Histamine/Anti-Histamines
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
histamine is formed by the decarboxylation of the amino acid _______ via what enzyme?
histidine; histidine decarboxylase
chemically, histamine is classified as an?
amine
while histamine can be derived from _____ _____ or _______ in the GI, it is mostly formed from ______ ______
dietary sources; bacteria; amino acids
histamine is highly concentrated where?
lung, intestinal mucosa, skin
what cell type stores histamine
mast cells, leukocytes, enterochromaffin cells, neurons
what is it called when histamine is released from mast cells
degranulation (or exocytosis)
histamine is stored in a vesicle/complex with ______ or ______ ______ within the mast cell
heparin; chondroitin sulfate
what antibody is often found on mast cells
IgE
When an allergen binds with _____ antibodies on mast cells, this results in release of chemical mediators, called:
IgE; degranulation
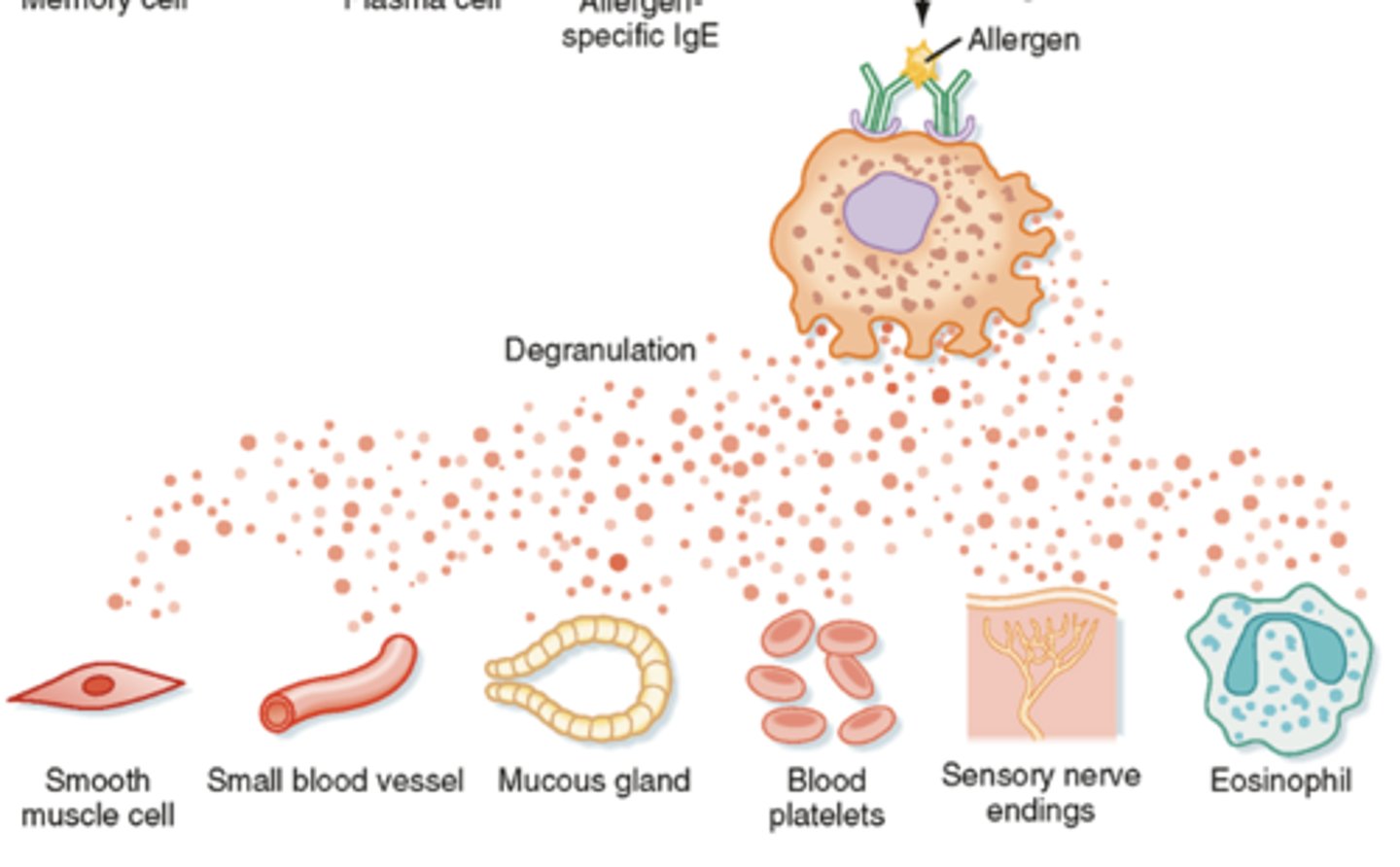
what are the main causes to histamine release
tissue injury, allergic rxns, drugs or foreign substances
if a tissue injury occurs, the initial histamine release causes?
