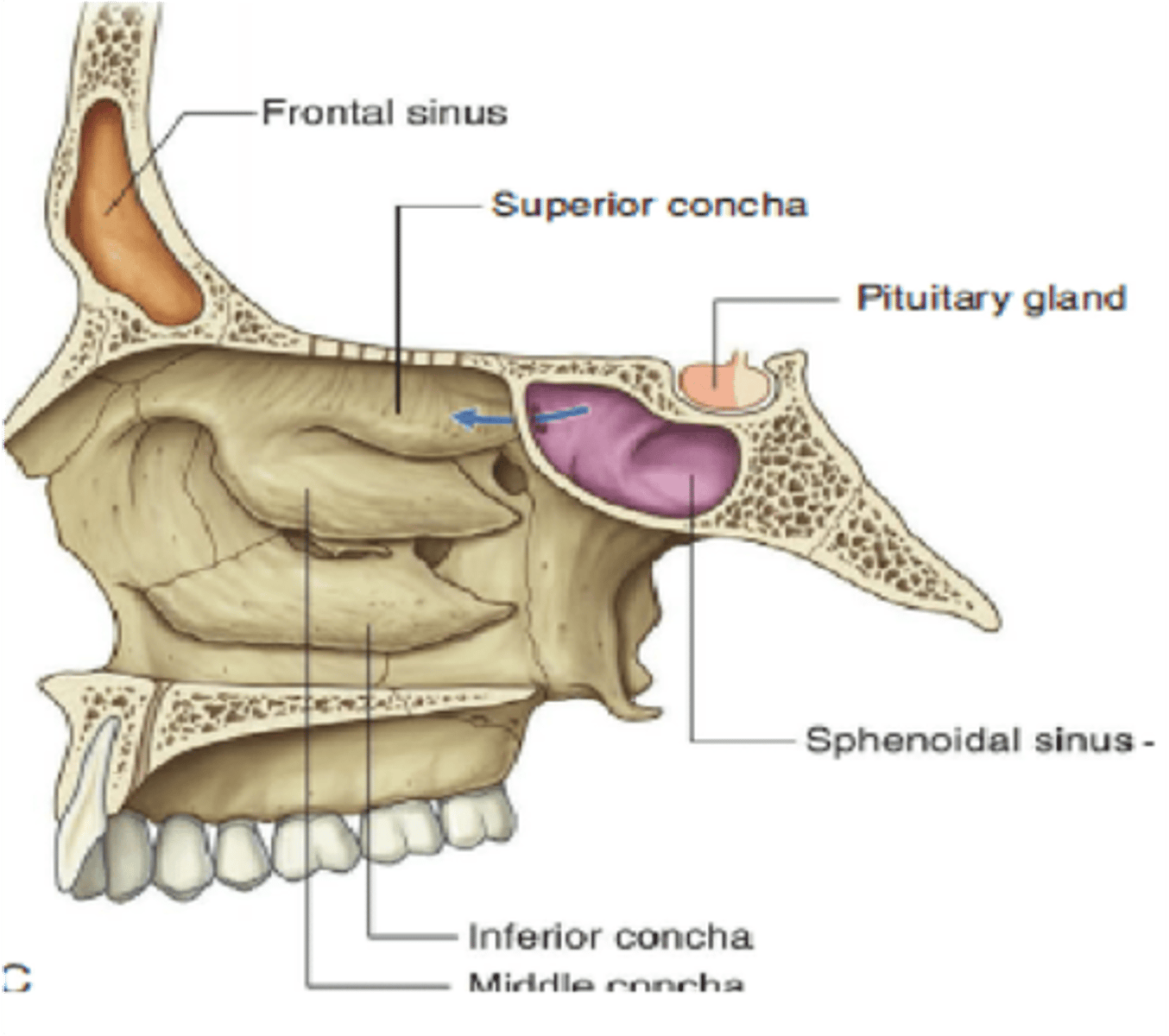
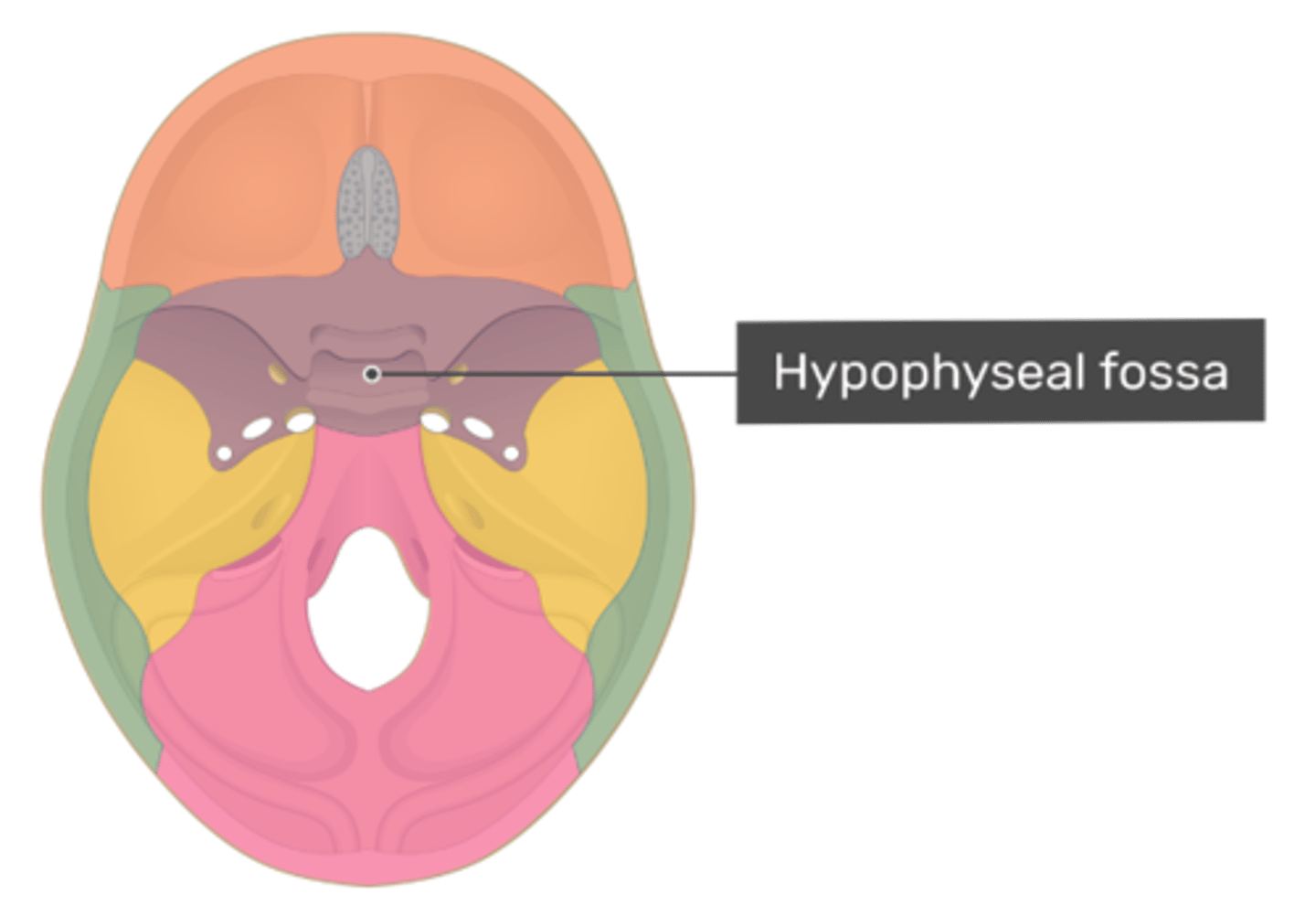
What sinus is immediately anterior and inferior to the pituitary gland?
Sphenoid sinus
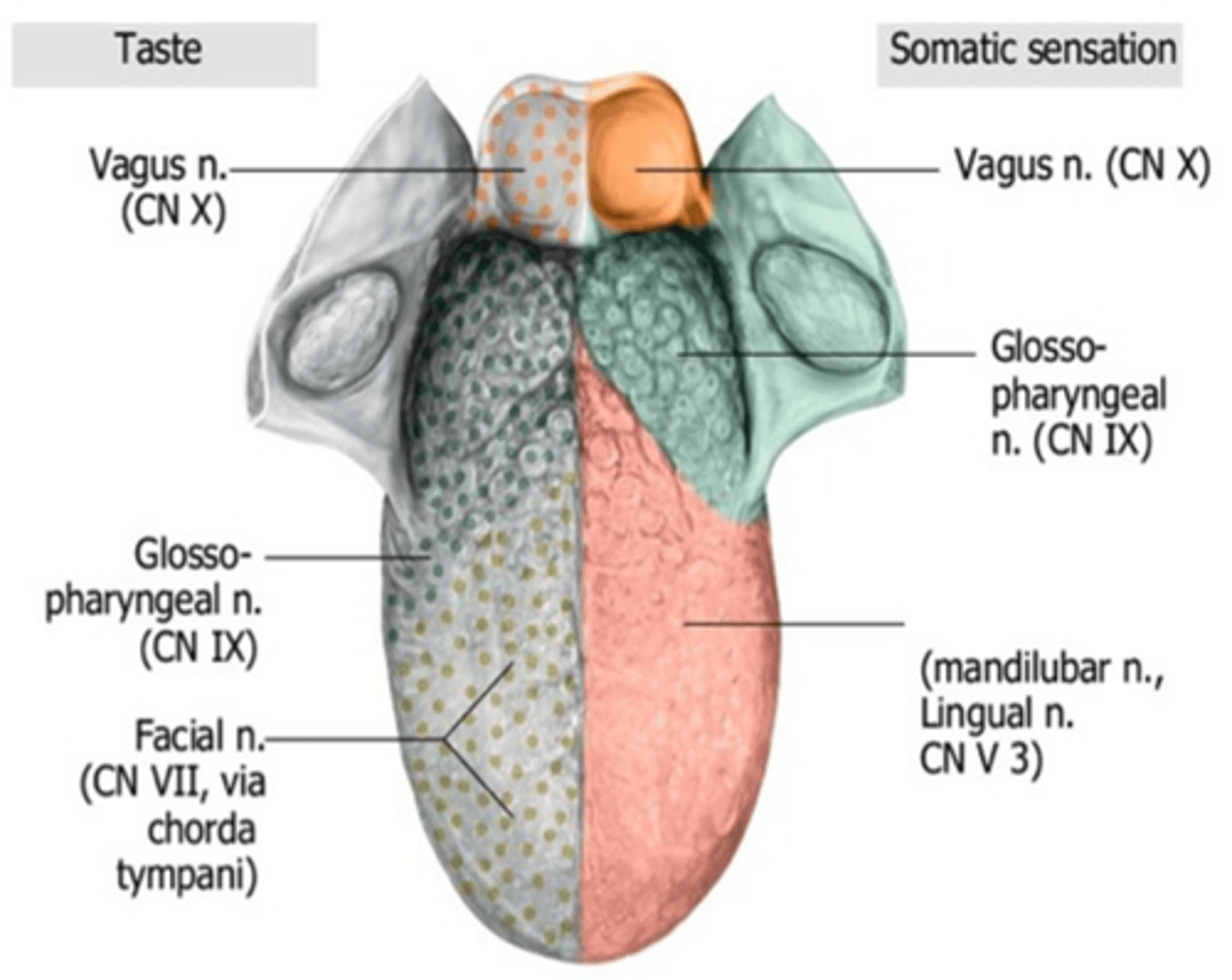
What nerve detects taste sensation from the posterior one-third of the tongue?
Glossopharyngeal nerve
The sella turcica/hypophyseal fossa is situated in what cranial bone?
Sphenoid bone
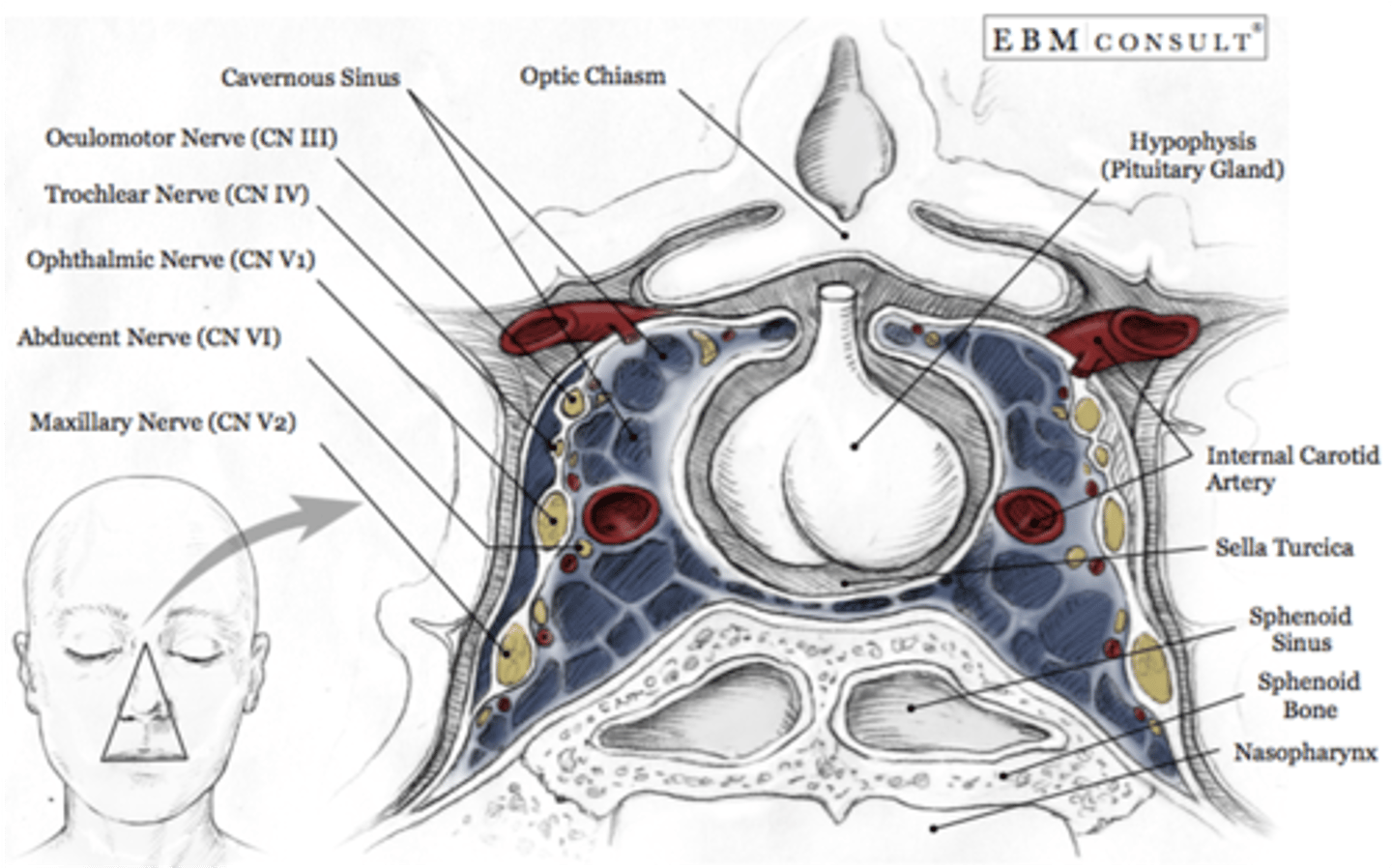
What dural venous sinus is located closest to the pituitary gland?
Cavernous sinus
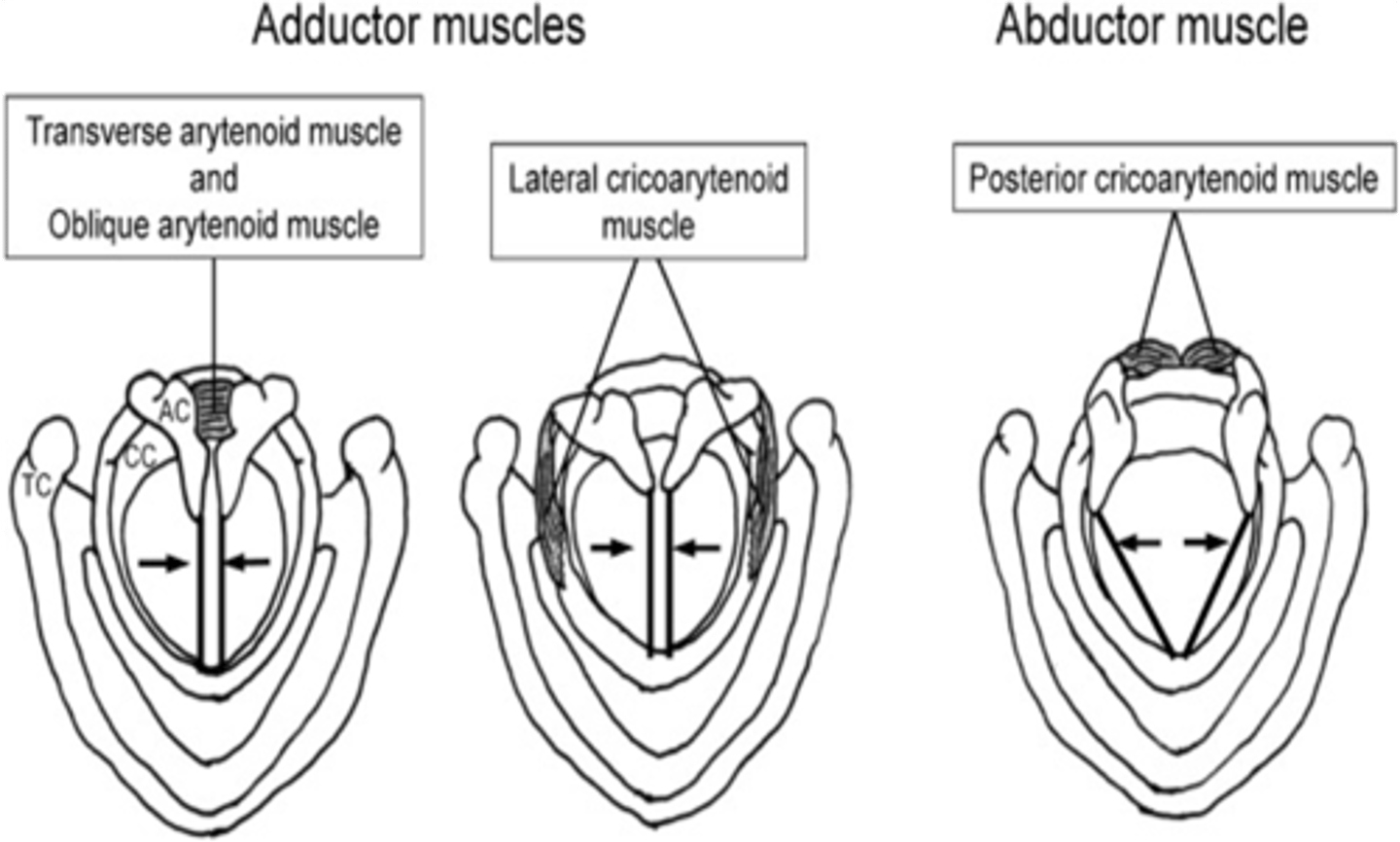
What is the only laryngeal muscle that works to abduct the vocal cords?
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
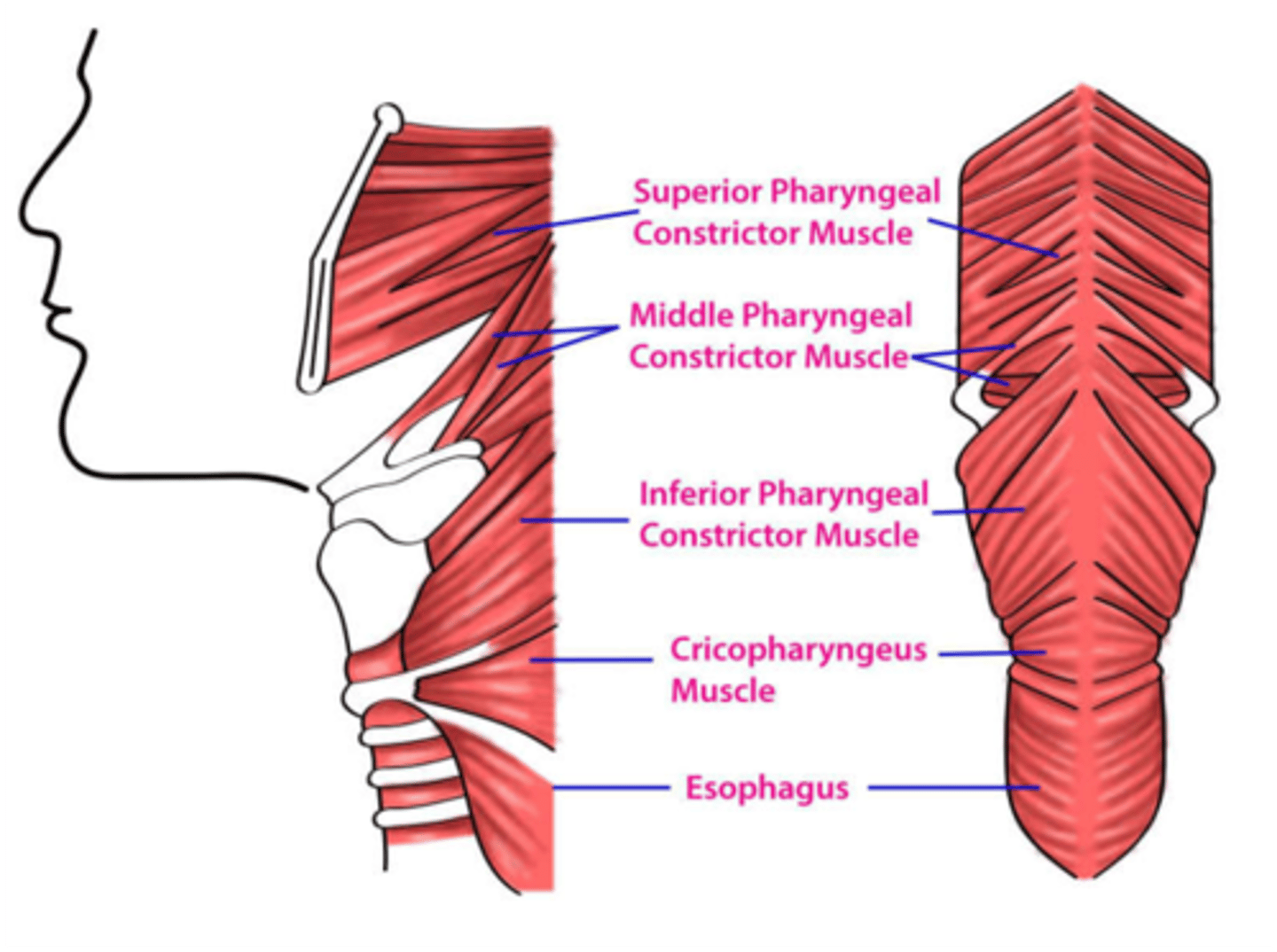
What fibers of the inferior pharyngeal constrictors act as a sphincter that prevents air from entering the esophagus?
Cricopharyngeus fibers
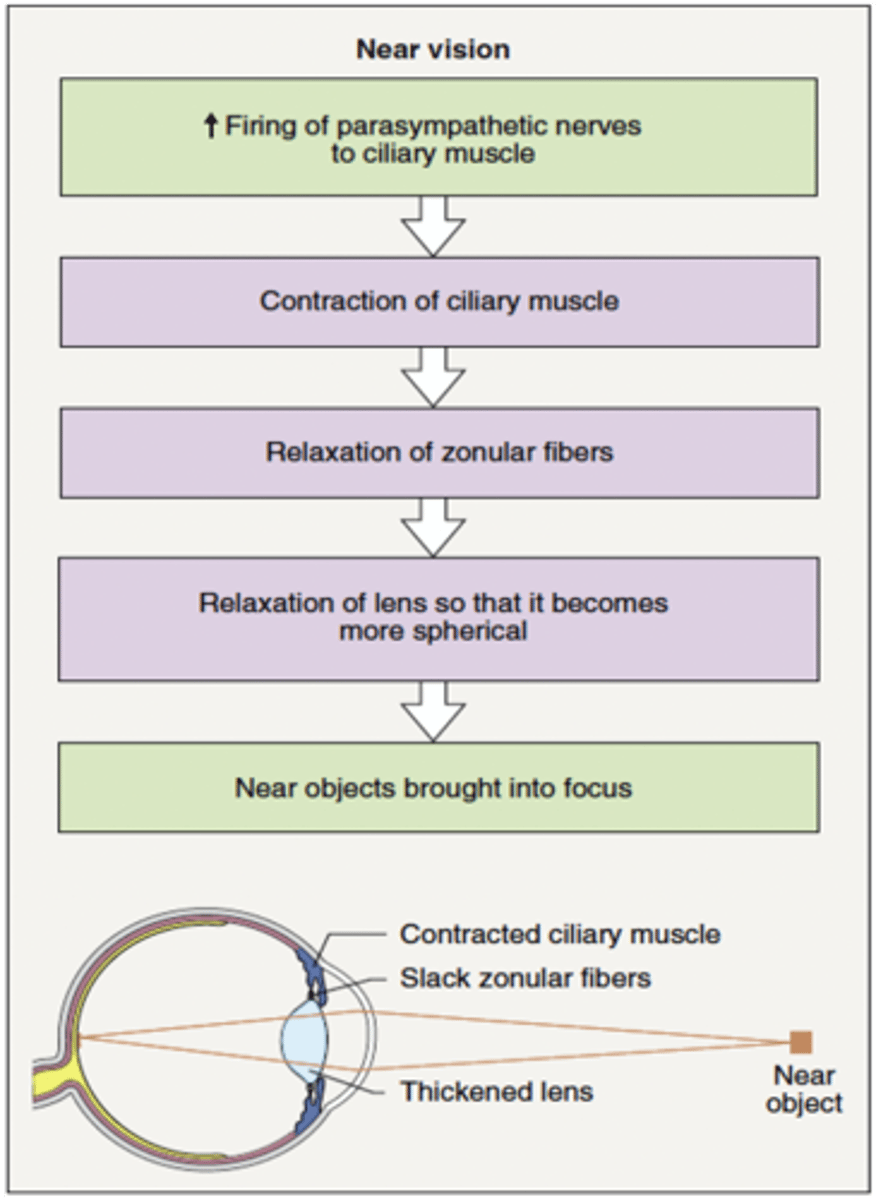
What are the effects of parasympathetic stimulation of the eyeball?
Pupil constriction
Contraction of ciliary muscle
Relaxation of zonular fibers
Thickening of lens
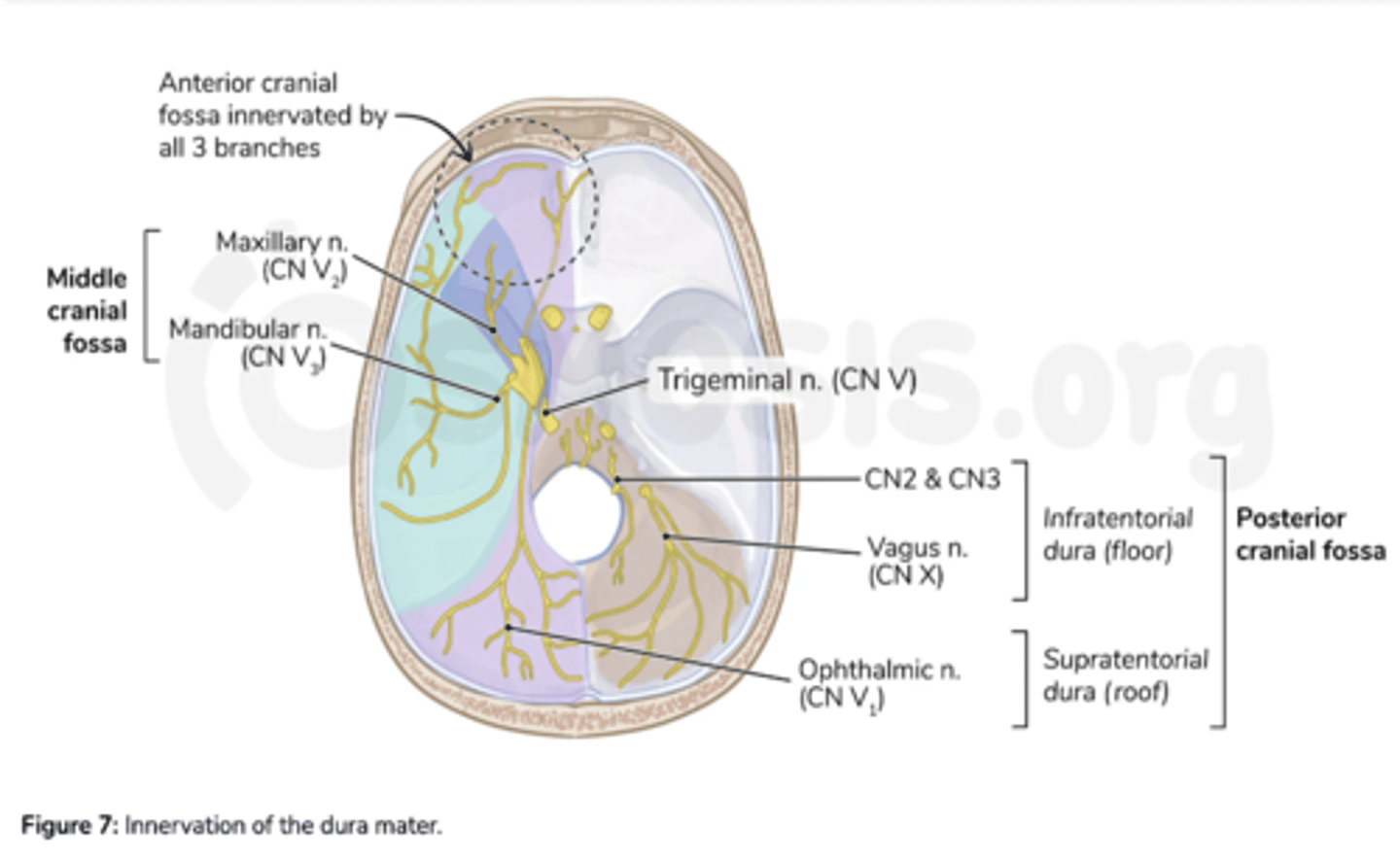
What is the innervation of the dura mater in the middle cranial fossa?
Meningeal branches of V2 and V3
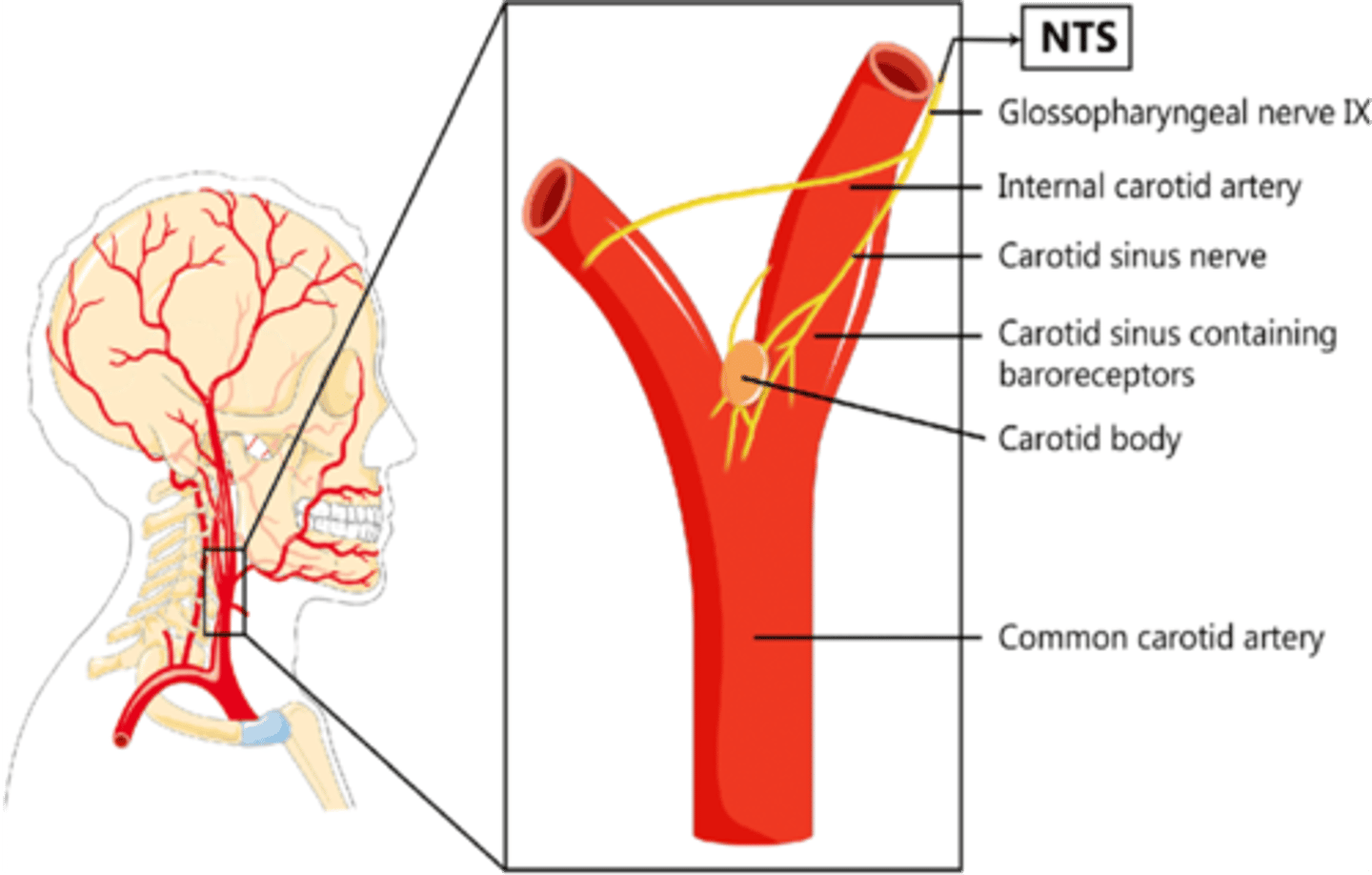
The carotid sinus is what type of receptor?
Baroreceptor
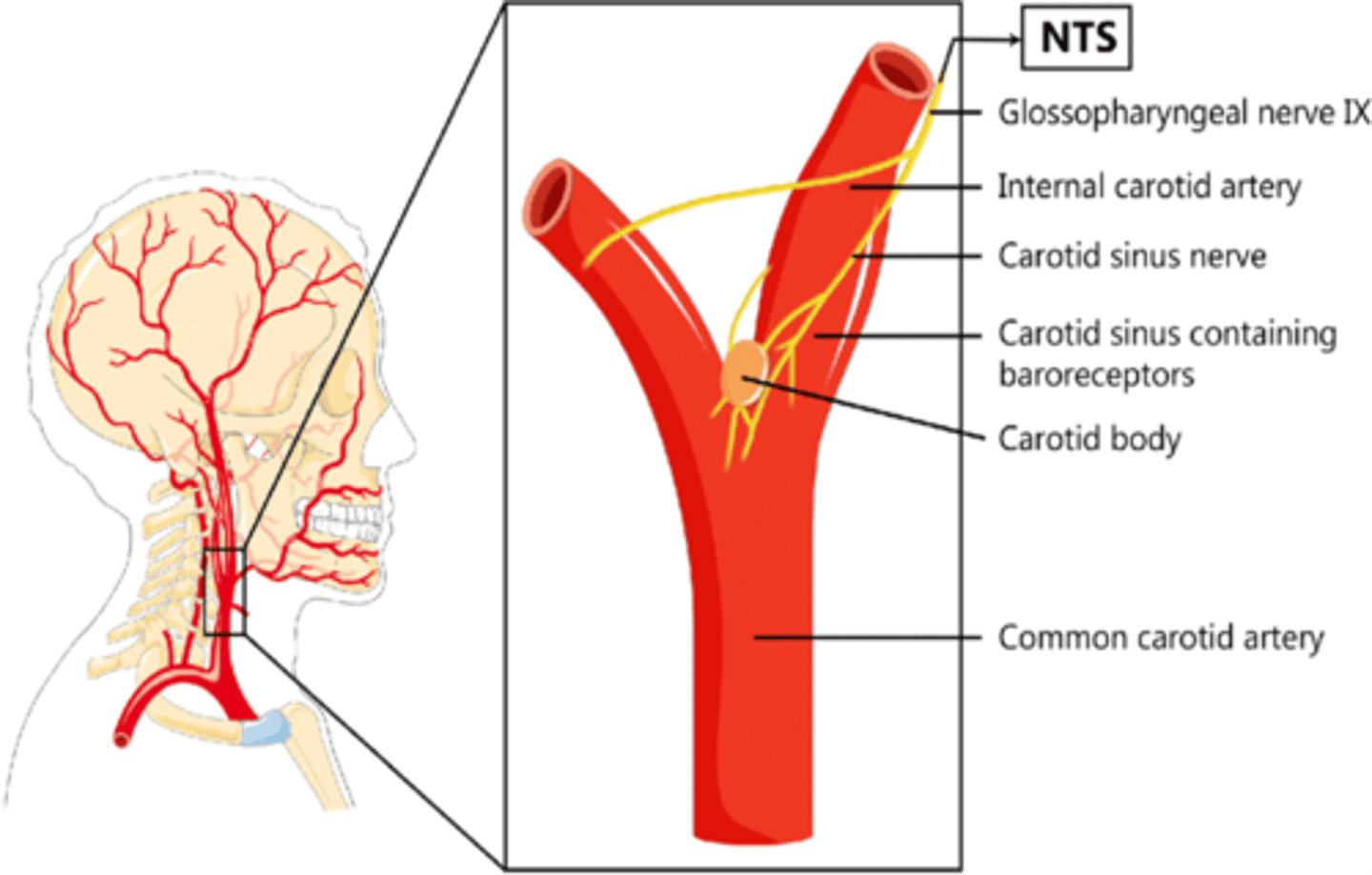
The carotid body is what type of receptor?
