Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
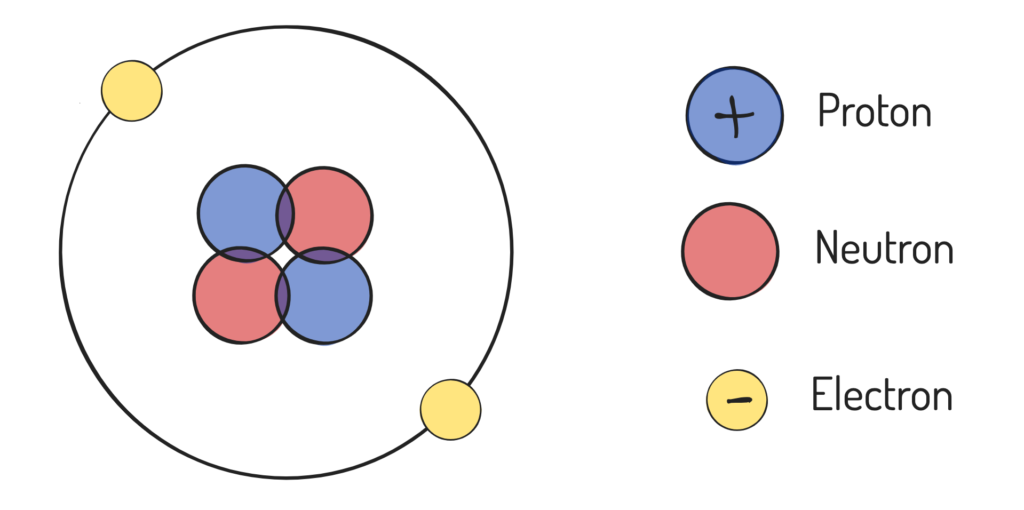
Atom
Made out of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, while neutrons orbit the nucleus
Cation
Atom that loses electrons and has more protons than electrons, so it becomes positively charged
Anion
Atom that gains electrons and has more electrons than protons, so it becomes negatively charged.
Proton
A positively charged subatomic particle found within the nucleus that determines element
Electron
A negatively charged subatomic particle and subside in an atoms shell
Neutron
A uncharged subatomic particle found within the nucleus
Valence Electron
Outermost electron
Ionic bonds
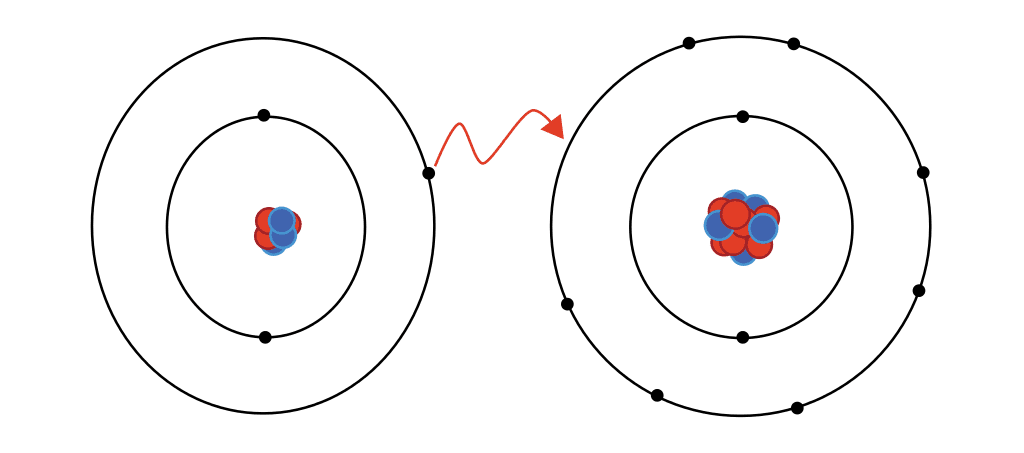