increase in vascular permeability
what are the two generalized phases of histamine response? which stage do antihistamines work best on/in?
initial sharp phase, sustained response; initial phase
if an individual is already in anaphylaxis, will antihistamines still work?
no; they are now in the sustained phase and will need epi
can drugs induce a histamine response with prior sensitization?
no
what are common drugs that induce a histamine response
morphine, dextran, antimalarial drugs, abx
what are common foreign compounds that induce histamine repsonses
dyes, chemicals, toxins/venoms
what are the pharmacological effects of histamine on the arterioles, mj capillaries, venules
vasodilation, systemic hypotension, increased permeability (edema)
what are the pharmacological effects of histamine on the terminal vasculature
triple effect
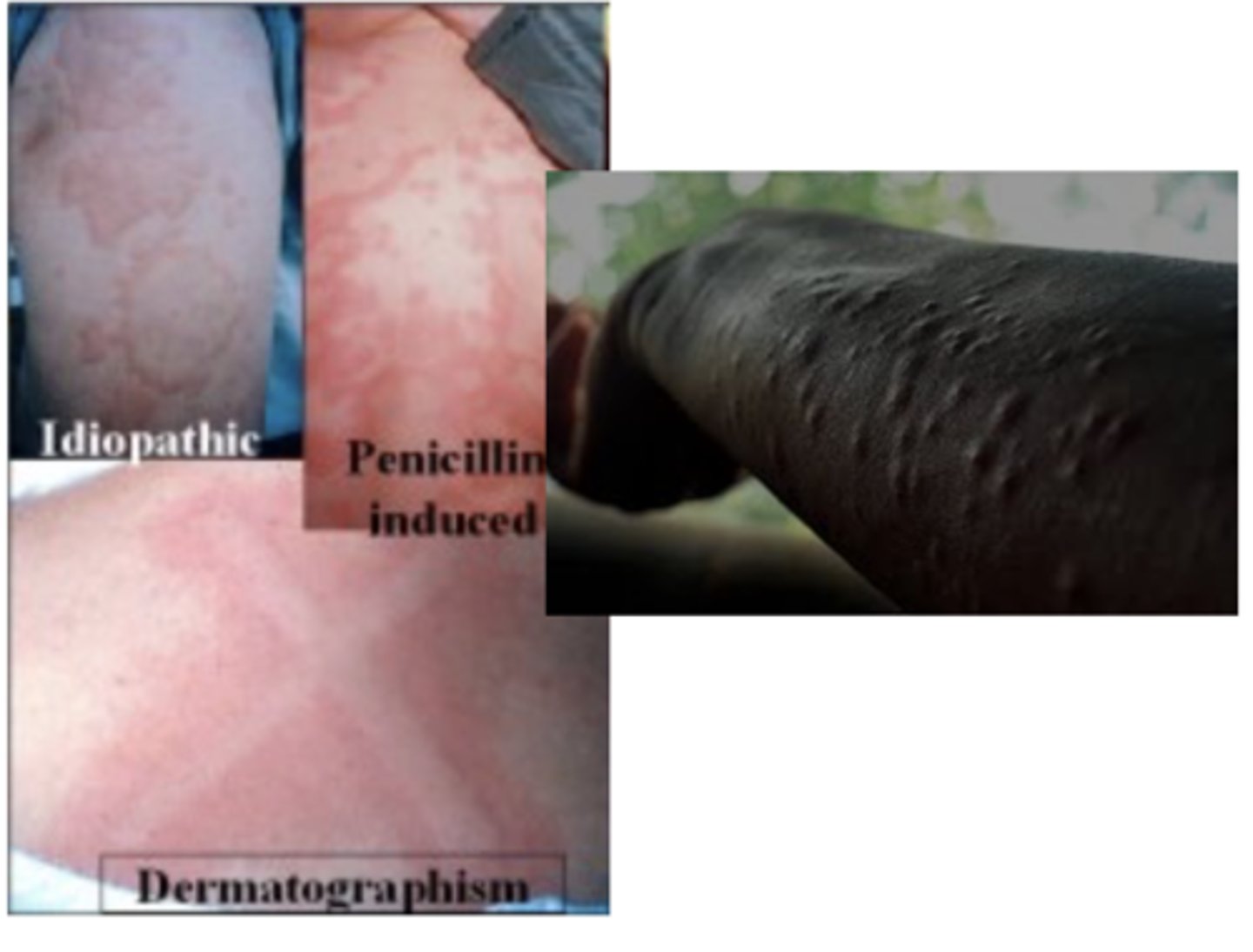
what is the triple effect? what is an example
reddening at the side of vasodilation; ex. hives
drugs that inhibit the _____ receptor inhibit the triple effect
H1
what are the pharmacological effects of histamine on the smooth muscle of bronchioles
contraction of non-vascular smooth muscle (bronchoconstriction)
what are the pharmacological effects of histamine on the exocrine glands
increase secretions
what are the pharmacological effects of histamine on the peripheral ns
itching, pain
what type of receptors are Histamine receptors
GPCR
how many histamine receptors are there
4 (H1-4)
H1 receptor is responsible for ______ condition
allergic
what does the H1 receptor stimulate in response?
bronchoconstriction, vasodilation, separation of endothelial cells (edema), pain/itching, allergic rhinitis, motion sickness
