Chemotherapy Drugs Revised
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
Genes that normally function to restrain cell growth. However, they can become defective and lose ability to inhibit cell growth/division → allows cancer formation.
Tumor suppressor genes
Ex of tumor suppressor gene
p53 gene is a tumor suppressor gene in cells that controls cellular apoptosis (natural death of cells with damaged DNA). Defect of this gene can lead to cancer formation
Genes that stimulate and regulates a cell’s movement through the cell cycle, resulting in cellular growth and proliferation
Proto-oncogenes/oncogenes
What happens when proto-oncogenes become mutated?
These proto-oncogenes genes become oncogenes that stimulate constant, unrelenting proliferation and cell cycling → cancer
Cancer treatment that involves short course of high-dose drug therapy after radiation, OR surgery to destroy residual cancer cells to prevent recurrence. Or drugs used to kill any residual cancer cells after surgery.
Adjuvant treatment
Cancer treatment done prior to surgery. Radiation to shrink tumor and improve outcomes.
Neoadjuvant treatment
Cancer treatment to control symptoms, comfort, improve QOL if cure not available.
Palliative treatment
Cancer treatment involving potentially curative high dose for recurrence or treatment failure.
Salvage treatment
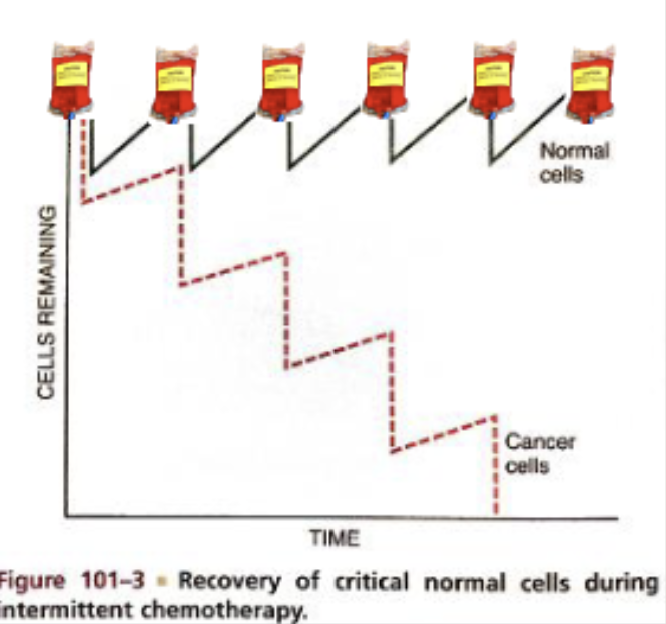
Why is cancer/chemo treatment intermittent?
So normal cells can replenish while maximizing killing of cancer cells
Reduces drug resistance
Increase cancer kill count
Reduces injury to normal cells
Combination therapy
Why does combination therapy reduce drug resistance of cancer cells?
Multiple drugs with different MOAs overwhelm cancer cells so that cancer cells do not have time to adapt resistance to just one drug; combination therapy is also more likely to kill cancer cells. Some meds also protect normal cells from other chemo drugs → give concurrently
Regional drug therapy
Chemotherapy can target specific spots of the body depending on where they are administered
Cell-cycle phase-specific drugs (cytotoxic agents) MOA
Toxic only to cells in a particular phase
Cells in G0 phase are not harmed
Schedule dependent
Cells in G0 phase are harmed/attacked by cell-cycle phase-specific cytotoxic agents. True or false?
False
Phase non-specific drugs (cytotoxic agents) MOA
Acts during any phase, including G0
More toxic to proliferating cells than cells in G0
Safe handling of cytotoxic agents
Protect yourself from exposure
Don appropriate PPE (gown, gloves, mask, face shield/goggles, shoe covers)
Follow institutional guidelines
Nursing implications for cytotoxic agents
High-alert medication
2 nurse check with several additional “Rights”
BSA/Weight based dosing (mostly use BSA-dosing; body surface area)
Monitor/double check administration rate
Cell-cycle phase-specific drugs vs phase non-specific drugs
Phase non-specific acts during any phase, including G0 (cell-cycle phase-specific does NOT act on G0)
Phase non-specific drugs are more toxic to proliferating than cells in G0
Safe IV administration of cytotoxic agents
Central line vs peripheral IV access (most cytotoxic agents/chemo drugs are given IV central line)
Cytotoxic agents are an irritant (causes extravasation/phlebitis) → usually occurs peripheral IV
Vesicant (term given to drug that can cause tissue necrosis or damage if it leaks outside the vein and enters tissue (can lead to permanent destruction, nerve damage, limb loss)
Hourly IV checks and documentation
Vesicants best given central line to not worry about extravasation
Term given to drug that can cause tissue necrosis or damage if it leaks outside the vein and enters tissue (can lead to permanent destruction, nerve damage, limb loss; caused by cytotoxic agents.