Chemoreceptor
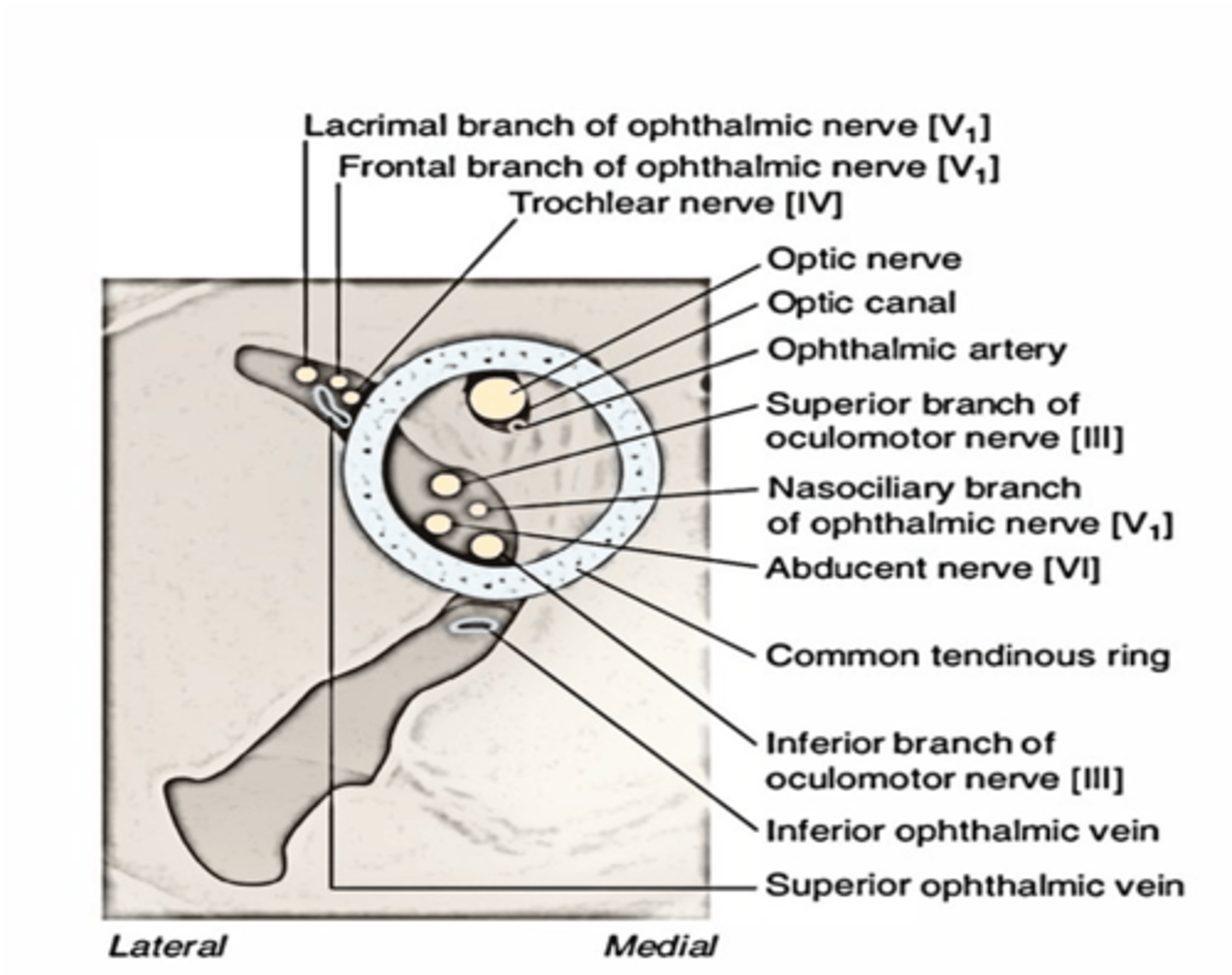
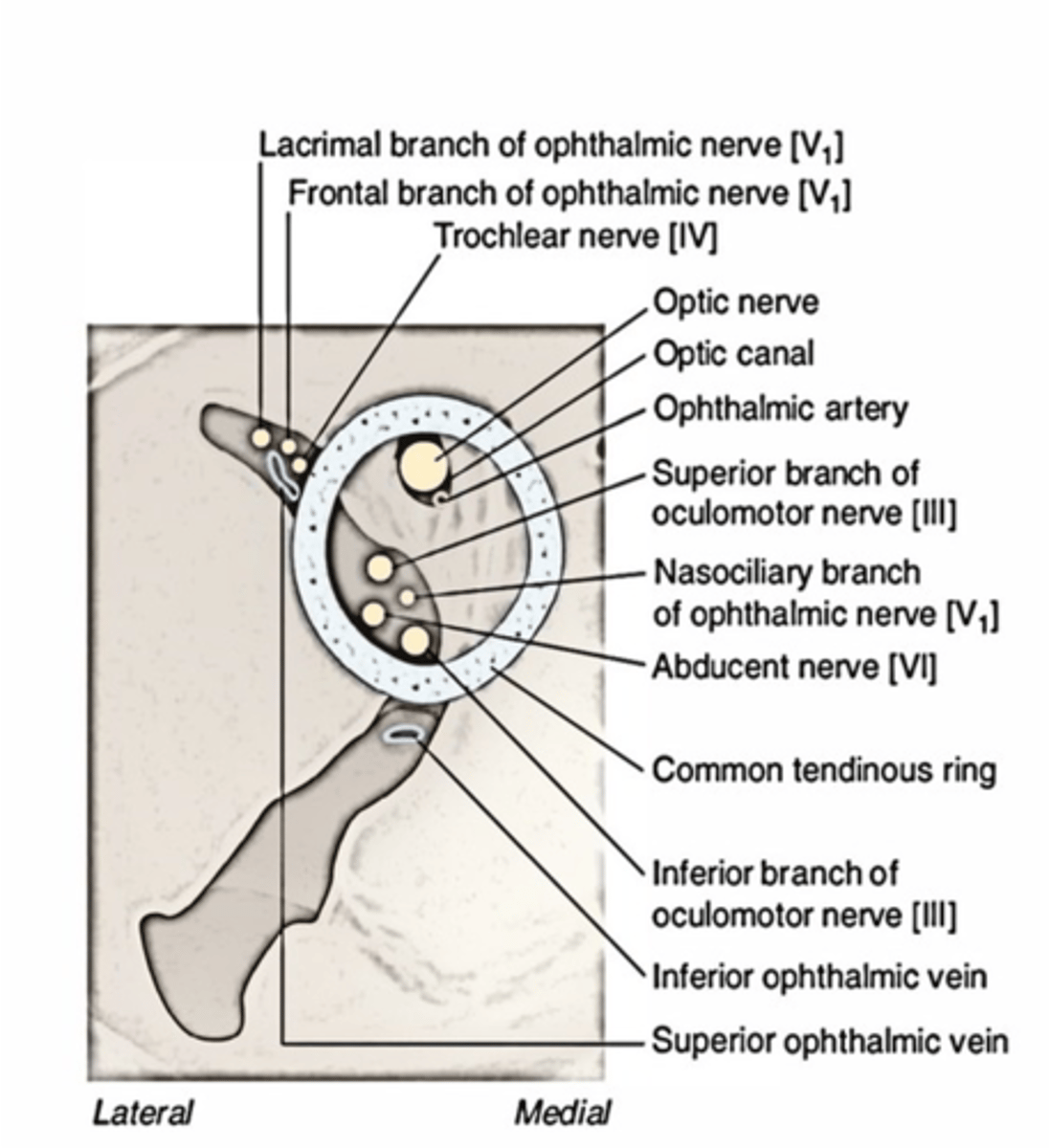
What structures are found inside the optic canal?
Optic nerve
Ophthalmic artery
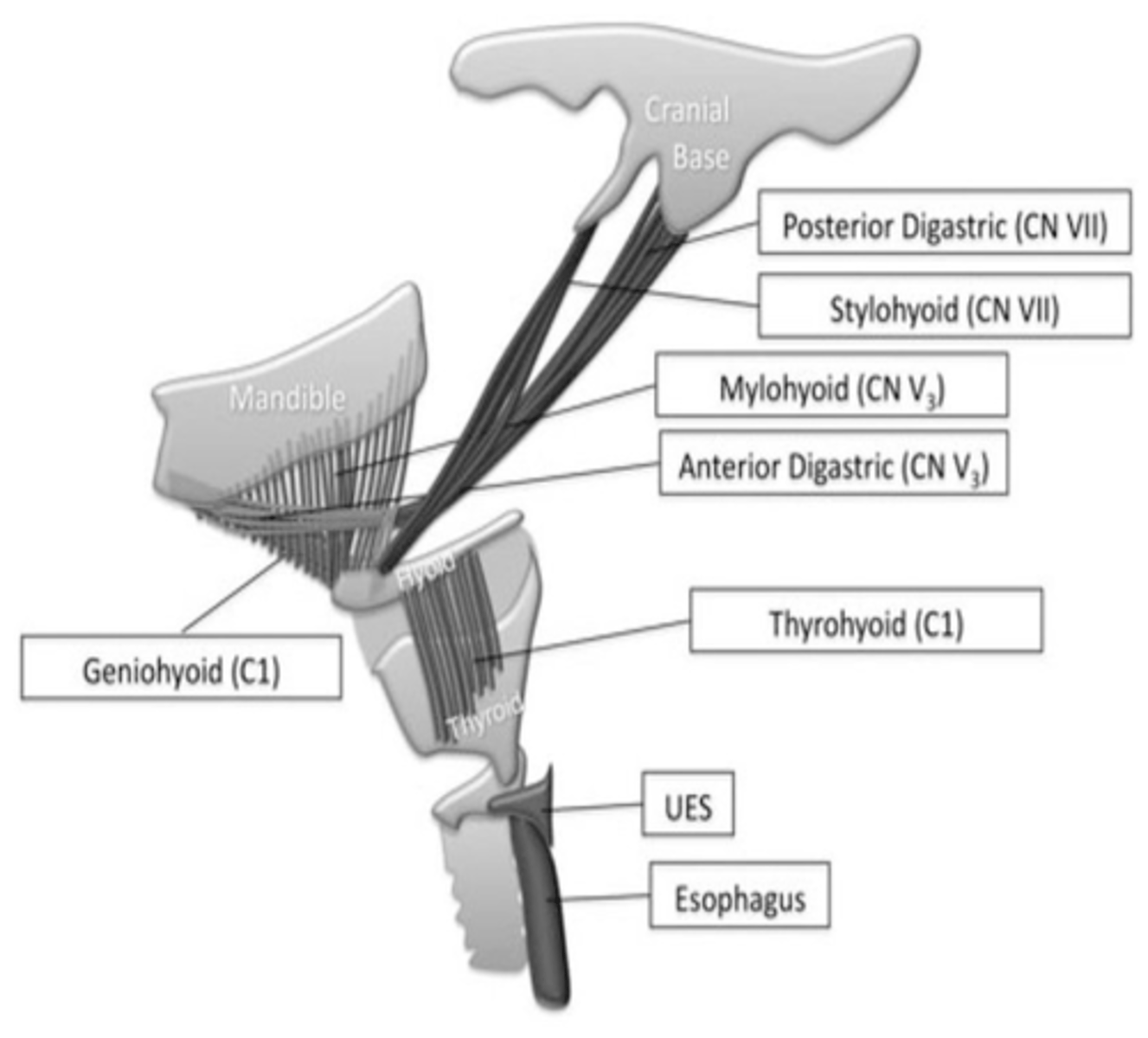
What are the respective innervation of the anterior and posterior bellies of digastric muscle?
Anterior: CN V
Posterior: CN VII
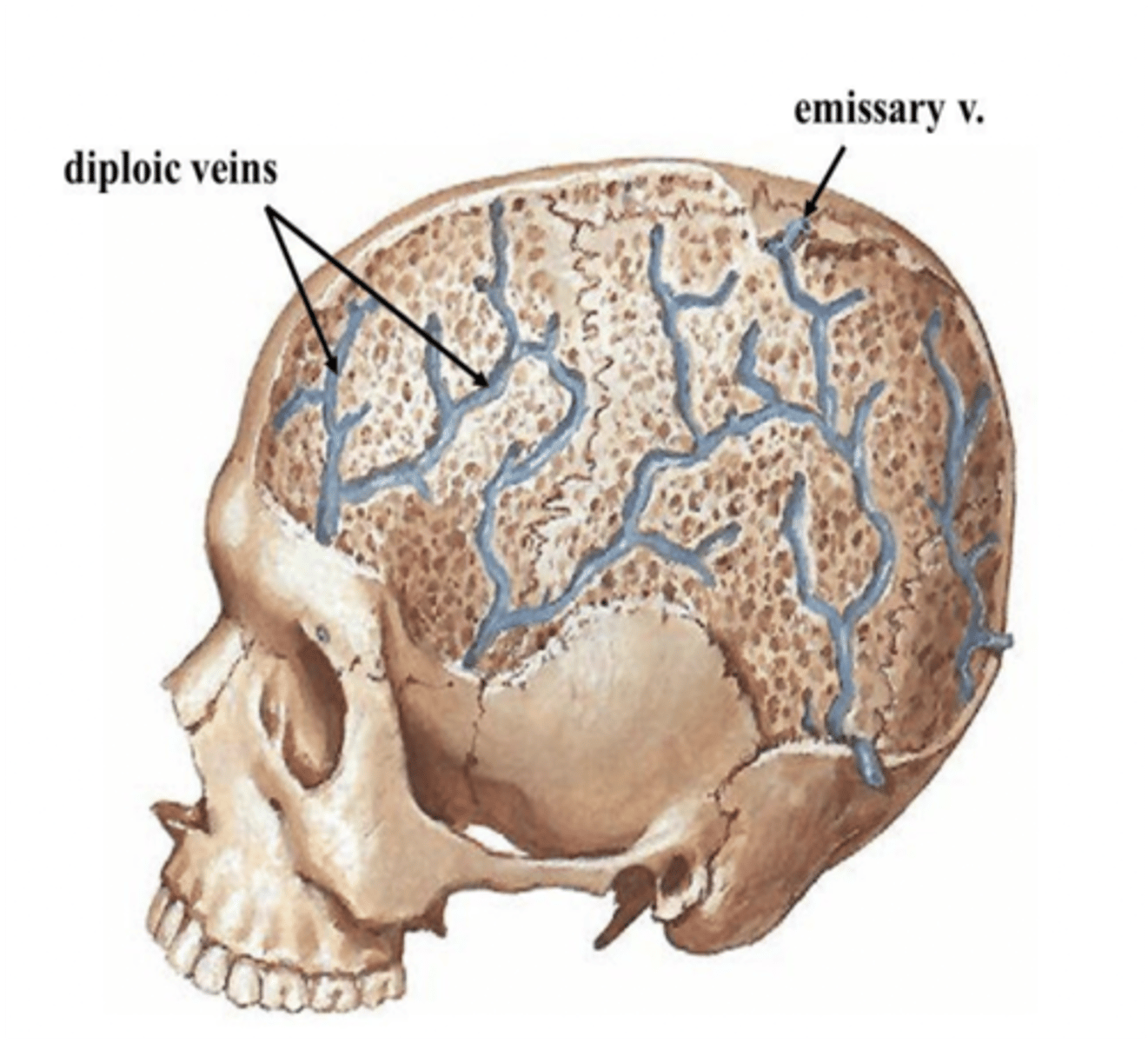
What veins connect the dural venous sinuses with the veins of the scalp?
Emissary veins
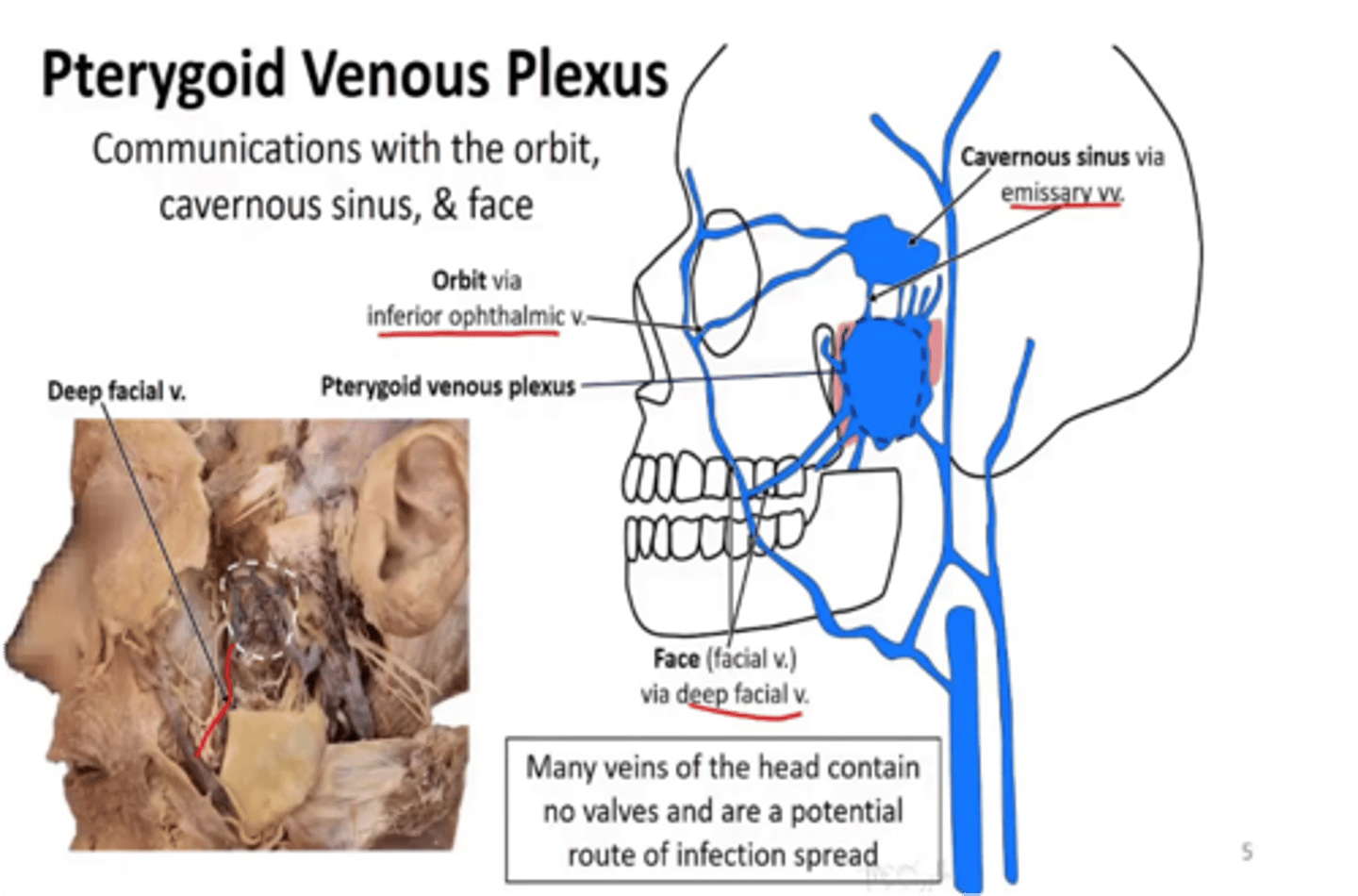
What venous plexus communicates with the cavernous sinus through an emissary vein?
Pterygoid venous plexus
What veins lie in channels in the diploe of the skull?
Diploic veins
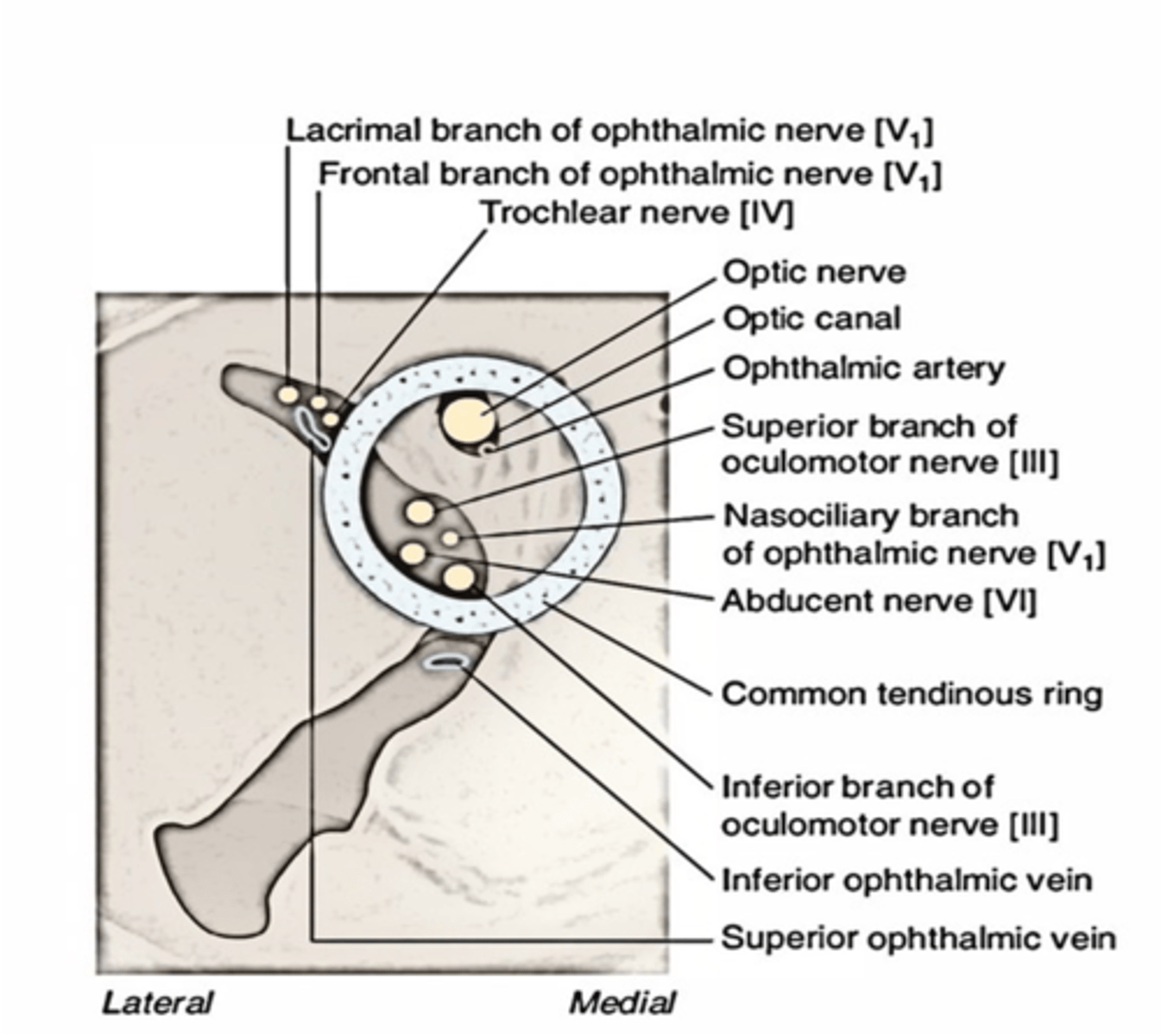
What structures run through both the superior orbital fissue and the common tendinous ring?
CN III, Nasociliary nerve, CN VI
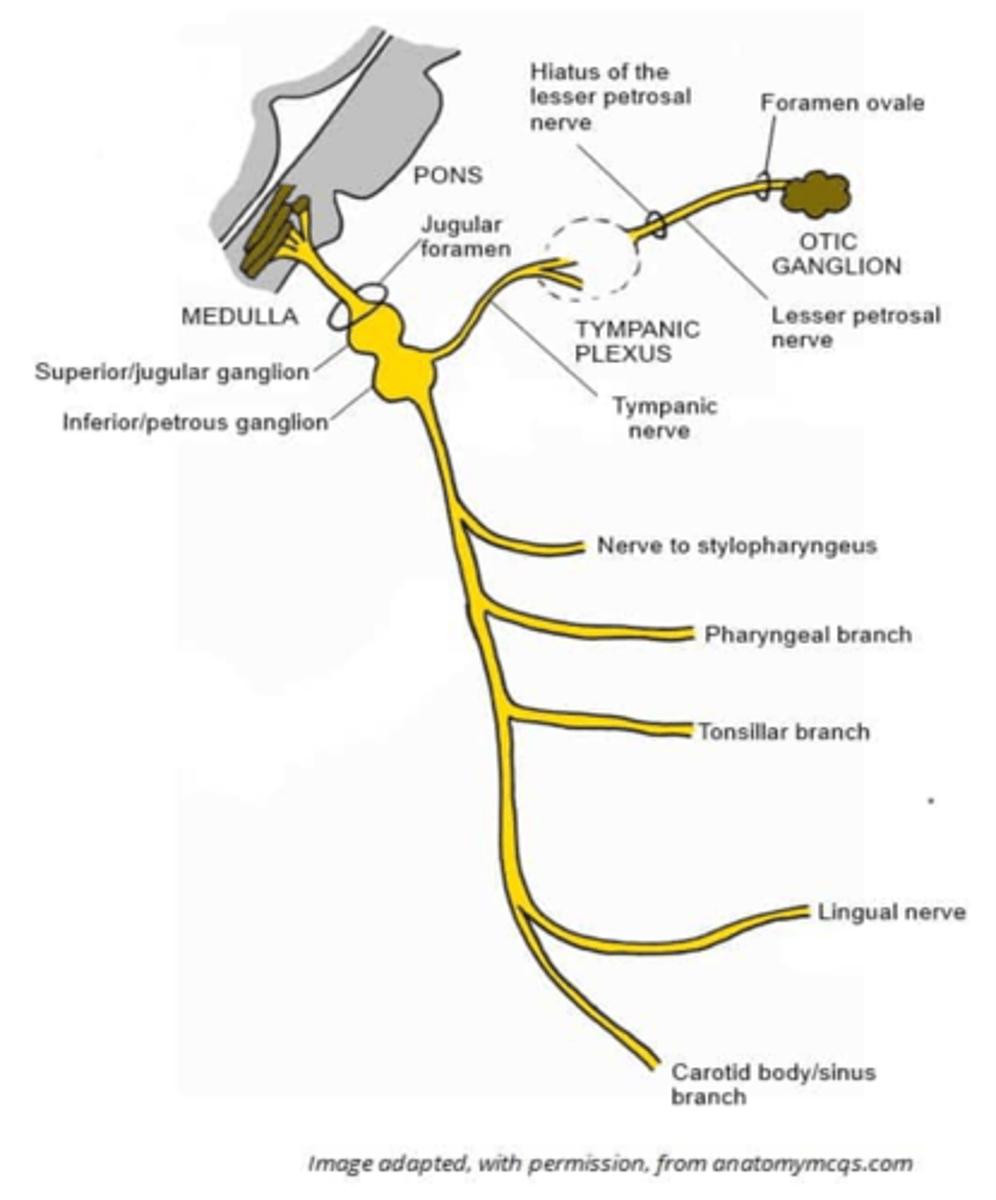
What is another term for the tympanic nerve of the glossopharyngeal nerve?
Jacobson nerve
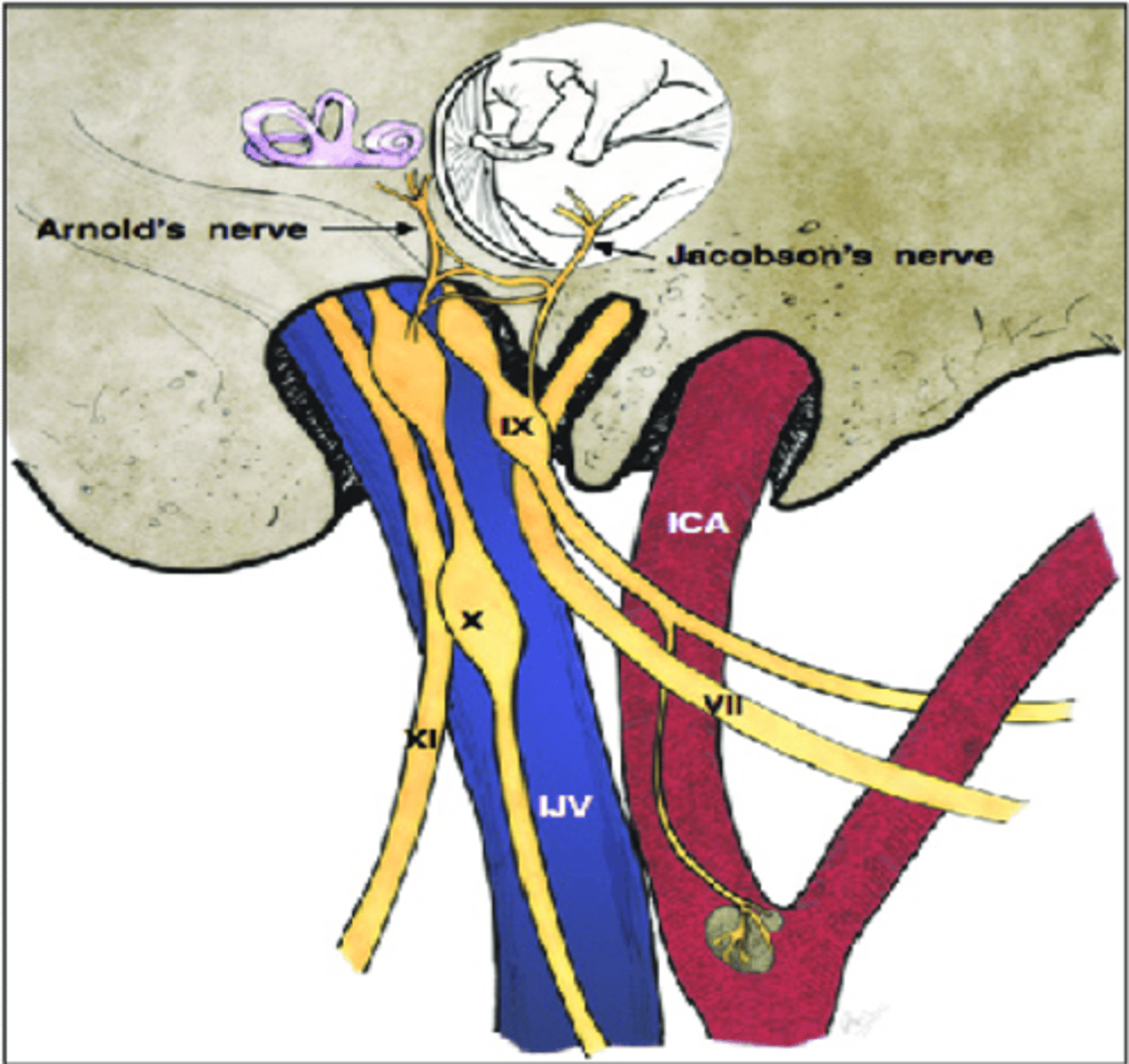
This branch of CN IX contains preganglionic parasympathetic fibers and forms a tympanic plexus on the medial wall of the middle ear with sympathetic fibers
Tympanic nerve (Jacobson nerve)
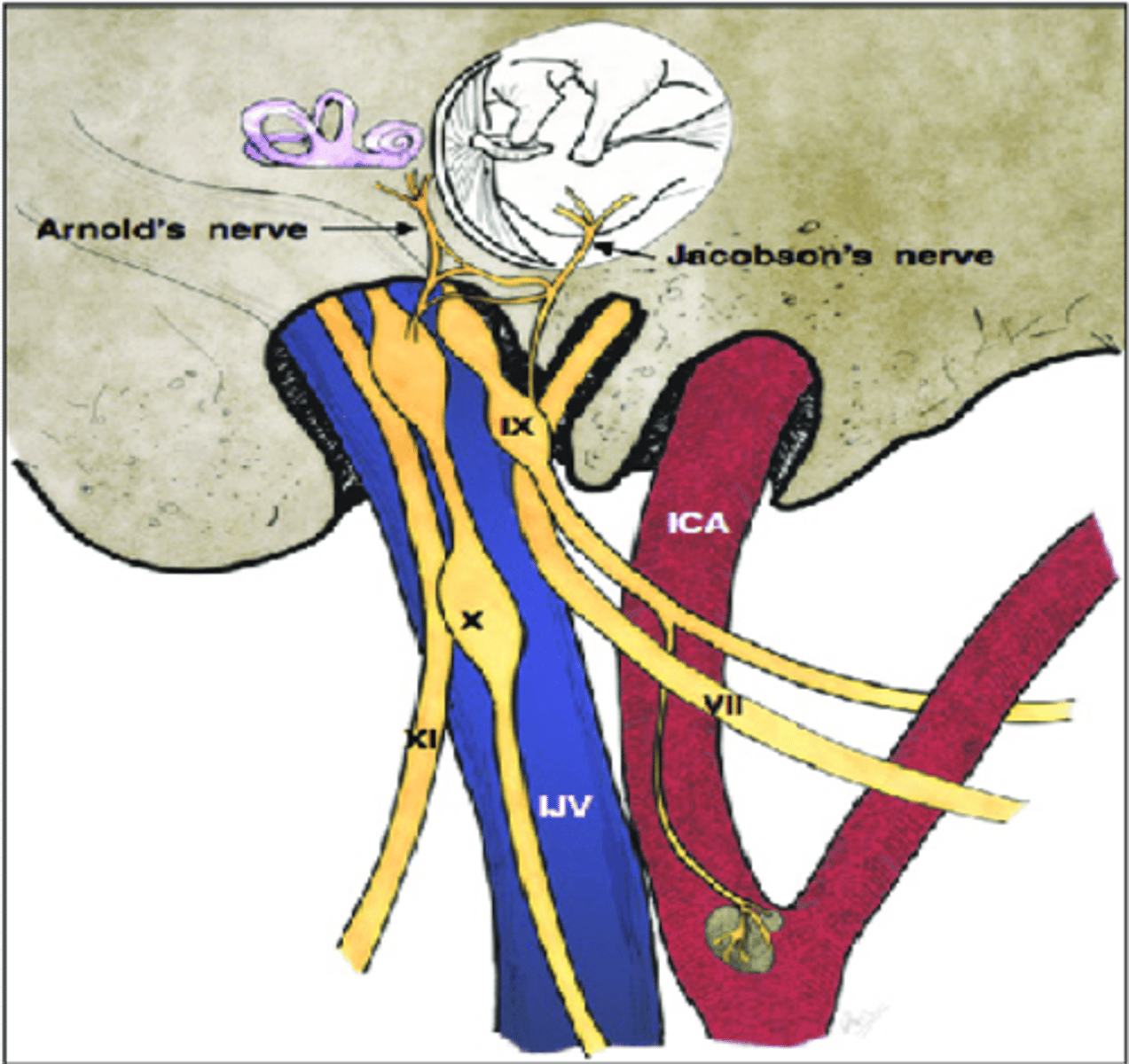
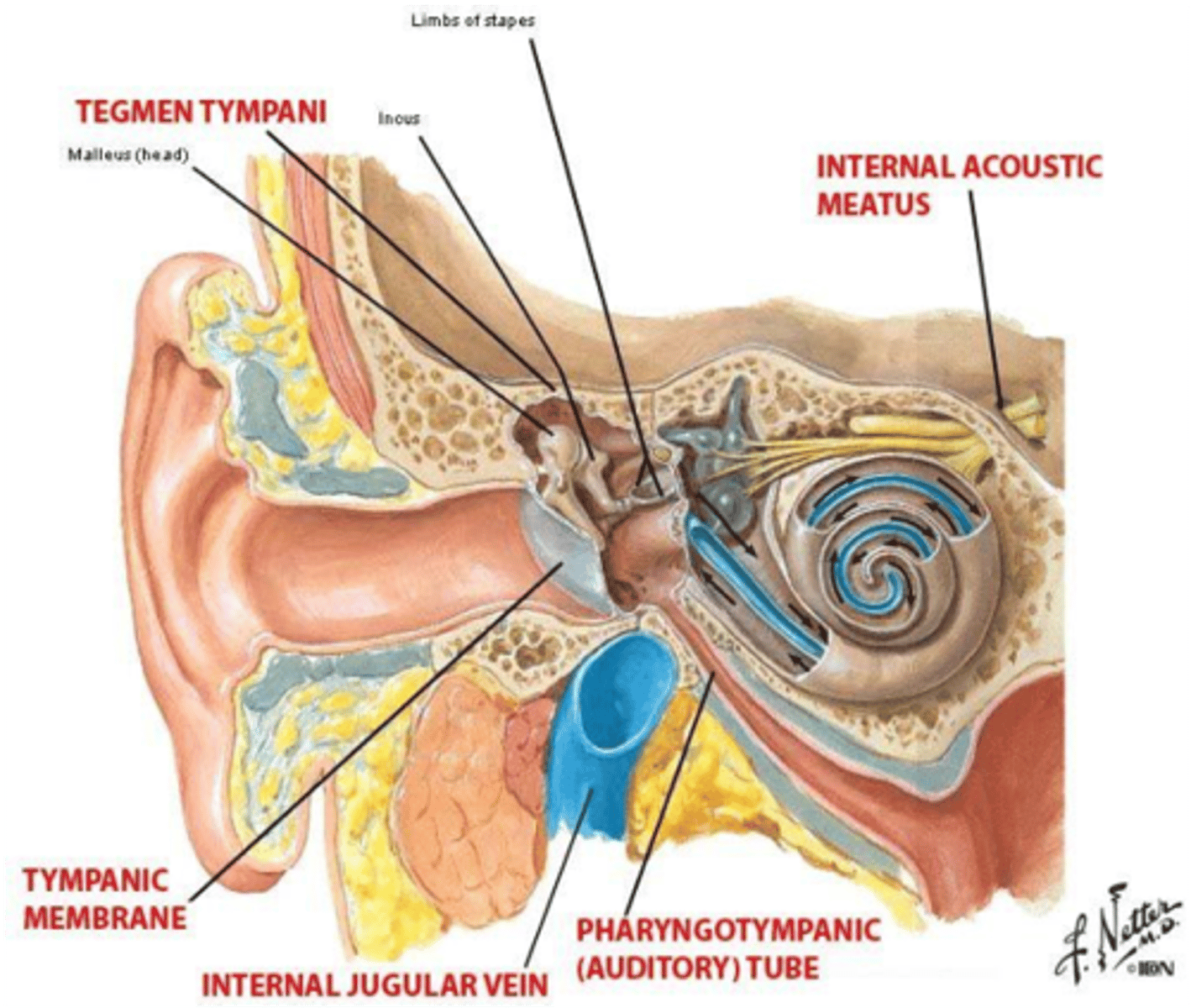
What structure separates the middle ear cavity from the middle cranial fossa?
Tegmen tympani
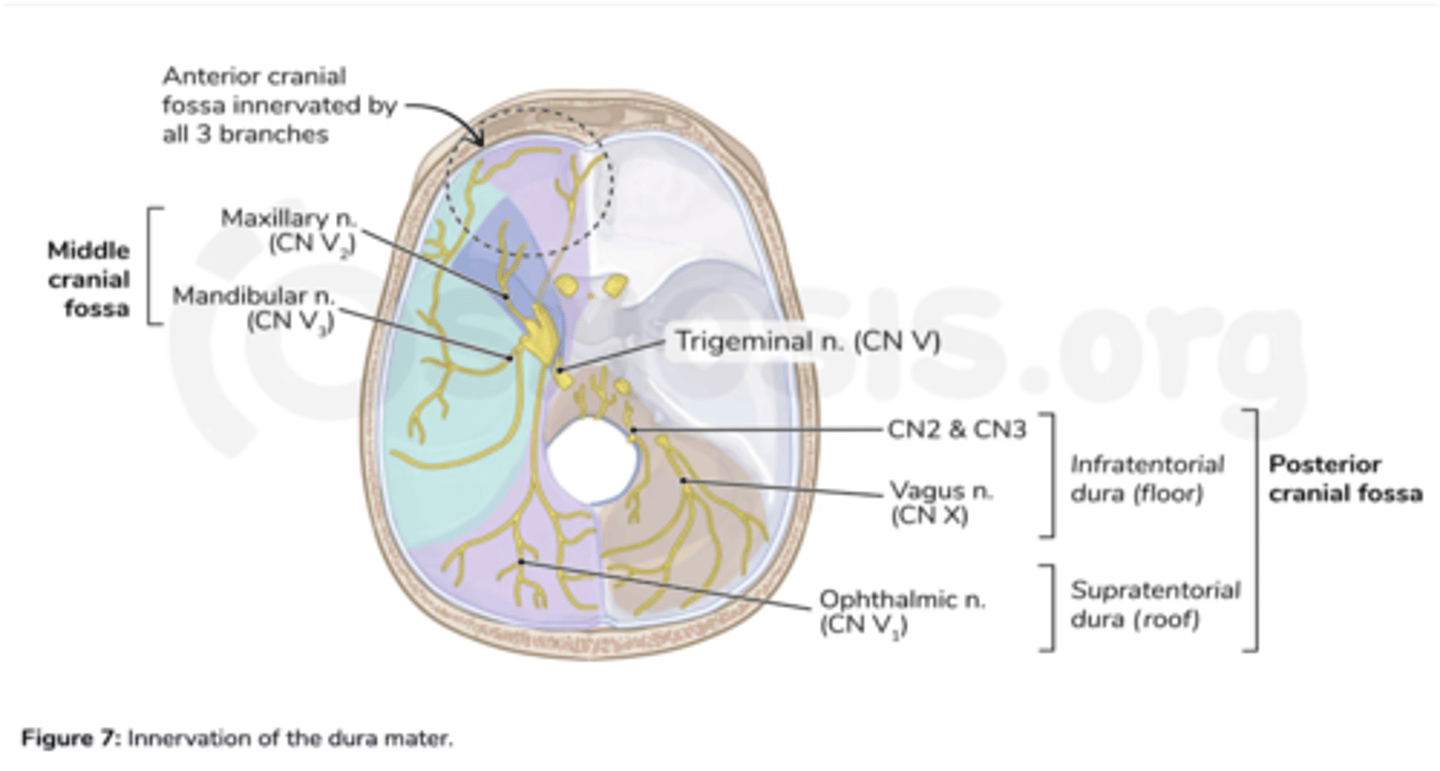
What nerves innervate the dura in the middle cranial fossa?