A form of chemical connection in which one atom loses valence electrons and gives them to another
Covalent Bond
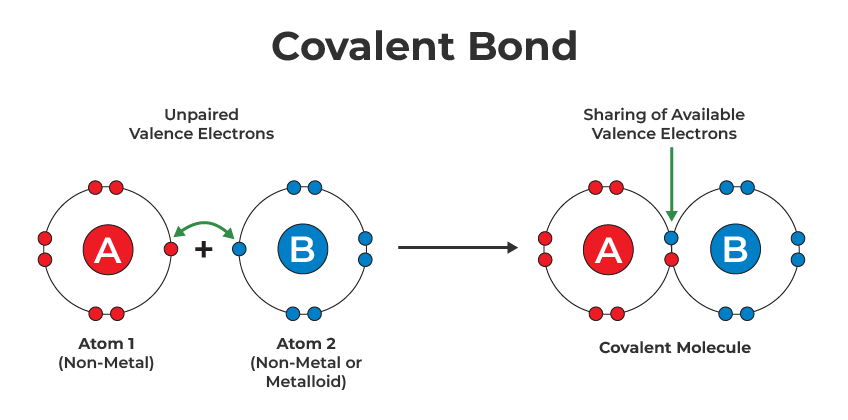
Chemical bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms, typically nonmetal atoms
Non-polar covalent bond
When two atoms share electrons equally
Polar covalent
A type of covalent bond where electrons are unequally shared between two atoms due to differing electronegativity values
Electronegativity
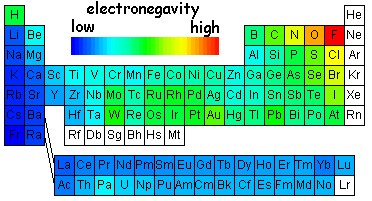
The tendency for an atom to attract shared electrons
Dipole
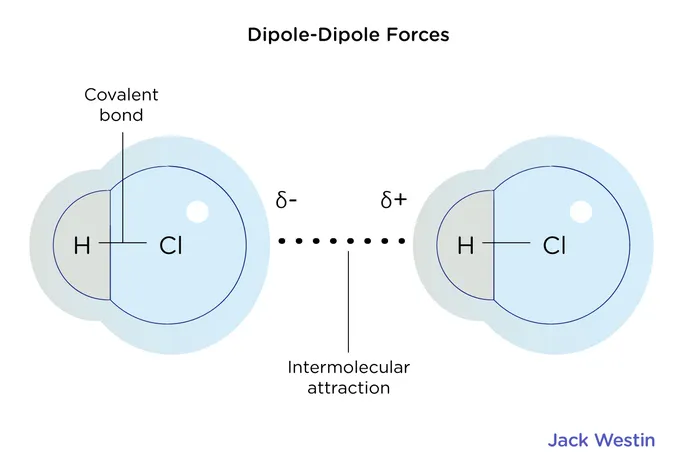
A type of intermolecular bond that occurs between polar molecules.
Intramolecule
Something occurring or existing within a molecule
Intermolecular