Vesicant
Vesicants (e.g. cytotoxic agents) are best given central or peripheral line to not worry about extravasation or irritation?
Central line
It is important to note that the vast majority of chemotherapeutic drugs are administered by a ______ line indwelling catheter device to minimize the risk for extravasation.
Central line
S&S of IV infiltration of tissue
Redness at or near the insertion site with swollen, taut skin with pain
Blanching, and coolness of skin around the IV site
Slowed or stopped IV infusion
No blood return obtained
Treating extravasation/irritant/vesicant
Notify provider
Administer antidote in same IV to prevent damage from leakage of drug into tissues
Follow hospital policy
Central line vs peripheral IV access (most cytotoxic agents/chemo drugs are given IV central line)
Cytotoxic agents are an irritant (causes extravasation/phlebitis) → usually occurs peripheral IV
Vesicant (term given to drug that can cause tissue necrosis or damage if it leaks outside the vein and enters tissue (can lead to permanent destruction, nerve damage, limb loss)
Hourly IV checks and documentation
Vesicants best given central line to not worry about extravasation
Safe IV administration cytotoxic agents
Preventing IV extravasation from cytotoxic agents
Follow hospital policy/protocol
Check for blood return in IV prior to administering chemo
Assess patient for pain, burning regularly
Stop drug immediately if signs of infiltration are noted
Give antidote through existing IV if extravasation happens
Aspiration of drug (5 mL blood) prior to IV removal
Elevate extremity
Warm compress/cold compress
Determined by specific chemo drug
Types of cytotoxic drug classifications based on MOA
MOA
Cell-cycle phase-specific drugs
Phase non-specific drugs
Types of cytotoxic agents
Alkylating agents
Platinum compounds
Antimetabolites
Antitumor abx
Mitotic inhibitors
Other classes
Alkylating agents (cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan, Neosar)) MOA
Cell cycle non-phase specific
Alkyl groups are part of the alkylating drugs’ structure that attach to DNA molecules by forming covalent bonds.
As a result, abnormal chemical bonds form between the adjacent DNA strands, which leads to the formation of defective nucleic acids that are then unable to perform the normal cellular reproductive functions, which leads to cell death.
Nitrogen mustard derivative cytotoxic agent transfers alkyl group that disrupts DNA replication → prevents cancer cells from reproducing leading to death.
Alkylating agents (cyclophosphamide) indication
Broad-spectrum chemo drug effective against a myriad of malignancies.
Among the first antineoplastic drugs developed
Alkylating agents (cyclophosphamide)
Cyclophosphamides (alkylating agents) AE/SE
Can cause acute hemorrhagic cystitis
Patient needs adequate hydration (2-3 L) for prevention
Concurrent mesna (Mesnex) for high dosages to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis (protect liver)
If using high dosage of this drug, administer concurrently mesna (Mesnex)
also provide adequate hydration (2-3 L) → both serve to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis
Cyclophosphamides (alkylating agents)
Drug that has AE of hemorrhagic cystitis
Cyclophosphamides (alkylating agents)
Platinum compounds MOA
Contains platinum that cross-links in cell DNA
Name the platinum compounds
Cisplatin (Platinol-AQ); oxaliplatin
Platinum compounds indication
Testicular cancer
Ovarian cancer
Bladder cancer
TOB (platinum compounds/cisplatin indication)
T – Testicular cancer
O – Ovarian cancer
B – Bladder cancer
Cytotoxic platinum compound that causes nephrotoxicity & ototoxicity
Cisplastin
Complications of chemo
Bone toxicity/bone marrow suppression
GI upset (NV)
Skin and hair loss (alopecia)
Sexual dysfunction
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS)
Carcinogenesis; treatment can cause cancer by damaging DNA in normal cells
Anemia/thrombocytopenia
Immunosuppression/neutropenia
Preventing nephrotoxicity caused by platinum compounds (cisplatin)
Vigorous hydration + diuretic administration
Cisplatin (platinum compound) AE
Nephrotoxicity & ototoxicity (drug toxicity)
Peripheral neuropathy
Name the antimetabolites
Methotrexate (Rheumatrex, Trexall)
Fluorouracil (Adrucil, 5 FU)
Antimetabolites MOA
Disrupt/antagonize critical metabolic processes for cellular reproduction (e.g. folic acid, purines, pyrimidines); methotrexate antagonizes folic acid.