Maxillary and mandibular divisions of the trigeminal nerve
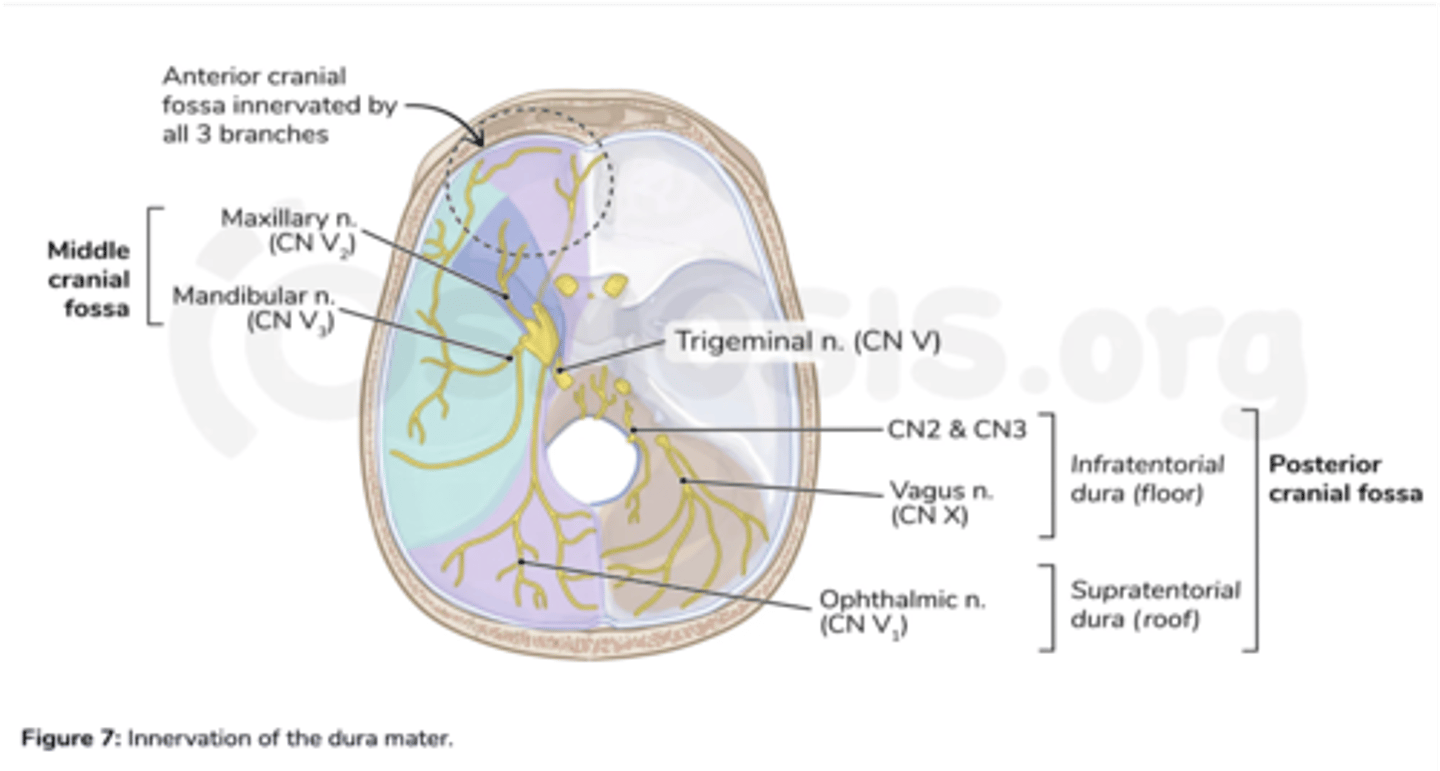
What nerve innervates the dura in the anterior cranial fossa?
Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve
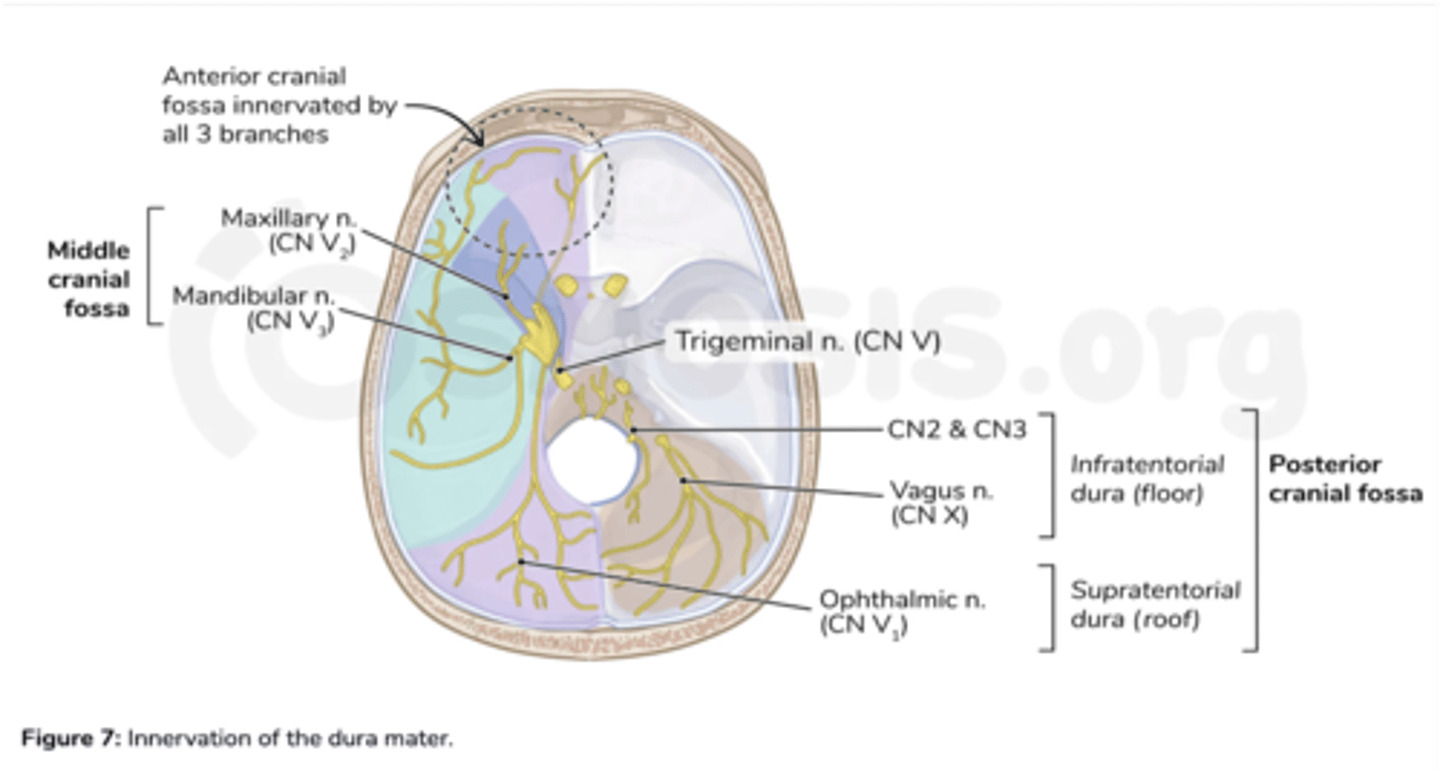
What nerves innervate the dura in the posterior cranial fossa?
Vagus nerve
Hypoglossal nerve
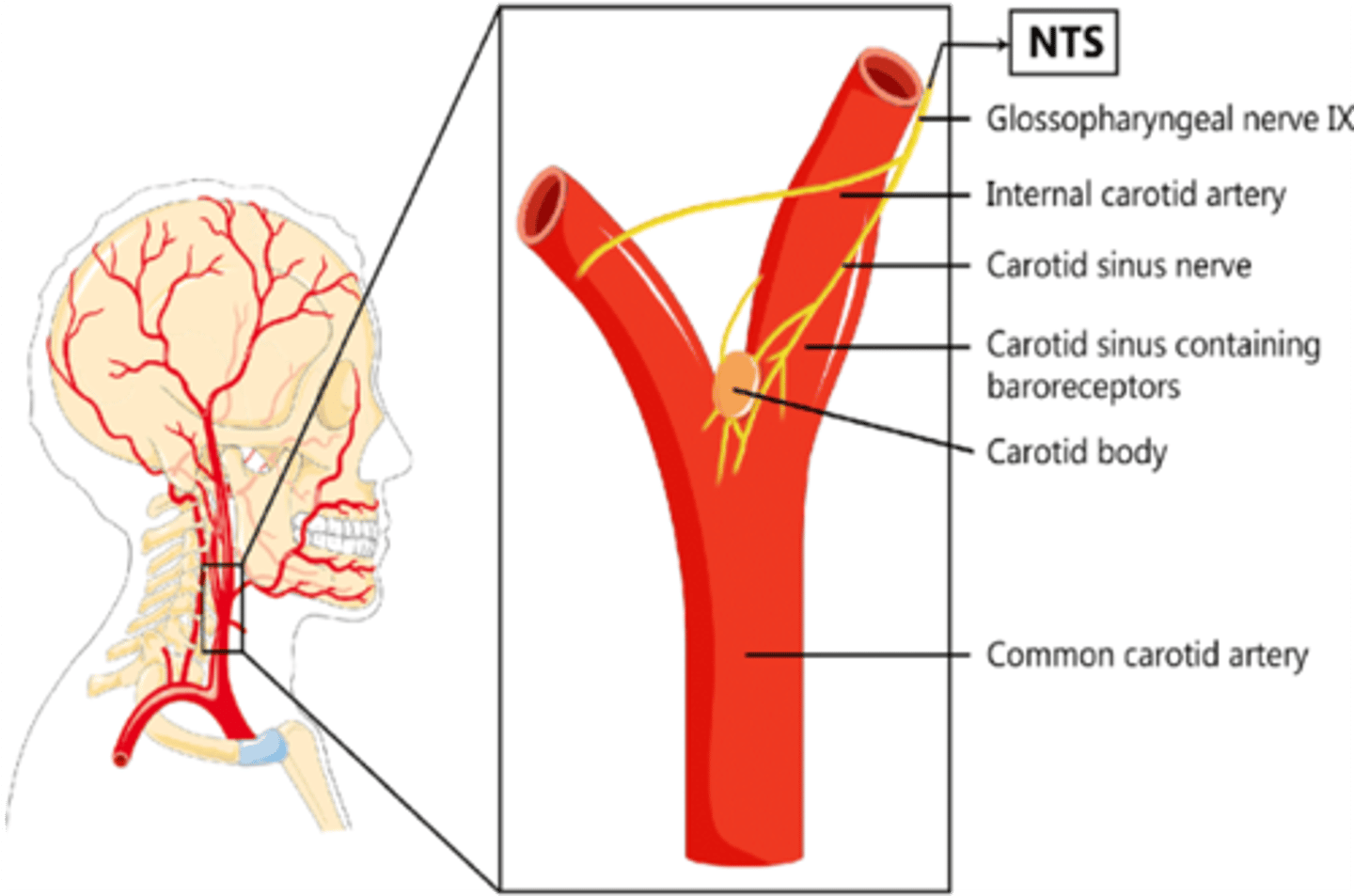
The ...(structure)... is a spindle shaped dilatation at the origin of the internal carotid artery that detects changes in blood pressure.
Carotid sinus
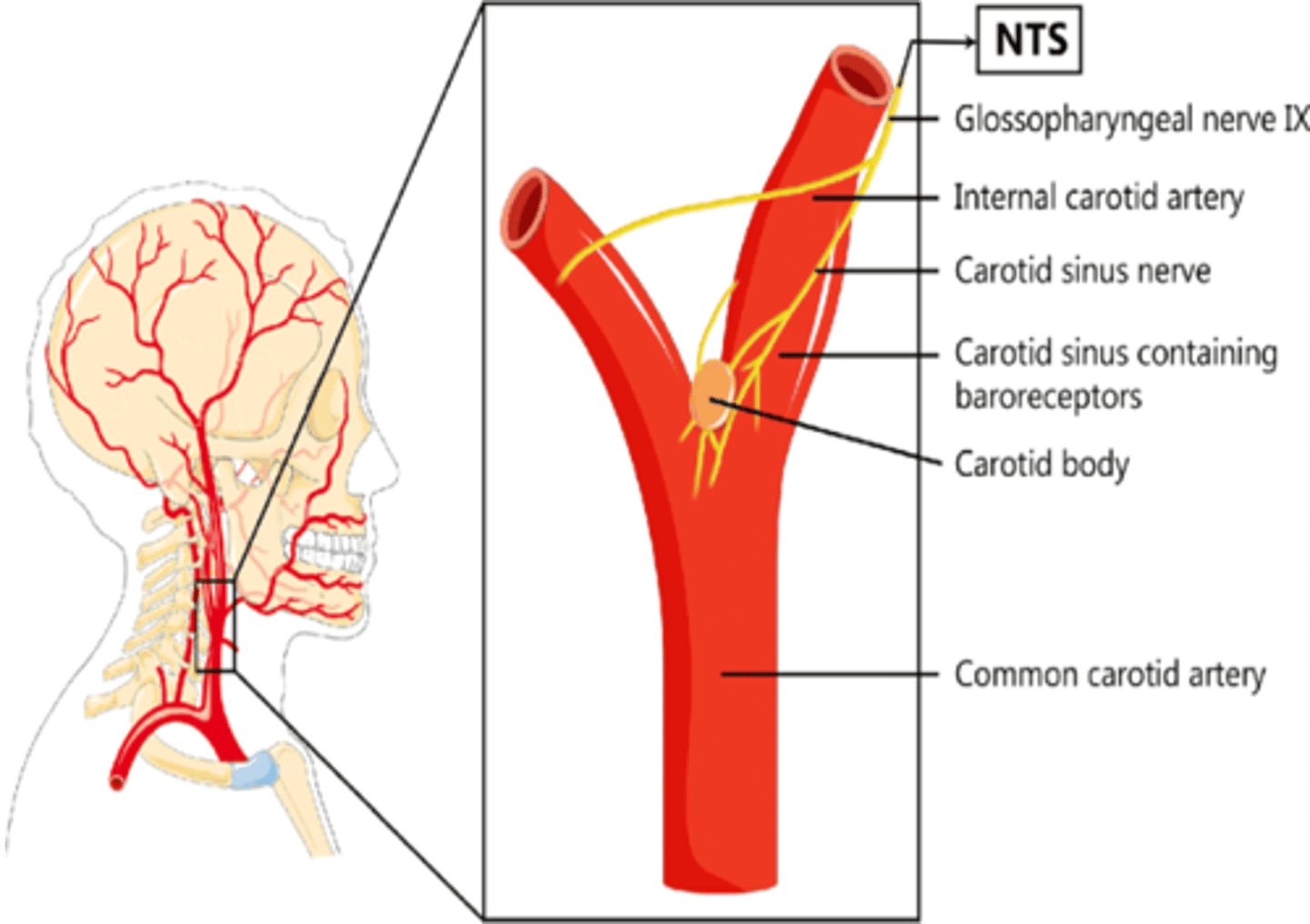
What branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve innervates the carotid sinus?
Carotid sinus branch
The carotid body is what type of receptor?
Chemoreceptor
What innervates the posterior belly of the digastric muscle?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
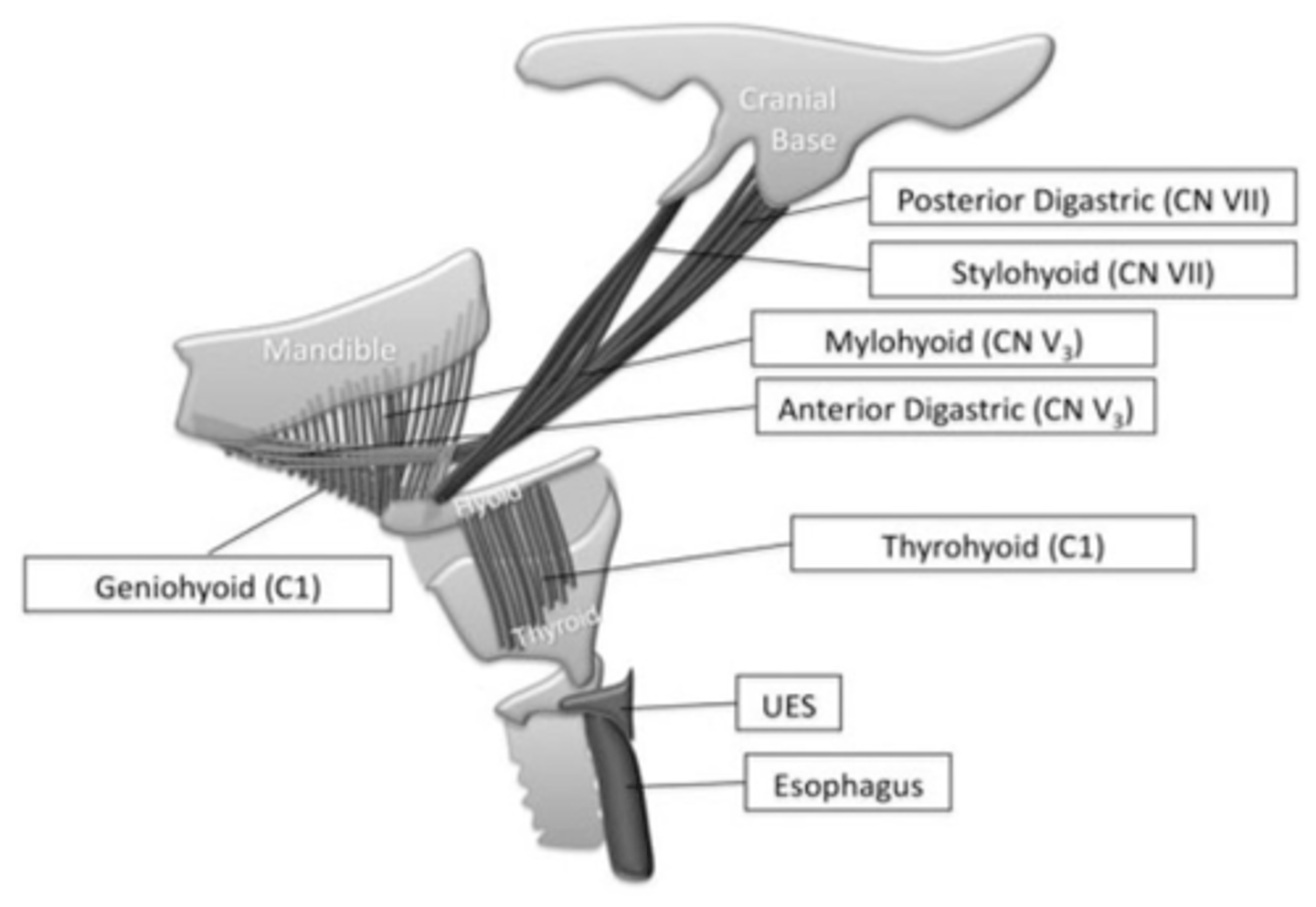
What innervates the anterior belly of the digastric muscle?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
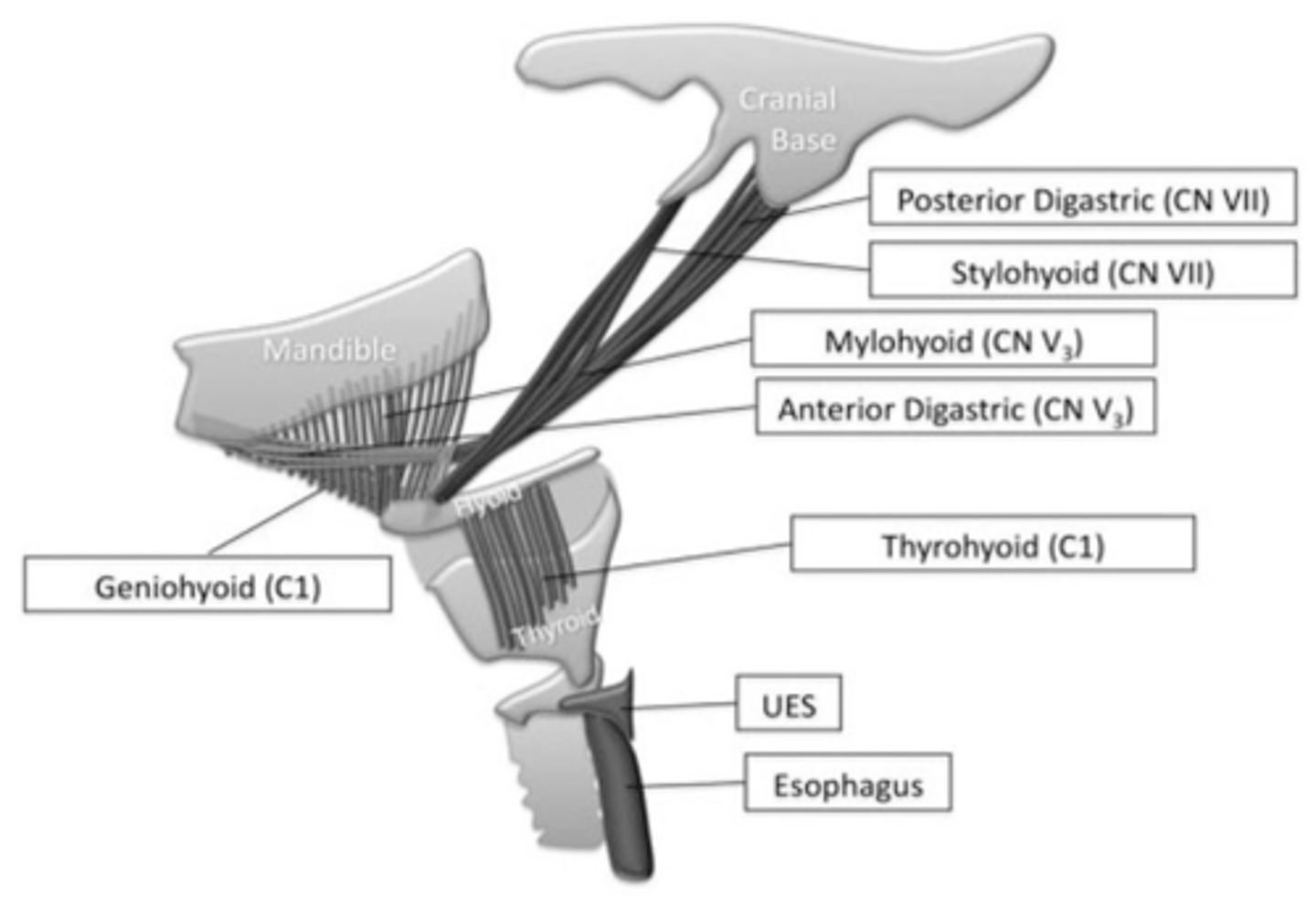
What innervates the infrahyoid (strap) muscles?
Ansa cervicalis
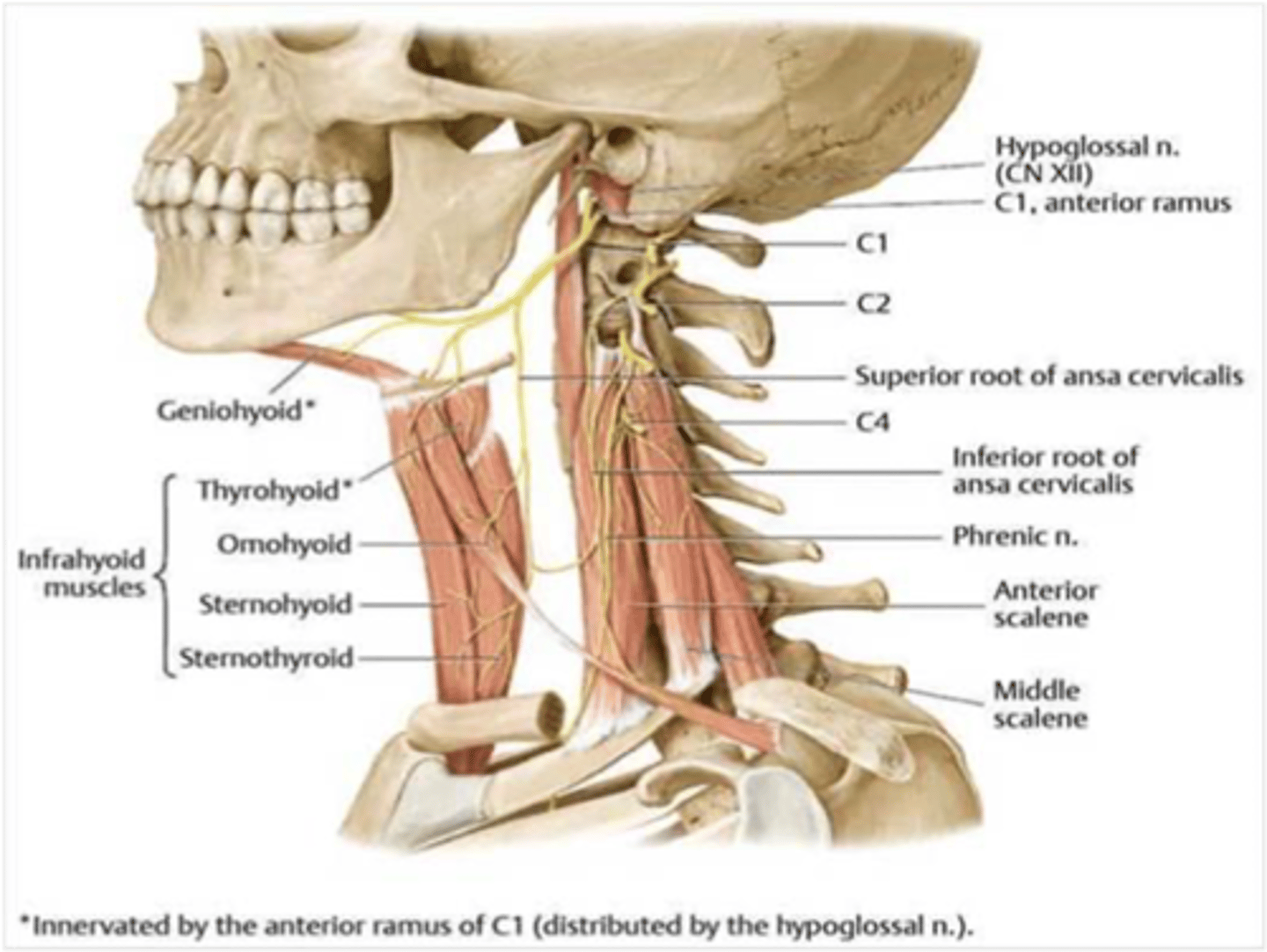
What cranial nerve supplies the tensor tympani muscle?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
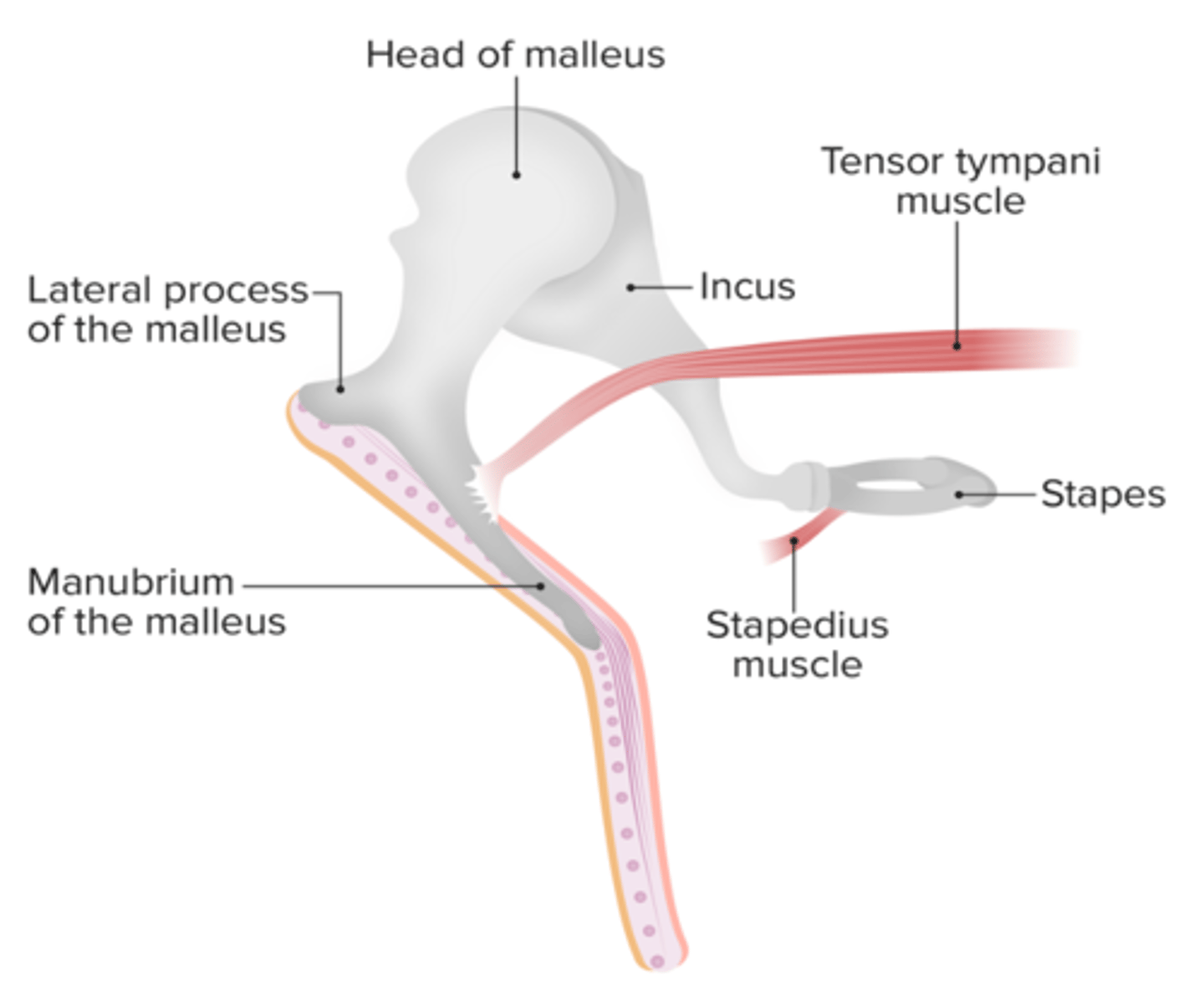
What cranial nerve innervates the stapedius muscle?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
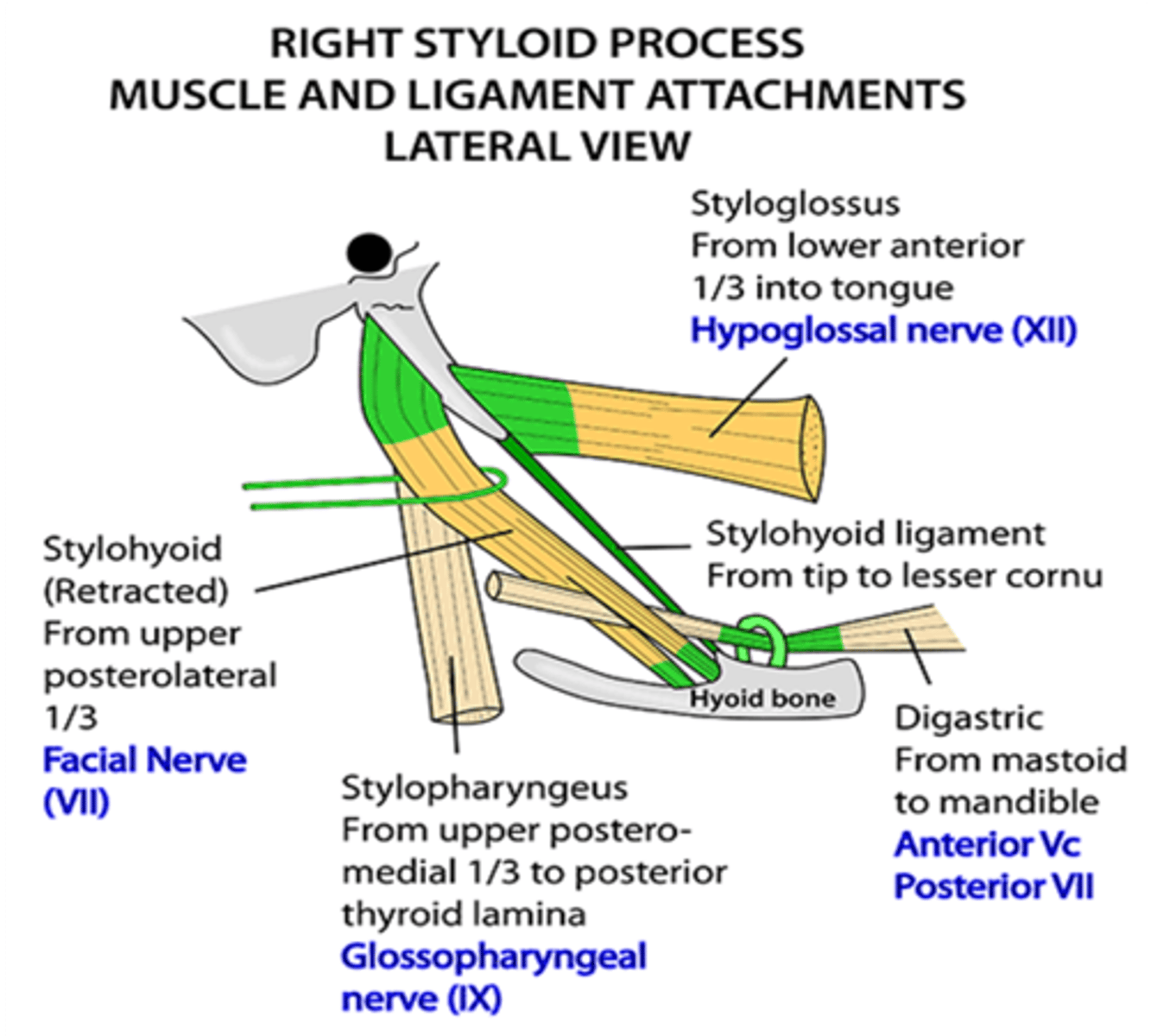
What three muscles attach to the styloid process?
Stylohyoid
Styloglossus
Stylopharyngeus
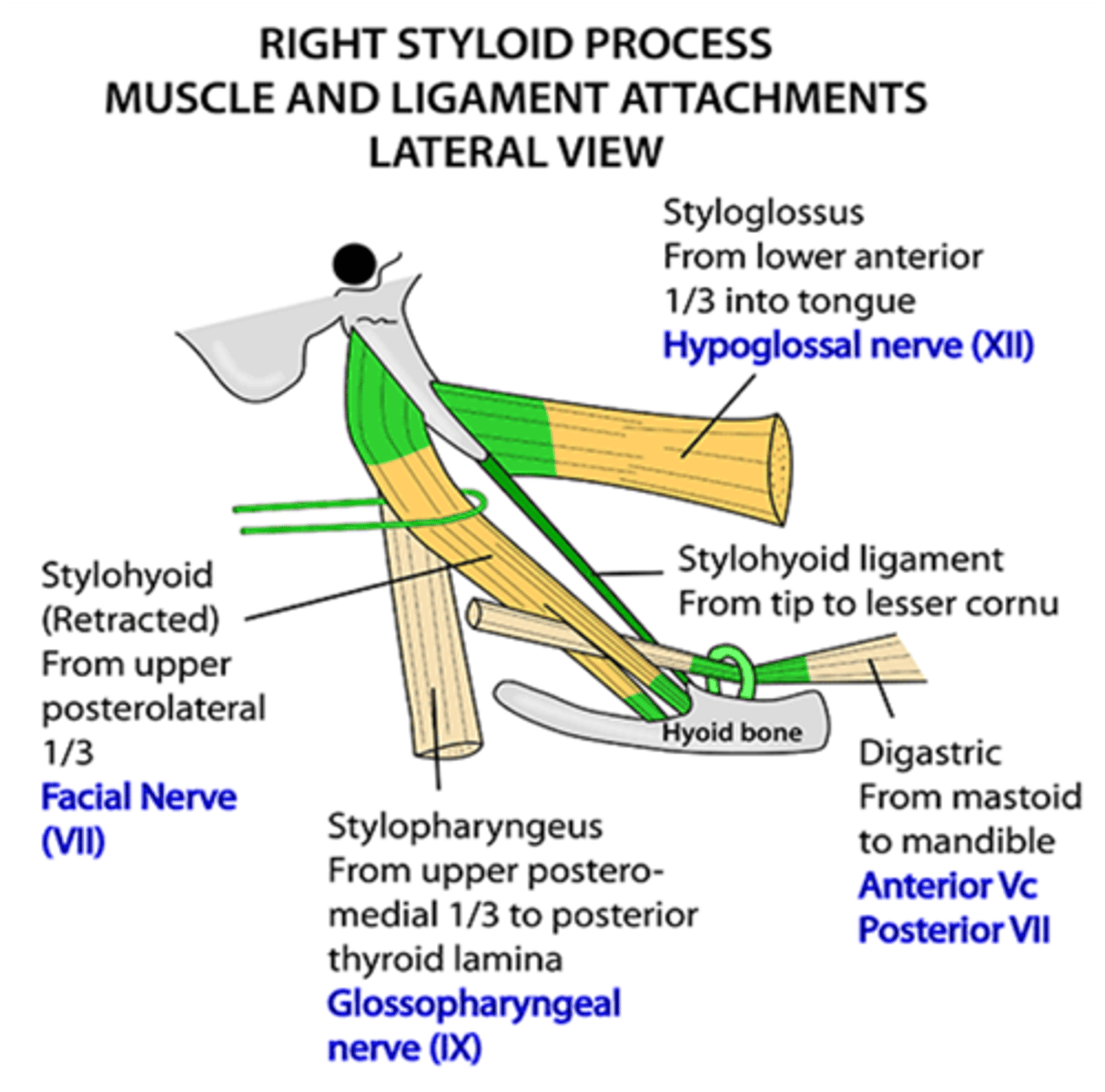
What nerve supplies the stylohyoid muscle?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
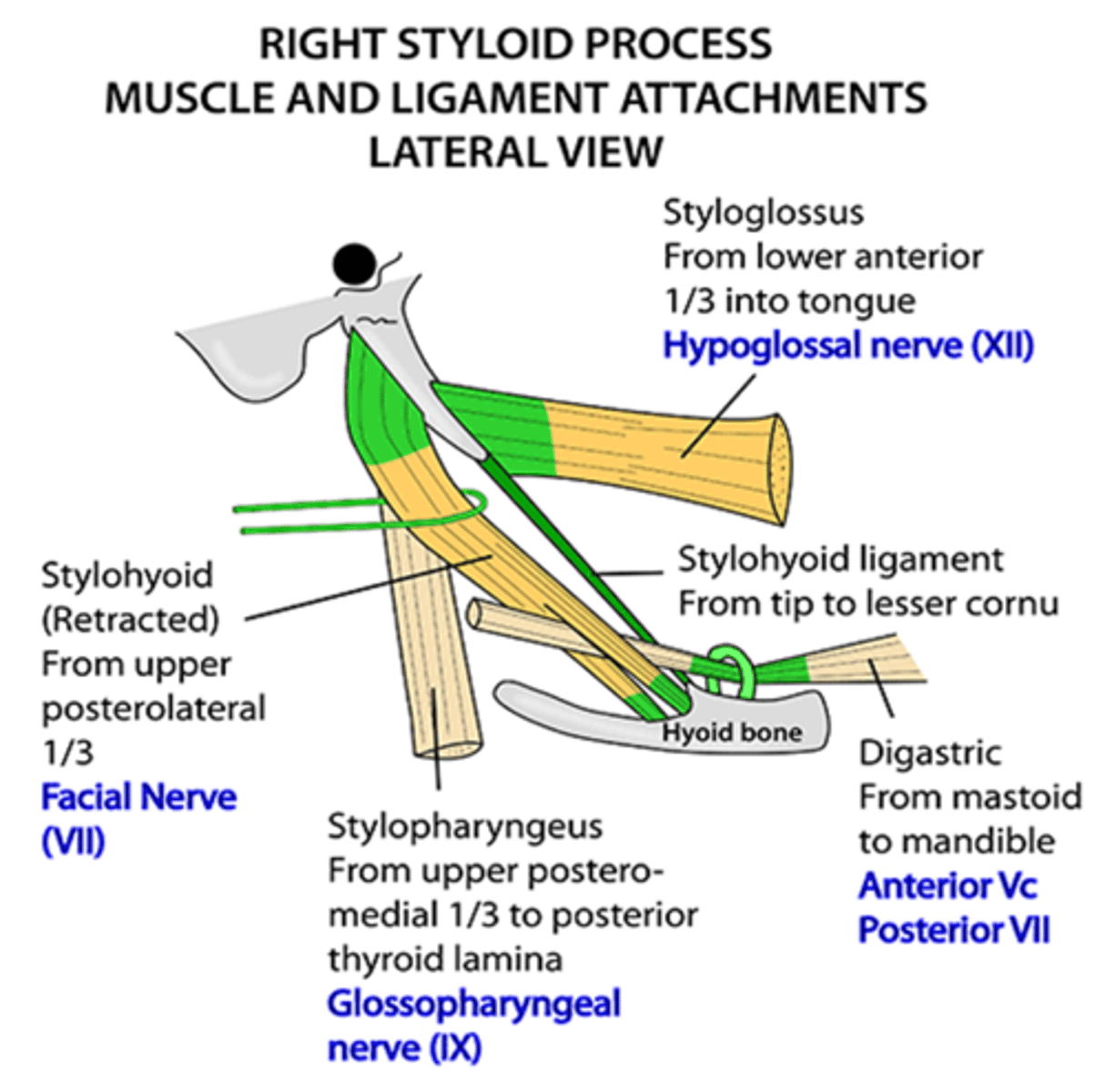
What innervates the styloglossus muscle?
