AP Human Geography Unit 6
1/57
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Urbanization
The movement of people from rural areas to cities.
Farmland Protection Policy
Minimize the impact Federal programs have on the unnecessary and irreversible conversion of farmland to urban use.
Urban Growth Boundary
The line that defines the edge of an urban area and limits where new development can occur.
Brownfields
Previously developed land that is not currently in use and may be contaminated.
Remedation
The process of cleaning up contaminated brownfield sites to make them safe for use or redevelopment.
Ecological Footprint
The amount of biological productive land and water needed to support a person or populations consumption of resources.
Urban Sutainability
The practice of building cities that are environmentally, socially, and economically sustainable.
Housing Discriminiation
The unfair treatment of individuals in housing markets based on characteristics such as race, ethnicity, religion, or disability, often resulting in denial of housing opportunities.
Blockbusting
Real estate agents inducing panic selling neighborhoods, often by displaying racial fears.
Housing Affordibility
The ability of household to afford housing costs, often measured by spending no more than 30% of their income.
Disamenity Zone
An area within a city characterized by informal housing, precarious environmental conditions, and lack of basic infrastructure and public services.
Gentrification
Process where higher income residents move to traditionally lower income neighborhoods, leading to increase property values.
Redlining
Financial institutions denying services like mortgages and loans to residents to certain neighborhoods.
Urban Renewal
Redeveloping of urban areas often to address decay, but can lead to gentrification.
Zone of Abandonment
An area that has experienced significant population decline and economic disinvestment, often resulting in vacant properties and diminished infrastructure.
Environmental Injustice
Refers to the disproportionate impact of environmental hazards on marginalized communities, often involving unequal access to resources and decision-making.
Squatter Settlement
Informal settlement where residents lack legal rights to the land they occupy.
Local Food Movement
Connecting food producers and consumers withing a specific region.
Field Narrative
A qualitative research approach that explores the experiences and perceptions of people within a particular environment or context.
Field Study
A research method that involves observing and collecting data in a natural setting to understand social phenomena.
Qualitative Data
Information that is descriptive and conceptual, often used in research to capture people's experiences, opinions, or feelings.
Survey Data
Helps understand peoples opinions, behaviors, and characteristics, providing insightful patterns and trends.
Census Data
Provides a systematic collection of data about a population, enabling analysis of population distribution, trends, and demographic characteristics.
Quantitative Data
Numerical information that can be measured and analyzed statistically, often used to quantify variables and identify patterns.
De Facto Segregation
Seperation existing in practice despite of being legal equality, often resulting from economic or social factors.
New Urbanism
Planning and development approach that emphasizes walkable, mixed used public spaces.
Smart-Growth Policies
Urban planning strategies that promote sustainable and efficient land use, focusing on growth management and community development.
Transportation Oriented Development
A planning strategy that focuses on creating dense, walkable communities centered around public transportation to reduce reliance on cars.
Urban Walkability
The ease and safety in which people can walk somewhere in a city.
Mixed Land Use
A planning approach that integrates residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within proximity to promote community interaction and reduce travel distances.
Sustainable Design
Built environments to minimize environmental impact. It incorporates energy efficiency, resource conservation, and the use of renewable materials.
Infrastructure
The basic physical systems and structures that support a city, including transportation, utilities, and communication systems.
Infilling
Using ununitilized buildings instead of expanding into suburbs.
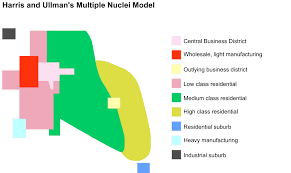
Harris and Ulman Multiple Nuclei Model
This urban model suggests that cities develop with multiple centers of activity rather than a single nucleus. Each nucleus caters to different functions, such as residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
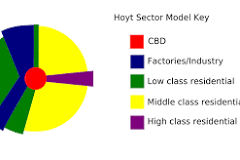
Hoyt Sector Model
This urban model proposes that cities develop in sectors or wedges, with each sector representing an area of specific land use, such as residential, industrial, or commercial, radiating out from the central business district.