where is the H1 receptor located
smooth muscle, endothelium, CNS, heart
location of H2 receptor
gastric parietal cells, vascular smooth muscle, neutrophils, CNS, heart, uterus
what does H2 receptor do in response to stimulation
regulate gastric acid secretion, vasodilation
location of H3 receptor
mainly CNS
anti-histamines competitively/noncompetitively block histamine
competitively
first generation H1 can/cannot cross the BBB
can
first generation H1 can be used for?
sedation
what is the major difference between H1/H2
second generation is designed to not cross the BBB with significantly decreased sedation
anti-histamines can potentiate ____ _____
CNS depressants
examples of CNS depressants that anti-histamines can potentiate
opioids, sedatives, narcotic analgesics, alcohol, anti-muscarinics
what histamine do we need to know for this lecture?? what is its general name
diphenhydramine; benadryl
what anti-histamine class does diphenhydramine belong to
ethanolamine
does diphenhydramine have sedative effects?
yes
what OTC drug is it often found in combination with?
Tylenol PM
diphenhydramine can also be used in what motion sickness drug?
dramamine
in taking dramamine, diphenhydramine blocks the _____ receptor in the brain which is responsible for ______ _______
H1; motion sickness
H2 receptor anti-histamines are commonly used for _____ ______
acid reflux
H2 receptor antagonists can actually (increase or decrease) the bioavailability of _______
increase; ethanol
(lowers alcohol tolerance)
new drugs targeting H3 receptors are likely to target?
neuronal diseases
new drugs targeting H4 receptors are likely to target?
immunomodulation