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
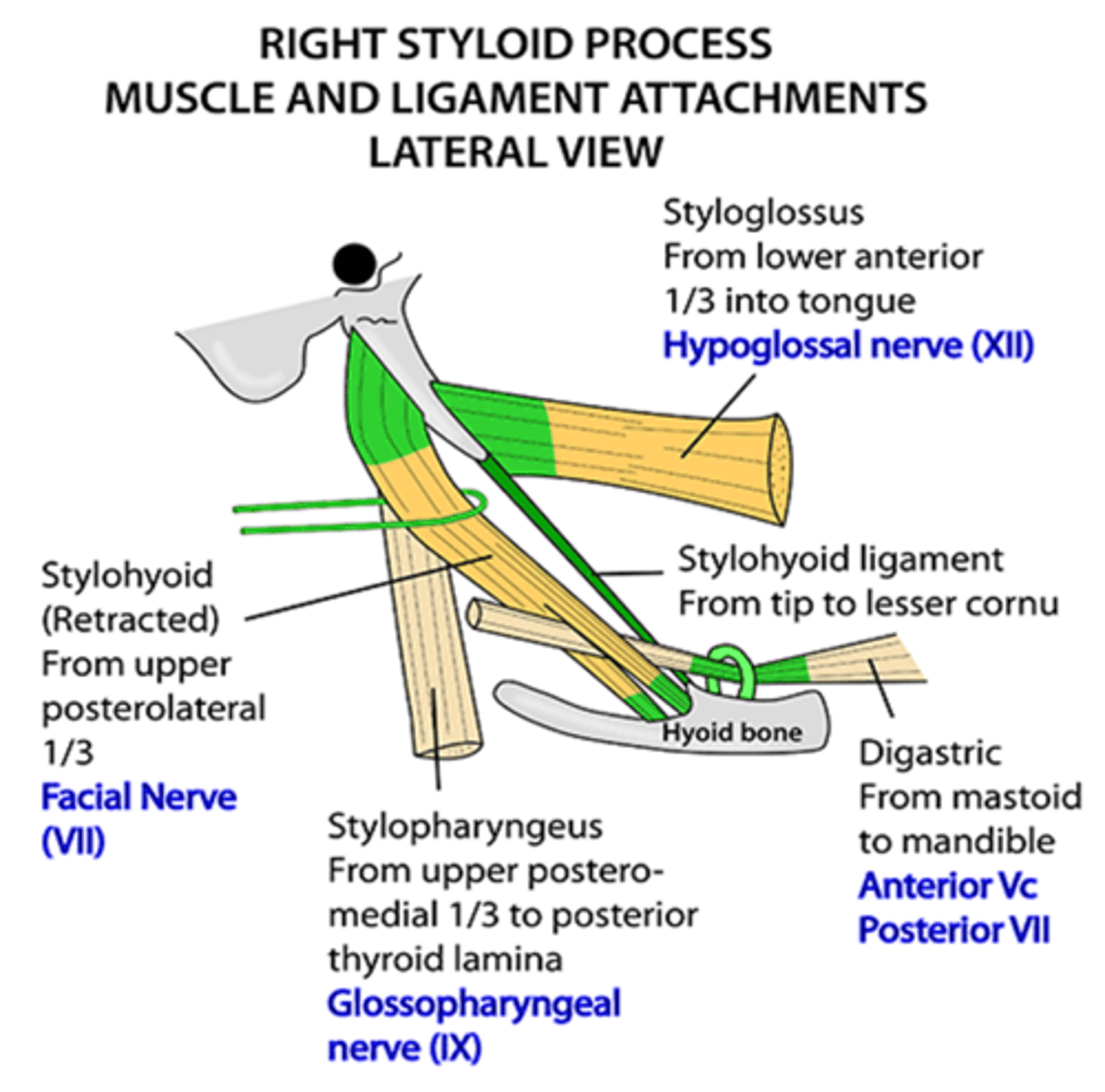
What innervates the stylopharyngesus muscle?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
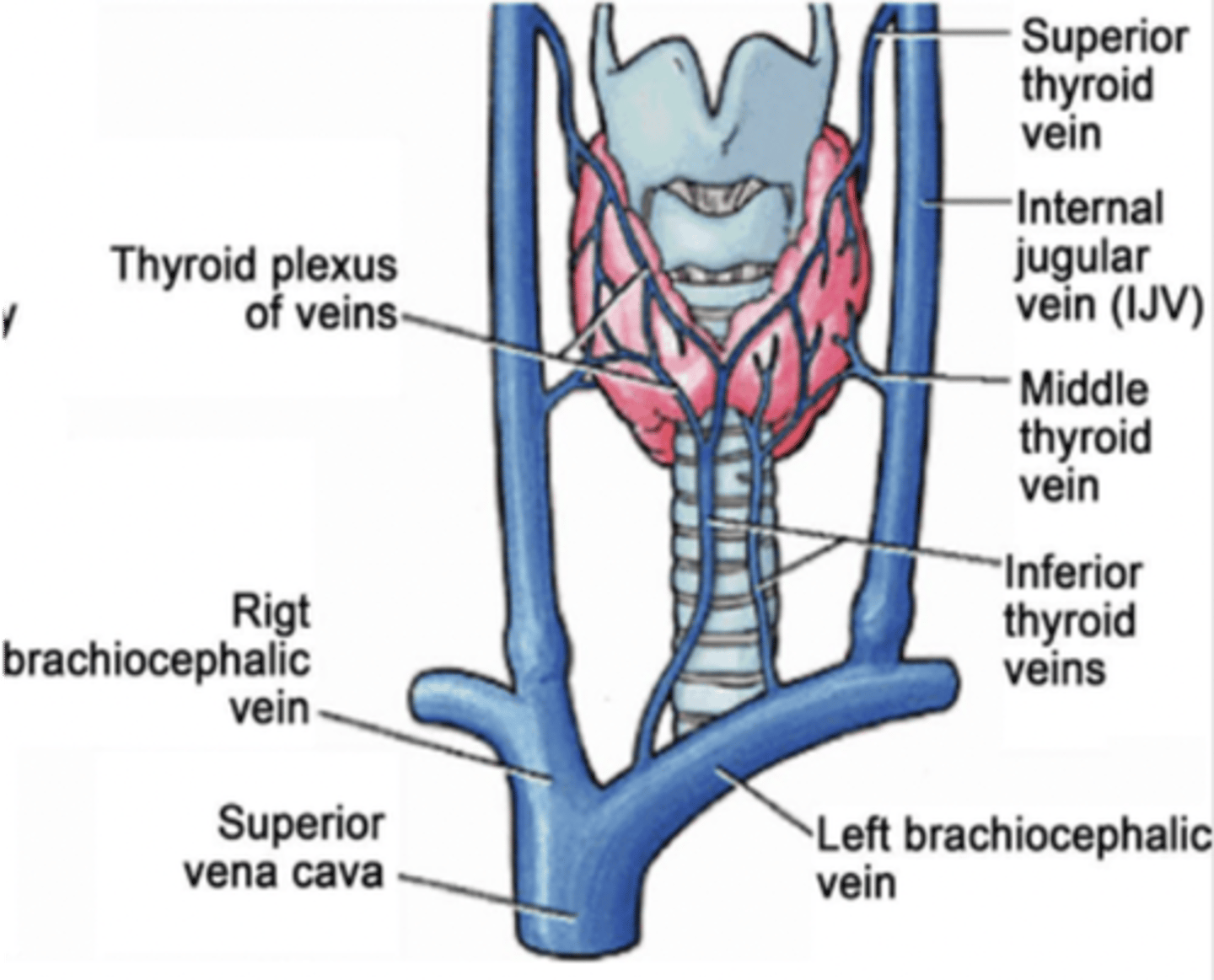
The inferior thyroid veins drain into what vein?
Brachiocephalic veins
What nerve turns around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and innervates the skin of the anterior cervical triangle?
Transverse cervical nerve
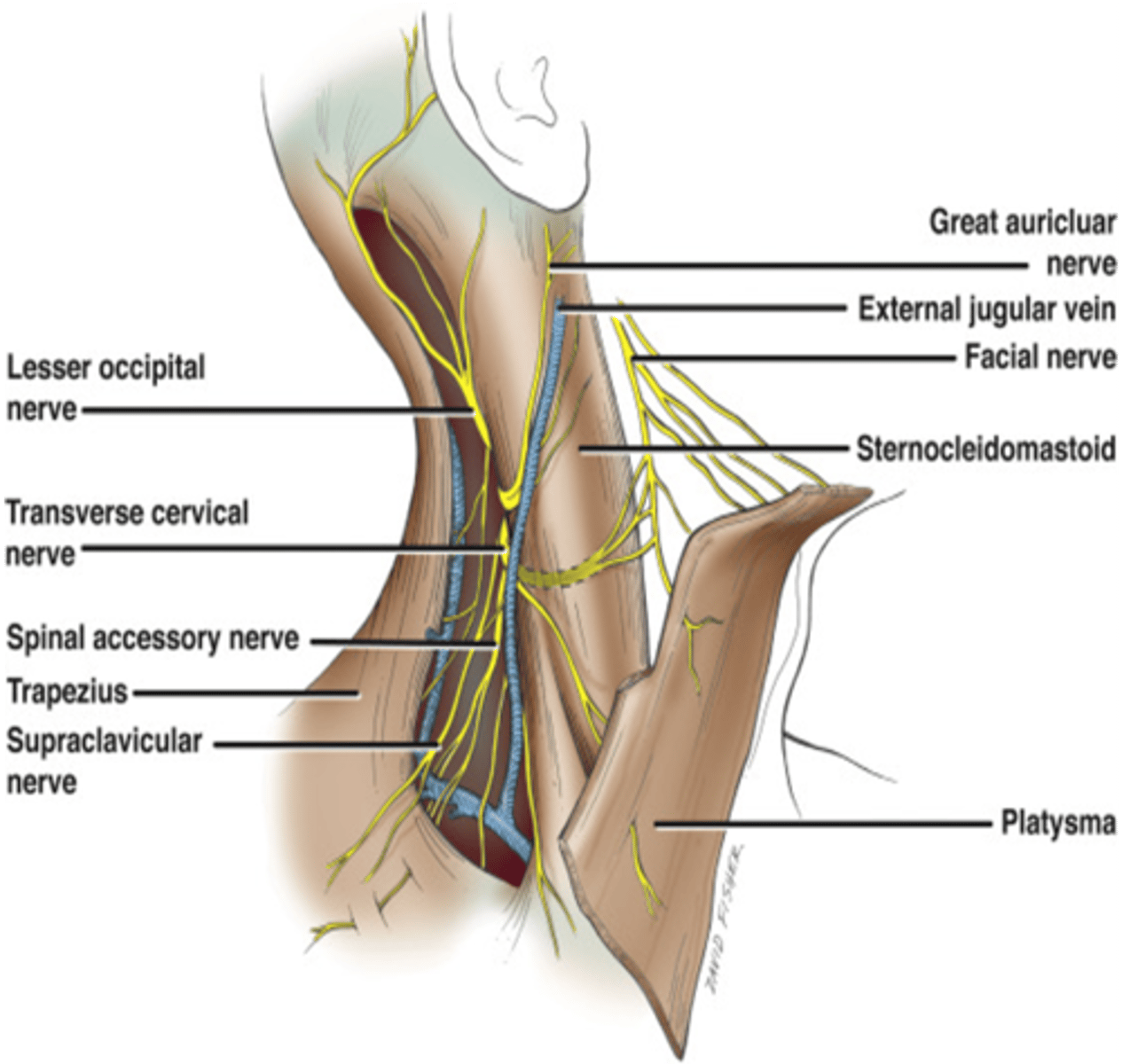
What nerve innervates the skin behind the auricle and on the parotid gland?
Greater auricular nerve

What nerve supplies the skin over the clavicle and the shoulder?
Supraclavicular nerve
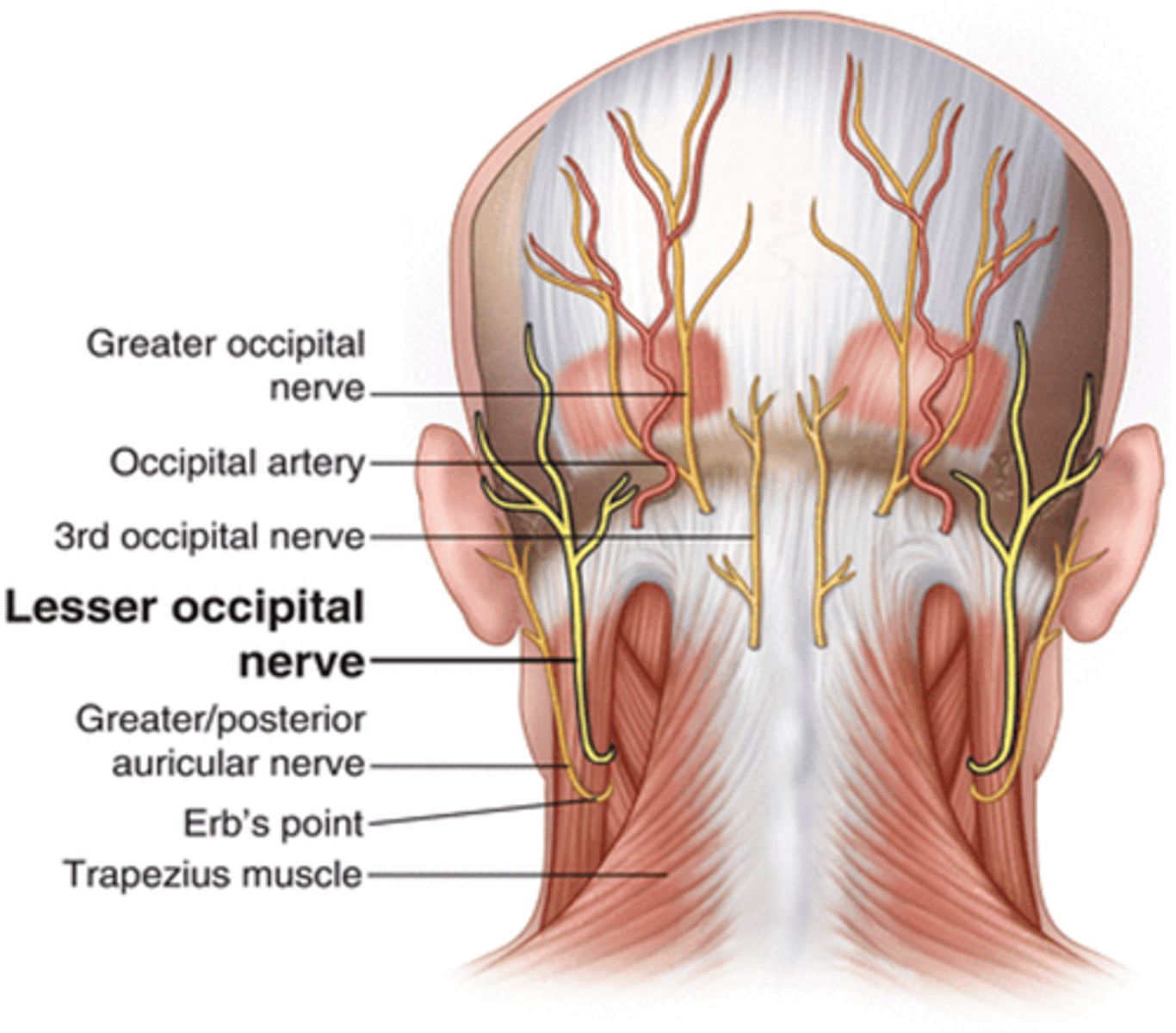
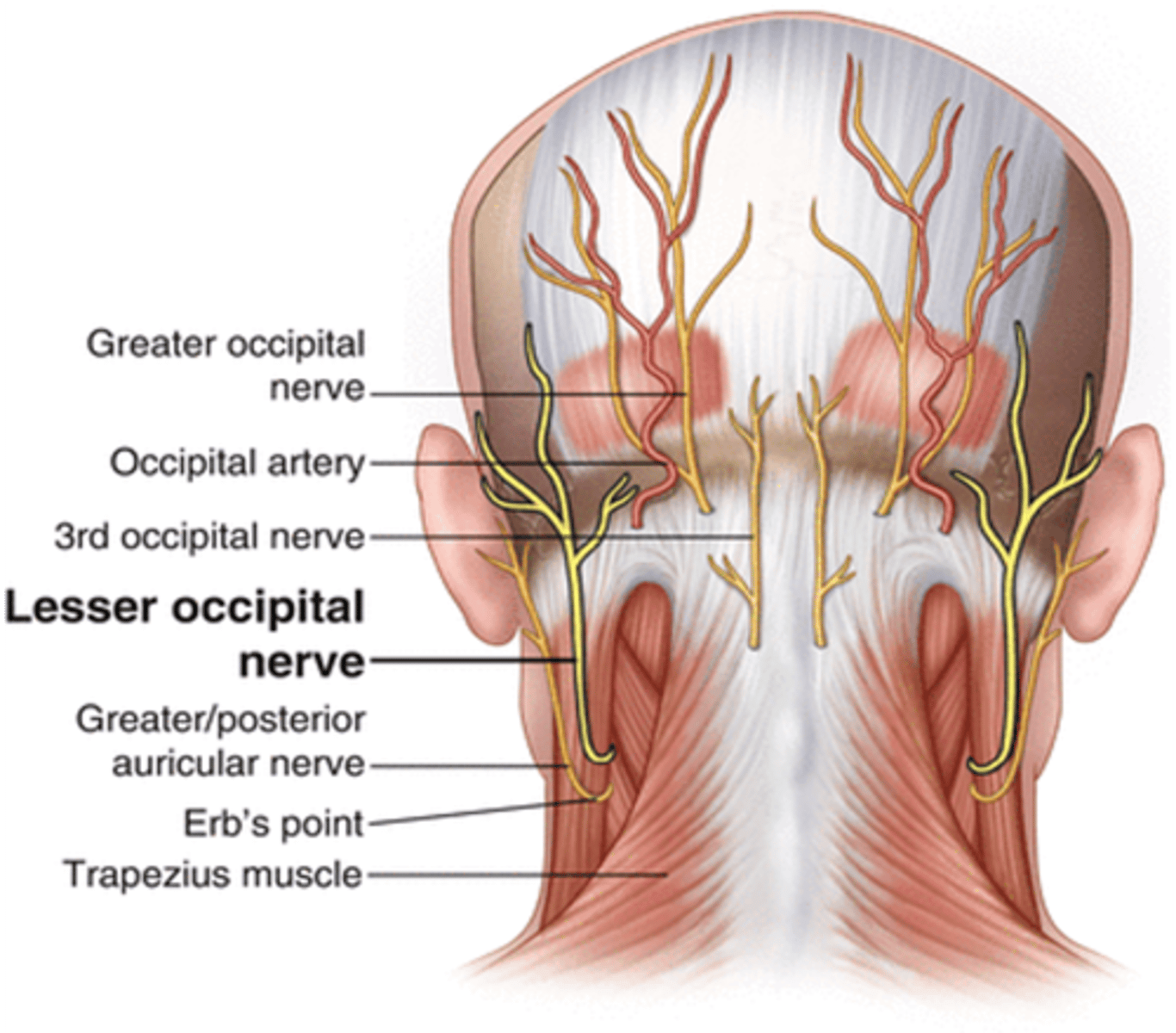
What nerve supples the scalp behind the auricle?
Lesser occipital nerve
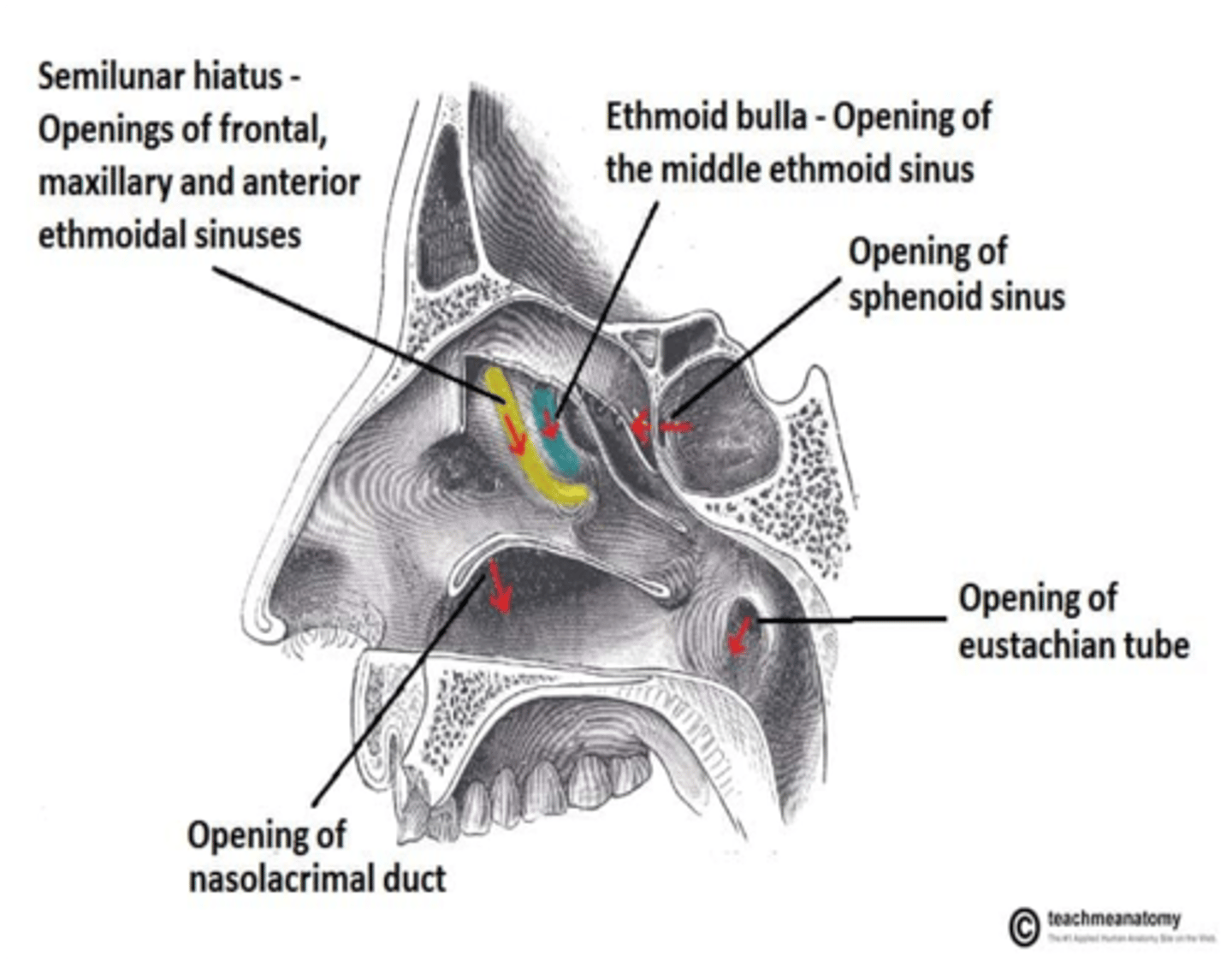
What paranasal sinus opens into the superior nasal meatus?
Posterior ethmoidal sinus
The posterior ethmoidal sinus opens into what nasal meatus?
Superior Nasal Metus
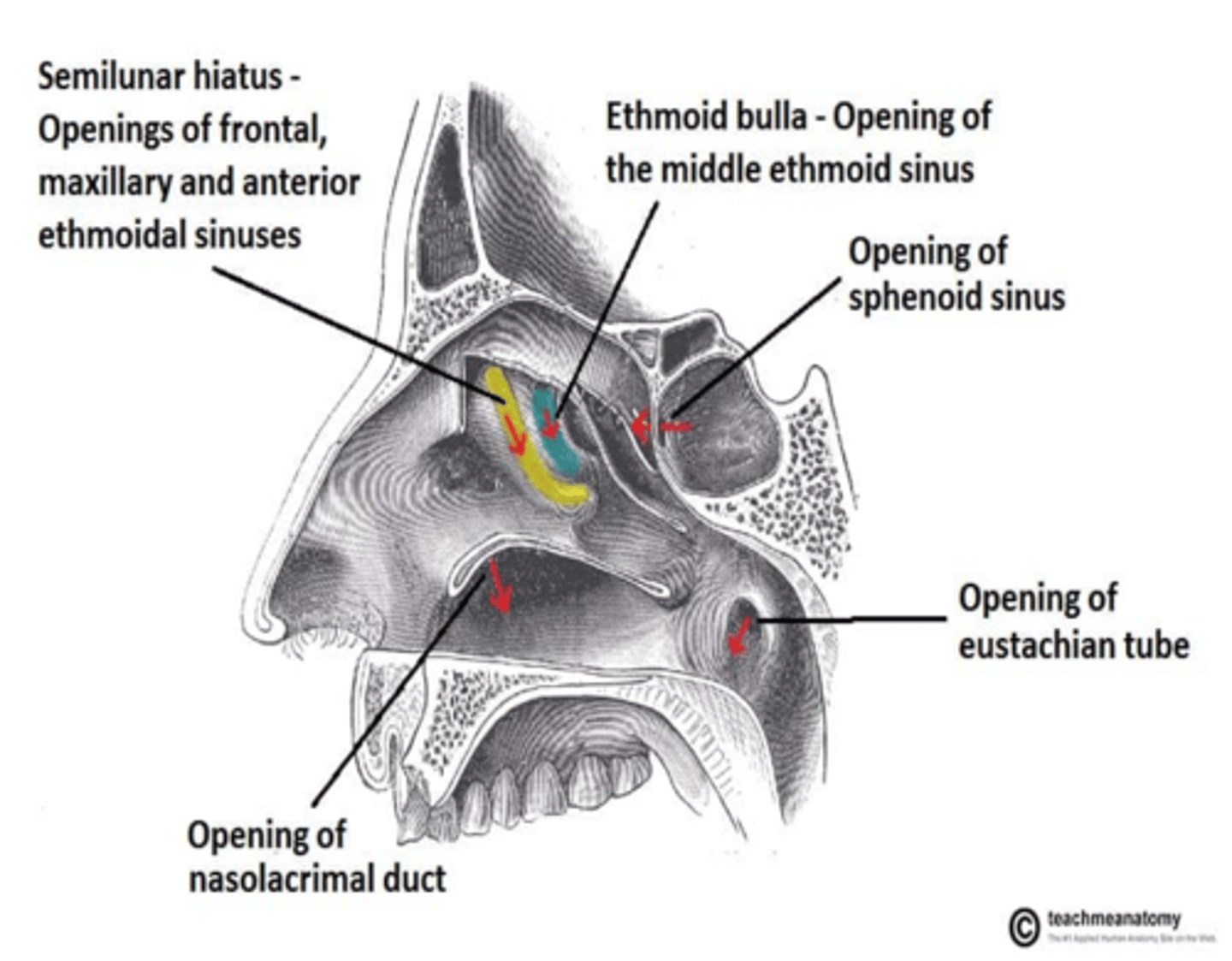
What paranasal sinuses open into the middle nasal meatus?
Maxillary sinus
Frontal sinus
Anterior ethmoidal sinus
Middle ethmoidal sinus
What structures pass through the optic canal?
Ophthalmic artery
Optic nerve
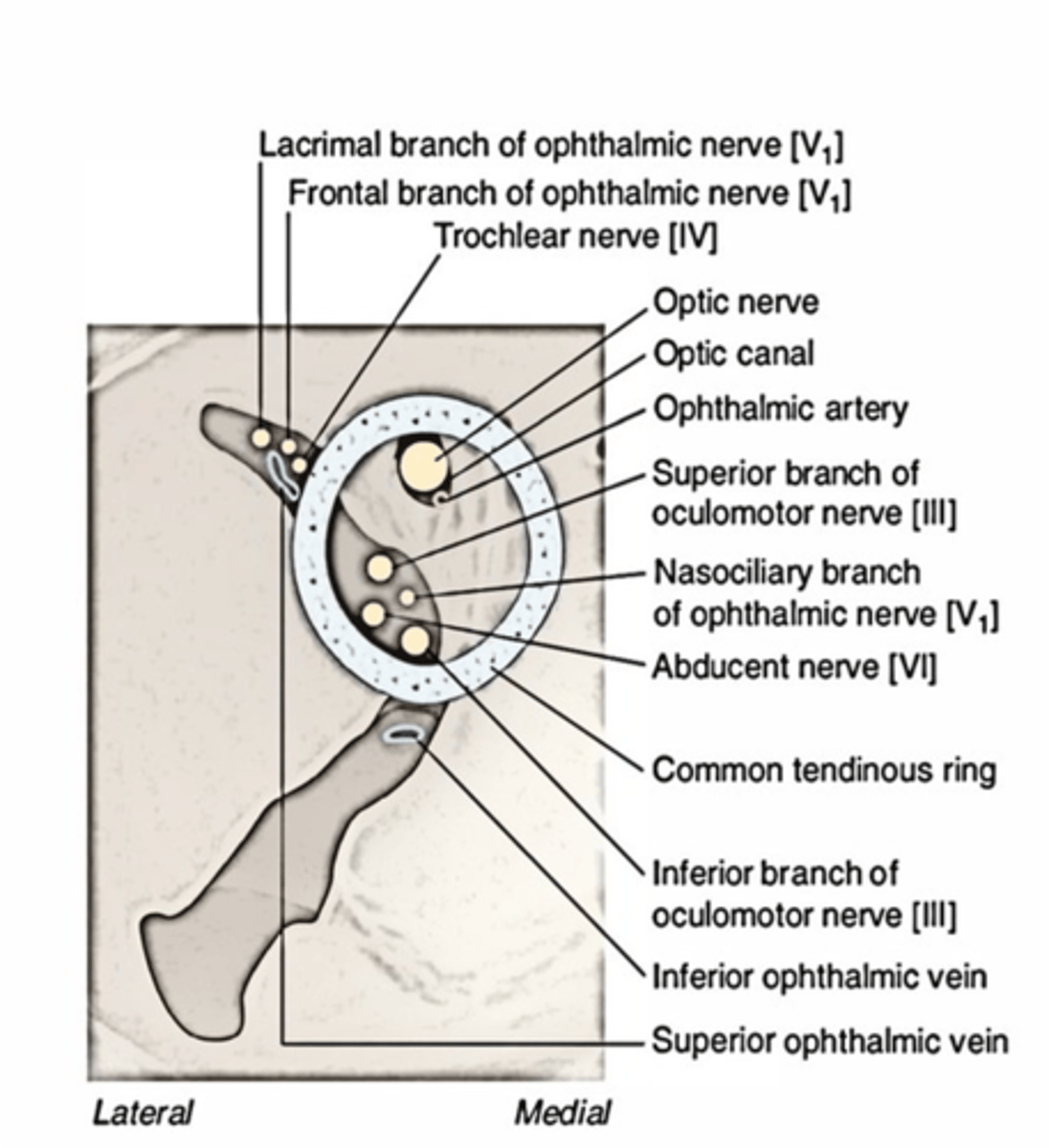
The ophthalmic division of CN V, ophthalmic vein, oculomotor and trochlear nerves enter the orbit through what foramen?
Superior Orbital Fissure
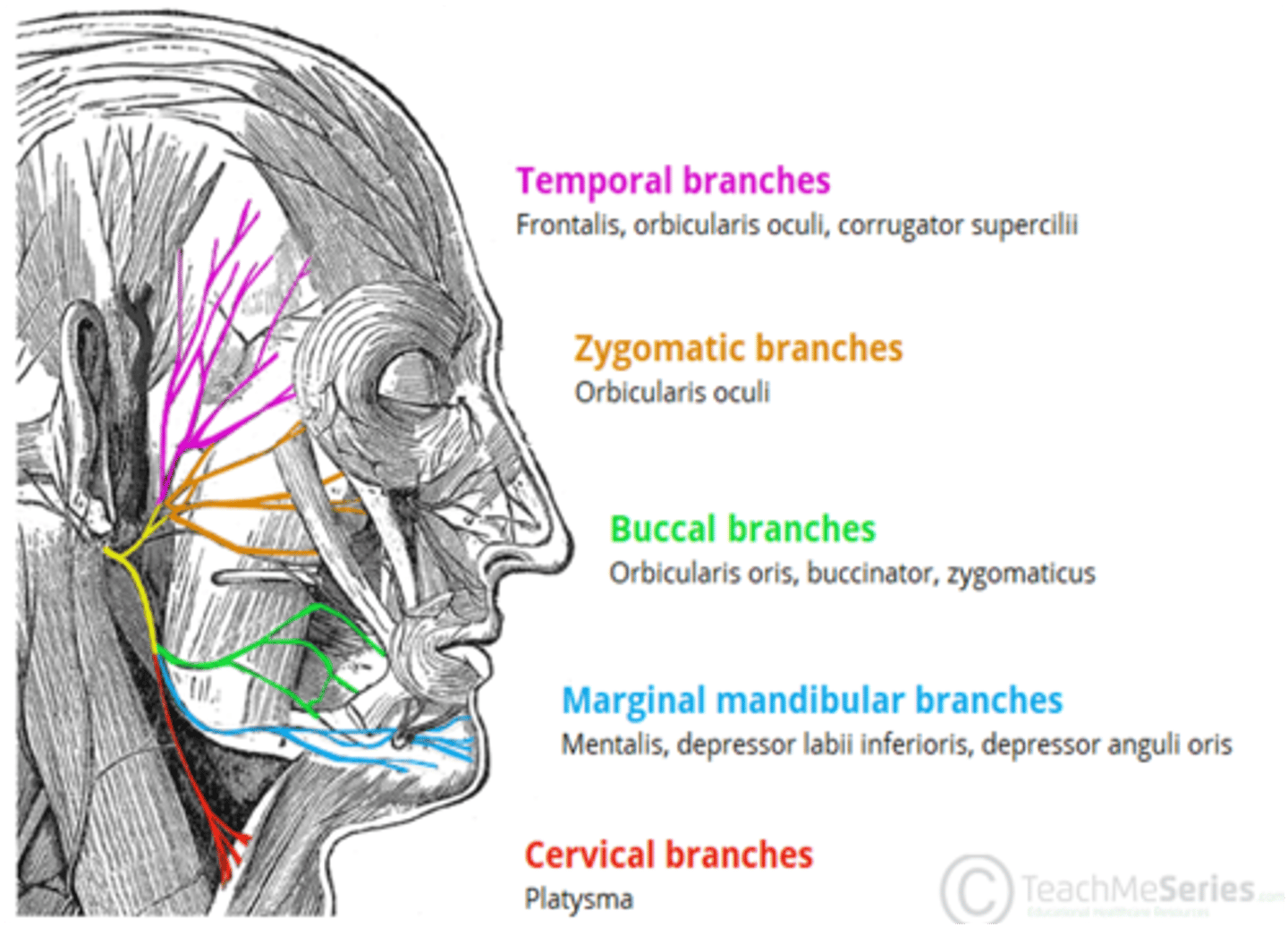
What cranial nerve innervates the buccinator muscle?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
What nerve supplies the stylopharyngeus muscle?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
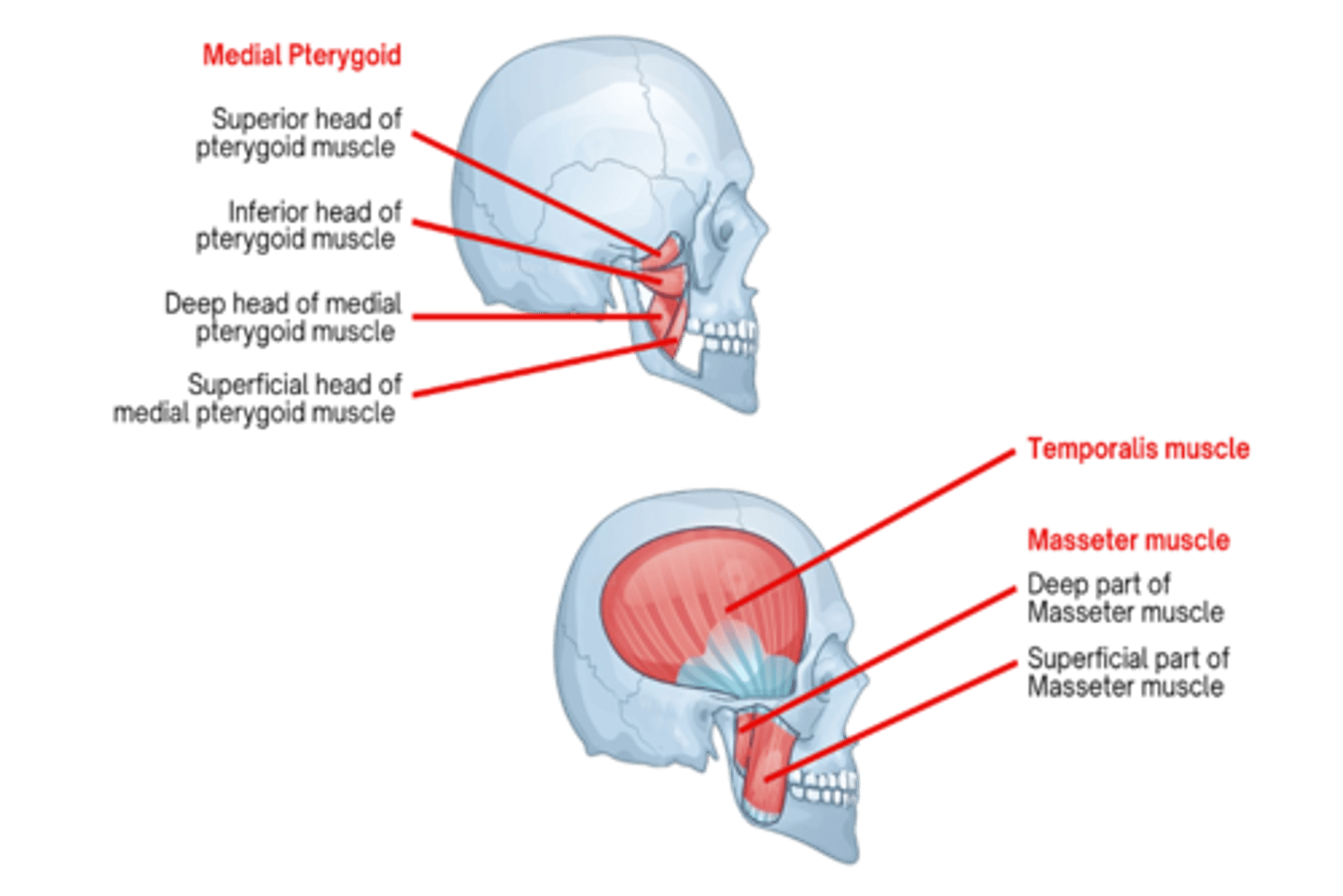
What cranial nerve supplies the muscles of mastication?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
What bones form the roof of the nasal cavity?