Interferes with body’s ability to use nutrients crucial for DNA synthesis.
Cell cycle specific; works primarily in S phase (phase where DNA synthesis most active)
DNA synthesis is disrupted by these drugs whether or not specific or nonspecific
Cytotoxic agents
Methotrexate AE/SE
Stomatitis (drug toxicity)
Photosensitivity
High doses (toxic effect/OD) can injure kidneys (nephrotoxicity)
maintain hydration & alkaline urine pH
AE of this drug toxicity is stomatitis; high doses (toxic effect/OD) can injure kidneys/nephrotoxicity.
Methotrexate
Methotrexate timed levels
NTI; scheduled blood draws to measure methotrexate concentration at set times after a high-dose infusion (e.g., at ~24, 48, and 72 hours).
High-dose methotrexate is associated with severe bone marrow suppression and is always given in conjunction with the “rescue” drug
Leucovorin. Leucovorin is an antidote for folic acid antagonists.
Drug given after/in conjunction w/ methotrexate to rescue healthy cells
Leucovorin
Fluorouracil (antimetabolite indication)
Antimetabolite used extensively to treat solid tumors
Fluorouracil AE
Hand-foot syndrome; form of dermatologic toxicity is known as palmar-plantar dysesthesia or paresthesia. It can range from mild symptoms such as painless swelling and erythema to painful blistering of the patient’s palms and soles.
Drug that causes hand-foot syndrome
Fluorouracil (antimetabolite)
Antitumor abx MOA
Injure cells through direct interaction with DNA
Intercalation: drug molecule is inserted between the two strands of a DNA molecule, ultimately blocking DNA synthesis.
These drugs inhibit the enzyme topoisomerase II, which leads to DNA strand breaks. Many of these drugs are able to generate free radicals, which also leads to DNA strand breaks and programmed cell death.
Only used to treat cancer, not infections
Antitumor abx can treat both infections and cancer. True or false?
False
Name the antitumor abx
Daunorubicin & doxorubicin
Bleomycin
Drugs that cause cardiotoxicity due to toxicity/OD
Daunorubicin & doxorubicin
Daunorubicin & doxorubicin (antitumor abx) cardiotoxicity monitoring
Perform ECHO & check LVEF prior to administration
Toxic levels/OD of this antitumor abx causes pulmonary toxicity (pulmonary fibrosis + pneumonitis)
Bleomycin
Antitumor abx indication
Treat a variety of solid tumors and also some hematologic malignancies.
Daunorubicin & doxorubicin AE
Hepatotoxicity/liver toxicity
Toxic effect → Cardiotoxicity/HF
Daunorubicin causes tissue damage if it extravasates
Mitotic inhibitors MOA
Cell-cycle specific (M phase)
Interfere with processes during mitosis → retard cell division, inhibit cell division → cell death
Vinca alkaloid
Name the mitotic inhibitors
Vincristine (Oncovin)
Vincristine (Oncovin) AE/SE
Peripheral neuropathy
Never administered intrathecally (into brain/subarachnoid space)
Constipation
Chemo drug never administer intrathecally
Vincristine (Oncovin; mitotic inhibitor)
Administer this drug on empty stomach. If severe stomach upset occurs, give with food.
Have patient drink 2 - 3 quarts of fluid daily and urinate often, especially at bedtime.
If hematuria or signs of hemorrhagic cystitis, report to provider.
High fluid intake and frequent emptying of the bladder help to decrease bladder damage
Cyclophosphamide specific concerns
Administer this drug on empty stomach. If severe stomach upset occurs, give with food.
Cyclophosphamide
High fluid intake and frequent emptying of the bladder help to decrease bladder damage from this drug
Cyclophosphamide
Drug causes urine to turn red for 1-2 days after administration → NORMAL (discoloration harmless; does not indicate bleeding)
Doxorubicin
Report edema, SOB, excessive fatigue for patients taking this drug (due to cardiotoxicity)
Doxorubicin/daunorubicin → drug may need to be stopped/held
Drink plenty of fluids while taking
Fluorouracil
Avoid alcohol, aspirin/ASA, and prolonged exposure to sunlight with this drug
Methotrexate
Avoid exposure to cold during, and 3-5 days after administration of this drug.
Oxaliplatin (alkylating drug)
Why avoid cold exposure during and 3-5 days after administration of oxaliplatin?
Helps prevent or minimize nerve damage that may cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the throat or hands.