Something occurring within two molecules
Hydrogen Bonds
Opposite charges attracting eachother
Water
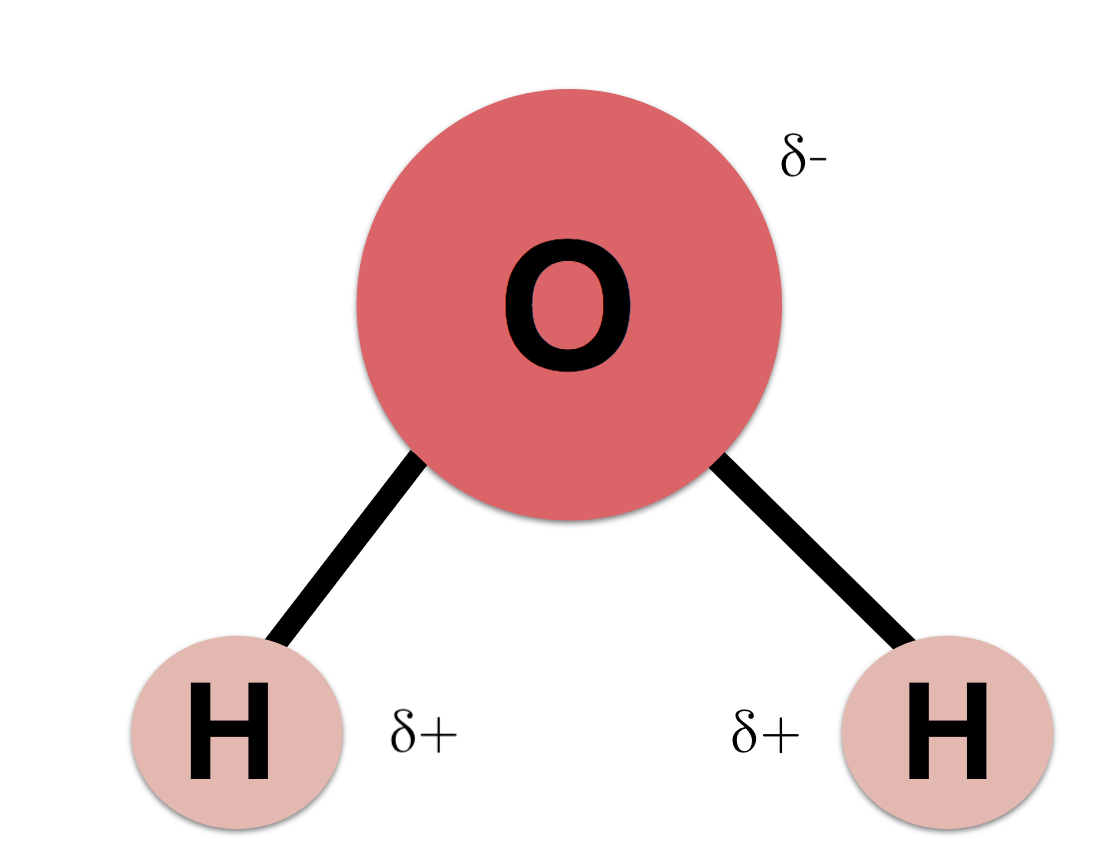
H20
Oxygen is very electronegative, so it attracts electrons, giving it a partial negative charge
Hydrogen itself is neutral, but it becomes partially positive because oxygen pulls electrons away from it
Hydrogen and Oxygen have a polar covalent bond
Adhesion
Water sticking to other things
Cohesion
Water sticking to water
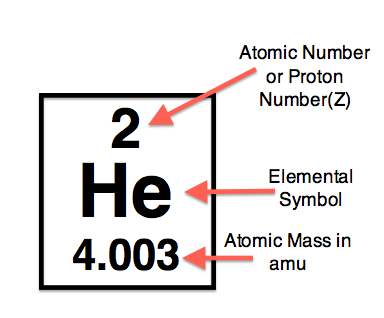
Atomic number
The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus
Carbohydrates (CHO)
Sugar, bread, potatoes
Monosachoride
Single simple form of carbohydrate
ex: glucose, fructose, galactose
disachoride
two monosachoride combined