Ethmoid bone (cribriform plate)
Nasal bone
Frontal bone
Sphenoid (body) bone
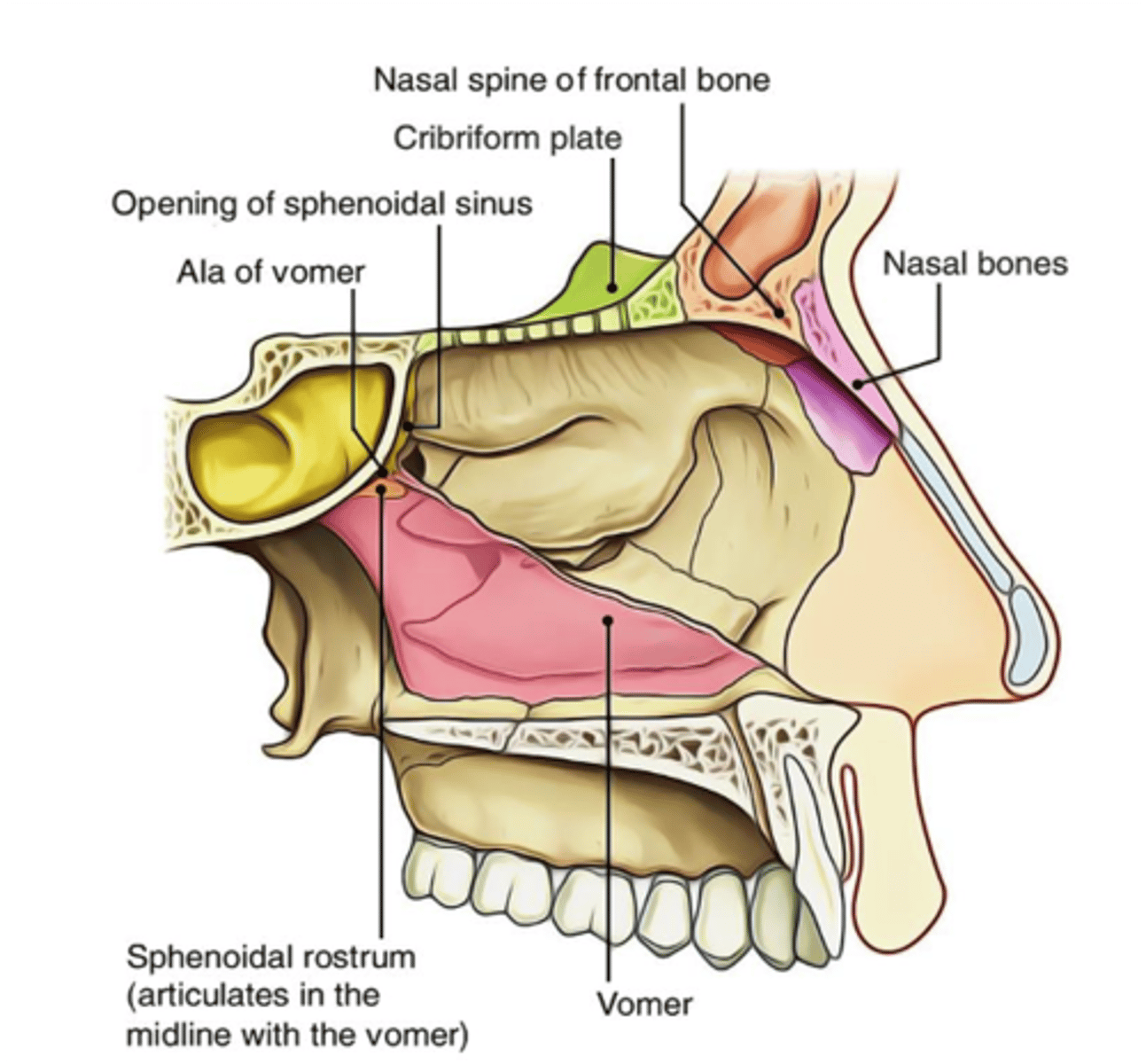
What bones form the floor of the nasal cavity?
Palatine process of the maxilla
Horizontal plate of the palatine bone
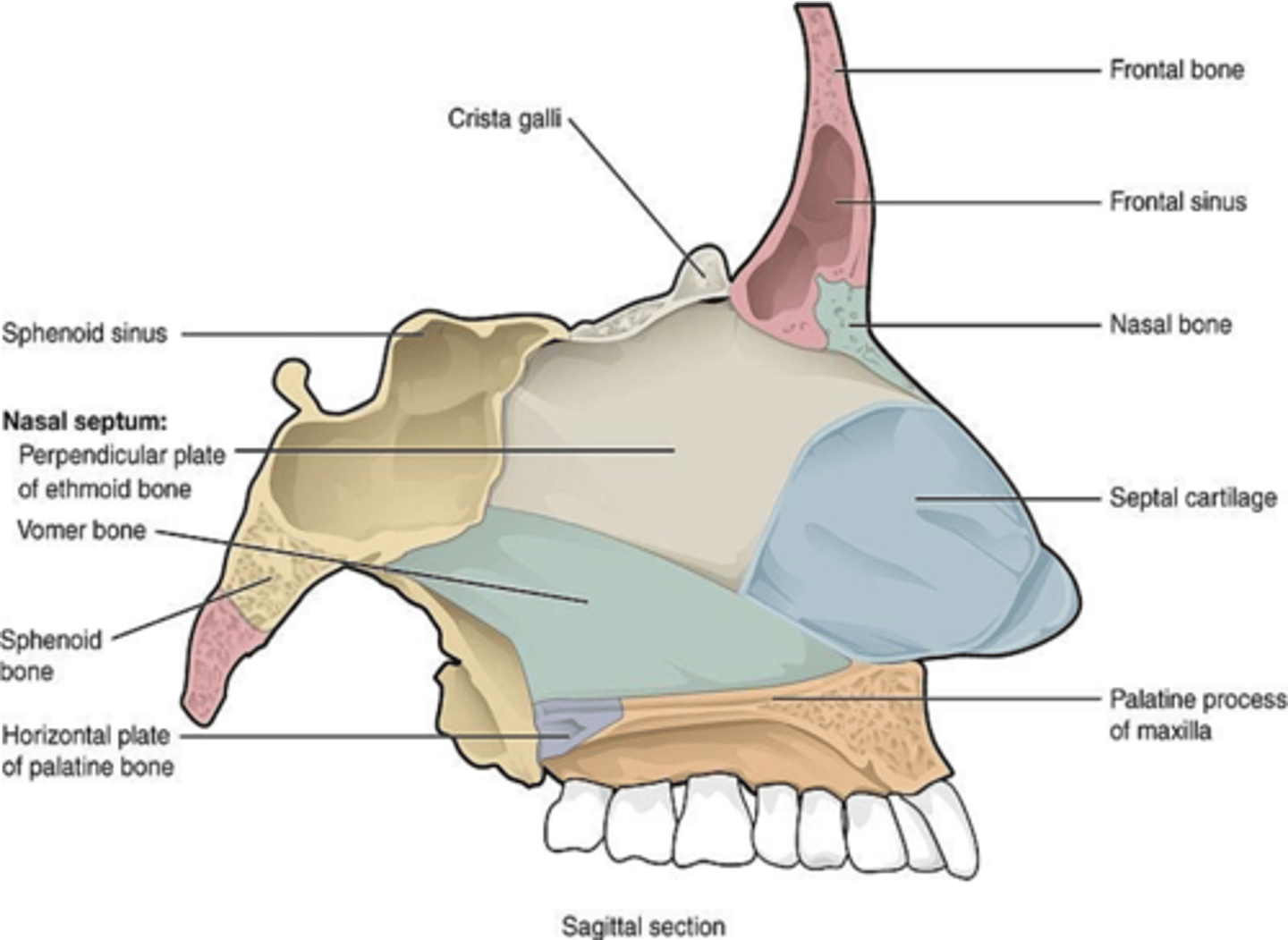
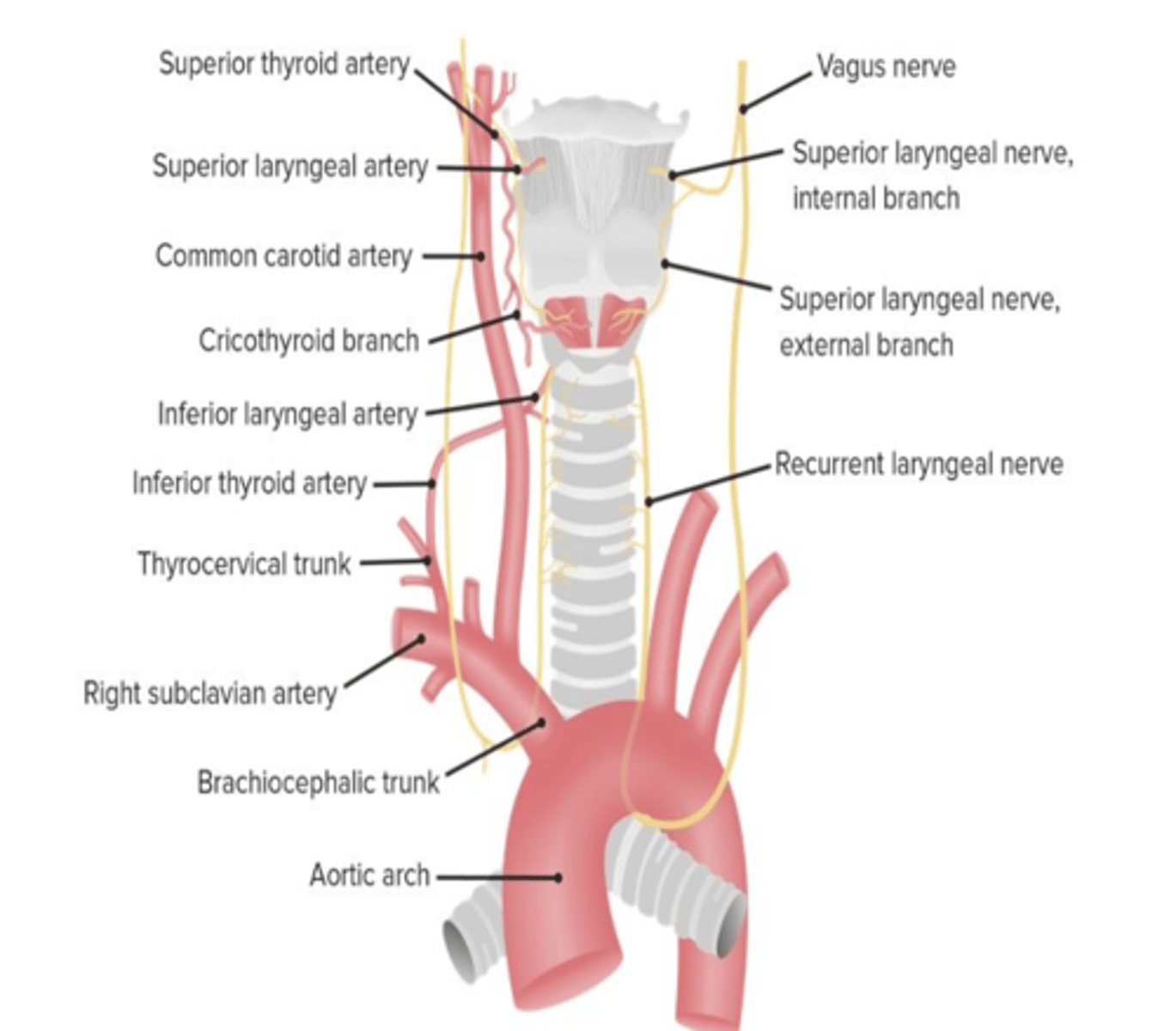
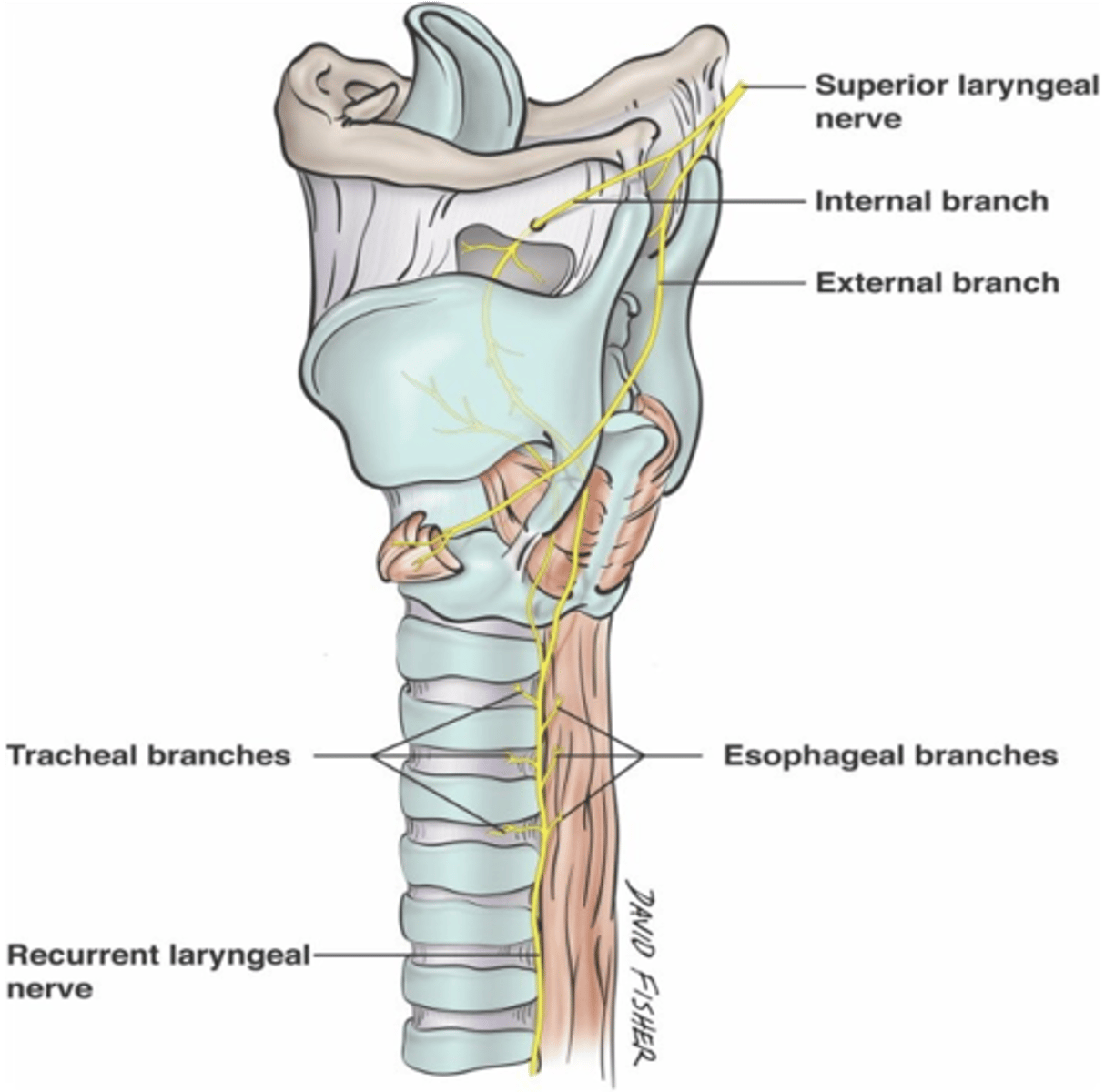
Loss of voice is a manifestation of an injury to what nerves?
Recurrent laryngeal nerves (of the vagus nerve)
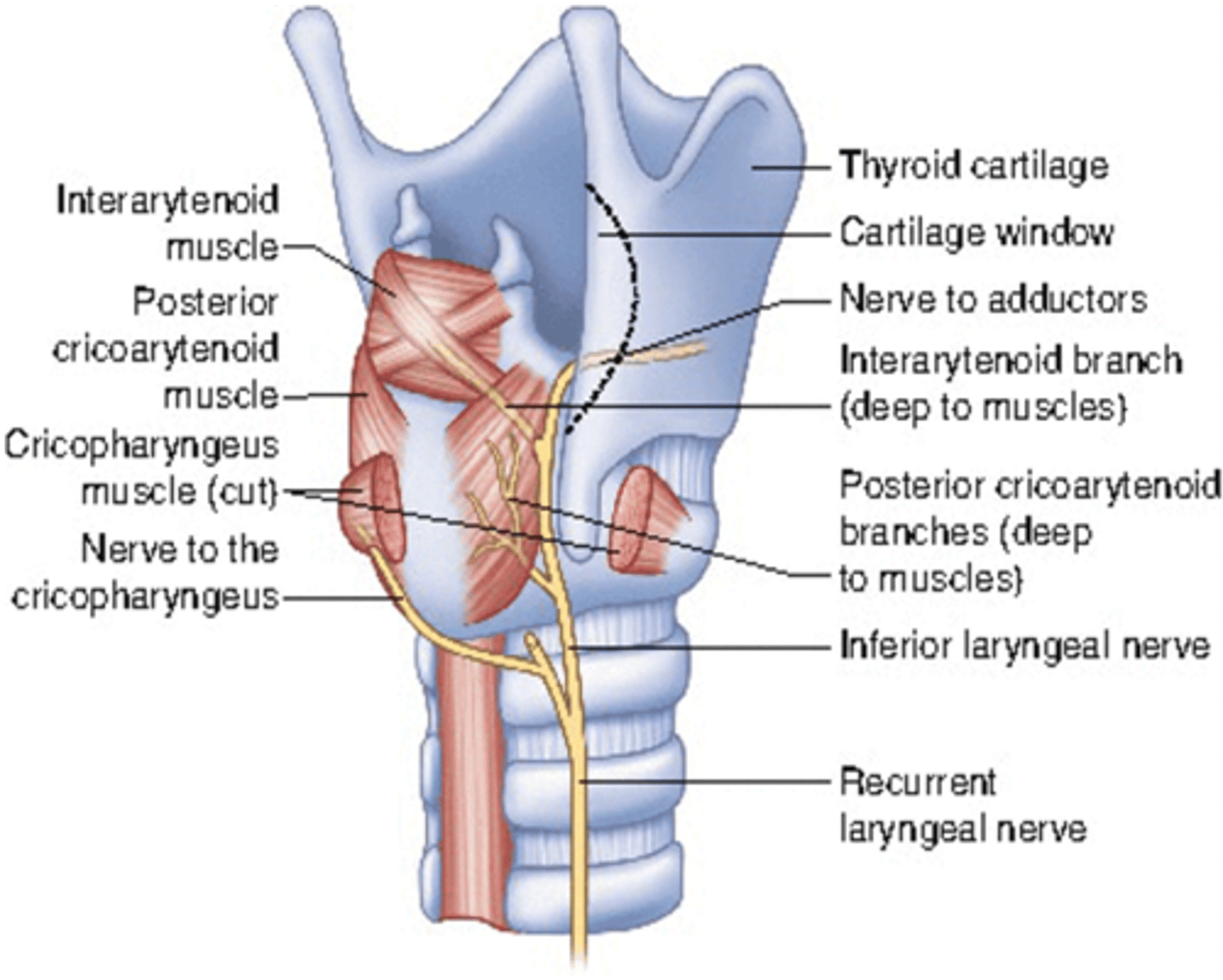
Lesion to what cranial nerve can manifest as numbness and loss of taste on the posterior part of the tongue
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Inability to shrug the shoulder is due to a damage of what cranial nerve?
Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)

What foramen transmits the middle meningeal artery?
Foramen spinosum
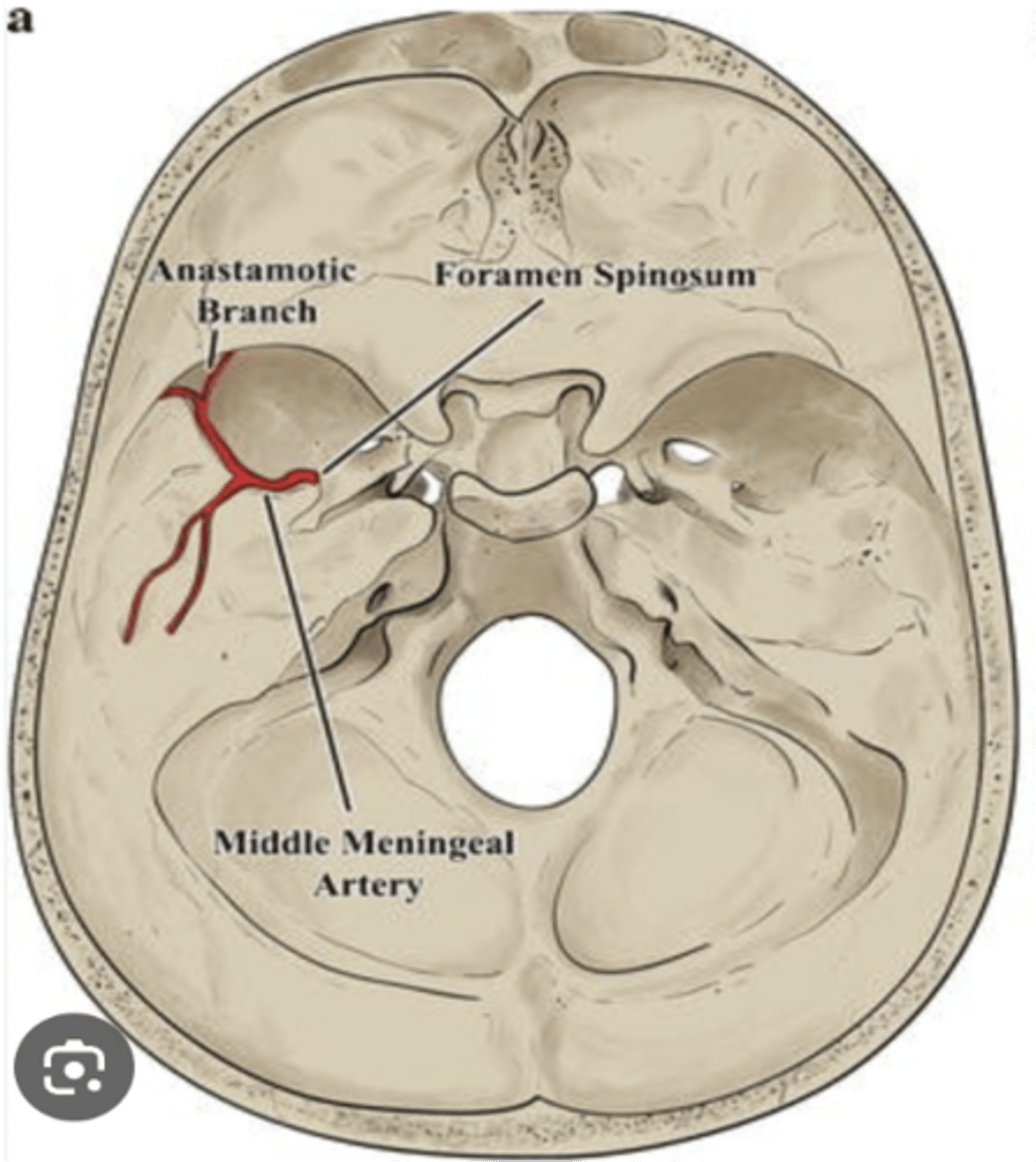
What artery passes through the foramen spinosum?
Middle meningeal artery
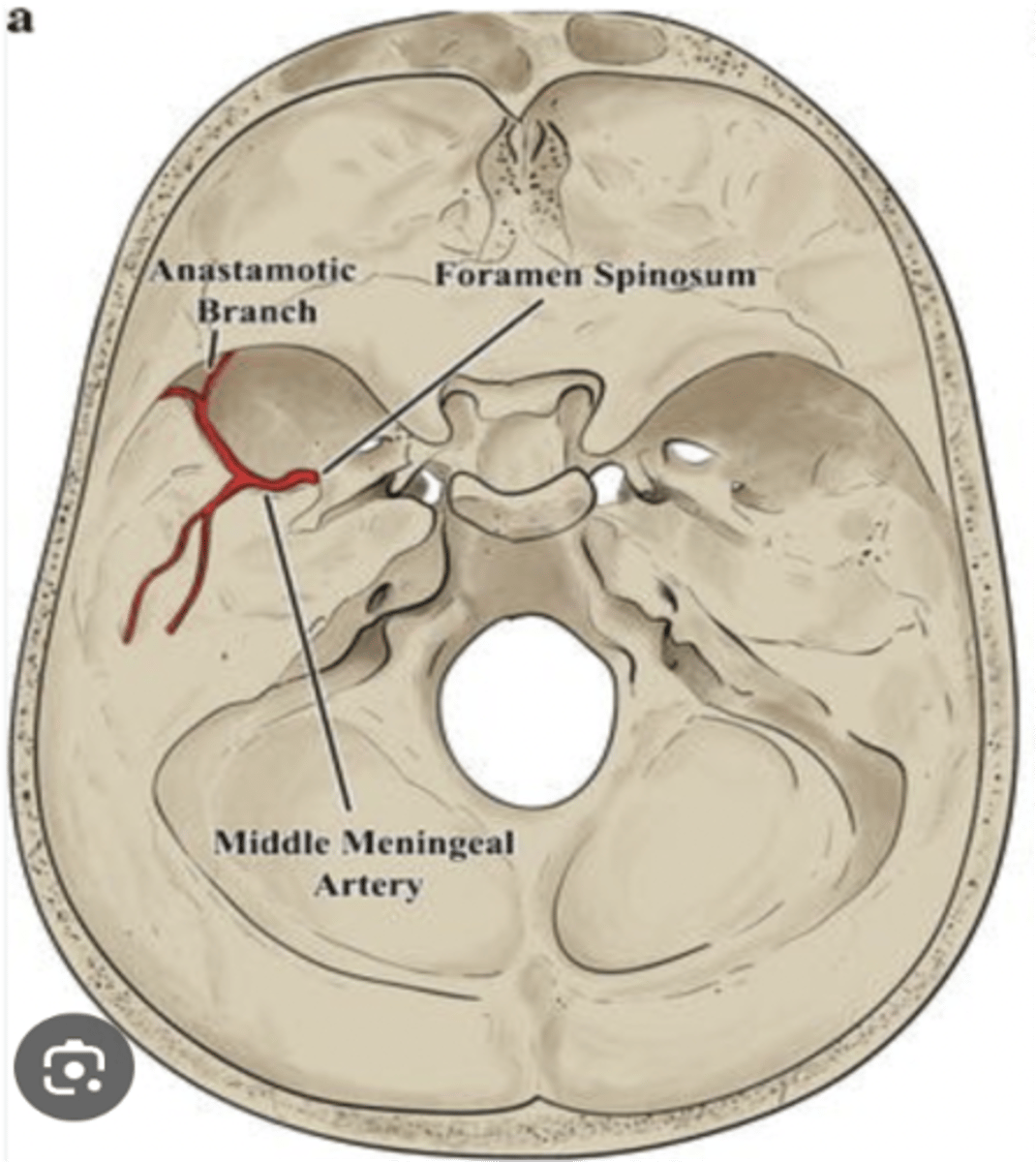
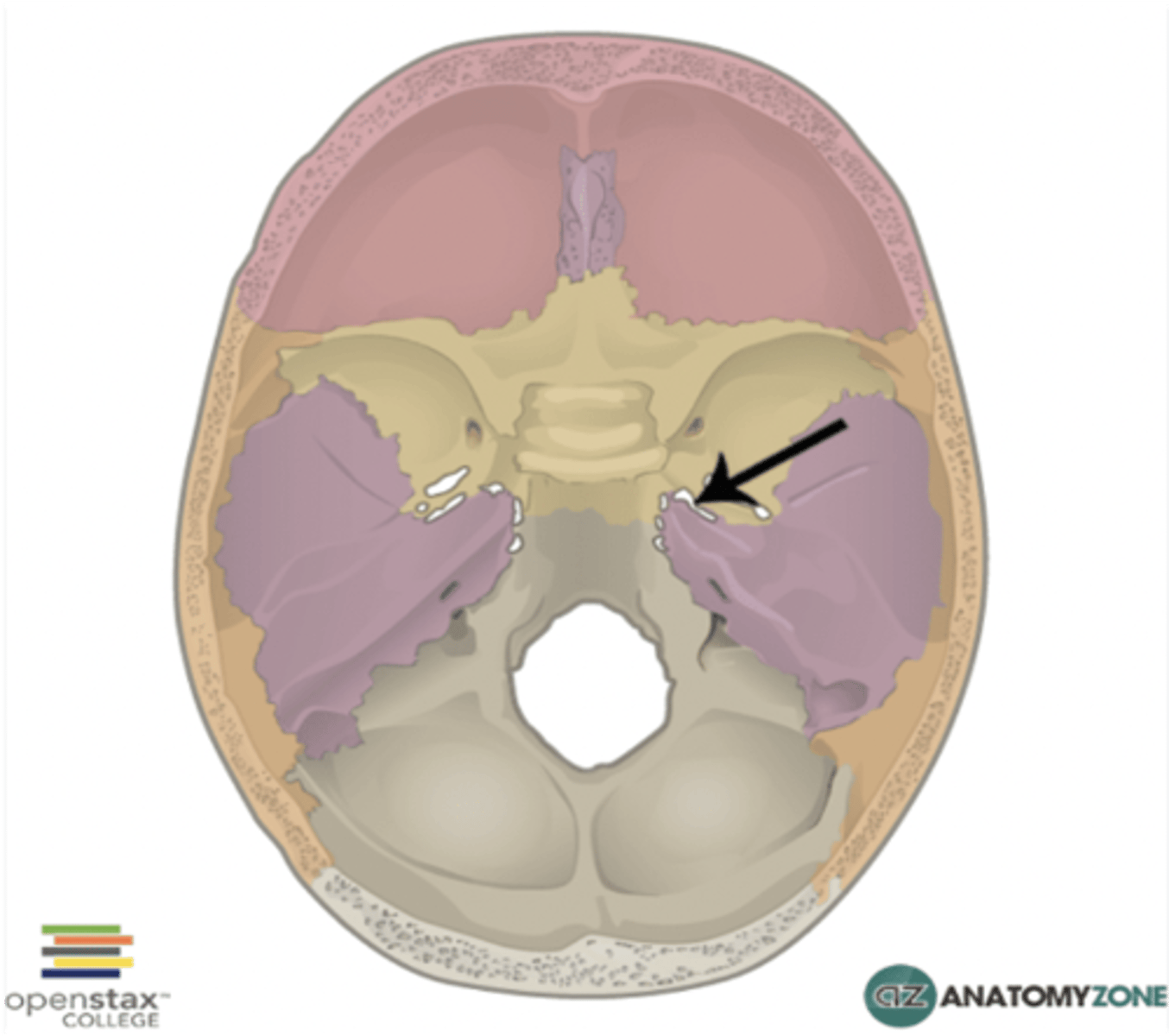
What foramen actually transmits nothing but is traversed by the internal carotid artery with sympathetic nerve plexus?
Foramen lacerum
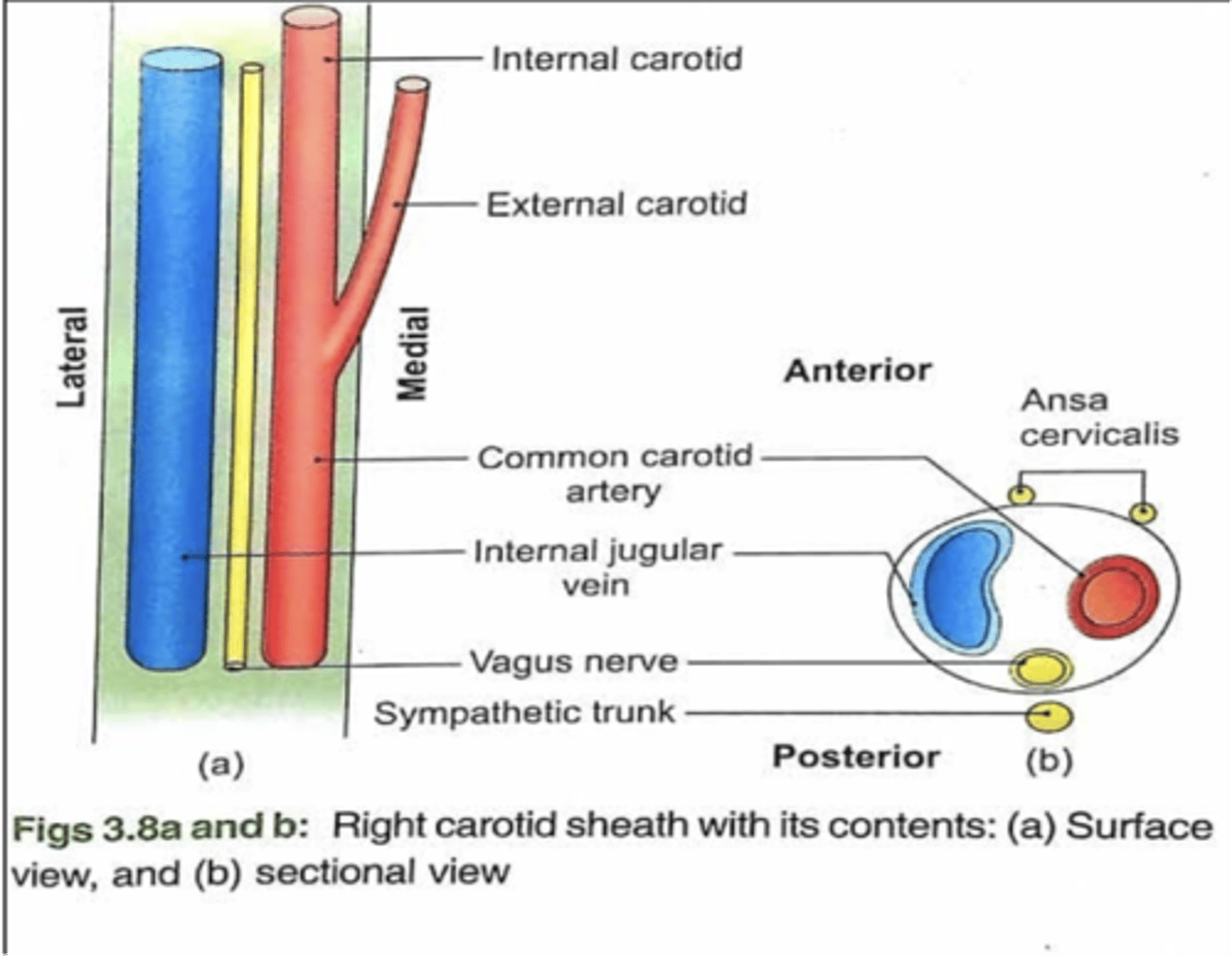
What are the contents of the carotid sheath?
Internal jugular vein
Vagus nerve
Common and internal carotid arteries
The recurrent laryngeal nerve lies in the groove between what two structures?