Swallowing (dysphagia) and daily activities that require hand grasping may be impaired if taking this drug
Oxaliplatin (platinum-compound)
Eat high-fiber foods such as whole cereal grains, to prevent constipation.
Maintain a high fluid intake
Stool softener or bulk laxative may be described for daily use
Vincristine
Stool softener or bulk laxative may be described for daily use for patients taking this drug
Vincristine
Drugs used for hormonal cancer therapy
Tamoxifen (more common)
Anastrozole
Flutamide
Leuprolide (more common)
Drugs used for breast cancer
Tamoxifen
Anastrozole
Tamoxifen/anastrozole MOA
Blocks estrogen receptors on breast cancer cells (tamoxifen)
Anastrozole reduces available estrogen to cancer cells
Hormonal therapy indication
Breast cancer & prostate cancer
Leuprolide/flutamide MOA
Suppresses androgen production (suppress testosterone; testosterone can drive prostate cancer) OR availability by binding to androgen receptor cells
Drugs used for prostate cancer
Leuprolide (more common) & flutamide
Hormone-receptive negative breast cancer →
Tamoxifen does not work
What chemo drug causes pulmonary fibrosis or pneumonitis as a toxic effect?
Bleomycin
Chemo drugs that cause peripheral neuropathy
Vincristine/Vinblastine
Cisplatin
Complications of chemotherapy
Bone marrow suppression → anemia
GI upset (NV)
Skin & hair loss (alopecia)
Sexual dysfunction
Tumor lysis (large amounts of cancer cells released into bloodstream after chemotherapy treatment)
Carcinogenesis; treatment can cause cancer by damaging DNA in normal cells
Immunosuppression/neutropenia
GI effects of chemo
Stomatitis
Oral thrush
NVD
Constipation
Interventions for stomatitis and oral thrush caused by chemotherapy
Maintain oral hygiene: soft toothbrush, baking soda mouthwash, assess for infections.
Educate to not eat tomatoes/acids to avoid irritating ulcers
Meds: cytoprotective agents, antifungals, local anesthetics (lidocaine), pain meds
Interventions for NV caused by chemotherapy
Eliminate triggers
Monitor nutrition/fluid status
Give antiemetics 30 min to 1 hr before meals (e.g. Zofran/aprepitant)
Interventions for diarrhea caused by chemo
Monitor nutrition/fluid status, skin integrity.
Meds → antidiarrheals/probiotics
Labs to monitor for chemotherapy patient
CBC; WBCs (neutropenia), RBCs (anemia/erythrocytopenia),
Platelets (thrombocytopenia) → S&S bleeding/bruising/epistaxis, GI bleeding/belly pain (melena, hematochezia)
Interventions for constipation caused by chemo
Activity level (encourage ambulation), fiber diet, fluids
Meds → stool softeners, laxatives
Interventions for mucositis caused by chemo
Use soft toothbrush
Avoid tart, salty or acidic food
Eat soft, bland or cool foods
Avoid alcohol-based mouthwash (give baking soda/lidocaine mouthwash)
Rinse before and after meals and bedtime
Use soft toothbrush
Avoid tart, salty or acidic food
Eat soft, bland or cool foods
Avoid alcohol-based mouthwash (give baking soda/lidocaine mouthwash)
Rinse before and after meals and bedtime
Interventions for mucositis caused by chemo drugs
Skin & hair effects caused by chemo
Maintain skin integrity
Rash, dry, peeling
Alopecia (loss of hair)
Hairpieces
Body image
Consider psychiatric referral
Oncologic medical emergency; when tumor cells lyse and contents release into bloodstream; releases potassium, phosphate, and uric acid; contributes to acidosis.
More common in leukemia and lymphoma patients; at beginning of treatment.
Tumor lysis syndrome
Electrolyte imbalances caused by TLS
hyperkalemia
hyperphosphatemia
Hyperuricemia
Hypomagnesemia
All contribute to metabolic acidosis
Interventions for TLS
Vigorous IV hydration (sodium bicarb), monitor I&Os
Frequent labs – electrolytes, uric acid, WBC, Cr
ECG/EKG monitoring (hyperkalemia/dysrhythmias and peaked T waves)
Allopurinol (Zyloprim, Aloprim) prevent gout due to uric acid buildup
Urate oxidase (Rasburicase) prevent gout due to uric acid buildup
Sevelamer (Renagel) → treat hyperphosphatemia
Dialysis for severe cases
Preventing gout caused by excess buildup of uric acid due to TLS
Administering drugs to prevent gout:
allopurinol (Zyloprim, Aloprim)
Urate oxidase (Rasburicase)