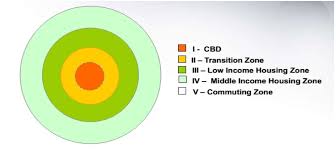
Burgess Concentric-Zone Model
An urban model that depicts cities as a series of concentric rings, each representing different land uses, with the central business district at the core, followed by zones of transition, working-class housing, and eventually suburbs.
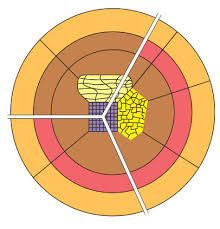
African City Model
A model that illustrates the unique urban structure of certain cities, characterized by multiple centers of activity, informal housing, and ethnic neighborhoods, reflecting colonial influences and post-colonial developments.
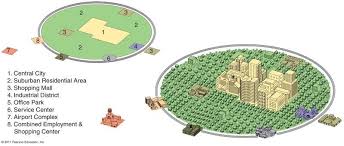
Galactic City Model
A model highlighting urban areas with a decentralized layout, featuring edge cities and a focus on transportation networks, where suburban developments around a core minimize reliance on the central business district.
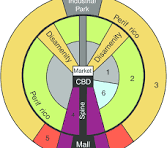
Latin American City Model
A model depicting the urban structure of certain cities, characterized by a CBD surrounded by commercial and residential areas, with poorer neighborhoods and squatter settlements on the outskirts.
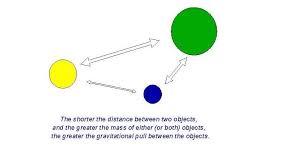
Gravity Model
A model used to predict the accessibility and interactions between two locations based on their population size and distance. It demonstrates that larger places attract more people while closer places have a stronger pull than distant ones.
Christaller’s Central Place Theory
Explains the size and distribution of human settlements. It posits that settlements serve as 'central places' providing services to surrounding areas, with a hierarchy based on the range and threshold of services offered.
Rank Size Rule
A principle suggesting that the population of a city or town is inversely proportional to its rank in the hierarchy of cities. It indicates that the next largest city is 1/2 the size of the largest city. (City's population divided by city rank.)
Primate City
is a city that is significantly larger than any other city in the country, often dominating the economic, political, and cultural life of the area.
Megactiy
A city with a population exceeding 10 million people.
Globalization
The process of increased interconnections among countries and cultures, often driven by trade, communication, and technology.
Urban Hierarchy
is a ranking of cities based on their size, importance, and functions in relation to each other, typically structured in a pyramid-like manner.
World City
A city that serves as a major center for finance, commerce, culture, and international influence.
Boomburb
A rapidly growing suburban area that becomes a significant economic and residential hub, often characterized by a mix of single-family homes and commercial developments.
Edge City
A suburban area that has developed its own economic base and is characterized by a concentration of business, retail, and entertainment outside of the traditional downtown.
Suburbanization
The process by which people move from urban areas to live in suburbs, resulting in the growth of suburban communities.
Urban Sprwal
The spread of a city and its suburbs into surrounding rural areas, often leading to the development of low-density housing and increased reliance on automobiles.
Exurb
A semi-rural area located beyond the suburbs, typically characterized by lower population density and residential development.
Metacity
A metropolitan area with a population of over 20 million people, often characterized by extensive urban sprawl and a complex socio-economic environment.
Urban Decentralization
The process in which population and industry move from urban centers to the outskirts or suburban areas, leading to a redistribution of economic activities and residential patterns.
Semi-Periphery
A classification of countries that are in between core and periphery nations, often exhibiting characteristics of both. These nations tend to have moderate levels of industrialization and economic development.
Periphery
A term used in world-systems theory to describe countries that are less economically developed than core nations, often reliant on core nations for resources and trade.
Site
A specific location's physical characteristics, including its natural resources, climate, and topography, that influence human activities and development.
Situation
Refers to the location of a place relative to its surroundings and other locations, which can affect accessibility, trade, and development.