Trachea
Esophagus
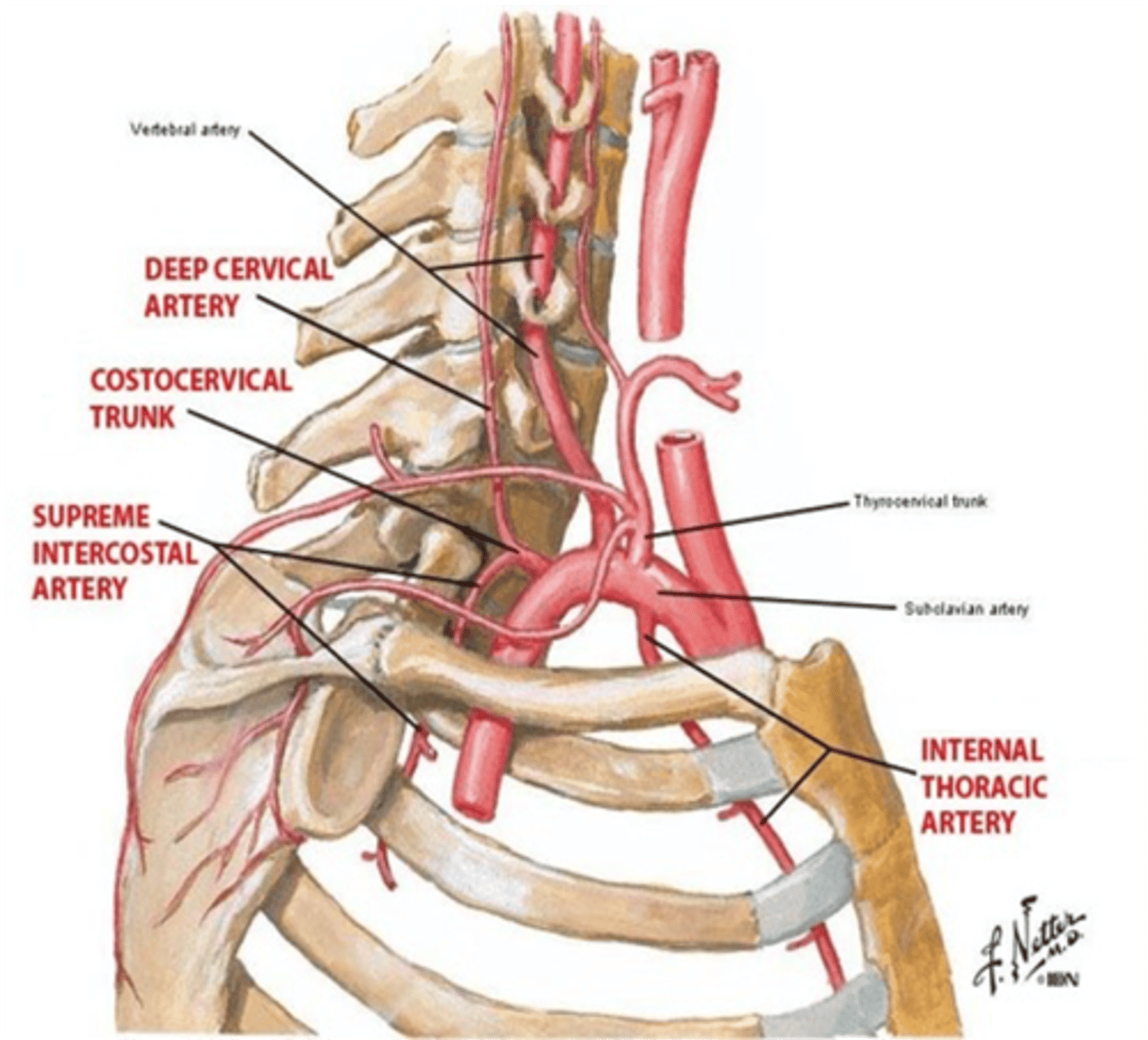
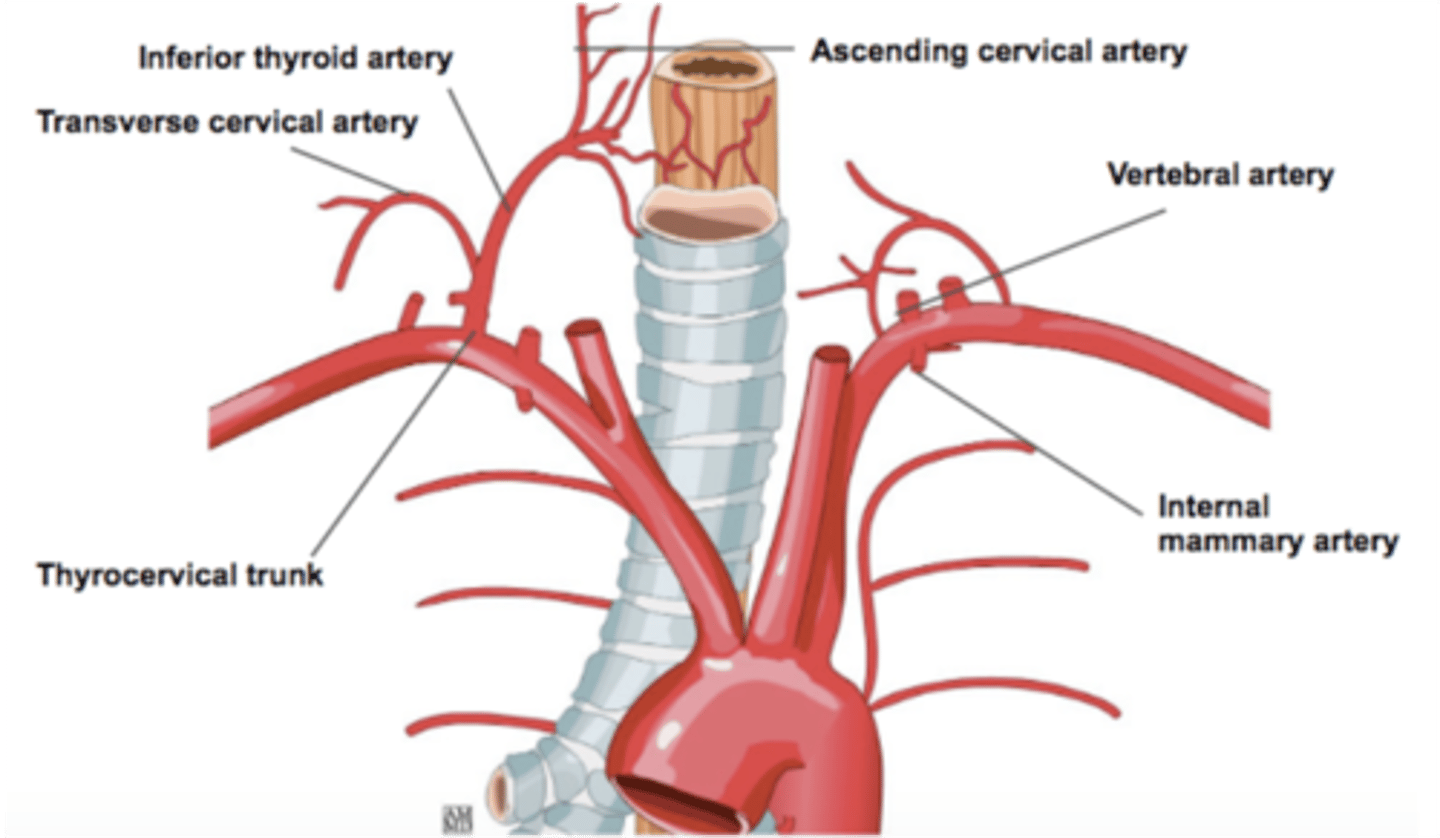
What artery gives rise to the deep cervical and superior intercostal arteries?
Costocervical trunk
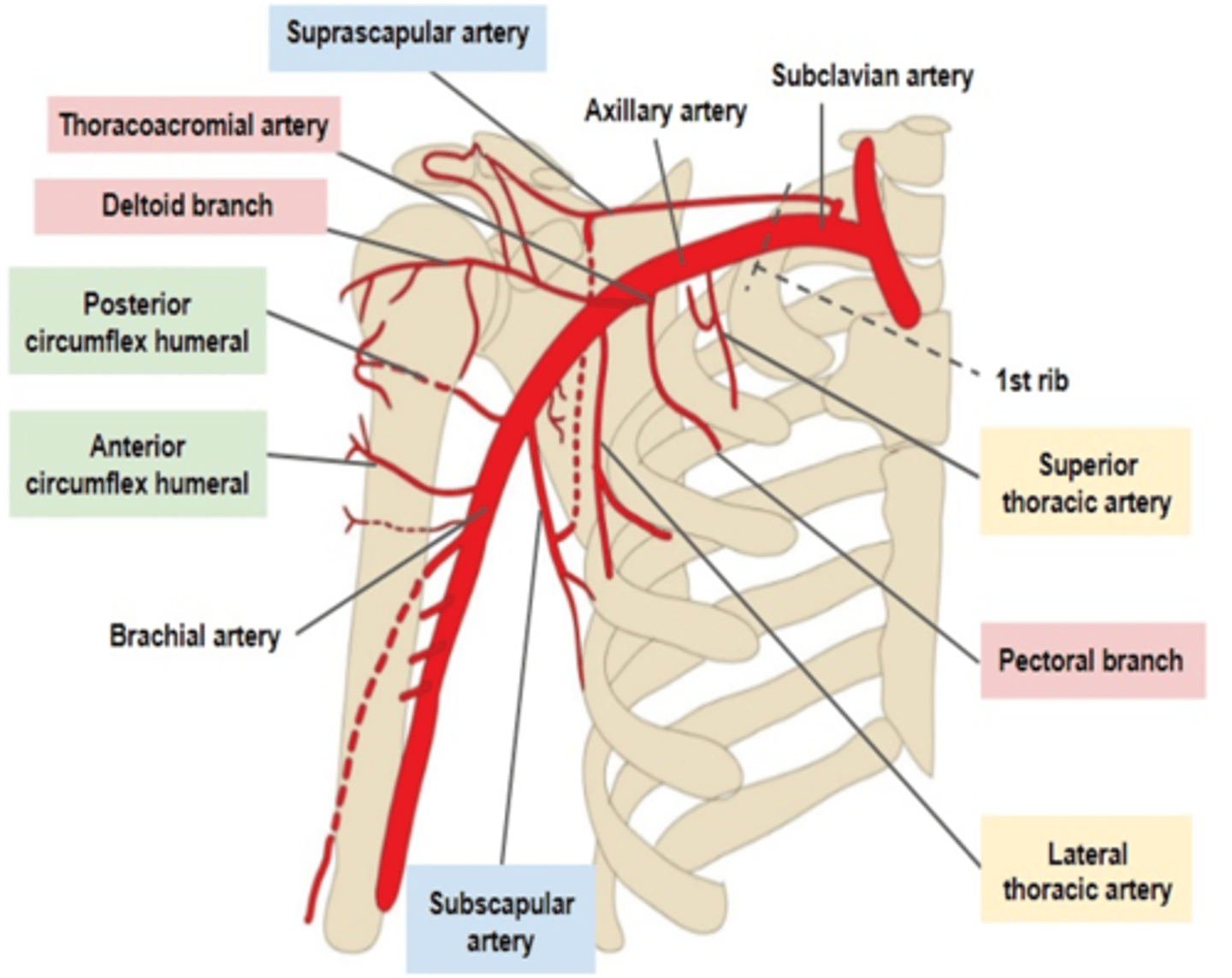
The superior thoracic artery arises from what artery?
Axillary artery
The transverse cervical, inferior thyroid and suprascapular arteries arise from what artery?
Thyrocervical trunk
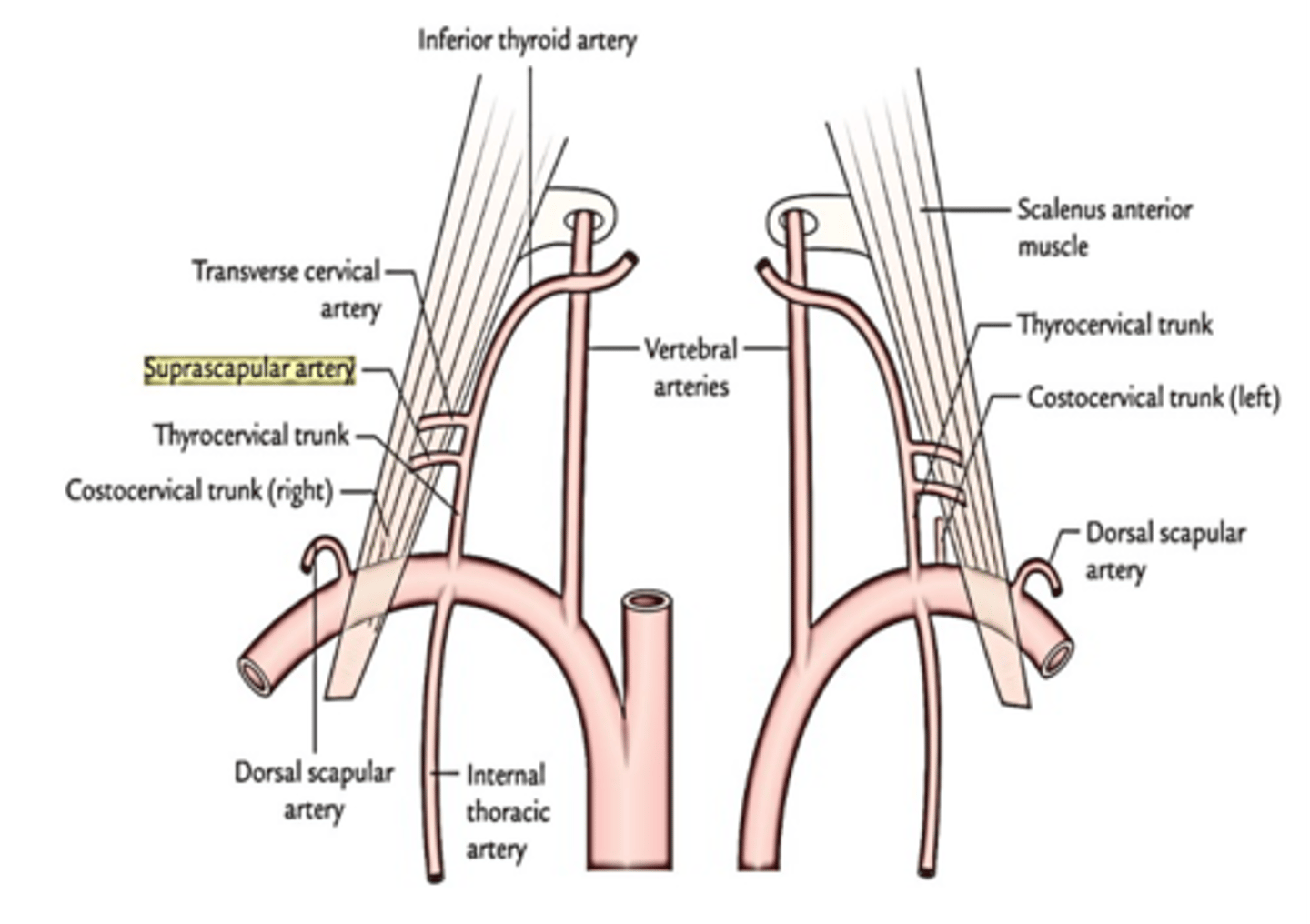
The ascending cervical artery arises from what artery?
Inferior thyroid artery
What nerves lie in the wall of the cavernous sinus?
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V1)
Trochlear nerve (CN IV)

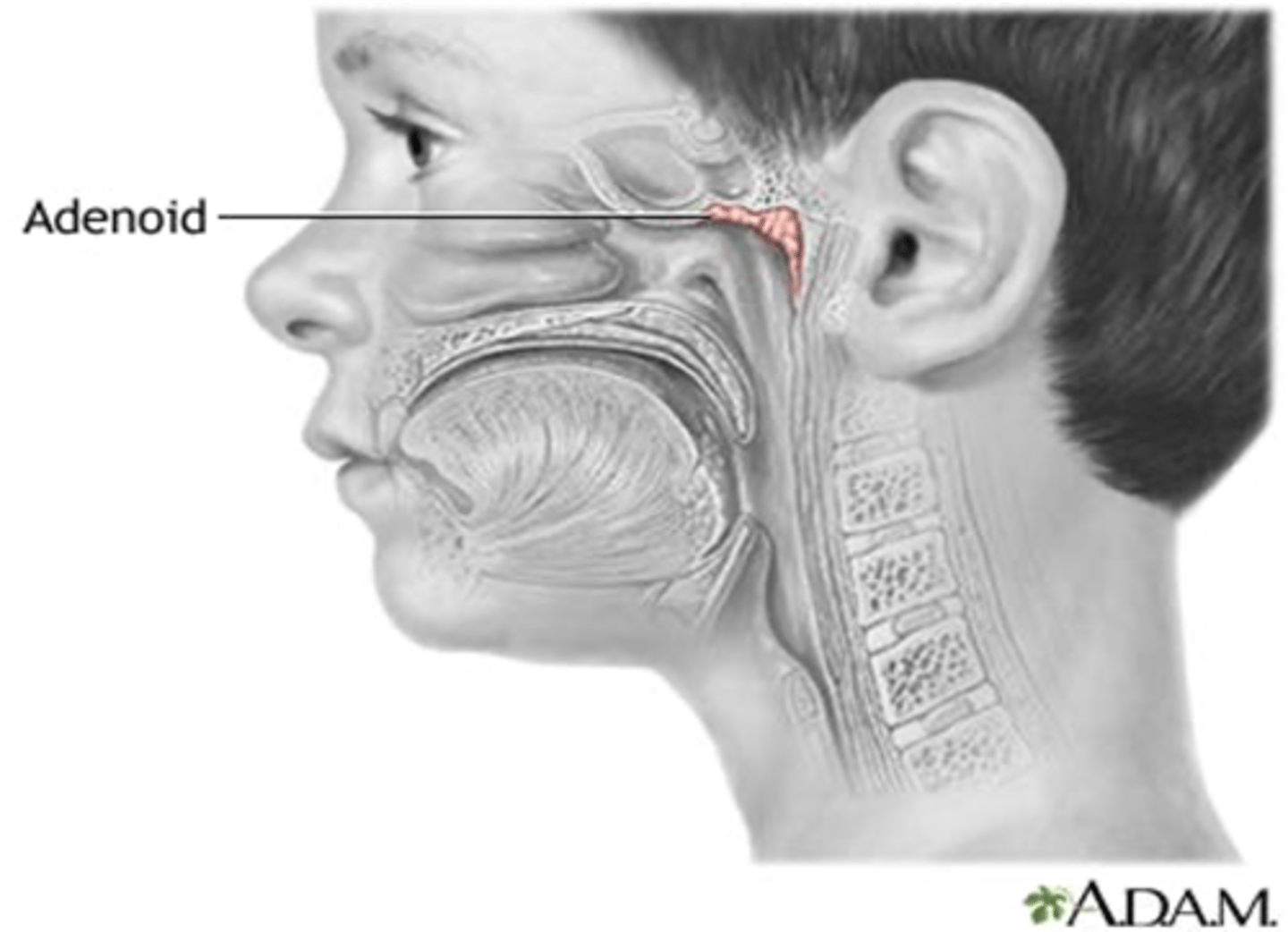
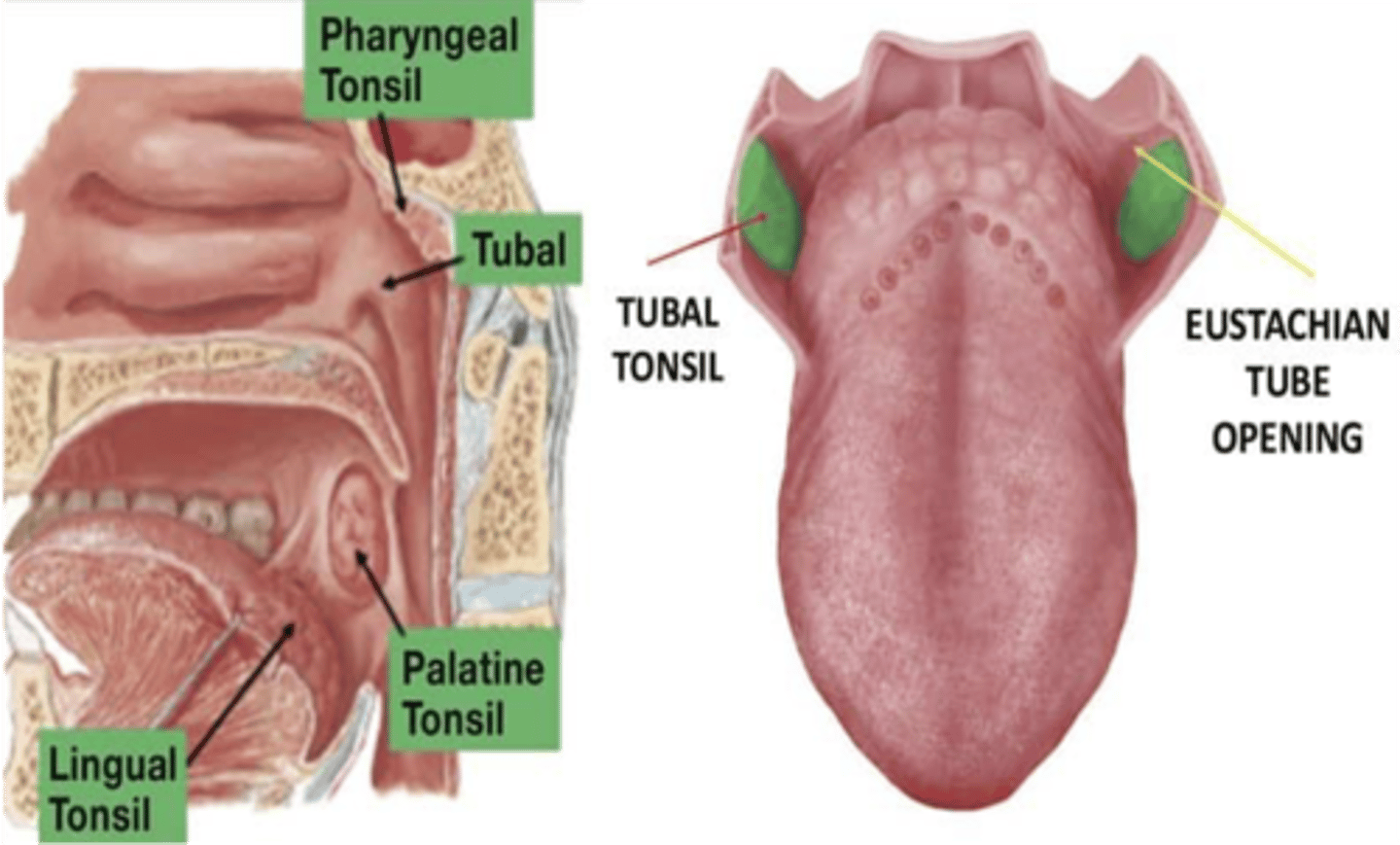
What term denotes an enlarged pharyngeal tonsil?
Adenoid
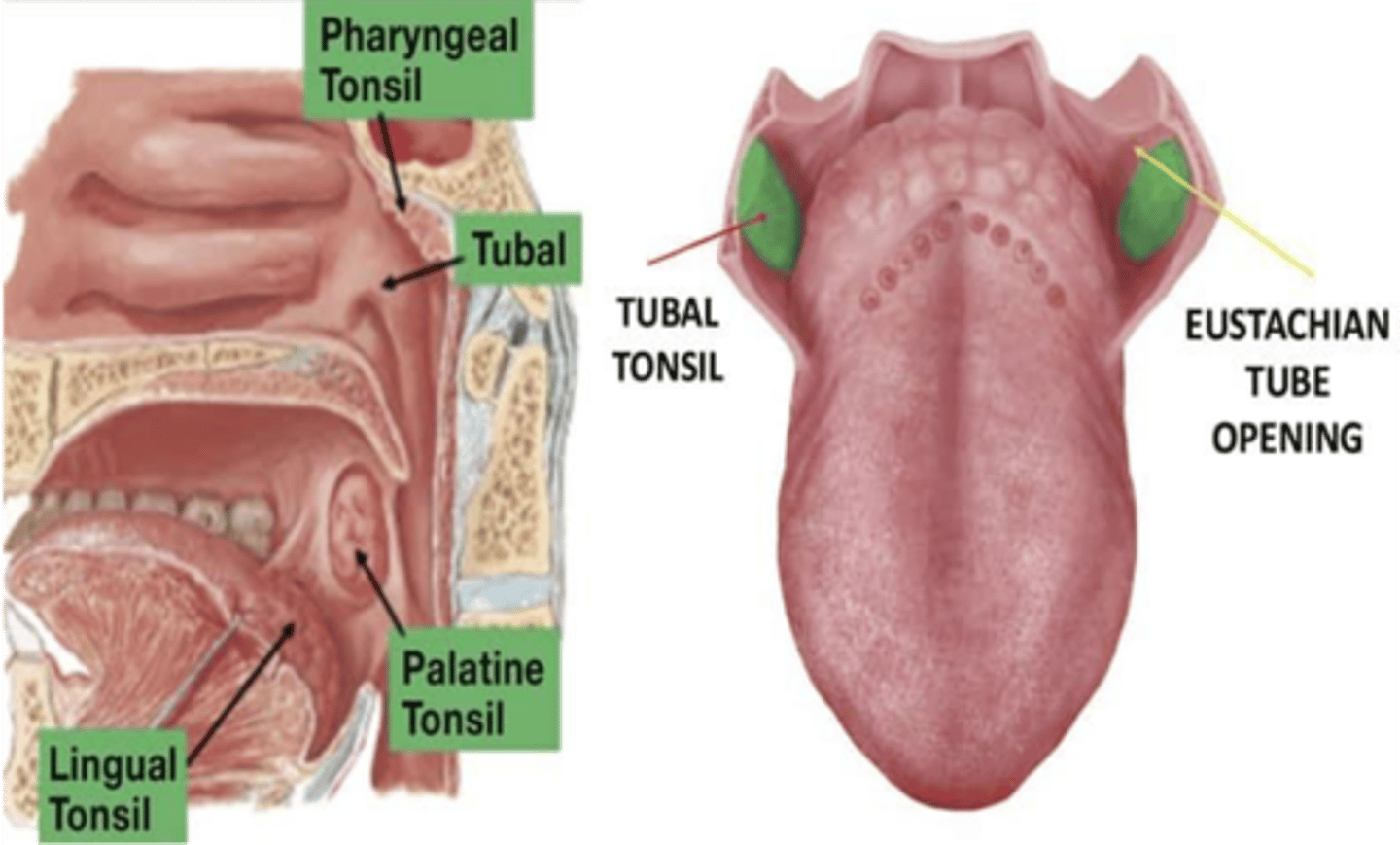
What is another term for tubal tonsils?
Eustachian tonsils
What is another term for palatine tonsils?
Faucial tonsils
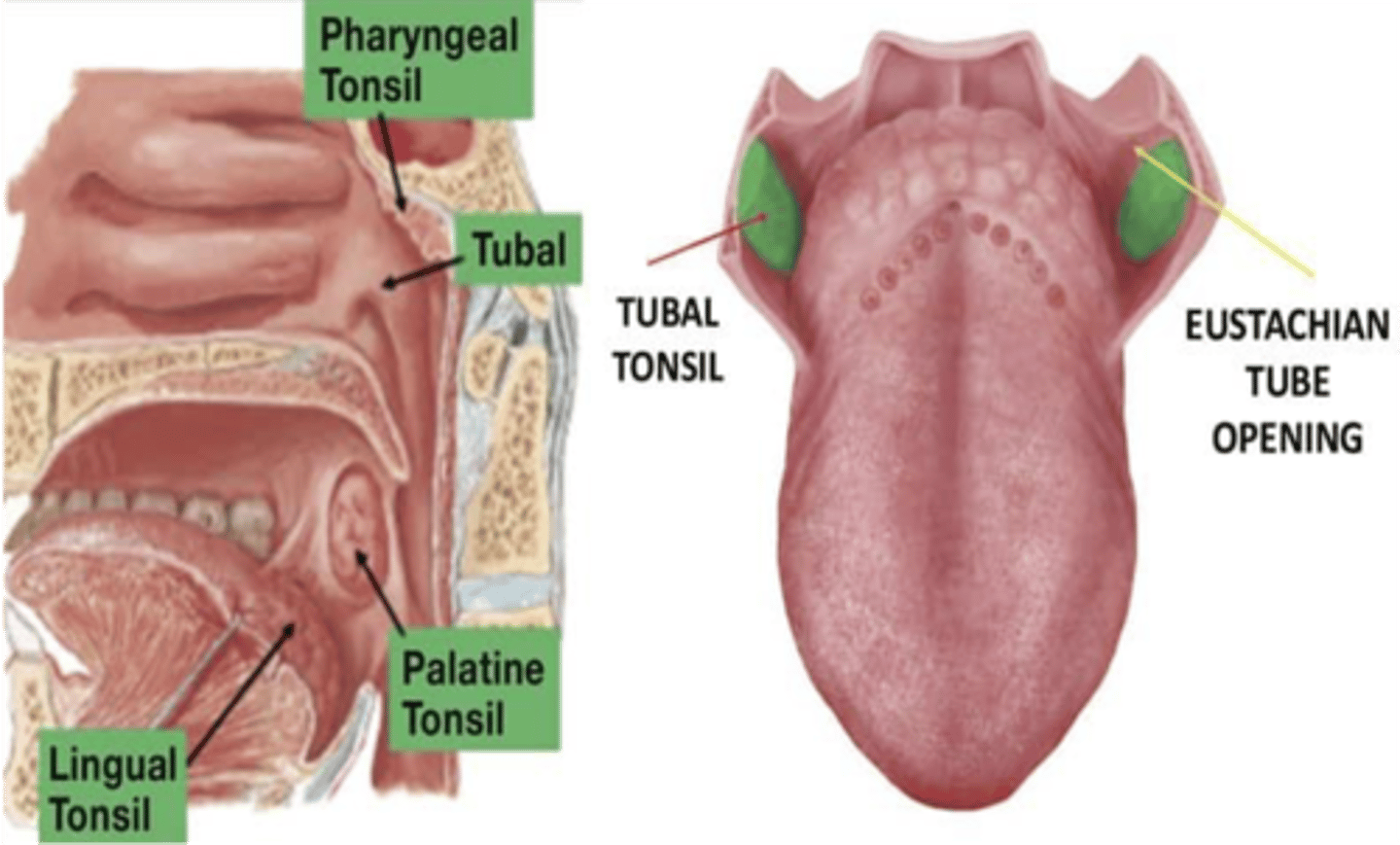
What term denotes a palatine tonsil that is shrunken and atrophied and is partly or entirely hidden by the palatoglossal arch
Submerged tonsil
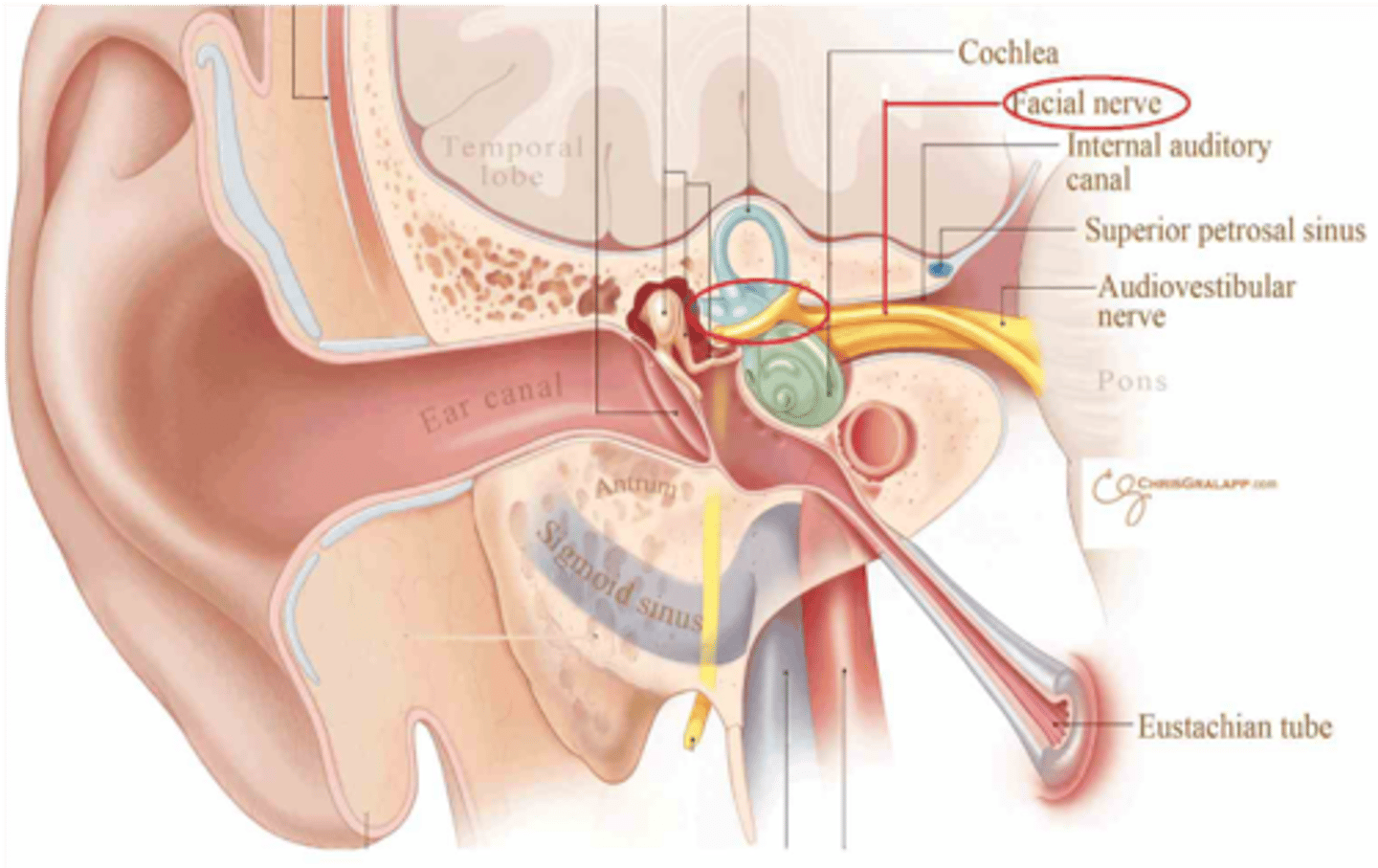
The facial and vestibulocochloear nerves pass through what skull opening?
Internal auditory meatus
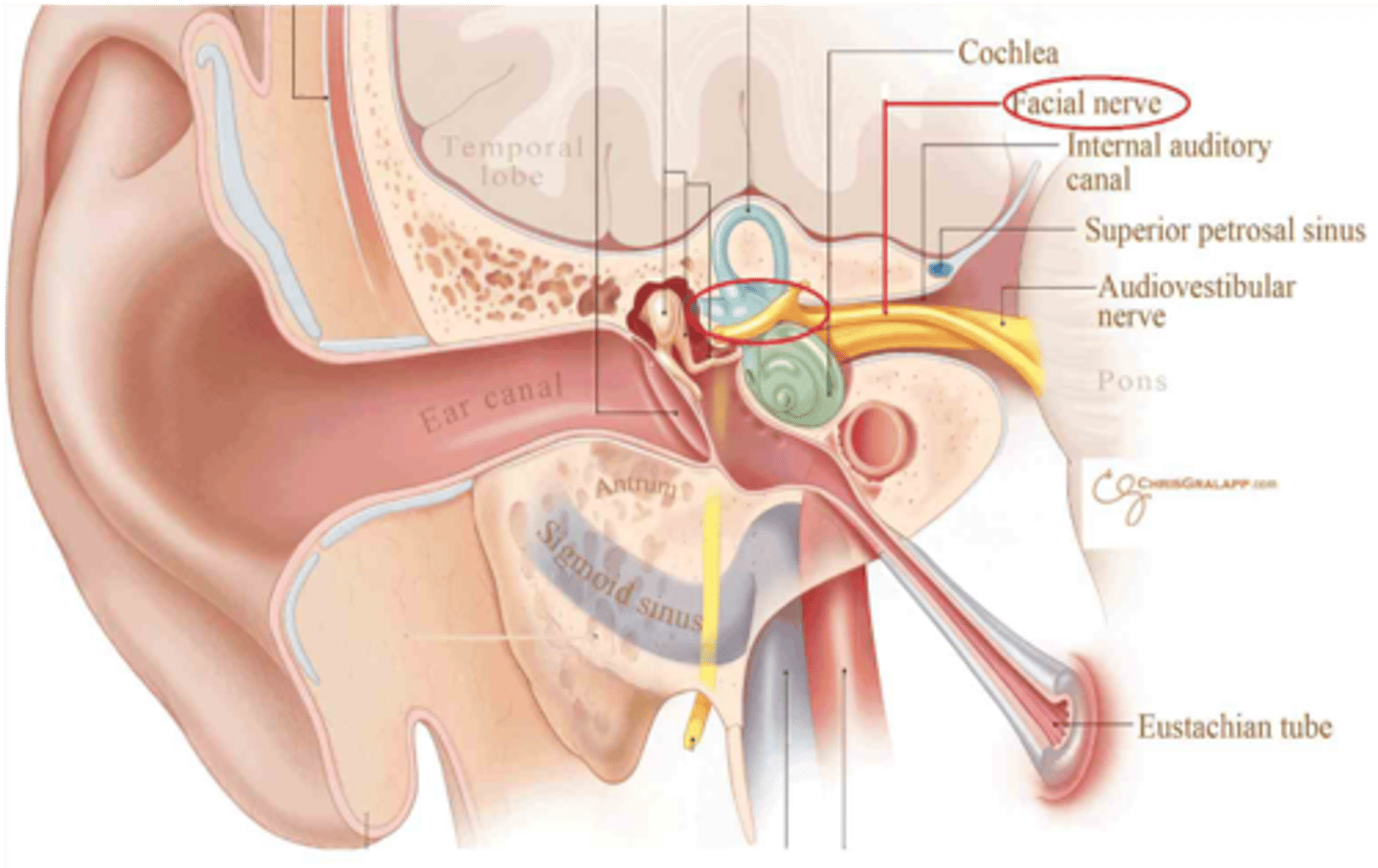
The internal auditory meauts transmits what 2 cranial nerves?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
What structures pass through the jugular foramen?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Vagus nerve (CN X)
Spinal accessory nerves (CN XI)
Internal jugular vein
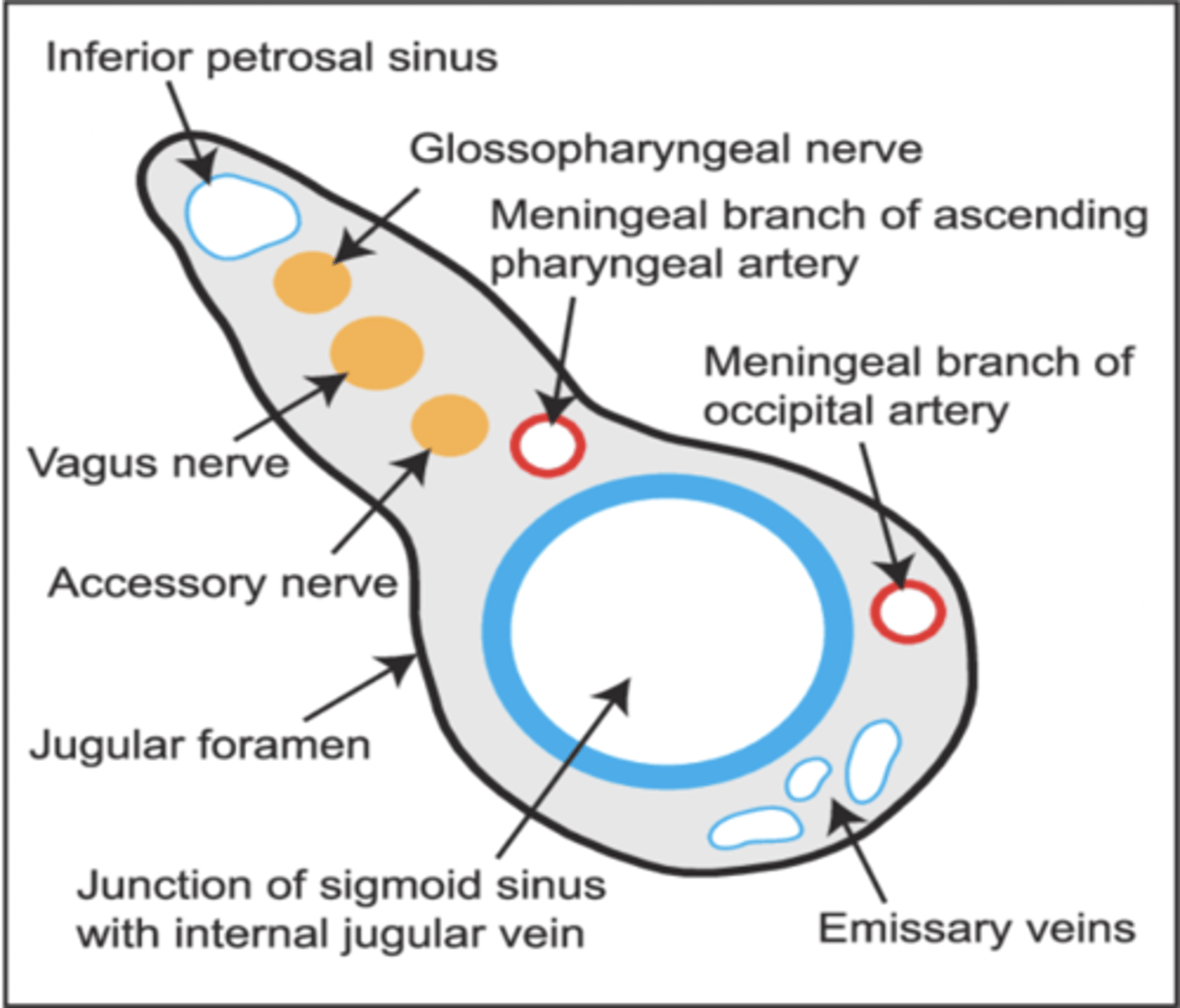
Cranial nerves IX, X and XI pass through what skull foramen?