ex: sucrose, lactose, maltose
polysachoride
long chain of monosachorides
ex; start, glycogen, cellulose
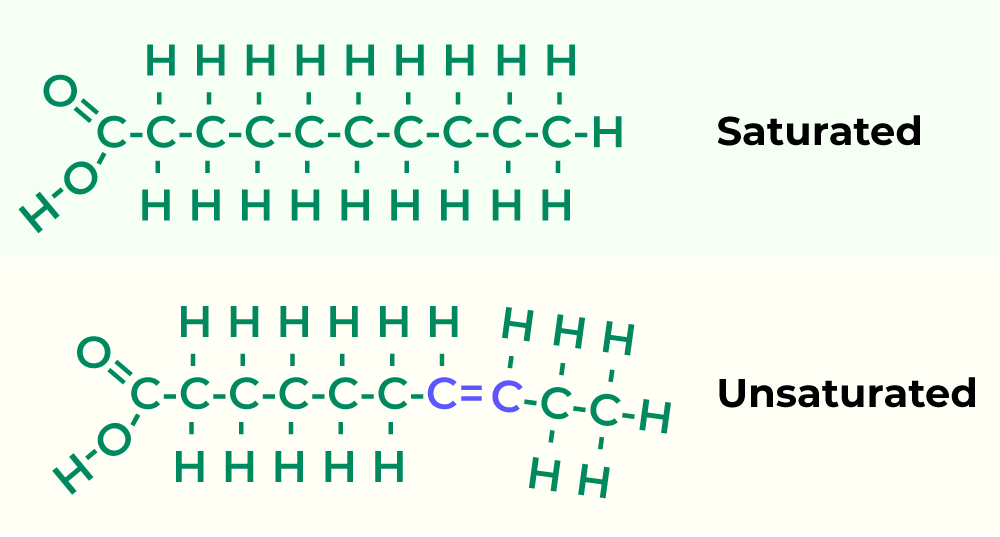
Lipids (CHO)
Unsaturated(double bond) - healthy
Saturated(straight) - unhealthy
Monomer of lipids
Glycoride
Diglyceride
two fatty acids bonded to glycerol
triglyceride
three fatty acids bonded to one glycerol
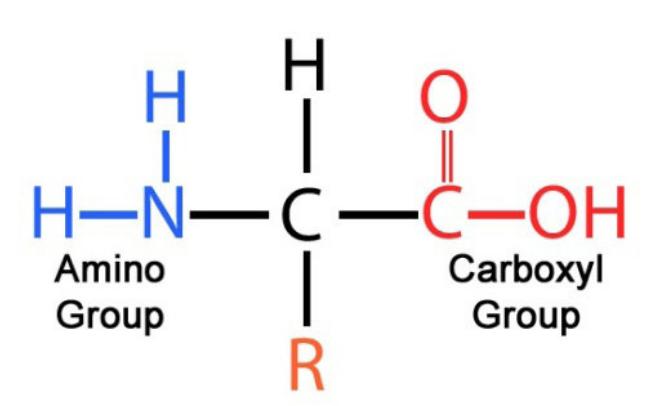
Protein (CHON)
Monomer of protein
amino acid
Dipeptide
two amino acids bonded
polypeptide
multiple amino acids bonded
Dehydration synthesis
Joins amino acids combine together by removing water
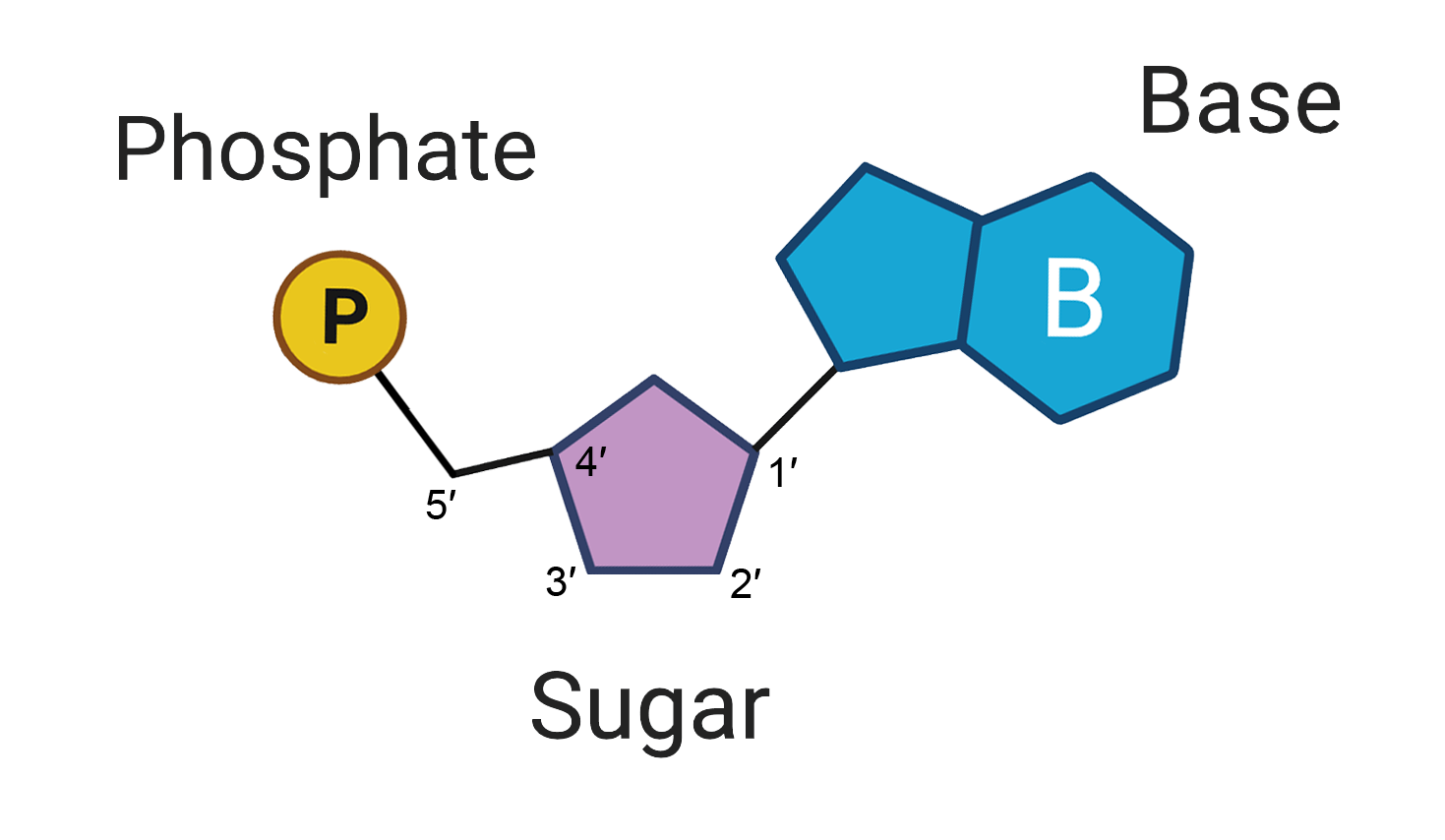
Nucleic Acid (CHONP)
nucleotide: single nucleic acid
DNA - deoxyribo nucleic acid
RNA - ribonucleic acid