Jugular foramen
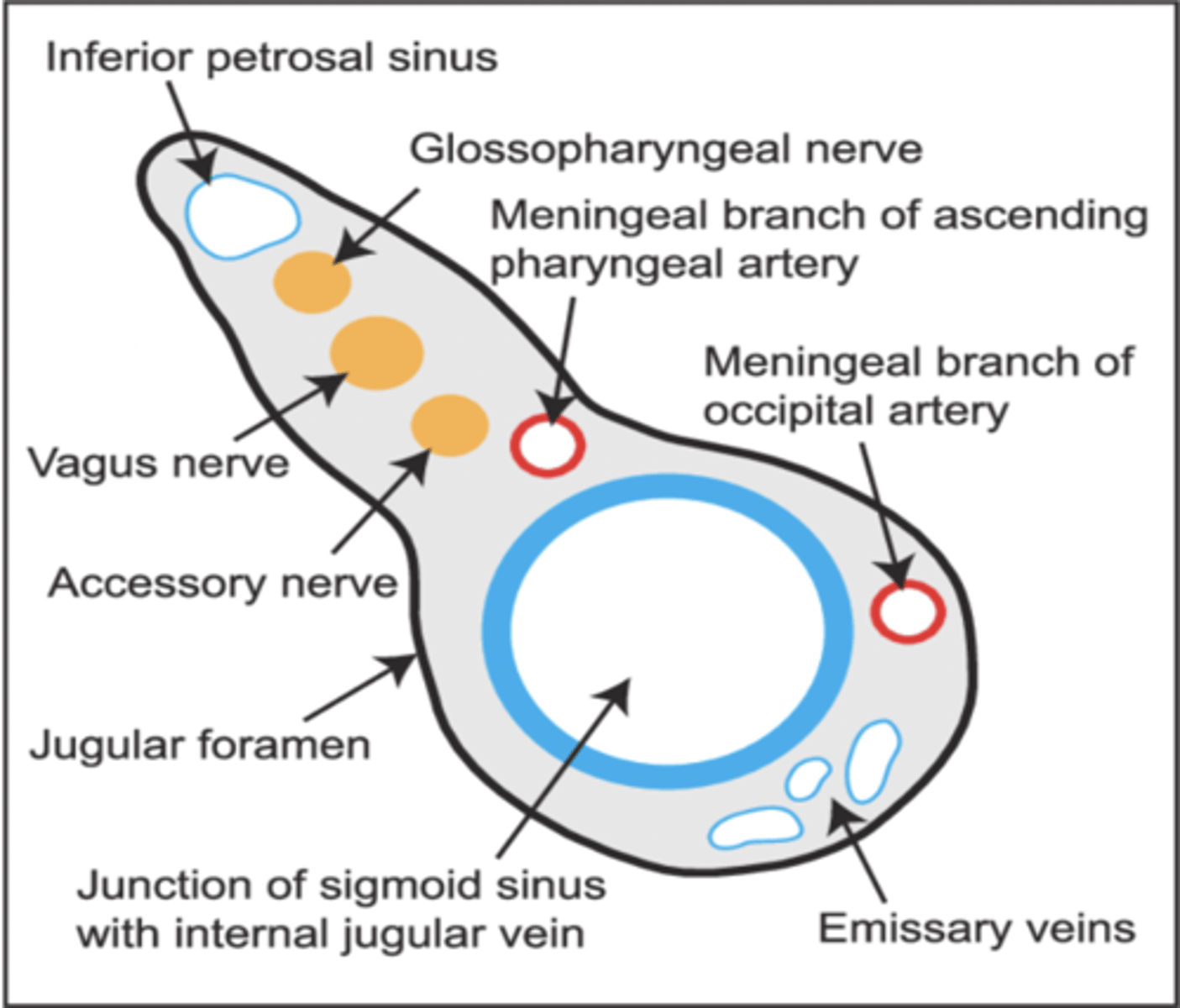
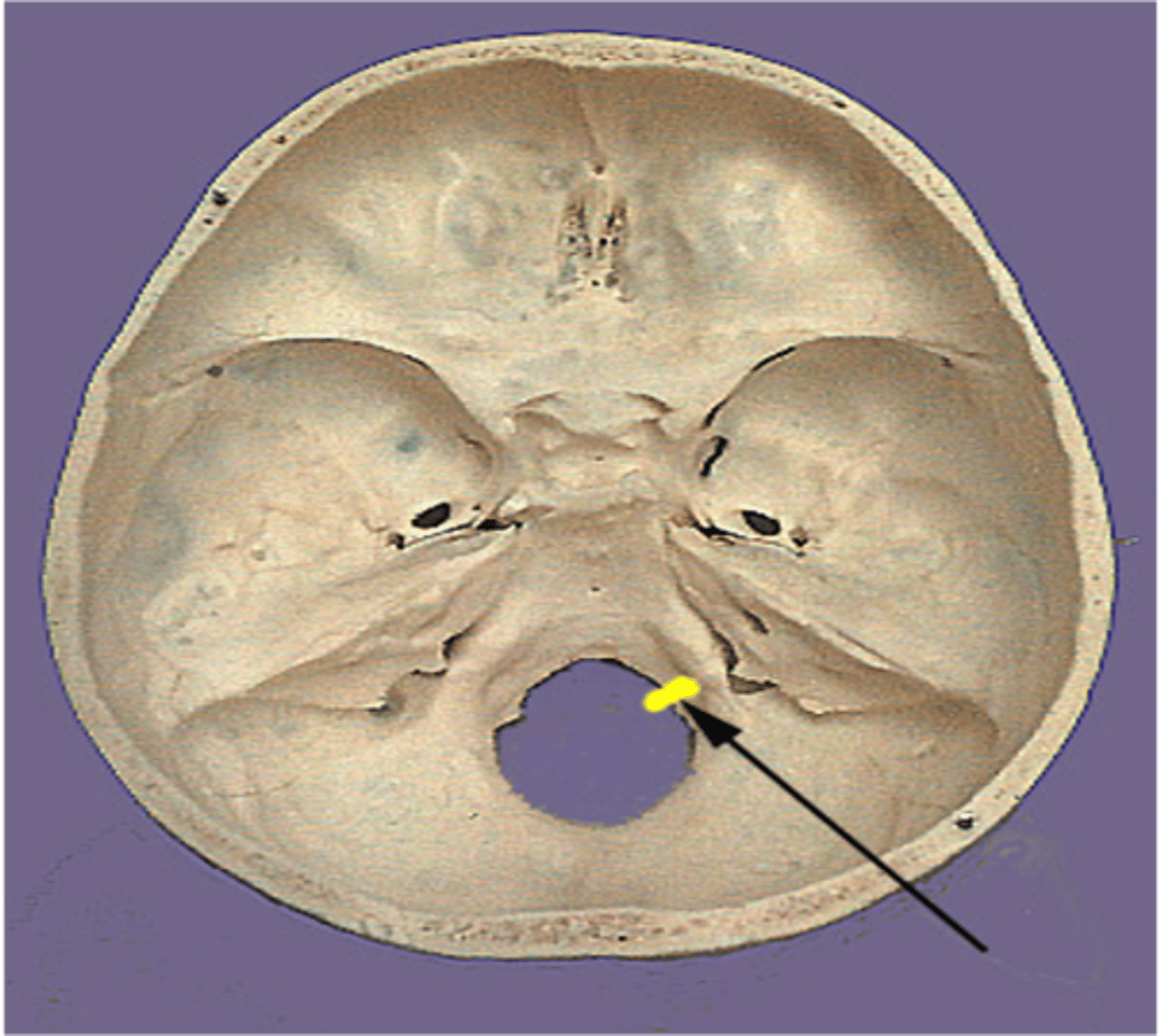
The hypoglossal nerve passes through what skull foramen?
Hypoglossal canal
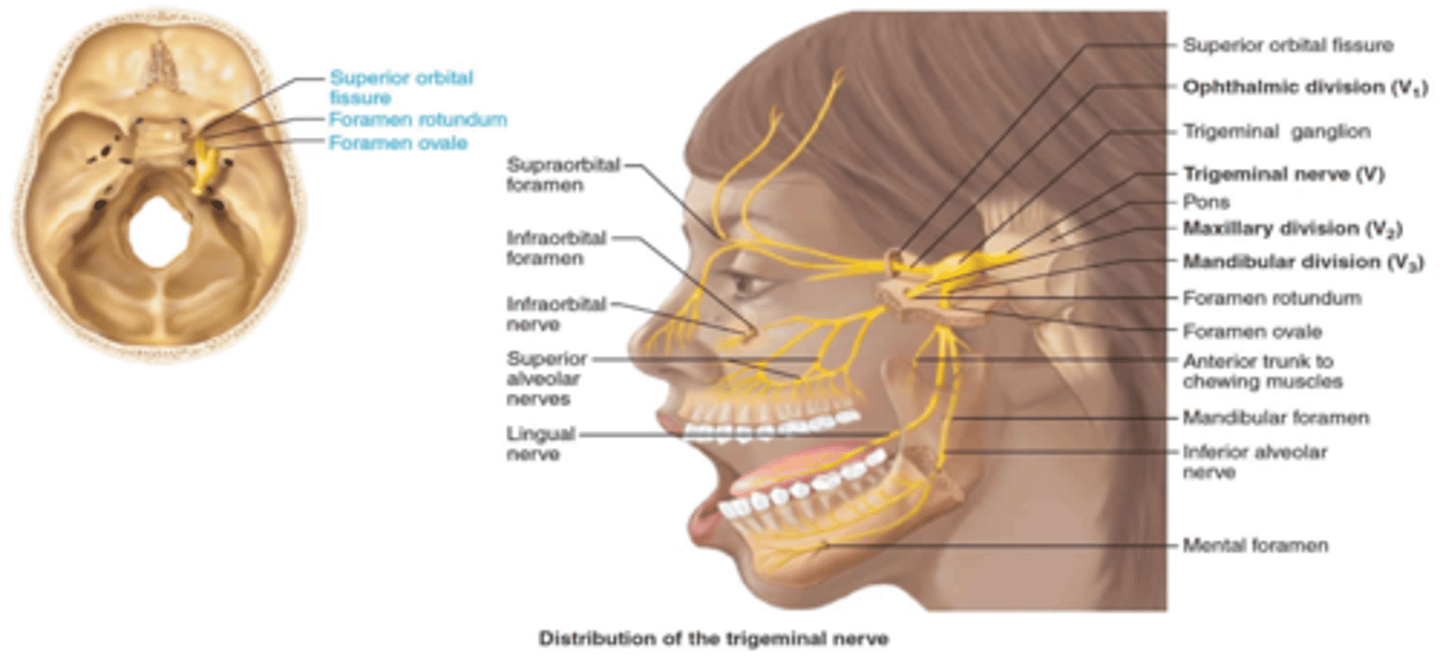
The ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve passes through what foramen?
Superior orbital fissure

The maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve passes through what foramen?
Foramen rotundum
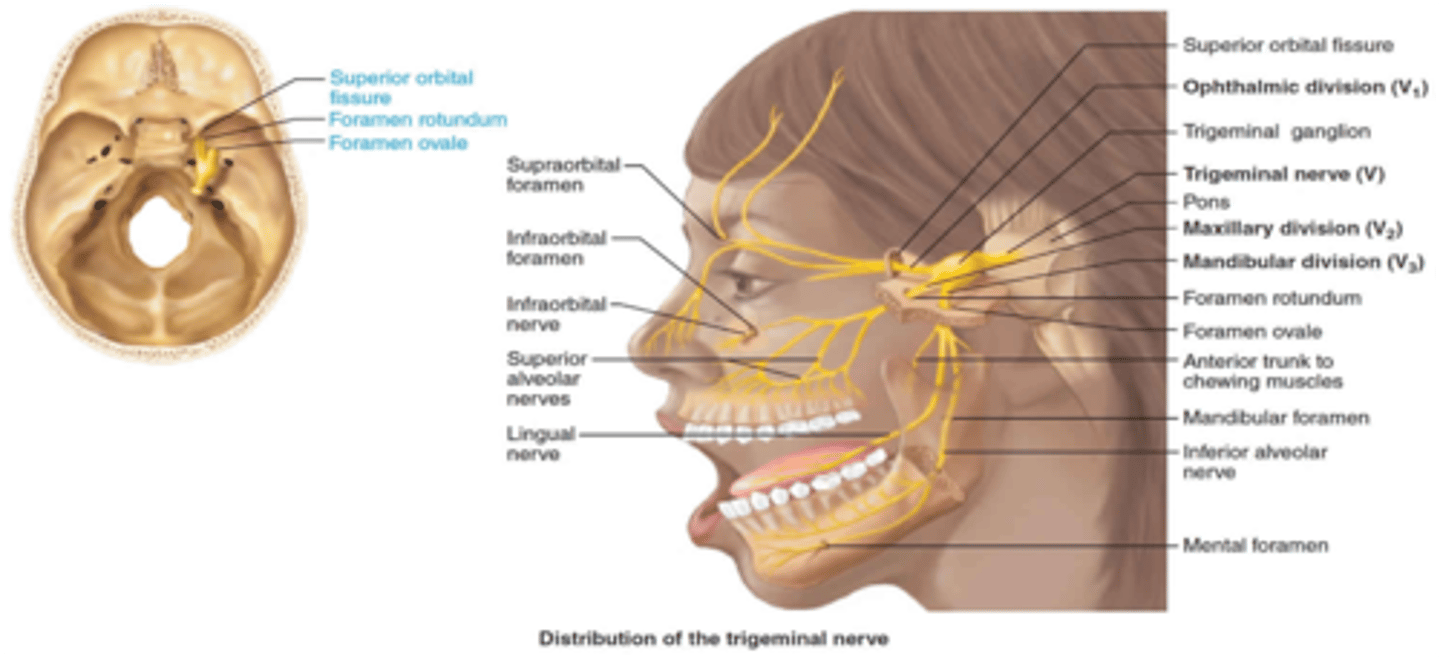
The mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve passes through what foramen?
Foramen ovale
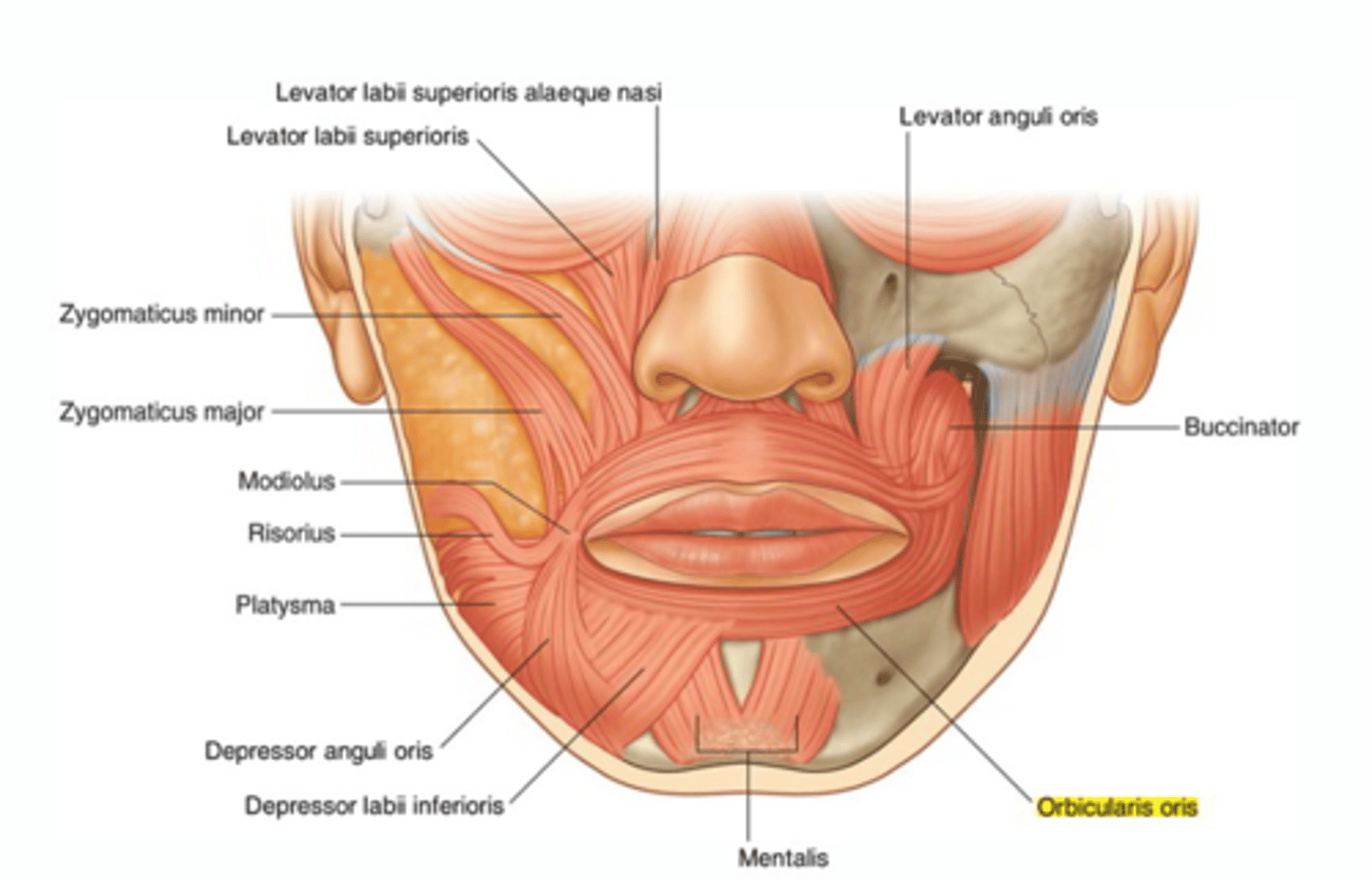
What is the action of the levator labii superioris, zygomatic minor, and depressor labii inferioris muscles?
Opens the lips
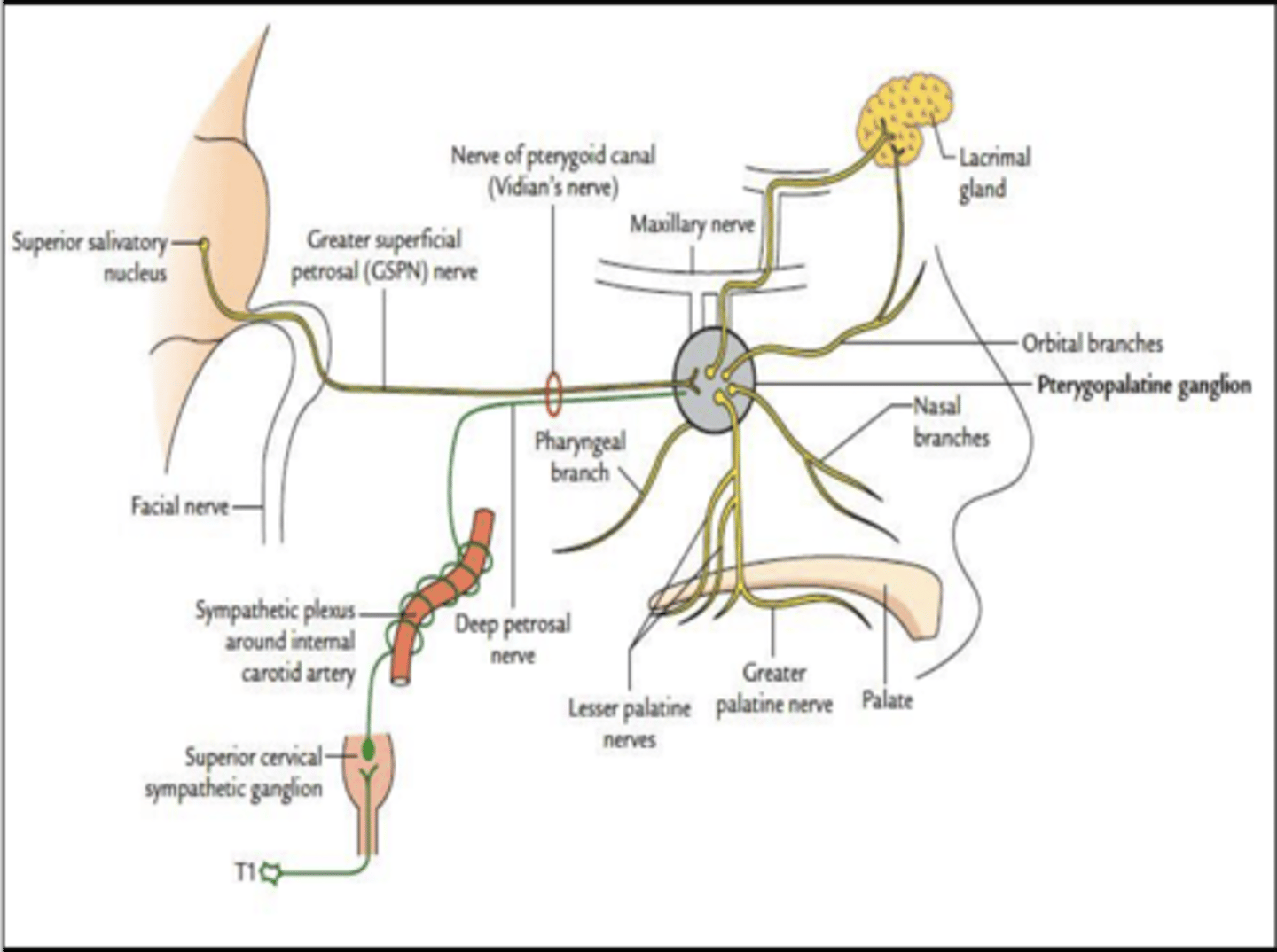
What nerve carries preganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibers to the lacrimal glands and mucous glands in the nasal cavity and palate?
Greater petrosal nerve
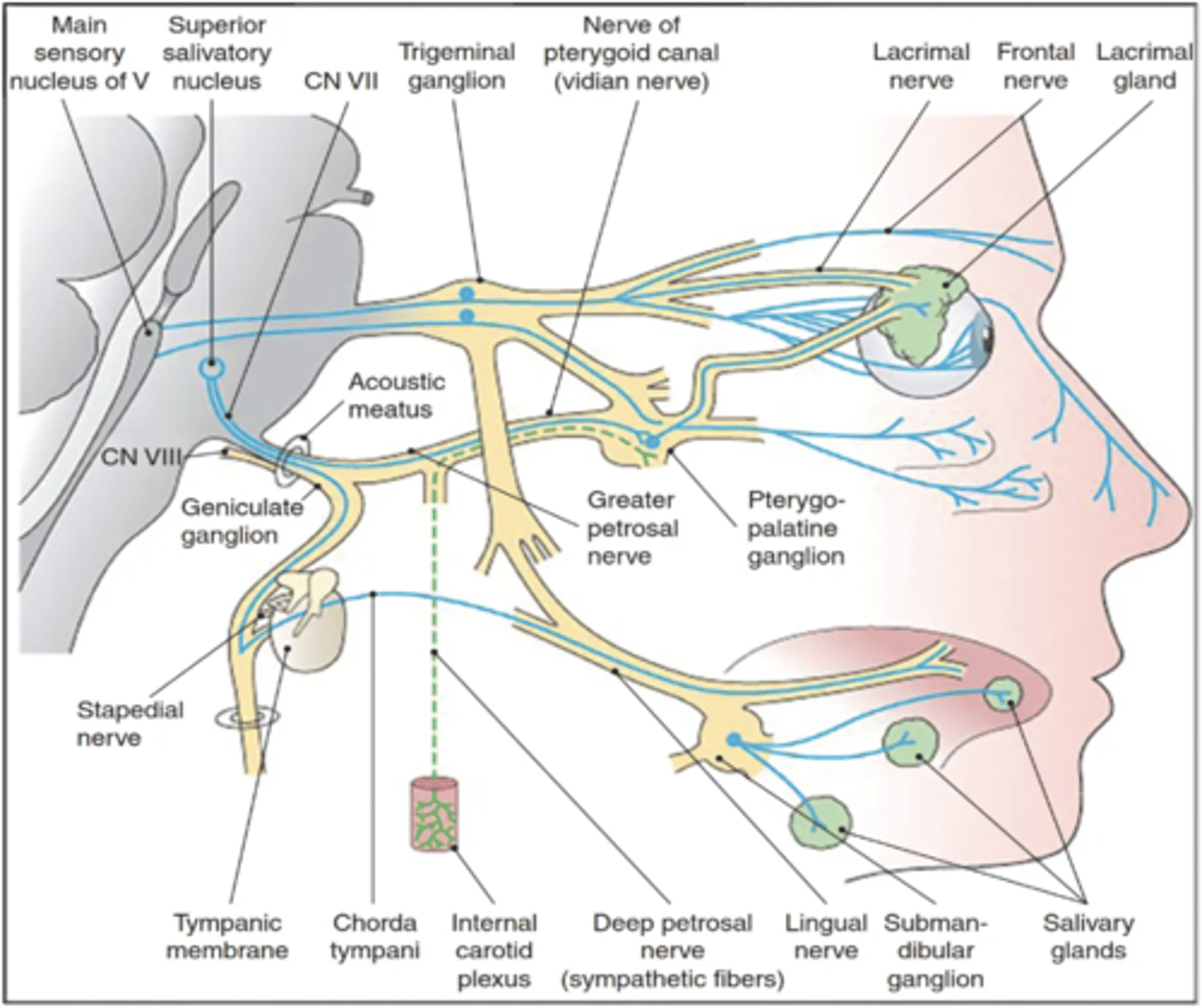
What nerve carries taste fibers from the palate?
Greater petrosal nerve
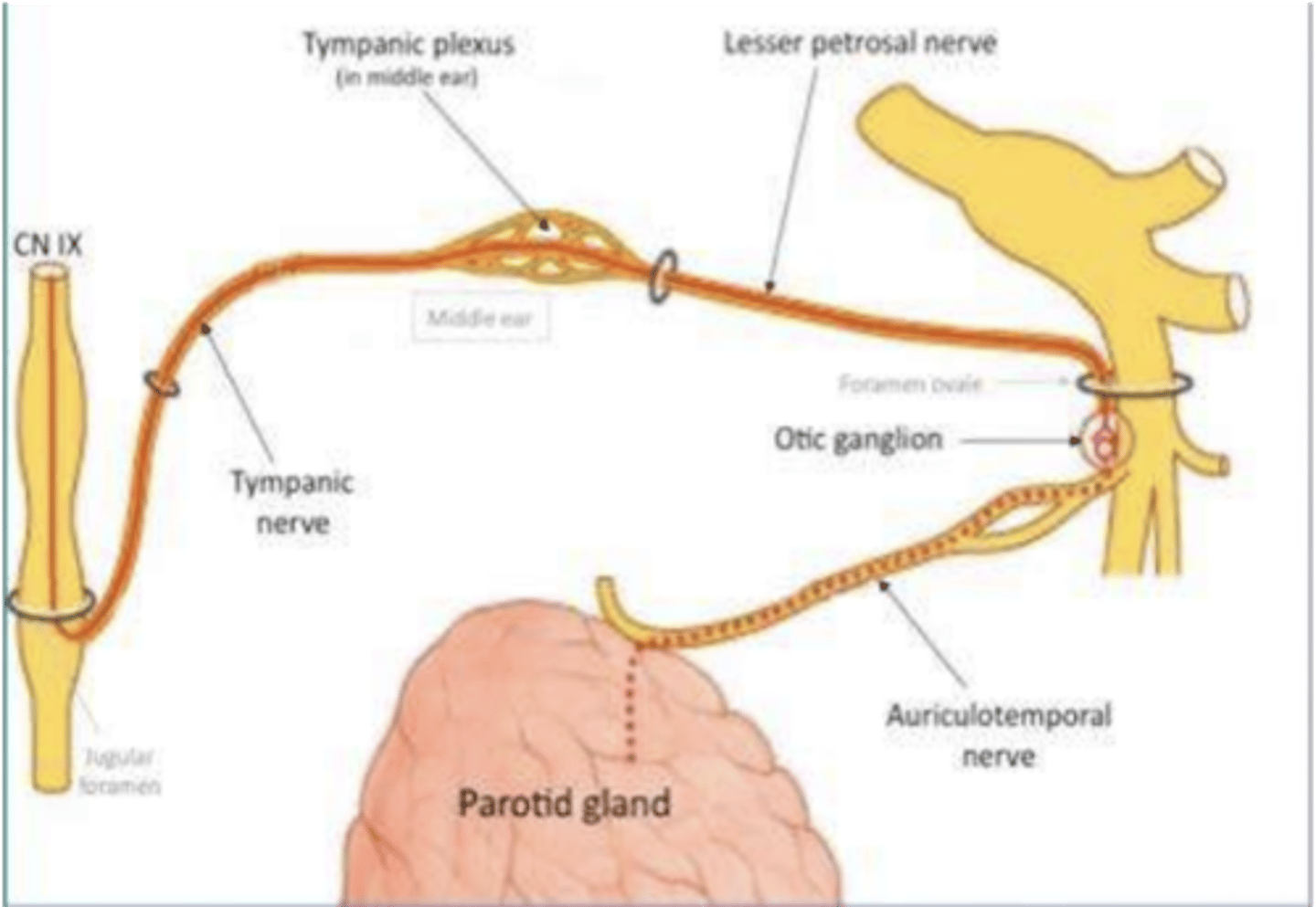
Decreased parotid gland secretion is due to a lesion of what nerve?
Lesser petrosal nerve
Taste sensation in the epiglottis is carried by what branch of the superior laryngeal nerve?
Internal laryngeal branch
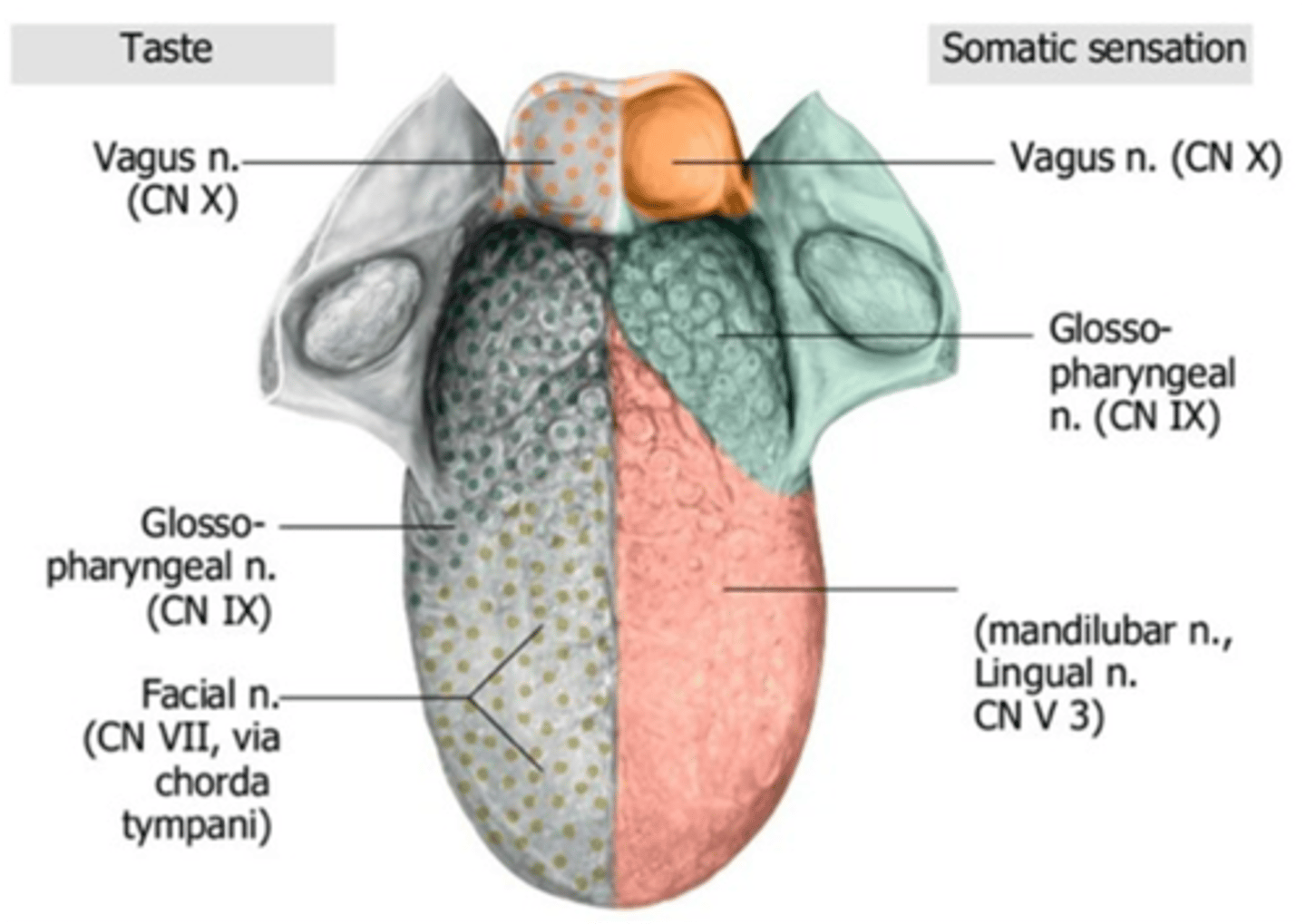
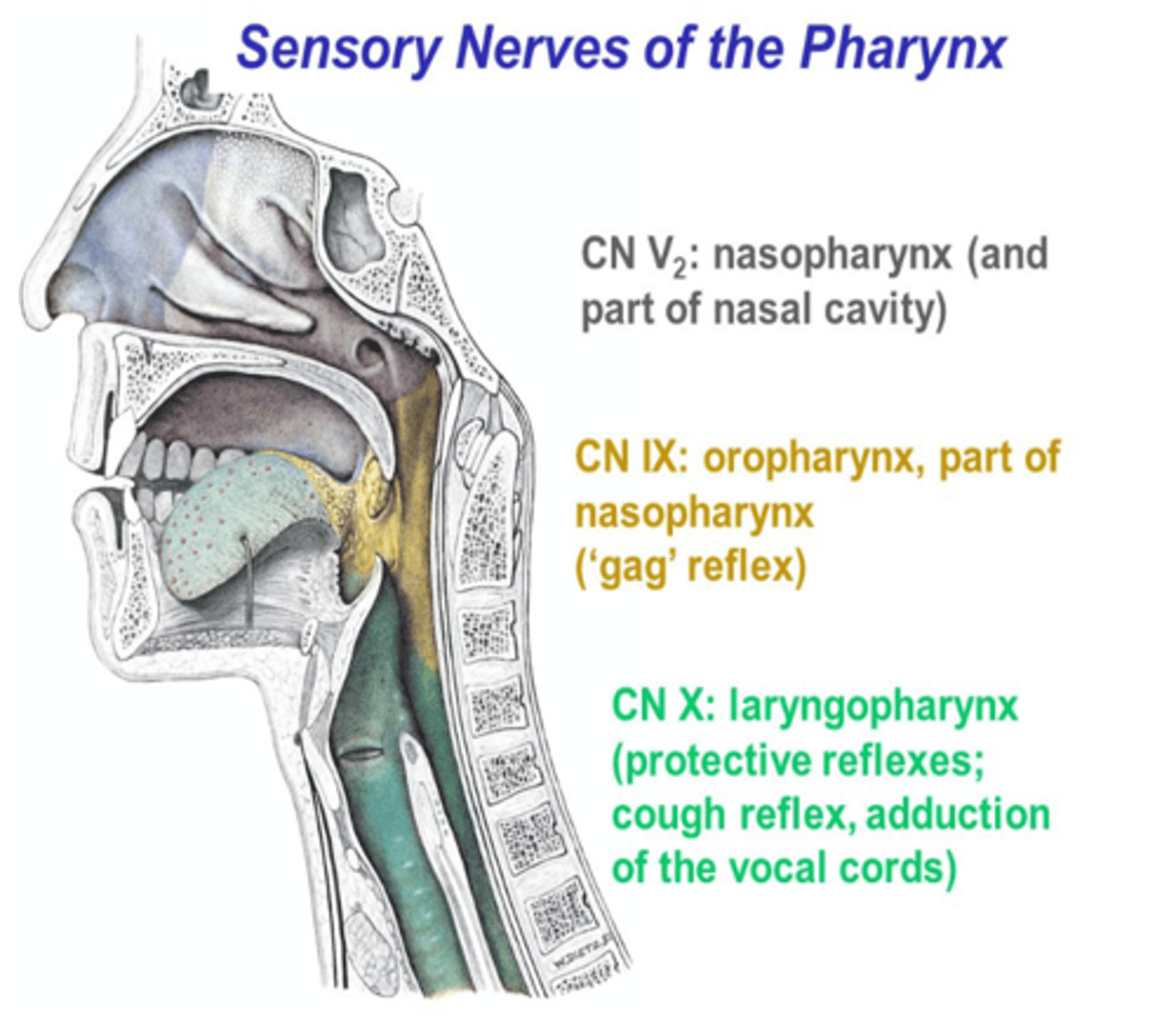
General visceral sensation in the oropharynx is carried by what cranial nerve?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
What cavity extends from the rima glottidis to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage?
Infraglottic cavity
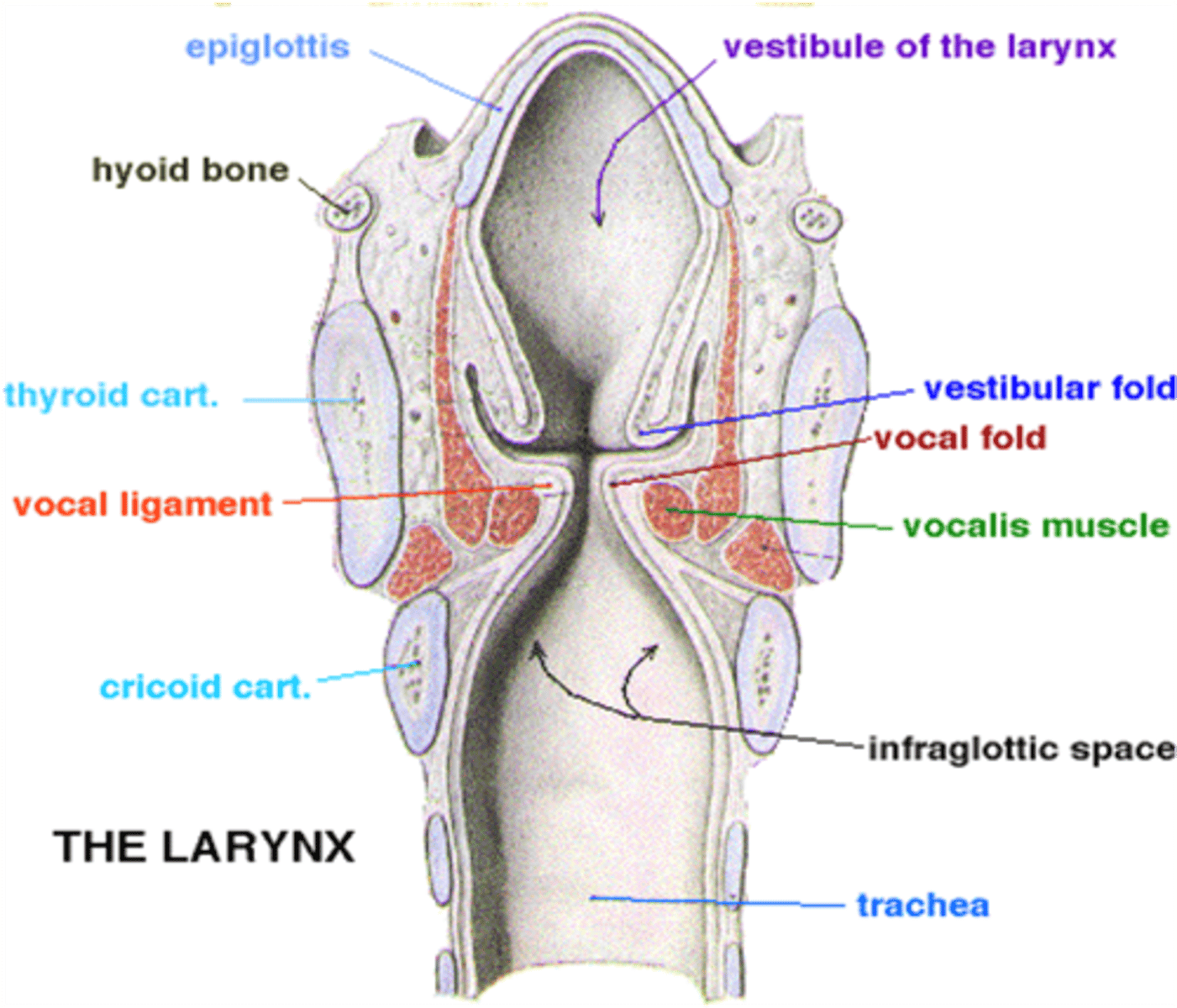
The ...(structure).. is the space between the vocal folds and arytenoid cartilages.
Rima glottidis
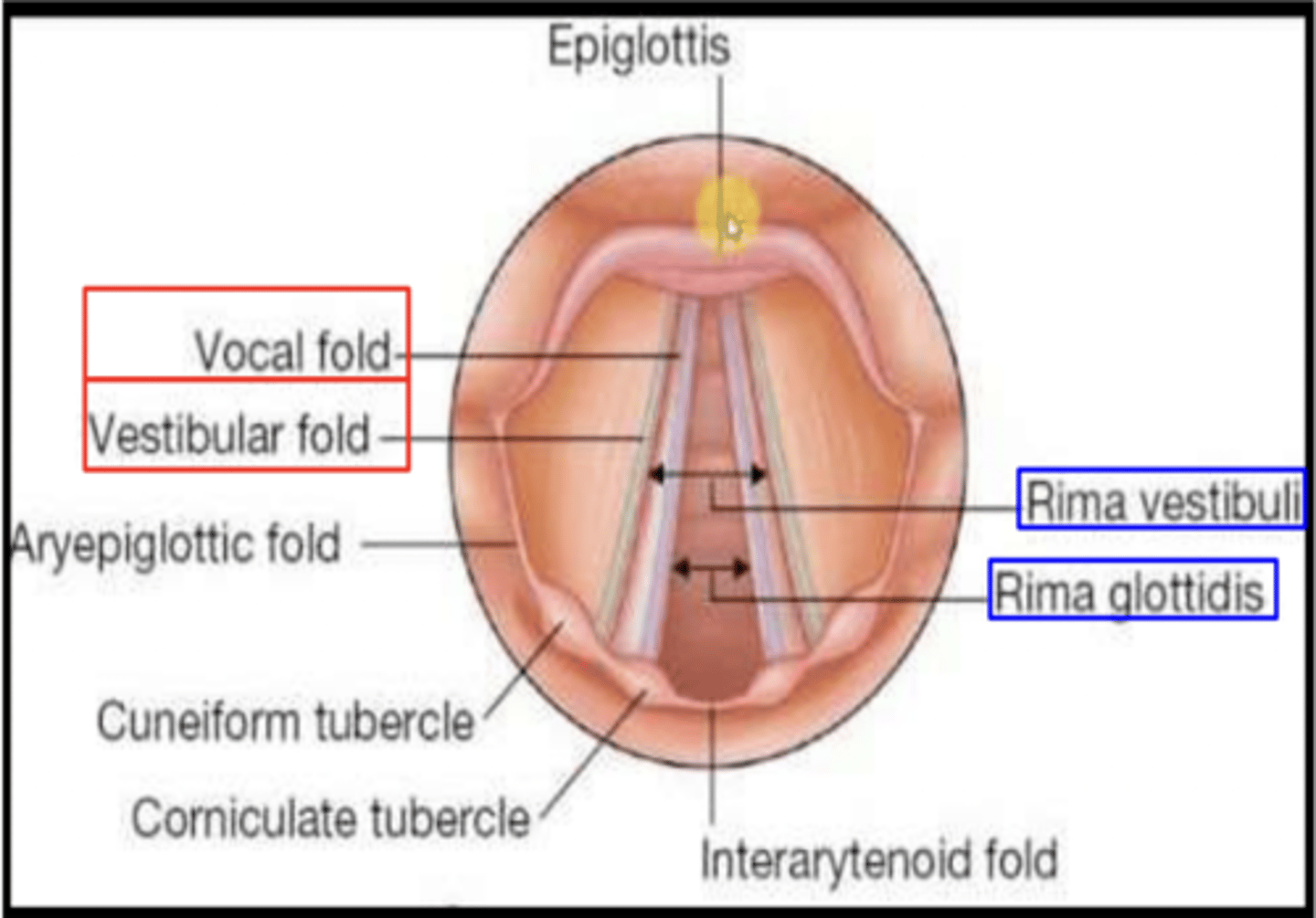
This laryngeal structure extends from the laryngeal inlet to the vestibular folds
Vestibule
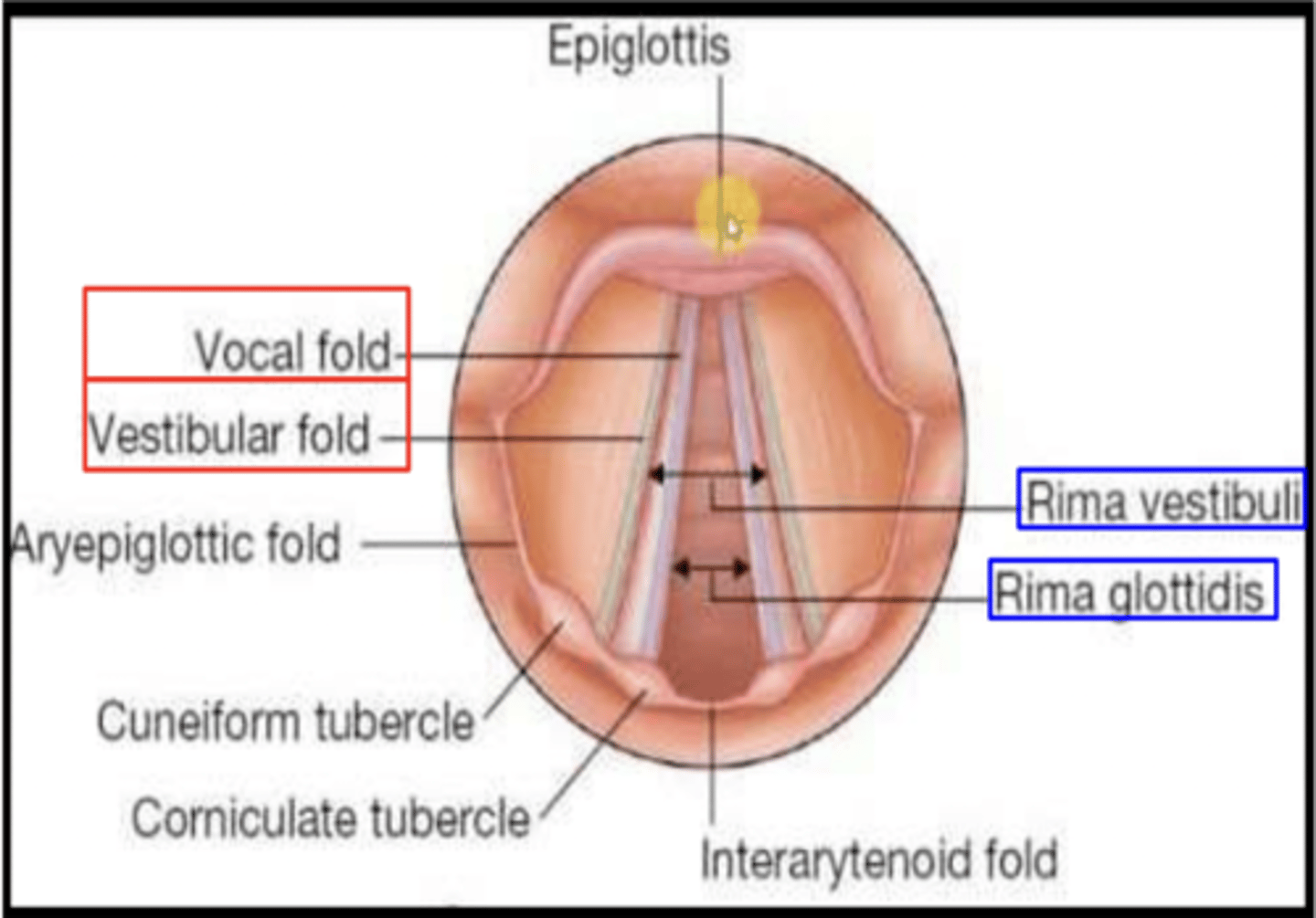
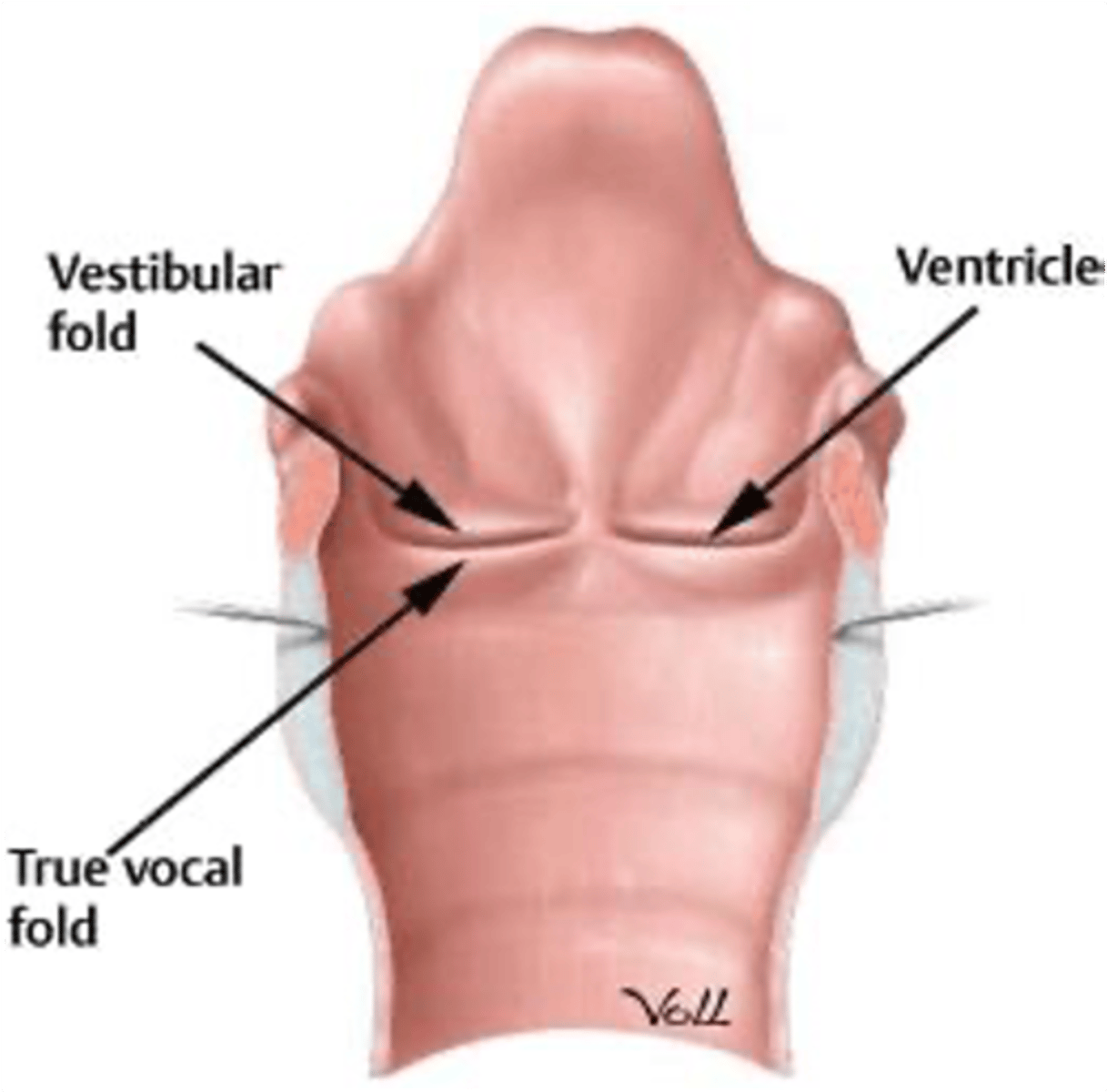
This laryngeal structure extends between the vestibular fold and the vocal fold.
Ventricle
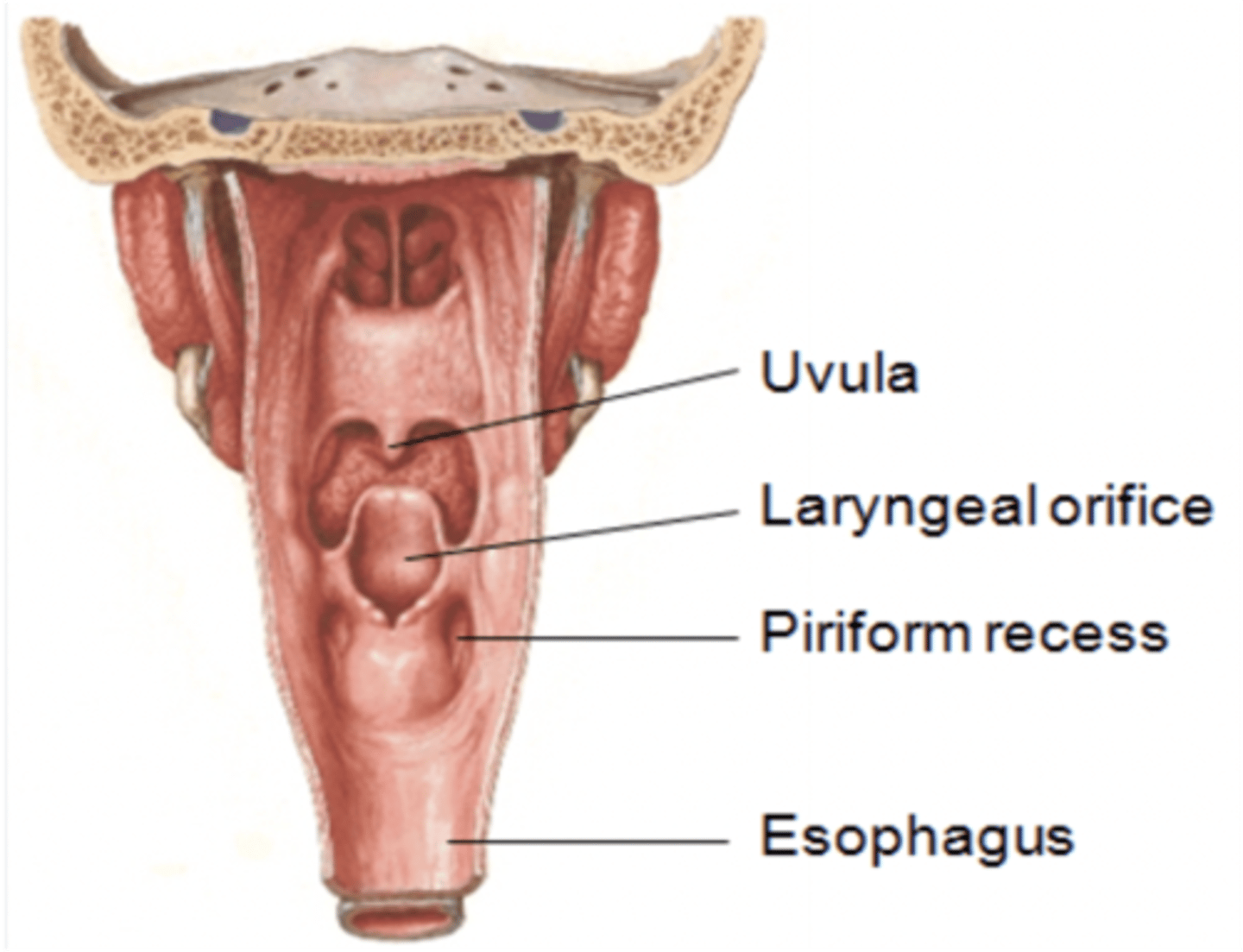
This structure is a pear-shaped fossa in the wall of the laryngopharynx lateral to the arytenoid cartilage.
Piriform recess
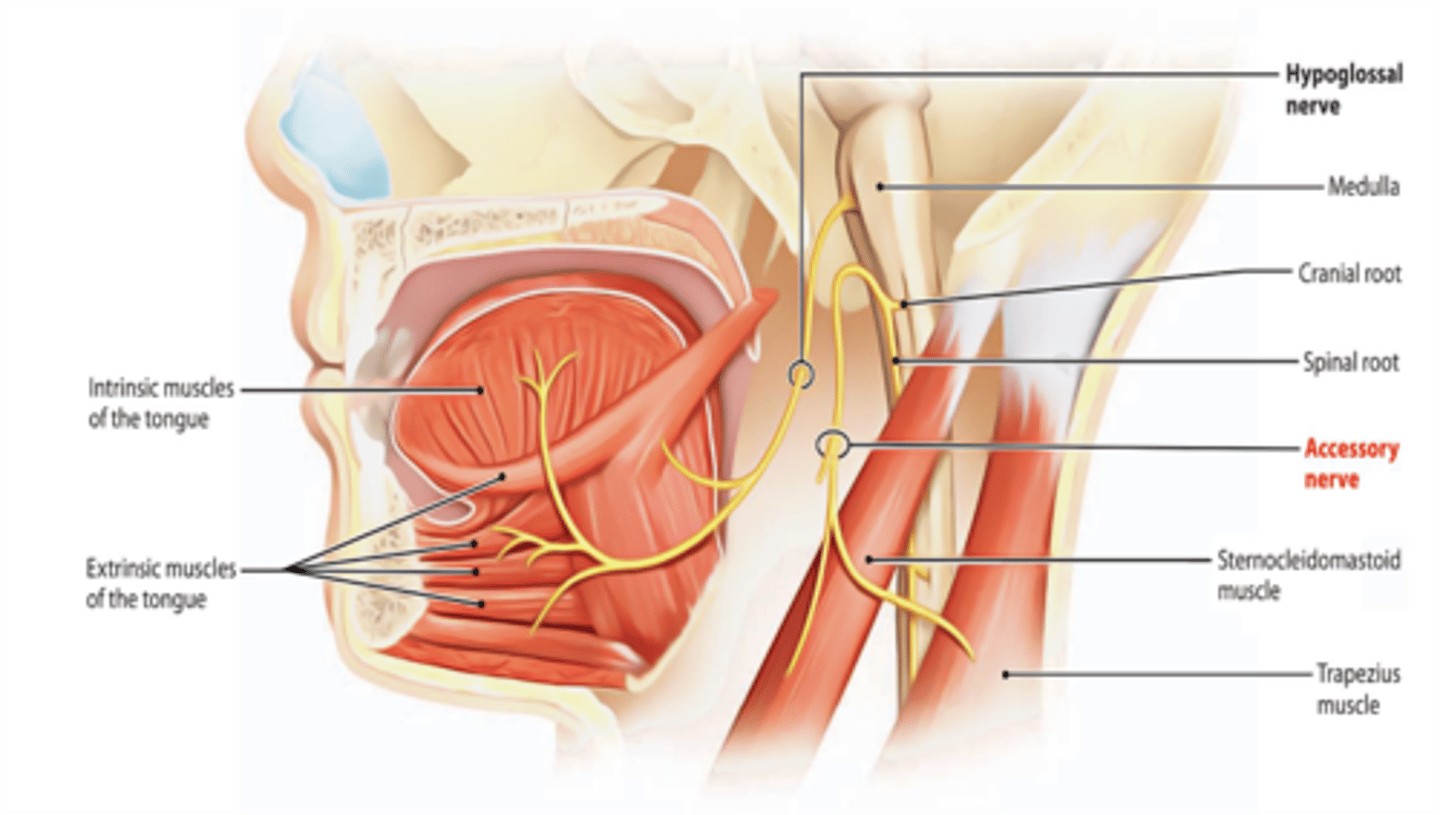
What two muscles are supplied by the spinal accessory nerve?
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
Trapezius muscle
The hypoglossal nerve supplies all tongue muscles except what muscle?
Palatoglossus muscle
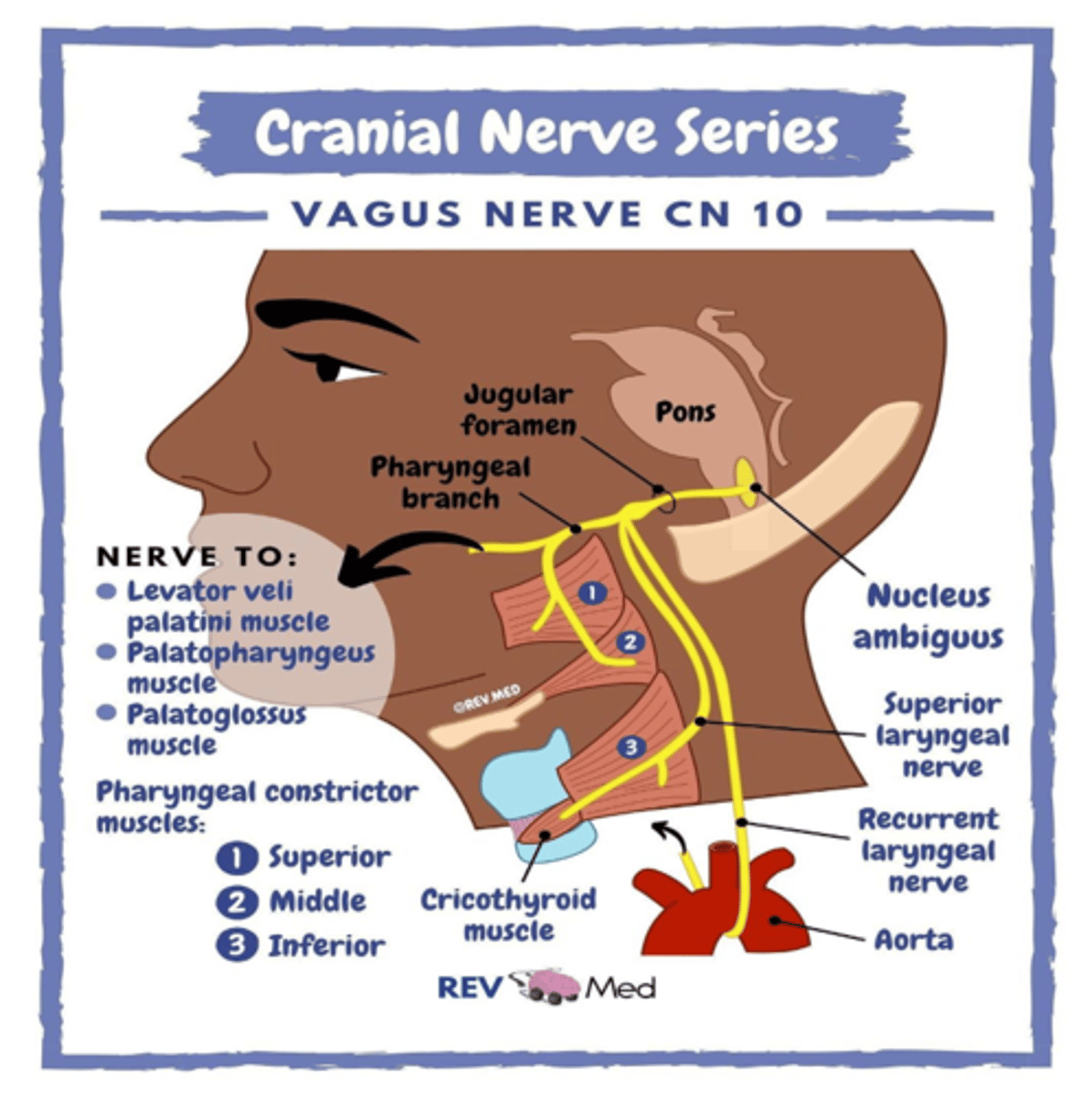
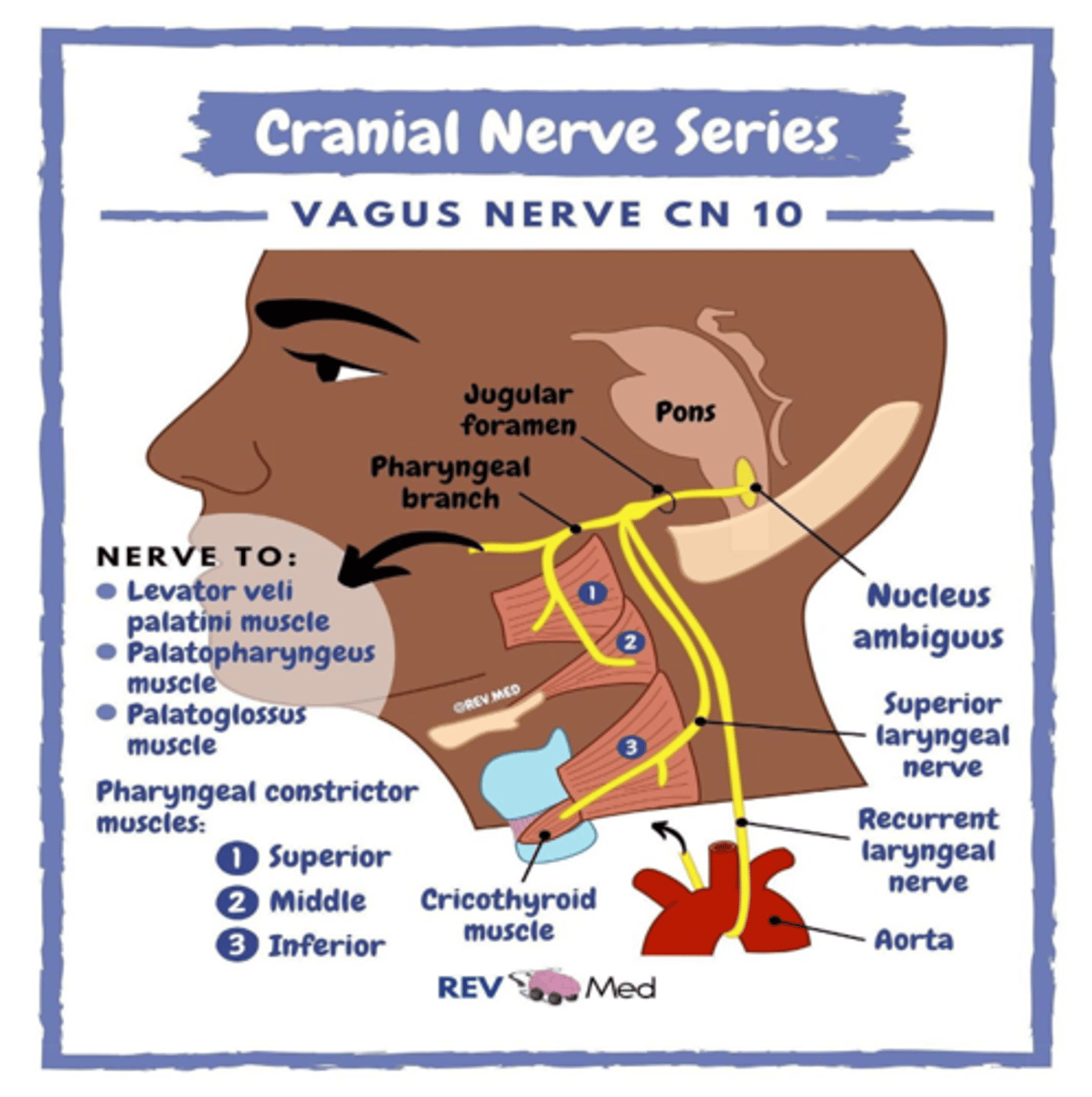
The palatoglossal muscle is the only tongue muscle not innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. What cranial nerve supplies this muscle?
Vagus nerve (CN X)
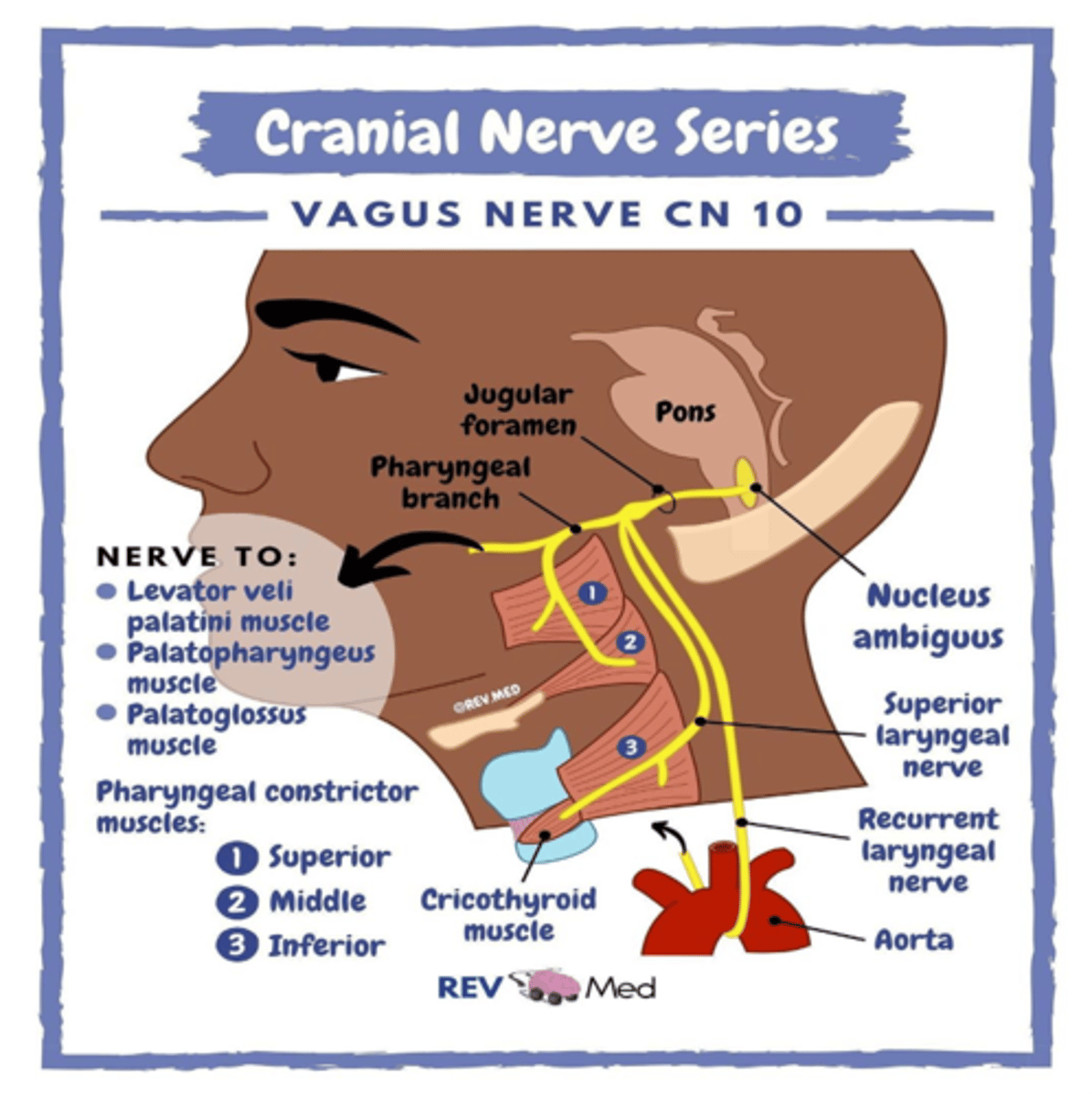
What cranial nerve innervates the muscles of the palate, larynx and pharynx?
Vagus nerve (CN X)
What cranial nerve supplies the mylohyoid muscles?
Trigeminal nerve (mandibular division) - CN V3
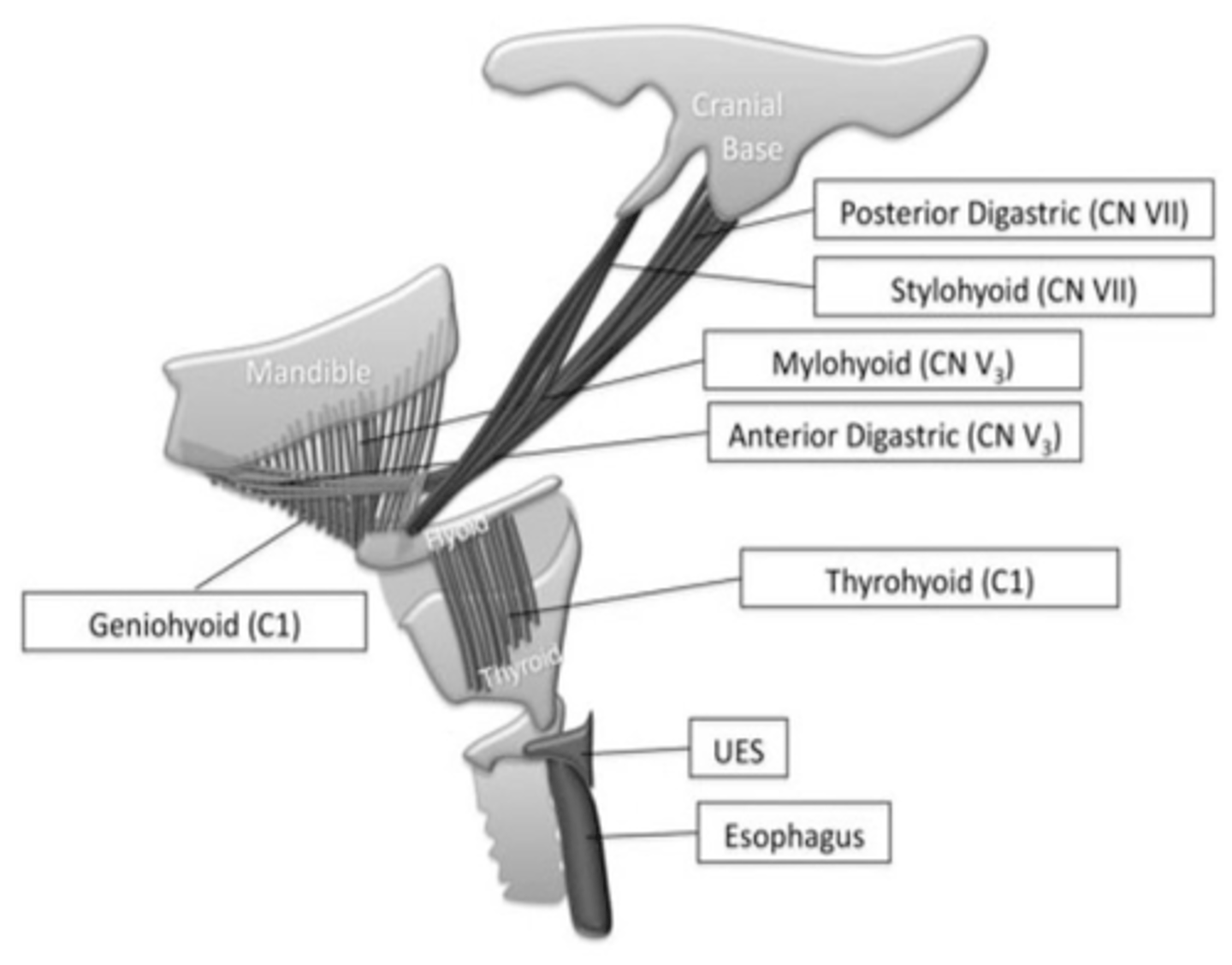
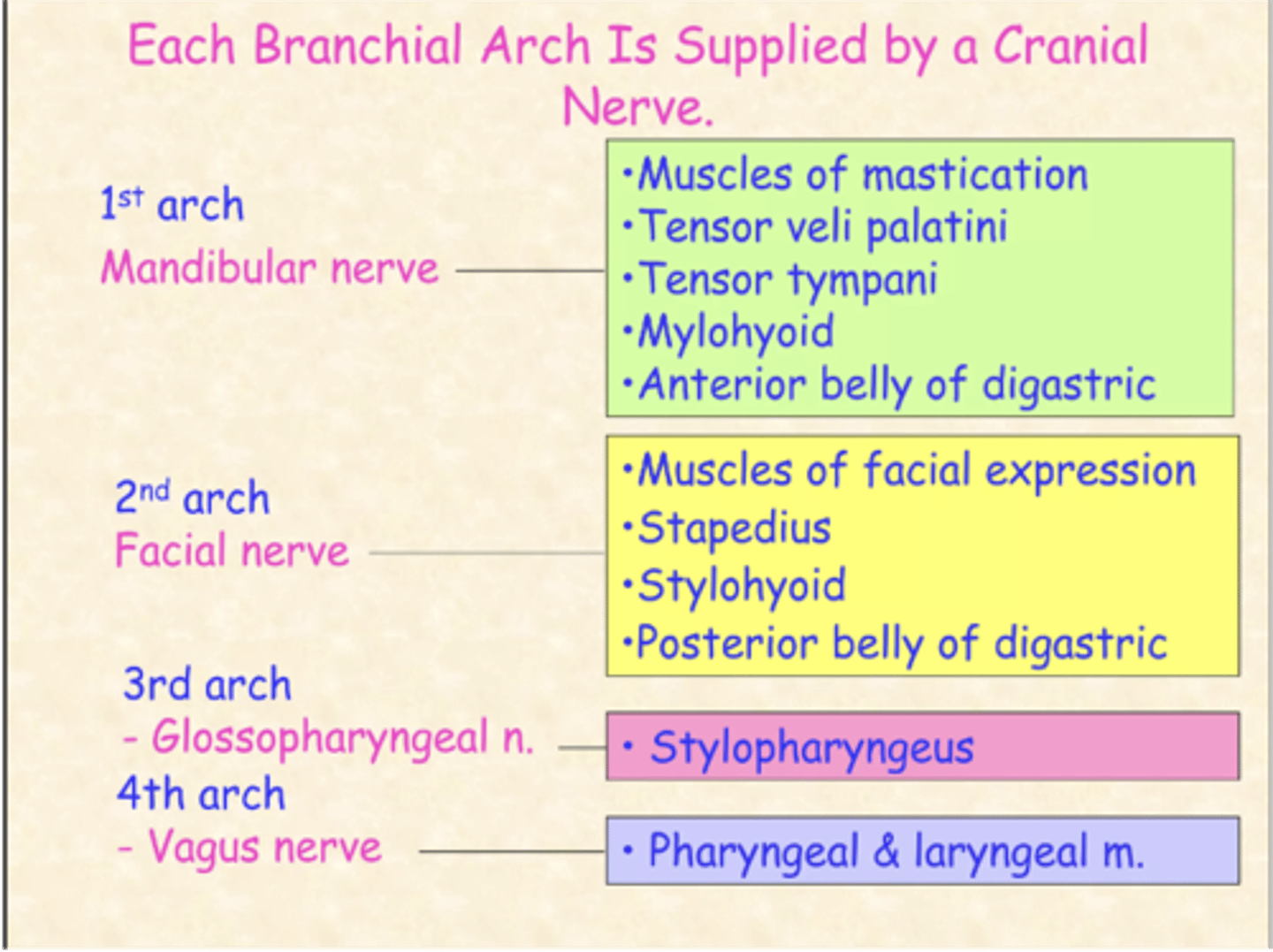
Which pharyngeal arch develops into muscle of mastication, mylohyoid, digastric anterior belly, tensor veli palatini, tensor tympani, maxilla, mandible, malleus, incus, zygomatic bone, temporal bone, palatine bone, vomer and sphenomandibular ligament?
First pharyngeal arch